Advancements in rheumatoid arthritis therapy: a journey from conventional therapy to precision medicine via nanoparticles targeting immune cells
Anwesha
Laha
 a,
Simran
Nasra
a,
Simran
Nasra
 a,
Dhiraj
Bhatia
a,
Dhiraj
Bhatia
 b and
Ashutosh
Kumar
b and
Ashutosh
Kumar
 *a
*a
aBiological and Life Sciences, School of Arts & Sciences, Ahmedabad University, Central Campus, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad 380009, Gujarat, India. E-mail: ashutosh.kumar@ahduni.edu.in
bIndian Institute of Technology Gandhinagar, Palaj, Gandhinagar – 382055, Gujarat, India
First published on 15th July 2024
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a progressive autoimmune disease that mainly affects the inner lining of the synovial joints and leads to chronic inflammation. While RA is not known as lethal, recent research indicates that it may be a silent killer because of its strong association with an increased risk of chronic lung and heart diseases. Patients develop these systemic consequences due to the regular uptake of heavy drugs such as disease-modifying antirheumatic medications (DMARDs), glucocorticoids (GCs), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), etc. Nevertheless, a number of these medications have off-target effects, which might cause adverse toxicity, and have started to become resistant in patients as well. Therefore, alternative and promising therapeutic techniques must be explored and adopted, such as post-translational modification inhibitors (like protein arginine deiminase inhibitors), RNA interference by siRNA, epigenetic drugs, peptide therapy, etc., specifically in macrophages, neutrophils, Treg cells and dendritic cells (DCs). As the target cells are specific, ensuring targeted delivery is also equally important, which can be achieved with the advent of nanotechnology. Furthermore, these nanocarriers have fewer off-site side effects, enable drug combinations, and allow for lower drug dosages. Among the nanoparticles that can be used for targeting, there are both inorganic and organic nanomaterials such as solid-lipid nanoparticles, liposomes, hydrogels, dendrimers, and biomimetics that have been discussed. This review highlights contemporary therapy options targeting macrophages, neutrophils, Treg cells, and DCs and explores the application of diverse nanotechnological techniques to enhance precision RA therapies.
1. Introduction
In the 1800s, while examining patients complaining of severe joint pain, Augustin Jacob Landré-Beauvais first described RA.1 It is now known to be an autoimmune disorder, which is chronic in patients and affects the synovial joint lining. The causes extend to environmental, genetic, or both.Under normal body physiology, an acellular synovial membrane is found, composed of a fine layer of mostly macrophages and cellular components derived from fibroblasts.2 These macrophages display an inflammatory and hypertrophic phenotype in RA.3 The other effector immune cells involved in the pathophysiology are antigen-presenting cells (APCs) like dendritic cells and B cells. Neutrophils are also known for their immune roles in RA. All these cells secrete a plethora of chemical activators such as chemokines and cytokines that escalate the inflammation.4
RA, due to its effects, needs a proper diagnosis followed by immediate care and treatment. Research has shown that when RA is left untreated, patients subsequently lose their ability to work or move. Even in certain cases, the disease onset becomes so severe that the patients show symptoms of pulmonary granulomas and keratitis, which can prove fatal.5,6 On the other hand, some therapies have been created to treat or lessen the effects of RA. The majority of them deal with anti-inflammatory issues. The conventional drugs are mostly effective and some of them have been named and described in Table 1.7 However, studies have shown them to be endowed with a range of side effects (Table 1) and resistance in patients, owing to their non-specific action, excess, and repeated dosage.8 This has paved the way for efforts to discover more cell-based therapies and natural compounds with fewer side effects.
| Class of drugs | Mechanism of action | Side effects |
|---|---|---|
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) | (a) Analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory properties | I. Non-specific drugs |
| (b) Effects are caused by the suppression of inflammatory mediators produced by the cyclooxygenase (COX) pathway | II. Acute kidney ischemia | |
| III. Increased blood pressure | ||
| IV. Increased bleeding | ||
| V. Upper gastrointestinal complications | ||
| VI. Rashes | ||
| VII. Cardio-vascular effects | ||
| Glucocorticoids | (a) Anti-inflammatory activity pertaining to its action by binding to its receptor. | I. Cataract |
| (b) Glucocorticoid-receptor complex binds to cis elements called glucocorticoid response elements and results in the downstream effect | II. Metabolic disorders | |
| III. Peptic ulcers | ||
| IV. Osteoporosis | ||
| V. Diabetes | ||
| Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) | (a) Disease-modifying agents, some of which, like methotrexate are chemotherapeutic in nature | I. Nephrotoxicity |
| (b) Function by blocking molecular metabolisms like inhibition of purine or pyrimidine synthesis | II. Gastro-intestinal disorders | |
| (c) Can also block cell signalling components or cell–cell interactions | III. Retinal toxicity | |
| IV. Hepatic dysfunction | ||
| V. Infections | ||
| VI. Hematological disorders | ||
| VII. Pneumonitis | ||
| VIII. Leukopenia, neutropenia | ||
| IX. Skin infections | ||
| X. Central nervous system toxicity | ||
| XI. Sepsis |
To make drug targeting more specific, nowadays, nanotechnology comes in most handy. Nanostructures hold great promise as innovative delivery systems for drugs (DDSs) because they can be designed to deliver certain medication dosages to targeted locations. By enabling temporal regulation over the release kinetics of the drug and raising the biological availability of the medicinal component, they contribute to safe and effective DDSs. Nanotechnology usage in physio-chemical therapies, like in the replacement of joints, photothermal therapy (PTT), and photodynamic therapy (PDT) are a few cutting-edge RA therapeutic techniques.9 Biological nanoparticles are of greater importance pertaining to their high biocompatibility in the body and low toxicity. All these make nanotherapy an ideal choice in biomedicine. Diseases that are challenging to treat by conventional therapies due to the lack of specificity in targeting or regional bioavailability, like those in mitochondrial disorders, can be effectively treated by the advent of nanodrugs.10 Stimuli-regulated nanozymes have also been used in photothermal therapy in tumor microenvironments to release reactive oxygen species (ROS) for killing cancerous cells.11 Nanoparticles have also shown potential in the monitoring and detection of cancers such as colorectal cancer.12 They can also be used in the theragnostics of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) with increasing opportunities for personalized medicines.13 Similarly, this review discusses the advancements in RA therapy aided by nanotechnology.
In RA, many patients die due to a lack of information or awareness about the management of their symptoms. Hence, this review brings to the readers the current updates on the strategies being used or in the process of being developed for both managing the disease and stopping its progression. It takes the reader through conventional therapies, their side effects, recent therapeutics, and emerging solutions aided by nanotechnology for treating RA. It also aims to convey the various nanocarriers available and the potential advantages and disadvantages that come with them for the treatment of RA.
2. Role of macrophages in RA
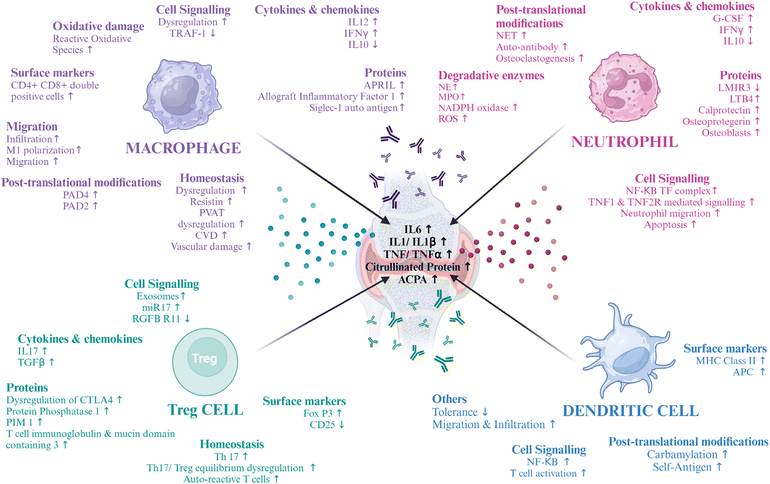
Macrophages are immune cells that are found in three different phenotypes, depending on the physiological condition of the body.14 M0 or naive macrophages are found under normal body physiology, which when intruded by pathogens or other potent harmful cells, get converted to activated or proinflammatory M1 macrophages, secreting inflammatory cytokines and other bioactive substances, to save their soul. These signals that convert M0 to M1 can be lipopolysaccharides (LPS), granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) or cytokines like interferon-gamma (IFNγ), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF). M1 macrophages are a repertoire of secreting inflammatory cytokines that lead to progressive joint erosion, namely interleukin 6, 12, 1β, and TNF.15 Similarly, certain cytokines like IL-10 can get these M1 macrophages transformed into anti-inflammatory macrophages (M2), which then secrete signals and get converted to M0 macrophages, returning to normal body homeostasis. This is the cycle of polarization of the macrophages by the immune system to protect the body from diseases. However, under certain disease conditions, this homeostasis is jeopardized, and there is hyperactivation of pro-inflammatory macrophages, which overexpress cytokines, attacking the own body tissues and cells, like in autoimmune diseases like RA.16 In RA, NF-κB, MAPK, JAK/STAT, Notch, and other signaling pathways control the M0–M1 phenotype conversion. Additionally, this process is aided by metabolic reprogramming, whereby M2 macrophages employ oxidative phosphorylation while M1 macrophages prioritize glycolysis.17 Maintenance of homeostasis is regulated by different receptors, one of which is colony stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R).18 Thus, these long-lived macrophages, which are tissue-resident cells, play an important role in determining inflammatory tissue priming with the infiltration of lymphoid and myeloid immune cells, secreting effector proteins, namely antibodies, cytokines, and vesicular structures, that can regulate systemic functions.19In macrophages and monocytes, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 1 (TRAF1) is thought and found to have an inhibitory role in the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, inflammasome-mediated IL1 secretion, and NF-κB activation. Thus, it is hypothesized that macrophages in RA lack TRAF1, but conducting conclusive experiments is difficult due to the polymorphisms found in TRAF1.20 An adipokine, resistin, has the potential to hyperactivate macrophages by adenylate cyclase associated protein 1 (CAP1), which leads to perivascular adipose tissue damage (PVAT), leading to cardiovascular diseases (CVD), one of the leading causes of death in RA.21 Double positive macrophages, that are both CD4 and CD8 positive macrophages, are markers of inflammation and are involved in inflammation of the Th1 type.22 Secretion of the soluble form of A proliferation inducing ligand (APRIL) from macrophages induces the viability and formation of B cells, leading to B cell-mediated auto-immunity. An Ig-like lectin family protein, Siaglec1, that can bind sialic acid, undergoes activation in macrophages, leading to an increase in C-reactive protein (CRP) and IgM – rheumatoid factor. Allograft inflammatory factor 1 is overexpressed in RA which initiates and maintains inflammation in the RA synovium.23 NF-κB signalling is crucial to the pathophysiology of RA. The involvement of NF-κB in the synthesis of the chemokine IL-8 and macrophage inflammatory protein-1α supports this claim.24
In the joint environment, monocytes are activated and polarized into pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages, which is a part of the pathophysiology of RA.25 Chemoattraction of monocytes to the arthritic joint is mediated by proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1, TNF and IL-6, produced by resident cells, such as macrophages and FLSs. By connecting to their receptors, these cytokines stimulate monocytes, which increases the expression of adhesion molecules and chemoattractant receptors on the surface of the cells. Consequently, the monocytes migrate into the synovial tissue and cling to the blood vessel endothelium. CD80 and CD86 and other markers present on the surface, which enable interactions and improve the presentation of the antigen via T cells, are expressed at higher levels by activated monocytes, along with CD14 and CD16.26
In RA, there is decreased autophagy in macrophages, which leads to ROS production. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARG) accelerates autophagy and prevents ROS-mediated macrophage polarization and “NOD-like” receptor protein (NLRP3) inflammasome activation, thus reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and their accompanying stress.27
In murine collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) and synovial biopsies from RA patients, macrophages in the secondary lymphoid organs (SLOs) and synovial ectopic lymphoid-like structures (ELSs) were found to produce peptidyl arginine deiminase 4 (PAD4). Intracellular citrullinated histone release and macrophage extracellular trap formation (METosis) were demonstrated by activated murine and synovial fluid macrophages. Hence, lymphoid tissue macrophages have a role in the synthesis of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs) and the citrullination of self-antigens, suggesting that focusing on them specifically can help treat autoimmune diseases that depend on citrullination.28 Thus, the various changes in macrophage physiology make them a good target for RA (Fig. 1). Various molecular markers of RA are being targeted to deliver a cell-based therapy, some of which have been cited in the table below (Table 2).
| Targets | Outcomes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| TRAF1 | An increase in the expression of TRAF1 or infiltration of macrophages with expressed TRAF1 can have a therapeutic effect | 20 |
| Resistin | Inhibition of resistin can control PVAT, thus lowering CVD | 21 |
| Iguratimod | Inhibits activation of the IL-4/STAT 6 signalling pathway and has anti-fibrotic effects and prevents chronic kidney disease (CKD), inhibits macrophage infiltration, M1 polarization, and RAW264.7 migration | 29–31 |
| CSF1 & IL34 | Can regulate macrophage homeostasis via CSF1R | 18 |
| APRIL | Inhibiting APRIL can lead to the lowering of B cell-mediated autoimmunity. Atacicept is an antagonist of APRIL. | 32 |
| Siaglec-1 | Downregulation of this can decrease the CRP and IgM – rheumatoid factor and reduce inflammation | 33 |
| Allograft inflammatory factor 1 | Inhibition of this can stop the proliferation of inflammatory macrophages | 34 |
| Pro-inflammatory cytokines | Reduction in the levels of IL12, TNF, IL1β, IL6, and IFNγ can help control immune reactions. A potent TNF antagonist is infliximab | 35 |
| CTLA4 | Inhibitor of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA4) shows antigen presentation by macrophage-T cell cooperation mediated by cell–cell contact | 36 |
| PPARG | Reduces ROS production in macrophages | 27 |
| Neutrophil cytosolic factor 4 (NCF4) | Cysteine peptides are kept in an oxidized crosslinked state by NCF4-dependent intracellular ROS, which shields against autoimmune arthritis by preventing the non-tolerized T cells from the presentation of peptides | 37 |
| JAK inhibitors | JAKi can increase MAFB expression, and it also promotes macrophage reprogramming toward the acquisition of a more anti-inflammatory/pro-resolution profile | 38 |
| Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) | Inhibition of this might have potential therapeutic effects on RA | 39 |
| Total glucoside of Paeonia (TGP) | Modulates various cell signalling pathways to control inflammation | 40 |
| Peptidylarginine deiminase 4 & 2 (PAD4 & PAD2) | Inhibition of these can lead to a decrease in the citrullination of peptides and reduce the formation of autoantigens | 28 and 41 |
| Acetylcholine | Dose-dependent inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine release from macrophages | 42 |
3. Role of neutrophils in RA
Neutrophils are a key player implicated in RA pathophysiology. Overexpression of Fcγ receptors is found on the surface of activated neutrophils. A plethora of bioactive inflammatory molecules are secreted by them. Some of them are IFNγ, TNFα, IL1β, IL6 and G-CSF, which are produced when immune cells interact with synoviocytes, causing synovitis.43 This can also lead to osteoclastogenesis via IL10, TGF-β, and IL6. The situation is further aggravated when these osteoclasts act as APCs and lead to the activation of Th and Tc cells.44,45Neutrophils are also associated with the release of degradative enzymes.46 Myeloperoxidase (MPO) is one such enzyme that activates T cells and DCs and is linked with the consumption of nitric oxide (NO), leading to the generation of nitrite ions (NO2−).47,48 Another serine protease named neutrophil elastase (NE)49 activates proteinase activating receptors (PARs)50,51 and leads to cartilage destruction.52 NADPH oxidase is also produced by neutrophils, which produces superoxide radicals, thus increasing the burden of reactive oxygen species (ROS).53 In RA, neutrophils are reported to decrease apoptosis, which is preceded by an increase in the upregulation of NF-κB transcription factor complexes. This leads to the upregulation of the TNF 1 and 2 receptors, and this mediates the migration of neutrophils in the RA synovial fluid. A chemoattractant leukotriene B4 (LTB4) can lead to increased neutrophil activation and recruitment.54 The upregulation of RANKL increases the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), which are composed of a network structure containing granular enzymes and chromatin that not only traps bacteria but also increases the quantum of autoantigens, as NETs are composed of citrullinated proteins mediated by PAD4. These NETs are then counter-attacked, generating auto-antibodies, i.e., anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs). NETs also increase osteoclastogenesis which leads to elevated bone erosion.55 NETs are found to be carbamylated, which is associated with signalling for rapid osteoclast formation.54 Thus, neutrophils are important in the pathophysiology of RA (Fig. 1) and are important targets for therapy, and some of the molecular targets are mentioned below in Table 3.
| Target | Outcomes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| NETs by inhibiting PAD4 | Inhibiting the formation of NETs by inhibiting PAD4, can prevent bone erosion and the generation of autoantibodies. Inhibiting carbamylation can also be a target | 56–58 |
| Apoptosis | Inducing apoptosis can help in downregulating signalling via the NF-κB pathway, helping in reducing inflammatory responses. Celastrol is a drug that can be used for this | 59 and 60 |
| TNFα | Inhibition of these can help reduce osteoclastogenesis and neutrophil migration | 43 |
| IL6 receptor | Inhibiting this can reduce osteoclastogenesis | 43 and 61 |
| MPO, NE, NADPH oxidase & glutathione peroxidase 3 (GPX3) | Inhibiting these degradative enzymes can help in decreasing the chemokines and ROS burden in the synovium | 43 and 62 |
| LTB4 receptor (BLT1) | Inhibiting this receptor can slow down bone erosion | 63 |
| Leukocyte mono-immunoglobulin-like receptor 3 (LMIR3) | It controls inflammation negatively and is highly expressed in neutrophils. Dehydroandrographolide can bind to LMIR3 and prevent neutrophil activation | 64 |
| Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) | Inhibition of PGE2 can decrease NETosis and neutrophil infiltration | 65 |
4. Role of Tregs in RA
FoxP3 expressing Tregs are known for their immunosuppressive functions.66 The prevention of autoimmunity and maintaining tolerance are their primary functions. However, there is a drop in their number as well as their function in RA.67,68 The levels of cytokines like IL6 and TNFα are upregulated, which has important implications for the improper expression of FoxP3, which leads to a deficiency in the function of Tregs. This regulation is there at both protein and gene levels and passes via cell signalling pathways.69,70 IL1β is another cytokine implicated in this.71 IL2 and IL21 are also important for maintaining the homeostasis of Tregs that are dysregulated in RA.72 The reduction of T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3 was found to play a role in the dysfunction of Tregs.73 Wang L. et al. found that a microRNA, miR-17, targets the TGFBRII receptor, thus leading to the suppression of Treg differentiation. This miRNA was found to be transferred via exosomes.74 In RA, Tregs and Th17 compete with one another to create a dynamic equilibrium. One important cause of RA is an imbalance in this immunological balance.75,76 Consequently, rectifying the Treg/Th17 cell imbalance, decreasing the number of Th17 or IL-17A levels, and raising peripheral blood Tregs in RA patients may be essential to treating the disease (Fig. 1). Some of the other therapeutic targets are mentioned in Table 4.| Target | Outcome | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| IL 6 receptor | Inhibitor or anti-IL6 antibodies can increase the number of Tregs | 77 |
| IL2 | Helps in the induction of Tregs | 78 |
| PI3K-Akt-mTOR signalling axis | Controlling this can help in controlling the regulation of Tregs. In this regard, rapamycin and all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) are potent candidates in the promotion of the proliferation of Treg cells | 79 |
| TNF | Administration of TNF blockers can help reduce inflammation by removing its suppressive function on the FoxP3 function | 80 |
| CTLA4 | Inhibiting this using a CTLA4-Ig can help in controlling RA by inducing the formation of Treg cells | 81 |
| Treg | 1. To restore quantity and function, Treg-based therapies can also serve as a potent therapeutic. | 82–89 |
| 2. Transfer of functional Tregs has been seen to be effective. | ||
| 3. Another strategy being used is the use of chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) for enhancing the inhibitory effect of Tregs on autoantigens. | ||
| 4. Combination therapy of polyclonal Tregs and IL2 is also in pre-clinical trials. | ||
| 5. Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) shows the potential to stabilize Tregs. | ||
| 6. Bifidobacterium's polysaccharide A is a bacterial product that has the capability of inducing Tregs. | ||
| 7. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and immunoglobulin D (Immunoglobulin D, IgD)-Fc-Ig can stabilize the Th17/Treg equilibrium. |
5. Role of dendritic cells in RA
The interaction between the antigens generated in the body and the adaptive immune cells is regulated by DCs. By cross-presenting antigen to CD8+ T cells, stimulating the generation of B cell antibodies, and activating and priming the effector CD4+ T cells, DCs serve as a link between the two types of immune systems in the body.90 Additionally, DCs are regarded as important in preserving immunological tolerance. It is believed that in RA, DCs activate Tfh or inflammatory T cells which react with self-epitopes and, subsequently, B cells, which in turn stimulate autoantibodies.91,92 The DCs are found in the center of clusters of T cells in the RA synovium, which express different receptors like CD80, CD86, adhesion molecules, and CCR7, which helps in Th1 and Th2 phenotype formation from T cells, producing various cytokines. In turn, the synovium of RA also promotes differentiation of the DCs.93 It is said that the hypoxic conditions in the RA environment, along with increased glycolysis and anabolism, lead to the reprogrammed metabolism of the inflammatory DCs, which leads to their hyperactivation.94 Thus, switching the DCs to catabolism can have therapeutic potential in RA.DCs are attracted in large quantities to the tissues and synovial fluid of RA patients’ joints.95 The majority of these synovial DCs are mature, and there is overexpression of NF-κB. Disease activity and nuclear RelB expression are correlated, suggesting that DCs are susceptible to local inflammatory PAMPs, DAMPs, and/or cytokines, such as TNF.96 RA synovial tissue contains several subsets of MHC class II+ APCs, such as MHC class IIhi fibroblast-like synoviocytes, CD11c + CD20+ activated B cells, and cells with activated Toll-like receptor (TLR), myeloid in origin.97 Multiple APC types may therefore continue to present synovial fibroblast or cartilage autoantigens, such as type II collagen (CII) and HCgp130, to primed migratory memory T cells of the synovium after inflammatory arthritis has begun.98 Self-epitopes found on autoantigens can be citrullinated to enhance binding to the shared epitope (SE) on HLA-DR alleles. Subsequently, this mechanism promotes autoreactive T-cell proliferation. Thus, neoepitopes add to the biological foundation of RA vulnerability, which is supplied by HLA-DR alleles that are SE-positive (SE+).99 Furthermore, during periods of stress or infection, cross-presenting DCs that take up citrullinated necrotic antigens may be co-stimulated by CD4+ T cells specific to citrullinated antigens. This may help in the establishment of B cell germinal center (GC) differentiation and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) specific to citrullinated peptides and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA+).
DCs play a significant role in peripheral tissues and the thymus’ ability to maintain tolerance. Nevertheless, persistent DC ablation breaks down this self-tolerance in CD4+ T cells, which triggers autoimmunity.100 DCs are therefore crucial therapeutic targets in the management of RA, and some of the molecular components that can be used to target these cells are mentioned below in Table 5 (Fig. 1).
| Target | Outcomes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| TGP | Modulates various cell signalling pathways to control inflammation | 38 |
| NF κB/nuclear RelB | A decrease in this signalling can decrease DC activation | 94, 101 and 102 |
| Citrullinated peptides | A decrease in the levels of these can decrease the number of autoantigens in the body, which can decrease their presentation by the DCs | 99, 101 and 103 |
| TNF, IL1 & IL6 | These cytokines are products of DCs and decreasing these can decrease the quantum of inflammation | 23, 98, 101 and 102 |
| Tolerogenic DC or immunometabolism of DCs | Making DCs tolerogenic by inducing apoptotic cell death or anergy is also a potent therapeutic for curing RA by producing high amounts of IL10 and TGF-β | 92, 98 and 104 |
| IL4 | Modifying DCs to modify the production of IL4 is a therapeutic strategy to reduce the impact of RA | 91 and 102 |
| GM-CSF | Controlling their production can control the differentiation and migration of the DCs. Mavrilimumab is a monoclonal antibody and a potent drug for targeting GM-CSF | 100, 102 and 105 |
6. Potential nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery in RA
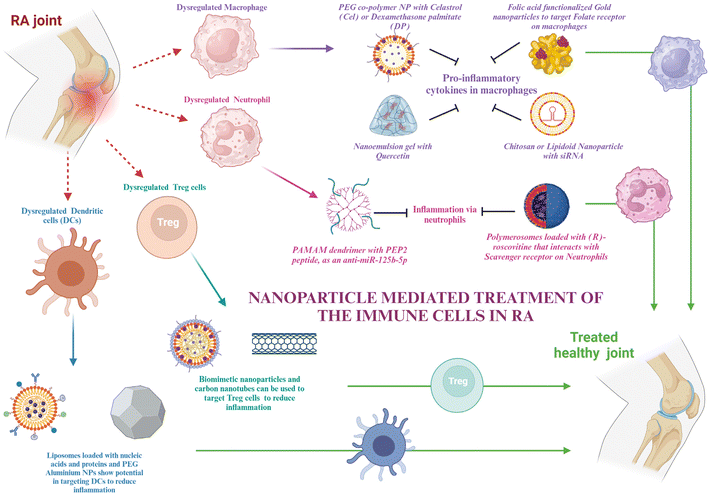
Nanotechnology is defined as the science of making structures that range in nanometers in terms of size. The smaller size of the particle not only helps in reaching regions that are deep-seated in the body but also increases the surface-to-volume ratio that allows us to functionalize the surface with different molecules. This functionalization is important for achieving very specific and targeted delivery. Functionalizations can be done using protein ligands, aptamers, or antibodies specific to the cells to which they are targeted. Moreover, nanoparticles show the properties of controlled release of drugs, enhanced circulation time, and reduced drug clearance. Based on these advantages, the dosage of the drugs can be reduced, which potentiates their reduction of toxicity and hence side effects along with negating off-target anomalies. The immune cells’ role in RA and their molecular components for therapeutic targets have been discussed in the earlier sections. This section talks about some inorganic and organic nanoparticles that are in use and have the potential to be used for RA therapeutics, along with their advantages and disadvantages in the subsequent sections (Fig. 2).For passive targeting, at the inflammatory site, due to the leaky vasculature and increased macrophage infiltration, the enhanced uptake and retention effect can select nanodrugs in the synovial tissue and retain them.106 Specifically, particles of size 100–200 nm are favorable as they are neither taken up by the spleen nor flushed out by the phagocytic system.107 Active targeting, however, is easy, as only the receptor for the cells needs to be known.
6.1. Nanoparticles to target macrophages
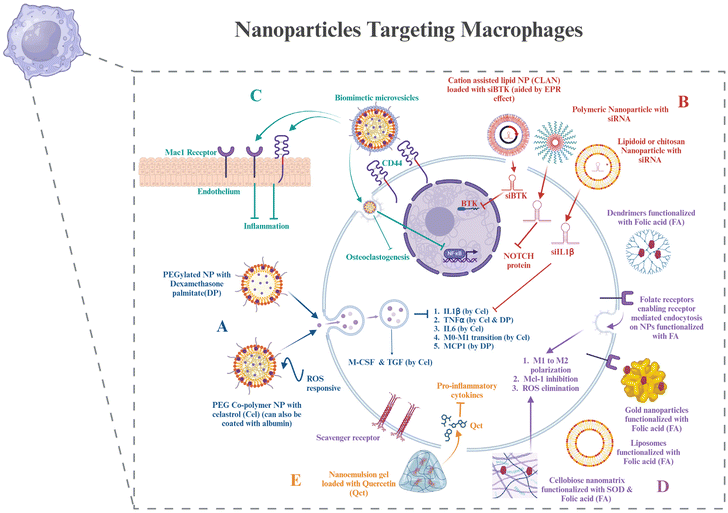
Macrophages, as discussed in section 2, are important mediators of RA. The molecular targets in macrophages that can help in the therapy have already been discussed. In this section, various nanomaterials that can encapsulate the target drug for macrophages and be used for targeted delivery will be discussed.Polyethylene glycol is used for making stealth nanoparticles, enhancing their retention at the targeted site. A diblock copolymer named PEG-block-poly(propylene sulphide) was synthesized and loaded with celastrol, which was ROS responsive. This nanoparticle prevented Notch1 and NF-κB activation, along with the suppression of proinflammatory cytokines like IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6. It also aided in the enhancement of anti-inflammatory cytokines like M-CSF and TGF and suppressed M1 macrophage activation.108 Cel has also been delivered using albumin-coated nanoparticles.109 Heo et al. synthesized PEGylated dexamethasone palmitate nanoparticles that showed high permeability at the inflammatory site, and dexamethasone palmitate helped in TNFα inhibition and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP1) inhibition in macrophages. They were also retained for a longer time due to PEGylation.110 An approach for downregulating BTK in macrophages was using siBTK delivered using cation lipid assisted nanoparticles (CLAN), which overcame the disadvantages of poor permeability and stability of siRNA due to the EPR effect.111 Amphiphilic PEG analog F127 (PEO-PPO-PEO) was used by scientists to modify lipidoid nanoparticles that delivered siIL-1β.112 Chitosan nanoparticles have been used to deliver siRNA for inhibiting the Notch pathway, preventing bone erosion.113 Researchers have designed polymerosomes functionalized with mannose for targeting macrophages. This can be used for the delivery of different drugs to macrophages to reduce inflammation, one of which is hydroxychloroquine.114 Polymeric nanoparticles are another group of nanoparticles that can be used in the treatment of RA.115
Nowadays, biomimetic nanoparticles are of great importance as they mimic the natural cell membrane components, thus causing the least immunogenic reaction in the body and prolonging the circulation time in the body.116 Scientists have used microvesicles, which are macrophage-derived, to decrease the host's ability to eliminate MNPs and extend their retention in the body. They can also detect CD44 or macrophage antigen 1 (Mac-1), impersonate a macrophage to interact with M-CSF and the NF-κB ligand–receptor activator (RANKL) for the suppression of osteoclastogenesis and attach to the endothelium to target the inflammatory region.117 Targeting the nanoparticles actively can also be a strategy by using the receptors of the macrophages, which are CD44, folate, and scavenger receptors. Their respective ligands can be used or antibodies against the receptors can also target the nanoparticles.118 Through the use of AgNPs tagged with FA ligands, researchers were able to specifically target M1 macrophages and cause intracellular GSH to release Ag+. It improved efficacy by leading to the death of M1 macrophages and the removal of ROS, allowing M1-to-M2 repolarization and lowering inflammation.119 The PEGylated liposome combined with folic acid (FA) may particularly target macrophages that are actively involved in using FRβ. Suppression of inflammatory cytokines and promotion of M1 macrophage polarization to M2 for RA therapy were achieved by the silencing of the canonical inflammatory signaling pathway, NF-κB p65.117 Among the antiapoptotic B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) protein family, the myeloid cell leukemia-1 (Mcl-1) protein was shown to be overexpressed in RA patients’ synovial macrophages. By preventing the proapoptotic protein Bax from being activated, Mcl-1 shields macrophages against apoptosis. In order to treat RA, NPs mediate the suppression of the Mcl-1 protein's expression in activated macrophages, causing apoptosis. Researchers used the FR-mediated transport of nanoparticles to deliver Mcl-1/siRNA for inducing apoptosis.120 Superoxide dismutase (SOD) can be used as a ROS scavenger and as a treatment for RA. For this, a cellobiose-coated nano-matrix (CNM) was made using a fiber disaccharide solution and a propylene sulfide nano-matrix. The targeted ligand FA was conjugated to SOD yielding F-SOD. After that, CNM was adsorbed to the F-SOD solution, resulting in the creation of cellobiose-coated FA-SOD NPs (FECNM). The porous cellobiose coating on the NPs provides the advantage of strong adsorption properties and thus proves to be an effective way to adsorb SOD.121
In Pandey et al.'s study, Au-NPs were modified with a thiolated dendritic polymer to produce nanogold core dendrimer NPs (Au-DEN-NPs). The –OH groups on the surface of the NPs were conjugated using methotrexate (MTX), and IR780, a near-infrared bioactive material, was enclosed to offer a photothermal advantage. MTX is an FA analog.122 Owing to the side effects of MTX, a similar dendritic nanoparticle can also be used to target any of the potential targets on macrophages, as discussed in section 2. Gokhale et al. developed a nanoemulsion (NE)-based gel loaded with quercetin (QCT) (QCT-NE gel) to treat RA. QCT-NE was prepared by spontaneous emulsification techniques. Because of its high skin permeability, it also reduces the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and can be applied transdermally.123 Hence, these are some strategies for targeting macrophages via nanotechnology for delivering cell-based therapeutics (Fig. 3).
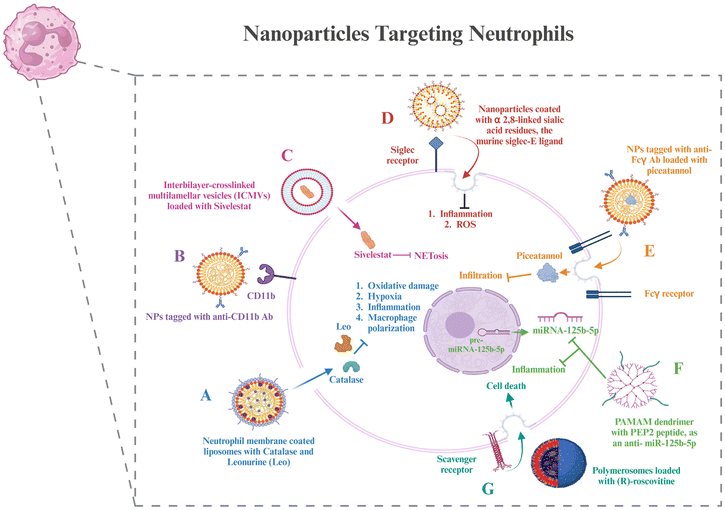
6.2. Nanoparticles to target neutrophils
Although several chemokines and signaling pathways have been shown to be useful targets for manipulating neutrophils, which include altering their properties and influencing their infiltration and activation, anti-neutrophil treatments and neutrophil depletion have not proved successful in clinical trials. This is probably because they have an indiscriminate effect on neutrophils throughout the body and exhibit very little selectivity for the inflammatory site. To accurately manipulate and prevent disturbing the innate immune homeostasis, tailored distribution to neutrophils precisely in the inflammatory areas is necessary.124 This section describes certain nanotechnological strategies that have been used to treat RA and can be used for delivering therapy to neutrophil targets, as discussed in section 3 (Fig. 4).Neutrophil membrane-coated nanoparticles were created by fusing neutrophil membranes onto polymeric cores. These nanoparticles inherit the antigenic exterior and related membrane functions of the donor cells, making them perfect decoys for biological agents that target neutrophils. These nanoparticles have demonstrated the ability to target deep into the cartilage matrix, decrease synovial inflammation, neutralize proinflammatory cytokines, and offer robust chondroprotection against joint injury.125 To modify the unfavorable microenvironment for RA remission, researchers have created a neutrophil membrane-cloaked, naturally occurring anti-arthritic drug called leonurine (Leo) and a catalase (CAT) co-loaded nanoliposomal system called Leo@CAT@NM-Lipo. It successfully reduced paw swelling, decreased the score for arthritis, lessened the damage to bone and cartilage, and cured several organ dysfunctions in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) by combining the synergistic actions of inflammation resolution, ROS scavenging, macrophage polarization, and hypoxia relief.126 CD11b and Fcγ receptors are receptors overexpressed on activated neutrophils. Antibodies against these can be coated onto different nanoparticles loaded with drugs to deliver them to neutrophils.127,128
Wang et al. administered piceatannol, a tiny chemical that inhibits “outside-in” β2 integrin signaling pathways in leukocytes, to active neutrophils in the bloodstream using albumin nanoparticles. The studies also showed that Fcγ receptors were required for albumin nanoparticle uptake by neutrophils connected to the inflammatory endothelium, which are highly expressed on activated neutrophils. Compared to free piceatannol, this method successfully separated adherent neutrophils from the endothelium, preventing neutrophil infiltration.129 Delivery techniques based on nanoparticles provide tools to target NETosis for better therapeutic outcomes. Mice exposed to LPS-induced endotoxic shock were saved by sivelestat, an inhibitor of neural epithelial cells, which was given through interbilayer-crosslinked multilamellar vesicles (ICMVs).130 A further investigation showed that siglec receptors can be targeted by nanoparticles coated with α2,8-linked sialic acid residues, the murine siglec-E ligand, which reduces inflammatory responses.131 It is interesting to note that α2,8-sialylated nanoparticles reduced ROS in neutrophils, which in turn prevented NET formation.132
Scavenger receptors were required in one investigation for the polymersomes’ transport of (R)-roscovitine to neutrophils.133 After that, the polymersomes broke free of the early endosomes due to a pH-triggered disintegration process, which made it possible to transfer R-roscovitine into the neutrophil cytoplasm without stimulating the cells. R-Roscovitine induced neutrophil death, which reduced inflammation. PEP2, a citrullinated peptide, and an antisense oligonucleotide that targets a microRNA, anti-miRNA-125b-5p, were combined into two different kinds of nanoparticle formulations: chitosan-hyaluronic acid and PAMAM dendrimers. Both varieties of nanoparticles demonstrated high cell targeting efficacy and provided effective drug delivery vehicles.134
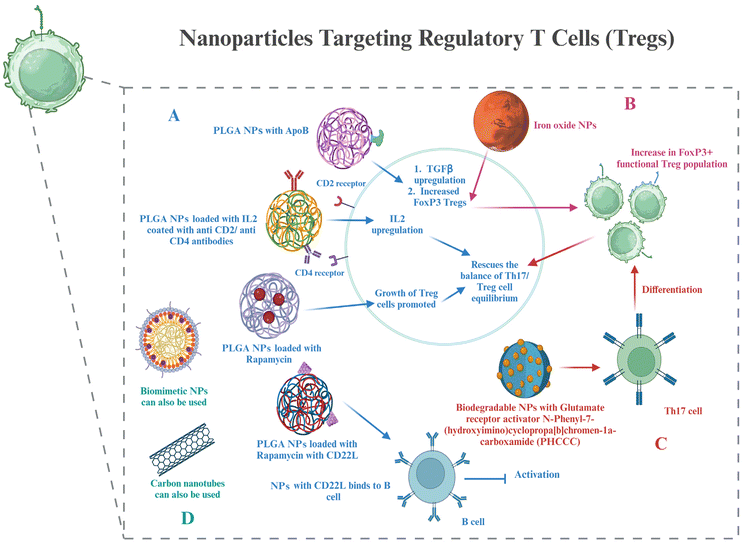
6.3. Nanoparticles to target Treg cells
Treg cells, as discussed in section 4, are important components for maintaining T cell homeostasis that gets dysregulated in RA. The quantity and function of Treg cells are both hampered in RA. Potential targets to resolve these issues have already been discussed. This section shows glimpses of certain approaches for targeting Treg cell therapies via nanotechnology. The creation of hybrid nanoparticles (NPs) that help B and T cells establish tolerance has been reported by researchers. The NPs are made up of a lipid monolayer that encloses a rapamycin-loaded PLGA core that stimulates the growth of regulatory T cells (Tregs). The lipid monolayer contains both the protein antigen and a ligand of the B cell inhibitory co-receptor CD22 (CD22L), which together block B cells from activating when they come into contact with the antigen. The outcomes demonstrate this adaptable NP platform's potential for reducing autoimmune illness and promoting immunological tolerance to a self-antigen.135Functionalization with the right ligand to target the highest affinity receptor plays a very important role in nanoparticle design. Evidence that ApoB coating on nanoparticles increases their rate of uptake by liver epithelial cells came from such a study, showing that ApoB's higher affinity for its cognate receptor can enhance drug uptake compared to the bare nanoparticles or using any other ligand–receptor complex. It resulted in enhanced secretion of TGF-β after receiving an injection of the nanoparticle formulation, and this increased FoxP3+ Tregs in the lungs, thus showing their potential in allergy treatment.136 Negatively charged particles may target LSECs due to the stabilin receptors on LSECs, which show preference for binding negatively charged particles.137 Carambia et al., for instance, produced anionic iron oxide nanoparticles with a poly(maleic anhydride-alt-1-octadecene) coat. Following intravenous injection, the particles were quickly removed from the plasma and gathered in LSECs together with their antigen load, which increased the number of Foxp3+ Tregs.138 All these studies have been done on liver cells; however, these same strategies can be used to target synovium cells as well.
A biodegradable nanoparticle containing a small chemical glutamate receptor enhancer, N-phenyl-7-(hydroxyimino)cyclopropa[b]chromen-1a-carboxamide (PHCCC), was utilized to change the development of Th17 cells into Treg cells, as well as to reduce the drug's toxicity by 36 times and release 89% of the drug under regulated conditions.139 FoxP3+ Treg plays a major role in the control of autoimmunity, and studies have shown that low doses of IL-2 can activate Tregs and enhance their capability of suppression.140 Because of this, a number of studies were based on utilizing IL-2 via nanocarriers to affect autoimmune events and alter the biology of regulatory T cells. Horwitz et al. loaded PLGA nanoparticles with IL-2 and TGF-β in an experimental context and then coated them with anti-CD2/anti-CD4 antibodies to achieve T cell-specific targeting.141 In a mouse model of lupus erythematosus, systemic treatment of these nanoparticles led to decreased disease activity in vivo and promoted the proliferation of Tregs both in vitro and in vivo. This same strategy can be used in the treatment of RA as well.
Biomimetic nanoparticles based on Treg cells have been synthesized and effectively used for immunomodulatory purposes.142 Single-walled carbon nanotubes have also been successfully used to target Treg cells in tumor microenvironments.143 Thus, even though not many nanoparticles targeting Treg cells have been used in RA treatment, all the above strategies can be used in the treatment of RA, which lies in the future scope (Fig. 5).
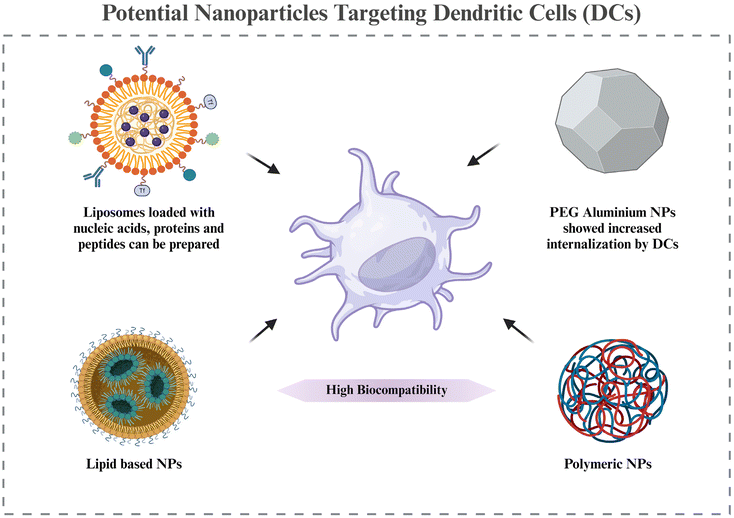
6.4. Nanoparticles to target DCs
Based on the discussion of the cellular targets of DCs in RA in section 5, this section discusses the possible strategies for targeting the DCs via nanomedicines. There is very little evidence of targeting DCs in RA via nanotechnology; however, the potential approaches by which DCs can be targeted for nanotherapy are being highlighted.Adaptive antitumor immunity depends on DCs’ capacity to collect, process, and present antigens to stimulate T cell priming. As a result, DC-targeting nanomaterials are thought to be a viable strategy for enhancing an effective and focused immune response against cancer. Additionally, multifunctional compounds are combined in nanomaterials to modify the antigen presentation in whole or in part.144 Lipid-based and polymeric nanoparticles have been shown to have greater biocompatibility when used to create DC-targeted vaccinations for antiviral and anticancer therapies.145,146 The potential of liposome-based nanoparticle encapsulating molecules such as heat shock proteins, OVA, and the trivalent influenza antigen to stimulate the immune system in the therapy of disease has been studied. In order to prepare DCs for later strategies that aim to directly activate them in vivo, it may be necessary to deliver protein, peptide, and nucleic acid antigens to them via nanomaterials. This could improve DC circulation and reduce DC breakdown in vivo. These antigens may trigger the right kind of immunological reaction.147 Additionally, nanomaterials (such as gold or aluminum nanoparticles) likely improve internalization at the single-cell level.148 Using PEG-stabilized nanoscale aluminum particles (100 nm) demonstrated increased internalization in antigen-presenting cells. Consequently, nanotechnology not only improves the bio- or physicochemical features of antigen formulations through antigen protection, quantity enhancement, function conjunction, and the presentation of antigens, but it also redefines the efficacy of conventional agents or materials with potentially novel functions in modulating antitumor immunity.149,150 All of these benefits are directed toward the development of adaptive immunity against cancers.
In cancer, there is a requirement for upregulation of DC activation, for which the above examples are cited. However, in RA, we need to downregulate DC activation. Hence, this section is just to take note of the nanocarriers and their advantages that can be used for targeting DCs in RA. The therapeutic molecules and their expected downstream regulations will be different in RA compared to cancer. Further research in making nanocarriers targeted to DCs, specifically in RA, is required, while also noting the potential effects of already known DC-targeted nanoparticles used in other diseases, as that might give an idea of the pros and cons of each of the nanomaterials in RA targeting (Fig. 6).
The discussions on targeting immune cells in RA give a clear idea that using nanotechnology not only reduces the quantum of side effects but also increases its efficacy by many folds. But when a wide range of nanoparticles is available for researchers to choose from, it becomes essential to take note of the advantages and disadvantages of each nanoparticle before using them. It is also important to note the possible routes of administration for them to improve patient convenience, depending on the disease severity. Tables 6 and 7 enlist the administration routes, advantages, and disadvantages of inorganic and organic nanoparticles that can be used for RA therapy.
| Nanoparticles | Administration route | Advantages | Disadvantages | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic nanoparticles | Intra-articular, intravenous, intra-peritoneal injection | I. Can be functionalized with multiple groups | I. Particle instability | 151–156 |
| II. Can be made of any size and shape | II. Toxicity in the human body | |||
| III. Due to their electric and magnetic properties, they can be coupled with different radiations for photothermal or photodynamic therapy | III. Generation of the nanoparticles can build up toxicity | |||
| IV. Many need triggers to release the cargo | ||||
| V. Poor solubility | ||||
| VI. Accumulation in the blood can block blood flow | ||||
| Non-metallic nanoparticles | Intra-articular injection | I. High loading capacity | I. Poor solubility | 155 |
| II. Good biological degradability | II. Biosafety is highly varied depending on the formulation | |||
| III. Silica has good surface properties enabling better functionalization | ||||
| Cationic nanoparticles | Intra-articular injection | I. Improved pharmacokinetic properties | I. Cause systemic toxicity | 157 and 158 |
| II. Longer retention time |
| Nanoparticles | Administration route | Advantages | Disadvantages | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomimetics | Subcutaneous injection | I. Used in targeted deliveries | I. Orientation of the nanomedicine with the membrane | 159–161 |
| II. Can escape the immune system and hence are less reactive in the body | II. Membrane fragility | |||
| III. Less irritability | ||||
| IV. High biocompatibility | ||||
| V. Prolonged circulation time in blood | ||||
| Liposomes | Intramuscular, subcutaneous, topical, pulmonary, nasal, oral, and intravenous routes | I. Biocompatible as their morphology is similar to cells of the body | I. Rancidification of lipids leading to a lower shelf life | 162–165 |
| II. Versatility | II. Instability at different pH values | |||
| III. Targeting abilities | III. Expensive formulation | |||
| IV. Controlled release | ||||
| V. Enhanced stability | ||||
| VI. Biodegradability | ||||
| VII. Scalability | ||||
| VIII. Encapsulation efficiency | ||||
| Hydrogel | Oral, intra-articular, intravenous, transdermal | I. Controlled release due to its structure | I. Mechanical strength is low | 166–170 |
| II. Biocompatible and biomimetic, thus reducing immunogenicity | II. Handling is difficult | |||
| III. Lubrication properties that protect joints from degradation and friction | III. Needs secondary dressing for securing it, as is non–adherent | |||
| IV. Can used for long periods of time | IV. Expensive | |||
| Solid–lipid nanoparticles | Targeted delivery can be achieved by topical or oral administration | I. Controlled release of drugs | I. Composition can often lead to the uncontrolled release of drugs and drug leaching | 171–177 |
| II. Enhanced delivery of hydrophobic and lipophilic drugs | II. Low drug loading capacity | |||
| III. Zero irritability of skin | III. More data are needed for confirmation of safety and toxicity. | |||
| IV. Highly stable | ||||
| V. Protected from degradation by enzymes | ||||
| VI. Very high tolerability in vivo | ||||
| VII. Higher penetration and permeability of drugs | ||||
| VIII. Targeted delivery | ||||
| Niosomes | Administration of the drug-loaded niosomes in the form of transdermal gels and patches | I. Enhanced shelf life | I. Can form aggregation | 178–181 |
| II. High chemical stability | II. Encapsulated drugs can leak | |||
| III. Cost-effective in making | ||||
| IV. High skin penetrability and retention | ||||
| V. Decreased irritation and haemolysis | ||||
| VI. Enhanced residence time of drugs and controlled release | ||||
| Ethosomes | Transdermal administration | I. Better skin penetrability due to their soft nature | I. Yield is poor | 182–186 |
| II. Higher alcohol content enhances the encapsulation capability | II. Chance of coalescing | |||
| III. On transfer from organic to water media, may lead to the loss of product. | ||||
| IV. Skin irritation or dermatitis | ||||
| V. Needs adequate solubility of the drug | ||||
| Transferosomes | Transdermal gels | I. Are elastic due to edge activators | I. Expensive to manufacture | 187 and 188 |
| II. Can encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs | II. Can be degraded oxidatively | |||
| III. Show high skin penetrability due to their elastic nature | III. Phospholipids can undergo reorganization | |||
| Nanoemulsions | Transdermal gels | I. Increased bioavailability of insoluble and impermeable drugs | I. Thermodynamically unstable | 189–192 |
| II. Escape the first-pass mechanism due to small size | II. Require external energy for formation | |||
| III. Enhanced skin penetrability | ||||
| Polymeric micelles | Intravenous injection, infusion, oral, topical | I. Circulation time in the blood is prolonged | I. Complex characterization | 193 and 194 |
| II. Controlled drug release | II. Low stability | |||
| III. Protection of the inside content from degradation | ||||
| IV. Enhance the solubility of drugs | ||||
| V. Can be passively targeted | ||||
| Dendrimers | Intravenous injection | I. Easy movement across cell surfaces | I. Can interact with cell membranes and disrupt them | 195–203 |
| II. Good targetability | ||||
| III. Enhanced rate of cell entry | II. Can interfere with neuronal signalling | |||
| IV. Monovalency | III. Can lead to haemolysis | |||
| V. Enhanced solubility | IV. Can be toxic to the healthy cells of the body | |||
| VI. Good hemocompatibility and cytocompatibility | V. Can show gastro-intestinal, renal and hepatic toxicity | |||
| VI. Highest toxicity is shown by cationic dendrimers |
7. Conclusion
The first description of the disease dates back to the 1800s. From defining it as primary asthenic gout to calling it rightly rheumatoid arthritis, research in this field has come a long way. Today, we have knowledge of most of the symptoms and common causes of the disease. Conventional treatments with which therapeutics in this field started are the most used ones to date. However, lately, these conventional treatments have started showing systemic side effects due to their repeated usage and off-target effects. Some patients show resistance to conventional drugs as well. Therefore, acquiring more knowledge of the specifics of the disease to devise more specific treatments, along with using nanotechnology to make the delivery of the drugs more targeted and controlled, ensuring the regulation of the dosage and retention time, was and will be the most suitable strategy in RA therapeutics. Organic nanoparticles like biomimetics and liposomes show good biocompatibility in the body due to their composition, which is very similar to the body's own cells, making them less immunogenic and giving more options for administration routes. However, there are certain shortcomings in nanotechnology as well, like scaling up production, unpredictability of the nanocarrier inside the system, and the difficulty of the synthesis of certain nanoparticles, claiming further research and developments in this field. There is a requirement to develop DC-targeted nanocarriers in RA. Also, despite well-established animal models of RA being useful, the human disease pattern is not always faithfully replicated in these animals. RA in humans has a far more complex pathogenic background than in animal models. More work is still required to progress the development of possible drug delivery methods for clinical trials and marketing in the RA treatment space. In the foreseeable future, we anticipate that treatments for RA and other autoimmune illnesses will advance quickly.Author contributions
AL: writing and image curation, SN: conceptualization and editing, DB: editing, and AK: funding acquisition and conceptualization.Data availability
No primary research results, software or code have been included and no new data were generated or analysed as part of this review.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest and there are no conflicts of interest.Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the Gujarat State Biotechnology Mission (GSBTM) (GSBTM/JD(R&D)/663/2023-24/02003699) and the Gujarat Institute for Chemical Technology (GICT) (AU/DBLS/GICT-nanomaterials/2016-17/01) for funding this work. A. L. and S. N. acknowledge Ahmedabad University, Gujarat, for their fellowships.References
- P. Entezami, D. A. Fox, P. J. Clapham and K. C. Chung, Handb. Clin., 2011, 27, 1–10 CrossRef PubMed.
- Q. Guo, Y. Wang, D. Xu, J. Nossent, N. J. Pavlos and J. Xu, Bone Res., 2018, 6, 15 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Alivernini, G. Peluso, A. L. Fedele, B. Tolusso, E. Gremese and G. Ferraccioli, Arthritis Res. Ther., 2016, 18, 1–7 CrossRef PubMed.
- E. Siouti and E. Andreakos, Biochem. Pharmacol., 2019, 165, 152–169 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Aletaha and J. S. Smolen, J. Am. Med. Assoc., 2018, 320, 1360–1372 CrossRef PubMed.
- C.-T. Lin, W.-N. Huang, W.-C. Tsai, J.-P. Chen, W.-T. Hung, T.-Y. Hsieh, H.-H. Chen, C.-W. Hsieh, K.-L. Lai and K.-T. Tang, PLoS One, 2021, 16, e0250877 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Grennan, J. Gray, J. Loudon and S. Fear, Ann. Rheum. Dis., 2001, 60, 214–217 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Wang, H. Zhou and L. Liu, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2018, 158, 502–516 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Rahimizadeh, Z. Rezaieyazdi, F. Behzadi, A. Hajizade and S. I. Lim, Int. J. Pharm., 2021, 609, 121137 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Long, M. Liu, Y. Nan, Q. Chen, Z. Xiao, Y. Xiang, X. Ying, J. Sun, Q. Huang and K. Ai, Adv. Mater., 2024, 36, 2308239 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Zhao, Y. Zhu, L. Feng, B. Liu, Y. Hu, H. Zhu, Z. Zhao, H. Ding, S. Gai and P. Yang, Adv. Mater., 2024, 36, 2307115 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Hajjafari, S. Sadr, A. Rahdar, M. Bayat, N. Lotfalizadeh, S. Dianaty, A. Rezaei, S. P. Moghaddam, K. Hajjafari and P. A. Simab, Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2024, 112409 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Ullah, M. Ullah and S. I. Lim, Curr. Probl. Cardiol., 2024, 102396 CrossRef PubMed.
- I. A. Udalova, A. Mantovani and M. Feldmann, Nat. Rev. Rheumatol., 2016, 12, 472–485 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. V. Mushenkova, N. G. Nikiforov, N. K. Shakhpazyan, V. A. Orekhova, N. K. Sadykhov and A. N. Orekhov, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23, 8381 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Austermann, J. Roth and K. Barczyk-Kahlert, Cells, 2022, 11, 1979 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zheng, K. Wei, P. Jiang, J. Zhao, Y. Shan, Y. Shi, F. Zhao, C. Chang, Y. Li and M. Zhou, Front. Immunol., 2024, 15, 1394108 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. J. Beaulaurier and J. W. Ashley, Post-translational modification of CSF1R as a mechanism for ligand preference 2024, 2024 Symposium, 22, https://dc.ewu.edu/srcw_2024/ps_2024/p2_2024/22.
- M. H. Hoffmann, H. Kirchner, G. Krönke, G. Riemekasten and M. Bonelli, Ann. Rheum. Dis., 2024, ard-2023-224092 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Mirzaesmaeili and A. A. Abdul-Sater, Biomolecules, 2024, 14, 864 CrossRef.
- A. G. Fedoce, F. P. Veras, M. H. Rosa, A. H. Schneider, I. M. Paiva, M. R. Machado, E. G. Freitas-Filho, J. F. Silva, C. C. Machado and J. C. Alves-Filho, Biochem. Pharmacol., 2024, 116245 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. A. Roberts, A. K. Dickinson and L. S. Taams, Front. Immunol., 2015, 6, 153682 Search PubMed.
- D. I. Salnikova, N. G. Nikiforov, A. Y. Postnov and A. N. Orekhov, Diseases, 2024, 12, 81 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. P. Murphy and D. Crean, Biomolecules, 2015, 5, 1302–1318 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y.-J. Wu, S.-S. Zhang, Q. Yin, M. Lei, Q.-H. Wang, W.-G. Chen, T.-T. Luo, P. Zhou and C.-L. Ji, Drug Des., Dev. Ther., 2023, 563–577 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Vasilevko, A. Ghochikyan, M. J. Holterman and M. G. Agadjanyan, DNA Cell Biol., 2002, 21, 137–149 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Geng, J. Xu, X. Cao, Z. Wang, Y. Jiao, W. Diao, X. Wang, Z. Wang, M. Zhang and L. Zhao, J. Autoimmun., 2024, 146, 103214 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. E. M. El Shikh, R. El Sayed, A. Nerviani, K. Goldmann, C. R. John, R. Hands, L. Fossati-Jimack, M. J. Lewis and C. Pitzalis, J. Autoimmun., 2019, 105, 102297 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Li, R. Yamasaki, M. Fang, K. Masaki, H. Ochi, T. Matsushita and J.-i. Kira, Sci. Rep., 2018, 8, 1933 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Hang, J. Wei, M. Zheng, Z. Gui, H. Chen, L. Sun, S. Fei, Z. Han, J. Tao and Z. Wang, Front. Pharmacol., 2022, 13, 865363 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Gan, L. Yang, L. Xu, X. Feng, Q. Zhang, F. Wang, W. Tan and M. Zhang, Int. Immunopharmacol., 2016, 35, 294–300 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Nagatani, K. Itoh, K. Nakajima, H. Kuroki, Y. Katsuragawa, M. Mochizuki, S. Aotsuka and A. Mimori, Arthritis Rheum., 2007, 56, 3554–3563 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y.-S. Xiong, Y. Cheng, Q.-S. Lin, A.-L. Wu, J. Yu, C. Li, Y. Sun, R.-Q. Zhong and L.-J. Wu, Rheumatology, 2014, 53, 250–259 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Piotrowska, S. Słuczanowska-Głabowska, M. Kurzawski, V. Dziedziejko, P. Kopytko, E. Paczkowska, D. Rogińska, K. Safranow, B. Machaliński and A. Pawlik, Biomolecules, 2020, 10, 1064 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Yan, L. Yao, Y. Tan and Y. Wang, Aging, 2023, 15, 14607 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F.-Y. Jiang, Y.-Z. Zhang, Y.-H. Tai, C.-Y. Chou, Y.-C. Hsieh, Y.-C. Chang, H.-C. Huang, Z.-Q. Li, Y.-C. Hsieh and I.-J. Chen, Inflammation Regener., 2023, 43, 13 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Xu, C. He, Y. Cai, X. Wang, J. Yan, J. Zhang, F. Zhang, V. Urbonaviciute, Y. Cheng and S. Lu, Redox Biol., 2024, 72, 103132 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. López-Navarro, M. Simón-Fuentes, I. Ríos, M. T. Schiaffino, A. Sanchez, M. Torres-Torresano, A. Nieto-Valle, I. Castrejón and A. Puig-Kröger, Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 2024, 81, 1–17 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. De Bondt, J. Renders, S. Struyf and N. Hellings, Autoimmun. Rev., 2024, 103532 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Zhao, N. Peng, Y. Zhou, Y. Qu, M. Cao, Q. Zou, Q. Yu, L. Lu and F. Xiao, J. Leukocyte Biol., 2024, qiae095 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. J. Bashar, C. L. Holmes and M. A. Shelef, Front. Immunol., 2024, 15, 1167362 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. V. Borovikova, S. Ivanova, M. Zhang, H. Yang, G. I. Botchkina, L. R. Watkins, H. Wang, N. Abumrad, J. W. Eaton and K. J. Tracey, Nature, 2000, 405, 458–462 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Cecchi, I. A. de la Rosa, E. Menegatti, D. Roccatello, E. Collantes-Estevez, C. Lopez-Pedrera and N. Barbarroja, Autoimmun. Rev., 2018, 17, 1138–1149 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. L. Wright, M. Lyon, E. A. Chapman, R. J. Moots and S. W. Edwards, Front. Immunol., 2021, 11, 584116 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. L. Wright, R. J. Moots and S. W. Edwards, Nat. Rev. Rheumatol., 2014, 10, 593–601 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Fresneda Alarcon, Z. McLaren and H. L. Wright, Front. Immunol., 2021, 12, 649693 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. P. Eiserich, S. Baldus, M.-L. Brennan, W. Ma, C. Zhang, A. Tousson, L. Castro, A. J. Lusis, W. M. Nauseef and C. R. White, Science, 2002, 296, 2391–2394 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Klinke, C. Nussbaum, L. Kubala, K. Friedrichs, T. K. Rudolph, V. Rudolph, H.-J. Paust, C. Schröder, D. Benten and D. Lau, Blood, 2011, 117, 1350–1358 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Watanabe, S. Hattori, S. Katsuda, I. Nakanishi and Y. Nagai, J. Biochem., 1990, 108, 753–759 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Busso, M. Frasnelli, R. Feifel, B. Cenni, M. Steinhoff, J. Hamilton and A. So, Arthritis Rheum., 2007, 56, 101–107 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Hollenberg, K. Mihara, D. Polley, J. Suen, A. Han, D. Fairlie and R. Ramachandran, Br. J. Pharmacol., 2014, 171, 1180–1194 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. M. Muley, A. R. Reid, B. Botz, K. Boelcskei, Z. Helyes and J. J. McDougall, Br. J. Pharmacol., 2016, 173, 766–777 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Panday, M. K. Sahoo, D. Osorio and S. Batra, Cell. Mol. Immunol., 2015, 12, 5–23 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Chen, B. K. Lam, Y. Kanaoka, P. A. Nigrovic, L. P. Audoly, K. F. Austen and D. M. Lee, J. Exp. Med., 2006, 203, 837–842 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. H. Schneider, T. M. Taira, G. A. Públio, D. da Silva Prado, P. B. Donate Yabuta, J. C. Dos Santos, C. C. Machado, F. F. L. de Souza, L. G. Rodrigues Venturini and R. D. R. de Oliveira, Br. J. Pharmacol., 2024, 181, 429–446 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. J. O'Neil, C. B. Oliveira, X. Wang, M. Navarrete, A. Barrera-Vargas, J. Merayo-Chalico, R. Aljahdali, E. Aguirre-Aguilar, P. Carlucci and M. J. Kaplan, Ann. Rheum. Dis., 2023, 82, 630–638 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. Wang, Z.-Q. Zhang, Y.-C. Zhang, Y.-Q. Wu, Z. Yang, Y.-Z. Zheng, J.-H. Lu, P.-F. Tu and K.-W. Zeng, Chin. Med., 2024, 19, 42 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Wang, J. Ma, W. Song and C. Zhao, Drug Delivery, 2023, 30, 2173332 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Liu, M. Liu, J. Xiu, T. Zhang, B. Zhang, D. Cun, C. Yang, K. Li, J. Zhang and X. Zhao, Acta Biomater., 2024, 174, 345–357 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Zeng, G. Yu, K. Yang, Q. He, W. Hao, W. Xiang, Z. Long, H. Chen, X. Tang and L. Sun, Sci. Rep., 2024, 14, 1604 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Muñoz-Barrera, C. Perez-Sanchez, R. Ortega-Castro, S. Corrales, M. Luque-Tevar, T. Cerdó, I. Sanchez-Pareja, P. Font, R. Lopez-Mejías and J. Calvo, Biomed. Pharmacother., 2024, 173, 116357 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Chen, Z. Zhou, M. Peng, H. Hu, R. Sun, J. Xu, C. Zhu, Y. Li, Q. Zhang and Y. Luo, Arthritis Res. Ther., 2023, 25, 66 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W.-H. Shao, A. Del Prete, C. B. Bock and B. Haribabu, J. Immunol., 2006, 176, 6254–6261 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Kong, H. Guan, X. Duan, R. Cao, H. Li, F. Xing, X. Du, Y. Zheng, L. Zhang and Y. Li, Cell Cycle, 2024, 1–14 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhao, Y. Liu, X. Shi, J. Dang, Y. Liu, S. Li, W. Cai, Y. Hou, D. Zeng and Y. Chen, J. Adv. Res., 2024, 58, 79–91 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Borna, E. Meffre and R. Bacchetta, Immunol. Rev., 2024, 322, 244–258 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Y. Shen, B. P. Jiang, M. F. Zhang, X. Wang, H. Zhu, Z. N. Gu, X. P. Zhou, Y. Lu and L. L. Zhou, J. Clin. Lab. Anal., 2023, 37, e24845 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Jiang, G. Yang, Q. Liu, S. Wang and D. Cui, Front. Immunol., 2021, 12, 626193 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Petrelli, F. M. Mariani, A. Alunno and I. Puxeddu, Clin. Exp. Rheumatol., 2022, 40, 475–482 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Li, F. Lin, C. Zhuo, G. Deng, Z. Chen, S. Yin, Z. Gao, M. Piccioni, A. Tsun and S. Cai, J. Biol. Chem., 2014, 289, 26872–26881 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Ikeda, S. Saijo, M. A. Murayama, K. Shimizu, A. Akitsu and Y. Iwakura, J. Immunol., 2014, 192, 1449–1458 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Attridge, C. J. Wang, L. Wardzinski, R. Kenefeck, J. L. Chamberlain, C. Manzotti, M. Kopf and L. S. Walker, Blood, 2012, 119, 4656–4664 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Morita, Y. Shima, J. B. Wing, S. Sakaguchi, A. Ogata and A. Kumanogoh, PLoS One, 2016, 11, e0162306 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Wang, C. Wang, X. Jia and J. Yu, Cell. Physiol. Biochem., 2018, 50, 1754–1763 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Paradowska-Gorycka, A. Wajda, K. Romanowska-Próchnicka, E. Walczuk, E. Kuca-Warnawin, T. Kmiolek, B. Stypinska, E. Rzeszotarska, D. Majewski and P. P. Jagodzinski, Front. Immunol., 2020, 11, 572858 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Su, B. Li, R. Wu, Y. Xie, A. Gao, C. Gao, X. Li and C. Wang, Arthritis Res. Ther., 2023, 25, 55 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Yoshida, M. Magi, H. Tamai, J. Kikuchi, K. Yoshimoto, K. Otomo, Y. Matsumoto, M. Noguchi-Sasaki, T. Takeuchi and Y. Kaneko, Rheumatology, 2024, keae196 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. N. Furlan, K. Singh, C. Lopez, V. Tkachev, D. J. Hunt, J. Hibbard, K. M. Betz, B. R. Blazar, C. Trapnell and L. S. Kean, Blood Adv., 2020, 4, 1594–1605 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Scottà, M. Esposito, H. Fazekasova, G. Fanelli, F. C. Edozie, N. Ali, F. Xiao, M. Peakman, B. Afzali and P. Sagoo, Haematologica, 2013, 98, 1291 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Bystrom, F. Clanchy, T. E. Taher, P. Mangat, A. S. Jawad, R. O. Williams and R. A. Mageed, Cytokine, 2018, 101, 4–13 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-J. Ko, M.-L. Cho, S.-Y. Lee, H.-J. Oh, Y.-J. Heo, Y.-M. Moon, C.-M. Kang, S.-K. Kwok, J. H. Ju and S.-H. Park, J. Autoimmun., 2010, 34, 111–120 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. E. Morgan, R. Flierman, L. M. van Duivenvoorde, H. J. Witteveen, W. van Ewijk, J. M. van Laar, R. R. De Vries and R. E. Toes, Arthritis Rheum., 2005, 52, 2212–2221 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. T. Harris and D. M. Kranz, Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 2016, 37, 220–230 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Scottà, G. Fanelli, S. J. Hoong, M. Romano, E. N. Lamperti, M. Sukthankar, G. Guggino, H. Fazekasova, K. Ratnasothy and P. D. Becker, Haematologica, 2016, 101, 91 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. H. Lee, J.-S. Park, J.-K. Byun, J. Jhun, K. Jung, H.-B. Seo, Y.-M. Moon, H.-Y. Kim, S.-H. Park and M.-L. Cho, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, 34617 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Verma, C. Lee, E.-J. Jeun, J. Yi, K. S. Kim, A. Ghosh, S. Byun, C.-G. Lee, H.-J. Kang and G.-C. Kim, Sci. Immunol., 2018, 3, eaat6975 CrossRef PubMed.
- E. Gonzalez-Rey and M. Delgado, Trends Mol. Med., 2007, 13, 241–251 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhang, X. Hu, X. Dong, W. Chen, L. Zhang, Y. Chang, Y. Wu and W. Wei, Front. Immunol., 2020, 11, 755 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhang, H. Liu, Y. Chen, H. Liu, S. Zhang, G. Yin and Q. Xie, Front. Immunol., 2024, 15, 1312919 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Ganguly, S. Haak, V. Sisirak and B. Reizis, Nat. Rev. Immunol., 2013, 13, 566–577 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Lutzky, S. Hannawi and R. Thomas, Arthritis Res. Ther., 2007, 9, 1–12 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. L. Jongbloed, R. A. Benson, M. B. Nickdel, P. Garside, I. B. McInnes and J. M. Brewer, J. Immunol., 2009, 182, 963–968 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Sarkar and D. A. Fox, Front. Biosci., 2005, 10, 656–665 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Suwa, Y. Nagafuchi, S. Yamada and K. Fujio, Front. Immunol., 2023, 14, 1161148 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. C. Lebre, S. L. Jongbloed, S. W. Tas, T. J. Smeets, I. B. McInnes and P. P. Tak, Am. J. Pathol., 2008, 172, 940–950 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. R. Pettit, C. Quinn, K. MacDonald, L. L. Cavanagh, G. Thomas, W. Townsend, M. Handel and R. Thomas, J. Immunol., 1997, 159, 3681–3691 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Zhang, K. Wei, K. Slowikowski, C. Y. Fonseka, D. A. Rao, S. Kelly, S. M. Goodman, D. Tabechian, L. B. Hughes and K. Salomon-Escoto, Nat. Immunol., 2019, 20, 928–942 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. B. Yu and W. H. Langridge, Rheumatol. Int., 2017, 37, 1043–1051 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. W. Scally, J. Petersen, S. C. Law, N. L. Dudek, H. J. Nel, K. L. Loh, L. C. Wijeyewickrema, S. B. Eckle, J. van Heemst and R. N. Pike, J. Exp. Med., 2013, 210, 2569–2582 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Khan, J. D. Greenberg and N. Bhardwaj, Nat. Rev. Rheumatol., 2009, 5, 566–571 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Wehr, H. Purvis, S. Law and R. Thomas, Clin. Exp. Immunol., 2019, 196, 12–27 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Wang, J. Zhang, F. An, J. Zhang, X. Meng, S. Liu, R. Xia, G. Wang and C. Yan, Arthritis Res. Ther., 2023, 25, 193 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. M. Curran, A. A. Girgis, Y. Jang, J. D. Crawford, M. A. Thomas, R. Kawalerski, J. Coller, C. O. Bingham III, C. H. Na and E. Darrah, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14, 1061 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Morante-Palacios, F. Fondelli, E. Ballestar and E. M. Martínez-Cáceres, Trends Immunol., 2021, 42, 59–75 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. M. Lellahi, W. Azeem, Y. Hua, B. Gabriel, K. Paulsen Rye, H. Reikvam and K.-H. Kalland, Front. Immunol., 2023, 13, 1058963 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Kumari, B. Ghosh and S. Biswas, J. Drug Targeting, 2016, 24, 179–191 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Kang, S. Rho, W. R. Stiles, S. Hu, Y. Baek, D. W. Hwang, S. Kashiwagi, M. S. Kim and H. S. Choi, Adv. Healthcare Mater., 2020, 9, 1901223 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. An, Z. Li, L. Shi, L. Wang, Y. Wang, L. Jin, X. Shuai and J. Li, Nano Lett., 2020, 20, 7728–7736 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Gong, P. Zhang, C. Deng, Y. Xiao, T. Gong and Z. Zhang, Nanomedicine, 2019, 14, 2169–2187 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Lorscheider, N. Tsapis, F. Gaudin, I. Stolfa, S. Abreu, S. Mura, P. Chaminade, M. Espeli and E. Fattal, J. Controlled Release, 2019, 296, 179–189 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Zhao, A. Liu, Y. Zhang, Z.-Q. Zuo, Z.-T. Cao, H.-B. Zhang, C.-F. Xu and J. Wang, Biomater. Sci., 2019, 7, 4698–4707 RSC.
- P. Song, C. Yang, J. S. Thomsen, F. Dagnæs-Hansen, M. Jakobsen, A. Brüel, B. Deleuran and J. Kjems, Mol. Ther., 2019, 27, 1424–1435 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. Kim, J.-S. Park, S. J. Lee, J. Jang, J. S. Park, S. H. Back, G. Bahn, J. H. Park, Y. M. Kang and S. H. Kim, J. Controlled Release, 2015, 216, 140–148 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Fang, Y. Sha, L. Yang, J. Jiang, L. Yin, J. Li, B. Li, B. Klumperman, Z. Zhong and F. Meng, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14, 8824–8837 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Tan, Q. Huang, W. Chu, B. Li, J. Wu, Q. Xia and X. Cao, Drug Delivery, 2022, 29, 692–701 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Mohamed, A. S. Abu Lila, T. Shimizu, E. Alaaeldin, A. Hussein, H. A. Sarhan, J. Szebeni and T. Ishida, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater., 2019, 20, 710–724 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Duan and H. Li, J. Nanobiotechnol., 2018, 16, 1–9 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Pirmardvand Chegini, J. Varshosaz and S. Taymouri, Artif. Cells, Nanomed., Biotechnol., 2018, 46, 502–514 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Yang, L. Guo, Z. Wang, P. Liu, X. Liu, J. Ding and W. Zhou, Biomaterials, 2021, 264, 120390 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Sun, S. Dong, X. Li, K. Yu, F. Sun, R. J. Lee, Y. Li and L. Teng, Nanomedicine, 2019, 20, 102017 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Srivastava, D. Singh and M. R. Singh, J. Pharm. Sci., 2018, 107, 1530–1539 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. K. Pandey, R. Maheshwari, N. Raval, P. Gondaliya, K. Kalia and R. K. Tekade, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2019, 544, 61–77 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. P. Gokhale, H. S. Mahajan and S. J. Surana, Biomed. Pharmacother., 2019, 112, 108622 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Wu, T. Ma, M. Zhu, T. Huang, B. Zhang, J. Gao and N. Lin, Nano Today, 2022, 46, 101577 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Zhang, D. Dehaini, Y. Zhang, J. Zhou, X. Chen, L. Zhang, R. H. Fang, W. Gao and L. Zhang, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2018, 13, 1182–1190 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Tang, S. Meng, X. Yang, Y. Xiao, W. Wang, Y. Liu, K. Wu, X. Zhang, H. Guo and Y. Z. Zhu, Small, 2023, 2307379 Search PubMed.
- D. Chu, X. Dong, Q. Zhao, J. Gu and Z. Wang, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1701021 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Nakatani, S. Takeshita, H. Tsujimoto, Y. Kawamura, H. Kawase and I. Sekine, Clin. Exp. Immunol., 1999, 117, 418–422 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Wang, J. Li, J. Cho and A. B. Malik, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2014, 9, 204–210 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. B. Okeke, C. Louttit, C. Fry, A. H. Najafabadi, K. Han, J. Nemzek and J. J. Moon, Biomaterials, 2020, 238, 119836 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Spence, M. K. Greene, F. Fay, E. Hams, S. P. Saunders, U. Hamid, M. Fitzgerald, J. Beck, B. K. Bains and P. Smyth, Sci. Transl. Med., 2015, 7, 303ra140 Search PubMed.
- K. F. Bornhöfft, T. Viergutz, A. Kühnle and S. P. Galuska, Nanomaterials, 2019, 9, 610 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. D. Robertson, J. R. Ward, M. Avila-Olias, G. Battaglia and S. A. Renshaw, J. Immunol., 2017, 198, 3596–3604 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Khatri, J. Hansen, A. C. Mendes, I. S. Chronakis, S.-C. Hung, E. D. Mellins and K. Astakhova, Bioconjugate Chem., 2019, 30, 2584–2593 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. A. Brzezicka, B. M. Arlian, S. Wang, M. Olmer, M. Lotz and J. C. Paulson, ACS Nano, 2022, 16, 20206–20221 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Liu, X. Wang, X. Liu, S. Kumar, G. Gochman, Y. Ji, Y.-P. Liao, C. H. Chang, W. Situ and J. Lu, ACS Nano, 2019, 13, 4778–4794 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Campbell, F. L. Bos, S. Sieber, G. Arias-Alpizar, B. E. Koch, J. R. Huwyler, A. Kros and J. Bussmann, ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 2138–2150 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Carambia, B. Freund, D. Schwinge, O. T. Bruns, S. C. Salmen, H. Ittrich, R. Reimer, M. Heine, S. Huber and C. Waurisch, J. Hepatol., 2015, 62, 1349–1356 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. M. Gammon, L. H. Tostanoski, A. R. Adapa, Y.-C. Chiu and C. M. Jewell, J. Controlled Release, 2015, 210, 169–178 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Klatzmann and A. K. Abbas, Nat. Rev. Immunol., 2015, 15, 283–294 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. D. McHugh, J. Park, R. Uhrich, W. Gao, D. A. Horwitz and T. M. Fahmy, Biomaterials, 2015, 59, 172–181 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Li, L. Wang, Y. Gu, L. Lin, M. Zhang, M. Jin, C. Mao, J. Zhou, W. Zhang and X. Huang, Matter, 2021, 4, 3621–3645 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Sacchetti, N. Rapini, A. Magrini, E. Cirelli, S. Bellucci, M. Mattei, N. Rosato, N. Bottini and M. Bottini, Bioconjugate Chem., 2013, 24, 852–858 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Parvanian, S. M. Mostafavi and M. Aghashiri, Sens. Biosensing Res., 2017, 13, 81–87 CrossRef.
- A. M. Reichmuth, M. A. Oberli, A. Jaklenec, R. Langer and D. Blankschtein, Ther. Delivery, 2016, 7, 319–334 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. K. Gulla, B. R. Rao, G. Moku, S. Jinka, N. V. Nimmu, S. Khalid, C. R. Patra and A. Chaudhuri, Biomater. Sci., 2019, 7, 773–788 RSC.
- T. J. Goodwin and L. Huang, Vaccine, 2017, 35, 2550–2557 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Li, W.-l. Chen, B.-g. You, Y. Liu, S.-d. Yang, Z.-q. Yuan, W.-j. Zhu, J.-z. Li, C.-x. Qu and Y.-j. Zhou, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8, 32146–32158 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Zupančič, C. Curato, M. Paisana, C. Rodrigues, Z. Porat, A. S. Viana, C. A. Afonso, J. Pinto, R. Gaspar and J. N. Moreira, J. Controlled Release, 2017, 258, 182–195 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Zhong, Y. Zhang, L. Tan, T. Zheng, Y. Hou, X. Hong, G. Du, X. Chen, Y. Zhang and X. Sun, J. Controlled Release, 2019, 300, 81–92 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X.-K. Chi, X.-L. Xu, B.-Y. Chen, J. Su and Y.-Z. Du, J. Nanobiotechnol., 2023, 21, 105 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Kumar, B. Kumar, R. Sehgal, M. Wani, D. Kumar, M. D. Sharma, V. Singh, R. Sehgal and V. Kumar, in Nanoparticles reinforced metal nanocomposites: mechanical performance and durability, Springer, 2023, pp. 209–235 Search PubMed.
- H. Kumar, N. Venkatesh, H. Bhowmik and A. Kuila, Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res., 2018, 4, 3765–3775 Search PubMed.
- P. G. Jamkhande, N. W. Ghule, A. H. Bamer and M. G. Kalaskar, J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol., 2019, 53, 101174 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Kwon, R. K. Singh, R. A. Perez, E. A. Abou Neel, H.-W. Kim and W. Chrzanowski, J. Tissue Eng., 2013, 4, 2041731413503357 Search PubMed.
- G. Nautiyal, S. K. Sharma, D. Kaushik and P. Pandey, Recent Pat. Nanotechnol., 2024, 18, 433–456 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Wu, H. Liang, Y. Li, Y. Shi, M. Bottini, Y. Chen and L. Liu, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 2000391 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Liu, H. Liang, Y. Yan, J. Wu, M. Bottini, L. Liu and Y. Chen, Bioact. Mater., 2022, 13, 249–259 CAS.
- J. Chen, J. Tan, J. Li, W. Cheng, L. Ke, A. Wang, Q. Wang, S. Lin, G. Li and B. Wang, Small Methods, 2023, 7, 2300678 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Vasdev, B. Pawar, T. Gupta, M. Mhatre and R. K. Tekade, Pharmaceutics, 2023, 15, 1150 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Song, Z. Zheng, S. Ouyang, H. Chen, M. Sun, P. Lin, Y. Chen, Y. You, W. Hao and J. Tao, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2023, 15, 33239–33249 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Bhardwaj, P. Tripathi, R. Gupta and S. Pandey, J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol., 2020, 56, 101581 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Y. W. Tseu and K. A. Kamaruzaman, Molecules, 2023, 28, 1498 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Pande, Artif. Cells, Nanomed., Biotechnol., 2023, 51, 428–440 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Didandeh, A. H. Souderjani, M. Montazeri, F. Rahimi and G. Amoabediny, in Nanomedicine, Elsevier, 2023, pp. 381–395 Search PubMed.
- L. Xu, J. Pan, Q. Chen, Q. Yu, H. Chen, H. Xu, Y. Qiu and X. Yang, Food Chem. Toxicol., 2008, 46, 3792–3799 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Fan, J. Li, J. Liu, H. Jiao and B. Liu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 23595–23604 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Dehghan-Baniani, Y. Chen, D. Wang, R. Bagheri, A. Solouk and H. Wu, Colloids Surf., B, 2020, 192, 111059 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Wu, J. Liu, X. Lin, Z. He, H. Zhang, L. Ji, P. Gong, F. Zhou and W. Liu, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2023, 644, 200–210 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. M. F. A. Baig, L. K. Wong, A. W. Zia and H. Wu, Asian J. Pharm. Sci., 2024, 100887 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. D. Mandawgade and V. B. Patravale, Int. J. Pharm., 2008, 363, 132–138 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Liu, M. Hu, W. Liu, C. Xue, H. Xu and X. Yang, Int. J. Pharm., 2008, 364, 135–141 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Maestrelli, M. Bragagni and P. Mura, J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol., 2016, 32, 192–205 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Desai, R. R. Patlolla and M. Singh, Mol. Membr. Biol., 2010, 27, 247–259 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Ghasemiyeh and S. Mohammadi-Samani, Res. Pharm. Sci., 2018, 13, 288–303 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. S. Alotaibi, M. K. Waqas, S. Saleem, H. Yasin, Z. Kharaba and G. Murtaza, ACS Omega, 2024, 9, 7003–7011 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. P. Alcantara, J. W. T. Malabanan, N. Nalinratana, W. Thitikornpong, P. Rojsitthisak and P. Rojsitthisak, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2024, 25, 4744 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Maheshwari, M. Sharma and V. R. Chidrawar, Ann. Pharm. Fr., 2024, 82, 473–482 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. R. Neupane, A. Mahtab, L. Siddiqui, A. Singh, N. Gautam, S. A. Rabbani, H. Goel and S. Talegaonkar, Curr. Pharm. Des., 2020, 26, 5488–5502 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. M. Hosseinikhah, M. Barani, A. Rahdar, H. Madry, R. Arshad, V. Mohammadzadeh and M. Cucchiarini, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22, 3092 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Kaur and S. Kumar, J. Drug Delivery Ther., 2018, 8, 35–43 CrossRef.
- M. Nimmathota, Asian J. Pharm., 2016, 10, 1998–409X Search PubMed.
- E. Touitou and B. Godin, J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol., 2007, 17, 303–308 CrossRef CAS.
- G. A. Ramakrishna, S. D. Manohar and S. R. Bhanudas, J. Adv. Pharm. Educ. Res., 2014, 4, 380–387 CAS.
- N. V. Pakhale, S. Gondkar and R. Saudagar, J. Drug Delivery Ther., 2019, 9, 729–733 CAS.
- S. N. Adin, I. Gupta, M. Aqil, M. Mujeeb and A. K. Najmi, J. Drug Targeting, 2024, 1–17 Search PubMed.
- P. Jain, P. Rahi, V. Pandey, S. Asati and V. Soni, Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci., 2017, 4, 89–100 Search PubMed.
- K. K. Sarwa, B. Mazumder, M. Rudrapal and V. K. Verma, Drug Delivery, 2015, 22, 638–646 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Kotta, A. W. Khan, K. Pramod, S. H. Ansari, R. K. Sharma and J. Ali, Expert Opin. Drug Delivery, 2012, 9, 585–598 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. J. Espitia, C. A. Fuenmayor and C. G. Otoni, Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf., 2019, 18, 264–285 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. R. Pawar and R. J. Babu, Critical Reviews™ in Therapeutic Drug Carrier Systems, 2014, pp. 31 Search PubMed.
- C. Li, Y. Jiang, H. Su and C. Li, Curr. Drug Delivery, 2024, 21, 1106–1113 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X.-r. Feng, J.-x. Ding, R. Gref and X.-s. Chen, Chin. J. Polym. Sci., 2017, 35, 693–699 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Shen, D. Li, J. Guan, J. Ding, Z. Wang, J. Gu, T. Liu and X. Chen, Nanomedicine, 2017, 13, 1279–1288 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Bosch, ACS Nano, 2011, 5, 6779–6785 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. M. Beddoes, C. P. Case and W. H. Briscoe, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2015, 218, 48–68 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Bhadra, A. Yadav, S. Bhadra and N. Jain, Int. J. Pharm., 2005, 295, 221–233 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Vidal, P. Vásquez, F. R. Cayumán, C. Díaz, J. Fuentealba, L. G. Aguayo, G. E. Yévenes, J. Alderete and L. Guzmán, Nanomaterials, 2017, 8, 7 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Jevprasesphant, J. Penny, R. Jalal, D. Attwood, N. McKeown and A. D'Emanuele, Int. J. Pharm., 2003, 252, 263–266 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Malik, R. Wiwattanapatapee, R. Klopsch, K. Lorenz, H. Frey, J. Weener, E. Meijer, W. Paulus and R. Duncan, J. Controlled Release, 2000, 65, 133–148 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Duncan and L. Izzo, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2005, 57, 2215–2237 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Santos, F. Veiga and A. Figueiras, Materials, 2019, 13, 65 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Li, H. Zhu, R. Liu, Y. Zhao and L. Sun, Small Sci., 2024, 4, 2300097 CrossRef CAS.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |