Supramolecular fluorescence sensing of L-proline and L-pipecolic acid†
Andrés Felipe
Sierra
 ab,
Gemma
Aragay
ab,
Gemma
Aragay
 a,
Guillem
Peñuelas-Haro
a,
Guillem
Peñuelas-Haro
 a and
Pablo
Ballester
a and
Pablo
Ballester
 *ac
*ac
aInstitute of Chemical Research of Catalonia (ICIQ), The Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology (BIST), Avgda. Països Catalans 16, 43007 Tarragona, Spain. E-mail: pballester@iciq.es
bUniversitat Rovira i Virgili (URV), Departament de Química Analítica i Química Orgànica, c/Marcel·lí Domingo, 1, 43007 Tarragona, Spain.
cICREA, Passeig Lluís Companys 23, 08018 Barcelona, Spain
First published on 8th April 2021
Abstract
The current library of synthetic molecular sensors for small polar molecules is limited. In this work, we describe the synthesis of two diastereomeric mono-phosphonate calix[4]pyrrole cavitands, 1in and 1out, acting as fluorescent sensors for amino acids. The two isomeric cavitands differ in the relative orientation, in (1in) and out (1out), of their P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bridging group and the N-phenyl-naphthalamine fluorophore directly attached to it, with respect to their polar aromatic cavities. Using 1H and 31P NMR spectroscopy and non-fluorescent cavitand analogues (5in and 5out), we demonstrate the formation of 1
O bridging group and the N-phenyl-naphthalamine fluorophore directly attached to it, with respect to their polar aromatic cavities. Using 1H and 31P NMR spectroscopy and non-fluorescent cavitand analogues (5in and 5out), we demonstrate the formation of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complexes with L-proline (L-Pro) and the relevance of the inwardly directed P
1 complexes with L-proline (L-Pro) and the relevance of the inwardly directed P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group in the binding of the amino acid. Only the L-Pro⊂5in complex establishes a charged hydrogen bonding interaction between the receptor P
O group in the binding of the amino acid. Only the L-Pro⊂5in complex establishes a charged hydrogen bonding interaction between the receptor P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group and the protonated amine of the bound zwitterionic amino acid. This interaction is responsible for an increase in the thermodynamic stability of the complex compared to the L-Pro⊂5out counterpart. We investigate the binding properties of the fluorescent cavitands, 1in and 1out, with L-Pro and L-pipecolic acid (L-Pip) at micromolar concentration using emission spectroscopy (direct binding-based sensing, BBS). The observed emission changes in the BBS experiments were small but evidenced the role of the cavitands as fluorescent sensors. In agreement with the millimolar concentration results (1H NMR experiments), the fluorescent 1in sensor displays a larger binding affinity for L-Pro than the 1out isomer. Conversely, the 1out isomer experienced larger emission changes upon amino acid binding. We developed FRET-based indicator displacement assays (IDA) owing to the small emission changes observed in the direct BBS experiments. At micromolar concentration, the competitive displacement of the quencher N-oxide 6 from the cavity of the 1
O group and the protonated amine of the bound zwitterionic amino acid. This interaction is responsible for an increase in the thermodynamic stability of the complex compared to the L-Pro⊂5out counterpart. We investigate the binding properties of the fluorescent cavitands, 1in and 1out, with L-Pro and L-pipecolic acid (L-Pip) at micromolar concentration using emission spectroscopy (direct binding-based sensing, BBS). The observed emission changes in the BBS experiments were small but evidenced the role of the cavitands as fluorescent sensors. In agreement with the millimolar concentration results (1H NMR experiments), the fluorescent 1in sensor displays a larger binding affinity for L-Pro than the 1out isomer. Conversely, the 1out isomer experienced larger emission changes upon amino acid binding. We developed FRET-based indicator displacement assays (IDA) owing to the small emission changes observed in the direct BBS experiments. At micromolar concentration, the competitive displacement of the quencher N-oxide 6 from the cavity of the 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 supramolecular ensemble (6⊂1in and 6⊂1out), by L-Pro, L-Pip, and L-phenylalanine (L-Phe) produced fluorescence “turn-on”. The results of the BBS and IDA experiments assigned a binding selectivity to the 1in isomer for L-Pro.
1 supramolecular ensemble (6⊂1in and 6⊂1out), by L-Pro, L-Pip, and L-phenylalanine (L-Phe) produced fluorescence “turn-on”. The results of the BBS and IDA experiments assigned a binding selectivity to the 1in isomer for L-Pro.
Introduction
There is an increasing demand in monitoring small polar molecules, which are relevant for disease diagnosis and training status, using portable and even wearable sensing devices.1 Ideally, the developed sensing devices should be designed for direct manipulation by end-users. This characteristic avoids the intervention of trained medical personnel and the commute to point-of-care facilities or hospitals. Moreover, the devices might transmit the results wirelessly to apps installed in mobile phones and share them with the electronic patient's record or the clinician.2 Biological and synthetic receptors are fundamental components of many small molecule sensing devices related to human health.3,4 The principle at work is supramolecular sensing, which relies on transduction mechanisms exclusively activated by molecular recognition events.5,6 This approach offers significant benefits for the design of synthetic selective molecular sensors, as well as for limiting the interferences caused by non-specific binding. Specific binding, a.k.a molecular recognition, builds on shape, size and function complementarity between receptor and analyte. In many cases, the transduction mechanism of the binding event demands the covalent incorporation of reporter units to the receptor's scaffolds i.e. the fluorescence, absorbance or redox properties of the receptor itself are not suitable for transduction in practical applications. The constructs resulting from the covalent connection of a synthetic receptor to a reporter unit are referred as molecular sensors. Molecular sensors are also key in the design of selective sensor nanomaterials able to discriminate analytes by molecular structure (specific binding) rather than by physical/chemical properties i.e. polarity (non-specific binding).Phosphonate calix[4]pyrrole cavitands are synthetic molecular receptors displaying one or more phosphonate bridging groups at the upper rim of “four wall” aryl-extended calix[4]pyrrole scaffolds. In previous studies, we described the use of these receptors for the selective recognition of ion-pairs and small polar neutral molecules.7,8 We showed that the mono-phosphonate calix[4]pyrrole cavitand 5in (Fig. 1) provided a three-dimensional polar aromatic cavity suitable for including creatinine and surrounding most of its surface.9
The receptor's aromatic cavity is functionalized with an inwardly directed phosphonate group at its open upper rim and by four pyrrole NHs at the opposed and closed end. These polar groups offer complementary hydrogen bonding donor and acceptor interactions to those of the included guest. We used the mono-phosphonate calix[4]pyrrole cavitand scaffold for the construction of ion selective electrodes, molecular sensors and indicator displacement assays for creatinine sensing and quantification.10,11 More recently, we demonstrated that the mono-phosphonate calix[4]pyrrole cavitand was also an effective synthetic carrier facilitating the selective diffusion of L-proline across membranes of liposomes and living cells.12L-Proline is also included in the aromatic cavity of the mono-phosphonate receptors establishing multiple charged hydrogen-bonds (carboxylate-pyrrole NHs, ammonium-phosphonate) and CH–π interactions.
