Enhanced photothermal catalytic CO2 reduction by CeO2-based multicomponent catalysts
Jialiang
Chen
 abc,
Huilin
Wang
*abc,
Qing
Xie
abc,
Yizhu
Fang
abc,
Lu
Sun
abc,
Xiao
Wang
*abc,
Shuyan
Song
abc,
Huilin
Wang
*abc,
Qing
Xie
abc,
Yizhu
Fang
abc,
Lu
Sun
abc,
Xiao
Wang
*abc,
Shuyan
Song
 *abc and
Hongjie
Zhang
*abc and
Hongjie
Zhang
 abd
abd
aState Key Laboratory of Rare Earth Resource Utilization, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun 130022, China. E-mail: wanghl@ciac.ac.cn; wangxiao@ciac.ac.cn; songsy@ciac.ac.cn
bSchool of Applied Chemistry and Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
cChina-Belarus Belt and Road joint laboratory on Advanced Materials and Manufacturing, Changchun 130022, China
dDepartment of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
First published on 6th January 2025
Abstract
Photothermal catalysis is an effective strategy to achieve CO2 reduction under mild conditions. CeO2-based catalysts with strong CO2 adsorption capacity and unique electronic structures are promising candidates for this reaction. However, improving their photothermal catalytic efficiency remains a great challenge due to the wide bandgap and poor light absorption of CeO2. In this review, we summarize the previous representative literature from the perspective of photothermal synergistic catalysis and focus on the effect of multicomponent catalyst structure on CO2 conversion and product selectivity. Subsequently, we discuss the three main CO2 reduction mechanisms, including thermally assisted photocatalytic reduction, photo-driven thermal catalytic reduction and photothermal synergistic catalytic reduction. Finally, we present the challenges and future directions for CeO2-based multicomponent catalysts in photothermal catalytic CO2 reduction.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of industrial technology, carbon emissions are increasing, and all types of carbon waste are generated, which seriously pollute the environment and threaten our health.1,2 Carbon dioxide (CO2), as one of the discarded carbon resources, is the main contributor to the greenhouse effect. Fortunately, CO2 is also a high-quality carbon resource that can be converted into fuels or other high-value-added products via green methods, thus enabling the upgrading of carbon waste.3 This may bring potential additional economic benefits and reduce the extraction and direct use of fossil fuels,4 thus improving the global environment and achieving sustainable development.5 The search for efficient CO2 conversion technologies has become a hot research topic in recent years.6 On the one hand, the high energy consumption and low product selectivity of traditional thermal catalysis technology pose great challenges in the design of reactors and catalysts.7 On the other hand, although solar energy is a widespread renewable energy source, the narrow photoresponse range and low efficiency of photogenerated carrier separation in catalysts severely restrict the industrial applications of photocatalysis. Photothermal catalysis is a promising technology developed in recent years, which enables efficient conversion under mild conditions. The synergistic effect between photocatalysis and thermocatalysis can simultaneously solve the problems of high energy consumption and low efficiency, thus improving the practicality of photothermal catalysis technology. Currently, photothermal catalysis has been widely studied in the fields of petrochemistry, environmental protection, seawater desalination, energy storage and conversion.8–11 In accordance with the photothermal effect, three different photothermal mechanisms exist, plasma local heating, nonradiative relaxation in semiconductors, and thermal vibrations of molecules. However, the complex reaction process poses a great challenge for synthesis of efficient photothermal catalysts. In this case, precise design of the composition and control of the size and morphology of materials to modulate their absorptive capacity and enhance their photothermal catalytic ability are of great importance for research in this field.Cerium oxide (CeO2) is a typical rare earth oxide with the advantages of low price and no generated pollution, which is widely used in important chemical reactions such as three-way catalysis, selective oxidation/hydrogenation, and CO2 reduction.12 As a versatile thermal and photocatalyst, CeO2 has strong ability to store and release oxygen and is well-suited for redox reactions on its surface.13 Different from traditional thermal catalyst supports, the lattice oxygen in CeO2 can follow the Mars–van Krevelen mechanism to react with the reactants, thus realizing higher reactivity. In addition, the oxygen vacancies induced by the Ce4+/Ce3+ redox pair have a higher anchoring capacity to the loaded metal, thereby ensuring good long-term stability, which is exactly required for photothermal reactions.14 Compared to the typical TiO2 photocatalysts, nanostructured CeO2 also has unique optical properties (Fig. 1). Although the absorption band of a single material is limited, CeO2 can still achieve the synergistic effects of ultrawideband strong light absorption,15 efficient photothermal conversion, low-temperature reduction, and high lattice oxygen mobility through loading, doping, and preparation of composite materials.16 Meanwhile, chemical bonds often occur between the carrier and the catalytic center, further enhancing the absorption capacity of sunlight.17
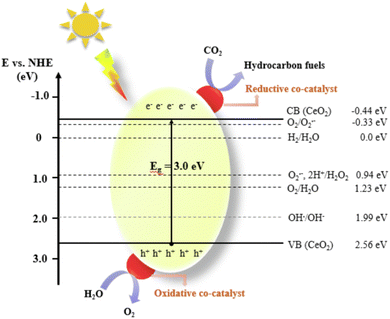 | ||
| Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the photocatalytic CO2 conversion process over a CeO2-based photocatalyst. Reproduced with permission from ref. 18. Copyright 2022, Elsevier B.V. | ||
CO2 reduction is a complex process, involving energy transfer, CO2 adsorption and activation, intermediate conversion and product desorption. This makes it a great challenge to design and synthesize efficient photothermal CO2 hydrogenation catalysts. Constructing multicomponent catalysts to meet the needs of multiple functions is a simple and efficient strategy. Single-component compounds usually have a specific absorption range and bandgap, leading to the poor utilization efficiency of light energy at ambient temperature, especially for CeO2-based catalysts.19 Thus, to achieve efficient catalytic effects, it is necessary to use multicomponent catalysts to achieve synergistic effects. Numerous experiments have shown that the carrier,18 co-catalyst,20 promoter,21 and other added components in the catalytic system, such as dopant,22 may directly and indirectly affect the catalytic effect.23 Multi-component catalysts regulated in the experimental design can significantly improve the catalytic reaction effect. Especially when a new catalyst is formed by adding a component, the reaction mechanism may undergo distinct changes, given that the structure of the catalyst surface can be optimized for the catalytic effect through design and regulation. According to the overall surface condition of the material, the components that have already participated in the reaction can often maintain their intrinsic properties if the structure is unchanged, which is also the reason for selecting stable and long-term usable components. Of course, the complex surface structure of catalysts also provides more possibilities for the preparation of various catalysts. By understanding the mechanism and improving the synthesis of materials, efficient catalysts can ultimately be prepared to achieve a forward cycle of hypothesis-testing-rethink to final optimization.
Although the components within the catalytic process are complex and varied, the fundamental goal is to improve the catalytic effect and enhance the cost-effectiveness of material use. Therefore, the microstructure of multicomponent compounds is often considered based on reliable principles, especially the electronic properties of the catalyst surface such as electronic band structure, surface active sites and electron hole separation. Specifically, the Mars–van Krevelen (MvK) mechanism is followed on the surface of metal oxygen-containing systems, including CeO2.24 Also known as the redox mechanism, the MvK mechanism is understood in reaction kinetic models as the migration and transformation of oxygen species on the catalyst surface. The “oxygen vacancy-type” MvK mechanism promotes the adsorption and activation of oxygen by synthesizing oxygen vacancies within metal oxide materials.25 Initially, the oxygen species on the surface of the catalyst interact with the reactants, and then the surface compounds react with oxygen-containing molecules in the gas phase to regenerate the active sites on the catalyst surface.26 The coupled high adsorption energies and adsorption rates can achieve high reaction rates, and vacancies can be regenerated through catalyst synthesis or post-treatment steps.
In this review, we introduce the fundamental principles of photothermal catalysis, including various mechanisms of photothermal conversion (i.e., plasma localized heating, thermal vibration in molecules and non-radiative relaxation of semiconductors). Then, we systematically review the recent progress in CeO2-based multicomponent catalysts for photothermal CO2 hydrogenation reactions. Depending on the different products (CO, CH4, CH3OH and C2+), we discuss in detail how the multiple compositions of materials alter the reaction paths and improve their catalytic properties. Finally, we prospect the opportunities and challenges that exist for rare-earth-based catalytic materials for the photothermal-catalyzed upgrading of carbon waste.
2. Principles of photothermal catalysis
For the catalytic reactions that utilize both light and heat energy simultaneously, the reaction mechanism on the surface of materials varies. The differentiated principle changes depending on the reaction conditions such as incident light intensity and proportion of light at different frequencies, the actual temperature of the catalytic surface, and the distribution of catalytic sites on the material surface.27 Based on the broadband light and potentially utilized thermal energy that interact with multicomponent materials, the photothermal effect can be understood as the utilization of light and thermal energy and the mutual conversion between light and heat. Alternatively, light energy can be utilized in catalytic reactions, radiated out, or ultimately converted into thermal energy, and thermal energy can be directly utilized by catalytic reactions.28 Under certain conditions, exciting the surface of materials can generate plasma, and photo-induced electrons can be transferred as energy carriers to adjacent catalytic active centers, which can be applied in surface chemical reactions for CO2 reduction. Ge et al.29 demonstrated that synthesized Ru/HxMoO3−yvia H-spillover exhibited plasmonic absorption in the visible-near-infrared region, achieving a CH4 yield of 20.8 mmol gcat−1 h−1 with 100% selectivity in CO2 methanation. Assembling two or more metal nanoparticles into a plasma-coupled structure can improve their broadband absorption range in the solar spectrum. In a recent study, Cai et al.30 combined the “nano-greenhouse effect” with plasma coupling, enhancing photothermal conversion by a greenhouse-like plasmonic superstructure of 4 nm cobalt nanoparticles. The optimized plasmonic catalyst exhibited a photothermal CO2 methanation performance with a rate of 2.3 mol gcat−1 h−1 and close to 100% CH4 selectivity. In addition, the interband or intraband electron transitions of nonplasmonic semiconductors can also exhibit photothermal effects by absorbing light energy.31 When semiconductor materials are excited by photons with sufficient energy, the energy of excited electrons can be transferred to the material lattice through nonradiative relaxation, resulting in a local temperature increase in the local lattice. Liu et al.32 prepared S-scheme heterostructures composed of NiOx subunits and α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles for solar-driven photothermal catalytic CO2 reduction. The apparent quantum yield of CO at 420 nm was 1.5%. This activity was attributed to the S scheme heterostructure, which promoted the interfacial charge transfer and provided spatially separated catalytic sites. Also, the photothermal effect of NiOx caused by nonradiative exciton recombination induced local heating of the catalyst, thereby enhancing the reaction kinetics. Commonly, carbon-based materials and some organic polymers can utilize light energy, and these materials have the ability to generate heat through lattice vibration. Loose electrons can easily be excited from the π orbitals to π* orbitals under low-energy irradiation.33 Then, the excited electrons relax to the ground state through vibration–electron coupling, and the excess energy is released in the form of heat. After the conversion of light energy into heat, the motion energy between molecules will be different. Molecular thermal vibration can achieve energy utilization through the exchange of heat energy.34 By utilizing the relaxation-converted heat energy or providing external heat, light energy can be indirectly utilized, ensuring the efficient progress of photothermal catalytic reactions.Given that photothermal catalysis occurs over a wide spectral and temperature range, catalysts must have the corresponding optical properties and thermal stability to obtain efficient catalytic performances. In photothermal catalytic reactions, CeO2 can effectively meet the multilevel requirements of catalyst design, whether as a carrier, promoter or catalytic active site. However, the broad forbidden band (about 3.2 eV) light absorption of CeO2 restricts the use of the weak ultraviolet (UV) band of visible light, resulting in insufficient light absorption and relatively low photothermal conversion efficiency in CeO2-based photothermal catalysts. In this case, by loading metal materials, doping, adding absorbing materials, and even fabricating fine composite materials, the absorption efficiency of catalysts in the UV-visible infrared spectrum can be improved and genuinely used in chemical reactions, such as accelerating reaction rates. Given the diverse structures of materials and the significant differences in actual catalytic effects, herein we categorize photothermal catalysis into photo-driven thermal catalysis, thermal-assisted photocatalytic, and photothermal synergistic catalysis based on their catalytic mechanisms. Finally, classification principles are combined to better understand specific reactions from a material structure perspective, providing direction for practical design and usage needs.
