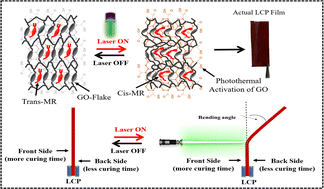
This study investigates the quantitative photomechanical actuation properties of a bifunctional acrylate liquid crystal (LC242) doped with azo dye and graphene oxide (GO) nanocomposites under a 40 mW cm−2 green laser. A photo-responsive liquid crystal polymer (LCP) was developed via UV curing, utilizing methyl red (MR) for its photoisomerism and GO for its photothermal properties. This investigation focuses on optimizing photo-actuating performance by tuning MR and GO doping concentrations as well as photopolymerization conditions. Experimental results show that with a doping concentration of 20% MR, the LCP achieves a photo-induced bending angle of approximately 35° and a response of 2 seconds and a recovery time of 1 second. Additionally, GO incorporation significantly reduces the critical laser power required for deformation; at a 10% concentration, the critical optical power is lowered to 25 mW cm−2. UV curing for 65 minutes (with a 5 : 1 front-to-back exposure ratio) optimizes strain characteristics, enhancing both bending deformation and recovery stability in LCP samples. The tailored photomechanical response allows for efficient and controllable actuation, enabling applications such as PDMS film switching in micropump systems. This LCP film demonstrates improved actuation strain and repeatability, promising advancements for smart material systems and biomedical devices. These results underscore the potential of doping strategies and photopolymerization control to enhance LCP photo-actuation capabilities for light-driven innovations.