B. S. Mhatre, S. Dutta, A. Reinicker, B. Karagoz and A. J. Gellman
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 14125-14128
DOI:
10.1039/C6CC06887A,
Communication
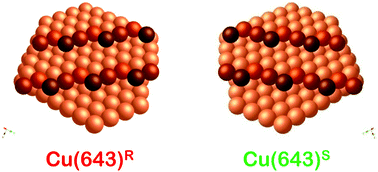
Aspartic acid adsorbed on Cu surfaces is doubly deprotonated. On chiral Cu(643)R&S its enantiomers undergo enantiospecific decomposition via an autocatalytic explosion. Once initiated, the decomposition mechanism proceeds via sequential cleavage of the C3–C4 and C1–C2 bonds each yielding CO2, followed by conversion of the remaining species into N![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CCH3.
CCH3.