2.1 Photo-driven thermocatalysis
In photothermal catalysis, light is used as a heat source to bring the catalyst to the reaction temperature that drives thermal catalysis, which is called optically driven thermal reduction of carbon dioxide. Essentially, it is mainly driven by thermal catalysis, but solar energy can be used instead of high-energy external heating sources. The active sites on the surface of the catalyst will only reach the local temperature, and the temperature of the entire reaction system will not increase. Metal transforms into plasma after being excited by light.Consequently, plasma metals have broad application prospects in catalyzing various reactions due to their unique ability to combine light capture, photothermal conversion and hot carrier excitation in materials. The localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) effect is a special phenomenon observed in subwavelength-sized metal structures. Plasma nanostructures can break the diffraction limit of traditional optics, further confining incident light to the nanoscale, thereby enhancing the interaction between light and matter. When metal particles are hit by light, oscillations called surface plasmons can be excited from the metal surface. The energy of the “hot” electrons generated by collective oscillation is much greater than that under standard thermal equilibrium conditions. The ability to concentrate such a large amount of energy in a narrow space has led to the initial application of photocatalysis. However, due to the competition between electron molecule reaction processes and fast carrier relaxation processes, only a small portion of photoexcited hot electrons can usually be used in practice. Thus, to effectively extract hot carriers from metals, semiconductor systems can be constructed. As a stable semiconductor, CeO2 can be used as a carrier for metal nano ions. Semiconductors can extend the lifetime of hot electron–hole pairs. Furthermore, the good electrical contact facilitated by the relatively large contact area between the semiconductor and metal is beneficial for electron transfer.
Loading metals onto a carrier directly is a common and effective method for the preparation of catalytic materials. Palladium-based catalysts have attracted attention due to their peculiar activity for the low-temperature oxidation of CO and hydrocarbons. CeO2 has been widely studied as a catalyst due to its excellent oxygen storage capacity. Zou et al. developed a new strategy to appropriately regulate the LSPR of palladium nanoparticles in the visible light region.35 When Pd was combined with CeO2, the dispersion of the loaded metal Pd improved. Due to the interaction between Pd and Ce particles, a wide Pd–CeO2 active interface will be formed (Fig. 2(a) and (b)). The Pd–CeO2 active interface improves the oxygen release characteristics and storage of CeO2 and enhances the photocatalytic activity of the active sites for the oxidation reaction. Under near-infrared light irradiation, the visible light-excited hot electrons could be transferred from Pd to the conduction band of CeO2, promoting the activation of oxygen at the Pd–CeO2 interface. Compared with thermal catalysis, this catalyst exhibited significant photothermal catalytic activity for the oxidation of CO and toluene (Fig. 2(c)–(f)). Light-driven photothermal catalytic reactions can also be realized directly using solar energy. Borjigin et al. assembled Ag3PO4 and CeO2 to achieve excellent solar light-induced photothermal catalysis, reducing persistent volatile organic compounds.36 A series of Z-shaped Ag/Ag3PO4/CeO2 composites was assembled using in situ light-reduced Ag3PO4 particles, CeO2 spheres, and ultrafine Ag NPs. The photothermal catalytic activity of the prepared catalyst was evaluated under sunlight using benzene, a difficult-to-degrade aromatic conjugated molecule, as a model pollutant. A new synergistic photothermal catalytic mechanism (Fig. 2(g)) was proposed by exploring the solar light collection, carrier transfer and separation, and C6H6 adsorption and removal. Here, CeO2 participates in the structural formation of composite materials and is applied in practical environments under sunlight irradiation. Based on special material morphologies, such as nanorods, more excellent photothermal catalytic reaction systems can be achieved. According to Guo et al., CuCeO2−x nanorod catalysts were synthesized at room temperature via a facile co-precipitation method.37 Under UV-Vis-IR irradiation, the catalyst exhibited co-oxidation activity in the CO photothermal preferential oxidation reaction (CO-PROX). The introduction of CuOx enhanced the light absorption capacity of the CeO2 nanorods, greatly expanding their absorption range and producing catalysts with high photothermal conversion ability. The researchers concluded that Cu doping enhanced the synergistic effect of Cu–Ce and accelerated the oxidation reaction at low temperatures.
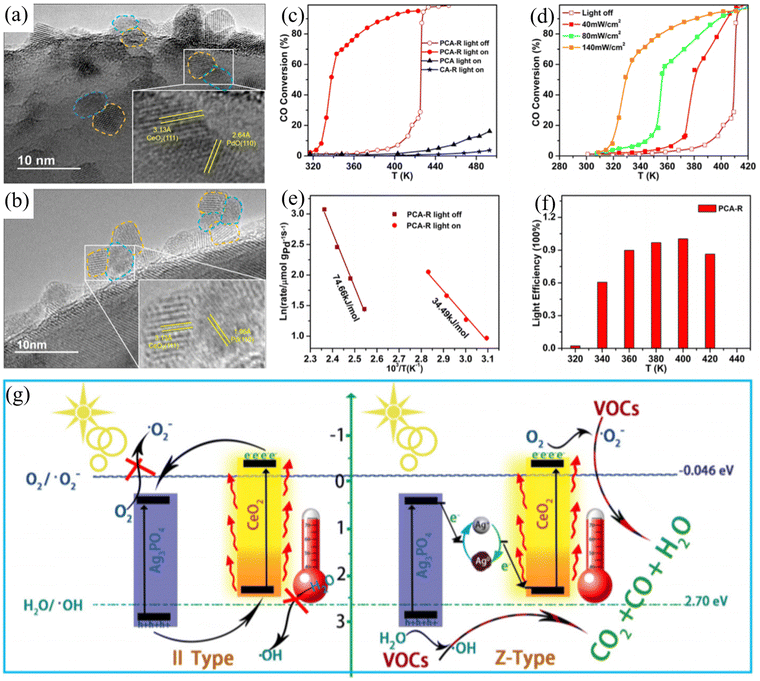 | ||
| Fig. 2 TEM images of (a) gray Pd–CeO2/Al2O3 (PCA) and (b) yellowish PdO–CeO2/Al2O3 (PCA-R). (c) Temperature dependence of CO conversion by catalysts and CO conversion by PCA-R under light irradiation of various intensities. (d) Arrhenius plots for PCA-R catalyst under visible light and dark conditions (e) and light efficiency (f). Reproduced with permission from ref. 35. Copyright 2016, the American Chemical Society. (g) Schematic of the synergistic effect between CeO2 and Ag3PO4 with Ag+–Ag0 pairs in the reaction. Reproduced with permission from ref. 36. Copyright 2020, Elsevier B.V. | ||
According to the design and application needs of multicomponent materials, optimizing the carrier by controlling different variables can facilitate the exploration of the role of CeO2. Li et al. reported the synthesis of CeO2/LaMnO3 nanomaterials that absorb infrared light and effectively degrade volatile organic compounds through the photothermal effect.38 The CeO2/LaMnO3 composite material exhibited a high stable catalytic performance under infrared radiation intensity, with a toluene conversion rate of 89% and a carbon dioxide yield of 87%. Its photothermal catalytic activity was enhanced due to the synergistic effect of strong light absorption, efficient photothermal conversion, good low-temperature reducibility, and accelerated lattice oxygen migration rate. This indicates that exploring infrared-driven LaMnO3-based composite materials in heterogeneous photothermal catalysis has broad prospects. Cheng et al. synthesized Bi/CuCeO2−x nanorod catalysts via co-precipitation hydrothermal and deposition precipitation methods to optimize the properties of CuCeO2−x nanorod catalysts. They employed dual doping to regulate the light absorption capacity and concentration of oxygen vacancies in the CuCeO2−x nanorod catalysts. Under sunlight, the CO conversion rate reached 90% and the surface temperature was 120 °C.39 The bismuth-doped CuCeO2−x nanorod catalyst exhibited strong absorption ability throughout the entire solar spectrum. The doped bismuth improved the light absorption and carrier separation ability of the CuCeO2−x nanorod catalyst in the UV visible wavelength range, further improving its performance, including photothermal conversion ability and photocatalytic activity. The nonradiative recombination of electron–hole pairs can also efficiently utilize light energy through new materials. By using techniques such as extrinsic polarization with a laser beam to investigate the changes in thermally activated ions in photorefractive crystals, it is possible to quantitatively analyze the changes in the internal structure of materials owing to the photothermal effect.40
Besides exciting LSPR in metal nanostructures, direct interband or intra-band electronic transitions in non-plasmonic semiconductors can also exhibit photothermal effects. When semiconductor materials are excited by photons with adequate energy, electron–hole pairs with energy equivalent to the bandgap are generated. The energy of hot electrons can be released and transferred to the material lattice or emit photons through non-radiative relaxation. When an electron–hole pair recombines without emitting photons, its energy can be transferred to a deeper hole in the valence band or a higher electron in the conduction band. The third energy carrier usually returns to the band edge through lattice vibration thermalization.41 Zhao et al. investigated the relationship between light-induced scattering and temperature in Ce, Fe, and LiNbO3 crystals. By considering the influence of heat in photorefractive crystals, it was shown that the activated ions neutralize the space charge field induced by light. Consequently, this neutralization leads to a reduction in scattering noise in the crystal. As an auxiliary agent, CeO2 can enhance the activity of CuO catalysts as a co-catalyst. Cu+ species and CuO typically have excellent light absorption abilities and narrow bandgap. The introduction of oxygen vacancies and surface defects around the copper active sites can create rich electron regions, and the bimetallic oxides can generate efficient redox cycles (Ce3+/Ce4+↔ O2− ↔ Cu2+/Cu+). The interaction between CeO2 and CuO metal oxides is pivotal for catalytic oxidation. Elimian et al. optimized the interaction between CeO2 and CuO, improving the electron–hole pair transfer, oxygen mobility, and catalytic performance.42 Through X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) characterization, it was determined that regulating the interaction between metal oxides by oxidation and reduction reactions results in the generation of surface defects. In addition, nanocomposites exhibit excellent photocatalytic activity. Liu et al. prepared a CeMnxOy/OMS-2 multicomponent compound by depositing different amounts of CeMnxOy on OMS-2 samples through a hydrothermal redox reaction. The formation of the multicomponent CeMnxOy/OMS-2 enhanced the photothermal catalytic activity of OMS-2 for oxidation reactions under UV-vis-IR illumination from an Xe lamp.43 The best nanocomposite materials exhibit photothermal catalytic activity and durability under UV-visible infrared irradiation. They also exhibit localized photothermal activity under visible and infrared illumination. This discovery is a novel photoactivation compared to photocatalysis on semiconductor photocatalysts and can promote solar-driven thermal catalytic activity. More elaborate work was reported by Wu et al.,44 where they prepared ambient sunlight-driven Cu0.15Mn0.15Ce0.7Ox hollow spheres. Compared with the bulk Cu0.15Mn0.15Ce0.7Ox–M, the surface area increased by 80.72% for Cu0.15Mn0.15Ce0.7Ox and it possessed more Mn4+ and oxygen vacancies, contributing to a better redox performance and more active oxygen species. Furthermore, the optimized catalyst exhibited good persistent stability. However, the utilization of light energy increased, and photo-driven thermal catalysis still largely relied on the effect of individual thermal reactions, with the light effect concentrated on the heat source, resulting in a low actual utilization rate of light energy. In the future, while further exploring bandgap materials that conform to incident light, the coupling mechanism under photo-driven sites, especially the migration of photo-generated electrons, should be investigated.
