Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleSilver-catalyzed radical carbofluorination of unactivated alkenes with acetic acid in aqueous solution†
He
Chen
a,
Lin
Zhu
a and
Chaozhong
Li
 *ab
*ab
aKey Laboratory of Organofluorine Chemistry and Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Life Sciences, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Road, Shanghai 200032, China. E-mail: clig@mail.sioc.ac.cn
bSchool of Chemical Engineering, Ningbo University of Technology, No. 89 Cuibai Road, Ningbo 315016, China
First published on 18th January 2017
Abstract
The AgNO3-catalyzed reactions of unactivated alkenes with acetic acid and Selectfluor reagent in aqueous solution afforded the corresponding γ-fluorinated carboxylic acids under mild conditions. Carbofluorination was not only efficient and regioselective, but also enjoyed a wide functional group compatibility.
Introduction
Fluorinated molecules have found increasingly important roles in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.1 The introduction of fluorine atoms into pharmaceuticals can make them more lipophilic and metabolically stable, and increase the strength of their interactions with target proteins.1a As a consequence, significant efforts have been devoted to the development of new methods for C–F bond formations under mild conditions in the past decade.2 In this aspect, γ-fluorinated aliphatic carboxylates are a class of compounds with important biological properties.3 They have also found applications as fluorinated probes in membrane topology and protein studies.4 In addition, they serve as useful building blocks for more complex molecules such as a fluorinated erythromycin antibiotic.5 However, these compounds required multistep syntheses, and the overall efficiencies were low. It is thus desirable to develop convenient and efficient methods for the synthesis of γ-fluorinated aliphatic carboxylic acids.We recently reported the silver-catalyzed oxidative decarboxylative fluorination of aliphatic carboxylic acids with Selectfluor6 reagent (1-chloromethyl-4-fluorodiazoniabicyclo-[2,2,2]octane bis(tetrafluoroborate)) in aqueous solution.7 However, during our extension of this method,8 we observed that the decarboxylation of acetic acid was so sluggish that it could be used as a co-solvent in Selectfluor-mediated oxidative radical fluorination reactions.8b,d Meanwhile, it is well documented that Mn(OAc)3-mediated oxidative radical addition of acetic acid to alkenes leads to γ-lactones.9 In light of these phenomena, we envisioned that acetic acid might be able to participate in the 1,2-carbofluorination of alkenes. It should be pointed out that only a few examples of intermolecular carbofluorination were reported and they mainly dealt with activated alkenes such as styrenes or enamines.8d,10 Herein we report the silver-catalyzed carbofluorination of unactivated alkenes by condensation with acetic acid and Selectfluor in aqueous solution, providing an efficient and general entry to various γ-fluorinated aliphatic carboxylic acids in one step.
Results and discussion
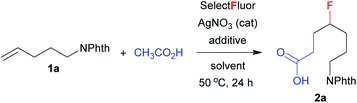
N-(Pent-4-en-1-yl)phthalimide (1a) was thus chosen as the model substrate for the optimization of reaction conditions (Table 1). In a preliminary test, alkene 1a was treated with Selectfluor (3 equiv.) and AgNO3 (20 mol%) in mixed solvents of H2O/dichloromethane(DCM)/AcOH at 50 °C for 24 h, a condition similar to the carbofluorination of alkenes with β-ketoesters.8d Gratifyingly, the expected carbofluorination product 2a was obtained in 57% yield (entry 1, Table 1). Both water and DCM were required as solvents, as evidenced by control experiments (entries 2 and 3, Table 1). Switching the catalyst AgNO3 to AgBF4, AgPF6 or AgOTf did not show any improvement (entries 4–6, Table 1). Next, several additives were screened in an attempt to increase the product yield. The addition of a base such as NaOAc inhibited the reaction (entry 7, Table 1). On the other hand, the addition of an acid such as trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) or nitric acid slightly increased the product yield (entries 8 and 9, Table 1). We then chose phosphoric acid as the co-solvent, and we were delighted to find that the carbofluorination product 2a was isolated in 84% yield (entry 11, Table 1). In the above cases, acetic acid was used as both the reagent and the co-solvent. Lowering the amount of AcOH to 3 equivalents significantly decreased the yield of 2a (entry 12, Table 1). Finally, the role of AgNO3 as a catalyst was proved by the control experiment (entry 13, Table 1).| Entrya | Solvent | Additive (equiv.) | Yieldb (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| a Conditions: 1a (0.2 mmol), AgNO3 (0.04 mmol), Selectfluor (0.6 mmol), solvent (2 mL), additive, 50 °C, 24 h. b Isolated yield based on 1a. c AgBF4 rather than AgNO3 was used. d AgPF6 rather than AgNO3 was used. e AgOTf rather than AgNO3 was used. f AcOH (3 equiv.) was used. g No AgNO3 was used. | |||
| 1 | H2O/DCM/AcOH (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5 0.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5) 0.5) |
— | 57 |
| 2 | H2O/AcOH (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
— | Trace |
| 3 | DCM/AcOH (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
— | Trace |
| 4c | H2O/DCM/AcOH (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5 0.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5) 0.5) |
— | 56 |
| 5d | H2O/DCM/AcOH (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5 0.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5) 0.5) |
— | 53 |
| 6e | H2O/DCM/AcOH (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5 0.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5) 0.5) |
— | 47 |
| 7 | H2O/DCM/AcOH (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5 0.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5) 0.5) |
NaOAc (3) | 28 |
| 8 | H2O/DCM/AcOH (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5 0.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5) 0.5) |
TFA (3) | 58 |
| 9 | H2O/DCM/AcOH (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5 0.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5) 0.5) |
HNO3 (3) | 64 |
| 10 | H2O/DCM/AcOH/H3PO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5 0.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5 0.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.6) 0.6) |
— | 82 |
| 11 |
H
2
O/DCM/AcOH/H
3
PO
4
(1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/b_char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/b_char_2009.gif) 0.5 0.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/b_char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/b_char_2009.gif) 0.5 0.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/b_char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/b_char_2009.gif) 0.8) 0.8)
|
— | 84 |
| 12f | H2O/DCM/H3PO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5 0.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.8) 0.8) |
— | 17 |
| 13g | H2O/DCM/AcOH/H3PO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5 0.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5 0.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.8) 0.8) |
— | 0 |
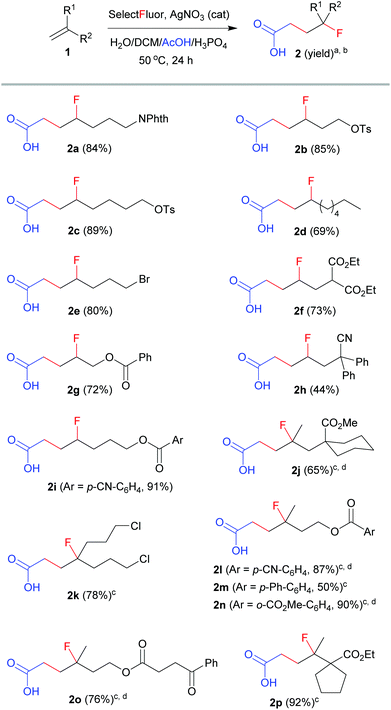
With the optimized conditions (entry 11, Table 1) in hand, we set out to explore the scope and limitation of this method. The results are summarized in Scheme 1. The reactions of mono-substituted alkenes proceeded smoothly to afford the corresponding products 2a–2i in satisfactory yields. Disubstituted alkenes underwent efficient carbofluorination under slightly milder conditions (2 equivalents of Selectfluor and less H3PO4), leading to the synthesis of γ-fluorinated carboxylic acids 2j–2p. A number of functional groups, including amide, tosylate, alkyl bromide or chloride, ester, nitrile, aryl and ketone, were well tolerated. All the reactions were carried out in aqueous solution and thus were very easy to operate. Nevertheless, the reaction was not applicable to activated alkenes such as styrene, in which a hydroxyfluorination product (2-fluoro-2-phenylethan-1-ol) was observed in about 40% yield.11 The extension of this method to propranoic acid or butanoic acid also failed because decarboxylative fluorination became competitive. These results clearly reveal the unique property of acetic acid from other alkanoic acids in silver-catalyzed radical fluorination reactions.7,8
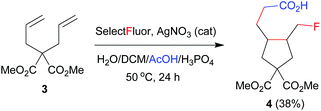
The above results indicate that the reaction may proceed via a radical fluorination mechanism. To provide further evidence, 1,6-diene 3 as a radical probe was prepared and subjected to the above optimized reaction conditions. Cyclopentane 4 was achieved in 38% yield as a mixture of two stereoisomers in an 83![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 17 ratio (eqn (1)).8b,e This addition–cyclization–fluorination sequence strongly supports the radical mechanism of carbofluorination.
17 ratio (eqn (1)).8b,e This addition–cyclization–fluorination sequence strongly supports the radical mechanism of carbofluorination.
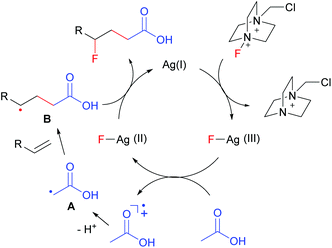
On the basis of the above results and literature reports,7,8 a plausible mechanism is proposed as shown in Fig. 1. The interaction of AgNO3 with Selectfluor generates the Ag(III)–F intermediate presumably via oxidative addition. The single electron transfer between acetic acid and Ag(III)–F leads to the formation of α-carbonyl radical A and Ag(II)–F. The electrophilic radical A then adds to an electron-rich alkene to give adduct radical B. Finally, the nucleophilic alkyl radical B abstracts a fluorine atom from Ag(II)–F to afford the carbofluorination product along with the regeneration of Ag(I). Thus, this reaction further expands the scope of radical fluorination.12
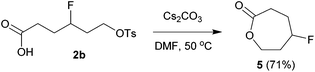
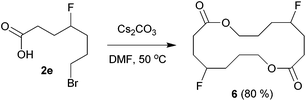
The above carbofluorination offers a convenient route to γ-fluorinated aliphatic carboxylic acids. The remarkable functional group compatibility also enables the carbofluorination products to be versatile building blocks for the synthesis of more complex fluorinated molecules. For example, upon treatment with Cs2CO3, the carbofluorination product 2b could be easily converted to γ-fluorocaprolactone 5 in 71% yield (eqn (2)). The reaction of analogous γ-fluoroacid 2e with Cs2CO3 in DMF did not offer the expected cyclization product γ-fluoroheptanolactone. Instead, the 16-membered cyclic dimer 6 was obtained exclusively in 80% yield as the mixture of two stereoisomers in a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 ratio (eqn (3)). It is worth mentioning that the reaction of 6-bromohexanoic acid under almost identical conditions produced the corresponding cyclic dimer (similar to 6) rather than 5.13 Thus, the formation of 5 from 2b might be attributed to the fluorine effect on substrate conformations.
1 ratio (eqn (3)). It is worth mentioning that the reaction of 6-bromohexanoic acid under almost identical conditions produced the corresponding cyclic dimer (similar to 6) rather than 5.13 Thus, the formation of 5 from 2b might be attributed to the fluorine effect on substrate conformations.
 | (1) |
 | (2) |
 | (3) |
Conclusion
In summary, we have successfully developed the silver-catalyzed radical carbofluorination of unactivated alkenes with acetic acid and Selectfluor in aqueous solution. This three-component condensation proceeds under mild conditions, providing a convenient and efficient entry into various γ-fluorinated alkanoic acids with wide functional group compatibility.Experimental section
Typical procedure for silver-catalyzed carbofluorination of unactivated alkenes with acetic acid
N-(Pent-4-en-1-yl)phthalimide (1a, 43.1 mg, 0.2 mmol), AgNO3 (6.8 mg, 0.04 mmol) and Selectfluor (212.6 mg, 0.6 mmol) were placed in a Schlenk tube under a nitrogen atmosphere. Dichloromethane (0.5 mL), water (1 mL), acetic acid (0.5 mL) and 85% phosphoric acid (0.8 mL) were added successively at room temperature. The reaction mixture was then stirred at 50 °C for 24 h. The resulting mixture was cooled down to room temperature and extracted with CH2Cl2 (3 × 10 mL). The organic phases were combined and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. After the removal of solvent under reduced pressure, the crude product was purified by column chromatography on silica gel with dichloromethane/methanol (60![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, v
1, v![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) v) as the eluent to give the pure product 2a as a white solid. Mp: 86–88 °C. Yield: 49.1 mg (84%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.83–7.85 (m, 2H), 7.70–7.72 (m, 2H), 4.48–4.64 (m, 1H), 3.69–376 (m, 2H), 2.46–2.57 (m, 2H), 1.55–1.96 (m, 6H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 178.6, 168.4, 133.9, 132.0, 123.2, 92.4 (d, J = 169.0 Hz), 37.5, 32.2 (d, J = 20.6 Hz), 29.9 (d, J = 21.0 Hz), 29.5 (d, J = 4.3 Hz), 24.3 (d, J = 3.9 Hz); 19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3): δ −183.8 (m, 1F); IR (KBr): ν (cm−1) 2942, 1772, 1719, 1713, 1707, 1440, 1400, 1367, 1051, 721; ESI-MS: (m/z) 316.1 (M + Na); HRMS calcd for C15H16FNNaO4 (M + Na): 316.0956, found 316.0966.
v) as the eluent to give the pure product 2a as a white solid. Mp: 86–88 °C. Yield: 49.1 mg (84%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.83–7.85 (m, 2H), 7.70–7.72 (m, 2H), 4.48–4.64 (m, 1H), 3.69–376 (m, 2H), 2.46–2.57 (m, 2H), 1.55–1.96 (m, 6H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 178.6, 168.4, 133.9, 132.0, 123.2, 92.4 (d, J = 169.0 Hz), 37.5, 32.2 (d, J = 20.6 Hz), 29.9 (d, J = 21.0 Hz), 29.5 (d, J = 4.3 Hz), 24.3 (d, J = 3.9 Hz); 19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3): δ −183.8 (m, 1F); IR (KBr): ν (cm−1) 2942, 1772, 1719, 1713, 1707, 1440, 1400, 1367, 1051, 721; ESI-MS: (m/z) 316.1 (M + Na); HRMS calcd for C15H16FNNaO4 (M + Na): 316.0956, found 316.0966.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (Grant 2015CB931900), by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 21272259, 21290180, 21421002, 21472220, 21502210, 21532008, 21602239, and 21361140377), and by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant XDB20020000).Notes and references
-
(a) K. Muller, C. Faeh and F. Diederich, Science, 2007, 317, 1881 CrossRef PubMed
; (b) S. Purser, P. R. Moore, S. Swallow and V. Gouverneur, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2008, 37, 320 RSC
; (c) P. Jeschke, ChemBioChem, 2004, 5, 570 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
-
(a) T. Liang, C. N. Neumann and T. Ritter, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 8214 CrossRef CAS PubMed
; (b) X. Mu and G. Liu, Org. Chem. Front., 2014, 1, 430 RSC
; (c) J. Ma and S. Li, Org. Chem. Front., 2014, 1, 712 RSC
; (d) A. J. Cresswell, S. G. Davies, P. M. Roberts and J. E. Thomson, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 566 CrossRef CAS PubMed
; (e) M. G. Campbell and T. Ritter, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 612 CrossRef CAS PubMed
; (f) C. Ni, M. Hu and J. Hu, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 765 CrossRef CAS PubMed
; (g) X. Yang, T. Wu, R. J. Phipps and F. D. Toste, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 826 CrossRef CAS PubMed
; (h) P. A. Champagne, J. Desroches, J.-D. Hamel, M. Vandamme and J.-F. Paquin, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 9073 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
-
(a) K. Lucet-Levannier, J.-P. Lellouche, C. Mioskowski, F. Schneider and C. Cassagne, Tetrahedron Lett., 1996, 37, 2007 CrossRef CAS
; (b) T. Verbrugghen, P. Cos, L. Maes and S. V. Calenbergh, J. Med. Chem., 2010, 53, 5342 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
-
(a) N. J. M. Birdsall, Tetrahedron Lett., 1971, 12, 2675 CrossRef
; (b) J.-D. Charrier, D. S. Hadfield, P. B. Hitchcock and D. W. Young, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2004, 2, 797 RSC
; (c) J. Guimond-Tremblay, M.-C. Gagnon, J.-A. Pineault-Maltais, V. Turcotte, M. Auger and J.-F. Paquin, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2012, 10, 1145 RSC
.
- R. J. M. Goss and H. Hong, Chem. Commun., 2005, 3983 RSC
.
-
(a) R. E. Banks, S. N. Mohialdin-Khaffaf, G. S. Lal, I. Sharif and R. G. Syvret, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1992, 595 RSC
; (b) R. P. Singh and J. M. Shreeve, Acc. Chem. Res., 2004, 37, 31 CrossRef CAS PubMed
; (c) P. T. Nyffeler, S. G. Durón, M. D. Burkart, S. P. Vincent and C.-H. Wong, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2005, 44, 192 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- F. Yin, Z. Wang, Z. Li and C. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 10401 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
-
(a) Z. Li, L. Song and C. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 4640 CrossRef CAS PubMed
; (b) C. Zhang, Z. Li, L. Zhu, L. Yu, Z. Wang and C. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 14082 CrossRef CAS PubMed
; (c) Z. Li, Z. Wang, L. Zhu, X. Tan and C. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 16439 CrossRef CAS PubMed
; (d) L. Zhu, H. Chen, Z. Wang and C. Li, Org. Chem. Front., 2014, 1, 1299 RSC
; (e) Z. Li, C. Zhang, L. Zhu, C. Liu and C. Li, Org. Chem. Front., 2014, 1, 100 RSC
.
-
(a) J. B. Bush Jr. and H. Finkbeiner, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1968, 90, 5903 CrossRef
; (b) B. B. Snider, Chem. Rev., 1996, 96, 339 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
-
(a) A. D. Dilman, P. A. Belyakov, M. I. Struchkova, D. E. Arkhipov, A. A. Korlyukov and V. A. Tartakovsky, J. Org. Chem., 2010, 75, 5367 CrossRef CAS PubMed
; (b) E. P. A. Talbot, T. A. Fernandes, J. M. McKenna and F. D. Toste, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 4101 CrossRef CAS PubMed
; (c) H. Wang, L.-N. Guo and X.-H. Duan, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 7382 RSC
; (d) S. Kindt and M. R. Heinrich, Chem. – Eur. J., 2014, 20, 15344 CrossRef CAS PubMed
; (e) R. Guo, H. Yang and P. Tang, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 8829 RSC
.
- For an example of 1,2-oxyfluorination of alkenes, see: Y.-Y. Liu, J. Yang, R.-J. Song and J.-H. Li, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2014, 356, 2913 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. P. Sibi and Y. Landais, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 3570 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- W. H. Kruizinga and R. M. Kellogg, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1981, 103, 5183 CrossRef CAS
.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Experimental details, characterization of products and copies of 1H, 13C and 19F NMR spectra. See DOI: 10.1039/c6qo00854b |
| This journal is © the Partner Organisations 2017 |