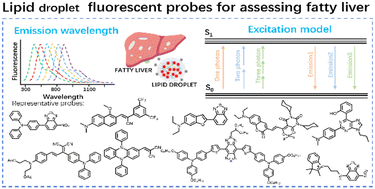
Fatty liver, a major health problem worldwide, is closely associated with aberrant accumulation and alteration of energy storage organelles, lipid droplets (LDs), in the disease process. Fluorescent probes with excellent optical performance, high sensitivity/selectivity and real-time monitoring have emerged as an attractive tool for the detection of LDs used in the diagnosis of fatty liver. In this review, we summarize various probes based on different response mechanisms to image LDs in the fatty liver process using different excitation imaging modes and emission wavelengths, including the visible to the near-infrared, two/three-photon, and the second near-infrared region. The perspectives and barriers associated with the reported lipid droplet (LD) probes for future development are also discussed.