2.2 Thermal-assisted photocatalysis
In the process of thermal-assisted photocatalysis, photocatalysis plays the dominant role, which introduces thermal energy based, while thermal assistance contributes to the entire reaction process. Thermal-assisted photocatalysis can utilize heat dissipation or achieve the effect of accelerating the reaction without requiring a large amount of heat from an additional source. The infrared ray (IR) component of the spectrum has never been effectively utilized in traditional photocatalysis due to energy limitations. In addition, the temperature increase caused by infrared radiation is mainly repulsive, given that it typically leads to severe lattice vibrations, significantly reducing the efficiency of photon-to-electron conversion. Once infrared energy can be integrated into solar energy conversion, it will achieve a milestone in its utilization. In fact, without considering photoexcitation, the increase in temperature owing to infrared radiation (20–80 °C) is widespread and highly advantageous in thermal catalysis, which is widely regarded as mature technology. Therefore, infrared-induced catalysis would have broad prospects for practical solar energy conversion. Thus far, few reports have focused on this topic, and almost all attempts have involved the use of precious metals as co-catalysts. Furthermore, in this case, researchers are concerned about the promotion of temperature rise in chemical reactions, which can be easily understood using the empirical Arrhenius equations. However, temperature can negatively affect the solar energy conversion. In addition, the cost-effective integration of infrared-driven thermal catalysis into actual solar energy conversion is also a problem that needs to be solved. Jiang et al. designed a bismuth-driven synergistic Ce1−xBixO2−δ nanorods photo/thermal catalyst (Fig. 3(a) and (b)), in which the coupled ion conductivity of highly reducing Bi and accompanying oxygen vacancies facilitated the integration of photocatalysis, proposing a novel strategy (Fig. 3(c)) utilizing infrared energy in the design of catalysts.45 In the case of thermally assisted photocatalytic systems, the absorption of a single photocatalytic spectrum is insufficient, especially in the near-infrared region. With the help of the near-infrared absorption properties of materials such as reduced graphene oxide (rGO), the surface temperature can rapidly increase. Sun et al. synthesized a photothermal catalyst by coating MnOx and rGO on melamine sponge, which increased the absorption of near-infrared light, and the surface temperature under a xenon lamp decreased to 70 °C.46 According to the light absorption performance of monolithic materials, Li et al.47 developed a CeO2–rGO-NF monolithic photothermal catalyst with anchoring force. The possible catalytic mechanism was proposed based on the experimental results, which followed an enhanced MvK mechanism. The stacked 2D rGO sheets with broad infrared light absorption resulted in efficient photothermal conversion, which also increased the oxygen vacancies on the catalyst surface through the strong interfacial interaction between CeO2 and rGO. Jing et al. used oil bath heating to encapsulate organic supramolecular self-assembled perylene diimide (PDI) semiconductors on the surface of a three-dimensional metal oxide frame. The photothermal-assisted S scheme PDIs/C, N, S-CeO2 derived from Ce of MOF-808 was used for the photocatalytic removal of organic molecules.48 In this work, the formation pathway of the intermediates in the reaction was proposed, and the photocatalytic activity of the catalyst was attributed to its matched band structure and more significant visible light absorption performance and enhanced photothermal ability (Fig. 3(d) and (e)). It is worth noting that the classification and definition of photothermal catalysis and thermally assisted photocatalysis are not very clear, which is due to the complex physical and chemical structure of the surface of materials. Inorganic materials always have certain crystal structures, plasmonic metals, and structures with characteristic light absorption. Overall, for systems that are not determined by thermal reactions, in photothermal catalysis, photocatalytic reactions take the lead, while thermal catalytic reactions serve as an auxiliary to achieve efficient reactions and more efficient energy utilization. The morphology of catalysts plays an important role in CO2 hydrogenation reactions. When CeO2 acts as a carrier, the exposed crystal faces of CeO2 with different morphologies can affect the structure-sensitive catalytic reaction. Tavasol et al.49 directly adjusted the surface of the catalyst by selectively phosphating the surface of the CeO2 nanorod support, thereby improving the catalytic performance. Simultaneously, Kong et al.50 synthesized CeO2 nanopolyhedra and CeO2 nanorods under different hydrothermal synthesis conditions. Experiments showed that the interaction between Cu and CeO2 nanorods is stronger at the interface, with the better dispersion of CuOx species. The activity of CO2 hydrogenation on Cu/CeO2 nanorods is much higher than that on Cu/CeO2 nanopolyhedra. It can be seen that nanorods are useful microstructures in photothermal catalysis, and the oxygen vacancy content on different crystal faces of CeO2 also varies. Zhao et al.51 exploited an “MoO42−-inducing” method by changing the exposed surface of CeO2 nanorods, inducing and regulating their surface. This generated the more reducible Ce4+ and edge/corner defect-derived Ce3+, exhibiting stronger ability to capture O2 and oxygen vacancy content. In the design of thermal-assisted photocatalysts, the energy band regulation corresponding to the structure of the main material for photocatalytic active centers needs to be more refined to better utilize its photochemical properties. The external auxiliary thermal energy achieved through infrared light or other conditions can to some extent reduce the catalytic energy barrier and accelerate the reaction, thereby better utilizing energy. Therefore, for thermal-assisted photocatalysis, it is not only necessary to improve the photocatalyst in the preparation of materials, but also to consider the limit of external thermal energy. Specifically, the introduction of thermal energy has a relative impact on the reaction.52 Excessive thermal energy can lead to thermodynamic inhibition being greater than kinetic promotion, reducing the catalytic efficiency of the reaction.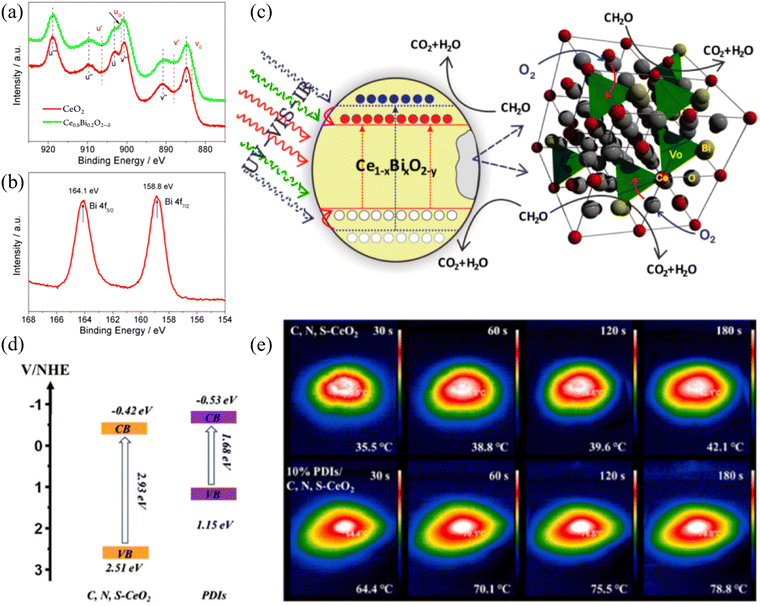 | ||
| Fig. 3 (a) Ce 3d XPS spectra of CeO2 and Ce0.8Bi0.2O2−δ. (b) Bi 4f XPS spectrum of Ce0.8Bi0.2O2−δ. (c) Proposed mechanism of Bi-induced integration of solar energy conversion. Reproduced with permission from ref. 45. Copyright 2013, the American Chemical Society. (d) Energy band diagram of C, N, S-CeO2 and PDI materials. (e) IR images of photothermal effect for C, N, S-CeO2 and 10% PDIs/C, N, S-CeO2. Reproduced with permission from ref. 48. Copyright 2024, Elsevier B.V. | ||
2.3 Photothermal synergistic catalysis
Photothermal synergistic catalysis means that both photoreaction and thermal reaction simultaneously occur at the catalytic site, and the electrons and reactive groups between photoreaction and thermal reaction couple and are promoted reciprocally, thereby achieving the in situ synergistic effect of photocatalysis and thermal catalysis in the same reaction time and space. Consequently, unlike photo-driven thermal catalysis and thermal-assisted photocatalysis, photothermal co-catalysis occurs simultaneously under the dual stimulation of light and heat. TiO2 is an excellent photocatalyst, but its application is hindered by some bottlenecks. At the same time, the rapid recombination of photogenerated electrons and holes results in a lower apparent quantum efficiency (AQE). Alternatively, it can only be activated by ultraviolet light, which explains its wide bandgap (3.0 eV for rutile and 3.2 eV for anatase), accounting for about 5% of sunlight. Furthermore, TiO2 is prone to deactivation owing to the deposition of by-products on its surface. As a high valence oxide, CeO2 is an n-type semiconductor with a narrower bandgap than TiO2, exhibiting more efficient photocatalytic activity under ultraviolet and visible light irradiation. Therefore, its catalytic effect can be improved by synergistically forming nanocomposites with TiO2. Zeng et al. developed a simple template-free method for synthesizing mesoporous CeO2.53 Compared with CeO2 nanoparticles without mesopores, mesoporous CeO2 exhibited significantly enhanced thermal catalytic activity. The TiO2/CeO2 nanocomposites formed by loading TiO2 nanoparticles onto mesoporous CeO2 exhibited effective catalytic activity under full solar spectrum irradiation. In addition, electrons can be transferred from transition metal oxides to the conduction band of CeO2, accelerating the process of reaction. Li et al. designed a novel photothermal catalyst, Au/VO2/CeO2, for the selective oxidation of aromatic alcohols to aromatic aldehydes.54 The optimized catalyst exhibited a selectivity of over 99% at atmospheric pressure. In the photocatalytic process, the adsorbed oxygen combines with the photo-generated electrons generated by CeO2, following the thermal cycling process of the MvK mechanism. Ce itself can serve as a catalytically active center. Kawada et al. utilized mesoporous SiO2 particles to support the catalytic active center, Ce–V, to investigate its catalytic capacity for SO3 decomposition.55 Compared with unloaded CeVO4, the prepared Ce–V/SiO2 catalyst had a more than 50-fold higher turnover frequency at 600 °C. This is consistent with the 13 nm CeVO4 particles dispersed in the pores of SiO2, while the size of the unsupported CeVO4 particles was approximately 600 nm. The previous section discussed the distribution of Ce4+, Ce3+, and oxygen vacancies in CeO2 at different crystal facets. Here, Ren et al. utilized the photothermal synergistic effect to induce bimetallic synergy for controlling the selectivity of CO2 reduction products on different CeO2 crystal planes (Fig. 4(h)).56 The solar-driven redox reaction was controlled by adjusting the spatial distance between the Pt and Au metal sites on different crystal planes of the CeO2 catalyst. Under concentrated solar radiation, the selectivity of the (100) plane towards CO was 100%, while the selectivity of the (111) plane and the (110) plane towards CH4 was 97.6% and 33.5%, respectively. Through the principle of the photothermal effect, atoms absorb light energy to excite electron hole pairs, while absorbing thermal energy to weaken the reaction energy barrier. Zhang et al. constructed a photothermal-coupled Ru1/Mg–CeO2-NR single-atom catalyst to investigate the electron transfer pathway.57 Under illumination, researchers found that the recombination rate of electron–hole pairs is affected by oxygen vacancies and Mg doping, leading to the migration of excited photoelectrons to the reaction site through the Ru–O–Ce structure, promoting the dry reforming of methane reaction.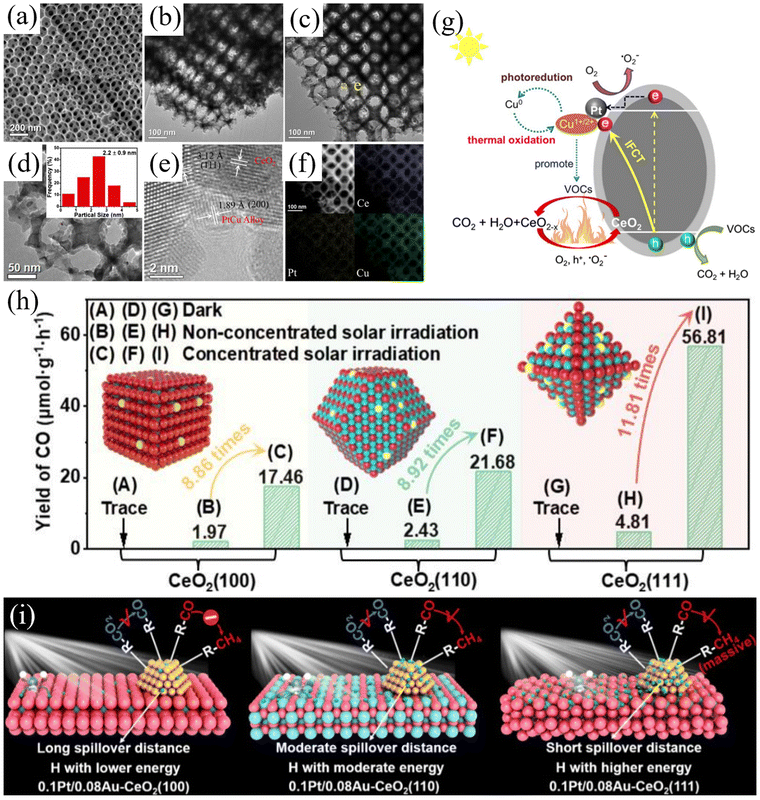 | ||
| Fig. 4 (a) and (b) SEM and TEM images of CeO2, respectively. (c)–(e) Particle size distributions and HR-TEM images of PtCu/CeO2. (f) HAADF images in STEM mode and corresponding EDX elemental mappings. (g) Mechanism of photothermal catalytic degradation of VOCs and stability over PtCu/CeO2. Reproduced with permission from ref. 58. Copyright 2019, Elsevier B.V. (h) Photothermal catalytic CO yields from CeO2(100), CeO2(110) and CeO2(111) under different conditions. (i) Schematic of the mechanisms of 0.1Pt/0.08Au–CeO2(100), 0.1Pt/0.08Au–CeO2(110) and 0.1Pt/0.08Au–CeO2(111) for CO2 reduction upon concentrated solar irradiation. Reproduced with permission from ref. 56. Copyright 2024, WlLEY-VCH. | ||
During photocatalytic oxidation, coke is always formed, while thermal catalysis promotes catalyst regeneration by the in situ elimination of coke. In the context of the known synergistic effect of photothermal catalysis over noble metal/semiconductor oxides, photothermal catalytic reactions may help improve coke resistance. Kong et al. developed a 2.2 nm PtCu/CeO2 catalyst with small PtCu alloy dispersed on CeO2 (Fig. 4(a)–(f)), which was applied to simulate the photothermal catalytic mineralization of pentane under solar radiation.58 PtCu/CeO2 exhibited light collection efficiency, charge separation, high ability to generate reactive oxygen species, and activity with stability towards the mineralization of n-pentane. The researchers attributed the synergistic mechanism (Fig. 4(g)) of the photothermal performance of PtCu/CeO2 to its metal low loading, leading to enhanced light collection, increased ability to generate reactive oxygen species, and dynamic formation of Cu1+, Cu2+, and Cu0, which resulted in a more stable photothermal performance. The photocatalytic enhancement of the thermal catalytic efficiency helps accelerate the MvK redox cycle and reduce the activation energy under simulated solar irradiation. The thermal catalysis-assisted photocatalytic efficiency can promote the oxidation of coke and reduce the negative impact of carbon deposition on photocatalysts. Infrared-induced solar heating is typically repulsive, given that it often causes severe lattice vibrations, which disrupt the conversion of photons to electrons. Jiang et al. proposed a feasible strategy to address this issue by integrating solid-state ions into photocatalysts to resolve the aforementioned contradictions related to infrared spectroscopy.59 In the optimized MnOx–CeO2 catalyst, the coupled electron and ion conduction helped to improve the negative temperature effects and integrate synergistic low-temperature catalysis into solar energy utilization. The material can also take into account the natural alternation between day and night, and under in situ light, the depleted material, after prolonged dark reactions, exhibited self-healing ability.
The introduction of various heteroatoms into CeO2 helps to promote its spectral response and oxygen mobility. These enhancements stem from complex factors, including band modulation, abundant vacancies, and more open crystal structures. Even if catalysts can be designed through repetitive micro-assembly structures, structured materials become complex after a series of treatments, such as calcination, resulting in the interaction of various components within the composite material. Deng et al. prepared a series of Ga–Cu/CeO2 catalysts using the MOF template method and carried out a photothermal CO2 reduction reaction on these catalysts.60 Due to the synergistic effect of the photothermal promotion by copper, higher activity was obtained. The optimized catalyst exhibited 100% CO selectivity under illumination. The mechanistic studies suggest that the reaction reduces the apparent activation energy, and the introduction of Ga promotes the generation of oxygen vacancies on the carrier surface, increasing the Cu and Ce, thereby enhancing the formation of CO2 intermediates on the catalyst surface, ultimately leading to the production of CO.
In summary, for photothermal synergistic catalytic processes, including sunlight, light can induce the generation of active sites by exciting electron–hole pairs, and photoactivation can thermodynamically reduce the energy barrier of the reaction. Meanwhile, heat can enhance the diffusion and adsorption ability of substances by accelerating molecular motion, promoting the interaction of various components on the material surface. However, due to the simultaneous action of heat and light, the understanding of the photothermal synergistic mechanism and synergistic sites in the photothermal effect of in situ coupling mechanism is not fully clear. Future research urgently needs to further reveal the reaction mechanism under the synergistic effect of light and heat.
3. CO2 hydrogenation reactions
In recent years, the extensive use of fossil fuels has led to a sharp rise in the atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, not only causing serious harm to the natural environment but also threatening human health. Thus, converting excess carbon dioxide into high value-added chemicals can not only mitigate the greenhouse effect, but also promote the sustainable use of natural resources. CO2 hydrogenation is one of the most promising CO2 conversion technologies, which can be carried out in three ways including thermal catalysis, photocatalysis and photothermal catalysis. Among them, thermal catalytic technologies are easier to scale up and industrialize and have desirable CO2 conversion efficiencies. However, due to the high stability and activation energy of carbon dioxide molecules, higher temperatures are required to overcome the energy barrier, which poses a great challenge to the stability of the catalyst. Photocatalysis relies on clean solar energy as energy input, and therefore environmentally friendly, but its limited light utilization efficiency and energy conversion efficiency severely constrain the practical application of this technique. Photothermal catalysis is efficient catalytic technology that integrates thermochemistry and photochemistry. Due to the synergistic effect of thermal and photocatalysis, the reaction conditions of photothermal-catalyzed CO2 hydrogenation are more moderate, more efficient, and more cost-effective than the former two technologies. In the photothermal redox process catalyzed by multicomponent materials, the actual structure and composition of the chemical reaction surface are complex. Selecting appropriate components and reaction conditions is crucial, and the CO2 reduction reaction requires the specific analysis of the target product, thus listing the standard potential as a reference (Table 1). It is not difficult to discover through the exploration of the principle of photothermal catalytic materials that can effectively utilize the full spectrum and infrared energy of solar energy that they are composed of many factors. With the exploration of micro and meso levels, nanoparticles have received great attention in materials science. Catalysts are typically composed of metal or metal oxide nanoparticles dispersed on a high surface area support. With a change in the size of nanoparticles, their surface structure and electronic characteristics may change, which will affect the catalytic performance of the catalyst. The unique electron and oxygen vacancy transfer ability of CeO2, together with its strong interaction with loaded metal nanoparticles make it a classical carrier for nanoparticles. CeO2 has a large specific surface area, which can improve the physical and chemical properties of the metal, such as size and dispersion, and then enhance the absorption of visible light. In addition, CeO2 has a wide range of acid–base properties, unique electron and oxygen vacancy transfer ability, and can produce strong interaction with its loaded metal. It is commonly used in photothermal CO2 hydrogenation reactions, which greatly improves the catalytic performance.| Reaction | E θ (V vs. NHE) pH = 7 |
|---|---|
| CO2 + e− → CO2− | −1.90 |
| CO2 + 2H+ + 2e− → HCOOH | −0.53 |
| CO2 + 2H+ + 2e− → CO + H2O | −0.51 |
| CO2 + 6H+ + 6e− → CH3OH + H2O | −0.38 |
| CO2 + 8H+ + 8e− → CH4 + 2H2O | −0.24 |
| 2CO2 + 12H+ + 12e− → C2H5OH + 3H2O | −0.32 |
| 2CO2 + 12H+ + 12e− → C2H4 + 4H2O | −0.33 |
| 2CO2 + 14H+ + 14e− → C2H6 + 4H2O | −0.27 |
3.1 CO2 hydrogenation to CH4 and CO
Among the various products produced from carbon dioxide hydrogenation reaction, CO and CH4 are two important industrial feedstocks. On the one hand, CO is the initial product during the whole hydrogenation reaction, and the syngas consisting of CO and H2 can be used to manufacture more valuable liquid fuels through Fischer–Tropsch synthesis (FTS). On the other hand, CH4 is regarded as an important energy carrier due to its high energy density and ease of storage and transport. CO and CH4 are mainly produced through the reserve water–gas shift reaction (RWGS) and the Sabatier reaction, respectively, according to the following chemical equations: Sabatier reaction (CO2 + 4H2 ↔ CH4 + 2H2O, ΔH0 = −165 kJ mol−1)62 and reserve water–gas shift reaction (CO2 + H2 ↔ CO + H2O, ΔH0 = 42.1 kJ mol−1).In the Sabatier reaction, the mechanism of CO2 methanation is complex and controversial due to the diversity of products and intermediates such as CH3OH, HCOOH, CO, and CH4. Currently, two main reaction pathways, namely, formate and CO pathways, have been extensively studied. As mentioned earlier, CeO2 has strong redox properties and significant oxygen storage capacity. When CO2 is oxidized, the oxygen atoms in the CeO2 lattice are removed, leading to the formation of oxygen vacancies. When CO2 is oxidized, the oxygen atoms in the CeO2 lattice are removed, resulting in the formation of oxygen vacancies. Finally, the oxygen atom in the reactant molecule again restores the oxygen vacancy to the initial state, thus completing the catalytic cycle. The size of the metal oxide will directly affect the reaction efficiency. Arenas et al. prepared a NiO–CeO2 mixed oxide catalyst composed of 6–7 nm nanoparticles and compared it with other NiO–CeO2 reference catalysts, including uncontrolled-size mixed oxides, reverse catalysts composed of three-dimensional ordered macroporous (3DOM) structures, and block-shaped NiO–CeO2 nanoparticles.63 The results showed that at 275 °C, the CO2 methanation rate was nearly 3 times higher than the corresponding reference catalyst prepared without controlling the size. In general, for the CO2 hydrogenation reaction in Sabatier reaction, a carrier is required to provide oxygen vacancies, and precious metals can serve as catalytic centers. Wang et al. prepared an Ru/CeO2 catalyst as a targeted sample to explore the active site-dependent reaction mechanism in depth.64 It was found that the two reaction mechanisms of CO2 methanation depend on the influence of different active sites (Ru surface or oxygen vacancies) on the rate-determining step. Zhang et al. reported that the photothermal catalytic CO2 methanation on an Ru/Mg–CeO2 monatomic catalyst resulted in a CH4 formation rate of 469 mmol gcat−1 h−1, which showed good catalytic stability under the photothermal condition of 400 °C (Fig. 5(a) and (b)).65 Although precious metals can exhibit strong spectral absorption in the ultraviolet visible light range, non-precious metals have unique light absorption bands and specific catalytic effects in actual photothermal catalytic reactions. Also, they can achieve a better photothermal effect. Ye et al. reported the preparation of a nanostructured Ni/CeO2 catalyst via a simple sol–gel method, achieving the CO2 conversion of 80.5% and CH4 selectivity as high as 95.8%.66 Nanocatalysts prepared by simple methods using inexpensive materials still have great potential in further reducing the cost of converting CO2 into useful and high-demand products. The wavelength and intensity of light have a significant effect on the photoabsorption ability of the catalyst. Ullah et al. found that irradiation of Co10/CeO2 with blue light (450–460 nm) during the reaction increased the catalyst activity by 116% at 300 °C, and the selectivity for CH4 was up to 94%. Researchers believe that photo-induced electrons on the surface of Co directly activate the adsorption reaction intermediates. Hot electrons may contribute to the generation of oxygen vacancies in CeO2 carriers. Le et al. investigated the CO2 methanation reaction on Ni catalysts loaded on different supports including Al2O3, SiO2, TiO2, CeO2, and ZrO2.67 Among them, Ni/CeO2 was determined to be the most active for CO2 methanation. These catalytic activities increased with an increase in the surface area of CeO2. By controlling variables, the optimal carrier can be well selected from a series of carriers. However, it is important to note that the support may interact with the catalytic center on the surface, which does not necessarily interfere with the reaction, and the support may also facilitate the reaction to proceed more efficiently by reacting with the nanoparticles. Jantarang et al. loaded nickel onto a cerium dioxide titanium dioxide mixed oxide (Ni/CexTiyO2) at different ratios to evaluate the role of the carrier in the Sabatier reaction.68 Researchers have found that as the content of CeO2 increases, Ni is more easily reduced, indicating that the CeO2 carrier activates Ni. Due to the reduction temperature of the Ni catalyst being below 200 °C, this means that the photothermal reaction is sufficient to activate the Ni/CexTiyO2 catalyst, thereby achieving the effect of utilizing light and heat energy.
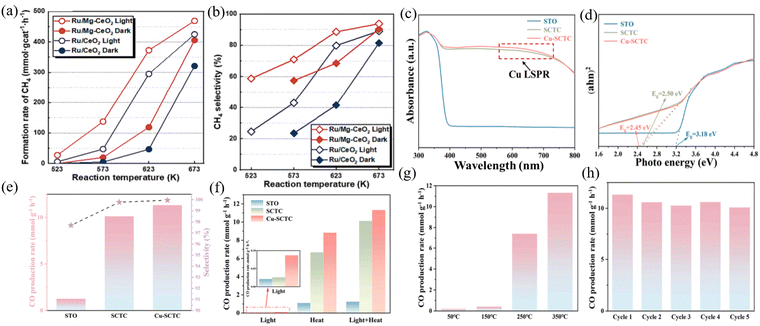 | ||
| Fig. 5 (a) Initial CH4 formation rate. (b) CH4 selectivity over Ru/CeO2 and Ru/Mg–CeO2 under thermal and photo-thermal conditions. Reproduced with permission from ref. 67. Copyright 2024, Elsevier B.V. (c) UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectra. (d) Tauc plots. (e) CO production rates and selectivity of SrTiO3 (STO), Cu2+-doped SrTiO3−δ/CeO2 (SCTC) and Cu-SCTC catalysts under full spectrum irradiation and photothermal conditions at 350 °C. (f) CO production rates of STO, SCTC and Cu-SCTC catalysts under dark, light and photothermal conditions. (g) CO production rates of STO, SCTC and Cu-SCTC catalysts under full spectrum irradiation and different temperatures. (h) Photothermal stability cycling experiments of Cu-SCTC catalysts. Reproduced with permission from ref. 69. Copyright 2024, Elsevier B.V. | ||
CO can be used as a reducing agent for smelting many metals, and therefore the efficient conversion of CO2 into CO will bring enormous economic and environmental benefits to future society. A catalyst with both high activity and antioxidant properties is crucial for industrializing photothermal RWGS. In the reaction between CO2 and H2, it is generally believed that at least two active sites are required, namely the dissociation of H2 on metal nanoparticles and the preferential occurrence of CO2 dissociation on oxygen vacancies in the carrier. Compared to the Sabatier reaction, the RWGS reaction generates CO, which requires the catalytic center and carrier to have more precise reduction ability for CO2. Kang et al. synthesized CeO2 nanosheets loaded with Bi single atoms using a soft template method, which exhibited stable RWGS reaction and antioxidant properties under air corrosion at 400 °C.70 The Bi single atom maintained a +3 valence state during the RWGS process, which has a lower energy barrier for RWGS, thus making RWGS highly active and antioxidant. Zhao et al.71 prepared a series of FeO–CeO2 nanocomposite catalysts for the photothermal reduction of CO2 to CO by varying the H2 reduction temperature in the range of 200 °C to 600 °C. The results showed that the FeCe-300 catalyst with an Fe![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ce molar ratio of 2
Ce molar ratio of 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 exhibited CO selectivity in the photothermal CO2 hydrogenation to CO, with a selectivity of 99.87%; CO productivity of 19.61 mmol gcat−1 h−1; and cycling stability for 50 h. In addition, based on existing excellent photothermal catalysts, different ratios of catalytic active components and the introduction of dopants or oxides can be adjusted to affect the catalytic effect of the system, thereby achieving synergistic effects in heterojunction structures. Dai et al. synthesized CuCe bimetallic catalysts with different proportions of components via the sol–gel method.72 Under visible photothermal catalytic conditions at 450 °C, the CO yield increased by about 20% compared to thermal catalysis. The characterization showed that the efficiency of electron hole separation was the highest when Cu/Ce = 1. The hot electrons generated by the LSPR effect of Cu can be effectively separated and transferred, resulting in more oxygen vacancies and suitable alkaline sites. Zhu et al. synthesized a three-phase Cu–CeO2–SrTiO3−δ heterojunction catalyst via the sol–gel method and rapid plasma exsolution method.73 Its activity was mainly attributed to the synergistic effect generated by the combination of Cu nanoparticles, CeO2, and SrTiO3−δ phases and their interfaces. The increase in oxygen vacancies in CeO2 enhanced the adsorption of CO2, and according to the LSPR effect, the doping and dissolution of Cu helped to broaden the range of light absorption (Fig. 5(c)–(h)). Jia et al. synthesized N-doped CeO2 (Ni/N–CeO2) composite catalysts using a three-step method. Under illumination, the CO yield was 20.9 mmol gcat−1 h−1, and through photothermal CO2 reduction, the CO selectivity was almost 100%. The doping of nitrogen promoted the formation of N–H bonds, facilitated the reduction of CO2 to CO, and inhibited the CO2 methanation process.
1 exhibited CO selectivity in the photothermal CO2 hydrogenation to CO, with a selectivity of 99.87%; CO productivity of 19.61 mmol gcat−1 h−1; and cycling stability for 50 h. In addition, based on existing excellent photothermal catalysts, different ratios of catalytic active components and the introduction of dopants or oxides can be adjusted to affect the catalytic effect of the system, thereby achieving synergistic effects in heterojunction structures. Dai et al. synthesized CuCe bimetallic catalysts with different proportions of components via the sol–gel method.72 Under visible photothermal catalytic conditions at 450 °C, the CO yield increased by about 20% compared to thermal catalysis. The characterization showed that the efficiency of electron hole separation was the highest when Cu/Ce = 1. The hot electrons generated by the LSPR effect of Cu can be effectively separated and transferred, resulting in more oxygen vacancies and suitable alkaline sites. Zhu et al. synthesized a three-phase Cu–CeO2–SrTiO3−δ heterojunction catalyst via the sol–gel method and rapid plasma exsolution method.73 Its activity was mainly attributed to the synergistic effect generated by the combination of Cu nanoparticles, CeO2, and SrTiO3−δ phases and their interfaces. The increase in oxygen vacancies in CeO2 enhanced the adsorption of CO2, and according to the LSPR effect, the doping and dissolution of Cu helped to broaden the range of light absorption (Fig. 5(c)–(h)). Jia et al. synthesized N-doped CeO2 (Ni/N–CeO2) composite catalysts using a three-step method. Under illumination, the CO yield was 20.9 mmol gcat−1 h−1, and through photothermal CO2 reduction, the CO selectivity was almost 100%. The doping of nitrogen promoted the formation of N–H bonds, facilitated the reduction of CO2 to CO, and inhibited the CO2 methanation process.
Based on this, researchers need to comprehensively consider the selection of metals, the particle size of metals, the preparation of carriers, the surface structure of carriers, the comprehensive effect of composite materials, the direction of electron migration, the synergistic effect of heterojunctions, and the actual results of composite materials. However, overall, there are many similarities between the RWGS reaction and the Sabatier reaction. For example, the non-chemical processes of diffusion, adsorption, and desorption are basically the same, and the mechanisms of initial activation of CO2 and chemical adsorption of H2 are universal. Therefore, many researchers apply the same type of material to both reactions simultaneously, which can also broaden the range of material applications. In use, CeO2 can also be expanded to rare earth elements as carriers or even catalytic centers to participate in catalytic reactions.69
3.2 CO2 hydrogenation to CH3OH
The conversion of CO2 to methanol is a renewable pathway. Generally, methanol is used as a solvent in industrial chemical reactions. Nowadays, the CO2 hydrogenation to CH3OH reaction can alleviate the pressure caused by CO2 on the environment, store carbon resources, and the reaction tends to proceed thermodynamically in a positive direction (CO2 + 3H2 ↔ CH3OH + H2O, ΔH298![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) K = −49.4 kJ mol−1). However, due to the thermodynamic stability of CO2, the activation energy of the reaction is very high. Raising the reaction temperature can promote the activation of CO2. Nevertheless, excessively high reaction temperatures can cause methanol to further react to produce CO. In this case, photothermal catalysis can effectively reduce the reaction temperature.74 In most photothermal catalytic reactions, thermal energy is the main driving force, and light plays a promoting role in the photothermal reaction. Catalytic reactions can be achieved at lower temperatures by converting light into heat energy. The synergistic effect of heat and light is more efficient than separate thermal catalysis and photocatalysis, thus exhibiting excellent catalytic activity in the CO2 hydrogenation to CH3OH reaction. Semiconductor catalysts can be used to separate the electron–hole pairs generated by absorbing photons to promote reactions. Some of the electrons can migrate to the adsorbed CO2 molecules, thereby promoting the corresponding reduction process. Therefore, most of the active sites for CO2 reduction to CH3OH are located on the surface of semiconductor materials and at the interface between metal nanoparticles and semiconductors.
K = −49.4 kJ mol−1). However, due to the thermodynamic stability of CO2, the activation energy of the reaction is very high. Raising the reaction temperature can promote the activation of CO2. Nevertheless, excessively high reaction temperatures can cause methanol to further react to produce CO. In this case, photothermal catalysis can effectively reduce the reaction temperature.74 In most photothermal catalytic reactions, thermal energy is the main driving force, and light plays a promoting role in the photothermal reaction. Catalytic reactions can be achieved at lower temperatures by converting light into heat energy. The synergistic effect of heat and light is more efficient than separate thermal catalysis and photocatalysis, thus exhibiting excellent catalytic activity in the CO2 hydrogenation to CH3OH reaction. Semiconductor catalysts can be used to separate the electron–hole pairs generated by absorbing photons to promote reactions. Some of the electrons can migrate to the adsorbed CO2 molecules, thereby promoting the corresponding reduction process. Therefore, most of the active sites for CO2 reduction to CH3OH are located on the surface of semiconductor materials and at the interface between metal nanoparticles and semiconductors.
Pd/CeO2 was one of the early catalysts employed for CO2 hydrogenation to produce CH3OH.75 CeO2 is suitable as a catalyst support for methanol production. Tsubaki et al. pointed out that the strong metal-support interaction is the main reason for the stable activity in the hydrogenation of carbon dioxide to CH3OH. After selecting Pd as having higher methanol selectivity compared to other metal materials, researchers prepared a series of Pd-based catalysts containing different supports (as shown in Fig. 6(a)).76 Jiang et al. investigated the effect of CeO2 crystal planes on CO2 hydrogenation to methanol over a Pd/CeO2 catalyst.77 DFT calculations indicated that Pd nanoparticles are stable species under realistic reaction conditions compared to a single Pd atom (Fig. 6(b)–(f)).
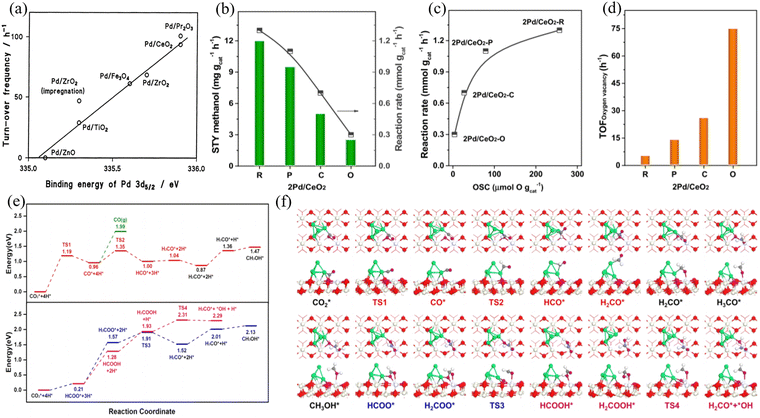 | ||
Fig. 6 (a) Relationship between the binding energy of Pd 3d5/2 and the activity to methanol decomposition at 473 K. Reproduced with permission from ref. 77. Copyright 2003, Springer. (b) Reaction rate and space-time yield (STY) of methanol over various Pd/CeO2 catalysts. (c) Reaction rate as a function of the number of surface oxygen vacancies (OSCs). (d) TOFoxygen![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) vacancy over various Pd/CeO2 catalysts. Reaction conditions: catalyst = 0.3 g; H2:CO2 = 3:1; GHSV = 2 L gcat−1 h−1; 3 MPa; 10 h; 240 °C. (e) and (f) Calculated energy profile and intermediate structures for methanol formation on Pd/CeO2 (110), respectively. Red, O atoms in CeO2; ivory, Ce atoms; green, Pd atoms; gray, C atoms; purple, O atoms in CO2; white, H atoms. Reproduced with permission from ref. 78. Copyright 2020, the American Chemical Society. vacancy over various Pd/CeO2 catalysts. Reaction conditions: catalyst = 0.3 g; H2:CO2 = 3:1; GHSV = 2 L gcat−1 h−1; 3 MPa; 10 h; 240 °C. (e) and (f) Calculated energy profile and intermediate structures for methanol formation on Pd/CeO2 (110), respectively. Red, O atoms in CeO2; ivory, Ce atoms; green, Pd atoms; gray, C atoms; purple, O atoms in CO2; white, H atoms. Reproduced with permission from ref. 78. Copyright 2020, the American Chemical Society. | ||
The wide bandgap of semiconductors can significantly utilize solar energy by forming heterojunctions. Mou et al. used a CdS@CeO2 heterojunction to catalyze the photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CH3OH and CO at room temperature, with maximum yields of 1534 μmol g−1 and 213 μmol g−1 for CH3OH and CO, respectively. The CdCe-100 photocatalyst was stable under the reaction conditions and maintained its activity during six cycles.78 Similarly, to increase the solar energy utilization efficiency, the ratio between semiconductors can be controlled. Chang et al. investigated the effect of the Zn/Ce ratio on CO2 hydrogenation to synthesize methanol over a Cu/ZnO–CeO2 catalyst.79 It was found that a 30% Ce content resulted in the better dispersion of the active component Cu, which led to a smaller Cu grain size and increased oxygen vacancies density. With an increase in CeO2 content, more alkaline sites and oxygen vacancies are formed, making it easier to activate CO2 and produce formate. In situ DRIFTS showed that formate is an active intermediate for CO2 hydrogenation to synthesize methanol. In addition to CeO2 as a high-valence oxide, WO3 has attracted attention due to its strong oxidation performance, nontoxicity, low cost and ordered mesoporous structure. Wang et al. reported that H2 and CO2 were captured by oxygen vacancies in WO3−x to generate fuel by photothermal hydrogenation.80 However, WO3 contains fewer oxygen vacancies. The number of oxygen vacancies of WO3 can generally be increased by doping various metals to increase the yield of methanol.81 The results proved that in the currently reported semiconductor composite materials that utilize the photothermal effect to catalyze CO2 hydrogenation to CH3OH, different interfaces can promote the rational design and development of multifunctional catalysts.82 The mechanism of photothermal interaction is similar to thermal catalysis, and thus a greater photothermal effect can be achieved by optimizing and upgrading the thermal catalytic system.