Herein, we describe the synthesis of two novel fluorescent molecular sensors based on a mono-phosphonate calix[4]pyrrole cavitand scaffold. The introduced approach hinges on the covalent attachment of the fluorescent signalling unit directly to the phosphonate bridging group. The design is inspired by the work of Dalcanale and co-workers with mono-phosphonate fluorescent cavitands based on resorcin[4]arene scaffolds.13 We also report the binding properties of mono-phosphonate calix[4]pyrrole cavitands and their fluorescent derivatives with a reduced series of amino acids: L-proline (L-Pro), L-pipecolic acid (L-Pip) and L-phenylalanine (L-Phe). Using a direct binding-based sensing (BBS) approach, we determined that the binding constant of the fluorescent 1in isomer for L-Pro was one order of magnitude larger than that of L-Pip. Surprisingly to us, the direct BBS experiments of L-Pro and L-Pip with the 1out isomer produced larger changes in emission intensity in comparison to those of the 1in counterpart. Nevertheless, the binding constant values determined for the 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 inclusion complexes of 1out and the amino acids were one order of magnitude smaller than those of the 1in isomer. Due to the small changes observed with the direct BBS approach, we considered that an improved fluorescent sensing of the amino acids required the development of indicator displacement assays (IDA).14 To this end, we used the pyridine-N-oxide 6 as analogue of the well-known DABCYL ((4-dimethylaminoazo)benzene-4-carboxylic acid) black-hole quencher (Fig. 1). Pyridine N-oxide 6 formed thermodynamically and kinetically highly stable 1
1 inclusion complexes of 1out and the amino acids were one order of magnitude smaller than those of the 1in isomer. Due to the small changes observed with the direct BBS approach, we considered that an improved fluorescent sensing of the amino acids required the development of indicator displacement assays (IDA).14 To this end, we used the pyridine-N-oxide 6 as analogue of the well-known DABCYL ((4-dimethylaminoazo)benzene-4-carboxylic acid) black-hole quencher (Fig. 1). Pyridine N-oxide 6 formed thermodynamically and kinetically highly stable 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 non-emissive complexes with 1in and 1out. The displacement of 6 from the 1
1 non-emissive complexes with 1in and 1out. The displacement of 6 from the 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complexes produced fluorescence “turn-on”. The BBS and IDA experiments produced analogous binding constant values for all complexes. They assigned a superior stability to the L-Pro⊂1in complex compared to L-Pip⊂1in and L-Phe⊂1in analogues, and the 1out counterparts. The obtained binding results are supported by direct inspection of the molecular interactions present in the energy-minimized structures of the inclusion complexes.
1 complexes produced fluorescence “turn-on”. The BBS and IDA experiments produced analogous binding constant values for all complexes. They assigned a superior stability to the L-Pro⊂1in complex compared to L-Pip⊂1in and L-Phe⊂1in analogues, and the 1out counterparts. The obtained binding results are supported by direct inspection of the molecular interactions present in the energy-minimized structures of the inclusion complexes.
Results and discussion
Synthesis
The fluorescent phosphonate calix[4]pyrrole cavitands 1in and 1out were prepared in two synthetic steps starting from the known α,α,α,α-isomer of tetra-meta-hydroxyphenyl-tetra-methyl-calix[4]pyrrole 2 (Scheme 1).7 Firstly, the mono-methylene bridged calix[4]pyrrole 3 was obtained by reacting α,α,α,α-2 tetrol with 1.2 equiv. of bromochloromethane in DMSO solution in the presence of potassium carbonate as base. The mono-methylene bridged compound 3 was isolated in 48% yield after column chromatography purification of the reaction crude and crystallization of the isolated fraction in acetonitrile. Secondly, the incorporation of the fluorescent unit at the upper rim of 3 involved the room temperature reaction with freshly prepared 6-(phenylamino)-naphthalen-2-yl phosphonic acid dichloride 4,13 in THF solution during 2h and using triethylamine as base. The reaction produced a mixture of the two mono-phosphonate diastereoisomers 1in and 1out. The two pure stereoisomers were isolated by separation of an enriched fraction of the reaction crude (see ESI† for details) by means of analytical HPLC (Waters Spherisorb®, 5.0 μm Silica, 4.6 mm × 250 mm) using isocratic elution (DCM![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) AcOEt 90
AcOEt 90![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10).
10).
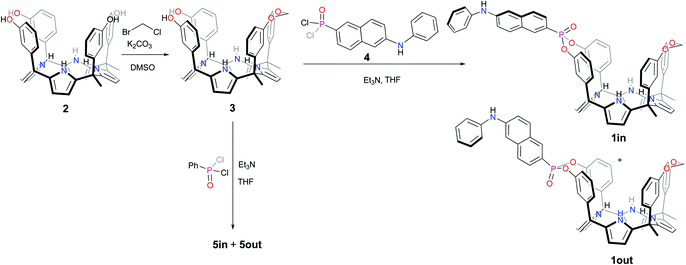 | ||
| Scheme 1 Synthetic scheme for the preparation of the isomeric mono-phosphonate mono-methylene fluorescent calix[4]pyrrole cavitands 1in and 1out and non-fluorescent analogues 5in and 5out. | ||
The 1out isomer eluted first. The 1in isomer, presenting the P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group inwardly oriented with respect to its aromatic cavity, was more polar and eluted second. This latter arrangement of functional groups should allow that suitable bound guests can establish simultaneous hydrogen-bonding intermolecular interactions with both the P
O group inwardly oriented with respect to its aromatic cavity, was more polar and eluted second. This latter arrangement of functional groups should allow that suitable bound guests can establish simultaneous hydrogen-bonding intermolecular interactions with both the P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group and the NHs of the calix[4]pyrrole core of the fluorescent receptor. The isolated 1out isomer will be used as a control to validate this hypothesis.
O group and the NHs of the calix[4]pyrrole core of the fluorescent receptor. The isolated 1out isomer will be used as a control to validate this hypothesis.
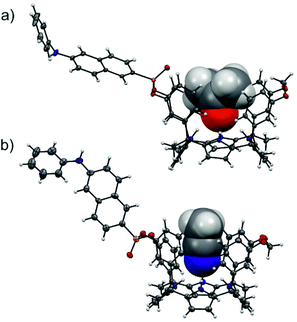
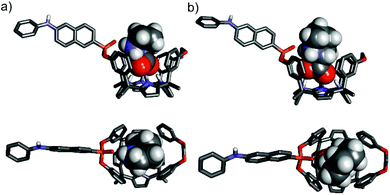
The configurational assignment of the two diastereoisomeric cavitands, 1in and 1out, was achieved by a combination of 1H, 31P NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallographic analysis. Single crystals of 1in grew from a deuterated acetone solution used to acquire its NMR spectra. On the other hand, we used acetonitrile to obtain single crystals of 1out. The solid-state structures of the two fluorescent calix[4]pyrrole isomers are depicted in Fig. 2. In both of them, the calix[4]pyrrole core adopts the cone conformation and one molecule of the solvent, used to grow the crystals, is included in its polar aromatic cavity. The included solvent forms four simultaneous hydrogen-bonding interactions between its heteroatom (oxygen or nitrogen) and the pyrrole NHs. In the solid state and for the two isomers, the 14-membered rings delineated by the bridged phosphonate-group, two meso-phenyl groups, their corresponding meso-carbons and one pyrrole ring, present a conformation locating the phenyl-amino-naphthyl substituent of the phosphorous atom in equatorial orientation and pointing away from the aromatic cavity.
The outwardly oriented fluorescent unit, which is observed in both solid-state structures of the calix[4]pyrrole diastereoisomers, is in striking contrast to the observation made in structurally related isomers of mono-phosphonate resorcin[4]arene cavitands.13 In the latter case, the 1H NMR spectrum of the out isomer showed the protons assigned to the phenyl-amino-naphthyl substituent upfield shifted compared to those of the in counterpart. This difference was attributed to dissimilar orientations of the substituent with respect to the receptor's aromatic cavity. In short, the resorcin[4]arene out isomer directs the fluorescent substituent towards the receptor's cavity experiencing the shielding effect exerted by the aromatic rings.
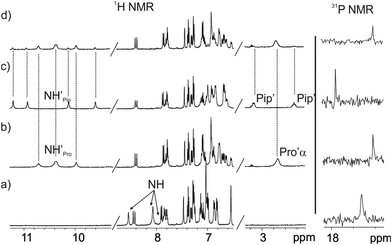
We did not observe significant chemical shift changes for the signals of the hydrogen atoms of the fluorescent substituent when comparing the 1H NMR spectra of the 1in and 1out isomers in acetone-d6 or dichloromethane-d2 solutions (Fig. 3). This finding indicated that in agreement with the solid-state structures, in solution, the two isomers of 1 also featured the fluorescent substituent outwardly directed with respect to their aromatic cavities. However, the signals for H8 and H7 (Fig. 1), corresponding to the meso-aryl hydrogen atoms that are ortho with respect to the bridging phosphonate group, showed very different chemical shift values in the two isomers. For example, in the 1out isomer H8 resonates significantly downfield shifted compared to the chemical shift value for the analogous proton signal in the 1in counterpart (Fig. 3). This chemical shift difference is due to the positioning of H8 in the deshielding zone of the magnetic anisotropy cone generated by the out P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group. For the same token, proton H7 becomes partially deshielded when the P
O group. For the same token, proton H7 becomes partially deshielded when the P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group is inwardly directed.
O group is inwardly directed.
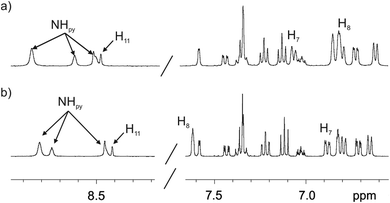 | ||
| Fig. 3 Selected regions of the 1H (400 MHz, 298 K) spectra of 1in (a) and 1out (b) isomers in acetone-d6 solution. The pyrrole NH, β-pyrrole, H11 and the two proton signals of the meso-aryl groups, H8 and H7, that are ortho with respect to the phosphonate bridging groups are indicated. See Fig. 1 for proton assignment. | ||
The chemical shift values of the phosphorous atoms of the 1in and 1out isomers are in agreement with those observed for structurally related mono- and bis-phosphonate calix[4]pyrrole cavitands (Fig. S12 and S20†).7,9 The phosphorous atom of the out isomer resonates slightly upfield, possibly due to the shielding effect exerted by the aromatic cavity. In acetone-d6 solution, both isomers showed three highly downfield shifted signals for the pyrrole NHs. This is due to the involvement of the NHs in hydrogen bonding interactions with the oxygen atom of one included acetone molecule. The bound acetone molecule locks the cavitands in their cone conformation as observed for 1in in the solid-state (Fig. 2a). The 1H NMR spectra of the two isomers in chlorinated solvents (vide infra) are significantly different to those registered in acetone. Most likely, in dichloromethane-d2 solution the receptors adopted alternate conformations of their calix[4]pyrrole core and are involved in conformation exchange processes that are fast on the chemical shift timescale.
NMR binding studies
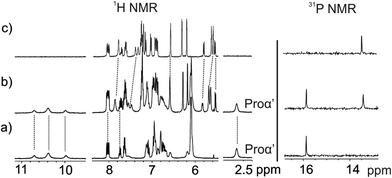
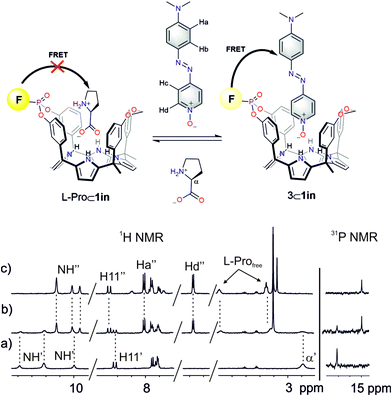
We became interested in investigating the binding properties of these type of cavitands as receptors for L-Pro and the 6-membered ring α-amino acid analogue, L-pipecolic acid (L-Pip). L-Pip has been described as a diagnostic marker of pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy.15We first performed separate solid–liquid extraction experiments with L-Pro or L-Pip and the fluorescent cavitand 1in in CD2Cl2. We added an excess of the solid amino acid (∼2mg L-Pro or L-Pip) to a 2 mM CD2Cl2 solution of the cavitand 1in. We hand-shook the suspensions for several minutes and filtered off the remaining solid. The 1H NMR spectra of the filtered solutions showed significant differences compared to that of the free cavitand 1in in the same solvent (Fig. 4). In both cases, only a single set of sharp signals was observed for the hydrogen atoms of the receptor.
The signals corresponding to the pyrrole NHs were the ones experiencing the most important chemical shift changes. These signals moved downfield compared to those in free 1in (Δδ = 1.8–1.5 and 2.3–1.1 ppm, for L-Pro and L-Pip, respectively), suggesting their involvement in hydrogen bonding interactions with the corresponding included guest. On the other hand, we observed the appearance of a new set of signals in the upfield region of the spectra. These signals were indicative of the inclusion of the guests in the polar aromatic cavity of 1in. Specifically for L-Pro extraction, we observed a broad signal centred at δ = 2.7 ppm. We attributed this signal to the proton α to the carboxylate group of the bound L-Pro. This signal appeared upfield shifted compared to that of the free guest in (CD3)2SO solution (Δδ = −1.2 ppm). Thus, the proton atoms of the included L-Pro experienced the shielding effect exerted by the four meso-phenyl substituents of 1in. Analogously, the signals of bound L-Pip also appeared upfield shifted compared to those in the free guest in (CD3)2SO solution. The integral values of selected proton signals for the host and the guest indicated the quantitative formation of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complexes: L-Pro⊂1in and L-Pip⊂1in. That is, receptor 1in extracted 1 equiv. of L-Pro and L-Pip in the independent solid–liquid extractions experiments.
1 complexes: L-Pro⊂1in and L-Pip⊂1in. That is, receptor 1in extracted 1 equiv. of L-Pro and L-Pip in the independent solid–liquid extractions experiments.
The binding of the guest was also supported by the chemical shift changes observed in the 31P NMR spectra of the filtered solutions. The 31P NMR spectrum of free 1in shows a singlet resonating at δ = 17.3 ppm. Remarkably, after the extraction experiments of L-Pro and L-Pip, the phosphorous signal of bound 1in resonated at δ = 17.0 ppm and 17.9 ppm, respectively (Fig. 4 right).
Next, we performed a competitive solid–liquid extraction experiment by adding equimolar amounts of solid L-Pro and L-Pip (∼2 mg of each guest) to a millimolar CD2Cl2 solution of the fluorescent receptor 1in. The 1H NMR spectra of the filtered solution clearly showed two sets of proton signals for the NHs of bound 1in. Moreover, the integral values of the two sets of NH signals were significantly different (Fig. 4d). By comparison to the 1H NMR spectra of the solid–liquid extraction experiments performed separately, we easily assigned the two sets of signals to the protons of the bound receptor in the L-Pro⊂1in and L-Pip⊂1in complexes (Fig. 4b and c). Integration of the pyrrole NH signals for the two complexes assigned a 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 molar ratio to the mixture of L-Pro⊂1in and L-Pip⊂1in complexes.‡ Considering that the solubility of L-Pro is slightly higher than that of L-Pip, the result of the competitive extraction experiment is not conclusive in assigning a larger binding affinity of 1in for L-Pro compared to L-Pip.§ Nevertheless, it provides an initial hint in this direction.
1 molar ratio to the mixture of L-Pro⊂1in and L-Pip⊂1in complexes.‡ Considering that the solubility of L-Pro is slightly higher than that of L-Pip, the result of the competitive extraction experiment is not conclusive in assigning a larger binding affinity of 1in for L-Pro compared to L-Pip.§ Nevertheless, it provides an initial hint in this direction.
We were also interested in evaluating the importance of the hydrogen bonding interaction established between the inwardly directed P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group of cavitand 1in and the protonated amino group of the bound amino acid guests. With this aim, we performed analogous solid–liquid extraction experiments of L-Pro with non-fluorescent cavitands 5in and 5out. We used the non-fluorescent receptors as model compounds of the fluorescent counterparts due to their ease of synthesis (Fig. 1). We hypothesized that 5out could bind and extract L-Pro through the formation of four hydrogen bonds with the pyrrole NHs and additional CH–π interactions. In contrast, the outwardly directed P
O group of cavitand 1in and the protonated amino group of the bound amino acid guests. With this aim, we performed analogous solid–liquid extraction experiments of L-Pro with non-fluorescent cavitands 5in and 5out. We used the non-fluorescent receptors as model compounds of the fluorescent counterparts due to their ease of synthesis (Fig. 1). We hypothesized that 5out could bind and extract L-Pro through the formation of four hydrogen bonds with the pyrrole NHs and additional CH–π interactions. In contrast, the outwardly directed P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group of 5out should not participate in hydrogen bonding interactions with the protonated amino group of bound L-Pro. Thus, we expected a decrease in the binding constant of the L-Pro⊂5out complex compared to that of the 5in isomer.
O group of 5out should not participate in hydrogen bonding interactions with the protonated amino group of bound L-Pro. Thus, we expected a decrease in the binding constant of the L-Pro⊂5out complex compared to that of the 5in isomer.
The solid–liquid extraction experiments of L-Pro using the non-fluorescent model receptor 5in produced similar changes in the 1H and 31P NMR spectra to those described above for the fluorescent cavitand 1in (Fig. 4). To our surprise, the 1H NMR spectrum of the filtered solution obtained after extraction of L-Pro with 5out showed broad proton signals. The corresponding 31P NMR spectrum did not produce any observable signal. We detected a significant increase in the signal-to-noise ratio of the spectra. We considered this observation as indicative of a diminution of the concentration of 5out in solution after the extraction experiment. To clarify this issue, we evaporated the CD2Cl2 and re-dissolved the solid residue in (CD3)2SO. The obtained (CD3)2SO solution was analysed using 1H NMR spectroscopy. We observed the diagnostic signals of the protons of free 5out and free L-Pro. The L-Pro signals displayed a significantly reduced intensity. This result suggested that 5out was not able to extract 1 equiv. of L-Pro. To investigate the insolubility of the putatively formed L-Pro⊂5out complex in CD2Cl2, we acquired a 1H NMR spectrum of the filtered solid by dissolving it in (CD3)2SO. The 1H NMR spectrum of the solution displayed the diagnostic signals of free 5out and free L-Pro. The observation of the signals of free 5out indicates that the L-Pro⊂5out complex features a reduced solubility in CD2Cl2, falling out of solution during the solid–liquid experiment and hampering its use for quantitative purposes.
For this reason, we decided to perform a competitive binding experiment starting from a millimolar CD2Cl2 solution of the L-Pro⊂5in complex. The addition of 1 equiv. of the 5out isomer to the above solution did not induce significant changes to the proton signals of the L-Pro⊂5in complex (Fig. 5b). We detected the appearance of a new set of proton signals that almost coincided with those of the free 5out receptor. The broadening and small chemical shift changes observed for the new set of signals (Fig. 5b) suggested the existence of a binding equilibrium in solution. In short, we propose that the L-Pro⊂5out complex is formed in solution to a reduced extent and the binding equilibrium between free and bound 5out shows fast/intermediate exchange dynamics on the chemical shift timescale. The 31P NMR spectrum of the mixture also supports this hypothesis. It displayed two singlets centred at δ = 15.8 and 13.4 ppm. The one appearing downfield is quite sharp and corresponds to the L-Pro⊂5in complex. In contrast, the upfield-shifted singlet is slightly broadened due to the chemical exchange between free and bound 5out. The lack of separate signals for the phosphorous atoms of free 5in results from its low concentration in solution (Fig. 5b, right). Taken together, these results indicate that the binding affinity of 5in for L-Pro is significantly larger (approximately 7–10-fold, vide infra) than that of the 5out isomer. We attributed the increased binding affinity to the additional hydrogen bond interaction provided by the inwardly directed P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group in the L-Pro⊂5in complex.
O group in the L-Pro⊂5in complex.
UV–Vis and emission spectroscopy binding studies
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group for the binding of L-Pro with the 5in model cavitand, we carried out direct binding-based sensing (BBS) studies with the analogous fluorescent 1in cavitand. Some years ago, Dalcanale and co-workers reported the use of somewhat structurally related fluorescent resorcin[4]arene receptors for the optical sensing of alkyl-chain C1–C4 alcohols.13 The authors claimed that the hydrogen bonding interaction established between the alcohol OH function and the P
O group for the binding of L-Pro with the 5in model cavitand, we carried out direct binding-based sensing (BBS) studies with the analogous fluorescent 1in cavitand. Some years ago, Dalcanale and co-workers reported the use of somewhat structurally related fluorescent resorcin[4]arene receptors for the optical sensing of alkyl-chain C1–C4 alcohols.13 The authors claimed that the hydrogen bonding interaction established between the alcohol OH function and the P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group of the receptor could decrease the electronic density on the phosphorus atom and modify the energy of the excited state of the naphthalene unit directly attached to it. The electronic modification was expected to alter the maximum of the emission band.
O group of the receptor could decrease the electronic density on the phosphorus atom and modify the energy of the excited state of the naphthalene unit directly attached to it. The electronic modification was expected to alter the maximum of the emission band.
The UV–Vis absorption spectra of 1in and 1out showed very similar features (Fig. S21†). Concretely, two intense absorption bands with maxima at 275 (ε = 34![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 M−1 cm−1) and 328 nm (ε = 24
000 M−1 cm−1) and 328 nm (ε = 24![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 M−1 cm−1) and a shoulder at 370 nm. These bands are characteristic of π–π* and n–π*-transitions of the phenyl-amino-naphthyl moiety, as demonstrated by simple comparison with the UV–Vis spectrum of diethyl 6-(phenylamino)naphthalene-2-phosphonate 7 (Fig. 1) used as model compound (Fig. S22†).
000 M−1 cm−1) and a shoulder at 370 nm. These bands are characteristic of π–π* and n–π*-transitions of the phenyl-amino-naphthyl moiety, as demonstrated by simple comparison with the UV–Vis spectrum of diethyl 6-(phenylamino)naphthalene-2-phosphonate 7 (Fig. 1) used as model compound (Fig. S22†).
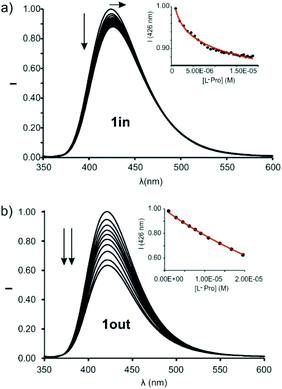
The incremental addition of L-Pro to separate micromolar dichloromethane solutions of 1in and 1out did not produce changes in their corresponding UV–Vis spectra (Fig. S24†). Spectral changes were more evident using emission spectroscopy to monitor the titration experiment. The excitation at 335 nm of a 5 × 10−7 M dichloromethane solution of 1in resulted in an intense and broad emission band with a maximum at 422 nm. The incremental addition of L-Pro provoked a concomitant red-shift of the maximum (Δλmax = 3–4 nm) and a decrease in emission intensity (Fig. 6a). Similar changes were observed during the incremental addition of L-Pip to 1in using analogous experimental conditions (Fig. S26†).
We also performed emission titration experiments with the fluorescent compound 7. This compound was used as reference of the fluorescent signalling unit incorporated in the 1in and 1out receptor cavitands. In this case, the incremental addition of L-Pro did not produce noticeable changes in the emission of 7 (Fig. S23†). This result evidenced the relevance of the aryl-extended calix[4]pyrrole scaffold for the efficient binding of L-Pro by 1in and the transduction of the binding event in the modification of the emission properties of the signalling unit.
The changes in emission intensity observed during the titrations of 1in with L-Pro and L-Pip were rather small. Even so, we fit the obtained experimental titration data to a theoretical 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 binding model considering two emissive species: free and bound 1in. We determined the binding constant values for the complexes of 1in with L-Pro and L-Pip as, K(L-Pro⊂1in)BBS = 3.2 × 105 M−1 and K(L-Pip⊂1in)BBS = 6.3 × 104 M−1, respectively. Surprisingly to us, the titrations of the 1out isomer with L-Pro and L-Pip produced greater emission intensity changes (Fig. 6b and S27†).¶ Conversely, the bathochromic shift experienced by the emission band of 1out was reduced compared to that of 1in (Δλmax < 1 nm). The mathematical analysis of the titration data of 1out, using a 1
1 binding model considering two emissive species: free and bound 1in. We determined the binding constant values for the complexes of 1in with L-Pro and L-Pip as, K(L-Pro⊂1in)BBS = 3.2 × 105 M−1 and K(L-Pip⊂1in)BBS = 6.3 × 104 M−1, respectively. Surprisingly to us, the titrations of the 1out isomer with L-Pro and L-Pip produced greater emission intensity changes (Fig. 6b and S27†).¶ Conversely, the bathochromic shift experienced by the emission band of 1out was reduced compared to that of 1in (Δλmax < 1 nm). The mathematical analysis of the titration data of 1out, using a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 binding model considering two emissive species, returned very similar binding constant values for the two complexes of the amino-acids, K(L-Pro⊂1out)BBS = 3.9 × 104 M−1 and K(L-Pip⊂1out)BBS = 2.3 × 104 M−1. The magnitudes of the binding constants for the complexes with 1out are close to one order of magnitude lower than those of the 1in isomer.
1 binding model considering two emissive species, returned very similar binding constant values for the two complexes of the amino-acids, K(L-Pro⊂1out)BBS = 3.9 × 104 M−1 and K(L-Pip⊂1out)BBS = 2.3 × 104 M−1. The magnitudes of the binding constants for the complexes with 1out are close to one order of magnitude lower than those of the 1in isomer.
The observation of larger emission changes in the titrations of the 1out isomer was completely unexpected. The spatial orientation of the P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group in the free isomer and its complexes is not geometrically suitable for the involvement in charged hydrogen bonding interactions with the bound guests. Dalcanale et al. hypothesized that hydrogen bonding interactions with the inwardly directed P
O group in the free isomer and its complexes is not geometrically suitable for the involvement in charged hydrogen bonding interactions with the bound guests. Dalcanale et al. hypothesized that hydrogen bonding interactions with the inwardly directed P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group were responsible for the observed emission changes in the gas-phase sensing of short alkyl chain alcohols using structurally related phosphonate resorcin[4]arene cavitands. The authors did not observe emission changes in the sensing experiments using the out isomer. Based on our findings, we suggest that the cavitand-amino acid binding, especially for the 1out isomer, induces changes in the conformation (and possibly steric effects) of the receptor, which directly affects the properties of the signalling unit. These changes are transduced into non-radiative decay processes of the excited states of the 1
O group were responsible for the observed emission changes in the gas-phase sensing of short alkyl chain alcohols using structurally related phosphonate resorcin[4]arene cavitands. The authors did not observe emission changes in the sensing experiments using the out isomer. Based on our findings, we suggest that the cavitand-amino acid binding, especially for the 1out isomer, induces changes in the conformation (and possibly steric effects) of the receptor, which directly affects the properties of the signalling unit. These changes are transduced into non-radiative decay processes of the excited states of the 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complexes. Accordingly, the binding event is responsible for the observed decrease in fluorescence intensity of the signaling unit.||
1 complexes. Accordingly, the binding event is responsible for the observed decrease in fluorescence intensity of the signaling unit.||
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 500 M−1 cm−1). DABCYL is used in the development of Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based nucleic acid probes. We already applied N-oxide 6 for the optical sensing of creatinine using an IDA. We used a calix[4]pyrrole phosphonate cavitand equipped with a dansyl group as fluorophore. We reported that the binding of 6 in the cavity of the receptor produced the efficient quenching of the fluorescence of the dansyl group through a FRET process.11
500 M−1 cm−1). DABCYL is used in the development of Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based nucleic acid probes. We already applied N-oxide 6 for the optical sensing of creatinine using an IDA. We used a calix[4]pyrrole phosphonate cavitand equipped with a dansyl group as fluorophore. We reported that the binding of 6 in the cavity of the receptor produced the efficient quenching of the fluorescence of the dansyl group through a FRET process.11
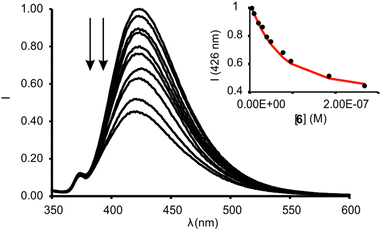
We calculated the spectral overlap between the absorption spectrum of N-oxide 6 and the emission spectrum of 1in to be J = 2.5 × 10−9 cm6 mol−1 (Fig. S28†). This value is even larger than the one calculated for the FRET pair formed by 6 and the phosphonate calix[4]pyrrole containing the dansyl fluorophore, which resulted in ca. 95% quenching of the receptor's fluorescence in the 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complex. The addition of 1 equiv. of 6 to a 5 μM dichloromethane solution of 1in produced a strong quenching of the emission band of the receptor at 422 nm (>95%, λexc = 335 nm) (Fig. S30†).** The fluorescence quenching is the direct consequence of the FRET process operating in the formed 1
1 complex. The addition of 1 equiv. of 6 to a 5 μM dichloromethane solution of 1in produced a strong quenching of the emission band of the receptor at 422 nm (>95%, λexc = 335 nm) (Fig. S30†).** The fluorescence quenching is the direct consequence of the FRET process operating in the formed 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 inclusion complex. The phenyl-amino-naphthyl substituent of the 1in receptor acts as energy donor and the bound N-oxide 6 as the acceptor. We obtained analogous results for the equimolar mixture of 1out and 6 (Fig. S31†). The quantitative formation of the complexes 6⊂1in and 6⊂1out in the presence of 1 equiv. of the N-oxide allowed us to estimate their binding constants as larger than 107 M−1. We expected similar binding constant values for the two complexes owing to the lack of additional interaction of guest 6 with the P
1 inclusion complex. The phenyl-amino-naphthyl substituent of the 1in receptor acts as energy donor and the bound N-oxide 6 as the acceptor. We obtained analogous results for the equimolar mixture of 1out and 6 (Fig. S31†). The quantitative formation of the complexes 6⊂1in and 6⊂1out in the presence of 1 equiv. of the N-oxide allowed us to estimate their binding constants as larger than 107 M−1. We expected similar binding constant values for the two complexes owing to the lack of additional interaction of guest 6 with the P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group of the receptors. We performed a titration of 1in with 6 using more diluted conditions ([1in] = 5 × 10−8 M, Fig. 7) and determined the accurate binding constant of the 1
O group of the receptors. We performed a titration of 1in with 6 using more diluted conditions ([1in] = 5 × 10−8 M, Fig. 7) and determined the accurate binding constant of the 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complex to be K(6⊂1in) = 3.2 × 107 M−1.†† The incremental addition of 6 to a 1μM solution of 7, used as reference of the fluorescent substituent of the receptors, did not produce noticeable emission changes. This result demonstrated that the formation of the 1
1 complex to be K(6⊂1in) = 3.2 × 107 M−1.†† The incremental addition of 6 to a 1μM solution of 7, used as reference of the fluorescent substituent of the receptors, did not produce noticeable emission changes. This result demonstrated that the formation of the 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complexes induces the observation of the FRET-quenching process.
1 complexes induces the observation of the FRET-quenching process.
Next, we studied the competitive displacement of the indicator N-oxide 6, involved in the 6⊂1in complex, by L-Pro and L-Pip at micromolar concentrations using emission spectroscopy. We prepared an equimolar dichloromethane solution of 6 and 1in (1 μM). At this concentration and taking in consideration the binding constant determined in the previous section, the 6⊂1in complex is present in 84% extent. Thus, the fluorescence observed for the ensemble is assigned to the 16% of dye 6 remaining free in solution (Fig. 9).
