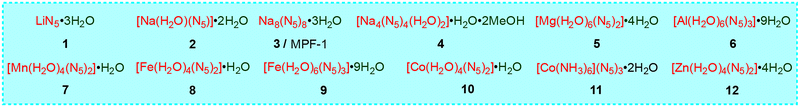Syntheses and properties of energetic cyclo-pentazolate cocrystals
Fanle
Meng
a,
Zihong
Ye
b,
Hongwei
Zhu
a,
Lianghe
Sun
a,
Ming
Lu
 *a and
Yuangang
Xu
*a and
Yuangang
Xu
 *a
*a
aSchool of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Xiaolingwei 200, Nanjing 210094, China. E-mail: luming@njust.edu.cn; yuangangxu@163.com
bQian Xuesen College, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Xiaolingwei 200, Nanjing 210094, China
First published on 18th November 2024
Abstract
As a new type of polynitrogen species that is stable at room temperature, the pentazolate anion (cyclo-N5−) has attracted much attention in the field of high-energy density materials, but its energy and stability are unbalanced. Cocrystallisation can balance their properties to some extent by forming new chemical compositions from existing cyclo-N5− compounds through non-covalent interactions. This article reviews the research progress of cyclo-N5− cocrystals in recent years, including synthetic methods, cocrystals of metal-N5− compounds, and cocrystals of nonmetallic pentazolate salts. The cocrystals of metal-N5− compounds mainly include metal-N5− solvates, cocrystals composed of metal-N5− compounds and amines/MSM, and metal-containing composite salts. The cocrystals of nonmetallic pentazolate salts include cocrystals composed of cyclo-N5− salts and solvents, cocrystals composed of cyclo-N5− salts and N-heterocyclic molecules, and non-metallic composite salts. The fascinating crystal structures (in some cases topological structures), stable forms, and physicochemical properties of representative cocrystals were highlighted. In addition, the future directions that need to be focused on in this field were pointed out, including the development of more preparation methods, especially those suitable for scaling up; higher precision calculation or testing of enthalpy of formation; improvement of their thermal stabilities; creation of cocrystals of cyclo-N5− salts and high-density, high-oxygen balance, high-energy oxidizers; and exploration of the formation mechanism.
1 Introduction
High nitrogen energetic materials, as an important class of high-energy density materials (HEDMs), have great potential for military and civilian applications. Among them, polynitrogen species have attracted much attention due to their ultra-high energy and environmental friendliness.1 The pentazolate anion (cyclo-N5−) is a pentagon composed entirely of aromatic N–N bonds. Its thermal stability (a thermal decomposition temperature of about 100 °C, with an activation energy of about 100 kJ mol−1)2 is much better than that of the V-shaped N5+ cation, and its enthalpy of formation is as high as 3.66 kJ g−1 (256 kJ mol−1).3 The stability and energy of cyclo-N5− have been accurately predicted by quantum chemistry studies.4 Over the past half century, extensive theoretical studies and experimental explorations have been carried out on stable HN5 and cyclo-N5−; however, the isolation of room-temperature stable cyclo-N5− compounds has been a great challenge for a long time. It was not until 2017 that Zhang et al.5 successfully synthesized a cyclo-N5− composite salt (N5)6(H3O)3(NH4)4Cl, whose structure was controversial but clearly confirmed the existence of cyclo-N5− in solid crystals. Subsequently, Xu et al.2 reported a series of metal cyclo-N5− hydrates. Since then, synthetic studies of cyclo-N5− derivatives have entered a new phase. At present, the highest detonation velocity of the synthesized cyclo-N5−-containing compounds exceeds 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 m s−1, but their density (<1.7 g cm−3) and decomposition temperature (<125 °C) are generally not high, and they also have varying degrees of hygroscopicity.6 These defects seriously limit the development of cyclo-N5− based energetic materials, and currently, the commonly used modification methods mainly include coating and doping. However, these methods do not change the internal composition and crystal structure of energetic materials, and the addition of non-energetic components reduces their energetic performance. Therefore, to further improve the modification effect, it is necessary to start from the internal composition and structure of the target molecules and combine the cyclo-N5− compounds and suitable coformers microscopically in the same crystal lattice through intermolecular non-covalent interactions to form cyclo-N5−-containing cocrystals with enhanced stability and performance.
000 m s−1, but their density (<1.7 g cm−3) and decomposition temperature (<125 °C) are generally not high, and they also have varying degrees of hygroscopicity.6 These defects seriously limit the development of cyclo-N5− based energetic materials, and currently, the commonly used modification methods mainly include coating and doping. However, these methods do not change the internal composition and crystal structure of energetic materials, and the addition of non-energetic components reduces their energetic performance. Therefore, to further improve the modification effect, it is necessary to start from the internal composition and structure of the target molecules and combine the cyclo-N5− compounds and suitable coformers microscopically in the same crystal lattice through intermolecular non-covalent interactions to form cyclo-N5−-containing cocrystals with enhanced stability and performance.
In recent years, cocrystallization has attracted much attention and has become an effective way to balance the energy and safety of energetic materials.7 By purposefully introducing a second molecule called a coformer, the intermolecular interactions that determine the stacking arrangement of the target energetic molecule can be disrupted and replaced, resulting in a novel crystal structure called an energetic cocrystal, which incorporates both molecules in a well-defined stoichiometry. Energetic cocrystals have been reported to have improved thermal stability, enhanced detonation properties, and reduced sensitivity to external stimuli.8 However, while cocrystallization has now been widely studied, the advancement of cocrystallization of energetic ion salts has been slow, with typical examples being 2,4,6,8,10,12-hexanitrate-2,4,6,8,10,12-hexaazaisowoodzane (CL-20)![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1-amino-3-methyl-1,2,3-triazolium nitrate,9 2 ammonium dinitramide (ADN)
1-amino-3-methyl-1,2,3-triazolium nitrate,9 2 ammonium dinitramide (ADN)![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) pyrazine-1,4-dioxide,10 2 ammonium nitrate (AN)
pyrazine-1,4-dioxide,10 2 ammonium nitrate (AN)![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5,5′-dinitro-2H,2H′-3,3′-bi-1,2,4-triazole (DNBT), and 2 ADN
5,5′-dinitro-2H,2H′-3,3′-bi-1,2,4-triazole (DNBT), and 2 ADN![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) DNBT cocrystals.11 The cyclo-N5− ion carries a negative charge and is not only a good hydrogen bond acceptor but also a planar structure that easily experiences π–π stacking, exhibiting the structural characteristics of cocrystallization. Therefore, cyclo-N5−-containing energetic cocrystals can be formed by suitable coformers to change the molecular composition and crystal structure of cyclo-N5− salts, increase their decomposition temperatures and densities, reduce their sensitivities, improve their hygroscopicity, and prepare new high-performance and high-stability cyclo-N5− based energetic materials.
DNBT cocrystals.11 The cyclo-N5− ion carries a negative charge and is not only a good hydrogen bond acceptor but also a planar structure that easily experiences π–π stacking, exhibiting the structural characteristics of cocrystallization. Therefore, cyclo-N5−-containing energetic cocrystals can be formed by suitable coformers to change the molecular composition and crystal structure of cyclo-N5− salts, increase their decomposition temperatures and densities, reduce their sensitivities, improve their hygroscopicity, and prepare new high-performance and high-stability cyclo-N5− based energetic materials.
This frontier article reviews the methods for synthesizing cyclo-N5− containing energetic cocrystals in recent years, their crystal structures, classification, thermal stabilities, energy properties (density, detonation velocity, and detonation pressure), and sensitivities. In order to encourage innovative research on cyclo-N5− cocrystals, the challenges and application prospects related to them are outlined.
2 Synthetic methods for accessing cyclo-N5− cocrystals
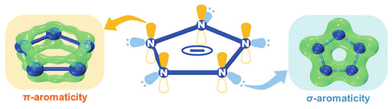
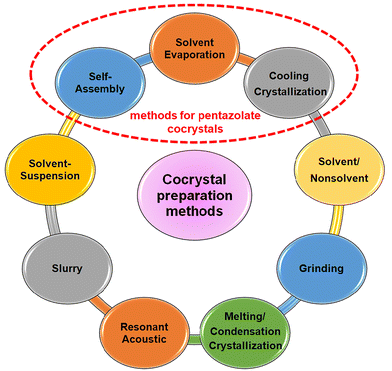
Cyclo-N5− has D5h symmetry, with all of its five nitrogen atoms being sp2 hybridized.12 As shown in Fig. 1, it has a dual aromatic skeleton with six π-electrons delocalized in a conjugated manner above and below the cyclo-N5− ring plane, conferring cyclo-N5− π-aromaticity; meanwhile, in the equatorial plane of the cyclo-N5− ring, the lone pair of electrons from the five N atoms leads to flower-like delocalization of the electrons, indicating the σ-aromaticity of cyclo-N5−. Thus, its unique structure implies good adaptability to form cocrystals with other molecules.Cocrystal preparation methods include solvent evaporation, solvent/nonsolvent, cooling crystallization, grinding methods, melting/condensation crystallization, resonant acoustic methods, slurry methods, solvent-suspension methods, and self-assembly methods, all of which have been widely reported thus far (Fig. 2).13 Currently, there are two main methods for the syntheses of cyclo-N5− cocrystals: solvent evaporation and self-assembly methods. However, neither method can proceed without a metathesis reaction. Since 2017, our group has reported on metathesis reactions of [Na(H2O)(N5)]·2H2O with chlorides or nitrates.2,3 Similar to our work, metathesis reactions of [Mg(H2O)6(N5)2]·4H2O with some sulfates were subsequently developed.14 However, unless the target product can precipitate, both routes require repeated recrystallization in other cases and are cumbersome and inefficient since NaCl and MgSO4 are difficult to remove completely from commonly used solvents. In 2019, we found that protonation and metathesis reactions can be completed in one pot,15 but only two cyclo-N5− hydrates were synthesized. Then metathesis reactions driven by the precipitation of AgCl and BaSO4 were invented in the same year.16,17 In particular, the method driven by AgCl has the advantages of simple, rapid, high yields, and high universality and has become the most widely used method for synthesizing cyclo-N5− derivatives. These methods provide a variety of coformers for creating cyclo-N5− cocrystals.
3 Cocrystals of metal-N5− compounds
Cyclo-N5− cocrystals can be divided into cocrystals of metal-N5− compounds and non-metallic pentazolate salts. Among them, cocrystals of metal-N5− compounds can be further divided into three categories: metal-N5− solvates, cocrystals composed of metal-N5− compounds and amines/MSM, and metal-containing composite salts. Similarly, cocrystals of non-metallic pentazolate salts can also be divided into three categories: cocrystals composed of cyclo-N5− salts and solvents, cocrystals composed of cyclo-N5− salts and N-heterocyclic molecules, and non-metallic composite salts.3.1 Metal-N5− solvates
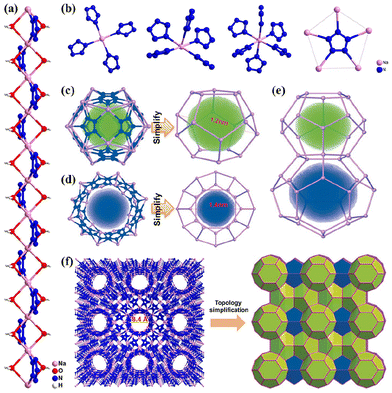
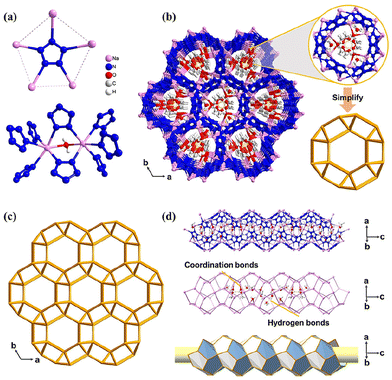
Our early research suggested that the coordination of cyclo-N5− to metals reduces its decomposition barrier in the gas phase, making it kinetically unstable (e.g. the thermal and kinetic stabilities have the order of Fe(N5)2 < Ni(N5)2 < NaN5 < cyclo-N5−).18,19 Subsequent experiments proved that these metal-N5− compounds formed hydrate cocrystals with water molecules through hydrogen bonds and sometimes coordination bonds, improving their stability and safety. To date, 12 metal-N5− hydrates (1–12) have been synthesized,2,20–26 of which 4 is also a solvate (Fig. 3). [Na(H2O)(N5)]·2H2O (2) was first reported by Xu et al.2 and is considered the most important precursor for the synthesis of metal hydrates. Two types of hydrogen bonds, O–H⋯O and O–H⋯N, constitute the main stabilization mechanism for stabilizing crystal 2 and its cyclo-N5−, constructing an intralayer 3D hydrogen bond network in 2.27 The O–H⋯O bond is stronger and can stabilize the crystal, while O–H⋯N is connected with N in cyclo-N5−, so it mainly stabilizes cyclo-N5−. For [M(H2O)4(N5)2]·4H2O (M = Mn, Fe, Co, and Zn; 7, 8, 10, 12), two types of water (i.e., coordinated water (c-H2O) and hydrogen-bonded water (h-H2O)) significantly contribute to stability but via different modes (Fig. 4). The role of c-H2O is to bind with M to reduce the interactions between M and cyclo-N5−, leading to a less active cyclo-N5− and higher kinetic barriers (Eas) and reaction energies (ΔEs) for its decomposition. The Eas and ΔEs increased by an average of 7.6 and 15.1 kcal mol−1, respectively. Compared with the reactant, h-H2O enforces fewer electrostatic interactions on cyclo-N5− in the transition state to suppress decomposition, similar to c-H2O.28Some representative cocrystals with different but fascinating structures can be obtained by adjusting the proportion of the coformer (H2O). The 1D coordination chain in the single-crystal structure of 2 is demonstrated in Fig. 5a, where Xu et al.21 synthesized a new 3D open-framework (3/MPF-1) by changing the stoichiometric ratio of NaN5 to H2O from 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 to 8
3 to 8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3. Compound 3/MPF-1 exhibits an aesthetic zeolitic MEP topology featuring two types of nanocages, Na20N60 and Na24N60, in which the strong coordination bonds between cyclo-N5− and Na+ play vital roles in stabilizing the cyclo-N5− anions (Fig. 5b–f).
3. Compound 3/MPF-1 exhibits an aesthetic zeolitic MEP topology featuring two types of nanocages, Na20N60 and Na24N60, in which the strong coordination bonds between cyclo-N5− and Na+ play vital roles in stabilizing the cyclo-N5− anions (Fig. 5b–f).
The different types of coformers can also lead to different cocrystal structures. Xu et al.23 synthesized a UNJ-type zeolite topology framework, [Na4(N5)4(H2O)2]·H2O·2MeOH (4), by introducing MeOH molecules into 2. The framework features multiple 1D tubular channels filled with MeOH and H2O molecules through coordination and hydrogen bonding, whose walls are constructed from Na+ and cyclo-N5− (Fig. 6). Each channel is enclosed by six identical channels, indicating that the adjacent nanotubes are fused together by edge sharing. The network has helical channels along the c-axis direction. Each enclosed helical channel is assembled from two right-handed helical chains by sharing the sides of multiple pentagons (Fig. 6d).
Due to the low density of the coformer, the crystal densities of cocrystals 1–12 are below 1.7 g cm−3, even at low temperatures.2,20–26 These cocrystals are stable at room temperature, and most of them have a decomposition temperature of approximately 100 °C (Table 1). Notably, cocrystal 6 has the highest thermal stability among all metal-N5− solvates, and studies have shown that hydrogen bonding, van der Waals, and π–π stacking interactions play significant roles in the stabilization mechanism.24 Cocrystals 1 and 3 also exhibit remarkable thermal decomposition temperatures, reaching 139 °C and 129 °C, respectively. In contrast, the decomposition temperature of 10 is only 59 °C, which may be due to the stronger interaction between Co2+ and cyclo-N5− (Co–N: 2.122 Å) compared to other complexes. Once c-H2O is lost, cyclo-N5− undergoes N–N bond cleavage and decomposition.
| Comp. | d (g cm−3) | T d (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| a Density from single-crystal X-ray diffraction. b Decomposition temperature (DSC). | ||
| 1 | 1.37 (298 K) | 139 |
| 2 | 1.47 (170 K) | 104 |
| 3 | 1.30 (100 K) | 129 |
| 4 | 1.61 (100 K) | 110 |
| 5 | 1.44 (205 K) | 104 |
| 6 | 1.38 (150 K) | 141 |
| 7 | 1.61 (205 K) | 104 |
| 8 | 1.60 (205 K) | 115 |
| 9 | 1.43 (193 K) | 109 |
| 10 | 1.70 (170 K) | 59 |
| 11 | 1.65 (296 K) | 102 |
| 12 | 1.67 (205 K) | 108 |
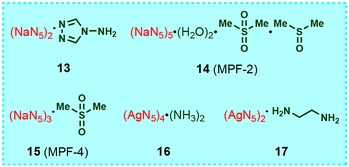
3.2 Cocrystals composed of metal-N5− compounds and amines/MSM
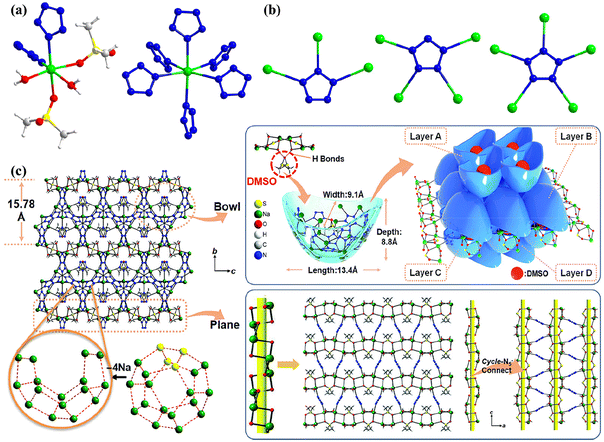
The structural formula of the cocrystals composed of metal-N5− compounds and amines/dimethyl sulfone (MSM) is shown in Fig. 7, where three are NaN5 cocrystals (13–15)29–31 and the other two are AgN5 cocrystals (16 and 17).32,33 We recently discovered that 1329 also has a UNJ-type zeolite topology framework (Fig. 8) similar to that of 4. The framework features multiple 1D tubular channels filled with 4-amino-1,2,4-triazole molecules through coordination and hydrogen bonds. Each channel is also surrounded by six identical channels, indicating that adjacent nanotubes are fused together through edge sharing. Similar to 4, the network also has helical channels along the c-axis. But each enclosed helical channel is assembled by two left-handed helical chains sharing multiple pentagonal sides (Fig. 8d).Cao et al. obtained two cocrystals, 14 (MPF-2) and 15 (MPF-4), by adding NaN5 hydrate and MSM at a specific ratio to a DMSO/amine aqueous solution using MSM as a coformer.30,31 Each cyclo-N5− ring in 14 bridges Na+ through η3, η4, and η5 coordination modes to form a “chiral bowl-shaped” Na16N50 molecular container (Fig. 9). These containers are sealed and assembled by parallel arranged trapezoidal 1D helical chains through a 2D chiral layer “molecular plane” formed by sharing cyclo-N5−. Each container has an ovoid cavity with a volume of approximately 13.4 × 9.1 × 8.8 Å3 occupied by one DMSO guest molecule fixed by hydrogen bonds. It is worth mentioning that the Na16N50 bowl in 14 is closely related to the Na20N60 (simplified 512) nanocage in 3, which is formed by removing 4 Na+ vertices from the 512 nanocage (Fig. 9c). Both 4-amino-1,2,4-triazole and MSM can be regarded as bidentate ligands, but the stoichiometric ratios of NaN5 to them in their cocrystals (13, 15) are different (2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 vs. 3
1 vs. 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). Even more surprising, both of these cocrystals have a homochiral framework with two left-handed helices interpenetrating each other to form a UNJ topology (Fig. 10). Since the structure of 15 is extremely similar to that of 13, we do not discuss it in detail here.
1). Even more surprising, both of these cocrystals have a homochiral framework with two left-handed helices interpenetrating each other to form a UNJ topology (Fig. 10). Since the structure of 15 is extremely similar to that of 13, we do not discuss it in detail here.
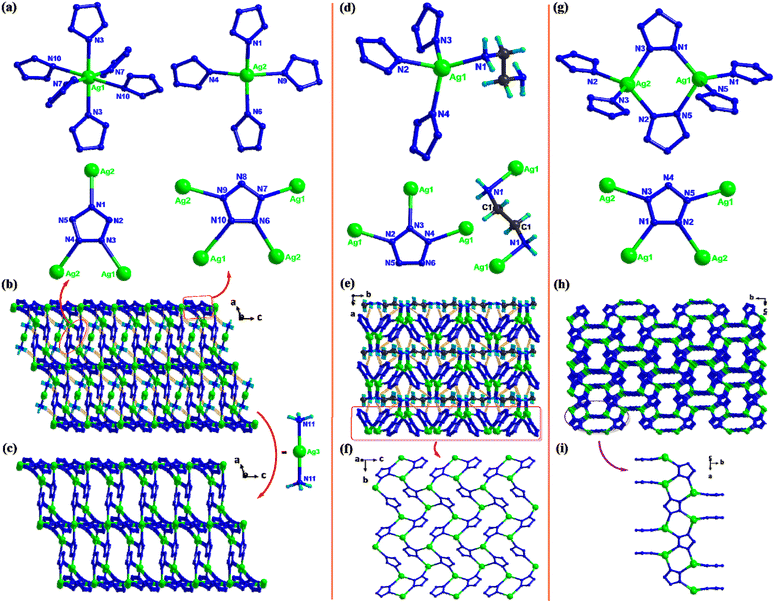
AgN5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 34 is one of the most important intermediates for the syntheses of various cyclo-N5− energetic materials. In order to improve the thermal stability and safety performance of AgN5, cocrystals 16 and 17 were synthesized (Fig. 11).32,33 Their coformers are all amines, and their stoichiometric ratio to AgN5 is 1
34 is one of the most important intermediates for the syntheses of various cyclo-N5− energetic materials. In order to improve the thermal stability and safety performance of AgN5, cocrystals 16 and 17 were synthesized (Fig. 11).32,33 Their coformers are all amines, and their stoichiometric ratio to AgN5 is 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2. Similar to AgN5, there are also two types of coordinated Ag+ (different connected configurations) in 16. However, only one type of Ag+ was observed in 17. Besides, only one type of cyclo-N5− ring is present in AgN5 and 17, while in 16, there are two types of cyclo-N5− rings that are coordinated to three and four Ag+ ions. Moreover, the π–π interactions between cyclo-N5− anions in AgN5 are much stronger than those in 16 and 17. Therefore, the 3D frameworks of 16 and 17 are different from that of AgN5 (PtS topology). The negatively charged 3D supramolecular framework Ag3(N5)4 in 16 is regularly filled with Ag(NH3)2+ counter ions by hydrogen bonds, while the 2D AgN5 networks in 17 are connected layer-by-layer by ethylenediamine molecules through Ag–N coordination bonds, thereby forming a regular 3D supramolecular network.
2. Similar to AgN5, there are also two types of coordinated Ag+ (different connected configurations) in 16. However, only one type of Ag+ was observed in 17. Besides, only one type of cyclo-N5− ring is present in AgN5 and 17, while in 16, there are two types of cyclo-N5− rings that are coordinated to three and four Ag+ ions. Moreover, the π–π interactions between cyclo-N5− anions in AgN5 are much stronger than those in 16 and 17. Therefore, the 3D frameworks of 16 and 17 are different from that of AgN5 (PtS topology). The negatively charged 3D supramolecular framework Ag3(N5)4 in 16 is regularly filled with Ag(NH3)2+ counter ions by hydrogen bonds, while the 2D AgN5 networks in 17 are connected layer-by-layer by ethylenediamine molecules through Ag–N coordination bonds, thereby forming a regular 3D supramolecular network.
The crystal densities of two AgN5 cocrystals (16 and 17) are higher than those of three NaN5 cocrystals (13–15), with the highest density of 16 reaching 3.21 g cm−3 (Table 2). However, the thermal stabilities of 16 and 17 (≤105 °C) are worse than those of 13–15 (119–127 °C). The detonation velocities (D: 6427 and 6272 m s−1) and detonation pressures (P: 29.00 and 23.51 GPa) of 16 and 17 are slightly lower than those of AgN5. Compared with those of extremely sensitive AgN5, the mechanical sensitivities of the two cocrystals are significantly reduced (Table 2).
| Comp. | d (g cm−3) | T d (°C) | D (m s−1) | P (GPa) | ISe (J) | FSf (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Density from single-crystal X-ray diffraction. b Decomposition temperature (DSC). c Detonation velocity. d Detonation pressure. e Impact sensitivity. f Friction sensitivity. | ||||||
| 13 | 1.73 (173 K) | 127 | 7863 | 26.4 | ||
| 14 | 1.65 (296 K) | 119 | ||||
| 15 | 1.66 (295 K) | 119 | ||||
| 16 | 3.21 (220 K) | 90 | 6427 | 29.00 | 7.5 | 60 |
| 17 | 2.73 (170 K) | 105 | 6272 | 23.51 | 15 | 120 |
| AgN5 | 3.02 (173 K) | 98 | 7782 | 34.67 | 0.5 | 1 |
3.3 Metal-containing composite salts
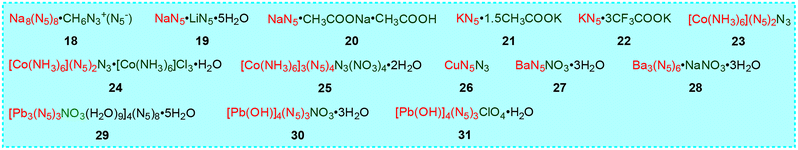
There are 14 metal-containing composite salts in cyclo-N5− cocrystals, including two (1829 and 1935) with two cations, nine (20–23,25,29,36,3726,3427,34 and 29–3138) with two anions, two (2425 and 2525) with three anions, and one (2834) with two cations and two anions (Fig. 12). Cocrystal 18, the earliest synthesized metal-containing composite salt, has a zeolite-like 3D framework with a SOD topology. 19 has a 3D heterometallic framework with left- and right-handed helical chains. Although 20 is a byproduct obtained during the synthesis of pentazolate N-oxide, we discovered the miraculous effect of coformers containing acetate ions on the structural regulation of metal-N5− compounds through the structure of 20 and subsequently developed cocrystals 21 and 22 on the basis of KN5. The 3D topological network of KN5 is shown in Fig. 13a, which consists of a number of parallelograms neatly arranged in the framework.16 Unlike KN5, 21 has a zeolite-like UNJ topological network through hexagons (Fig. 13b), and cocrystal 22 has the same zeolite-like UNJ topological network through inverted triangles consisting of three small triangles and one hexagonal shape (Fig. 13c).Cocrystals 23–25 have the same hexaaminocobalt(III) cation [Co (NH3)6]3+, but with different types and numbers of anions, which crystallize in the monoclinic C12/m1 (23) and C2/m (24 and 25) space groups, respectively. However, 30 and 31 have the same [Pb4(OH)4]4+ cubic cation and number of anions, except for the types of anions and the number of H2O. They crystallize in triangular R3 (30) and orthorhombic Pca21 (31) space groups, respectively. It is worth mentioning that 26 is the only cyclo-N5− cocrystal composed of only two elements (Cu and N), but once it separates from the mother liquor, it can easily cause an explosion.
The densities of cocrystals 18–31 vary from 1.21 g cm−3 to 4.42 g cm−3 (Table 3), which is attributed mainly to the types of metal ions, coformed ions, and crystal water content, as well as the resulting differences in the crystal stacking patterns. Among these 14 cocrystals, 25 has the highest thermal decomposition temperature (163 °C), followed by 20 (139 °C) and 27 (130 °C). In order to evaluate the energetic performance of 23, detonation tests conducted in the literature have shown that the cocrystal has high priming ability and is expected to become a potential green primary explosive.25
| Comp. | d (g cm−3) | T d (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| a Density from single-crystal X-ray diffraction. b Decomposition temperature (DSC). | ||
| 18 | 1.21 (170 K) | 118 |
| 19 | 1.55 (173 K) | 106 |
| 20 | 1.71 (100 K) | 139 |
| 21 | 1.75 (298 K) | 100 |
| 22 | 2.10 (298 K) | 100 |
| 23 | 1.72 (170 K) | 98 |
| 24 | 1.63 (296 K) | 104 |
| 25 | 1.60 (296 K) | 163 |
| 26 | 2.62 (173 K) | 90 |
| 27 | 2.59 (100 K) | 130 |
| 28 | 2.34 (100 K) | 121 |
| 29 | 2.85 (296 K) | 89 |
| 30 | 3.91 (296 K) | 97 |
| 31 | 4.42 (296 K) | 110 |
4 Cocrystals of non-metallic pentazolate salts
4.1 Cocrystals composed of cyclo-N5− salts and solvents
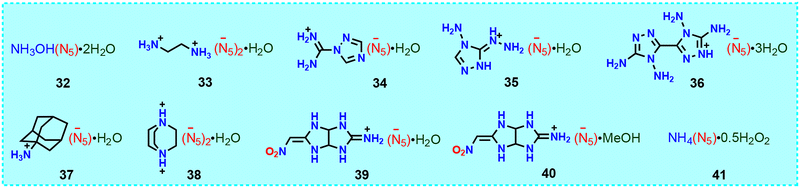
Hydrates (or solvates) of non-metallic pentazolate salts are very common. On the one hand, cations in non-metallic pentazolate salts are good donors of hydrogen bonds (rich in N–H), cyclo-N5− anions are good acceptors of hydrogen bonds, and water molecules are both excellent donors and acceptors of hydrogen bonds. During the crystallization process, owing to weak interactions or crystal stacking, smaller water molecules are needed to fill the crystal cell to form a cocrystal. On the other hand, water, as a green solvent with a strong ability to dissolve energetic salts, is inevitable in the synthesis of cyclo-N5− and its conversion to non-metallic salts. Fig. 14 shows the chemical formula of 10 hydrates (or solvates) of non-metallic pentazolate salts (32–41)15–17,39–43 and the stoichiometric ratio of cyclo-N5− salts to water (or solvent molecules) (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.5/1/2/3). Among them, 34–36 have –NH2 rich triazolium cations; 37 and 38 have cage-like cations; and 39 and 40 have the same 5/5 fused imidazolium pentazolate. These cocrystals have a density below 1.6 g cm−3 and a thermal decomposition temperature of ≤115 °C (Table 4).
0.5/1/2/3). Among them, 34–36 have –NH2 rich triazolium cations; 37 and 38 have cage-like cations; and 39 and 40 have the same 5/5 fused imidazolium pentazolate. These cocrystals have a density below 1.6 g cm−3 and a thermal decomposition temperature of ≤115 °C (Table 4).
| Comp. | d (g cm−3) | T d (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| a Density from single-crystal X-ray diffraction. b Decomposition temperature (DSC). Except for 83 and 100, other data are from the corresponding anhydrous salts. | ||
| 32 | 1.49 (173 K) | 106 |
| 33 | 1.46 (100 K) | 98 |
| 34 | 1.49 (173 K) | 96 |
| 35 | 1.58 (170 K) | 83 |
| 36 | 1.52 (173 K) | 95 |
| 37 | 1.23 (296 K) | 79 |
| 38 | 1.48 (293 K) | 92 |
| 39 | 1.66 (193 K) | 115 |
| 40 | 1.61 (193 K) | 115 |
| 41 | 1.49 (295 K) | 100 |
One of the strategies for reducing the mechanical sensitivity of highly sensitive energetic materials (such as metal-N5− compounds) is to form cocrystals of energetics and solvent molecules.44 The sensitivities of non-metallic pentazolate salts are moderate, and there is no need to passivate them through hydrates or solvates. Therefore, researchers do not want to obtain hydrates or solvates of non-metallic pentazolate salts, but rather pure salts, to obtain more accurate structures, interactions, and physicochemical properties. However, H2O2 is both a solvent and a green oxidizer, with low environmental impact and insensitivity in its solvent form. If H2O2 can be embedded into cyclo-N5− salts with a negative oxygen balance through a solvation strategy, it is expected that the oxygen balance and energy of the developed cyclo-N5− cocrystal will be correspondingly improved. In 2020, Luo et al. successfully produced 41 by utilizing the effective strategy of a CL-20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) H2O2 (2
H2O2 (2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) cocrystal45 proposed by Matzger et al.
1) cocrystal45 proposed by Matzger et al.
In cocrystal 41, H2O2 molecules are incorporated into the crystal lattices of NH4N5 to construct a novel 3D hydrogen-bonding network, where cyclo-N5− rings are layer-by-layer stacked and NH4+ cations are embedded in the layers and connected by hydrogen bonding (Fig. 15). This cocrystal has a high oxygen balance and high D and P values (8938 m s−1 and 26.37 GPa), which are much higher than those of NH4N5. In addition, 41 exhibits an astonishing specific impulse (Isp: 260 s), which is approximately 15% higher than that of NH4N5 (225 s). Furthermore, the combustion products of 41 are mostly composed of clean N2, H2 and H2O, indicating its great potential as a component of high-energy propellants.
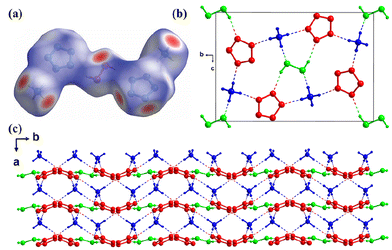 | ||
| Fig. 15 (a) Single-crystal X-ray structure of 41 (with Hirshfeld surfaces). (b and c) Stacking diagram of 41 viewed along the a and c axis. | ||
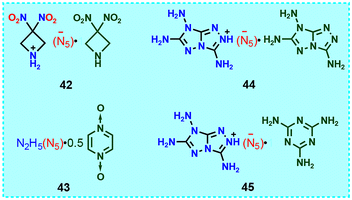
4.2 Cocrystals composed of cyclo-N5− salts and N-heterocyclic molecules
Cocrystals composed of cyclo-N5− salts and N-heterocyclic molecules are relatively rare, with only four cocrystals (42–45) being reported (Fig. 16). Therefore, obtaining novel cocrystals of cyclo-N5− salts with a balance between high energy and good stability is a considerable challenge. The combination of a nonmetallic cyclo-N5− salt and a neutral molecule in a certain proportion to form a cocrystal compound has a positive effect on the detonation performance and hygroscopic properties of the cyclo-N5− salt. 4246 is a cocrystal composed of 3,3-dinitroazetidine (DNAZ) and HDNAZ+N5− at a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 stoichiometry, which is an unexpected product targeting a DNAZ+N5− salt. However, by studying its crystal structure, we found that the crystal is disordered with the H3A proton of the DNAZ cation fixed at 50% occupancy, indicating that the cation is completely occupied and semi-protonated. Therefore, it could be a (2 DNAZH)+N5− salt.
1 stoichiometry, which is an unexpected product targeting a DNAZ+N5− salt. However, by studying its crystal structure, we found that the crystal is disordered with the H3A proton of the DNAZ cation fixed at 50% occupancy, indicating that the cation is completely occupied and semi-protonated. Therefore, it could be a (2 DNAZH)+N5− salt.
In order to solve the hygroscopicity problem of N2H5N5, pyrazine-1,4-dioxide (PDO) molecules were introduced to synthesize cocrystal 43, which reduced the moisture absorption of N2H5N5 from 45% to 15%.47 The PDO and cyclo-N5− rings are parallel, and the distance between them is 3.44 Å, indicating the presence of extensive π–π interactions. There are numerous hydrogen bonds in 43, which play an important role in the construction of 3D-cube layered stacking (Fig. 17). In addition, after the formation of the cocrystal, the density increased compared with that of N2H5N5, but the sensitivity decreased.
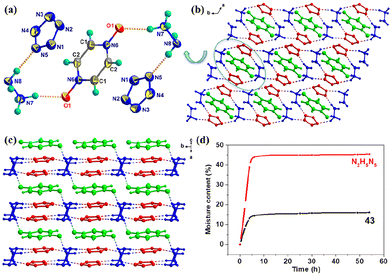 | ||
| Fig. 17 (a) Single-crystal X-ray structure of 43. (b and c) Stacking diagram of 43. (d) Moisture content curves of N2H5N5 and 43 under a 75% relative humidity at 25 °C. | ||
Cocrystals 4439 and 4548 differ only in their coformer, with one being 3,6,7-triamine-7H-[1,2,4]triazole[4,3-b][1,2,4]triazole (TATOT) and the other being melamine. Both of them have a layered stacking structure, and each cyclo-N5− in the 2D layer is fixed by seven hydrogen bonds (Fig. 18). Owing to the combined effects of various non-covalent interactions, 45 forms a hydrogen-bonded organic framework (HOF) with 1D pores, and cyclo-N5− rings occupy these pores and are stabilized by hydrogen bonds, π–π interactions between the cyclo-N5− rings, and attraction between the cyclo-N5− anions and the cationic HOF. These factors increase its thermal stability to 153 °C (Table 5), exceeding that of 44 (122 °C) and TATOTN5 (121 °C).16 Overall, the D and P values of the four cocrystals composed of cyclo-N5− salts and N-heterocyclic molecules are 8029–8735 m s−1 and 24.6–29 GPa, respectively (Table 5), which are slightly lower than those of RDX. But they are significantly less sensitive than RDX.
| Comp. | d (g cm−3) | T d (°C) | D (m s−1) | P (GPa) | ISe (J) | FSf (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Density from single-crystal X-ray diffraction. b Decomposition temperature (DSC). c Detonation velocity. d Detonation pressure. e Impact sensitivity. f Friction sensitivity. | ||||||
| 42 | 1.67 (193 K) | 116 | 8441 | 29.0 | 11 | 252 |
| 43 | 1.61 (296 K) | 101 | 8735 | 26.6 | 35 | 300 |
| 44 | 1.66 (193 K) | 122 | 8605 | 26.0 | >40 | >360 |
| 45 | 1.69 (100 K) | 153 | 8029 | 24.6 | >40 | >360 |
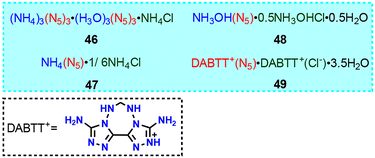
4.3 Non-metallic composite salts
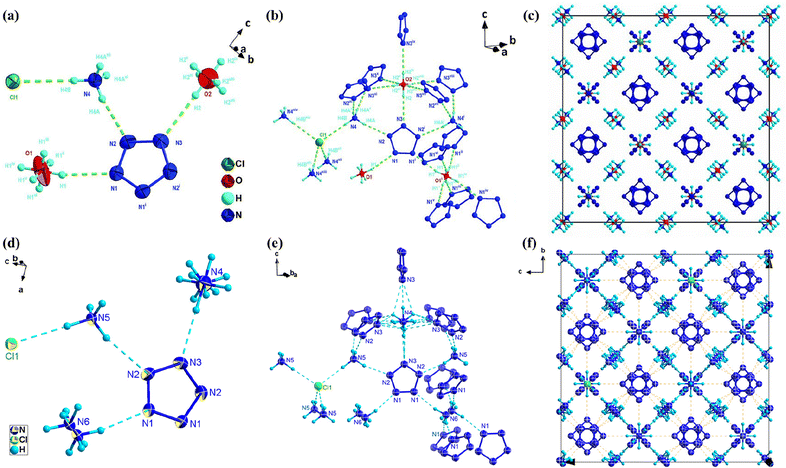
The number of non-metallic composite salts of cyclo-N5− is much less than that of its metal-containing composite salts of only four (46–49).5,15,49,50 Their common feature is that they contain both cyclo-N5− and Cl− ions (Fig. 19). Among them, both 46 and 47 crystallize in the cubic Fd![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m space group, with almost identical unit cell parameters (Fig. 20). Although the unusual structure of 46 was resolved by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis, the presence of hydronium ions (H3O+) has not been confirmed by other experiments. Thus, a series of debates51–54 have ensued, such as the correctness of O2 atom assignment, the possible existence of a HN5 species in this salt, and the pathways and influencing factors for interconversion among HN5 and cyclo-N5−.
m space group, with almost identical unit cell parameters (Fig. 20). Although the unusual structure of 46 was resolved by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis, the presence of hydronium ions (H3O+) has not been confirmed by other experiments. Thus, a series of debates51–54 have ensued, such as the correctness of O2 atom assignment, the possible existence of a HN5 species in this salt, and the pathways and influencing factors for interconversion among HN5 and cyclo-N5−.
A comparison of the crystal structures of these two cocrystals revealed the following points. First, the ordered H3O+ (O1) in 46 formed only three hydrogen bonds with three cyclo-N5− rings, but a pair of lone-pair electrons on O1 did not have a hydrogen-bonding interaction with other atoms. The ordered NH4+ (N6) in 47, at the same position as H3O+ (O1) in 46, can form good hydrogen bonds with all the surrounding cyclo-N5− rings. Second, the isotropic temperature factors of the atomic thermal vibration for the two oxygen atoms, O1 and O2, in 46 are 0.082(3) and 0.071(3), respectively, which are 1.5–2.0 times greater than those of the other atoms (N1–N4 and Cl1). While the thermal vibration temperature factors of all the atoms in 47 are at the same level. Finally, 47 has lower R and wR indices than 46, and the goodness-of-fit on F2 of 47 (1.075) is closer to 1 than that of 46 (1.208). In addition, the correctness of structure 47 was also supported by the experimental results of DSC-TG-MS, SEM-EDX, IR spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy.
The properties of the four non-metallic composite salts are shown in Table 6. Compared with their corresponding cyclo-N5− salts, cocrystals 47 and 48 have lower friction and impact sensitivities. Moreover, 47 exhibited better thermal stability (10 °C higher than that of NH4N5) and good detonation performance (D: 8300 m s−1, P: 21.4 GPa) than did FOX-12.49
| Comp. | d (g cm−3) | T d (°C) | D (m s−1) | P (GPa) | ISe (J) | FSf (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Density from single-crystal X-ray diffraction. b Decomposition temperature (DSC). c Detonation velocity. d Detonation pressure. e Impact sensitivity. f Friction sensitivity. | ||||||
| 46 | 1.34 (123 K) | 117 | ||||
| 47 | 1.34 (150 K) | 109 | 8300 | 21.4 | 31 | 300 |
| 48 | 1.59 (100 K) | 95 | 8260 | 23.8 | >40 | >360 |
| 49 | 1.62 (173 K) | 99 | 7615 | 23.6 | ||
5 Summary and outlook
The pentazolate anion and its derivatives represent one of the most important research advances in the field of energetic materials. In the past seven years, many energetic cyclo-N5− cocrystals have been developed through metathesis reactions combined with solvent evaporation or self-assembly methods. Cyclo-N5− cocrystals can be divided into cocrystals of metal-N5− compounds and non-metallic pentazolate salts according to their composition. Each major category can be further divided into three subcategories: solvates (mainly hydrates), cocrystals composed of cyclo-N5− compounds and neutral molecules, and composite salts. Among them, metal composite salts represent the largest number (14), followed by solvates of metal (12) and non-metallic salts (10). Overall, the number of water-containing cocrystals (32) accounts for nearly two-thirds of that of cyclo-N5− cocrystals, and synthesizing anhydrous cyclo-N5− cocrystals remains a challenge.Cyclo-N5− cocrystals, especially those containing metals, have fascinating crystal structures, including pentasil-zeolite topological networks, metal pentazolate frameworks, and hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks. The thermal stabilities of some cocrystals exceed those of their pentazolate precursors, providing ideas for the development of more promising cyclo-N5− derivatives.
Suggestions for future key research directions for cyclo-N5− cocrystals are as follows:
(1) On the basis of the existing synthetic methods for cyclo-N5− cocrystals, more preparation methods should be developed, especially methods suitable for scale up.
(2) All reported enthalpies of formation of cyclo-N5− cocrystals were theoretically determined. In order to accurately evaluate their energy, more attention must be paid to using high-precision calculation methods and experimental measurements.
(3) The activation energy barrier for the decomposition of cyclo-N5− is only about 100 kJ mol−1, so the decomposition temperatures of cyclo-N5− cocrystals are relatively lower than those of traditional energetic materials such as RDX and HMX. In the direction of application, it is necessary to further increase the thermal stability of cyclo-N5− cocrystals.
(4) The energetic properties of cyclo-N5− cocrystals are often between those of the precursors, which means that the energy of a cyclo-N5− cocrystal is slightly lower than that of a cyclo-N5− precursor. Therefore, further research is expected to increase the energy through the cocrystallization of cyclo-N5− compounds and high-density, high-oxygen balance, high-energy oxidizer molecules.
(5) By using advanced methods such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and high-throughput experiments to study the formation mechanism of cyclo-N5− cocrystals, we can grasp the key influencing factors of cocrystal formation, which has guiding significance for the future creation of energetic cocrystals and even polynitrogen compounds.
Data availability
No primary research results, software or code have been included and no new data were generated or analysed as part of this review.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 22105102 and 22135003), the Young Elite Scientist Sponsorship Program by CAST (no. YESS20210074), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (no. 30921011204).References
- V. E. Zarko, Combust., Explos. Shock Waves, 2010, 46, 121–131 Search PubMed.
- Y. Xu, Q. Wang, C. Shen, Q. Lin, P. Wang and M. Lu, Nature, 2017, 549, 78–81 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Xu, Q. Lin, P. Wang and M. Lu, Chem. – Asian J., 2018, 13, 924–928 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. A. Dixon, D. Feller, K. O. Christe, W. W. Wilson, A. Vij, V. Vij, H. D. B. Jenkins, R. M. Olson and M. S. Gordon, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 834–843 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Zhang, C. Sun, B. Hu, C. Yu and M. Lu, Science, 2017, 355, 374–376 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Zhong and C. Zhang, Chem. Eng. J., 2024, 483, 149202 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) J. C. Bennion and A. J. Matzger, Acc. Chem. Res., 2021, 54, 1699–1710 CrossRef CAS; (b) L. M. Foroughi, R. A. Wiscons, D. R. D. Bois and A. J. Matzger, Chem. Commun., 2020, 56, 2111–2114 RSC.
- (a) O. Bolton and A. J. Matzger, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 8960–8963 CrossRef CAS; (b) S. Hanafi, D. Trache, A. Mezroua, H. Boukeciat, R. Meziani, A. F. Tarchoun and A. Abdelaziz, RSC Adv., 2021, 11, 35287–35299 RSC; (c) A. Abdelaziz, D. Trache, A. F. Tarchoun, H. Boukeciat, D. E. Kadri, H. Hassam, S. Ouahioune, N. Sahnoun, S. Thakur and T. M. Klapötke, Chem. Eng. J., 2024, 487, 150654 CrossRef CAS; (d) H. Boukeciat, A. F. Tarchoun, D. Trache, A. Abdelaziz, R. Meziani and T. M. Klapötke, Polymers, 2023, 15, 1799 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Zhang, S. Chen, Y. Wu, S. Jin, X. Wang, Y. Wang, F. Shang, K. Chen, J. Du and Q. Shu, Chem. Commun., 2018, 54, 13268–13270 RSC.
- M. K. Bellas and A. J. Matzger, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 17185–17188 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. J. Bennett, L. M. Foroughi and A. J. Matzger, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2024, 146, 1771–1775 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Zhang, C. Yao, Y. Yu, S. Jiang, C. Sun and J. Chen, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2019, 10, 2378–2385 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Sultan, J. Wu, I. U. Haq, M. Imran, L. Yang, J. Wu, J. Lu and L. Chen, Molecules, 2022, 27, 4775 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Yang, C. Zhang, Z. Zheng, C. Jiang, J. Luo, Y. Du, B. Hu, C. Sun and K. O. Christe, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 16488–16494 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Xu, L. Tian, P. Wang, Q. Lin and M. Lu, Cryst. Growth Des., 2019, 19, 1853–1859 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Xu, L. Tian, D. Li, P. Wang and M. Lu, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 12468–12479 RSC.
- L. Tian, Y. Xu, Q. Lin, P. Wang and M. Lu, Chem. – Asian J., 2019, 14, 2877–2882 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Zhang, J. Yang, M. Lu and X. Gong, Struct. Chem., 2015, 26, 785–792 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Zhang, J. Yang, M. Lu and X. Gong, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 21823–21830 RSC.
- Y. Xu, L. Ding, F. Yang, D. Li, P. Wang, Q. Lin and M. Lu, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 429, 132399 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Xu, P. Wang, Q. Lin, X. Mei and M. Lu, Dalton Trans., 2018, 47, 1398–1401 RSC.
- W. Zhang, K. Wang, J. Li, Z. Lin, S. Song, S. Huang, Y. Liu, F. Nie and Q. Zhang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 2592–2595 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Xu, Z. Xu, X. Zhang, T. Hou and M. Lu, CrystEngComm, 2022, 24, 4853–4856 RSC.
- L. Chen, C. Yang, H. Hu, L. Shi, C. Zhang, C. Sun, C. Gao, Y. Du and B. Hu, CrystEngComm, 2022, 24, 8152–8159 RSC.
- Y. Xu, J. Zhou, D. Li, P. Wang, Q. Lin and M. Lu, Cryst. Growth Des., 2022, 23, 811–819 CrossRef.
- Y. Xu, P. Wang, Q. Lin and M. Lu, Dalton Trans., 2017, 46, 14088–14093 RSC.
- X. Li, Y. Long, C. Zhang, C. Sun, B. Hu, P. Lu and J. Chen, ACS Omega, 2022, 7, 6627–6639 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Luo, L. Chen, D. N. Nguyen, D. Guo, Q. An and M. Cheng, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2018, 122, 21192–21201 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Wang, Y. Xu, Q. Wang, Y. Shao, Q. Lin and M. Lu, Sci. China Mater., 2018, 62, 122–129 CrossRef.
- Y. Cao, S. Huang, Q. Zhang and W. Zhang, Dalton Trans., 2020, 49, 17542–17546 RSC.
- Y. Cao, H. Xia, K. Wang, Q. Zhang and W. Zhang, Inorg. Chem., 2021, 60, 8409–8413 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Zhang, T. Hou, Q. Lin, P. Wang, D. Li, Y. Xu and M. Lu, CrystEngComm, 2022, 24, 1900–1906 RSC.
- C. Sun, C. Zhang, C. Jiang, C. Yang, Y. Du, Y. Zhao, B. Hu, Z. Zheng and K. O. Christe, Nat. Commun., 2018, 9, 1269 CrossRef.
- Y. Xu, Q. Lin, P. Wang and M. Lu, Chem. – Asian J., 2018, 13, 1669–1673 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Li, K. Wang, S. Song, X. Qi, W. Zhang, M. Deng and Q. Zhang, Sci. China Mater., 2018, 62, 283–288 CrossRef.
- Z. Xu, S. Jiang, T. Hou, X. Zhang, M. Lu and Y. Xu, New J. Chem., 2023, 47, 5616–5620 RSC.
- S. Jiang, J. Zhou, Y. Xu, Q. Lin, P. Wang and M. Lu, CrystEngComm, 2024, 26, 951–956 RSC.
- Y. Yuan, Y. Xu, Q. Xie, D. Li, Q. Lin, P. Wang and M. Lu, Dalton Trans., 2022, 51, 5801–5809 RSC.
- C. Yang, L. Chen, W. Wu, C. Zhang, C. Sun, Y. Du and B. Hu, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 4, 146–153 CrossRef.
- S. Chen, C. Yang, C. Sun, C. Zhang, C. Gao, Y. Du and B. Hu, J. Mol. Struct., 2022, 1249, 131521 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Jiang, H. Xia, W. Zhang, Z. Cai, S. Song and T. Liu, CrystEngComm, 2024, 26, 977–984 RSC.
- L. Shi, P. Wang, C. Gao, C. Zhang, Y. Du, C. Sun and B. Hu, Cryst. Growth Des., 2023, 24, 669–677 CrossRef.
- J. Luo, H. Xia, W. Zhang, S. Song and Q. Zhang, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8, 12334–12338 RSC.
- D. I. A. Millar, H. E. Maynard-Casely, D. R. Allan, A. S. Cumming, A. R. Lennie, A. J. Mackay, I. D. H. Oswald, C. C. Tang and C. R. Pulham, CrystEngComm, 2012, 14, 3742–3749 RSC.
- J. C. Bennion, N. Chowdhury, J. W. Kampf and A. J. Matzger, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 13118–13121 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Yang, L. Chen, S. Chen, W. Wu, W. Yuan, J. Yao, C. Zhang, C. Sun, Y. Du and B. Hu, Cryst. Growth Des., 2021, 21, 4329–4336 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhou, X. Li, T. Hou, Z. Xu, P. Wang, M. Lu and Y. Xu, CrystEngComm, 2023, 25, 2027–2031 RSC.
- Y. Xu, J. Zhou, X. Li, T. Hou, Z. Xu, P. Wang and M. Lu, Commun. Mater., 2024, 5, 25 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Xu, D. Li, P. Wang, Q. Lin, L. Ding, T. Hou, Y. Yuan and M. Lu, J. Energ. Mater., 2021, 41, 99–116 CrossRef.
- Y. Yuan, T. Hou, D. Li, Y. Xu and M. Lu, Chin. J. Energ. Mater. (Hanneng Cailiao), 2022, 30, 96–102 CAS.
- R. Huang and H. Xu, Science, 2018, 359, eaao3672 CrossRef.
- C. Jiang, L. Zhang, C. Sun, C. Zhang, C. Yang, J. Chen and B. Hu, Science, 2018, 359, eaas8953 CrossRef.
- H. Huang, J. Zhong, L. Ma, L. Lv, J. S. Francisco and X. C. Zeng, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 2984–2989 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Chen, Z. Liu, Y. Zhao, X. Yi, Z. Chen and A. Zheng, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2018, 9, 7137–7145 CrossRef CAS.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |