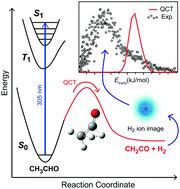
The first experimental observation of the primary photochemical channel of acetaldehyde leading to the formation of ketene (CH2CO) and hydrogen (H2) molecular products is reported. Acetaldehyde (CH3CHO) was photolysed in a molecular beam at 305.6 nm and the resulting H2 product characterized using velocity-map ion (VMI) imaging. Resonance-enhanced multiphoton ionization (REMPI), via two-photon excitation to the double-well EF 1Σ+g state, was used to state-selectively ionize the H2 and determine angular momentum distributions for H2 (ν = 0) and H2 (ν = 1). Velocity-map ion images were obtained for H2 (ν = 0 and 1, J = 5), allowing the total translational energy release of the photodissociation process to be determined. Following photolysis of CH3CHO in a gas cell, the CH2CO co-fragment was identified, using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, by its characteristic infrared absorption at 2150 cm−1. The measured quantum yield of the CH2CO + H2 product channel at 305.0 nm is ϕ = 0.0075 ± 0.0025 for both 15 Torr of neat CH3CHO and a mixture with 745 Torr of N2. Although small, this result has implications for the atmospheric photochemistry of carbonyls and this reaction represents a new tropospheric source of H2. Quasi-classical trajectory (QCT) simulations on a zero-point energy corrected reaction-path potential are also performed. The experimental REMPI and VMI image distributions are not consistent with the QCT simulations, indicating a non reaction-path mechanism should be considered.