Dissociation and aggregation behaviors of starch in choline amino acid ionic liquid solvents: the anion structure effect†
Abstract
To fully explore choline amino acid ([Cho][AA]) ionic liquids (ILs) as starch solvents in various applications, the effects of anion structure (reflected from choline lysine ([Cho][Lys])) and choline aspartic acid ([Cho][Asp]) of [Cho][AA]–water solvents on the dissociation and aggregation behaviors of starch were investigated. Compared with water (66.05 °C), the decreased gelatinization temperatures of starch achieved at water/IL (w : IL) ratios of 5 : 5 (64.09 °C) and 4 : 6 (46.96 °C) of [Cho][Lys] solvents indicated the improved dissociation behaviors of starch (also indicated by large 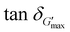 values). In contrast, all proportions (w : IL-9:1–2 : 8) of [Cho][Asp] solvents inhibited the dissociation behaviors of starch, leading to increased gelatinization temperatures (above 85 °C). Moreover, after dissolution, the viscosity and G′ values of starch–[Cho][Lys] solutions were lower than those of [Cho][Asp], indicating the reduced aggregation of starch molecules. These differences emerged from the structural differences of AA− anions. Compared to acidic [Cho][Asp], the longer side chain and the basic NH2 group of Lys−, which has a weaker hydrogen bonding ability than that of the –COOH group of Asp−, endowed [Cho][Lys] solvents with high pH, weaker Cho+–Lys− interactions (indicated by low viscosity), and stronger starch–[Cho][Lys] ion interactions. This allowed [Cho][Lys] ions to interact strongly with starch, thereby promoting the dissociation and inhibiting the aggregation of starch molecules. These findings could pave the way for designing solvent media with [Cho][AA] ILs for specific applications of starch.
values). In contrast, all proportions (w : IL-9:1–2 : 8) of [Cho][Asp] solvents inhibited the dissociation behaviors of starch, leading to increased gelatinization temperatures (above 85 °C). Moreover, after dissolution, the viscosity and G′ values of starch–[Cho][Lys] solutions were lower than those of [Cho][Asp], indicating the reduced aggregation of starch molecules. These differences emerged from the structural differences of AA− anions. Compared to acidic [Cho][Asp], the longer side chain and the basic NH2 group of Lys−, which has a weaker hydrogen bonding ability than that of the –COOH group of Asp−, endowed [Cho][Lys] solvents with high pH, weaker Cho+–Lys− interactions (indicated by low viscosity), and stronger starch–[Cho][Lys] ion interactions. This allowed [Cho][Lys] ions to interact strongly with starch, thereby promoting the dissociation and inhibiting the aggregation of starch molecules. These findings could pave the way for designing solvent media with [Cho][AA] ILs for specific applications of starch.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...