3.3 CO2 hydrogenation to C2+
CO2 hydrogenation to C2+ can be employed to prepare hydrocarbons, alcohols, and lipid compounds. Small-molecule hydrocarbons and alcohols are often considered vital chemical raw materials for synthesizing polymers, solvents, drugs, and fuels. The modulation of C2+ hydrocarbon production (e.g., ethane, propane, and higher alkanes) by CO2 photothermal hydrogenation is more favorable but more challenging. Alternatively, the preparation of C2+ products by CO hydrogenation can be obtained indirectly or directly. For products with multiple active sites, Xie et al. developed a well-defined nanostructured catalyst using a cascade catalytic strategy, CeO2–Pt@mSiO2–Co.83 CO2 was converted into C2–C4 hydrocarbons by two metal oxide interfaces. It was found that the production of C2–C4 hydrocarbons had a selectivity of 60%, which was speculated to be the result of the unique two-step cascade process allowed by this catalyst. To achieve one-step direct synthesis by photothermal catalysis, Tian et al. synthesized BaZr0.5Ce0.3Y0.2O3 (BZCY532) and reduced carbon dioxide under ultraviolet light irradiation to investigate its catalytic activity under photothermal catalysis.84 Using BZCY532 as a photocatalyst, the total yield of CH4, C2H6, and C3H8 was 39.1 μmol g−1, 8.6 μmol g−1, and 3.2 μmol g−1 over the course of more than 5 h runs, respectively. BZCY532 could successfully convert CO2 and H2O into CH4 and generate longer chain-hydrocarbons such as C2H6 and C3H8 (Fig. 7(f)). Tian et al. investigated the selectivity of light, temperature, and doping (Ni and Co) for C1, C2, and C3. Guo et al. prepared a bifunctional catalyst, Ni-BNCNTs@HMPs-NH2, using Lewis acid sites and nucleophiles for the synergistic catalysis of CO2 cycloaddition reactions.85 The conversion of CO2 to dimethyl carbonate (DMC) (CO2 + 2CH3OH ↔ DMC + H2O) is an attractive process. Including the RWGS reaction of the CO2 hydrogenation, formic acid/formate salts are considered important intermediates that will be involved in the catalytic surface reaction process, and their formation may even be the rate-determining step in the overall reaction.86 Among them, formic acid (HCOOH) is an important chemical raw material and intermediate product due to its non-toxicity, relatively simple preparation principle, numerous downstream products and safe processing in aqueous solutions. Also, considering its ability to provide high energy density, it also has great potential as an in situ hydrogen source for fuel cells.87 Wu et al. reported the use of an Rh-SAs/CeO2 catalyst for CO2 hydrogenation to HCOOH.88 Rh-SAs/CeO2 exhibited catalytic activity with a TON of 221 h−1 at 200 °C and HCOOH selectivity of 85%. The mechanism studies revealed that the Rh single atoms in Rh-SAs/CeO2 not only provided abundant active sites to promote the catalytic activity, but also suppressed the decomposition of HCOOH to CO and benefited the formation of HCOOH. Senanayake et al.89 studied the redox reaction of HCOOH on CeO2. Based on the relationship between temperature and surface species, it was found that formate is a more common intermediate for redox reactions on CeO2 surface compared to formic acid. Zeng et al.90 unraveled the role and mechanism of crystal facets in the photothermal catalytic oxidation of methanol. Wherein, the study of the reaction mechanism showed that the generation of formate is a key step in the conversion of formaldehyde. The key step on the (110) Co3O4 crystal plane is to convert formaldehyde into monodentate formate, while the conversion on the (111) and (112) crystal planes is mainly to form bidentate formate. In addition, the synthesis of similar structures, such carbonate compounds, can effectively utilize CO2 through photothermal catalysis. Chen et al.91 conducted a photothermal catalytic CO2 cycloaddition reaction under near-infrared conditions through the electrostatic adsorption of Ce-sub-structured polyoxometalate (POM) clusters on the surface of GO, with a photothermal catalytic reaction efficiency of 98.9%. Guan et al. synthesized a series of CeO2 nanoparticles derived from Ce-MOF (Fig. 7(a) and (e)).92 Researchers believe that the catalytic performance is influenced by the Lewis acid–base sites, light absorption capacity, and hydrophobic factors. Thus, the ratio between metal and ligand was adjusted to control the size of the CeO2 nanoparticles derived from Ce-MOF, thereby achieving effective CO2 activation in photothermal systems (Fig. 7(b)–(d)).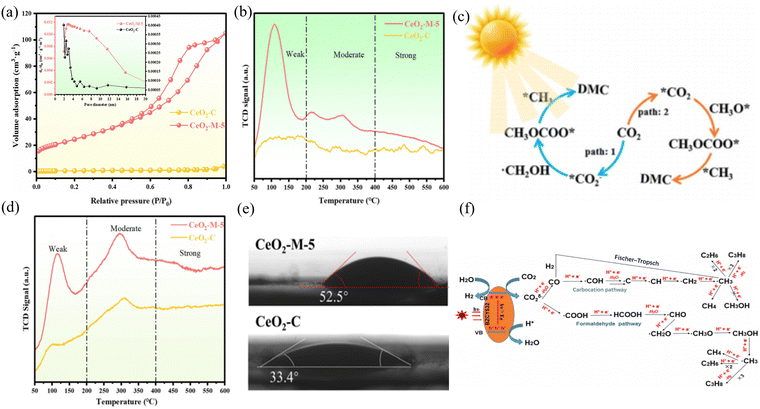 | ||
| Fig. 7 (a) N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms and pore size distribution. (b) CO2-TPD. (c) Proposed mechanism of DMC synthesis on CeO2-M-5 under photothermal synergistic system. (d) NH3-TPD and (e) water contact angles of CeO2-M-5 and CeO2-C samples. Reproduced with permission from ref. 92. Copyright 2023, WlLEY-VCH. (f) Mechanism of photocatalytic reduction CO2 into CH4, C2H6 and C3H8 by BZCY532. Reproduced with permission from ref. 85. Copyright 2020, Institute of Physics. | ||
Some researchers have achieved efficient selectivity for some C2+ products by studying 2D materials and attempting to understand their reaction mechanisms. Defective engineering of 2D materials results in high selectivity for preparing valuable hydrocarbon fuels and alcohols under mild reaction conditions. They are attractive for solar-driven processes on 2D-related composite materials under certain materials and specific conditions. Feng et al. used DFT calculations and investigated the formation configuration and activity of boron nitrogen cluster-doped graphdiyne (BN-doped GDY).93 The band structure and optical adsorption spectra revealed that BN-doped GDY exhibited semiconductor properties with a band gap of 0.902 eV and showed photothermal effect under visible and even infrared light irradiation. Chen et al. reduced CoFeAl layered double hydroxide nanosheets.94 DFT calculations confirmed the crucial role of the CoFe alloy structure in promoting the C–C coupling reaction during the CO2 hydrogenation process. Similarly, Zhao et al. prepared three different transition metal alloy nanoparticle catalysts derived from layered double hydroxide nanosheets to compare their actual catalytic performance.95 G-C3N4 is a typical polymer semiconductor with unique semiconductor properties and band absorption range. The CeO2/g-C3N4 Z-type heterojunction can form a matching band structure and has been widely reported for reducing carbon dioxide emissions, but the composite process is complex and requires high temperatures, resulting in poor selectivity for specific C2+ products. Zhou et al. introduced atomic transition metals such as Cu, Co, and Ce into the g-C3N4 matrix or CeO2 lattice to regulate the electronic structure.96 The prepared Cu@g-C3N4/CeO2-like Z-scheme heterojunction exhibited 100% CO selectivity.
It should be noted that the literature on the production of C2+ compounds by CO2 hydrogenation in CeO2-based photothermal catalytic systems is limited. However, there are more studies on synthesizing C2+ compounds by CO2 hydrogenation. Therefore, before exploring photothermal catalysis, we can refer to the processes and principles of CeO2-based catalysts used for photocatalysis, thermocatalysis, and electrocatalysis to get regular conclusions to guide our research on photothermal catalytic CO2 reduction. In the hydrogenation of CO2 to produce oxygen-containing C2+, H2O may be a good reducing agent candidate because it is abundant, nontoxic, effective, and can serve as a source of H+ to provide protons.97 Sharma et al. conducted thermodynamic analysis on the cracking cycle of H2O using CeO2 and evaluated the conversion efficiency of solar energy to fuel in this cycle.98 Lou et al.99 used CeO2-loaded Pd dimers to convert CO2 to ethanol, with a selectivity of 99.2%. These researchers found that the Pd dimer in Pd2/CeO2, which has a unique Pd2O4 conformation and a high degree of homogeneity, can directly bind CO obtained from the dissociation of CO2 firmly and initiate C–C coupling, as well as preventing CO desorption and facilitating the formation of precursors for ethanol by coupling between CO and CH3 intermediates. Kou et al. prepared CeO2–Cu composite catalysts to convert CO2 gas into value-added chemicals such as polyols electrochemically.100 The CeO2 Cu catalyst achieved a yield of C2+ alcohols of 32.9%. Ayodele et al. modelled the thermal catalytic CO2 oxidation coupling of CH4 and C2 hydrocarbons using a radial basis function artificial neural network.101 The analysis of each of the radial basis function artificial neural networks (ANNs) showed that the model performance in terms of the prediction of the C2 hydrocarbon selectivity and yield is strongly dependent on the number of hidden neurons. The radial basis function ANN configuration with 20 hidden artificial neurons displayed the best performance. In general, the significant differences in the selectivity of CO2 hydrogenation reaction products with CeO2 as the base material are determined by the composition of the catalyst, reaction conditions, and the actual catalytic performance (Table 2). In addition, CO2 can be used as a direct carbon source for the synthesis of C2+ hydrocarbons (such as olefins, alkanes, and alcohols) through 1–2 step dry reforming or by replacing CO in FTS with CO2, and further synthesizing other chemical industrial products with added value. Overall, we can use reasonable material structure design such as exploring the acidity and alkalinity of active sites102 and grafting rGO on composite materials103 and comprehensively achieve efficient CO2 hydrogenation to C2+ in many directions, such as photochemistry,104 thermochemistry,105 electrochemistry,106 and calculations in practical systems.