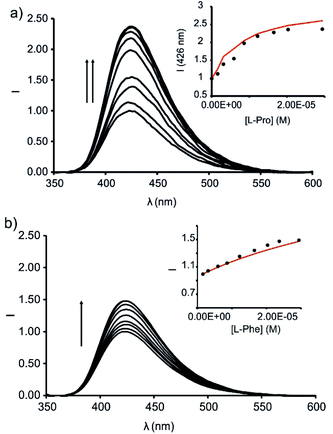
The titration of the solution with incremental amounts of L-Pro evidenced a gradual increase of the fluorescence emission. In the presence of 30 equiv. of L-Pro, the observed intensity for the maximum of the emission band was 2.5 times higher than the initial one (I0). We rationalized the noticed fluorescence “turn-on” by considering the displacement of 6, as quencher of the fluorescence of the phenyl-amino-naphthyl group in the 6⊂1in complex, by L-Pro. This displacement leads to the formation of the fluorescent L-Pro⊂1in complex. It is worthy to note that the identical titration monitored using absorption spectroscopy produced negligible changes in the registered spectra.
We analysed mathematically the titration data obtained in the emission IDA experiment using a theoretical binding model considering the competitive formation of two 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complexes (6⊂1in and L-Pro⊂1in). We assigned emissive properties to only two (free 1in and L-Pro⊂1in) of the six species involved the binding model.§§ We fixed the binding constant of the 6⊂1in complex to the previously determined value of K = 3.2 × 107 M−1 (vide supra). The fit of the experimental data to the model was good and returned the stability constant value for the L-Pro⊂1in as K(L-Pro⊂1in)IDA = 4.5 × 105 M−1. This value is in good agreement with the one determined previously using direct BBS titration experiments (K(L-Pro⊂1in)BBS = 3.2 × 105 M−1, vide supra). The fit of the experimental data also provided the calculated emission spectra for 1in and L-Pro⊂1in. The calculation of the spectra of the emissive (a.k.a. coloured) species is one of the advantages of performing global fitting multivariate data analysis compared to the simpler single or even multiple wavelength fitting alternatives. Obtaining sensible calculated spectra for the coloured species is a necessary condition to support the quality and fit of the data analysis. To our delight, the calculated spectra showed a nice agreement with the experimental ones registered in separate experiments. We also tested the performance of the ensemble of 6 and 1out in emission IDA experiments with L-Pro (Fig. S32†). Using this methodology, the calculated binding constant for the L-Pro⊂1out complex was K(L-Pro⊂1out)IDA = 7.9 × 104 M−1. In short, the emission IDA experiments reflected that the difference in the binding constant values of the L-Pro⊂1in and L-Pro⊂1out inclusion complexes is close to one order of magnitude, in favour of the former. In addition, the binding constant values measured for the complexes using IDA and BBS experiments are fully consistent.
1 complexes (6⊂1in and L-Pro⊂1in). We assigned emissive properties to only two (free 1in and L-Pro⊂1in) of the six species involved the binding model.§§ We fixed the binding constant of the 6⊂1in complex to the previously determined value of K = 3.2 × 107 M−1 (vide supra). The fit of the experimental data to the model was good and returned the stability constant value for the L-Pro⊂1in as K(L-Pro⊂1in)IDA = 4.5 × 105 M−1. This value is in good agreement with the one determined previously using direct BBS titration experiments (K(L-Pro⊂1in)BBS = 3.2 × 105 M−1, vide supra). The fit of the experimental data also provided the calculated emission spectra for 1in and L-Pro⊂1in. The calculation of the spectra of the emissive (a.k.a. coloured) species is one of the advantages of performing global fitting multivariate data analysis compared to the simpler single or even multiple wavelength fitting alternatives. Obtaining sensible calculated spectra for the coloured species is a necessary condition to support the quality and fit of the data analysis. To our delight, the calculated spectra showed a nice agreement with the experimental ones registered in separate experiments. We also tested the performance of the ensemble of 6 and 1out in emission IDA experiments with L-Pro (Fig. S32†). Using this methodology, the calculated binding constant for the L-Pro⊂1out complex was K(L-Pro⊂1out)IDA = 7.9 × 104 M−1. In short, the emission IDA experiments reflected that the difference in the binding constant values of the L-Pro⊂1in and L-Pro⊂1out inclusion complexes is close to one order of magnitude, in favour of the former. In addition, the binding constant values measured for the complexes using IDA and BBS experiments are fully consistent.
We carried out analogous IDA experiments with L-Pip. We observed a 1.7 times fluorescence enhancement for the ensemble of 6 and 1in in the presence of 30 equiv. of L-Pip (i.e. I30 = 1.7 × I0) (Fig. S33†). The measured fluorescence enhancement factor is reduced when compared to the 2.5-fold observed for L-Pro under identical conditions. The fit of the data of the IDA experiments to the same theoretical binding model used before for L-Pro returned a binding constant for L-Pip⊂1in complex of K(L-Pip⊂1in)IDA = 6.3 × 104 M−1. Again, this value is in line with the one obtained in direct BBS experiments. It is worthy to mention that under the used experimental conditions for the IDA, and considering the calculated binding constant for the L-Pip⊂1in complex, this species is only formed in a 20% extent. The reduced extension in which the L-Pip⊂1in complex is formed diminishes the accuracy of the calculated binding constant value. Unfortunately, the low solubility of L-Pip in dichloromethane hampered the formation of the L-Pip⊂1in complex to a larger extent.
We also determined the binding constant of L-phenylalanine (L-Phe) with 1in using analogous competitive IDA experiments. We observed a 1.5 times fluorescence enhancement in the presence of 30 equiv. of L-Phe (Fig. 9b). This result hinted to similar binding constant values for the L-Phe⊂1in and L-Pip⊂1in complexes. The fit of the experimental data returned a binding constant of K(L-Phe⊂1in)IDA = 3.5 × 104 M−1.
To gain some insight on the structures of the amino acid's inclusion complexes with receptor 1in, we computed their energy-minimized structures at the BP8617,18/def2SVP level of theory using GAUSSIAN 09.19 In all the computed inclusion complexes, the calix[4]pyrrole core adopts the cone conformation by establishing four hydrogen bonding interactions with one of the oxygen atoms of the carboxylate group of the included guest (Fig. 10 and Fig. S34†). It is also possible to infer the presence of multiple CH–π and O–π interactions in the complexes (Fig. S35†). Moreover, all complexes display a charged hydrogen bonding interaction between the inwardly directed P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group of the receptor and the protonated amino group of the zwitterionic form of the bound amino acids (Fig. S35†).
O group of the receptor and the protonated amino group of the zwitterionic form of the bound amino acids (Fig. S35†).
In the particular case of the L-Pip⊂1in complex, we computed two different binding geometries. One of them involved the energetically more favourable conformation of L-Pip, L-Pipeq (i.e. COO− substituent equatorial in the protonated piperidine chair conformation). The other one considers the higher energy conformer, L-Pipax (i.e. COO− substituent is axial in the protonated piperidine chair conformation). The results of the calculations indicated that both inclusion complexes were isoenergetic.
A simple visual inspection of the energy-minimized structures of the amino acid's inclusion complexes revealed that those of L-Pro featured a superior match in size and shape between the cavity of 1in and the included amino acid (Fig. 10). Most likely, the L-Pro⊂1in inclusion complex establishes energetically more favourable dispersive, van der Waals and hydrogen bonding intermolecular interactions than the other counterparts (L-Pip⊂1in and L-Phe⊂1in) (Fig. S34†).
The experimentally determined values for the association constants of the complexes of the amino acids with receptors 1in and 1out are summarized in Table 1. We draw the following conclusions from the tabulated data.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 inclusion complexes of the 1in and 1out receptors in dichloromethane and free Gibbs energy ΔG (kcal mol−1)
1 inclusion complexes of the 1in and 1out receptors in dichloromethane and free Gibbs energy ΔG (kcal mol−1)
| 1in | 1out | ΔΔG(1in–1out) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K a and ΔG are the average values from two independent titrations. Errors are reported as standard deviation for Ka and propagated for ΔG.a Determined by direct BBS experiments.b Determined by IDA experiments. n.d. Not determined. | ||||
| L-Pro | K a | 3.2 ± 0.6 × 105a | 3.9 ± 0.8 × 104a | ∼−1.1 |
| 4.5 ± 0.9 × 105b | 7.9 ± 1.5 × 104b | |||
| ΔG | −7.5 ± 0.1a | −6.3 ± 0.1a | ||
| −7.7 ± 0.1b | −6.7 ± 0.1b | |||
| L-Pip | K a | 6.3 ± 1.3 × 104a | 2.3 ± 0.5 × 104a | −0.5a |
| 6.3 ± 1.3 × 104b | ||||
| ΔG | −6.5 ± 0.1a | −6.0 ± 0.1a | ||
| −6.5 ± 0.1b | ||||
| L-Phe | K a | 3.5 ± 0.7 × 104b | n.d. | n.d. |
| ΔG | −6.2 ± 0.1b | n.d. | ||
On the one hand, the determined ΔG values for L-Pro⊂1in and L-Pro⊂1out complexes assigned a free energy gain of ∼−1.1 kcal mol−1 (ΔΔG(L-Pro⊂1in–L-Pro⊂1out)) in favour to L-Pro⊂1in complex. We attributed this difference to the additional polar hydrogen bonding interaction established in the inclusion complex with 1in. This interaction involves the oxygen atom of the P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group inwardly directed towards the receptor's cavity and the protonated amino group of the included L-Pro. Due to geometrical reasons, this interaction is not present in the L-Pro⊂1out complex. Thus, receptor 1out binds L-Pro through the formation of only four hydrogen bonds involving the carboxylate group of the L-Pro and pyrrole NHs of 1out. Additional CH–π interactions also assist in the stabilization of both complexes.
O group inwardly directed towards the receptor's cavity and the protonated amino group of the included L-Pro. Due to geometrical reasons, this interaction is not present in the L-Pro⊂1out complex. Thus, receptor 1out binds L-Pro through the formation of only four hydrogen bonds involving the carboxylate group of the L-Pro and pyrrole NHs of 1out. Additional CH–π interactions also assist in the stabilization of both complexes.
On the other hand, the calculated free energy difference between the analogous complexes of L-Pip (ΔΔG(L-Pip⊂1in–L-Pip⊂1out) is reduced to just −0.5 kcal mol−1. Most likely, this is due to the formation of a weaker polar hydrogen bond in the L-Pip⊂1in complex in comparison to the L-Pro counterpart.
We measured a small free energy difference for the complexes of L-Pro and L-Pip with the 1out receptor (∼−6.3 and −6.0 kcal mol−1, respectively) that we assigned it to the better fit of the former in the cavity of the latter. Taken together, these results indicate that the polar intermolecular hydrogen bond interaction N–H⋯O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) P plays a pivotal role in the binding selectivity featured by 1in for L-Pro over L-Pip, ΔΔG(L-Pro⊂1in–L-Pip⊂1in) ∼-1.0 kcal mol−1.
P plays a pivotal role in the binding selectivity featured by 1in for L-Pro over L-Pip, ΔΔG(L-Pro⊂1in–L-Pip⊂1in) ∼-1.0 kcal mol−1.
Conclusions
We report the synthesis of two unprecedented diastereoisomeric mono-phosphonate calix[4]pyrrole cavitands featuring a N-phenyl-naphthalamine fluorophore directly attached to its phosphorous atom. The two isomers differ in the relative orientation (in/out) of the P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bridging group with respect to its polar aromatic cavity (1in and 1out). We characterized the two isomers in solution using NMR and optical (UV–Vis absorption and emission) spectroscopies and in the solid state by X-ray diffraction studies. We used the non-fluorescent model receptors 5in and 5out to perform a competitive binding experiment with L-Pro. The analyses of the mixtures using 1H and 31P NMR spectroscopy showed that the L-Pro was preferentially bound to the 5in isomer. We attributed the higher thermodynamic stability exhibited by the L-Pro⊂5in complex to the existence of an additional charged hydrogen bonding interaction between the protonated amino group of bound L-Pro and the inwardly directed bridging P
O bridging group with respect to its polar aromatic cavity (1in and 1out). We characterized the two isomers in solution using NMR and optical (UV–Vis absorption and emission) spectroscopies and in the solid state by X-ray diffraction studies. We used the non-fluorescent model receptors 5in and 5out to perform a competitive binding experiment with L-Pro. The analyses of the mixtures using 1H and 31P NMR spectroscopy showed that the L-Pro was preferentially bound to the 5in isomer. We attributed the higher thermodynamic stability exhibited by the L-Pro⊂5in complex to the existence of an additional charged hydrogen bonding interaction between the protonated amino group of bound L-Pro and the inwardly directed bridging P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O function of the receptor. We developed two different supramolecular approaches for the sensing of L-Pro and L-Pip using the fluorescent receptor 1in: direct binding-based sensing (BBS) and a FRET-based indicator displacement assay (IDA). The BBS strategy produced a small reduction of the emission intensity of 1in upon binding L-Pro or L-Pip. The fit of the reduced emission changes to a simple 1
O function of the receptor. We developed two different supramolecular approaches for the sensing of L-Pro and L-Pip using the fluorescent receptor 1in: direct binding-based sensing (BBS) and a FRET-based indicator displacement assay (IDA). The BBS strategy produced a small reduction of the emission intensity of 1in upon binding L-Pro or L-Pip. The fit of the reduced emission changes to a simple 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 binding model allowed us to determine the binding constants of the inclusion complexes of 1in with L-Pro and L-Pip as, K(L-Pro⊂1in)BBS = 3.2 × 105 M−1 and K(L-Pip⊂1in)BBS = 6.3 × 104 M−1, respectively. Analogous titration experiments of the 1out isomer with the two amino acids resulted in greater decreases of the emission intensity of the free receptor. In contrast, the binding constant values determined for the complexes of 1out with L-Pro and L-Pip are close to one order of magnitude lower than those of 1in. The increased binding affinity of the amino acids for the 1in receptors is assigned to the charged hydrogen-bonding interaction established between the protonated amino group of the bound guest and the bridging P
1 binding model allowed us to determine the binding constants of the inclusion complexes of 1in with L-Pro and L-Pip as, K(L-Pro⊂1in)BBS = 3.2 × 105 M−1 and K(L-Pip⊂1in)BBS = 6.3 × 104 M−1, respectively. Analogous titration experiments of the 1out isomer with the two amino acids resulted in greater decreases of the emission intensity of the free receptor. In contrast, the binding constant values determined for the complexes of 1out with L-Pro and L-Pip are close to one order of magnitude lower than those of 1in. The increased binding affinity of the amino acids for the 1in receptors is assigned to the charged hydrogen-bonding interaction established between the protonated amino group of the bound guest and the bridging P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O function inwardly directed with respect to the polar aromatic cavity of the receptor.
O function inwardly directed with respect to the polar aromatic cavity of the receptor.
The sensing of amino acids (e.g.L-Pro, L-Pip and L-Phe) using IDA experiments with the ensemble composed by 1in and N-oxide 6 produced more significant emission changes than those of the direct BBS strategy. Remarkably, the IDA experiments induced fluorescence “turn on” instead of quenching. The binding constant values determined for the amino acid's inclusion complexes with 1in using IDA experiments were in complete agreement with those derived from the direct BBS counterparts. Receptor 1in showed binding selectivity for L-Pro over the other amino acids tested. Conversely, receptor 1out did not feature a noticeable selectivity in the amino acids’ binding. We assign the dissimilar receptors’ binding selectivity to the existence of an intermolecular hydrogen bond interaction between the bound amino acid and the P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group of the receptor. For geometrical reasons, the required arrangement of functional groups is only possible for the 1in diastereoisomer. The obtained results demonstrate the importance of dedicated polar interactions in determining binding selectivity.
O group of the receptor. For geometrical reasons, the required arrangement of functional groups is only possible for the 1in diastereoisomer. The obtained results demonstrate the importance of dedicated polar interactions in determining binding selectivity.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
We thank Gobierno de España MCIN/AEI/FEDER, UE (projects CTQ2017-84319-P and CEX2019-000925-S), the CERCA Programme/Generalitat de Catalunya, and AGAUR (2017 SGR 1123) for financial support. We thank Dr Eduardo C. Escudero-Adán, the X-ray Diffraction Unit of ICIQ, for help with the analysis of the X-ray crystallographic data.Notes and references
- Z. Lou, L. Wang and G. Shen, Recent Advances in Smart Wearable Sensing Systems, Adv. Mater. Technol., 2018, 3, 1800444 CrossRef.
- B. Purohit, A. Kumar, K. Mahato and P. Chandra, Smartphone-assisted personalized diagnostic devices and wearable sensors, Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng., 2020, 13, 42–50 CrossRef.
- S. Subrahmanyam, S. A. Piletsky and A. P. F. Turner, Application of Natural Receptors in Sensors and Assays, Anal. Chem., 2002, 74, 3942–3951 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Pinalli, A. Pedrini and E. Dalcanale, Biochemical sensing with macrocyclic receptors, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018, 47, 7006–7026 RSC.
- C. Guo, A. C. Sedgwick, T. Hirao and J. L. Sessler, Supramolecular fluorescent sensors: An historical overview and update, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2021, 427, 213560 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Pirondini and E. Dalcanale, Molecular recognition at the gas–solid interface: a powerful tool for chemical sensing, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2007, 36, 695–706 RSC.
- M. Ciardi, F. Tancini, G. Gil-Ramírez, E. C. Escudero-Adán, C. Massera, E. Dalcanale and P. Ballester, Switching from Separated to Contact Ion-Pair Binding Modes with Diastereomeric Calix[4]pyrrole Bis-phosphonate Receptors, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 13121–13132 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Ciardi, A. Galán and P. Ballester, Tetra-phosphonate Calix[4]pyrrole Cavitands as Multitopic Receptors for the Recognition of Ion Pairs, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 2047–2055 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Guinovart, D. Hernandez-Alonso, L. Adriaenssens, P. Blondeau, M. Martinez-Belmonte, F. X. Rius, F. J. Andrade and P. Ballester, Recognition and Sensing of Creatinine, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 2435–2440 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. M. Erenas, I. Ortiz-Gómez, I. de Orbe-Payá, D. Hernández-Alonso, P. Ballester, P. Blondeau, F. J. Andrade, A. Salinas-Castillo and L. F. Capitán-Vallvey, Ionophore-Based Optical Sensor for Urine Creatinine Determination, ACS Sens., 2019, 4, 421–426 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. F. Sierra, D. Hernández-Alonso, M. A. Romero, J. A. González-Delgado, U. Pischel and P. Ballester, Optical Supramolecular Sensing of Creatinine, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 4276–4284 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Martínez-Crespo, J. L. Sun-Wang, A. F. Sierra, G. Aragay, E. Errasti-Murugarren, P. Bartoccioni, M. Palacín and P. Ballester, Facilitated Diffusion of Proline across Membranes of Liposomes and Living Cells by a Calix[4]pyrrole Cavitand, Chem, 2020, 6, 3054–3070 Search PubMed.
- F. Maffei, P. Betti, D. Genovese, M. Montalti, L. Prodi, R. De Zorzi, S. Geremia and E. Dalcanale, Highly Selective Chemical Vapor Sensing by Molecular Recognition: Specific Detection of C1–C4 Alcohols with a Fluorescent Phosphonate Cavitand, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 4654–4657 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. C. Sedgwick, J. T. Brewster, T. Wu, X. Feng, S. D. Bull, X. Qian, J. L. Sessler, T. D. James, E. V. Anslyn and X. Sun, Indicator displacement assays (IDAs): the past, present and future, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50, 9–38 RSC.
- B. Plecko, C. Hikel, G. C. Korenke, B. Schmitt, M. Baumgartner, F. Baumeister, C. Jakobs, E. Struys, W. Erwa and S. Stöckler-Ipsiroglu, Pipecolic Acid as a Diagnostic Marker of Pyridoxine-Dependent Epilepsy, Neuropediatrics, 2005, 36, 200–205 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Peñuelas-Haro and P. Ballester, Efficient hydrogen bonding recognition in water using aryl-extended calix[4]pyrrole receptors, Chem. Sci., 2019, 10, 2413–2423 RSC.
- J. P. Perdew, Density-functional approximation for the correlation energy of the inhomogeneous electron gas, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 1986, 33, 8822–8824 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. D. Becke, Density-functional exchange-energy approximation with correct asymptotic behavior, Phys. Rev. A, 1988, 38, 3098–3100 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, G. E. Scuseria, M. A. Robb, J. R. Cheeseman, G. Scalmani, V. Barone, G. A. Petersson, H. Nakatsuji, X. Li, M. Caricato, A. Marenich, J. Bloino, B. G. Janesko, R. Gomperts, B. Mennucci, H. P. Hratchian, J. V. Ortiz, A. F. Izmaylov, J. L. Sonnenberg, D. Williams-Young, F. Ding, F. Lipparini, F. Egidi, J. Goings, B. Peng, A. Petrone, T. Henderson, D. Ranasinghe, V. G. Zakrzewski, J. Gao, N. Rega, G. Zheng, W. Liang, M. Hada, M. Ehara, K. Toyota, R. Fukuda, J. Hasegawa, M. Ishida, T. Nakajima, Y. Honda, O. Kitao, H. Nakai, T. Vreven, K. Throssell, J. A. Montgomery Jr., J. E. Peralta, F. Ogliaro, M. Bearpark, J. J. Heyd, E. Brothers, K. N. Kudin, V. N. Staroverov, T. Keith, R. Kobayashi, J. Normand, K. Raghavachari, A. Rendell, J. C. Burant, S. S. Iyengar, J. Tomasi, M. Cossi, J. M. Millam, M. Klene, C. Adamo, R. Cammi, J. W. Ochterski, R. L. Martin, K. Morokuma, O. Farkas, J. B. Foresman and D. J. Fox, Gaussian 09, Revision A.02, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford, CT, 2016 Search PubMed.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Synthetic procedures, characterization data, UV–Vis and fluorescence titrations, energy minimized structures. CCDC 2053978 and 2053980. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/d1qo00517k |
| ‡ We performed an additional solid–liquid extraction competitive experiment in which we left the suspension under stirring overnight. The 1H NMR spectra of the filtered solution did not show significant changes to the one obtained after 5 minutes hand-shook extraction. |
| § Solubility was calculated by preparing 1 mL saturated solutions of L-Pro and L-Pip in dichloromethane at 298 K. Evaporation of the solvent and accurate weight of the resulting solids returned the solubility of L-Pro and L-Pip in dichloromethane as 8 × 10−4 and 5 × 10−4 mol L−1, respectively. |
| ¶ We did not find significant differences in the fluorescence emission of 1in and 1out in dichloromethane. |
| || We did not see the formation of any precipitate after the addition of L-Pip to a micromolar dichloromethane solution of 1out as observed in the analogous experiments at millimolar concentration (i.e. NMR experiments). We consider that at micromolar concentration the L-Pip⊂1out complex is soluble in dichloromethane. Therefore, we conclude that the decrease in fluorescence intensity is not related to the precipitation of the complex. |
| ** Slit width of the monochromator as 1 nm. |
†† These experimental conditions forced us to modify the slit width of the monochromator settings (from 1 nm to 5 nm). These new parameters did not allow us to consider the 6⊂1in host–guest complex non-emissive as occurred with the previous instrument set-up. Hence, the titration data was fit to a theoretical 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 binding model that considered two emissive species (free and bound 1in). 1 binding model that considered two emissive species (free and bound 1in). |
| ‡‡ The competitive displacement of guest 6 from the cavity of 1in by L-Pro in CD2Cl2 was not possible at millimolar concentration due to the poor solubility of L-Pro in this solvent. |
| §§ The 6⊂1in complex was considered non-emissive under the experimental conditions and the instrument set up used for the titration (slit width of the monochromator = 1 nm). |
| This journal is © the Partner Organisations 2021 |