Synergistic Ce/In dual-doping in La0.3Sr0.7FeO3−δ: breaking the activity–stability trade-off in SSOFC electrodes†
Abstract
This study develops La0.3Sr0.6Ce0.1Fe0.9In0.1O3−δ (LSCeFIn-0.1) as a symmetric electrode for symmetrical solid oxide fuel cells (SSOFCs) through Ce/In dual-doping. Ce stabilizes the perovskite structure, while In enhances oxygen vacancy 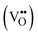 concentration and O2− mobility. The LSCeFIn-0.1 exhibits low polarization resistances of 0.097 Ω cm2 in H2 and 0.037 Ω cm2 in air. The LSGM-based cells achieve a peak power density (PPD) of 1049 mW cm−2 and demonstrate stable operation over 300 h at 800 °C. Dual-doping effectively balances structural stability and ion transport, advancing perovskite electrodes for efficient SSOFCs.
concentration and O2− mobility. The LSCeFIn-0.1 exhibits low polarization resistances of 0.097 Ω cm2 in H2 and 0.037 Ω cm2 in air. The LSGM-based cells achieve a peak power density (PPD) of 1049 mW cm−2 and demonstrate stable operation over 300 h at 800 °C. Dual-doping effectively balances structural stability and ion transport, advancing perovskite electrodes for efficient SSOFCs.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...