| Catalysis | Catalytic conditions | Products | Yield | Ref. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light intensity | Temp. | H2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CO2 CO2 |
Pressure | Space velocity | Conv. | Sel. | |||
| Ni/CeO2 | — | 250 °C | 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
1 bar | 40 L g−1 h−1 | CH4 | 80.5% | 95.8% | 64 |
| NiO–CeO2 | — | 275 °C | 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
1 atm | 200 ml min−1 | CH4 | 70% | 100% | 65 |
| Ru/CeO2 | — | 250 °C | 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
1 atm | 360 ml g−1 h−1 | CH4 | 1.1 μmol g−1 s−1 | 66 | |
| Ru/Mg–CeO2 | Xe lamp, 3 W cm−2 | 350 °C | 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
1 atm | 200 L g−1 h−1 | CH4 | 469 mmol g−1 h−1 | 67 | |
| Ni0.8Ce0.2Ox | — | 220 °C | 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
1 atm | 1000 ml min−1 g−1 | CH4 | 100% | 99% | 68 |
| Ni/CexTiyO2 | 300 W Xe lamp | 285 °C | 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
1 atm | 200 ml min−1 | CH4 | 93% | 100% | 70 |
| BiOx/CeO2 | 3 sun units | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
1 atm | 55 ml min−1 | CO | 31.0 mmol g−1 h−1 | 71 | ||
| FeO–CeO2 | 300 W Xe lamp | 400 °C | 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
0.18 MPa | 15 ml min−1 | CO | 19.6 mmol g−1 h−1 | 72 | |
| CuCe | 300 W Xe lamp | 450 °C | 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
1 atm | 15 ml min−1 | CO | 48% | 100% | 73 |
| Cu–CeO2/SrTiO3 | 300 W Xe lamp | 350 °C | Pure CO2 | 1 atm | 10 ml min−1 | CO | 11.3 mmol g−1 h−1 | 69 | |
| Cu@g-C3N4/CeO2 | Xe lamp, 1 W cm−2 | 6 °C | Pure CO2 | 1 atm | Liquid phase | CO | 33.8 μmol g−1 | 96 | |
| Pd/CeO2 | — | 500 °C | 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
30 bar | 10 g h−1 mol−1 | CH3OH | 12% | 79.2% | 76 |
| Pd/CeO2 | — | 240 °C | 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
3 MPa | 2 L g−1 h−1 | CH3OH | 1.2 mmol g−1 h−1 | 78 | |
| CdS@CeO2 | 300 W Xe lamp | 25 °C | Pure CO2 | 1 atm | Liquid phase | CH3OH | 1534 μmol g−1, | 79 | |
| CO | 213 μmol g−1 | ||||||||
| Cu/ZnO–CeO2 | — | 280 °C | 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
3 MPa | 12 L h−1 | CH3OH | 15.6% | 64.5% | 80 |
| CeO2–Pt@mSiO2–Co | — | 250 °C | 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
90 psi | 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 400 ml h−1 400 ml h−1 |
CH4 | 3% | 59% | 84 |
| C2–4 | 3% | 77% | |||||||
| BZCY532 | 300 W Xe lamp | 350 °C | Pure CO2 | 1 atm | 27 ml min−1 | CH4 | 39.1 μmol g−1 | 85 | |
| C2H6 | 8.6 μmol g−1 | ||||||||
| C3H8 | 3.2 μmol g−1 | ||||||||
| Pd2/CeO2 | — | 240 °C | 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
3 MPa | 3 L g−1 h−1 | C2H5OH | 45.6 gethanol gPd−1 h−1 | 99 | |
| Ce-MOF-derived CeO2 | 300 W Xe lamp | 140 °C | Pure CO2 | 1 MPa | Liquid phase | DMC | 2.5 mmol g−1 | 92 | |
| POMs@GO-PEI | 808 nm laser, 1 W cm−2 | 75 °C | Pure CO2 | 1 atm | Liquid phase | Carbonate | 96.8% | 99% | 61 |
4. Conclusions and outlooks
In summary, we presented the recent research progress on CeO2-based multicomponent catalysts for photothermal catalytic CO2 reduction. According to the different reaction mechanisms, the CO2 hydrogenation process can be divided into photo-driven thermocatalysis, thermal-assisted photocatalysis and photothermal synergistic catalysis. Under the joint action of light and heat, light can induce active sites and reduce the energy barrier of the reaction. At the same time, heat can enhance the adsorption and diffusion ability of CO2, accelerating the reaction. Photo-driven thermocatalysis can effectively reduce the reaction temperature compared to the photocatalytic reaction. Alternatively, thermal-assisted photocatalysis can further accelerate the rate of the original photocatalytic reaction through efficient utilization of thermal energy. For available multicomponent compounds, photothermal synergistic catalysis can simultaneously utilize both light and heat energy at the reaction site.In recent years, photothermal catalytic CO2 reduction, which combines the advantages of traditional thermal and solar energy, has emerged as one of the most promising strategies to meet the global sustainable demands.107 Materials such as high-entropy multicomponent,108 rare-earth-based MOFs,109 topological insulator heterostructure and MXenes are emerging. In addition to the universal principle of photothermal catalysis, the actual catalytic mechanism is not yet fully understood.110 Among them, rare earth catalysts are widely used due to their abundant possibilities of multiple elements,111 high catalytic activity,112 ability to achieve efficient catalytic reactions at lower temperatures, high selectivity and stability and environmental performance.113 Rare earth oxides such as La2O3, CeO2, and Y2O3 have been widely used in photothermal reaction research due to their unique electronic structure, efficient conductivity, stability, and excellent catalytic activity.114 CeO2, as an exceptional substrate for catalytic centers, can increase the specific surface area of the material, broaden the spectrum of the catalytic center, and synergistically catalyze electron transfer with other structures. Meanwhile, CeO2 of composite materials often act with other structures, resulting in a higher oxygen vacancy content and better participation in chemical reactions. Given the enhancing effect of CeO2, it can be applied in photothermal catalysis, including CO2 reduction, for semiconductor energy conversion, fuel production, and plastic degradation. In addition, through multicomponent coupling, CeO2-based materials can overcome a series of problems such as the insufficient absorption and utilization of solar light, low energy conversion efficiency, and poor catalytic stability, and have better performance than traditional TiO2-based materials.
However, the catalytic efficiency and product selectivity of photothermal catalytic CO2 reduction reactions are still far from satisfactory, and both challenges and opportunities exist in the catalyst design, as follows: (1) photothermal-catalyzed carbon dioxide hydrogenation is a complex reaction process. Conventional characterization techniques are no longer sufficient to investigate the catalytic mechanism adequately. It is necessary to develop advanced characterization techniques with higher resolution and combine multiple characterization strategies to further explore the “structure–performance” relationships of CeO2-based multicomponent catalysts. (2) Besides CeO2, other rare earth oxides with abundant 4f-orbital electrons also have good optical properties and show great potential in catalysis.115 Exploring the application of multiple rare earth elements in photothermal catalysis is crucial for the development of new catalysts.116–118 (3) In addition to carbon dioxide, plastics are a major source of carbon waste. Thus, the development of efficient conversion technologies to convert waste plastics into low carbon number liquid fuels is an important strategy for waste carbon upgrading. Inspired by many successful cases of photothermal CO2 hydrogenation catalyzed by CeO2-based multicomponent catalysts, the development of rare earth-based catalysts for the photothermal conversion of plastics may be the future direction of plastic degradation.119 (4) Considering the unique surface electronic properties of CeO2, utilizing the photothermal effect to achieve CO2 catalytic hydrogenation at a low temperature to produce formic acid, dimethyl ether and carbonate, is also a worthwhile research direction.120 We believe that there will be more research on rare earth-based catalysts in waste carbon upgrading. We hope that this review will provide references and insights for the future design of rare earth-based high-efficiency photothermal catalysts.
Data availability
No primary research results, software, or code have been included, and no new data were generated or analyzed as part of this review.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the financial aid from National Science and Technology Major Project of China (2020YFE0204500), National Natural Science Foundation of China (22020102003, 22025506, 22271274 and U23A20140), Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Plan Project (20230101035JC, 20230101022JC and 20240402056GH), Jilin Province Innovation and Entrepreneurship Talent Project (E31S6105) and Yunan Province Science and Technology Development Plan Project (202301BC070001-003). X. W. acknowledges funding from National Natural Science Foundation of China Outstanding Youth Science Foundation of China (Overseas).References
- J.-T. Liu, Y.-C. Zheng, X. Hou, X.-R. Feng, K. Jiang and M. Wang, Chem. Eng. J., 2024, 496, 154013 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Luo, X. Lin, E. Lichtfouse, H. Jiang and C. Wang, Environ. Chem. Lett., 2023, 21, 3127–3158 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Fan, M. Zhang, B. Bhandari and C.-H. Yang, Trends Food Sci. Technol., 2020, 95, 86–96 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Mujtaba, L. Fernandes Fraceto, M. Fazeli, S. Mukherjee, S. M. Savassa, G. Araujo de Medeiros, A. do Espírito Santo Pereira, S. D. Mancini, J. Lipponen and F. Vilaplana, J. Cleaner Prod., 2023, 402, 136815 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Lee, Y. Jing, Y. Wang and N. Yan, Nat. Rev. Chem., 2022, 6, 635–652 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. F. Bashir, M. Shahbaz, B. Ma and K. Alam, J. Environ. Manage., 2024, 351, 119709 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Dai, N. Zhou, Y. Lv, Y. Cheng, Y. Wang, Y. Liu, K. Cobb, P. Chen, H. Lei and R. Ruan, Prog. Energy Combust. Sci., 2022, 93, 101021 CrossRef.
- H. Jiang, X. Liu, D. Wang, Z. Qiao, D. Wang, F. Huang, H. Peng and C. Hu, J. Energy Chem., 2023, 79, 581–600 CrossRef CAS.
- J. D. Xiao and H. L. Jiang, Acc. Chem. Res., 2019, 52, 356–366 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Dai, G. Zhang, Y. Xiao, Y. Ding, Y. Li, X. She, X. Zhang and D. Zhao, Chem. Eng. J., 2024, 484, 149203 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Duan, Y. Hu, Y. Zhao, K. Tang, Z. Zhang, Z. Liu, Y. Wang, H. Guo, Y. Miao, H. Du, D. Yang, S. Li and J. Zhang, RSC Adv., 2023, 13, 14443–14460 RSC.
- A. Trovarelli, Catal. Rev., 1996, 38, 439–520 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Zhao, M. Tang, F. Wang and X. Qiu, Fuel, 2023, 331, 125748 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Xiao, S. Tan, D. Wang, J. Wu, T. Jia, Q. Liu, Y. Qi, X. Qi, P. He and M. Zhou, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 530, 147116 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Huang, Y. Lu, Y. Lin, Y. Mao, G. Ouyang, H. Liu, S. Zhang and Y. Tong, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6, 24740–24747 RSC.
- P. Dorenbos, J. Lumin., 2003, 104, 239–260 CrossRef CAS.
- D. P. H. Tran, M.-T. Pham, X.-T. Bui, Y.-F. Wang and S.-J. You, Sol. Energy, 2022, 240, 443–466 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Chen, X. Li, R. Zheng, R. Chen and X. Sun, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5, 13382–13391 RSC.
- M. Shi and X. Meng, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48, 34659–34676 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Singh and A. Chandra, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41, 1913–1920 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wu, X. Wang, L. Zhang, X. Wang, S. Song and H. Zhang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2024, 63, e202317594 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Cheng, X. Yue, J. Fan and Q. Xiang, Adv. Mater., 2022, 34, 2200929 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Murali, J. K. Reddy Modigunta, Y. H. Park, J. H. Lee, J. Rawal, S. Y. Lee, I. In and S. J. Park, ACS Nano, 2022, 16, 13370–13429 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Wang, X.-K. Gu, H. Yan, Y. Lin, J. Li, D. Liu, W.-X. Li and J. Lu, ACS Catal., 2016, 7, 887–891 CrossRef.
- S. Ding, Y. Zhang, F. Lou, M. Li, Q. Huang, K. Yang, B. Xia, C. Tang, J. Duan, M. Antonietti and S. Chen, Mater. Today Energy, 2023, 38, 101430 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Mars and D. W. van Krevelen, Chem. Eng. Sci., 1954, 3, 41–59 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Luo, X. Ren, H. Lin, H. Song and J. Ye, Chem. Sci., 2021, 12, 5701–5719 RSC.
- C. Chen, Y. Kuang and L. Hu, Joule, 2019, 3, 683–718 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Ge, Y. Kuwahara, K. Kusu, Z. Bian and H. Yamashita, Appl. Catal., B, 2022, 317, 121734 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Cai, C. Li, X. An, B. Zhong, Y. Zhou, K. Feng, S. Wang, C. Zhang, M. Xiao, Z. Wu, J. He, C. Wu, J. Shen, Z. Zhu, K. Feng, J. Zhong and L. He, Adv. Mater., 2024, 36, 2308859 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Sundararaman, P. Narang, A. S. Jermyn, W. A. Goddard, 3rd and H. A. Atwater, Nat. Commun., 2014, 5, 5788 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Liu, B. Kaihui, Y. Nie, X. Wang and L. Pei, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2024, 671, 160747 CrossRef CAS.
- R. N. Garner, L. E. Joyce and C. Turro, Inorg. Chem., 2011, 50, 4384–4391 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Tao, G. Ni, C. Song, W. Shang, J. Wu, J. Zhu, G. Chen and T. Deng, Nat. Energy, 2018, 3, 1031–1041 CrossRef.
- J. Zou, Z. Si, Y. Cao, R. Ran, X. Wu and D. Weng, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016, 120, 29116–29125 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Borjigin, L. Ding, H. Li and X. Wang, Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 402, 126070 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Guo, W. Ye, Z. A. Chen, A. Zhou, D. Jin and T. Ma, Appl. Catal., B, 2022, 310, 121334 CrossRef CAS.
- J.-J. Li, E.-Q. Yu, S.-C. Cai, X. Chen, J. Chen, H.-P. Jia and Y.-J. Xu, Appl. Catal., B, 2019, 240, 141–152 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Cheng, D. Huang, J. Zeng, M. Fan, D. Jin, T. Ma and X. Guo, Appl. Catal., A, 2024, 670, 119540 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Cui, Q. Ruan, X. Zhuo, X. Xia, J. Hu, R. Fu, Y. Li, J. Wang and H. Xu, Chem. Rev., 2023, 123, 6891–6952 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Zhao, H. Zhou, Z. Wu, F. T. S. Yu and D. K. McMillen, Opt. Eng., 1996, 35, 1985–1992 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Agbovhimen Elimian, M. Zhang, Q. Li, Y. Sun, J. He and H. Jia, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2024, 340, 126771 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Liu, Y. Li, Y. Yang, Z. Shi, Q. Zhang, S. Wu and X. Zhao, Catal. Today, 2019, 326, 46–53 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Wu, D. Yuan, H. Wang, C. Song, Q. Guan, W. Wang, Y. Li and J. Zhao, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2023, 13, 1173–1179 RSC.
- D. Jiang, W. Wang, E. Gao, L. Zhang and S. Sun, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117, 24242–24249 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Sun, H. Yu, T. Liu, Y. Li, Z. Wang, Y. Xiao and X. Dong, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2022, 33, 2564–2568 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Li, P. Sun, T. Liu, L. Cheng, R. Chen, X. Bi and X. Dong, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2023, 311, 123236 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Jing, Y. Xu, M. Xie, Y. Liu, X. Du and J. Hu, J. Alloys Compd., 2024, 979, 173568 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Tavasoli, A. Gouda, T. Zahringer, Y. F. Li, H. Quaid, C. J. Viasus Perez, R. Song, M. Sain and G. Ozin, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14, 1435 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Kong, Y. Shi, J. Wang, P. Lv, G. Yu and W. Su, Catal. Lett., 2022, 153, 477–492 CrossRef.
- J. Zhao, T. Wang, M. Qu, Z. Zhang, H. Li, C. Wang and Y. Li, J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2023, 11, 110427 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Sun, B. Zhao, F. Chen, C. Liu, S. Lu, Y. Yu and B. Zhang, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 408, 127280 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zeng, Y. Li, M. Mao, J. Bai, L. Ren and X. Zhao, ACS Catal., 2015, 5, 3278–3286 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Li, S. Zhang, S. Gui, G. Chen, Y. Wang, Z. Wang, X. Zheng, S. Meng, C. Ruan and S. Chen, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2023, 611, 155616 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Kawada, A. Ikematsu, T. Tajiri, S. Takeshima and M. Machida, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40, 10726–10733 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Li, Y. Ren, Y. Si, M. Du, C. You, C. Zhang, Y. H. Zhu, Z. Sun, K. Huang, M. Liu and L. Duan, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2024, 63, e202410474 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z.-Y. Zhang, Z.-X. Huang, X.-Y. Yu, L. Chen, H.-H. Ou, Z.-Y. Tang, T. Li, B.-Y. Xu, Y.-L. He and T. Xie, Nano Energy, 2024, 123, 109401 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Kong, G. Li, M. Wen, J. Chen, H. Liu and T. An, J. Catal., 2019, 370, 88–96 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Jiang, W. Wang, L. Zhang, R. Qiu, S. Sun and Y. Zheng, Appl. Catal., B, 2015, 165, 399–407 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Deng, H. Song, K. Peng, Q. Li and J. Ye, Appl. Catal., B, 2021, 298, 120519 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Li, B. Peng and T. Peng, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 7485–7527 CrossRef CAS.
- M. González-Castaño, B. Dorneanu and H. Arellano-García, React. Chem. Eng., 2021, 6, 954–976 RSC.
- A. Cárdenas-Arenas, H. S. Cortés, E. Bailón-García, A. Davó-Quiñonero, D. Lozano-Castelló and A. Bueno-López, Fuel Process. Technol., 2021, 212, 106637 Search PubMed.
- F. Wang, S. He, H. Chen, B. Wang, L. Zheng, M. Wei, D. G. Evans and X. Duan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 6298–6305 Search PubMed.
- Z.-Y. Zhang, T. Li, X.-L. Sun, D.-C. Luo, J.-L. Yao, G.-D. Yang and T. Xie, J. Catal., 2024, 430, 115303 CrossRef CAS.
- R.-P. Ye, Q. Li, W. Gong, T. Wang, J. J. Razink, L. Lin, Y.-Y. Qin, Z. Zhou, H. Adidharma, J. Tang, A. G. Russell, M. Fan and Y.-G. Yao, Appl. Catal., B, 2020, 268, 118474 Search PubMed.
- T. A. Le, M. S. Kim, S. H. Lee, T. W. Kim and E. D. Park, Catal. Today, 2017, 293–294, 89–96 Search PubMed.
- S. Jantarang, E. C. Lovell, T. H. Tan, J. Scott and R. Amal, Prog. Nat. Sci., 2018, 28, 168–177 CrossRef CAS.
- M. N. Ha, G. Lu, Z. Liu, L. Wang and Z. Zhao, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4, 13155–13165 RSC.
- X. Kang, D. Yuan, Z. Yi, C. Yu, X. Yuan, B. Liang, X. San, L. Gao, S. Wang and Y. Li, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2022, 12, 5559–5564 RSC.
- J. Zhao, Q. Yang, R. Shi, G. I. N. Waterhouse, X. Zhang, L.-Z. Wu, C.-H. Tung and T. Zhang, NPG Asia Mater., 2020, 12, 5 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Dai, A. Zhang, R. Wang, X. Xiao, X. Li and C. Zhou, Appl. Catal., A, 2024, 686, 119927 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Zhu, J. Zhou, Q. Li, Z. Liu, Q. Deng, Z. Zhou, C. Li, L. Fu, J. Zhou, H. Li, Q. Zhang and K. Wu, J. CO2 Util., 2024, 80, 102665 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Wang, C. Hao, Q. Zhang, Q. Meng and H. Liu, Appl. Catal., A, 2022, 643, 118738 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Tsubaki and K. Fujimoto, Top. Catal., 2003, 22, 325–335 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Matsumura and W. Shen, Top. Catal., 2003, 22, 271–275 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Jiang, S. Wang, B. Liu, J. Liu, L. Wang, Y. Xiao, Y. Xu and X. Liu, ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 11493–11509 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Mou, Z. Guo, Y. Chai, B. Liu and C. Liu, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B, 2021, 219, 112205 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Chang, W. Na, J. Zhang, L. Lin and W. Gao, New J. Chem., 2021, 45, 22814–22823 RSC.
- L. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Cheng, Z. Liu, Q. Guo, M. N. Ha and Z. Zhao, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4, 5314–5322 RSC.
- Y. Yan, R. J. Wong, Z. Ma, F. Donat, S. Xi, S. Saqline, Q. Fan, Y. Du, A. Borgna, Q. He, C. R. Müller, W. Chen, A. A. Lapkin and W. Liu, Appl. Catal., B, 2022, 306, 121098 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Wang, D. W. K. Tongo, L. Song and Z. Qu, Top. Catal., 2021, 64, 446–455 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Xie, C. Chen, Y. Yu, J. Su, Y. Li, G. A. Somorjai and P. Yang, Nano Lett., 2017, 17, 3798–3802 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Tian, Y. Ren, L. Liu, Q. Guo, N. Sha and Z. Zhao, Mater. Res. Express, 2020, 7, 085504 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Guo, W. Chen, L. Feng, Y. Fan, J. Liang, X. Wang and X. Zhang, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022, 10, 12418–12428 RSC.
- M. S. Spencer, Catal. Lett., 1995, 32, 9–13 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Tedsree, T. Li, S. Jones, C. W. Chan, K. M. Yu, P. A. Bagot, E. A. Marquis, G. D. Smith and S. C. Tsang, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2011, 6, 302–307 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Fan, J. Zhang, K. Ma, Y. Zhang, Y.-M. Hu, L. Kong, A.-P. Jia, Z. Zhang, W. Huang and J.-Q. Lu, J. Catal., 2021, 397, 116–127 CrossRef CAS.
- S. D. Senanayake and D. R. Mullins, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 9744–9752 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Wang, R. Pang, Z. Pan, Y. Zhu, C. Li, B. Liu and J. Shen, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022, 10, 22694–22700 RSC.
- X. Chen, M. Wei, A. Yang, F. Jiang, B. Li, O. A. Kholdeeva and L. Wu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14, 5194–5202 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Guan, X. Zhang, C. Zhang, R. Li, J. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Wang, C. Fan and Z. Li, Sol. RRL, 2023, 7, 2300493 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Feng, Y. Tang, W. Chen, Y. Li, R. Li, Y. Ma and X. Dai, Nanotechnology, 2020, 31, 495401 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Chen, R. Gao, Y. Zhao, Z. Li, G. I. N. Waterhouse, R. Shi, J. Zhao, M. Zhang, L. Shang, G. Sheng, X. Zhang, X. Wen, L. Z. Wu, C. H. Tung and T. Zhang, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1704663 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Zhao, R. Shi, G. I. N. Waterhouse and T. Zhang, Nano Energy, 2022, 102, 107650 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhou, J. Cai, Y. Sun, S. Jia, Z. Liu, X. Tang, B. Hu, Y. Zhang, Y. Yan and Z. Zhu, Catalysts, 2024, 14, 546 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Tian, R. Han, Q. Guo, Z. Zhao and N. Sha, Catalysts, 2022, 12, 612 CrossRef CAS.
- J. P. Sharma, R. Kumar, M. H. Ahmadi, J. Najser, V. Blazek, L. Prokop, Z. Assel Akanovna and Y. Sarsenbayev, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 53, 1259–1268 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Lou, F. jiang, W. Zhu, L. Wang, T. Yao, S. Wang, B. Yang, B. Yang, Y. Zhu and X. Liu, Appl. Catal., B, 2021, 291, 120122 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Kou, S. Wang, S. Yang, Q. Ren, R. Ball, D. Rao, S. Chiovoloni, J. Q. Lu, Z. Zhang, E. B. Duoss and Y. Li, ACS Mater. Lett., 2022, 4, 1999–2008 CrossRef CAS.
- B. V. Ayodele, S. I. Mustapa, T. Witoon, R. Kanthasamy, M. Zwawi and C. N. Owabor, Top. Catal., 2020, 64, 328–337 CrossRef.
- Istadi and N. A. S. Amin, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2006, 259, 61–66 CrossRef CAS.
- H. R. Park, A. U. Pawar, U. Pal, T. Zhang and Y. S. Kang, Nano Energy, 2021, 79, 105438 CrossRef.
- T. Wang, L. Chen, C. Chen, M. Huang, Y. Huang, S. Liu and B. Li, ACS Nano, 2022, 16, 2306–2318 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. He, B. Yang and G. Cheng, Catal. Today, 2004, 98, 595–600 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Wang, H. Chen, W. Lin, W. Zhou, X. Lv, J. Wang and J. Fu, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2022, 61, 16445–16452 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Sun, X. Yuan, B. Liu, S. Ma and C. Qiao, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024, 12, 2859–2867 RSC.
- C. Oses, C. Toher and S. Curtarolo, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2020, 5, 295–309 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Mahata, S. K. Mondal, D. K. Singha and P. Majee, Dalton Trans., 2017, 46, 301–328 RSC.
- Z. Wu, C. Li, Z. Li, K. Feng, M. Cai, D. Zhang, S. Wang, M. Chu, C. Zhang, J. Shen, Z. Huang, Y. Xiao, G. A. Ozin, X. Zhang and L. He, ACS Nano, 2021, 15, 5696–5705 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. M. van der Ende, L. Aarts and A. Meijerink, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009, 11, 11081–11095 RSC.
- C. Li, P. Wang, M. He, X. Yuan, Z. Fang and Z. Li, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2023, 489, 215204 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Huang, P. Li, X. Li, J. Gu, N. Fu and W. Zhang, Sol. RRL, 2023, 7, 2300518 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Man, Y. Chang and J. Jia, Mol. Catal., 2024, 565, 114389 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Balaram, Geosci. Front., 2019, 10, 1285–1303 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Dong, S. Xu, J. Sun, S. Bi, D. Li, X. Bai, Y. Wang, L. Wang and H. Song, J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21, 6193 RSC.
- R. Zhang, X. Wang, K. Wang, H. Wang, L. Liu, X. Wu, B. Geng, X. Chu, S. Song and H. Zhang, Adv. Energy Mater., 2023, 13, 2203806 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Chen, X. Duan, H. Fang, X. Liang and Y. Yuan, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2018, 8, 1062–1069 RSC.
- C. Lv, X. Bai, S. Ning, C. Song, Q. Guan, B. Liu, Y. Li and J. Ye, ACS Nano, 2023, 17, 1725–1738 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Xie, Q. Guo, S. Yu, H. Feng and Y. Xu, Carbon, 2024, 228, 119322 CrossRef CAS.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |








