Recent progresses in the modification strategies of MXene-based membranes for water and wastewater treatments
Yingchao
Du
ab,
Jingyu
Yu
ab,
Baoliang
Chen
 ab and
Xiaoying
Zhu
ab and
Xiaoying
Zhu
 *ab
*ab
aCollege of Environmental and Resource Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China. E-mail: duyc@zju.edu.cn; 22314074@zju.edu.cn; blchen@zju.edu.cn; zhux@zju.edu.cn
bInnovation Center of Yangtze River Delta, Zhejiang University, Jiashan 314100, China
First published on 22nd October 2024
Abstract
Membrane technology stands as a leading method for water and wastewater treatments. MXene, a type of two-dimensional material, has garnered significant interest as a promising next-generation membrane material. Its customizable pore structure, uniform pore size, and hydrophilicity make it highly suitable for membrane separation technologies. This work elucidates the modification strategies employed by MXene-based membranes (MBMs) and evaluates their performances. Initially, the preparation of MXene nanosheets, pivotal to membrane fabrication, is detailed. Subsequently, the fabrication methods and existing problems of MBMs are presented. Furthermore, we emphasize the modification strategies employed to enhance the performance of MBMs. These encompass the regulation of MXene nanosheets in terms of lateral size, terminal functional groups, and in-plane pores. Furthermore, adjustments are made to the membrane assembly processes, focusing on controlling the interlayer spacing. This includes methods such as self-crosslinking, insertion, and the incorporation of hybrid functional layers. Additionally, surface modifications encompass the regulation of surface charge, surface wettability, and management of surface defects. Next, we delineate the key membrane applications, encompassing separation mechanisms and their promising utilities. Lastly, we present the challenges and opportunities that MBMs face in the field of water purification, with the hope of providing profound insights into the design and synthesis of advanced MBMs.
Environmental significanceSubstantial progress has been achieved in the development of highly selective separation membranes for a range of water treatment processes, including desalination, water purification, pollution remediation, and resource recovery. Research has been intensively targeted on advanced materials to boost the separation efficiency. Notably, atomic-thin 2D materials are widely studied for their potential in fabricating high-performance membranes with nanoscale precision. The rise of MXene-based membranes, known for their selective ion transport and regulated molecular flow, has piqued significant scientific curiosity in water treatment advancements. This review summarizes the common modification strategies of MXene-based membranes in water and wastewater treatment, aiming to design advanced membranes. It is expected to provide valuable insights for implementing MXene-based membranes with excellent performances, thus contributing significantly to the field. |
1. Introduction
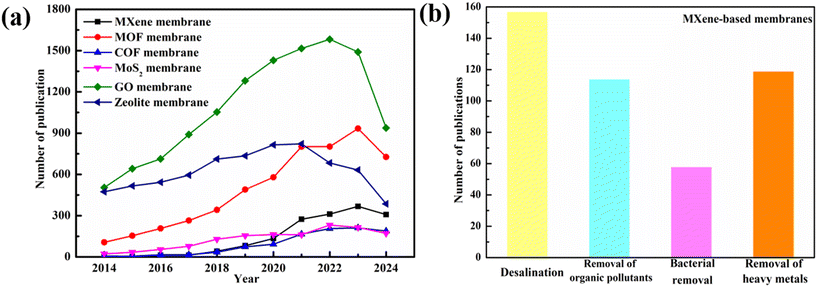
Membrane separation is widely recognized as an effective water purification technology due to its numerous advantages, including low energy consumption, easy operation, and high efficiency.1 The pressure-driven membranes including nanofiltration (NF), reverse osmosis (RO), ultrafiltration (UF), and microfiltration (MF) membranes are widely used in various water treatment processes, encompassing desalination, water purification, pollution remediation, and resource recovery.2 In addition, 2D materials have gained significant attention in the field of environmental remediation and are often referred to as “wonder materials” due to their unique properties, such as high aspect ratio, excellent mechanical properties, and customizable and controllable structure, and potential applications in addressing environmental challenges.3 Additionally, the unique properties of 2D materials have made them attractive for the fabrication of high-performance membranes with both high separation and performance capabilities. Graphene-based membranes, in particular, have paved the way for the development of various 2D materials for membrane applications. Consequently, the development of 2D material-based membranes, including graphene, MoS2, zeolites, covalent organic frameworks, and metal–organic frameworks, hold great promises in various membrane separation applications.4–7MXenes, a family of 2D transition metal carbides, nitrides, and carbonitrides, were introduced in 2011 by Yury Gogotsi's group at Drexel University and quickly drew attention due to their impressive properties. These materials, derived from the selective etching of A layers from MAX phases, had shown potential in areas such as catalysis, energy, and environmental applications.8,9 The MAX phases can be expressed by the formula Mn+1AXn, where M is an early transition metal, A is a IIIA or IVA element (Si, Al, Ga and Ge), X is a carbon or nitrogen atom, and n ranges from 1 to 3. As for the first artificially prepared MXene Ti3C2Tx, T stands for the terminal functional groups, such as oxygen, fluorine and hydroxyl, and X stands for the number of these functional groups. The unique properties of MXenes, including their customized pore structure, uniform pore size distribution, hydrophilicity, and strength, make them promising candidates for membrane fabrication. Over the past few decades, researchers have successfully synthesized over 30 different types of MXenes whose potentials for advanced membrane preparation have been explored on a laboratory scale, exploring their potential applications in membrane technology.10 As shown in Fig. 1, the MXene-based membranes have received widespread attention and have shown a fast growing tendency as compared to the membranes prepared from other 2D materials; in addition, the applications of the MXene-based membrane in water and wastewater treatments are rapidly increasing.
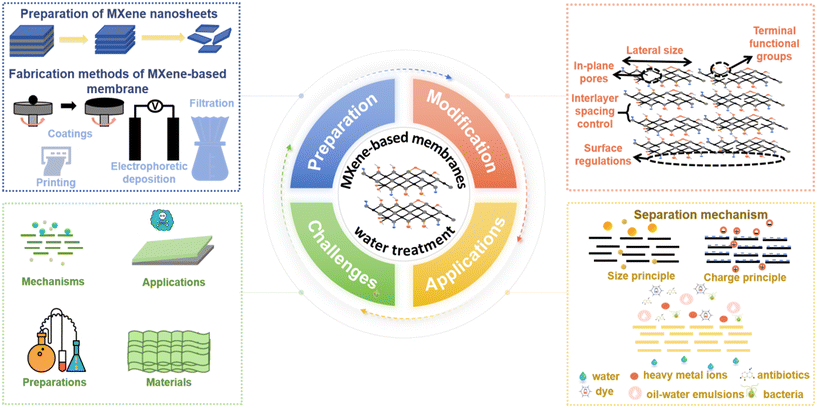
Given the promising, accessible, and versatile nature of MXenes as 2D materials, several reviews have covered the performance-enhancing modifications of MBMs in separation processes. For instance, Sun et al. provided a concise overview of the new designing approaches to enhance the performance of MXene-based membranes including physical intercalation, chemical cross-linking, and membrane surface modification.2 Kwon et al. mentioned the membrane modification strategies of the interlayer control and surface modification.11 In addition, Lin et al. described the preparation and physicochemical properties of MXene nanomaterials, as well as the construction and modification of MBMs.12 Khosla et al. introduced the latest MXene-polymer hybrid membranes, focusing on advancement and tuning in attributes of MXene-polymer hybrid membranes.13 Nonetheless, it was frequently overlooked that the alteration of MXene nanosheets and the manipulation of MXene-based membranes (MBMs) were equally crucial to the separation efficiency of membrane materials. Consequently, there was a paucity of reports delving into the modification strategies that specifically enhanced the filtration performance of MBMs, particularly from the perspectives of regulating the MXene nanosheets and optimizing the assembly process of the membranes. Herein, it is vital to sum up a comprehensive review covering the modification strategies of the MXene-based membranes in the water and wastewater treatment for designing and exploiting advanced membranes. As shown in Fig. 2, the main contents of this review are divided into four parts: 1) preparation methods of MXene nanosheets and MBMs, respectively, 2) strategies for the performance improvement of MBMs, covering the regulations of MXene nanosheets and the adjustments of membrane assembly process, 3) applications of MBMs in water and wastewater treatment and separation mechanisms, and 4) challenges and opportunities for MBMs in water treatment. This review is expected to provide valuable insights into the design and implementation of MBMs with excellent performance.
2. A brief introduction to MXene nanosheets
Thus far, more than 30 types of MXenes have been synthesized and examined in laboratory settings. MXene nanosheets, crucial for MXene membrane fabrication, required specific methods for isolation due to their strong bonding within MAX phases. Generally, a three-step (etching-intercalation-delamination) procedure was put forward to obtain few-layer or single-layer MXene sheets.14 The properties of MXene nanosheets depended on the preparation conditions, etchants used, and their concentration. These resulting 2D MXenes possessed negative charges and hydrophilic surfaces, rendering them highly attractive for developing membranes with exceptional properties.152.1 Preparation of MXene nanosheets
Since 2011, MXene nanomaterial preparation techniques have advanced significantly, with synthesis methods represented in detail in Fig. 3, including representative preparation strategies. These strategies allowed for the isolation of MXene nanosheets from MAX or non-MAX phase precursors, facilitating the formation of MXene phases from diverse element combinations. The preparation methods of MXene nanosheets generally fall into two categories, namely chemical and physical methods.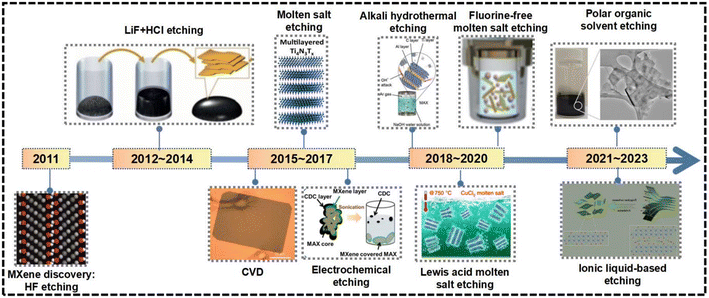 | ||
| Fig. 3 Timeline of synthesis development to fabricate novel MXene nanomaterials.9,16–24 (Reproduced from ref. 9 with permission from Wiley Online Library, copyright 2011; reproduced from ref. 16 with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2014; reproduced from ref. 17 with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2015; reproduced from ref. 18 with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry, copyright 2016; reproduced from ref. 19 with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry, copyright 2017; reproduced from ref. 20 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2018; reproduced from ref. 21 with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2020; reproduced from ref. 22 with permission from Wiley Online Library, copyright 2020; reproduced from ref. 23 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2022; reproduced from ref. 24 with permission from the American Chemical Society, copyright 2017). | ||
| Mn+1AlXn + 3HF = AlF3 + 1.5H2 + Mn+1Xn | (1) |
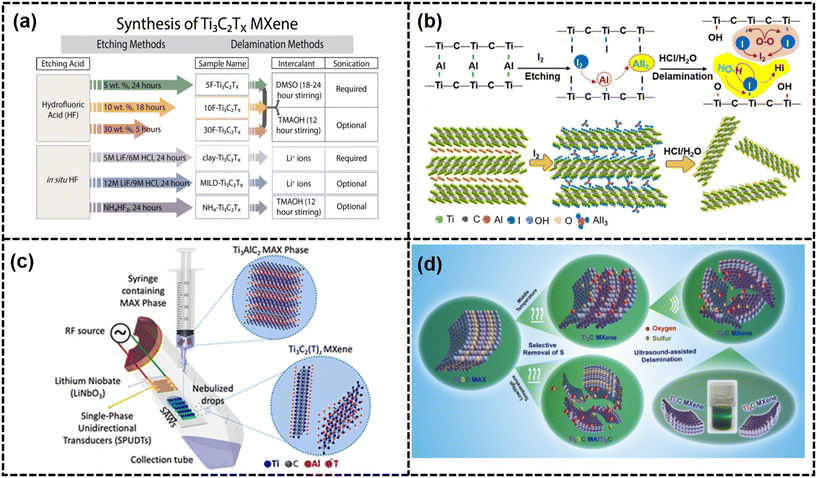 | ||
| Fig. 4 (a) General map for Ti3C2Tx synthesis from Ti3AlC2 (ref. 24) (reproduced from ref. 24 with permission from the American Chemical Society, copyright 2017), (b) iodine-assisted etching and delamination towards 2D MXene sheets32 (reproduced from ref. 32 with permission from Wiley-VCH GmbH, copyright 2021), (c) schematic of the experimental setup and underlying physiochemical mechanism responsible for the SAW-facilitated derivation of Ti3C2Tz MXene33 (reproduced from ref. 33 with permission from the American Chemical Society, copyright 2021) and (d) schematic of the fabrication of 2D Ti2C MXenes via an effective thermal reduction approach34 (reproduced from ref. 34 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2020). | ||
Alternative etching techniques to HF, such as electrochemical etching in HCl, have been developed. In dilute HCl, Al from a MAX electrode could form a MXene layer electrochemically. This fluoride-free process has a predictable byproduct, and a core–shell model was suggested to control the etching parameters and avoid over-etching.19 As for the selective removal of Al layers, the design and choice of electrolytes was significant. Furthermore, these MXenes exclusively featured –Cl terminal groups, alongside commonly found groups such as –O and –OH. Nonetheless, electrochemical etching can lead to the subsequent over-etching of parent MAX phases, resulting in the formation of carbide-derived carbon (CDC).19 Similarly, a binary aqueous system was used as the electrolyte to achieve the anodic corrosion of Ti3AlC2 in high yields (>90%) and large average dimension, which was comparable or even better than those techniques using HF or LiF/HCl. Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a versatile method for producing ultrathin, consistent Mo2C MXene films, capable of being deposited on various substrates such as Cu/Mo bilayers, graphene, and MoO2. The process involved exposing substrates to a precursor gas mixture in a controlled atmosphere, facilitating Mo2C MXene layer formation via chemical reactions.17,35,36 The one-step direct synthesis of a 2D Mo2C-on-graphene membrane by molten copper-catalyzed CVD has been documented. High-quality and uniform Mo2C membranes, spanning centimeters, can be grown on graphene using a Mo–Cu alloy catalyst. The graphene-templated growth of Mo2C yielded well-faceted, large-sized single crystals with low defect density. Salt-templated growth was a method commonly used for the synthesis of various metal nitrides including Mn3N2, W2N, and V2N, which involved dissolving metal salts in suitable solvents and adding a reducing agent to prompt precipitation. The ammoniation of the 2D h-MoO3@NaCl powder and the subsequent dissolution of the salt template resulted in the production of hydrophilic 2D MoN nanosheets with subnanometer thickness, dispersed in water.37 The resulting particles were typically trapped in the template pores, creating hierarchical structures with distinctive properties.37 NaCl and KCl templates could cause lattice distortion, leading to various MXene structures.38 Adjusting precursors and synthesis parameters can trigger the formation of diverse 2D metal nitrides and carbides with a subnanometer thickness. Inspired by the Bayer process used in bauxite refining, an alkali-assisted hydrothermal method was developed to fabricate multilayer MXenes without F terminations. The temperature and concentration of NaOH played crucial roles in breaking the barrier of the dynamic process and eliminating the generation of oxide hydroxides.20
A chemical-combined ball-milling method combines the appropriate etchants with ball milling, which is a simple and green technique for the large-scale production of MXenes. In addition, this approach enabled the production of Ti3C2Tx with extra-high specific surface area and hierarchical porosity, featuring solely oxygen-containing groups without over-oxidation.39 Thus, this simple strategy could be extended as a universal approach for preparing various fluorine-free and porous MXenes with a significantly increased specific surface area, which was 8 times higher than that of Ti3C2 obtained from traditional HF treatment.39
No scandium-based MXenes have ever been successfully fabricated, and magnetron sputtering was employed to fabricate semiconductive MXenes with a direct band gap, complemented by a thermal annealing process to introduce further oxidation.40 Magnetron sputtering of Ti, Al and C can form a few-nanometer TiC incubation layer on a sapphire substrate, followed by the deposition of epitaxial Ti3AlC2, and then selectively etched Al from MAX. Through improved control of the deposition process to minimize or eliminate non-basal growth, there exists the potential to enhance the conductivity.40
An innovative thermal reduction strategy was introduced for producing MXenes from sulfur-containing MAX phases. In this method, weakly bonded S atoms reacted with hydrogen, forming a volatile gas and leaving behind 2D graphene-like Ti2C nanosheets, which is shown in Fig. 4(d).34 Diverging from conventional acid etching, our approach involved conducting the etching step under reducing conditions in the presence of hydrogen gas. At an optimal treatment temperature, the weakly sandwiched sulfur layers between metal ions and carbon layers in the MAX phase crystals were nearly eliminated, resulting in weakly stacked Ti2C MXene structures. Notably, if the reduction temperature was too low or too high, a mixture of Ti2SC MAX phase and Ti2C layered structures was obtained, underscoring the criticality of the reaction temperature. This innovative synthetic method represents a groundbreaking approach to producing 2D MXenes from sulfur-containing MAX phases. The controllable thermal reduction strategy is easily scalable, avoids the use of hazardous acids, and thus, holds tremendous potential for future industrial production.34
MXenes were obtained through high-temperature etching of MAX phases, such as the treatment of Ti4AlN3 in a molten fluoride salt mixture at 550 °C under an argon atmosphere to form Ti4N3 MXenes.18 Temperature and atmosphere are pivotal factors in the synthesis and annealing of MXenes. At moderate temperatures, molten salts can form Lewis acids and basic molten salts containing CuCl2 and CdCl2, facilitating the etching of A-layer elements from the MAX phase. This process led to the generation of Cl− and Br−−terminated MXenes due to the easy oxidation of A elements to produce volatile compounds.21 Additionally, it was feasible to modify the weak bond energy of M–Cl and M–Br bonds, enabling the design of MXenes with terminal versatility, incorporating oxygen, sulfur, and imido groups.41
2.2 Structure and chemistry of MXene nanosheets
The 2D morphology of MXenes is of particular importance due to the high aspect ratio of regular MXene nanosheets. These nanosheets endowed the resulting membranes with nanochannels, which lengthened diffusion pathways for solute transport. These nanochannels were formed by pinholes, internal spacings between parallel and wrinkled nanosheets (known as nanogalleries), and voids between the nanosheet edges, which could be considered as nanoslits. The elongation of permeation pathways allows for the differentiation of solute transport rates, forming the basis of selectivity for MXene membranes.42 Moreover, by engineering the interlayer spacing of 2D MXene assemblies, well-defined transport channels can be created, enabling size-exclusion-based molecular separation. The interlayer spacing between Ti3C2Tx nanosheets can be reduced to a range of 0.52–0.38 nm when dried and/or heated. Additionally, the lateral dimension (flake size) of MXene nanosheets is adjustable from 6 to <1 μm by varying the etching and exfoliation conditions. Furthermore, MXenes are not perfectly flat materials and can become wrinkled, adding to their microstructural properties.43The processibility of MXene nanosheets plays a crucial role in the membrane preparation process, particularly their excellent dispersity and stability in aqueous solution. The surface of MXene nanosheets typically contains abundant hydrophilic functional groups such as –OH, which help to form and stabilize dispersions.44 Moreover, this excellent dispersity is conducive to functionalizing the MXene nanosheets. MXenes are well-suited for light-to-heat harvesting due to their high electromagnetic interference shielding effect, which is related to their prominent absorption ability. The exceptional electromagnetic wave absorption of MXenes prompted researchers to investigate their sunlight absorption ability and corresponding heat conversion. Furthermore, MXenes exhibit excellent electrical conductivity, which has the potential to modify the surface charge and control ion permeation. The high chemical and mechanical stabilities of MXenes are advantageous for water purification. Recent research has also demonstrated that MXenes possess high antibacterial efficiency towards both Gram-negative E. coli and Gram-positive B. subtilis. The versatile chemistry of MXenes allows for the control of properties for a wide range of applications including energy storage, biosensing, lubrication, and catalysis.15
3. Fabrication, characterization and existing problems of MXene-based membranes
Membranes made from 2D materials can be divided into two main types: those with in-plane pores and lamellar membranes without pores in their sheets. MXene membranes fall into two categories, namely lamellar MXene membranes and MXene nanosheets dispersed within a polymer matrix (MMMs).45 Lamellar membranes are characterized by layered structures of stacked MXene nanosheets, while MMMs incorporated MXene nanosheets as fillers in a polymer matrix to enhance the membrane performance.463.1 Fabrication of MXene-based membranes
The stacking order and arrangement of MXene nanosheets in lamellar membranes significantly affect their separation properties, determining the interlayer spacing and molecule/ion transport. Preparation methods are crucial for achieving the desired membrane structure, with techniques such as filtration, coatings, and other methods evolving to improve the fabrication of MBMs. These methods are primarily categorized into three types, as shown in Fig. 5.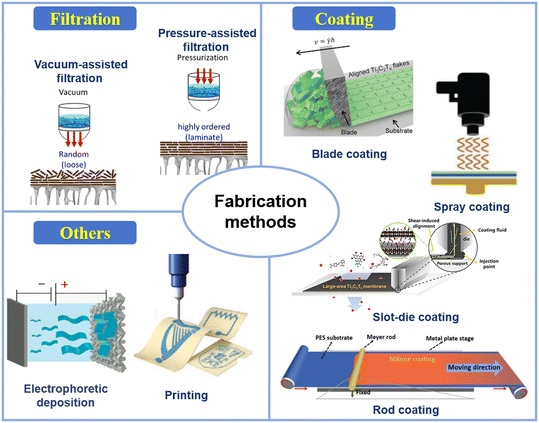 | ||
| Fig. 5 Fabrication methods of MXene-based membranes47–54 (reproduced from ref. 47 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2021; reproduced from ref. 48 with permission from Wiley Online Library, copyright 2020; reproduced from ref. 49 with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2019; reproduced from ref. 50 with permission from Wiley Online Library, copyright 2020; reproduced from ref. 51 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2020; reproduced from ref. 52 with permission from the American Chemical Society, copyright 2021; reproduced from ref. 53 with permission from Wiley Online Library, copyright 2023; reproduced from ref. 54 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2015). | ||
The high dispersibility of MXenes in solutions is crucial for the development of MXene-based printing inks, enabling efficient integration into ink formulations and ensuring a uniform distribution. This allows for precise and controlled printing, potentially transforming manufacturing and applications by enabling the direct printing of functional materials and structures.50 Printing techniques are generally categorized as digital (e.g., inkjet and 3D printing) and nondigital (e.g., screen and transfer printing), with the choice for MXene membranes depending on the required structure, resolution, scalability, and method-specific capabilities.48,49
MXene flakes, abundant in hydrophilic terminations, readily disperse in polar solvents, offering the potential for polymerization with various monomers. Furthermore, the unique channels formed by the nanosheet stacking enable precise molecular separation through prepared MXene membranes. The VAF or PAF technique, relying on interlayer van der Waals (VDW) and hydrogen bonding interactions of MXene nanosheets, is widely used as a direct approach to produce freestanding or supported membranes based on MXenes. The physicochemical characteristics of MXenes are generally unaffected by these approaches, as the interactions between MXene sheets primarily involve VDW interactions, electrostatic repulsion, and hydrogen bonding. However, these methods were notably contentious, primarily due to low stability and potential defects arising from external forces, thereby limiting the use of more robust physical cleaning methods and consequently restricting the membrane's lifespan. The principal drawbacks of these approaches included the lack of uniform membrane development and precise control of thickness. Thicker MXenes with fully exfoliated high-quality MXenes enable a highly aligned space in the horizontal direction, thereby enhancing molecular separation efficiency.15 The coating assembly can overcome the repulsive interactions between the edges of MXene sheets to form densely stacked MXene layers by using attractive capillary forces. These methods strive to scale up and commercialize MXene membranes with tailored separation performance and controllable thickness. Advanced coating assembly, such as roll-to-roll coating, can achieve the oriented assembly of MXene nanosheets with uniform nanochannels and ordered interlayer distance.53 Membranes obtained through blending casting exhibit a more stable structure and a lower loss of MXenes during the separation process. Good compatibility is crucial for constructing mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) with outstanding separation performance. Nanofillers prepared by casting usually possess strong mechanical stability, effectively minimizing material loss since the nanofillers are encapsulated by the polymeric substrate. However, the uneven distribution of MXenes doped therein might occur, necessitating further regulation of the dispersion of MXene nanosheets in the polymer. The ECD (electrophoretic deposition) is an emerging method for preparing MXene-based membranes, enabling the production of membranes with a large specific surface area, facile surface modification, and tunable thermomechanical properties. The remarkable mechanical properties and flexibility of MXene nanosheets align with the characteristics of this process.73 Each printing technique including inkjet, screen, and 3D printing provides distinct benefits and can be customized for specific MXene membrane needs.
3.2 Characterization of MXene-based membranes
The characterization of MXene structures and compositions often requires the use of multiple advanced techniques within a single study. Techniques such as X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, electron microscopy/spectroscopy, and atomic force microscopy (AFM) are commonly used to assess the suitability of the precursor (MAX phase) for MXene synthesis, confirm the successful synthesis of MXene, and determine its composition, structure, and properties.74,75Density functional theory (DFT) calculations enable the direct visualization of the electronic properties of MXenes and the prediction of intermediate evolution kinetics by simulating the interaction of reactants with the active site.76 For instance, DFT calculations are used to study the behavior of bilayer Ti3C2T2 (T = non, F, O, and OH) MXenes in the presence of different ions between the layers. Additionally, the dynamic response of functionalized MXenes to intercalating ions was obtained through both DFT and ReaxFF MD simulations. This dynamic behavior of the MXene layers arises from the charged nature of the material, which was confirmed in simulations by injecting external charges to the O-terminated MXene layers.77In situ liquid time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS) has been established as a new experimental technique to obtain dynamic information regarding the structure of solvated ions, enabling novel investigatory science in nanofluidics and related fields. It allowed for the first in situ observation of changes in the hydration state of solvated ions following transport across extremely confined environments.78 The presence of –OH and –F terminations has been identified in the 1H and 19F nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra of MXene. Additionally, H2O has found to be still present between the nanosheets after vacuum drying at 200 °C. Two-dimensional correlation experiments confirmed the connectivity of the –OH and –F terminations and revealed that they are all present in close vicinity to each other between the metal carbide layers. Quantitative NMR experiments showed that there were significantly fewer –OH terminations than –F and –O terminations and that the surface termination was highly sensitive to the synthesis method used.79 ToF-SIMS was recognized for its exceptional sensitivity and ability to analyze the surfaces and interfaces with a remarkable level of spatial resolution, making it a valuable mass spectrometric technique.80 Molecular simulation has been used to explore the performance of molecular transportation through nanochannels from a microscopic perspective, predicting membrane performance and illustrating the separation mechanism at the all-atom level. It has been found that the arrangements of solvents in the membrane are mainly regulated by the interaction between solvents and MXene surfaces.81 The extended Derjaguin–Landau–Verwey–Overbeek theory can be applied to the high interaction energy between the membrane and pollutants.82
3.3 Existing problems of MXene-based membranes
Membranes made from previously mentioned preparation methods showed promise in ion and molecular selectivity. However, MBMs faced challenges in structure and applications, as shown in Fig. 6, with susceptibility to challenges such as oxidation issues, over-restacking, swelling, and fouling, which could hamper separation performance and stability.12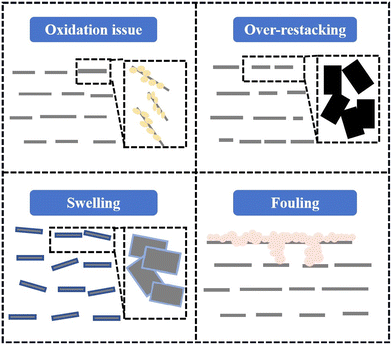 | ||
| Fig. 6 Current challenges of MXene-based membranes: oxidation issue, over-restacking, swelling and fouling. | ||
Over-restacking. Concurrently, the Ti3C2Tx nanosheets typically tended to form a dense structure through a face-to-face stacking pattern. The restacking of MXene nanoflakes and their small interlayer spacing imposed limitations on their application.86 The challenge of over-restacking of MXene nanosheets, arising from strong interfacial interactions, was primarily propelled by interlayer van der Waals forces.87 The inherent repulsive force between Ti3C2Tx nanosheets led to non-selective defects, which restricted the exposed surface area and reduced water penetration.88 Consequently, the over-restacked MXene membrane failed to provide sufficient access for ions to contact the active material, resulting in poor rate performance. Moreover, the interlayer stacking introduced additional resistance, thereby deteriorating ionic dynamic diffusion. It was imperative to pay more attention to the inevitable stacking constraints, given the close influence of the stacked structure on the transport pathway.89 To mitigate this issue, numerous strategies had been developed to curb over-restacking, including freeze-drying, intercalation, and crosslinking.
Swelling. The abundance of oxygen-containing functional groups such as –OH and –O on MXene nanosheets contributed significantly to their outstanding hydrophilicity and their capacity to absorb water.90 This hydrophilic characteristic could lead to an expansion of the interlayer spacing, known as the d-spacing, when MXene nanosheets encounter an aqueous environment.91 In lamellar membranes, the size of the d-spacing is a pivotal factor influencing both permeability and rejection. It is crucial to consider the potential for overexpansion or excessive swelling of MXene nanosheets in aqueous solutions, as this can result in undulations or distortions in membranes.92 MXene membranes has a propensity to absorb numerous water molecules when immersed in water, salt solutions, or when subjected to hydrodynamic flow conditions. This led to an increase in interlayer spacing, membrane delamination, and a decrease in structural stability and separation selectivity. While the numerous surface end groups of MXenes serve as sites for water molecule adsorption, they also have the potential to act as sites for reducing swelling.93 As a result, various research endeavors had been pursued to enhance the anti-swelling resistance of MBMs, including methods such as insertion, crosslinking, and self-crosslinking. These approaches aimed to mitigate the swelling tendencies of MBMs, thereby enhancing their stability and performance in aqueous environments.
Fouling. Membrane fouling, particularly in organic pollutant separation, poses a significant challenge. The issue of surface fouling is a critical concern due to the presence of pollutants in various feed streams, which can precipitate, adsorb, and block pores, thereby reducing the lifespan of membranes. Water treatment separation membranes are highly susceptible to fouling by organic and biological contaminants, leading to the formation of a thick, gel-like biofilm that can significantly decrease flux and degrade separation performance. Membrane fouling presents a persistent challenge in water treatment processes, often requiring the frequent use of chemical agents to mitigate fouling effects. However, this practice results in increased energy consumption and reduced membrane lifespan. Addressing biofouling was particularly crucial in wastewater treatment systems.94 Specifically, hydrophilic MXene coatings demonstrated remarkable antibacterial activity against common waterborne bacteria including E. coli and B. subtilis. The surface oxidation of aged membranes showed a notable improvement in antibacterial activity compared to freshly prepared membranes, attributed to the synergistic effect between Ti3C2Tx nanosheets and TiO2/C formed on the surface.95 MXene-coated anti-biofouling membranes exhibited excellent antibacterial activity by causing irreparable damage to bacterial cell membranes, probably due to the direct physical contact between bacterial surfaces and highly defective MXene sharp edges, leading to physical stress and disruption of cellular membranes.96 Additionally, the hydrophilic nature of MXene nanosheets provided self-cleaning ability, potentially extending the lifespan of MXene membranes. Furthermore, conductive MXene-based membranes could induce fouling on the membrane surface rather than allowing more contaminants to enter the membrane pores, making it easier to restore their flux after cleaning.97
4. Modification strategies of MXene-based membranes
Accordingly, it is essential to employ tailored modification techniques on MBMs to achieve attributes such as high selectivity, superior water flux, resistance to fouling, and exceptional stability. As shown in Fig. 7, these modification strategies for MBMs briefly described the regulations of MXene nanosheets and adjustments of the membrane assembly process, which had great effects on the structure and performance of MBMs.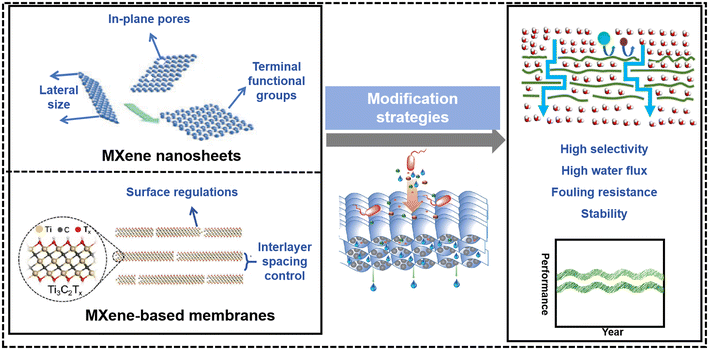 | ||
| Fig. 7 Modification strategies of MXene-based membranes56,58,98,99 (reproduced from ref. 56 with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry, copyright 2018; reproduced from ref. 58 with permission from the American Chemical Society, copyright 2015; reproduced from ref. 98 with permission from Wiley Online Library, copyright 2018; reproduced from ref. 99 with permission from Wiley Online Library, copyright 2019). | ||
4.1 Regulation of MXene nanosheets
The properties of MXene nanosheets produced by various preparation methods vary based on their morphology and structure, which in turn can influence nanosheet stacking.100 To improve the filtration efficiency of MXene membranes, it is crucial to modify the nanosheets, focusing on three key areas: in-plane pores, terminal functional groups, and lateral size, as shown in Fig. 8.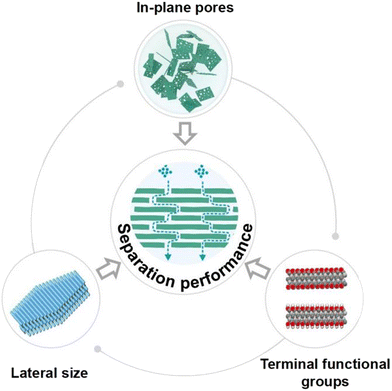 | ||
| Fig. 8 Main aspects for the regulation of MXene nanosheets77,101,102 (reproduced from ref. 77 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2022; reproduced from ref. 101 with permission from the American Chemical Society, copyright 2022; reproduced from ref. 102 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2022). | ||
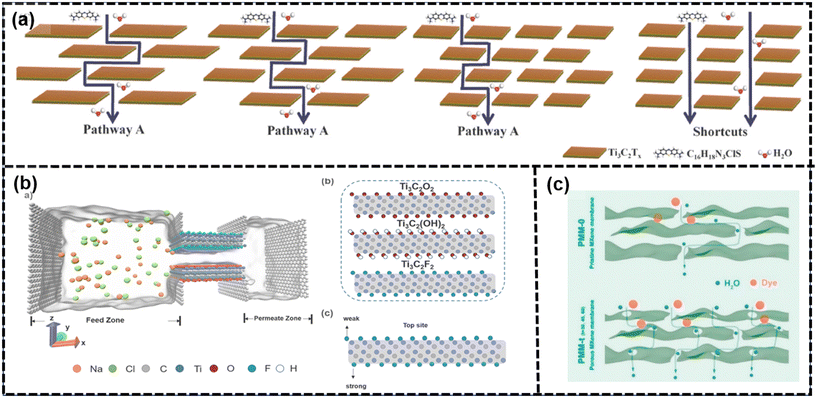 | ||
| Fig. 9 (a) Mass transfer mechanism of methylene blue solution through MXenes with different lateral sizes103 (reproduced from ref. 103 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2022), (b) heterogenous simulation model for desalination: MXenes with different termination groups and electrostatic interaction sites107 (reproduced from ref. 107 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2023), and (c) schematic of the water transport and dye rejection in pristine and porous MXene membranes.108 (reproduced from ref. 108 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2021). | ||
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O and OH, which unavoidably exist on the MXene surface after deintercalation from MAX to MXene, can also serve as reactive forms of O2. These surface species have the potential to induce MXene oxidation during heat treatment, even in the absence of an external oxidant supply in the system. Research indicated that the as-synthesized MXenes with Cl terminations exhibited superior stability to those terminated with F and
O and OH, which unavoidably exist on the MXene surface after deintercalation from MAX to MXene, can also serve as reactive forms of O2. These surface species have the potential to induce MXene oxidation during heat treatment, even in the absence of an external oxidant supply in the system. Research indicated that the as-synthesized MXenes with Cl terminations exhibited superior stability to those terminated with F and ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O. Consequently, the influence of additional and innovative surface terminations on the stability of MXenes can impact the chemical stability of MBMs.120
O. Consequently, the influence of additional and innovative surface terminations on the stability of MXenes can impact the chemical stability of MBMs.120
4.2 Interlayer spacing control of MBMs
Precisely controlling the interlayer spacing and tuning the surface structure is crucial for membranes to achieve desirable selectivity and stability. Various chemical and physical approaches had been employed to address these challenges and enhance the performance of membranes.128 Generally, it is perceived that molecules and ions are transported through interconnected interlayer spacings of adjacent stacked nanosheets in these lamellar membranes.129 Many researchers had verified that super-fast and accurate ion selectivity in these laminar membranes is facilitated by the sizable equivalent diameter between interlayer spacing and hydrated ions.130,131 However, the practical separation performance is far from the theoretical prediction, due to the expansion of interlayer spacing in solution.16,28 Even though stacked MXene nanosheets could exhibit a more uniform pore structure and well-distributed nanochannels compared to other 2D nanomaterials, the transport through the interlayer nanochannels could be long and winding, leading to a reduction in water permeation and mass transport.132,133 To address the challenge of long and winding transport pathways in stacked MXene nanosheets, it is necessary to develop ultrathin and well-established MBMs rather than ultrathin hybrid membranes with a random distribution of MXene nanosheets and free penetration of solutes.134 The abundant terminal functional groups present on MXene nanosheets provide opportunities for introducing polymeric materials with new functionalities and inorganic particles into MXene membranes. This incorporation can lead to improvements in membrane stability and selectivity. Additionally, the adjustable layer spacing of MXene nanosheets allows for the embedding of various intercalators, enabling the formation of sandwich structures with enhanced laminar membranes.135 As shown in Fig. 10(a), apart from these routine strategies of some crosslinkers to modify MXene membranes, the self-crosslinking and the construction of hybrid functional layers are employed to improve the performance of MBMs.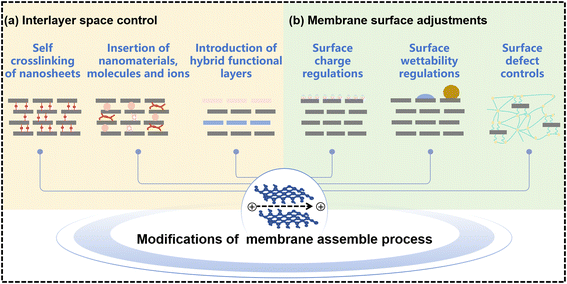 | ||
| Fig. 10 Modifications of the membrane assembly process: (a) interlayer space control and (b) membrane surface adjustments. | ||
The thermal treatment was applied to fabricate MXene membranes via a self-crosslinking reaction (–OH + –OH = –O– + H2O).141 These membranes showed excellent monovalent ion exclusion properties and suppressed swelling performance with favorable long-term stability, which is shown in Fig. 11(a).141 In addition, the self-crosslinking MXene membranes (SCMMs) possessed a steady nanochannel relying on the dehydration and self-crosslinking reaction. The size of the hydrated ions and the energy barrier of dehydration determined these hydration ions through the narrow and empty spacing of membranes. According to previous papers, partial dehydration occurs when all of the hydrated monovalent metal ions are transferred into the nanochannels of membranes.142 More importantly, the facile thermal self-crosslinking strategy provides a method to synthesize membranes with enhanced monovalent metal ion rejection and suppressed swelling performance. These ultrathin MBMs with α-Al2O3 tubular substrates were prepared by calcination for improving ion rejection, which reduced the interlayer spacing from 3.71 Å (60 °C) to 2.65 Å (450 °C). Below 400 °C, the reduced interlayer spacing endowed a compact layer nanostructure with controllable ion rejection properties. In addition, the wrinkled microstructure on the surface became less progressive, and the surface got relatively smooth. With the increase in sintering temperature (above 400 °C), the wrinkled micro-structure gradually disappeared.143,144 It was observed that the model of filtration transformed from interlayer transport pathways to longitudinal nanochannels, causing a decrease of ion retention.145
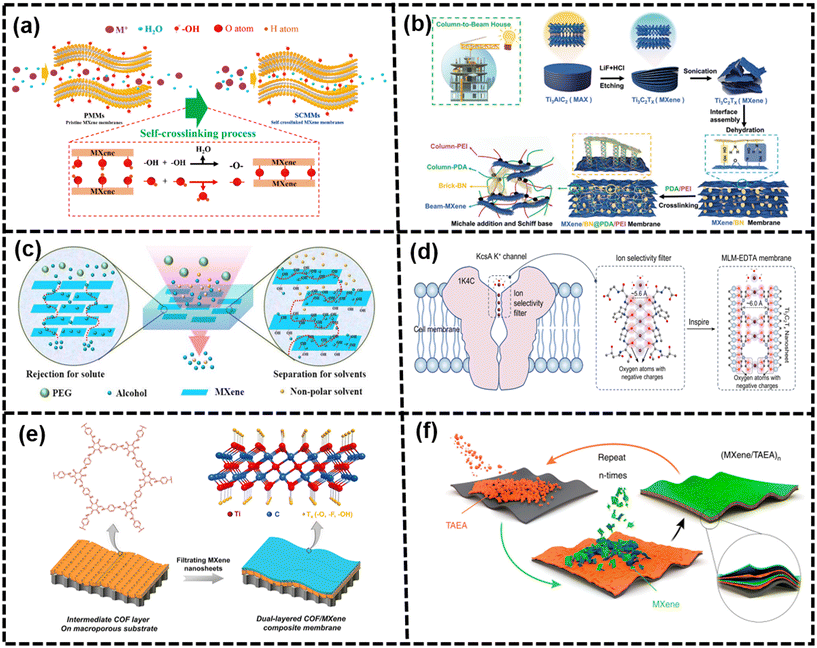 | ||
| Fig. 11 (a) Self-crosslinking process of the MXene membranes141 (reproduced from ref. 141 with permission from the American Chemical Society, copyright 2019), (b) fabrication process of the MXene/BN@PDA/PEI membrane for water purification146 (reproduced from ref. 146 with permission from Wiley Online Library, copyright 2022), (c) transfer and rejection mechanisms of PAN/PEI-Ti3C2Tx-X,147 (reproduced from ref. 147 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2016), (d) design of MLM-EDTA membranes with numerous negatively charged oxygen atoms and a 6.0 Å two-dimensional channel148 (reproduced from ref. 148 with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2023), (e) preparation of the dual-layered COF/MXene composite membranes149 (reproduced from ref. 149 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2022), and (f) LbL self-assembly of (MXene/TAEA)n multilayers onto planar substrates150 (reproduced from ref. 150 with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2019). | ||
Covalent crosslinking, in particular, had been demonstrated as a valid approach to impose restrictions on the interlayer spacing of hydrophilic laminate membranes. When selecting a crosslinker, it is beneficial to choose one with a large dimension and rich reactive terminal functional groups. Various polymers including polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), polyacrylonitrile (PAN), and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) were considered promising crosslinkers for forming composite membranes due to their excellent properties such as flexibility, favorable microporous structure, and high mechanical strength. By incorporating crosslinkable functional groups or monomers into the membrane structure, the formation of covalent bonds between adjacent layers could occur, leading to a controlled interlayer spacing and enhanced stability of the membrane.35,159,160 For example, borate and PEI molecules could be interlocked into MXene layers to regulate the interlayer spacing of MXene nanosheets, revealing the transformation from “diffusion-controlled” to “solution-controlled” channels after chemical tuning.98 It is an interesting finding by Wu et al., where they incorporated two polymer matrices, hydrophilic polyethyleneimine (PEI) and hydrophobic polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), into MXene nanosheets to create polymer-MXene composite membranes, which is shown in Fig. 11(c).147 Covalent modification was mostly applied to adjust the channel size and functionality, but it could disrupt the structure of this membrane. Herein, a less intrusive and effective non-covalent modification by solvent treatment is reported, and then these channels are decorated by protic solvents via a hydrogen bond network to achieve membrane integrity and channel alignment. The angstrom-scale channel width facilitated the nanoconfinement effect to tune the distance and orientation of the solvent to channel walls, endowing the improvement of ion sieving and separation performance.161
Ren et al. confirmed that these MXene membranes could exhibit selectivity of cations with various charges and did not show the permeation cutoff, attributing to the intercalation of cations into MXene laminates.58 These ion intercalation behaviors had nothing to do with anions, but were mainly affected by the type of cations.11 Thus, cation intercalation was proposed to confine the interlayer spacing, which is regardless of the size and valences. Besides, cationic control of the interlayer spacing of MXene membranes could achieve Ångström precision using Li+, Na+, Mg2+, and Al3+ ions. The study revealed that the vacuum hot pressing molten salt intercalation technique effectively promoted the intercalation of Al3+ ions into MXene membranes, thereby enhancing their ability to retain consistent spacing under varying dynamic voltages.162 Many researchers attempted to modify the surface of nanosheets before the cationic intercalation to tune the ion selectivity.19,163 For example, Wang et al. used alginate hydrogel pillars to stabilize the interlayer spacing of the MXene laminar membranes. At first, the sodium alginate (SA) molecules were homogeneously anchored on the surface of MXene nanosheets and assembled by van der Waals forces. Then, the cross-linking reaction occurred after the SA-MXene membranes were immersed in the multivalent cation solution. It was observed that the nanochannel diameters were fixed at 7.4 ± 0.2 Å by the pillar of Ca-alginate, and these membranes showed a permeation cutoff and an excellent selectivity of cations.132 As shown in Fig. 11, Xu et al. built cation sieving membranes by the combination of MXene nanosheets and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) molecules, which were inspired by the K+ channel of Streptomyces A (KcsA K+). The biomimetic channel structure, chemical functional groups, and tunable charge density of the membrane were derived from the 6.0 Å sub-nanochannels of MXene nanosheets and numerous negatively charged oxygen atoms of EDTA molecules. These membranes exhibited an outstanding ability in sieving monovalent and divalent cations, particularly in K+/Mg2+ selectivity. These characterizations and simulations suggested that partial dehydration effects, the increasing charge density in sub-nanochannels, and the cation recognition of EDTA significantly enhanced the cation-selective sieving.148
Even though masses of intercalators were inserted into these MBMs, which indeed showed expanding interlayer nanochannels and high chemical stability, the water permeance was difficult to achieve as the ideal target, owing to the steric effect of the intercalators. In addition, it could lead to a decrease in the selectivity of ions or molecules, especially for small ions.164 This is because the intercalation and size effect of cross-linking agents could occupy the space of the interlayer within membranes, which would result in an increase in d-spacing and further reduce the ion rejection. Even though membranes were linked with other cross-linking agents to suppress the swelling phenomenon, these membranes showed low ion rejection, especially for these monovalent salts.149,165
As demonstrated in previous papers, dual-layered COF/MXene composite membranes were fabricated by creating an intermediate COF layer on macroporous substrates and then vacuum filtering MXene nanosheets, as shown in Fig. 11(e). The smooth and hydrophilic COF layer could modify the surface properties of macroporous substrates by covering multidistributed macropores and providing intrinsic and crispation-induced pores, contributing to the fine assembly and uniform deposition to generate an integrated and ultrathin MXene layer. The construction of the COF layer not only facilitated the well-assembled MXene layer with an ultrathin thickness of 8 nm and narrow interlayer nanochannels, but also introduced intrinsic nanopores and crispation-induced pores for mass transport. Thus, the dual-layered COF/MXene composite membranes possessed a high flux due to short pathways from the porous COF layer and the ultrathin MXene layer, and high rejection due to the confined interlayer nanochannels between these well-assembled MXene nanosheets. Moreover, the content of MXene nanosheets and COFs had a crucial effect on the separation performance of the composite membranes.149 Nevertheless, in most cases, these nanofillers were limited to intrinsically porous 2D nanosheets, which could limit their application. In addition, layer-by-layer (LbL) self-assembly technology could facilitate deposition on various substrates. The small molecule of tris(2-aminoethyl)amine (TAEA) could enlarge the interlayer spacing of MXene sheets by approximately 1 Å and enhance the interconnection.150
In a previous work, amino-modified boron nitride nanosheets and GO nanosheets were alternated to fabricate a hybrid membrane with low defects containing edge-edge covalent bonding and plane-plane conformation. The decrease in electrostatic repulsion between the nanosheets, overlap, and dislocation contributed to strong interactions, resulting in a highly ordered and compact structure.54,172 In order to obtain membranes with free defects or few defects, it is necessary to optimize the nanosheet stacking. For example, Tang et al. synthesized layer-by-layer repaired lamellar membranes via multiple repetitions of delayed vacuum filtration, crosslinking, glass rod rolling treatment and self-crosslinking.89,150 The total thickness of these ultrathin layer-by-layer repaired MXene membranes was approximately 50 nm, containing very few-layer MXene nanosheets of 2 nm. Moreover, the ordered structure and smooth surface of MBMs with few defects and wrinkles were achieved through a series of craft processes. The MXene membranes, meticulously repaired layer by layer, demonstrated exceptional separation performance and remarkable stability in their interlayer spacing throughout the filtration process. Consequently, the judicious employment of various techniques proved advantageous in enhancing the anti-swelling capacity and filtering efficiency. However, the complexity of the fabrication process presented a significant challenge, making practical implementation somewhat problematic.89,150
4.3 Membrane surface adjustments
Enhancing the permeability and selectivity of MXene membranes could be achieved through deprotonation of the surface groups on MXene nanosheets. Deprotonation involved the removal of protons (H+) from functional groups, leading to changes in the surface charge and properties of the MXene material.128,173 Molecular interactions play a crucial role in achieving highly ordered stacking of nanosheets, which is essential for good molecular sieving performance. These interactions include electrostatic attractions with polymer chains and hydrogen bonding. It is evident that the surface hydrophilicity and charges of MXene membranes could be adjusted via electrostatic functionalization with cationic surfactants or cationic/neutral polymers. This tuning process could significantly impact the membrane's performance in terms of permeability and selectivity and chemical stability. As shown in Fig. 10(b), membrane surface adjustments covered three aspects, namely surface charge regulations, surface wettability regulations and surface defect controls.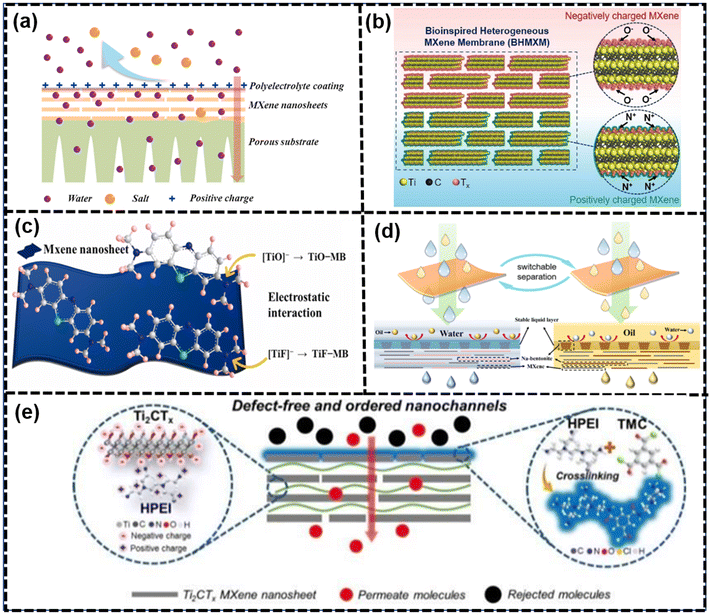 | ||
| Fig. 12 (a) Schematic of SC-MXene membrane and their application on water desalination174 (reproduced from ref. 174 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2021), (b) schematic of the bioinspired heterogeneous MXene membrane (BHMXM)175 (reproduced from ref. 175 with permission from Wiley Online Library, copyright 2022), (c) schematic of electrostatic interaction between Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheet and MB dye molecules176 (reproduced from ref. 176 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2023), (d) mechanism diagram of the switchable wettability membrane for oil/water emulsion separation177 (reproduced from ref. 177 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2023) and (e) synthesis process of Ti3C2Tx-M and the microstructure of composite membranes.178 (reproduced from ref. 178 with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry, copyright 2019). | ||
Furthermore, functionalization by poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDDA) was able to reverse the surface charge of the MXene nanosheets to a positive value of +50 mV, interacting with negatively charged MXenes to produce bioinspired heterogeneous MXene membranes, exhibiting excellent osmotic energy conversion, which is shown in Fig. 12(b).175 Additionally, the application of KOH to substitute –F with –OH enhanced the surface charges, resulting in outstanding ion rejection due to the hydroxylation of MXene membranes.179 Moreover, to leverage silanol chemistry on –OH groups, organosiloxanes were used to graft onto the MXene nanosheets to introduce functional groups such as –NH2, –COOR, and –C6H6.180 Although thermal self-crosslinking could address the swelling issue, the decrease in negative charges could contribute to a reduction in ion sieving due to weakened adsorption or charge controlling effects. A membrane of poly(4-vinylphenylboric acid)-grafted MXene was created, binding interchangeable diols using dynamic boronic ester chemistry, called dynamic covalent interface engineering (DCIE). The diols anchored in the interlayer transitioned from anionic to cationic and from hydrophilic to hydrophobic states via reversible covalent bond formation and cleavage, without any residual effect from previous diols. Consequently, the membrane, with rapidly adjustable nanochannel properties, displayed exceptional switchable permeability and selectivity (98% for Congo red and 97% for Gentian violet) and exhibited high stability in various water treatment scenarios.181
In the realm of superwetting materials, the hydrophilic groups on the membrane surface could rapidly absorb water molecules to generate a hydrate layer barrier, which facilitated the rapid passage of water molecules.177 As shown in Fig. 12(d), Zhang et al. developed a series of Na-Bentonite@MXene (NBM) composite membranes through a one-step hydrothermal pretreatment and vacuum self-assembly on the surface of polyvinylidene fluoride membranes. These membranes, with a sandwich structure and micro-nano structures on the surface, exhibited switchable wettability. The pretreatment is dependent on the surface wettability, and the hydrophilic/hydrophobic or hydrophobic/oleophilic property arise from the treatment of water or oil.177 Similarly, Feng et al. regulated the surface wettability by bioinspired polydopamine-triggered chemical crosslinking with polyethyleneimine (PEI), resulting in membranes with super-hydrophilic and underwater super-oleophobic properties.183 Liao et al. produced multicomponent lamellar nanofilms with dual and ordered nanochannels in confined spacings through tunable ligand conformation and favorable hydrophilicity of dual-functionalized zwitterionic MXenes. The introduction of zwitterionic MXenes improved the distribution of surface functional groups and prevented nanochannel contortions, leading to high permeability and low fouling propensity.119
Moreover, the presence of numerous hydrophilic groups on the surface of Ti3C2Tx nanoparticles is noteworthy, endowing them with the potential to act as superior additives for membrane anti-fouling enhancement. While it is a prevalent approach to blend MXenes with polymer membranes to bolster their anti-fouling prowess, the distribution of MXene nanoparticles predominantly within the membrane matrix often failed to capitalize on their benefits in the critical uppermost layer - a region pivotal for membrane permeability. Conversely, the strategic employment of an external magnetic field during a phase transition effectively concentrated magnetic Ni@MXene nanoparticles atop the PES membrane. Consequently, the resulting composite membrane exhibited excellent separation properties, especially for the separation of organic pollutants.184
As shown in Fig. 12(e), negatively charged MXene nanosheets electrostatically interacted with positively charged hyperbranched polyethylenimine (HPEI) to form ordered stacking structures. Subsequently, the acyl chloride groups of trimesoyl chloride (TMC) were used to interfacially polymerize with the amine groups of HPEI, further sealing non-selective in-plane slit-like pores.178 Researchers investigated the role of HPEI molecules and interfacial polymerization in the process of membrane assembly, demonstrating that the introduction of HPEI created a smooth membrane surface with abundant wrinkles.178 Furthermore, the surface of these membranes exhibited few visible defects and low roughness, indicating an ordered assembly of the nanosheets and numerous ordered channels.178 Additionally, interfacial polymerization primarily occurred on the membrane surface to seal these interior non-selective pores, resulting in defect-free membranes with highly ordered stacking structures and sub-nanometer size channels that possessed excellent molecular separation and water/isopropanol dehydration performance. According to experimental data, Ti3C2Tx-HPEI/TMC membranes had a high average surface area and water-adsorbing capability, leading to a high water content in the water permeate.178 Fu et al. discovered that heterostructural MXene-TiO2 was used as the intermediate layer to prepare thin and crumpled composite nanofiltration membranes with a polyamide selective layer via interfacial polymerization reaction. These MXene-TiO2 particles, prepared by in situ MXene oxidation, facilitated the regulation of the interlayer nanostructure and nanosheet stacking, contributing to the rapid transport of water molecules. The high specific area and numerous edges of MXene-TiO2 accelerated the adsorption and desorption of amine monomers, leading to the formation of a crumpled structure.187
5. MXene-based membranes for water and wastewater treatments
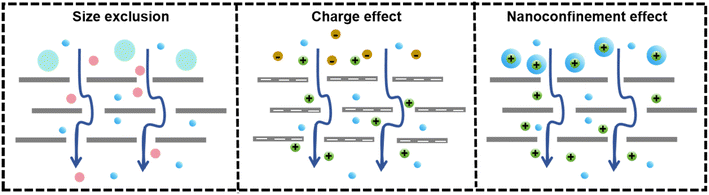
It was clear that MXenes and other polymers or inorganic materials had been utilized to produce various composite membranes, with significant efforts aimed to enhance water separation ability and long-term stability.188 Several studies have focused on the separation of water and wastewater containing pollutants with varying sizes, ranging from micrometers to sub-nanometers. In addition, it was crucial to clarify the complex separation mechanisms underlying the separation behavior of MBMs.455.1 Separation mechanisms of MXene-based membranes
Water and wastewater separation mechanisms generally fall into three categories: size exclusion, charge effect, and nanoconfinement effect, as depicted in Fig. 13.189,190 The interlayer spacing between MXene nanosheets, governed by van der Waals forces and electrostatic repulsion, formed slit-shaped nanochannels that were critical for molecule transport, particularly water permeation.58 The interlamellar distance could be chemically adjusted for selective transport, with d-spacings below 4 Å preventing water entry and the size of ions with their hydration shells determining passage through the 6 Å channel, which was effective for water purification.45,163 Size exclusion was significantly influenced by the interlayer spacing, and pollutants larger than the nanochannel size were sieved out, while smaller ones could pass through.190 The size-based separation of small molecules using MXene membranes was accomplished by adjusting the interlayer spacing between the MXene nanosheets. The flow of a solvent through MXene-based membranes can be described using the Hagen–Poiseuille (H–P) equation:191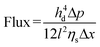 | (2) |
The MXene nanosheets had numerous terminal surface groups, giving them a negative surface charge with a Zeta potential of −35 mV in water.192,193 This negative charge allowed the separation of charged pollutants such as ions, organic dyes, and polyelectrolytes. The Donnan exclusion theory can be used to achieve the separation of charged ions and organic dyes, owing to the strongly negative charge characteristic of MXene nanosheets, as depicted by eqn (3):91
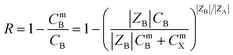 | (3) |
 | (4) |
The nanoconfinement effect is crucial in explaining the differences in mass transfer within nanofluid ion channels compared to larger-scale systems. Ionic movement across MXene membranes is a two-step process involving initial dehydration followed by diffusion in the interlayer spaces. It had been found that Li+ ions passed through these nanoconfined channels faster than K+ and Na+ due to the tight control of interlayer spacing, which reduced Li+ interaction with the ionic terminal.198 The rapid and selective transport of Li+ was enabled by electrostatic interactions, and the energy barriers for interlayer insertion varied with the charge state. The charge selectivity is a result of the charged MXene layers.161
The incorporation of MXene nanosheets in mixed-matrix membranes (MMMs) introduced a more complex separation mechanism, involving the synergistic effect of multiple components. While the incorporation of MXene nanosheets could increase the length of transport, the pathway could be optimized to achieve the goal of an ultra-fast and precise sieving process.199 MXene nanosheets leveraged their unique advantages of electrostatic interaction and nanochannels without interfering with the diffusion mechanism or charge effect of the polymer matrix.200 This demonstrated the potential of MBMs in advanced separation applications.
5.2 Applications of MBMs for water and wastewater treatment
MBMs attracted widespread attention due to MXene's unique characteristics, offering exceptional selectivity and water permeation capabilities.201 Solutions with complex chemistry, including hydration, pH, and ionic strength, significantly influenced transport pathways.99 Hydration caused membrane swelling, and changes in pH and ionic strength altered the charge of membranes, affecting the interlayer distance of expandable laminar membranes and thus impacting its permeability.58,159 Applied potentials could control water ion diffusion by adjusting the ionization degree of water molecules in nanochannels.202 Light or heat could be used to regulate MBMs' mass transport based on their photothermal properties, as shown in the ionic flow control in MXene laminates using laser light.203 Researchers, such as Shao et al., had proposed improved post-treatment methods such as air-drying and fan-drying to achieve stable, partially dehydrated MXene membranes.204Table 1 presents the comparison of MBMs for separating different pollutants, showcasing their versatility across a range of separation and purification applications including desalination, and heavy metal, organic pollutant, and bacterial removal.| Applications | Membrane | Pollutants | Results | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Removal of bacteria | Ti3C2Tx-pillararene | Bacitracin | Rejection: 95.8% | 205 |
| Permeability: 350 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 | ||||
| Ag@MXene | Gram-negative bacteria | Rejection: 99% | 56 | |
| Permeability: 420 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 | ||||
| Modified Ag@MXene | Gram-negative bacteria | Rejection: 99.99% | 206 | |
| Removal of organic pollutants | MXene-Si@PES | Emulsions | Rejection: 99% | 157 |
| CuO@MXene-PAN | Emulsions | Rejection: 98% | 207 | |
| Permeability: 2365 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 | ||||
| MXene/ZnO | Emulsions | Rejection: >99.4% | 208 | |
| Permeability: 5133 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 | ||||
| MXene/COF | Congo red | Rejection: 98.2% | 88 | |
| Chrome black T | Rejection: 98.7% | |||
| Permeability: up to 300 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 | ||||
| Methyl blue | Rejection: 96.4% | |||
| Methyl orange | Rejection: 97.2% | |||
| MXene@TiO2/PEN | Methyl orange | Rejection: 93.5% | 183 | |
| Crystal violet | Rejection: 98.06% | |||
| Methylene blue | Rejection: 99.30% | |||
| Permeability: up to 2507.5 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 | ||||
| MXene@CS/MCN | Antibiotics | Rejection: 93.4% | 209 | |
| PVDF/TiO2@MXene | Tetracycline | Rejection: 87.8% | ||
| Meropenem | Rejection: 60.7% | |||
| Permeability: up to 293 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 | ||||
| Removal of heavy metals | Fe3O4@MXene | Cu2+ | Rejection: 63.2% | 205 |
| Cd2+ | Rejection: 64.1% | |||
| Cr6+ | Rejection: 70.2% | |||
| Permeability: up to 125.1 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 | ||||
| MXene/CNFs | Pb2+ | Rejection: 89% | 151 | |
| As3+ | Rejection: 81% | |||
| Adsorption capacity: 12.5 and 3.3 mg g−1 | ||||
| MXene | Pb2+ | Rejection: 99% | 207 | |
| Separation factor of K+/Pb2+: 78 | ||||
| MXene/PDA/Sep@ZIF-67-1 | Cu2+ | Rejection: 79.9% | 210 | |
| Desalination | UiO-66-NH2@MXene | Na2SO4 | Rejection: 91% | 211 |
| MgSO4 | Rejection: 87% | |||
| MgCl2 | Rejection: 79% | |||
| NaCl | Rejection: 62% | |||
| MXene | NaCl | Rejection: 99.5% | 57 | |
| Permeance: 85.4 L m−2 h−1 (vaccum: 400 Pa) | ||||
| MXene/sulfonated TFN | Na2SO4 | Rejection: 96.68% (Na2SO4) | 212 | |
| NaCl | Permeability: 67.95 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 (NaCl) | |||
| SC-MXene | MgCl2 | Rejection: ∼82% | 174 | |
| Permeability: ∼9 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 |
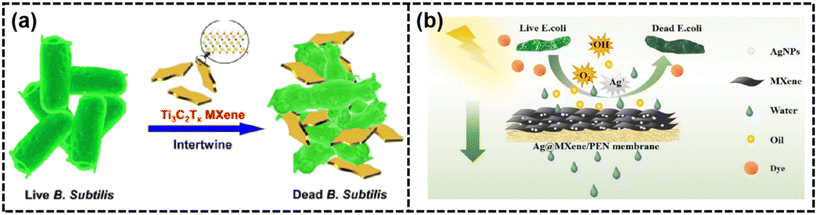 | ||
| Fig. 14 (a) Schematic of the antibacterial activity of Ti3C2Tx MXene213 (reproduced from ref. 213 with permission from the American Chemical Society, copyright 2016) and (b) separation and anti-fouling mechanism of the Ag@MXene/PEN fibrous composite membrane206 (reproduced from ref. 206 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2022). | ||
Oil–water emulsions. Rapid urbanization and industrial growth led to a surge in oily wastewater and oil spills, threatening the environment and human health. MBMs had been developed to combat this issue, offering superhydrophilic/superoleophobic membranes that excelled at separating oil–water mixtures due to their low oil adhesion and hydrophilic nature.176 To overcome the challenge of water barrier resistance, researchers created novel TA-ZIF-8@MXene membranes, which incorporated tannic acid-modified ZIF-8 nanoparticles to achieve high flux recovery ratios.152 The integration of hydrophilic TA-ZIF-8 nanoparticles resulted in an improved water flux, leading to a highly hydrophilic and oleophobic membrane surface.152 Additionally, 2D Na-Bentonite@MXene composite membranes with switchable wettability had been developed, demonstrating a rejection ratio of 96% and a recovery rate exceeding 86% after 8 cycling tests. These membranes could switch between hydrophilic/hydrophobic and hydrophobic/oleophobic surfaces depending on the presence of water or oil.177 By modifying the pyromellitic acid group of MXene nanosheets, MBMs had been prepared, showing excellent superwettability and effective separation of harsh emulsions with a surfactant-stabilized emulsion separation efficiency of over 99.97%.219 As shown in Fig. 15(a), MXene@TiO2/PEN fibrous composite membranes with increased interlayer spacings and super-hydrophilic/underwater superoleophobic properties had been developed, effectively separating various surfactant-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions with high oil rejection rates.183 Huang and colleagues developed MCE-MNR membranes, integrating MXene nanoribbons with a cellulose mix. This innovation yielded a water permeance of 15
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 860 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 and 99% + oil rejection, credited to a surface water layer and the self-cleaning photoactivity of the membrane.220
860 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 and 99% + oil rejection, credited to a surface water layer and the self-cleaning photoactivity of the membrane.220
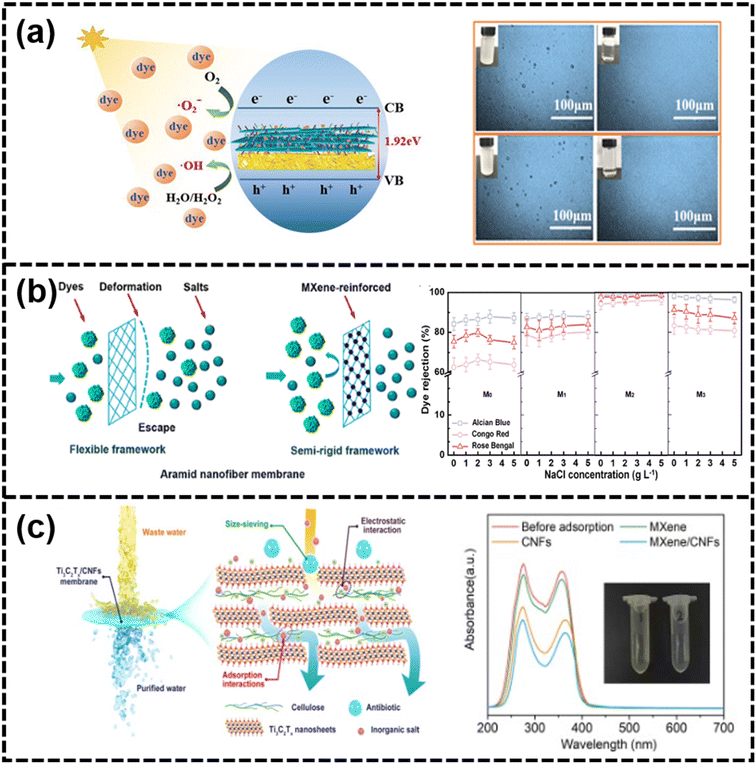 | ||
| Fig. 15 (a) Mechanism diagram of photocatalytic degradation of dyes with microscopic images of isooctane emulsion before and after separation183 (reproduced from ref. 183 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2016), (b) schematic of the mechanism of dye rejection for the MXene nanosheet-reinforced ANF membrane with the effect of NaCl concentration on the dye rejection221 (reproduced from ref. 221 with permission from the American Chemical Society, copyright 2021), and (c) schematic of the separation mechanism of Ti3C2Tx/CNF membranes from antibiotic-/salt-contaminated wastewater with UV-vis spectra before and after static adsorption experiments222 (reproduced from ref. 222 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2016). | ||
Dye. The textile industry is a major consumer of water, using around 150 m3 per ton of processing, resulting in over 3 billion tons of wastewater annually.223 MXene-based materials had proven to be effective adsorbents for cationic dye molecules, and UV light could enhance dye degradation in their presence.215 Flexible MXene/COF membranes, self-assembled through electrostatic forces, had a hierarchical structure with micropores and mesopores, and they also possessed strong photothermal conversion abilities, showing high water permeance and excellent recyclability under UV light.224 ZnO@Ti3C2Tx MXene nanofiltration membranes, responsive to visible light, removed organic dyes and exhibited a high rejection rate for CR and good water permeability.53 Moreover, the addition of Ti3C2Tx nanosheets into polyacrylonitrile (PAN) endowed the dual-functional superhydrophilic/underwater superoleophobic MXene-PAN membranes with outstanding adsorption capacity for dyes.176 MXene-PANI/PES composite ultrafiltration membranes, prepared via non-solvent induced phase separation, showed high retention rates for CR and MB dyes. The application of negative voltage repelled negatively charged contaminants, reducing fouling on the membrane surface.225 Two-dimensional porous MXene membranes with perforative pore formation on nanosheets enhanced the water permeability and achieved nearly 100% rejection for small-molecule dyes like CR.108 When NaCl was introduced during fabrication and application, a membrane with high salt and dye separation efficiency was obtained.226 As shown in Fig. 15(b), MXene-reinforced aramid nanofiber membranes improved rigidity and selectivity for dyes, achieving high recovery rates and low salt rejection.221 As for the mechanism of dye separation, it was mainly divided into electrostatic interactions such as hydrogen bonding and π–π interaction and size sieving for passing or blocking dye molecules.227
Antibiotics. Emerging micropollutants such as antibiotics widely existed in the surface water, ground water and drinking water.228 “We will miss antibiotics when they're gone” was newspaper headlines indicating the threat of the antibiotic crisis.229 To treat wastewater containing antibiotics, membranes with well-designed pores and good anti-fouling properties are necessary.193 MXene membranes with nanosheets having large aspect ratios had been used to fabricate laminated membranes with ordered stacking and equidistant nanosheets, demonstrating excellent separation performance and anti-fouling ability for antibiotic-containing wastewater. These membranes featured regular slit-shaped nanochannels that overcame the trade-off between selectivity and permeability for a range of antibiotics.94 The optimized membranes, composed of Ti3C2Tx-pillararene hybrid nanosheets, showed high rejection rates for various antibiotics and high water permeance.205 The exceptional permeance and rejection are ascribed to the considerable lateral size of the nanosheets, uniform interlayer spacing, and electrostatic interaction between the membrane and the antibiotics.205 The optimized membranes, composed of Ti3C2Tx-pillararene hybrid nanosheets, showed high rejection rates for various antibiotics and high water permeance. In Fig. 15(c), the addition of carboxylated cellulose nanofibers (CNFs) stabilized the MXene laminar structure, enhancing molecular transport and anti-swelling performance.222 The size-selective sieving, combined with the impacts of adsorption and electrostatic interaction, is predominantly accountable for the swift and efficient removal of diverse antibiotics and salts from contaminated water. The ultrafine interconnected nanofiber structure of CNFs functions similarly to “natural aquatic plants,” enabling the natural purification of water through adsorption effects.222 To combat fouling, Yang et al. developed a ternary heterojunction photocatalytic composite membrane incorporating MXene, Bi2MoO6, and BiOBr nanomaterials, which demonstrated high water permeability and effective antibiotic removal, showcasing the potential of MXene-based materials for advanced wastewater treatment.230 A range of 2D g-C3N4@MXene composite membranes had been developed, exhibiting responsiveness to visible light. The enhanced metal conductivity of MXenes facilitated the separation of CN e−/h+ pairs, resulting in outstanding removal efficiency for various small molecules in water. Furthermore, the composite membrane displayed self-cleaning capabilities attributed to the incorporation of CN sheets, effectively mitigating membrane pollution concerns.231
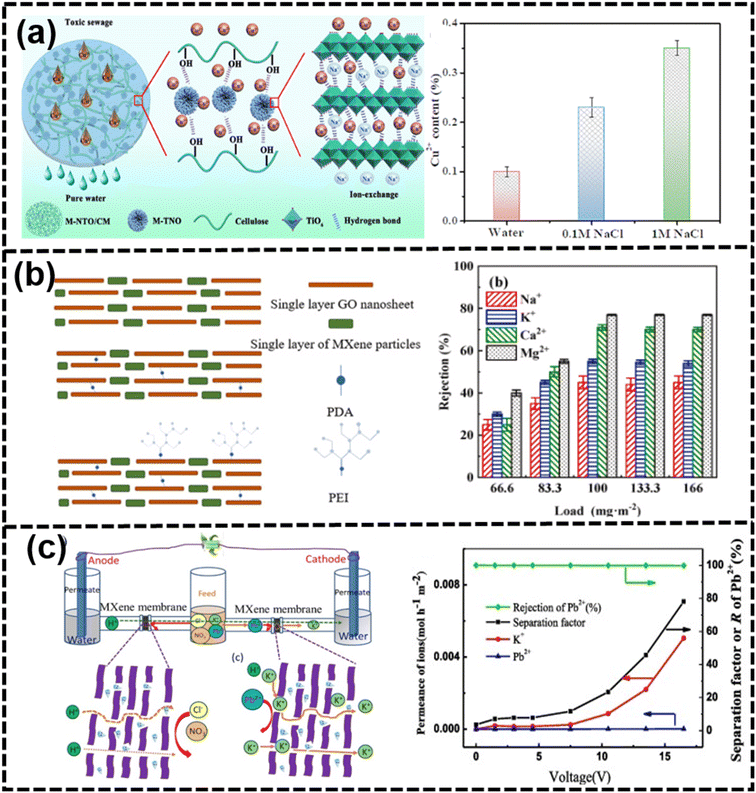 | ||
| Fig. 16 (a) Schematic of Cu2+ ion adsorption using M-NTO/CM with leaching rate235 (reproduced from ref. 235 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2024), (b) schematic of GO/MXene_PEI membranes with ion rejection237 (reproduced from ref. 237 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2021), and (c) schematic of the ion sieving mechanism with the separation of mixed ions (K+/Pb2+) for MXene membranes under different voltages238 (reproduced from ref. 238 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2020). | ||
The voltage-gated approach had been used to improve the rejection of ions and molecules. MXene membranes with increased hydroxylation showed excellent wettability and zeta potential, with electrical voltage further enhancing the rejection of heavy metal cations up to 99.5%.179 Electrostatic membranes, leveraging the electrostatic interaction between ions and membranes, had attracted attention for their gating capabilities.239,240 Porous membranes with small nanochannels allowed for the overlap of electrical double layers, aiding in the electrostatic control of ions.241 In an external electric field, membranes were oxidized by positive charges or reduced by negative charges to gate rejection, such as polypyrrole-based membranes and graphene-based membranes.191,242 Inserting cations with solvation shells between MXene layers could potentially increase the interlayer spacing of MXenes. However, it was important to note that the electrostatic attraction between the negatively charged MXene layers and the cations might counteract this effect, potentially leading to a decrease in the interlayer spacing.243 MXenes possessed excellent electronic conduction and negatively charged surface (−39.5 mV) with a tunable interlayer spacing by ion intercalation with electrical voltages.28,192 Thus, MXene membranes had an advantage on the removal of molecules and ions from water, which was attributed to the interlayer spacing (2–3 layers of water molecules) under equilibrium in aqueous environments.244 Moreover, the solution concentration and ion species are the main factors for the strength of the voltage-gating effect.245 For example, MBMs with an external potential could effectively control the ion rejection, such as organic MB molecules and inorganic salts (MgSO4 or NaCl).202 Negative voltages led to an increase in ion rejection, while positive voltages resulted in a decrease in ion rejection across MXene membranes. In addition, the external voltage could control the swelling problem and maintain the high rejection of the heavy metal ion Pb2+.238 In Fig. 16(c), the hydrated K+ ion, with a smaller diameter of 6.62 Å, could effectively traverse the channels of the MXene membrane. Conversely, the hydrated Pb2+ ion, possessing a larger diameter of 8.01 Å, was hindered from diffusing, resulting in a rejection rate exceeding 99%.238
On the one hand, compared with the other membranes, exploiting the surface and edge abundant functional groups is an effective strategy to improve the 2D nanochannel structure and enhance the swelling resistance.246 Additionally, charged MXene membranes had been developed for desalination, with the surface-coating of polyelectrolyte layers tuning the charge and hydrophilicity without compromising the lamellar structure.174 Polyelectrolytes such as poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons had been used to regulate the physicochemical structure for size-based and electrostatic interactions in desalination.173 As shown in Fig. 17(a), through the intercalation of AgNPs into the laminar structure of Ti3C2Tx and subsequent cross-linking with HPEI, a highly permeable and positively charged HPEI-AgNP@Ti3C2Tx MXene nanofiltration (NF) membrane has been developed for the first time.247 While the intercalation of AgNPs efficiently enhances the water permeability of the Ti3C2Tx MXene membrane, the prepared AgNP@Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes are constrained by a trade-off effect. Notably, the HPEI-Ag-0.6@MX-0.40 membrane exhibits outstanding NF performance, achieving rejections of 84.15% for MgSO4, 77.01% for MgCl2, 74.67% for Na2SO4, and 56.58% for NaCl solutions at a concentration of 1000 ppm.247 As shown in Fig. 17(b), a cutting-edge thin-film nanocomposite reverse osmosis (RO) membrane, integrating two-dimensional MXene Ti3C2Tx within the polyamide (PA) layer through in situ interfacial polymerization, had been successfully engineered.248 By leveraging the remarkable diffusion-regulating effect of Ti3C2Tx, following Fick's first law, water permeability had been enhanced to a peak value of 2.53 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 while maintaining a high NaCl salt rejection of 98.5%. Through microstructural observation and mechanism analysis, this enhancement in chlorine resistance was primarily attributed to the interaction between the surface functional groups of Ti3C2Tx nanosheets and active chlorine, effectively shielding the PA matrix from chlorine attack.248
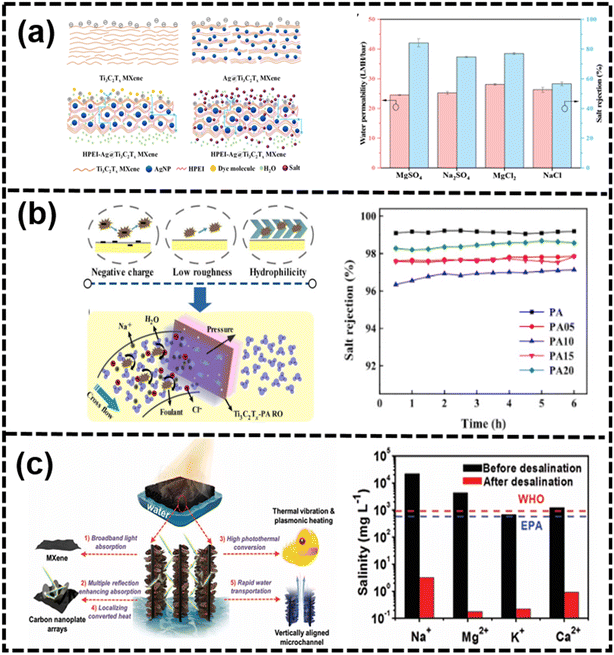 | ||
| Fig. 17 (a) Schematic of the mechanism of HPEI-AgNP@MXene composite membrane with NF performance of the HPEI-AgNP@Ti3C2Tx MXene membrane247 (reproduced from ref. 247 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2023), (b) desalination and anti-fouling process with salt rejection of different membranes248 (reproduced from ref. 248 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2020) and (c) schematic of the highly efficient solar-vapor generation from the solar absorber of the Co-CNS/M foam in an actual seawater sample before and after desalination249 (reproduced from ref. 249 with permission from Wiley Online Library, copyright 2020). | ||
On the other hand, combining solar-driven water evaporation with photodegradation is a significant strategy for achieving sustainable freshwater with improved energy efficiency.250,251 Materials that possess both photocatalytic activity and cooperative photothermal conversion had been widely used for this purpose.252 MXene nanosheets, in particular, had shown extended solar absorption and significant photothermal effects due to their unique localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) and tunable band gap.178,253–255 For instance, Zhang et al. developed a MXene hydrogel membrane containing porphyrin and polyvinyl alcohol, which formed a dynamic hydrophilic network.256 By harnessing the coupling interactions and charge redistribution between MXene and porphyrin, the hydrogel membrane had been enriched with captivating physicochemical properties, amalgamating stable hydrophilic dynamic networks, synergistically enhanced photothermal effects, and photothermal-enabled photocatalytic activity. The interaction between MXenes and porphyrin resulted in an excellent solar-driven water evaporation rate of 1.82 kg m−2 h−1 and a photocatalytic degradation efficiency of 90.5%.256 In addition, the flexible porphyrin-Ti3C2Tx MXene Janus membrane could create dual-function-enabled photothermal desalination with a stable hydrophobic/hydrophilic Janus structure.257 MXenes were also coated onto commercial polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membranes to establish a self-heated photothermal membrane distillation process with excellent temporal responses.258 Zhao et al. introduced a method to prepare hydrophobic salt-blocking MXene membranes that involved modifying delaminated MXene nanosheets with trimethoxy silane to enhance sunlight harvesting, demonstrating remarkable solar evaporation performance.96 As shown in Fig. 17(c), a sophisticated solar-absorbing architecture had been conceptualized and manufactured, featuring a 3D MXene microporous skeleton adorned with vertically aligned MXene nanosheets.249 This structure was further enhanced with vertical arrays of metal organic framework-derived 2D carbon nanoplates embedded with cobalt nanoparticles. Consequently, under one sun irradiation, the solar-vapor conversion efficiency of the MXene-based hierarchical design could reach approximately 93.4% and sustain over 91% efficiency for over 100 hours, facilitating the production of clean vapor for stable and continuous water desalination.249
6. Challenges and opportunities
The exponential growth of 2D materials had expanded the options for membrane development, with MXenes emerging as a promising solution for advanced membranes. In comparison to other 2D materials, MXenes offered several distinct advantages. For example, the uniformly distributed surface groups on MXene nanosheets ensured predictable stacking behavior and consistent channels, while their strong hydrophilicity aided in water transport. While MXene-based membranes had demonstrated exceptional separation performance, there remained significant potential for further enhancement. In Fig. 18, challenges and opportunities related to their production, preparation, mechanisms and applications needed to be addressed to advance MXene-based membranes.1) MXenes encompassed more than 30 varieties, yet the majority of research primarily focused on Ti3C2Tx. Particularly in the context of membrane preparation, only Ti3C2Tx and Ti2CTx had been employed for synthesizing membranes, with over 99% of MXene membranes originating from Ti3C2Tx. Given the diverse properties of different MXene types, these membranes could possess unique surface microstructures and transport channels, resulting in exceptional separation processes. Therefore, the development of innovative and efficient MXene membranes could significantly rely on other types of MXene nanosheets. While Ti3C2Tx particles remained stable up to 800 °C in an inert atmosphere, their stability decreased significantly to only 200 °C under oxidative conditions. Even when exposed to ambient conditions, Ti3C2Tx sheets tended to oxidize, forming TiO2 crystals.259 This susceptibility to oxidation was particularly unfavorable for membrane applications and was accelerated by exposure to aqueous media, high temperatures, oxygen-rich environments, and ultraviolet (UV) light. Thus, the storage and preparation methods are vital to the chemical stability of MXene nanosheets.
2) The prevalent approach to synthesizing MXenes entailed the application of hydrofluoric acid (HF) or other liquid etchants such as lithium fluoride (LiF) and hydrochloric acid (HCl). The production of MXenes had faced challenges, particularly in developing eco-friendly synthesis methods. Despite research efforts, key issues persisted, including safety, scalability, and cost. For instance, while various etchants were available, HF remained the highest yielding and highest quality etchant, despite its high toxicity, necessitating the use of HF-specific personal protective equipment (PPE) and gloves. Furthermore, the intercalants used were toxic, requiring proper handling.163,260 Cost-efficient methods used inexpensive resources to fabricate MAX phases, subsequently reducing the cost of MXene phases, including the use of TiO2, carbon recovered from waste tires, and recycled aluminum scrap.261 For instance, reports indicated that MAX phases could be produced using a molten salt-shielded synthesis/sintering method, which could be carried out in air and at low temperatures to fabricate large-scale MAX powders.262–264 Thus, it is necessary to explore even more green and cost-efficient methods to synthesize MXene nanosheets. As of now, while successful preparation had been achieved on a few-gram laboratory scale, efforts were underway to scale production to the kilogram level.3
3) In order to further understand the structural design principles and separation applications of MXene-based membranes, there is an urgent need for advanced characterization techniques to deeply explore transport mechanisms within confined MXene nanochannels. For example, the in situ characterization of ion dehydration during ion transport in restricted MXene nanochannels could be achieved using in situ liquid time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS) in combination with molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. Additionally, low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (LF-NMR) allowed for the precise detection of interlayer confined structures within the membranes. Presently, the application of simulation and modeling techniques such as density functional theory (DFT) and MD significantly advances our understanding of membrane separation mechanisms, enabling the molecular-level rational structural design of MXene-based membranes.265 A comprehensive exploration of the mechanisms governing pollutant behavior in wastewater is essential. This entailed performing thorough analyses using a range of available characterization tools and theoretical models to gain a deep understanding of the processes involved.
4) Numerous characteristics of MXene-based membranes had been investigated, including permeability, anti-fouling potential, and hydrophilicity. However, the biocompatibility and cytotoxicity of MXene-based membranes had received little attention. Prior to applying these membranes for water purification, it is essential to assess these characteristics to prevent potential additional harms and toxicity resulting from membrane use. The stability of the membrane hinged on the interfacial adhesion between the substrate and the MXene layer.266 MXene membranes were often made on thin commercial polymeric ultrafiltration filters. While the membrane size was not crucial in lab-scale settings, practical conditions required larger membranes that could endure high pressures and crossflows. To fully utilize MXene-based membranes, specific equipment tailored to these requirements must be designed and optimized for module operations. The application of these membranes is currently confined to laboratory conditions, and limited research focuses on real-world scenarios. Therefore, investigations into MXene-based membranes should be rooted in actual water environments. Moreover, greater efforts should be made to enhance the regeneration and reusability of these membranes, thereby achieving long-term membrane functionality.
In conclusion, the vast potential and challenges of MXene membranes suggested a promising future for their development. By addressing the key issues, we believe MXene-based membranes will continue to grow rapidly in the next five years, contributing to membrane design and implementation.
Abbreviation
| 2D | 2 Dimension |
| AAO | Anodic aluminum oxide |
| AB | Alcian blue |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| B. subtilis | Bacillus subtilis |
| CV | Crystal violet |
| CdCl2 | Cadmium chloride |
| CNT | Carbon nanotube |
| COF | Covalent-organic framework |
| CR | Congo red |
| CuCl2 | Copper chloride |
| CVD | Chemical vapor deposition |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| GO | Graphene oxide |
| HCl | Hydrochloric acid |
| HF | Hydrogen fluoride |
| KCl | Potassium chloride |
| LiF | Lithium fluoride |
| MB | Methylene blue |
| MBM | MXene-based membrane |
| MeB | Methylene blue |
| MMM | Mixed-matrix membrane |
| MO | Methyl orange |
| Mo2C | Molybdenum carbide |
| MOF | Metal–organic framework |
| MoS2 | Molybdenum disulfide |
| NaCl | Sodium chloride |
| NH4HF2 | Ammonium dihydrogen fluoride |
| PA | Polyamide |
| PAN | Polyacrylonitrile |
| PEI | Polyethyleneimine |
| PEN | Poly(arylene ether nitrile) |
| PES | Poly(ether sulfones) |
| PSF | Polysulfone |
| PVA | Poly(vinyl alcohol) |
| PVDF | Poly(vinylidene fluoride) |
| RhB | Rhodamine B |
| RB | Rose Bengal |
| TBAOH | Tetrabutylammonium hydroxide |
| TB | Trypan Blue |
| TC | Tetracycline hydrochloride |
| TiO2 | Titanium dioxide |
| TMAOH | Tetramethylammonium hydroxide |
| rGO | Reduced graphene oxide |
Data availability
No data were used for the research described in this article.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China [No. 2022YFC3703102], National Natural Science Foundation of China [No. 22276163] and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China [No. LR22B070002].References
- Z. Jiang, S. Karan and A. G. Livingston, Water transport through ultrathin polyamide nanofilms used for reverse osmosis, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(15), e1705973 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Sun, J. Lu, S. Li, C. Dai, D. Zou and W. Jing, MXene-based membranes in water treatment: Current status and future prospects, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2024, 331, 125640 CrossRef CAS.
- C. E. Shuck and Y. Gogotsi, Taking MXenes from the lab to commercial products, Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 401, 125786 CrossRef CAS.
- K. J. Berean, J. Z. Ou, T. Daeneke, B. J. Carey, E. P. Nguyen and Y. Wang, et al., 2D MoS2 PDMS nanocomposites for NO2 separation, Small, 2015, 11(38), 5035–5040 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. H. Bae, J. S. Lee, W. Qiu, W. J. Koros, C. W. Jones and S. Nair, A high-performance gas-separation membrane containing submicrometer-sized metal-organic framework crystals, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49(51), 9863 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Fan, J. Gu, H. Meng, A. Knebel and J. Caro, High-flux membranes based on the covalent organic framework COF-LZU1 for selective dye separation by nanofiltration, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57(15), 4083–4087 CrossRef CAS.
- R. T. Adams, J. S. Lee, T.-H. Bae, J. K. Ward, J. R. Johnson and C. W. Jones, et al., CO2–CH4 permeation in high zeolite 4A loading mixed matrix membranes, J. Membr. Sci., 2011, 367(1–2), 197–203 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Chen, G. Shi, J. Shen, B. Peng, B. Zhang and Y. Wang, et al., Ioen sieving in graphene oxide membranes via cationic control of interlayer spacing, Nature, 2017, 550(7676), 380–383 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Naguib, M. Kurtoglu, V. Presser, J. Lu, J. Niu and M. Heon, et al., Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2, Adv. Mater., 2011, 23(37), 4248–4253 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. S. Ray, T. S. K. Sharma, R. Singh, A. Ratley, W. M. Choi and Y.-H. Ahn, et al., Towards the next generation improved throughput MXene-based membrane for environmental applications: A holistic review, J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2023, 11(3), 110243 CrossRef CAS.
- O. Kwon, Y. Choi, J. Kang, J. H. Kim, E. Choi and Y. C. Woo, et al., A comprehensive review of MXene-based water-treatment membranes and technologies: Recent progress and perspectives, Desalination, 2022, 522, 115448 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Lin, Y. Liu, Z. Yang, Z. He, H. Wang and L. Zhang, et al., Construction and application of two-dimensional MXene-based membranes for water treatment: A mini-review, Results Eng., 2022, 15, 100494 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Khosla, Sonu, H. T. A. Awan, K. Singh, Gaurav and R. Walvekar, et al., Emergence of MXene and MXene-polymer hybrid membranes as future-environmental remediation strategies, Adv. Sci., 2022, 9(36), 2203527 CrossRef CAS.
- O. M. Michael Naguib, J. Carle, V. Presser, J. Lu, L. Hultman, Y. Gogotsi and M. W. Barsoum, Two-dimensional transition metal carbides, ACS Nano, 2012, 6(2), 1322–1331 CrossRef.
- J. Li, X. Li and B. Van der Bruggen, An MXene-based membrane for molecular separation, Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2020, 7(5), 1289–1304 RSC.
- M. Ghidiu, M. R. Lukatskaya, M. Q. Zhao, Y. Gogotsi and M. W. Barsoum, Conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide 'clay' with high volumetric capacitance, Nature, 2014, 516(7529), 78–81 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Xu, L. Wang, Z. Liu, L. Chen, J. Guo and N. Kang, et al., Large-area high-quality 2D ultrathin Mo2C superconducting crystals, Nat. Mater., 2015, 14(11), 1135–1141 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Urbankowski, B. Anasori, T. Makaryan, D. Er, S. Kota and P. L. Walsh, et al., Synthesis of two-dimensional titanium nitride Ti4N3 (MXene), Nanoscale, 2016, 8(22), 11385–11391 RSC.
- W. Sun, S. A. Shah, Y. Chen, Z. Tan, H. Gao and T. Habib, et al., Electrochemical etching of Ti2AlC to Ti2CTx (MXene) in low-concentration hydrochloric acid solution, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(41), 21663–21668 RSC.
- W. Qian, C. Yan, D. He, X. Yu, L. Yuan and M. Liu, et al., pH-triggered charge-reversible of glycol chitosan conjugated carboxyl graphene for enhancing photothermal ablation of focal infection, Acta Biomater., 2018, 69, 256–264 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Li, H. Shao, Z. Lin, J. Lu, L. Liu and B. Duployer, et al., A general Lewis acidic etching route for preparing MXenes with enhanced electrochemical performance in non-aqueous electrolyte, Nat. Mater., 2020, 19(8), 894–899 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Natu, R. Pai, M. Sokol, M. Carey, V. Kalra and M. W. Barsoum, 2D Ti3C2Tz MXene synthesized by water-free etching of Ti3AlC2 in polar organic solvents, Chemistry, 2020, 6(3), 616–630 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Wang, Y. Guo, Q. Zhang, Z. Li, Y. Zhao and H. Wang, Alkanolamine intercalation assisted liquid phase exfoliation of titanium carbide MXene nanosheets for highly efficient photocatalytic CO2 reduction, J. Mol. Liq., 2022, 367, 120578 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Alhabeb, K. Maleski, B. Anasori, P. Lelyukh, L. Clark and S. Sin, et al., Guidelines for synthesis and processing of two-dimensional titanium carbide (Ti3C2Tx MXene), Chem. Mater., 2017, 29(18), 7633–7644 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Naguib, V. N. Mochalin, M. W. Barsoum and Y. Gogotsi, 25th anniversary article: MXenes: A new family of two-dimensional materials, Adv. Mater., 2014, 26(7), 992–1005 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Anasori, M. R. Lukatskaya and Y. Gogotsi, 2D metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for energy storage, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2017, 2, 16098 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Naguib, R. R. Unocic, B. L. Armstrong and J. Nanda, Large-scale delamination of multi-layers transition metal carbides and carbonitrides “MXenes”, Dalton Trans., 2015, 44(20), 9353–9358 RSC.
- O. Mashtalir, M. Naguib, V. N. Mochalin, Y. Dall'Agnese, M. Heon and M. W. Barsoum, et al., Intercalation and delamination of layered carbides and carbonitrides, Nat. Commun., 2013, 4, 1716 CrossRef.
- X. Zhao, M. Radovic and M. J. Green, Synthesizing MXene nanosheets by water-free etching, Chemistry, 2020, 6(3), 544–546 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Oh, S. Lee, H. Kim, T. Y. Ko, S. J. Kim and C. M. Koo, Fast and high-yield anhydrous synthesis of Ti3C2Tx MXene with high electrical conductivity and exceptional mechanical strength, Small, 2022, 18(46), e2203767 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Jawaid, A. Hassan, G. Neher, D. Nepal, R. Pachter and W. J. Kennedy, et al., Halogen Etch of Ti3AlC2 MAX Phase for MXene Fabrication, ACS Nano, 2021, 15(2), 2771–2777 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Shi, P. Zhang, Z. Liu, S. Park, M. R. Lohe and Y. Wu, et al., Ambient-stable two-dimensional titanium carbide (MXene) enabled by iodine etching, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60(16), 8689–8693 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. E. Ghazaly, H. Ahmed, A. R. Rezk, J. Halim, P. O. A. Persson and L. Y. Yeo, et al., Ultrafast, one-step, salt-solution-based acoustic synthesis of Ti3C2 MXene, ACS Nano, 2021, 15(3), 4287–4293 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Mei, G. A. Ayoko, C. Hu and Z. Sun, Thermal reduction of sulfur-containing MAX phase for MXene production, Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 395, 125111 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Jia, T. Xiong, L. Zhao, F. Wang, H. Liu and R. Hu, et al., Ultrathin N-doped Mo2C nanosheets with exposed active sites as efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reactions, ACS Nano, 2017, 11(12), 12509–12518 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Geng, X. Zhao, Z. Chen, W. Sun, W. Fu and J. Chen, et al., Direct synthesis of large-area 2D Mo2C on in situ grown graphene, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(35), 1700072 CrossRef.
- X. Xiao, H. Yu, H. Jin, M. Wu, Y. Fang and J. Sun, et al., Salt-templated synthesis of 2D metallic MoN and other nitrides, ACS Nano, 2017, 11(2), 2180–2186 CrossRef CAS.
- N. C. Frey, J. Wang, G. I. Vega Bellido, B. Anasori, Y. Gogotsi and V. B. Shenoy, Prediction of synthesis of 2D metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) and their precursors with positive and unlabeled machine learning, ACS Nano, 2019, 13(3), 3031–3041 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Xue, X. Li, M. Zhang, L. Han, Y. Liu and X. Tao, Chemical-combined ball-milling synthesis of fluorine-free porous MXene for high-performance lithium ion batteries, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 3(10), 10234–10241 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Chen, D. Zhang, J. Pan and W. Fan, Optical properties of two-dimensional semi-conductive MXene Sc2COx produced by sputtering, Optik, 2020, 219, 165046 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Kamysbayev, A. S. Filatov, H. Hu, X. Rui, F. Lagunas, D. Wang, R. F. Klie and D. V. Talapin, Covalent surface modifications and superconductivity of two-dimensional metal carbide MXenes, Science, 2020, 369, 979–983 CrossRef CAS.
- H. E. Karahan, K. Goh, C. J. Zhang, E. Yang, C. Yildirim and C. Y. Chuah, et al., MXene Materials for Designing Advanced Separation Membranes, Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(29), e1906697 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. A. Kumar, P. Prakash, T. Krithiga, D. J. Amarnath, J. Premkumar and N. Rajamohan, et al., Methods of synthesis, characteristics, and environmental applications of MXene: A comprehensive review, Chemosphere, 2022, 286(Pt 1), 131607 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Huang, L. Ding, J. Caro and H. Wang, MXene-based Membranes for Drinking Water Production, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62(52), e202311138 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Huang, L. Ding, J. Caro and H. Wang, MXene-based membranes for drinking water production, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, e202311138 CAS.
- D. Qadir, H. Mukhtar and L. K. Keong, Mixed matrix membranes for water purification applications, Sep. Purif. Rev., 2016, 46(1), 62–80 CrossRef.
- J. Deng, Z. Lu, L. Ding, Z.-K. Li, Y. Wei and J. Caro, et al., Fast electrophoretic preparation of large-area two-dimensional titanium carbide membranes for ion sieving, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 408, 127806 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Z. Zhang, Y. Wang, Q. Jiang, J. K. El-Demellawi, H. Kim and H. N. Alshareef, MXene printing and patterned coating for device applications, Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(21), e1908486 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. J. Zhang, L. McKeon, M. P. Kremer, S. H. Park, O. Ronan and A. Seral-Ascaso, et al., Additive-free MXene inks and direct printing of micro-supercapacitors, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 1795 CrossRef.
- H. Li and J. Liang, Recent development of printed micro-supercapacitors: Printable materials, printing technologies, and perspectives, Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(3), e1805864 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Chen, Y. Liu, Y. Li, Y. Wu, Y. Chen and Y. Liu, et al., Synthesis, application and mechanisms of Ferro-Manganese binary oxide in water remediation: A review, Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 388, 124313 CrossRef CAS.
- J. H. Kim, G. S. Park, Y. J. Kim, E. Choi, J. Kang and O. Kwon, et al., Large-area Ti3C2Tx-MXene coating: Toward industrial-scale fabrication and molecular separation, ACS Nano, 2021, 15(5), 8860–8869 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Li, H. Liu, C. Shi, J. Qin, Y. Fu and Y. Song, et al., Roll-to-roll fabricating MXene membranes with ordered interlayer distances for molecule and ion separation, Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2023, 10(21), 202300301 Search PubMed.
- C.-H. Tsou, Q.-F. An, S.-C. Lo, M. De Guzman, W.-S. Hung and C.-C. Hu, et al., Effect of microstructure of graphene oxide fabricated through different self-assembly techniques on 1-butanol dehydration, J. Membr. Sci., 2015, 477, 93–100 CrossRef CAS.
- A. P. Isfahani, A. Arabi Shamsabadi and M. Soroush, MXenes and other two-dimensional materials for membrane gas separation: Progress, challenges, and potential of MXene-based membranes, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2022, 62(5), 2309–2328 CrossRef.
- R. P. Pandey, K. Rasool, V. E. Madhavan, B. Aïssa, Y. Gogotsi and K. A. Mahmoud, Ultrahigh-flux and fouling-resistant membranes based on layered silver/MXene (Ti3C2Tx) nanosheets, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6(8), 3522–3533 RSC.
- G. Liu, J. Shen, Q. Liu, G. Liu, J. Xiong and J. Yang, et al., Ultrathin two-dimensional MXene membrane for pervaporation desalination, J. Membr. Sci., 2018, 548, 548–558 CrossRef CAS.
- C. E. Ren, K. B. Hatzell, M. Alhabeb, Z. Ling, K. A. Mahmoud and Y. Gogotsi, Charge- and size-selective ion sieving through Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2015, 6(20), 4026–4031 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Ding, Y. Wei, Y. Wang, H. Chen, J. Caro and H. Wang, A two-dimensional lamellar membrane: MXene nanosheet stacks, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56(7), 1825–1829 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Lu, Y. Wu, L. Ding, Y. Wei and H. Wang, A lamellar MXene Ti3C2Tx/PSS composite membrane for fast and selective lithium-ion separation, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60(41), 22265–22269 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Akbari, P. Sheath, S. T. Martin, D. B. Shinde, M. Shaibani and P. C. Banerjee, et al., Large-area graphene-based nanofiltration membranes by shear alignment of discotic nematic liquid crystals of graphene oxide, Nat. Commun., 2016, 7, 10891 CrossRef CAS.
- H. W. Kim, H. W. Yoon, S. M. Yoon, B. M. Yoo, B. K. Ahn and Y. H. Cho, et al., Selective gas transport through few-layered graphene and graphene oxide membranes, Science, 2013, 342(6154), 91–95 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhang, K. Sheng, Z. Wang, W. Wu, B. H. Yin and J. Zhu, et al., Rational design of MXene hollow fiber membranes for gas separations, Nano Lett., 2023, 23(7), 2710–2718 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. M. Weng, J. Li, M. Alhabeb, C. Karpovich, H. Wang and J. Lipton, et al., Layer-by-layer assembly of cross-functional semi-transparent MXene-carbon nanotubes composite films for next-generation electromagnetic interference shielding, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28(44), 1803360 CrossRef.
- Z. Liu, Y. Cui, Q. Li, Q. Zhang and B. Zhang, Fabrication of folded MXene/MoS2 composite microspheres with optimal composition and their microwave absorbing properties, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2022, 607(Pt 1), 633–644 CrossRef CAS.
- S. H. Yang, Y. J. Lee, H. Kang, S. K. Park and Y. C. Kang, Carbon-coated three-dimensional MXene/iron selenide ball with core-shell structure for high-performance potassium-ion batteries, Nano-Micro Lett., 2021, 14(1), 17 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. Couly, M. Alhabeb, K. L. Van Aken, N. Kurra, L. Gomes and A. M. Navarro-Suárez, et al., Asymmetric flexible MXene-reduced graphene oxide micro-supercapacitor, Adv. Electron. Mater., 2017, 4(1), 1700339 CrossRef.
- E. Aydin, J. K. El-Demellawi, E. Yarali, F. Aljamaan, S. Sansoni and A. U. Rehman, et al., Scaled deposition of Ti3C2Tx MXene on complex surfaces: Application assessment as rear electrodes for silicon heterojunction solar cells, ACS Nano, 2022, 16(2), 2419–2428 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Zhao, B. Xia, A. Hu, M. Hou, T. Li and S. Wang, et al., Preparation of high electromagnetic interference shielding and humidity responsivity composite film through modified Ti3C2Tx MXene cross-linking with sodium alginate, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2023, 236, 123939 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. J. Zhang, B. Anasori, A. Seral-Ascaso, S. H. Park, N. McEvoy and A. Shmeliov, et al., Transparent, flexible, and conductive 2D titanium carbide (MXene) films with high volumetric capacitance, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(36), 1702678 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Luo, Y. Huang, K. Cheng, A. Alhassan, M. Alqahtani and L. Tang, et al., MXene-GaN van der Waals metal-semiconductor junctions for high performance multiple quantum well photodetectors, Light: Sci. Appl., 2021, 10(1), 177 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Bian, G. He, W. Zhi, S. Xiang, T. Wang and D. Cai, Ultralight MXene-based aerogels with high electromagnetic interference shielding performance, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2019, 7(3), 474–478 RSC.
- Z. Huang, D. Ling Zhao, L. Shen, H. Lin, C. Chen and Y. Xu, et al., Mxenes for membrane separation: from fabrication strategies to advanced applications, Sci. Bull., 2024, 69(1), 125–140 CrossRef.
- M. Shekhirev, C. E. Shuck, A. Sarycheva and Y. Gogotsi, Characterization of MXenes at every step, from their precursors to single flakes and assembled films, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2021, 120, 100757 CrossRef CAS.
- S. M. M. Raj, A. K. Sundramoorthy, R. Atchudan, D. Ganapathy and A. Khosla, Review—Recent Trends on the Synthesis and Different Characterization Tools for MXenes and their Emerging Applications, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2022, 169(7), 077501 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhang and R. Wang, Heterointerface engineering of MXene: Advanced applications in environmental remediation, Chemosphere, 2024, 364, 143054 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Ma, X. Zhu, C. Huang and J. Fan, Revealing the effects of terminal groups of MXene on the water desalination performance, J. Membr. Sci., 2022, 647, 120334 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Lu, C. Hu, C. L. Ritt, X. Hua, J. Sun and H. Xia, et al., In Situ Characterization of Dehydration during Ion Transport in Polymeric Nanochannels, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143(35), 14242–14252 CrossRef CAS.
- M. A. Hope, A. C. Forse, K. J. Griffith, M. R. Lukatskaya, M. Ghidiu and Y. Gogotsi, et al., NMR reveals the surface functionalisation of Ti3C2MXene, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, 18(7), 5099–5102 RSC.
- K. Meidani, Z. Cao and A. Barati Farimani, Titanium Carbide MXene for Water Desalination: A Molecular Dynamics Study, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2021, 4(6), 6145–6151 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Liu, Z. Zhao, L. Li, Y. Wu and H. He, Molecular simulation study of 2D MXene membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration, J. Membr. Sci., 2023, 677, 121623 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Zeng, X. Zhou, L. Shen, D. L. Zhao, N. Kong and Y. Li, et al., Exceptional self-cleaning MXene-based membrane for highly efficient oil/water separation, J. Membr. Sci., 2024, 700, 122691 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Cao, Y. Zhang, H. Wang, K. Khan, A. K. Tareen and W. Qian, et al., Recent Advances in Oxidation Stable Chemistry of 2D MXenes, Adv. Mater., 2022, 34(13), e2107554 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Sun, J. Lu, S. Li, C. Dai, D. Zou and W. Jing, MXene-based membranes in water treatment: Current status and future prospects, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2024, 331, 125640 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Zhao, A. Vashisth, E. Prehn, W. Sun, S. A. Shah and T. Habib, et al., Antioxidants Unlock Shelf-Stable Ti3C2T (MXene) Nanosheet Dispersions, Matter, 2019, 1(2), 513–526 CrossRef.
- H. Zhang, B. Pang, A. Di, J. Chang, F. Heraly and A. Sikdar, et al., Harnessing Holey MXene/Graphene Oxide Heterostructure to Maximize Ion Channels in Lamellar Film for High-Performance Capacitive Deionization, Small, 2024, e2403518 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Peng, W. Yang, L. Li, K. Zhang, L. Wang and T. Hu, et al., Fast assembly of MXene hydrogels by interfacial electrostatic interaction for supercapacitors, Chem. Commun., 2021, 57(82), 10731–10734 RSC.
- Y. Zheng, H. Zhang, S. Yu, H. Zhou, W. Chen and J. Yang, Covalently bridged MXene/COF hybrid membrane toward efficient dye separation, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2024, 349, 127908 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Tang, B. Guo, S. Zhang, X. Tan and H. Zheng, Layer-by-layer repaired lamellar membrane for low stacking defect of MXene nanosheets and efficient separation performance in water purification, J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2023, 11(2), 109450 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Sun, D. Xu, S. Li, L. Cui, Y. Zhuang and W. Xing, et al., Assembly of multidimensional MXene-carbon nanotube ultrathin membranes with an enhanced anti-swelling property for water purification, J. Membr. Sci., 2021, 623, 119075 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Han, Z. Xu and C. Gao, Ultrathin graphene nanofiltration membrane for water purification, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2013, 23(29), 3693–3700 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Huang, X. Wang, W. Xiang, T. Wang, C. Otis and L. Sarge, et al., Forward-looking roadmaps for long-term continuous water quality monitoring: Bottlenecks, innovations, and prospects in a critical review, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2022, 56(9), 5334–5354 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Mu, N. Graham, W. Yu, K. Sun, X. Xu and T. Liu, Optimal cross-linking of MXene-based membranes for high rejection and low adsorption with long-term stability for water treatment, J. Membr. Sci., 2024, 701, 122738 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. K. Li, Y. Wei, X. Gao, L. Ding, Z. Lu and J. Deng, et al., Antibiotics separation with MXene membranes based on regularly stacked high-aspect-ratio nanosheets, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59(24), 9751–9756 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Rasool, K. A. Mahmoud, D. J. Johnson, M. Helal, G. R. Berdiyorov and Y. Gogotsi, Efficient Antibacterial Membrane based on Two-Dimensional Ti(3)C(2)T(x) (MXene) Nanosheets, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7(1), 1598 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Zhao, Y. Yang, C. Yang, Y. Tian, Y. Han and J. Liu, et al., A hydrophobic surface enabled salt-blocking 2D Ti3C2MXene membrane for efficient and stable solar desalination, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6(33), 16196–16204 RSC.
- G. Yi, L. Du, G. Wei, H. Zhang, H. Yu and X. Quan, et al., Selective molecular separation with conductive MXene/CNT nanofiltration membranes under electrochemical assistance, J. Membr. Sci., 2022, 658, 120719 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Shen, G. Liu, Y. Ji, Q. Liu, L. Cheng and K. Guan, et al., 2D MXene nanofilms with tunable gas transport channels, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28(31), 1801511 CrossRef.
- Y. Kang, Y. Xia, H. Wang and X. Zhang, 2D laminar membranes for selective water and ion transport, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29(29), 1902014 CrossRef.
- T. Wang, J. Lu, L. Mao and Z. Wang, Electric field assisted layer-by-layer assembly of graphene oxide containing nanofiltration membrane, J. Membr. Sci., 2016, 515, 125–133 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Shekhirev, J. Busa, C. E. Shuck, A. Torres, S. Bagheri and A. Sinitskii, et al., Ultralarge flakes of Ti3C2Tx/MXene via soft delamination, ACS Nano, 2022, 16, 13695–13703 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Cheng, Y. Xie, S. Yan, Z. Liu, Y. Ma and Y. Yue, et al., Maximizing the ion accessibility and high mechanical strength in nanoscale ion channel MXene electrodes for high-capacity zinc-ion energy storage, Sci. Bull., 2022, 67(21), 2216–2224 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Xiang, X. Wang, M. Ding, X. Tang, S. Zhang and X. Zhang, et al., The role of lateral size of MXene nanosheets in membrane filtration of dyeing wastewater: Membrane characteristic and performance, Chemosphere, 2022, 294, 133728 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Lin, Y. Li and J. Zhu, Cross-linked GO membranes assembled with GO nanosheets of differently sized lateral dimensions for organic dye and chromium separation, J. Membr. Sci., 2020, 598, 117789 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Backes, T. M. Higgins, A. Kelly, C. Boland, A. Harvey, D. Hanlon and J. N. Coleman, Guidelines for Exfoliation, Characterisation and Processing of Layered Materials Produced by Liquid Exfoliation, Chem. Mater., 2017, 29, 243–255 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Xu, Y. Sun, Y. Zhuang, W. Jing, H. Ye and Z. Cui, Assembly of 2D MXene nanosheets and TiO2 nanoparticles for fabricating mesoporous TiO2-MXene membranes, J. Membr. Sci., 2018, 564, 35–43 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Si, X. Ma, T. Wang, S. Tak Chu and J. Fan, Improvement of desalination performance by adjusting the arrangement of lamellar MXene membrane, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2023, 322, 124265 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Li, W. Gu, Y. Sun, D. Zou and W. Jing, Perforative pore formation on nanoplates for 2D porous MXene membranes via H2O2 mild etching, Ceram. Int., 2021, 47(21), 29930–29940 CrossRef CAS.
- J. L. Hart, K. Hantanasirisakul, A. C. Lang, B. Anasori, D. Pinto and Y. Pivak, et al., Control of MXenes' electronic properties through termination and intercalation, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 522 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. A. Hope, A. C. Forse, K. J. Griffith, M. R. Lukatskaya, M. Ghidiu and Y. Gogotsi, et al., NMR reveals the surface functionalisation of Ti3C2 MXene, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, 18(7), 5099–5102 RSC.
- J. Liu, H. B. Zhang, R. Sun, Y. Liu, Z. Liu and A. Zhou, et al., Hydrophobic, flexible, and lightweight MXene foams for high-performance electromagnetic-interference shielding, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(38), 1702367 CrossRef.
- F. Xu, M. Wei and Y. Wang, Effect of hydrophilicity on ion rejection of sub-nanometer pores, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2021, 257, 117937 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Hong, F. Ming, Y. Shi, R. Li, I. S. Kim and C. Y. Tang, et al., Two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes as nanofluidic osmotic power generators, ACS Nano, 2019, 13(8), 8917–8925 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Naguib, J. Halim, J. Lu, K. M. Cook, L. Hultman and Y. Gogotsi, et al., New two-dimensional niobium and vanadium carbides as promising materials for Li-ion batteries, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(43), 15966–15969 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Halim, S. Kota, M. R. Lukatskaya, M. Naguib, M. Q. Zhao and E. J. Moon, et al., Synthesis and characterization of 2D molybdenum carbide (MXene), Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26(18), 3118–3127 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zhang, K. Guan, Y. Ji, G. Liu, W. Jin and N. Xu, Controllable ion transport by surface-charged graphene oxide membrane, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 1253 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Shen, G. Liu, K. Huang, Z. Chu, W. Jin and N. Xu, Subnanometer two-dimensional graphene oxide channels for ultrafast gas sieving, ACS Nano, 2016, 10(3), 3398–3409 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Chen, Q. H. Yang, Y. Yang, W. Lv, Y. Wen and P. X. Hou, et al., Self-assembled free-standing graphite oxide membrane, Adv. Mater., 2009, 21(29), 3007–3011 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Liao, Z. Xu, Z. Fan, Q. Meng, B. Lv and X. Ye, et al., Confined assembly of ultrathin dual-functionalized Z-MXene nanosheet intercalated GO nanofilms with controlled structure for size-selective permeation, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9(20), 12236–12243 RSC.
- M. Bilal, I. Ihsanullah, M. Younas and M. Ul Hassan Shah, Recent advances in applications of low-cost adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals from water: A critical review, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2021, 278, 119510 CrossRef.
- Y. You, V. Sahajwalla, M. Yoshimura and R. K. Joshi, Graphene and graphene oxide for desalination, Nanoscale, 2016, 8(1), 117–119 RSC.
- A. Guirguis, J. W. Maina, L. Kong, L. C. Henderson, A. Rana and L. H. Li, et al., Perforation routes towards practical nano-porous graphene and analogous materials engineering, Carbon, 2019, 155, 660–673 CrossRef CAS.
- S. J. Gao, H. Qin, P. Liu and J. Jin, SWCNT-intercalated GO ultrathin films for ultrafast separation of molecules, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(12), 6649–6654 RSC.
- X. Long, G.-Q. Zhao, Y. Zheng, J. Hu, Y. Zuo and J. Zhang, et al., Porous and carboxyl functionalized titanium carbide MXene sheets for fast oil-in-water emulsion separation, J. Membr. Sci., 2022, 661, 120953 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Ying, L. Sun, Q. Wang, Z. Fan and X. Peng, In-plane mesoporous graphene oxide nanosheet assembled membranes for molecular separation, RSC Adv., 2014, 4(41), 21425–21428 RSC.
- Y. Li, W. Zhao, M. Weyland, S. Yuan, Y. Xia and H. Liu, et al., Thermally reduced nanoporous graphene oxide membrane for desalination, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2019, 53(14), 8314–8323 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Chang, Y. Shen, D. Kong, J. Ning, Z. Xiao and J. Liang, et al., Fabrication of the reduced preoxidized graphene-based nanofiltration membranes with tunable porosity and good performance, RSC Adv., 2017, 7(5), 2544–2549 RSC.
- J. Yang, D. Gong, G. Li, G. Zeng, Q. Wang and Y. Zhang, et al., Self-assembly of thiourea-crosslinked graphene oxide framework membranes toward separation of small molecules, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(16), e1705775 CrossRef.
- T. Jain, B. C. Rasera, R. J. Guerrero, M. S. Boutilier, S. C. O'Hern and J. C. Idrobo, et al., Heterogeneous sub-continuum ionic transport in statistically isolated graphene nanopores, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2015, 10(12), 1053–1057 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Thomas, B. Corry and T. A. Hilder, What have we learnt about the mechanisms of rapid water transport, ion rejection and selectivity in nanopores from molecular simulation?, Small, 2014, 10(8), 1453–1465 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. A. Richards, A. I. Schafer, B. S. Richards and B. Corry, The importance of dehydration in determining ion transport in narrow pores, Small, 2012, 8(11), 1701–1709 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Wang, Z. Zhang, J. Zhu, M. Tian, S. Zheng and F. Wang, et al., Ion sieving by a two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx alginate lamellar membrane with stable interlayer spacing, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1), 3540 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Du, K. Chen, Y. Zhang, Y. Wang, P. He and H.-Y. Mi, et al., Engineering multilayered MXene/electrospun poly(lactic acid) membrane with increscent electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding for integrated Joule heating and energy generating, Compos. Commun., 2021, 26, 100770 CrossRef.
- F. Yang, M. Wu, Y. Wang, S. Ashtiani and H. Jiang, A GO-induced assembly strategy To repair MOF nanosheet-based membrane for efficient H2/CO2 separation, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11(1), 990–997 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Zhong, D. Wang, J. Sheng, Z. Han, C. Sun and J. Tan, et al., Freestanding and sandwich MXene-based cathode with suppressed lithium polysulfides shuttle for flexible lithium-sulfur batteries, Nano Lett., 2022, 22(3), 1207–1216 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. F. X. Jia Zhang, G. Qian, X. Zhi Ping, C. Chen and Q. Liu, Reinvestigation of dehydration and dehydroxylation of hydrotalcite like compounds through combinedBTG-DTA-MS analyses, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 7 Search PubMed.
- L. Ding, Y. Wei, L. Li, T. Zhang, H. Wang and J. Xue, et al., MXene molecular sieving membranes for highly efficient gas separation, Nat. Commun., 2018, 9(1), 155 CrossRef.
- K. H. Thebo, X. Qian, Q. Zhang, L. Chen, H. M. Cheng and W. Ren, Highly stable graphene-oxide-based membranes with superior permeability, Nat. Commun., 2018, 9(1), 1486 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Wang, P. Zhang, B. Liang, Y. Liu, T. Xu and L. Wang, et al., Graphene oxide as an effective barrier on a porous nanofibrous membrane for water treatment, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8(9), 6211–6218 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Zhang, J. Sun, Y. Mao, G. Liu and W. Jin, Effect of substrate on formation and nanofiltration performance of graphene oxide membranes, J. Membr. Sci., 2019, 574, 196–204 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Lu, Y. Wei, J. Deng, L. Ding, Z.-K. Li and H. Wang, Self-crosslinked MXene (Ti3C2Tx) membranes with good antiswelling property for monovalent metal ion exclusion, ACS Nano, 2019, 13(9), 10535–10544 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Abraham, K. S. Vasu, C. D. Williams, K. Gopinadhan, Y. Su and C. T. Cherian, et al., Tunable sieving of ions using graphene oxide membranes, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2017, 12(6), 546–550 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Fang, Z. Liu, J. Han, Z. Jin, Y. Han and F. Wang, et al., High-performance electrocatalytic conversion of N2 to NH3 using oxygen-vacancy-rich TiO2 in situ grown on Ti3C2Tx MXene, Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9(16), 1803406 CrossRef.
- J. Zhu, Y. Tang, C. Yang, F. Wang and M. Cao, Composites of TiO2 nanoparticles deposited on Ti3C2 MXene nanosheets with enhanced electrochemical performance, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2016, 163(5), A785–A791 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Sun, S. Li, Y. Zhuang, G. Liu, W. Xing and W. Jing, Adjustable interlayer spacing of ultrathin MXene-derived membranes for ion rejection, J. Membr. Sci., 2019, 591, 117350 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhang, X. Chen, C. Luo, J. Gu, M. Li and M. Chao, et al., Column-to-beam structure house inspired MXene-based integrated membrane with stable interlayer spacing for water purification, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(22), 2111660 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wu, L. Hao, J. Zhang, X. Zhang, J. Wang and J. Liu, Polymer-Ti3C2Tx composite membranes to overcome the trade-off in solvent resistant nanofiltration for alcohol-based system, J. Membr. Sci., 2016, 515, 175–188 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Xu, Y. Kang, W. Zhang, B. Pan and X. Zhang, Two-dimensional MXene membranes with biomimetic sub-nanochannels for enhanced cation sieving, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14(1), 4907 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Feng, K. Ou, Z. Zhang, Y. Liu, Y. Huang and Z. Wang, et al., Dual-layered covalent organic framework/MXene membranes with short paths for fast water treatment, J. Membr. Sci., 2022, 658, 120761 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Tian, A. VahidMohammadi, Z. Wang, L. Ouyang, M. Beidaghi and M. M. Hamedi, Layer-by-layer self-assembly of pillared two-dimensional multilayers, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 2558 CrossRef.
- I. Mahar, F. K. Mahar, N. Mahar, A. A. Memon, A. A. A. Pirzado and Z. Khatri, et al., Fabrication and characterization of MXene/carbon composite-based nanofibers (MXene/CNFs) membrane: An efficient adsorbent material for removal of Pb+2 and As+3 ions from water, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 2023, 191, 462–471 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Zeng, Y. Liu, Q. Lin, S. Pu, S. Zheng and M. B. M. Y. Ang, et al., Constructing composite membranes from functionalized metal organic frameworks integrated MXene intended for ultrafast oil/water emulsion separation, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2022, 293, 121052 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Zhang, H. Xu, F. Xie, X. Ma, B. Niu and M. Chen, et al., General synthesis of ultrafine metal oxide/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for ultrahigh-flux nanofiltration membrane, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13(1), 471 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Li, X. Fu, G. Liu, J. Li, G. Zhou and G. Liu, et al., Room-temperature in situ synthesis of MOF@MXene membrane for efficient hydrogen purification, J. Membr. Sci., 2022, 664, 121097 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Zhao, L. Ding, R. Hinterding, A. Mundstock, C. Belke and R. J. Haug, et al., MXene assisted preparation of well-intergrown ZIF-67 membrane for helium separation, J. Membr. Sci., 2022, 652, 120432 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Xie, C. Chen, N. Zhang, Z.-R. Tang, J. Jiang and Y.-J. Xu, Microstructure and surface control of MXene films for water purification, Nat. Sustain., 2019, 2(9), 856–862 CrossRef.
- H. Younas, H. Ahmad, N. Baig and I. H. Aljundi, Improved Efficiency and Stability of MXene Membranes via Interlayer Space Tuning for Oily Water Separation, Langmuir, 2024, 40(39), 20452–20463 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Li, X. Zhu, Q. Gao, Y. Bai, M. Lou and S. Huang, et al., Regulating molecules/ions sieving channels of MXene-based membranes by edge-capping strategy, J. Membr. Sci., 2024, 712, 123236 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Zheng, Q. Tu, J. J. Urban, S. Li and B. Mi, Swelling of graphene oxide membranes in aqueous solution: Characterization of interlayer spacing and insight into water transport mechanisms, ACS Nano, 2017, 11(6), 6440–6450 CrossRef CAS.
- W.-S. Hung, C.-H. Tsou, M. De Guzman, Q.-F. An, Y.-L. Liu and Y.-M. Zhang, et al., Cross-linking with diamine monomers To prepare composite graphene oxide-framework membranes with varying d-spacing, Chem. Mater., 2014, 26(9), 2983–2990 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Kang, T. Hu, Y. Wang, K. He, Z. Wang and Y. Hora, et al., Nanoconfinement enabled non-covalently decorated MXene membranes for ion-sieving, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14(1), 4075 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Yuan, Y. Li, L. Qian, J. Xing, X. Wang and H. Zhang, et al., Molten salt intercalated MXene membrane for d-spacing stabilization under electrochemical assistance, ACS ES&T Eng., 2023, 3(12), 2233–2242 Search PubMed.
- L. Ding, L. Li, Y. Liu, Y. Wu, Z. Lu and J. Deng, et al., Effective ion sieving with Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes for production of drinking water from seawater, Nat. Sustain., 2020, 3(4), 296–302 CrossRef.
- J. Zhu, L. Wang, J. Wang, F. Wang, M. Tian and S. Zheng, et al., Precisely tunable ion sieving with an Al13-Ti3C2Tx lamellar membrane by controlling interlayer spacing, ACS Nano, 2020, 14(11), 15306–15316 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhang, S. Zhang and T. S. Chung, Nanometric graphene oxide framework membranes with enhanced heavy metal removal via nanofiltration, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49(16), 10235–10242 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Sui, Z. Yuan, C. Liu, L. Wei, M. Xu and F. Liu, et al., Graphene oxide laminates intercalated with 2D covalent-organic frameworks as a robust nanofiltration membrane, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8(19), 9713–9725 RSC.
- M. Ding, H. Xu, W. Chen, G. Yang, Q. Kong and D. Ng, et al., 2D laminar maleic acid-crosslinked MXene membrane with tunable nanochannels for efficient and stable pervaporation desalination, J. Membr. Sci., 2020, 600, 117871 CrossRef.
- X. Wu, M. Ding, H. Xu, W. Yang, K. Zhang and H. Tian, et al., Scalable Ti3C2Tx MXene interlayered forward osmosis membranes for enhanced water purification and organic solvent recovery, ACS Nano, 2020, 14(7), 9125–9135 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Sui, Y. Wang, F. Liu, Z. Yuan, C. Wang and Y. Yu, et al., The tripartite role of 2D covalent organic frameworks in graphene-based organic solvent nanofiltration membranes, Matter, 2021, 4(9), 2953–2969 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Lan, C. Feng, Z. Wang, L. Li, Y. Wang and T. Liu, Chemically laminating graphene oxide nanosheets with phenolic nanomeshes for robust membranes with fast desalination, Nano Lett., 2021, 21(19), 8236–8243 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Han, Z. Mai, Z. Wang, X. Zhang, J. Zhu and J. Shen, et al., Covalent organic framework-mediated thin-film composite polyamide membranes toward precise ion sieving, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14(2), 3427–3436 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Lin, N. Mehra, Y. Li and J. Zhu, Graphite oxide/boron nitride hybrid membranes: The role of cross-plane laminar bonding for a durable membrane with large water flux and high rejection rate, J. Membr. Sci., 2020, 593, 117401 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Liu, S. Liu, K. Ma, H. Wang, X. Wang and G. Liu, et al., Polyelectrolyte functionalized Ti2CTx MXene membranes for pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol/water mixtures, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2020, 59(10), 4732–4741 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Meng, G. Liu, Y. Mao, F. Liang, G. Liu and W. Jin, Fabrication of surface-charged MXene membrane and its application for water desalination, J. Membr. Sci., 2021, 623, 119076 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Ding, M. Zheng, D. Xiao, Z. Zhao, J. Xue and S. Zhang, et al., Bioinspired Ti3C2Tx MXene-based ionic diode membrane for high-efficient osmotic energy conversion, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2022, 61(41), e202206152 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Imsong and P. D. Dhar, Dual-functional superhydrophilic/underwater superoleophobic 2D Ti3C2TX MXene-PAN membrane for efficient oil-water separation and adsorption of organic dyes in wastewater, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2023, 306, 122636 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Zhang, Y. Liu, G. Zeng, Z. Yang, Q. Lin and Y. Wang, et al., Two-dimensional Na-Bentonite@MXene composite membrane with switchable wettability for selective oil/water separation, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2023, 306, 122677 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Liu, J. Shen, Y. Ji, Q. Liu, G. Liu and J. Yang, et al., Two-dimensional Ti2CTx MXene membranes with integrated and ordered nanochannels for efficient solvent dehydration, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7(19), 12095–12104 RSC.
- S. Wang, F. Wang, Y. Jin, X. Meng, B. Meng and N. Yang, et al., Removal of heavy metal cations and co-existing anions in simulated wastewater by two separated hydroxylated MXene membranes under an external voltage, J. Membr. Sci., 2021, 638, 119697 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Hao, H. Zhang, X. Wu, J. Zhang, J. Wang and Y. Li, Novel thin-film nanocomposite membranes filled with multi-functional Ti3C2Tx nanosheets for task-specific solvent transport, Composites, Part A, 2017, 100, 139–149 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Yang, X. Chen, Z. Lv, C. Luo, M. Chao and P. Zhang, et al., Dynamic covalent interface engineering for 2D MXene membrane with interchangeable surface groups and tunable layer spacing for water treatment, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2024, 348, 127525 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Ni, C. Yuan, S. Li, J. Lu, L. Yan and W. Gu, et al., Temperature-induced hydrophobicity transition of MXene membrane for directly preparing W/O emulsions, Chin. J. Chem. Eng., 2023, 55, 59–62 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Feng, Y. Zhan, W. Yang, A. Sun, H. Dong and Y. H. Chiao, et al., Bi-functional super-hydrophilic/underwater super-oleophobic 2D lamellar Ti3C2Tx MXene/poly (arylene ether nitrile) fibrous composite membrane for the fast purification of emulsified oil and photodegradation of hazardous organics, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2022, 612, 156–170 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Huang, J. Liu, Y. Liu, Y. Xu, R. Li and H. Hong, et al., Enhanced permeability and antifouling performance of polyether sulfone (PES) membrane via elevating magnetic Ni@MXene nanoparticles to upper layer in phase inversion process, J. Membr. Sci., 2021, 623, 119080 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Xie, Q. Fu, C. Xu, H. Lu, Q. Zhao and R. Curtain, et al., Continuous assembly of a polymer on a metal–organic framework (CAP on MOF): a 30 nm thick polymeric gas separation membrane, Energy Environ. Sci., 2018, 11(3), 544–550 RSC.
- P. Salehian and T.-S. Chung, Two-dimensional (2D) particle coating on membranes for pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol: A new approach to seal defects and enhance separation performance, J. Membr. Sci., 2017, 544, 378–387 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Fu, H. Xu, T. Lin, A. Wang, A. Wang and C. Yao, et al., Tailoring the crumpled structures of a polyamide membrane with a heterostructural MXene-TiO2 interlayer for high water permeability, Desalination, 2023, 549, 116352 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Ahmad, A. B. Alayande, H. Jee, Z. Wang, Y.-J. Park and K. S. Im, et al., Recent progress of MXene-based membranes for high-performance and efficient gas separation, Diamond Relat. Mater., 2023, 135, 109883 CrossRef CAS.
- H. E. Karahan, K. Goh, C. J. Zhang, E. Yang, C. Yildirim and C. Y. Chuah, et al., MXene materials for designing advanced separation membranes, Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(29), e1906697 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. M. Kang, D. W. Kim, C. E. Ren, K. M. Cho, S. J. Kim and J. H. Choi, et al., Selective molecular separation on Ti3C2Tx-graphene oxide membranes during pressure-driven filtration: comparison with graphene oxide and MXenes, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9(51), 44687–44694 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Wang, P. Chen, B. Shi, W. Guo, M. Jaroniec and S. Z. Qiao, A regularly channeled Lamellar membrane for unparalleled water and organics permeation, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57(23), 6814–6818 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Ling, C. E. Ren, M. Q. Zhao, J. Yang, J. M. Giammarco and J. Qiu, et al., Flexible and conductive MXene films and nanocomposites with high capacitance, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2014, 111(47), 16676–16681 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wu, X. Cui, W. Wu, J. Wang, Y. Li and Z. Jiang, Elucidating ultrafast molecular permeation through well-defined 2D nanochannels of lamellar membranes, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58(51), 18524–18529 CrossRef CAS.
- J. M. M. Peeters JPB, M. H. V. Mulder and H. Strathmann, Retention measurements of nanofltration membranes, J. Membr. Sci., 1998, 145, 11 Search PubMed.
- D. Li, W. Jing, S. Li, H. Shen and W. Xing, Electric Field-Controlled Ion Transport In TiO2 Nanochannel, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7(21), 11294–11300 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. L. Liu, C. Zhang, L. Guo, Q. Zeng, R. Wang and H. Chen, et al., Synergistically adsorbing and reducing Uranium from water by a novel nano zero-valent copper/MXene 0D/2D nanocomposite, Water Res., 2023, 245, 120666 CrossRef CAS.
- B. M. Jun, C. M. Park, J. Heo and Y. Yoon, Adsorption of Ba2+ and Sr2+ on Ti3C2Tx MXene in model fracking wastewater, J. Environ. Manage., 2020, 256, 109940 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Lu, Y. Wu, L. Ding, Y. Wei and H. Wang, A lamellar MXene Ti3C2Tx/PSS composite membrane for fast and selective lithium-ion separation, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60(41), 22265–22269 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Yang, Z. Xie, A. W. Thornton, C. M. Doherty, M. Ding and H. Xu, et al., Ultrathin poly (vinyl alcohol)/MXene nanofilm composite membrane with facile intrusion-free construction for pervaporative separations, J. Membr. Sci., 2020, 614, 118490 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Gao, C. Li, W. Huang, S. Mei, H. Lin and Q. Ou, et al., MXene/polymer membranes: Synthesis, properties, and emerging applications, Chem. Mater., 2020, 32(5), 1703–1747 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Sun and Y. Li, Potential environmental applications of MXenes: A critical review, Chemosphere, 2021, 271, 129578 CrossRef CAS.
- C. E. Ren, M. Alhabeb, B. W. Byles, M.-Q. Zhao, B. Anasori and E. Pomerantseva, et al., Voltage-gated ions sieving through 2D MXene Ti3C2Tx membranes, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2018, 1(7), 3644–3652 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Lao, R. Lv, J. Gao, A. Wang, J. Wu and J. Luo, Aqueous stable Ti3C2 MXene membrane with fast and photoswitchable nanofluidic transport, ACS Nano, 2018, 12(12), 12464–12471 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D.-D. Shao, Q. Zhang, L. Wang, Z.-Y. Wang, Y.-X. Jing and X.-L. Cao, et al., Enhancing interfacial adhesion of MXene nanofiltration membranes via pillaring carbon nanotubes for pressure and solvent stable molecular sieving, J. Membr. Sci., 2021, 623, 119033 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Sun, F. Yi, R. H. Li, X. Min, H. Qin and S. Q. Cheng, et al., Inorganic-organic hybrid membrane based on pillararene-intercalated MXene nanosheets for efficient water purification, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2022, 61(14), e202200482 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Feng, Y. Zhan, W. Yang, H. Dong, A. Sun and L. Li, et al., Ultra-high flux and synergistically enhanced anti-fouling Ag@MXene lamellar membrane for the fast purification of oily wastewater through nano-intercalation, photocatalytic self-cleaning and antibacterial effect, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2022, 298, 121635 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Imsong and P. D. Dhar, Superhydrophilic Photothermal-Responsive CuO@MXene Nanofibrous Membrane with Inherent Biofouling Resistance for Treating Complex Oily Wastewater, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2024, 16(15), 19537–19550 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Z. Ao Sun, Q. Feng, W. Yang, H. Dong, Y. Liu, X. Chen and Y. Chen, Assembly of MXene/ZnO heterojunction onto electrospun poly(arylene ether nitrile) fibrous membrane for favorable oil/water separation with high permeability and synergetic antifouling performance, J. Membr. Sci., 2022, 663, 120933 CrossRef.
- Q. Lin, G. Zeng, S. Pu, G. Yan, J. Luo and Y. Wan, et al., A dual regulation strategy for MXene-based composite membrane to achieve photocatalytic self-cleaning properties and multi-functional applications, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 443, 136335 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Wang, Z. Yu, X. Zhu, Q. Xiang, H. Chen and Y. Pang, ZIF-67 modified MXene/sepiolite composite membrane for oil–water separation and heavy metal removal, J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2022, 115, 314–328 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Maleki and A. Bozorg, MOF@MXene nanocomposite as a novel modifier to extend the application of PES mixed-matrix nanofiltration membranes for water treatment, Chemosphere, 2024, 364, 143273 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Usman, L. T. Yogarathinam, N. Baig, S. I. Abba, R. Chrystie and I. H. Aljundi, MXene-enhanced sulfonated TFN nanofiltration membranes for improved desalination performance, Desalination, 2024, 581, 117566 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Rasool, M. Helal, A. Ali, C. E. Ren, Y. Gogotsi and K. A. Mahmoud, Antibacterial activity of Ti3C2Tx MXene, ACS Nano, 2016, 10(3), 3674–3684 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Tian, X. Shi, L. Cheng, Y. Luo, Z. Dong and H. Gong, et al., Graphene-based nanocomposite as an effective, multifunctional, and recyclable antibacterial agent, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6(11), 8542–8548 CrossRef CAS.
- O. Mashtalir, K. M. Cook, V. N. Mochalin, M. Crowe, M. W. Barsoum and Y. Gogotsi, Dye adsorption and decomposition on two-dimensional titanium carbide in aqueous media, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2(35), 14334–14338 RSC.
- Q. Lin, G. Zeng, G. Yan, J. Luo, X. Cheng and Z. Zhao, et al., Self-cleaning photocatalytic MXene composite membrane for synergistically enhanced water treatment: Oil/water separation and dyes removal, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 427, 131668 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Zeng, Z. He, T. Wan, T. Wang, Z. Yang and Y. Liu, et al., A self-cleaning photocatalytic composite membrane based on g-C3N4@MXene nanosheets for the removal of dyes and antibiotics from wastewater, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2022, 292, 121037 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Kitchamsetti and A. L. F. de Barros, Recent advances in MXenes based composites as photocatalysts: Synthesis, properties and photocatalytic removal of organic contaminants from wastewater, ChemCatChem, 2023, 15(18), e202300690 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Long, G.-Q. Zhao, Y. Zheng, J. Hu, Y. Zuo and W. Luo, et al., A precise pyromellitic acid grafting prepared multifunctional MXene membranes for efficient oil-in-water emulsion separation and heavy metal ions removal, Chem. Eng. J., 2023, 472, 144904 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Huang, L. Shen, H. Lin, B. Li, C. Chen and Y. Xu, et al., Fabrication of fibrous MXene nanoribbons (MNRs) membrane with efficient performance for oil-water separation, J. Membr. Sci., 2022, 661, 120949 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Li, R. Dai, H. Zhou, X. Li and Z. Wang, Aramid nanofiber membranes reinforced by MXene nanosheets for recovery of dyes from textile wastewater, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2021, 4(6), 6328–6336 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Zhang, Y. Zheng, H. Zhou, S. Zhu and J. Yang, Nanocellulose-intercalated MXene NF membrane with enhanced swelling resistance for highly efficient antibiotics separation, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2023, 305, 122425 CrossRef CAS.
- X. He, Z. Qi, J. Gao, K. Huang, M. Li and D. Springael, et al., Nonylphenol ethoxylates biodegradation increases estrogenicity of textile wastewater in biological treatment systems, Water Res., 2020, 184, 116137 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Gong, G. Zhang, H. Dong, H. Wang, J. Nie and G. Ma, Self-assembled hierarchical heterogeneous MXene/COF membranes for efficient dye separations, J. Membr. Sci., 2022, 657, 120667 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Li, T.-J. Lou, W. Wang, M. Li, L.-C. Jing and Z.-X. Yang, et al., MXene-PANI/PES composite ultrafiltration membranes with conductive properties for anti-fouling and dye removal, J. Membr. Sci., 2023, 668, 121271 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Ye, R. Liu, X. Chen, Q. Chen, J. Lin and X. Lin, et al., Loose nanofiltration-based electrodialysis for highly efficient textile wastewater treatment, J. Membr. Sci., 2020, 608, 118182 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Ali, A. Ali, J. A. Buledi, A. A. Memon, A. R. Solangi and J. Yang, et al., MXene-based nanocomposites: emerging candidates for the removal of antibiotics, dyes, and heavy metal ions, Mater. Chem. Front., 2023, 7, 5519–5544 RSC.
- O. Jovanovic, C. F. Amábile-Cuevas, C. Shang, C. Wang and K. W. Ngai, What water professionals should know about antibiotics and antibiotic resistance: An overview, ACS ES&T Eng., 2021, 1(6), 1334–1351 Search PubMed.
- M. Lakemeyer, W. Zhao, F. A. Mandl, P. Hammann and S. A. Sieber, Thinking outside the box-novel antibacterials to tackle the resistance crisis, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57(44), 14440–14475 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Yang, Q. Lin, G. Zeng, S. Zhao, G. Yan and M. B. M. Y. Ang, et al., Ternary hetero-structured BiOBr/Bi2MoO6@MXene composite membrane: Construction and enhanced removal of antibiotics and dyes from water, J. Membr. Sci., 2023, 669, 121329 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Zeng, Z. He, T. Wan, T. Wang, Z. Yang and Y. Liu, et al., A self-cleaning photocatalytic composite membrane based on g-C3N4@MXene nanosheets for the removal of dyes and antibiotics from wastewater, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2022, 292, 121037 CrossRef CAS.
- F. A. Janjhi, I. Ihsanullah, M. Bilal, R. Castro-Muñoz, G. Boczkaj and F. Gallucci, MXene-based materials for removal of antibiotics and heavy metals from wastewater–a review, Water Resour. Ind., 2023, 29, 100202 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Huang, L. Ding and H. Wang, MXene-based membranes for separation applications, Small Sci., 2021, 1(7), 2100013 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Yang, Y. Liu, S. Hu, F. Yu, Z. He and G. Zeng, et al., Construction of Fe3O4@MXene composite nanofiltration membrane for heavy metal ions removal from wastewater, Polym. Adv. Technol., 2020, 32(3), 1000–1010 CrossRef.
- T. Xie, Y. Wang, Q. Zhang, W. Guo, S. Shen and Q. Wang, et al., Ti3C2Tx MXene-derived hydroxyl-rich titanate based hybrid membrane with cellulose as structural regulator for highly-efficient disposition of heavy metal ions, Desalination, 2024, 572, 117115 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Ghanbari, E. Nazarzadeh Zare, A. C. Paiva-Santos and N. Rabiee, Ti3C2Tx MXene@MOF decorated polyvinylidene fluoride membrane for the remediation of heavy metals ions and desalination, Chemosphere, 2023, 311(Pt 2), 137191 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Zhao, Y. Che, Y. Mo, W. Huang and C. Wang, Fabrication of PEI modified GO/MXene composite membrane and its application in removing metal cations from water, J. Membr. Sci., 2021, 640, 119847 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Fan, J. Li, S. Wang, X. Meng, W. Zhang and Y. Jin, et al., Voltage-enhanced ion sieving and rejection of Pb2+ through a thermally cross-linked two-dimensional MXene membrane, Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 401, 126073 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Forse Alexander, M. Griffin John, C. Merlet, J. Carretero-Gonzalez, O. Raji A-Rahman and M. Trease Nicole, et al., Direct observation of ion dynamics in supercapacitor electrodes using in situ diffusion NMR spectroscopy, Nat. Energy, 2017, 2(3), 16216 CrossRef.
- G. Wei, X. Quan, S. Chen, X. Fan, H. Yu and H. Zhao, Voltage-gated transport of nanoparticles across free-standing all-carbon-nanotube-based hollow-fiber membranes, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7(27), 14620–14627 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Guan, S. X. Li and M. A. Reed, Voltage gated ion and molecule transport in engineered nanochannels: theory, fabrication and applications, Nanotechnology, 2014, 25(12), 122001 CrossRef.
- M. N. Akieh, R.-M. Latonen, S. Lindholm, S. F. Ralph, J. Bobacka and A. Ivaska, Electrochemically controlled ion transport across polypyrrole/multi-walled carbon nanotube composite membranes, Synth. Met., 2011, 161(17–18), 1906–1914 CrossRef CAS.
- M. D. Levi, M. R. Lukatskaya, S. Sigalov, M. Beidaghi, N. Shpigel and L. Daikhin, et al., Solving the capacitive paradox of 2D MXene using electrochemical quartz-crystal admittance and in situ electronic conductance measurements, Adv. Energy Mater., 2014, 5(1), 1400815 CrossRef.
- E. S. Muckley, M. Naguib, H. W. Wang, L. Vlcek, N. C. Osti and R. L. Sacci, et al., Multimodality of structural, electrical, and gravimetric responses of intercalated MXenes to water, ACS Nano, 2017, 11(11), 11118–11126 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Wang, H. Zhang, Y. Kang, Y. Zhu, G. P. Simon and H. Wang, Voltage-gated ion transport in two-dimensional sub-1 nm nanofluidic channels, ACS Nano, 2019, 13(10), 11793–11799 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Qiu, J. Xiao, X. D. Chen, C. Selomulya, X. Zhang and M. W. Woo, Comparison of the effects of edge functionalized graphene oxide membranes on monovalent cation selectivity, J. Membr. Sci., 2021, 620, 118892 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Li, Z. Liu, S. Li, P. Nian, N. Xu and H. Luo, et al., Highly permeable and stable hyperbranched polyethyleneimine crosslinked AgNP@Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes for nanofiltration, J. Membr. Sci., 2023, 670, 121376 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wang, Q. Li, J. Zhang, H. Huang, S. Wu and Y. Yang, Novel thin-film reverse osmosis membrane with MXene Ti3C2T embedded in polyamide to enhance the water flux, anti-fouling and chlorine resistance for water desalination, J. Membr. Sci., 2020, 603, 118036 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Fan, Y. Yang, X. Shi, Y. Liu, H. Li and J. Liang, et al., A MXene-Based Hierarchical Design Enabling Highly Efficient and Stable Solar-Water Desalination with Good Salt Resistance, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30(52), 2007110 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Song, D. Qi, Y. Han, Y. Xu, H. Xu and S. You, et al., Volatile-organic-compound-intercepting solar distillation enabled by a photothermal/photocatalytic nanofibrous membrane with dual-scale pores, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2020, 54(14), 9025–9033 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Shi, Y. Shi, S. Zhuo, C. Zhang, Y. Aldrees and S. Aleid, et al., Multi-functional 3D honeycomb ceramic plate for clean water production by heterogeneous photo-Fenton reaction and solar-driven water evaporation, Nano Energy, 2019, 60, 222–230 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Tao, G. Ni, C. Song, W. Shang, J. Wu and J. Zhu, et al., Solar-driven interfacial evaporation, Nat. Energy, 2018, 3(12), 1031–1041 CrossRef.
- J. K. El-Demellawi, S. Lopatin, J. Yin, O. F. Mohammed and H. N. Alshareef, Tunable multipolar surface plasmons in 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene flakes, ACS Nano, 2018, 12(8), 8485–8493 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Chaudhuri, M. Alhabeb, Z. Wang, V. M. Shalaev, Y. Gogotsi and A. Boltasseva, Highly broadband absorber using plasmonic titanium carbide (MXene), ACS Photonics, 2018, 5(3), 1115–1122 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Kim, Z. Wang and H. N. Alshareef, MXetronics: Electronic and photonic applications of MXenes, Nano Energy, 2019, 60, 179–197 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Zhang, P. W. Wong and A. K. An, Photothermally enabled MXene hydrogel membrane with integrated solar-driven evaporation and photodegradation for efficient water purification, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 430, 133054 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Zhang, Q. Gu, C. Wang, Q. Gao, J. Guo and P. W. Wong, et al., Self-assembled hydrophobic/hydrophilic porphyrin-Ti3C2Tx MXene Janus membrane for dual-functional enabled photothermal desalination, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13(3), 3762–3770 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Mustakeem, J. K. El-Demellawi, M. Obaid, F. Ming, H. N. Alshareef and N. Ghaffour, MXene-coated membranes for autonomous solar-driven desalination, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14(4), 5265–5274 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Li, L. Wang, D. Sun, Y. Zhang, B. Liu and Q. Hu, et al., Synthesis and thermal stability of two-dimensional carbide MXene Ti3C2, Mater. Sci. Eng., B, 2015, 191, 33–40 CrossRef CAS.
- M. A. Unal, F. Bayrakdar, L. Fusco, O. Besbinar, C. E. Shuck and S. Yalcin, et al., 2D MXenes with antiviral and immunomodulatory properties: A pilot study against SARS-CoV-2, Nano Today, 2021, 38, 101136 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Jolly, M. P. Paranthaman and M. Naguib, Synthesis of Ti3C2Tz MXene from low-cost and environmentally friendly precursors, Mater. Today Adv., 2021, 10, 100139 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Barmann, L. Haneke, J. M. Wrogemann, M. Winter, O. Guillon and T. Placke, et al., Scalable synthesis of MAX phase precursors toward titanium-based MXenes for lithium-ion batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13(22), 26074–26083 CrossRef.
- G. Murali, J. K. Reddy Modigunta, Y. H. Park, J.-H. Lee, J. Rawal and S.-Y. Lee, et al., A review on MXene synthesis, stability, and photocatalytic applications, ACS Nano, 2022, 16(9), 13370–13429 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Dash, R. Vassen, O. Guillon and J. Gonzalez-Julian, Molten salt shielded synthesis of oxidation prone materials in air, Nat. Mater., 2019, 18(5), 465–470 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Li, T. Zhang, Y. Duan, Y. Wei, C. Dong and L. Ding, et al., Selective gas diffusion in two-dimensional MXene lamellar membranes: insights from molecular dynamics simulations, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6(25), 11734–11742 RSC.
- Z. Wang, F. He, J. Guo, S. Peng, X. Q. Cheng and Y. Zhang, et al., The stability of a graphene oxide (GO) nanofiltration (NF) membrane in an aqueous environment: progress and challenges, Mater. Adv., 2020, 1(4), 554–568 RSC.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |