 Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleReview of carbon-support-free platinum and non-platinum catalysts for polymer electrolyte fuel cells: will they feature in future vehicles?
Mitsuharu
Chisaka
 *
*
Department of Sustainable Energy, Hirosaki University, 3 Bunkyo-cho, Hirosaki, Aomori 036-8561, Japan. E-mail: chisaka@hirosaki-u.ac.jp; Fax: +81-172-39-3559; Tel: +81-172-39-3559
First published on 17th June 2024
Abstract
Polymer electrolyte fuel cells have attracted considerable attention as possible replacements for internal combustion engines (ICEs) in light duty vehicles for journeys typically over 300 miles as well as for medium/heavy duty vehicles. In these vehicle types, carbon black is currently used as the support for platinum (Pt)-based catalysts at the cathode and anode. Carbon black is protected from corrosion during startup/shutdown and unwanted fuel (H2) starvation by controlling the potential of both electrodes using high-cost system-level measures. Carbon-support-free Pt-based cathode catalysts, which are durable at the high potentials experienced during startup/shutdown due to the reverse current decay mechanism, have therefore been studied extensively over the last two decades. Anodes with impeded oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity have also been developed over the last decade to suppress cathode degradation, as the high potential at the cathode is caused by the reduction of contaminated O2 molecules at the anode. During H2 starvation, the potential of the anode exceeds that of the cathode, which reverses the cell voltage. Theoretical studies have predicted that binary and nonbinary stoichiometric oxides should be stable under these cathode and anode conditions. This paper focuses on non-carbon supports beyond the typical oxides. Both conductivity and the surface area are crucial in decreasing Pt loading to the platinum group metal (PGM) level used in exhaust gas catalytic converters in conventional gasoline-fueled ICE-powered vehicles. As the conductivity of powders/particles is a particular focus of this article, reports on suboxides and nitrides with metallic characters are covered. Some Pt/non-carbon catalysts exhibit higher ORR activity and durability against startup/shutdown at the cathodes, as well as higher durability against cell reversal at the anodes, compared with conventional carbon-supported Pt or platinum–cobalt (PtCo) catalysts under specific conditions such as high Pt loading or low relative humidity. The origin of these beneficial properties is reviewed. In contrast to these positive results, negative reports of non-carbon supports for the anode and cathode are also highlighted, and the advantages and disadvantages of using non-carbon supports are discussed. Recent improvements in carbon-support-free, non-PGM cathode materials with the use of conductive TiN and associated challenges are also reviewed.
1 Introduction
In many countries, the transport sector generates the largest share of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, for example, accounting for 29% of 2022 GHG emissions in the United States (US).1 Light duty vehicles (LDVs; <10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 lbs in weight) and medium/heavy duty vehicles (MDVs/HDVs, >10
000 lbs in weight) and medium/heavy duty vehicles (MDVs/HDVs, >10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 lbs in weight) are responsible for the majority of GHG emissions from the US transport sector (59% and 23% from LDVs and MDVs/HDVs, respectively).2 Policies to reduce GHG and particulate emissions from LDVs have been implemented worldwide, to reduce the future impact of climate change and to protect public health. Some cities, regions, and countries have planned to phase out conventional internal combustion engines (ICEs) in LDVs between 2025 and 2040,3 while California, the first state to introduce emission regulations, plans to phase out ICEs even in MDVs/HDVs. The California Air Resources Board (CARB) aims to phase out ICEs in all buses and trucks by 2045, with earlier goals recently being specified for trucks (2036)4 and public buses (2029).5
000 lbs in weight) are responsible for the majority of GHG emissions from the US transport sector (59% and 23% from LDVs and MDVs/HDVs, respectively).2 Policies to reduce GHG and particulate emissions from LDVs have been implemented worldwide, to reduce the future impact of climate change and to protect public health. Some cities, regions, and countries have planned to phase out conventional internal combustion engines (ICEs) in LDVs between 2025 and 2040,3 while California, the first state to introduce emission regulations, plans to phase out ICEs even in MDVs/HDVs. The California Air Resources Board (CARB) aims to phase out ICEs in all buses and trucks by 2045, with earlier goals recently being specified for trucks (2036)4 and public buses (2029).5
Electric vehicles (EVs) and fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) powered by secondary batteries such as lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) and polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs), respectively, are potential alternative zero-emission vehicles to replace ICE-powered conventional vehicles. Unlike EVs, FCVs are expected to be used in LDVs for journeys over 300 miles,6 as well as in MDVs/HDVs.7 Although a decade has passed since the launch of mid-sedan FCVs in 2014, these vehicles still represent a small percentage of the current market share. Currently, carbon black-supported platinum (Pt/C or Pt/CB) and platinum–cobalt (PtCo/C or PtCo/CB) catalysts are used to catalyze the hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR) at the anode and the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) at the cathode in PEFC catalyst layers, respectively.8,9 Due to the slower kinetics of the ORR compared with the HOR, the platinum loading of the cathode is four-fold that of the corresponding anode.9 The high platinum loading requirement is assumed to be the greatest cost barrier to the widespread adoption of FCVs.10 Therefore, efforts have been made over the last two decades to reduce the amount of platinum required in PEFCs by an order of magnitude to ∼20 g per 128 kW for a mid-sedan passenger vehicle.6,8 However, a further reduction to ∼6 g per vehicle is necessary to make PEFC-powered passenger vehicles affordable and allow their widespread adoption.9 This value is equivalent to the mass of platinum group metal (PGM) catalysts required in a catalytic converter used for the exhaust gas of a gasoline-fueled LDV.11
In addition to the high costs, carbon-supported platinum-based catalysts currently lack stability, with the instability of platinum/platinum alloy catalysts and the corrosion of carbon supports being two major challenges in improving the durability of PEFC stacks.10 In an ideal PEFC, the anode and cathode reactions are as follows (eqn (1) and (2)):
| HOR at anodes: H2 → 2H+ + 2e− | (1) |
| ORR at cathodes: O2 + 4H+ + 4e− → 2H2O | (2) |
During the startup and shutdown of PEFCs, the anode becomes contaminated with O2 molecules originating either from the cathode or the air. Later, the contaminating O2 molecules are reduced to water as the anode Pt/C catalyzes the ORR (eqn (2)), giving rise to a counter cathode potential of up to ∼1.5 V versus the reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) via a reverse current decay mechanism.12 Because in-plane proton conductivity in the catalyst layers is insufficient, protons in the anode ORR are sourced from the counter cathode, at which either the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) via eqn (3) or the carbon oxidation reaction (COR) via eqn (4) and/or (5) proceeds, as shown in Fig. 1.12 The carbon black in the PtCo/C cathode is easily oxidized at such high potentials.
| 2H2O → O2 + 4H+ + 4e− | (3) |
| C + 2H2O → CO2 + 4H+ + 4e− | (4) |
| C + H2O → CO + 2H+ + 2e− | (5) |
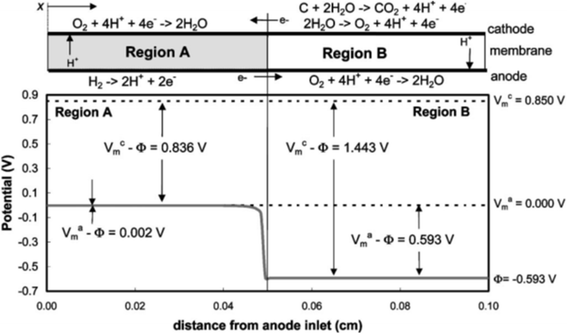 | ||
| Fig. 1 Potential distributions along the anode flow path under reverse current conditions, where Vmc, Vma and Φ denote the potential of cathode metal, anode metal and electrolyte, respectively. Reproduced with permission.12 Copyright 2005, The Electrochemical Society. | ||
The oxidation of carbon black supports has been experimentally confirmed by monitoring CO2 gas formation at PEFC cathodes.13 The PtCo nanoparticles on the carbon supports can no longer be used once the carbon supports are corroded. The startup/shutdown cycles cause more severe damage to the performance of conventional PEFC catalyst layers employing carbon black via the corrosion than load cycles, which induce the instability of platinum/platinum alloys.14 To avoid this issue, carbon supports are usually protected by system-level measures, such as reducing the cathode air flow rate during shutdown to minimize O2 diffusion to the anode through a membrane and injecting a small amount of H2 into the anode during FCV off-time to react with O2 contaminants.15 These measures further increase the cost of FCVs.
The COR ends when the contaminant O2 molecules are consumed after startup or when the load current is switched off after the shutdown of PEFCs. The cathode catalysts are thus left at a high potential for a short time during startup and shutdown if the system-level measures described above are not taken. The Fuel Cell Commercialization Conference in Japan (FCCJ) defined a protocol for evaluating the durability of FCVs against startup/shutdown, in which the potential was cycled between 1.0 and 1.5 V at a high scan rate of 0.5 V s−1 in both a half-cell and a single cell, in 2011.16 The protocol has been most widely used in the last decade and was later followed by the US Department of Energy (DOE) protocol, which set an identical potential range and scan rate.17 In the current review, this protocol is denoted as the “FCCJ startup/shutdown cycle” for the sake of simplicity. The protocols for evaluating the durability against the normal driving mode of FCVs have also been defined by the FCCJ and DOE, and both protocols have been updated since 2007. The FCCJ revised the protocol only once in 2011, in which the potential was cycled with symmetric rectangular waves (held at 0.6 V for 3 s as “load on” and then held at 1.0 V for 3 s as “load off” mode)16 and has been most widely used to date. The DOE protocol has been revised several times. In 2016, rectangular waves similar to those described in the FCCJ were set, and the sole difference was the upper potential at 0.95 V in the DOE protocol.17 These protocols are hereafter referred to as FCCJ or DOE load cycles.
Researchers in this community have paid less attention to the anode catalyst layers and have focused on developing cathode counterparts. The kinetics of the HOR in PEFC anodes are 3–4 orders of magnitude faster than those of the ORR in the cathodes18 to achieve low anode platinum loading, which is one-quarter of that of the cathode,9 while maintaining an anode potential below ∼0.1 V versus RHE. The standard electrode potential for eqn (4) and (5) is 0.207 and 0.518 V, respectively, versus the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE), and thus the COR does not proceed in Pt/C anodes during the normal operation of FCVs. However, the COR proceeds under some operating conditions such as “sub-zero startup,” which refers to startup at temperatures below 273 K to form ice, which blocks hydrogen flow fields, rapid load change with high fuel utilization, uneven current distribution in flow fields, and uneven reactant flux distributions between cells in a stack. Under these conditions, there is insufficient H2 gas for oxidation to maintain the current, and instead, both the OER (eqn (3)) and the COR (eqn (4) and/or (5)) proceed at the H2-starved anode to compensate for the current shortage. The anode potential increases to reverse the cell voltage and achieve a minus value during H2 starvation, as shown in Fig. 2.19 The anode potential after this phenomenon, which is called a cell reversal, shortly increases beyond 1.5 V versus RHE, and continuously increases. Similar to the cathode during startup/shutdown, carbon supports are easily oxidized via eqn (4) at such high potentials. The evolved O2 gas at the carbon-free platinum black anode20 and Pt/C anode21 due to the OER (eqn (3)) and CO2 gas at the Pt/C anode due to the COR (eqn (4))21,22 during cell reversal were experimentally confirmed by gas analyses. Interestingly, Baumgartner et al. reported that CO2 and CO gases have also been detected from PEFC anodes during cell reversal, although the precise mechanism for CO formation has not been clarified.22
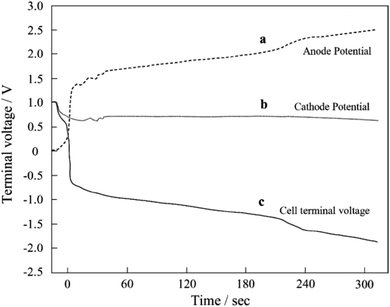 | ||
| Fig. 2 (a) Anode potential, (b) cathode potential, and (c) cell voltage versus time curves during cell reversal. Reproduced with permission.19 Copyright 2004, Elsevier. | ||
Upon cell reversal, the carbon supports at the Pt/C anodes face corrosion for longer durations than the PtCo/C cathodes during startup/shutdown, considerably reducing cell performance.19–21 In general, the COR proceeds with a high overpotential and is thus accompanied by heat loss, which leads to pinholes in the membrane.23,24 Anode H2 fuel and cathode air can be mixed through the pinholes to further generate heat,24 which may cause a fire in the worst case. To avoid cell reversal, current system-level measures include monitoring all cell voltages25 and low fuel utilization. However, once again, these measures increase the system cost of FCVs.25
The issues described in relation to currently available carbon black supports at the anode and cathode of the PEFC catalyst layers have motivated researchers to develop carbon-support-free platinum-based catalysts. Furthermore, the scarcity and price of PGMs have driven the development of PGM-free catalysts. The ultimate catalyst is therefore a carbon-support-free, non-PGM catalyst. In this paper, non-carbon-support alternatives to carbon black in the cathode and anode of PEFCs are reviewed first in Section 2. Pathways to enhance the startup/shutdown durability of cathodes developed in the last two decades include durable non-carbon cathode supports and HOR-selective anodes that impede the undesired ORR at the anode. As the conductivity of the new catalyst is crucial in all pathways, this paper focuses on conductivity at the bulk and the particulate, including contact resistance. Non-carbon anode supports that are durable against cell reversal have recently been developed with and without OER catalysts. Some negative reports on non-carbon supports in the anode and the cathode are also highlighted, and the merits and demerits of the use of non-carbon supports are discussed at the end of Section 2. The ultimate carbon-support-free, non-PGM catalysts are then reviewed in Section 3. Finally, the possible use of these carbon-support-free catalysts in FCVs is summarized, including the challenges and recommended experimental conditions for future work.
2 Carbon-support-free platinum/platinum alloy catalysts
2.1 Cathode catalysts
The cathode potential operates between 0.6 and 0.95/1.0 V versus RHE in FCVs in a normal operation mode.16,17 The normal potential range is much lower than that during startup/shutdown as mentioned in Section 1, and thus the cathode environment in the normal mode is gentler to catalysts compared with during startup/shutdown. However, few elements are stable even in the normal operating mode of PEFC cathodes, as shown in Fig. 3. Sasaki et al. reported the stability of 54 elements in PEFC cathodes, in which the potential was set at 1.0 V versus RHE at pH = 0 by using thermochemical calculations.26 The temperature was set at 353 K, which is the operating temperature of current PEFCs employing a perfluorosulfonate ionomer (PFSI) membrane such as Nafion™ produced by DuPont. Most elements exist as ions that may leach out, while stable elements exist as binary oxides, oxide hydrates, or metals under the given conditions. Pt is stable as the metallic element according to Fig. 3, while it is well-known to dissolve as Pt ions and then deposit on other Pt particles (Ostwald ripening) in the cathodes during long-term operation at 1.0 V. It then migrates from the cathodes to membranes, where it is redeposited to form a “Pt band” in the membranes.27 This inconsistency could be due to (i) deficiencies in the database, which describes the most stable substances,26 while minor soluble species such as Pt2+ and Pt4+ cause gradual Ostwald ripening, (ii) potential cycling in the normal driving mode (so-called “load cycling”), which accelerates Pt dissolution during the operation of FCVs,27 and (iii) small amounts of hydrogen peroxide byproducts formed during the ORR via a two-electron reaction represented by eqn (6) as they dissolve Pt.28,29| O2 + 2H+ + 2e− → H2O2 | (6) |
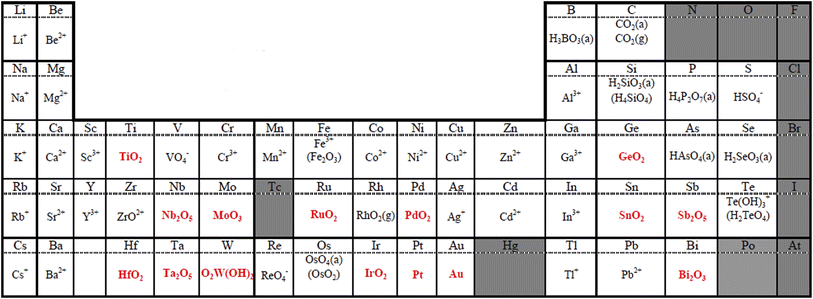 | ||
| Fig. 3 Most stable substances under typical polymer electrolyte fuel cell (PEFC) cathode conditions derived from thermochemically calculated pH-potential diagrams. The potential and the temperature were set at 1.0 V versus the reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) at pH = 0 and 353 K, respectively. Insoluble elements/compounds are shown in red, and the gray background indicates N/A. Reproduced with permission.26 Copyright 2010, The Electrochemical Society. | ||
Ten years after the publication of the work by Sasaki et al., the Nørskov group investigated the stability of 47![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 814 nonbinary metal oxides at 0.6–1.0 V (for the ORR) and 1.2–2.0 V (for the OER) versus RHE at pH = 0 using theoretical calculations.30 The stable candidates screened were Sb/Ti/Sn/Ge/Mo/W-based oxides. These theoretical calculation results based on binary26 and nonbinary30 oxides suggest that the abovementioned oxides are the most promising candidates for stable-support alternatives to the currently available carbon black. However, it is noted that there may be exceptions in the elements excluded from the screening using theoretical calculations. Lv et al. reported that nano-sized ZrO2 particles are electrochemically stable after 48 h of potential holding at 1.2 V versus RHE in 0.5 mol dm−3 H2SO4 solution, displaying negligible changes in the cyclic voltammograms (CVs).31 ZrO2 is dissolved away during the harsh oxidative treatment used in the study by Lv et al., judging from Fig. 3, while it survives as it was sufficiently stable or the dissolution process was kinetically slow. Both the instability of Pt27 and the stability of ZrO2 (ref. 31) reported in previous studies are inconsistent with Fig. 3 and suggest the absence of a perfect database for screening stable candidates in the PEFC cathodes, in which several factors affect the stability. In particular, factors (i)–(iii) mentioned in the previous paragraph are not simultaneously included in any database and therefore, in this subsection, cathode Pt/Pt-alloy catalysts on non-carbon supports are reviewed without limiting the scope to stoichiometric oxides. Suboxides, oxides and nitrides are considered as their particles can show high conductivity after applying pressure below that of hot-pressing membrane electrode assemblies (MEAs), typically 10 MPa. The conductivity is comparable to or only one order of magnitude lower than that of carbon black at room temperature, at least in some compositions.
814 nonbinary metal oxides at 0.6–1.0 V (for the ORR) and 1.2–2.0 V (for the OER) versus RHE at pH = 0 using theoretical calculations.30 The stable candidates screened were Sb/Ti/Sn/Ge/Mo/W-based oxides. These theoretical calculation results based on binary26 and nonbinary30 oxides suggest that the abovementioned oxides are the most promising candidates for stable-support alternatives to the currently available carbon black. However, it is noted that there may be exceptions in the elements excluded from the screening using theoretical calculations. Lv et al. reported that nano-sized ZrO2 particles are electrochemically stable after 48 h of potential holding at 1.2 V versus RHE in 0.5 mol dm−3 H2SO4 solution, displaying negligible changes in the cyclic voltammograms (CVs).31 ZrO2 is dissolved away during the harsh oxidative treatment used in the study by Lv et al., judging from Fig. 3, while it survives as it was sufficiently stable or the dissolution process was kinetically slow. Both the instability of Pt27 and the stability of ZrO2 (ref. 31) reported in previous studies are inconsistent with Fig. 3 and suggest the absence of a perfect database for screening stable candidates in the PEFC cathodes, in which several factors affect the stability. In particular, factors (i)–(iii) mentioned in the previous paragraph are not simultaneously included in any database and therefore, in this subsection, cathode Pt/Pt-alloy catalysts on non-carbon supports are reviewed without limiting the scope to stoichiometric oxides. Suboxides, oxides and nitrides are considered as their particles can show high conductivity after applying pressure below that of hot-pressing membrane electrode assemblies (MEAs), typically 10 MPa. The conductivity is comparable to or only one order of magnitude lower than that of carbon black at room temperature, at least in some compositions.
2.1.1.1 Titanium suboxide-supported catalysts. Oxide materials have been assumed to be the most stable supports for PEFC cathodes, and thus many research groups have focused on developing oxide supports. The predicted stable binary oxides shown in Fig. 3 have one common theme in that the metals are at the highest oxidation state, which is reasonable for stability in the highly oxidative environment of the PEFC cathodes. Except for PGM oxides, which have a black color, these oxides are all white or yellow in color, indicating their insulating nature. The geometrical current density of PEFCs is on the order of A cm−2, which is at least two orders of magnitude higher than that of conventional LIBs or even post-LIBs, such as state-of-the-art solid-state lithium batteries.32 Insulating materials have been used in the electrodes of the abovementioned batteries with low current densities, although they are used with difficulty in PEFCs with high current densities. Therefore, several strategies, such as introducing oxygen vacancies or doping other metals, have been used to enhance the conductivity of stable binary non-PGM oxides.
Among various oxides, titanium oxides have been most widely investigated as supports for PEFC cathodes owing to their high conductivity and natural abundance. Fig. 4(a) shows the crystal structure of rutile TiO2 and Ti4O7, one of the members of the Magnèli-phase titanium suboxide group, TinO2n−1 (4 ≤ n ≤ 10), which were discovered by Andersson and Magnèli in 1956.33,40 Rutile TiO2, the most thermodynamically stable and most common titanium dioxide polymorph in nature, consists of TiO6 octahedra in which six oxygen atoms at the corners surround a titanium atom at the center. Each octahedron shares two opposite edges and free corner oxygen atoms to link adjacent octahedra. In TinO2n−1, oxygen vacancies are present in every nth layer to produce shear planes. The electrical conductivities reported to date are shown in Fig. 4(b). The highest value at n = 4 is above 1000 S cm−1 at room temperature,41 which is 16 orders of magnitude higher than that of rutile TiO2 and comparable to that of graphite.42 The reported high conductivity motivated several researchers to develop Ti4O7 as supports for PEFC cathodes. Pioneering studies by Ioroi et al. in the 2000s displayed the significant potential of this material, although issues remained in terms of their use in vehicles. Fig. 4(c) shows the CVs of Ti4O7 powder synthesized by annealing commercial TiO2 powder at 1323 K for 6 h under H2 gas and commercial carbon black particles, Vulcan XC-72, in a PEFC single cell. Vulcan XC-72 has been the standard carbon support in Pt/C until the 2000s. Ti4O7 exhibited high stability up to 1.8 V versus RHE to show a small anodic current, whereas Vulcan XC-72 was oxidized to show a rapid increase in the anodic current as the potential increased above 0.9 V. These CVs also indicate that ∼20% of the Ti4O7 surface was electrochemically active, which is much lower than the ∼68% calculated for Vulcan XC-72 using the loading, theoretical double-layer capacitance and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area.34 The electrochemically active surface area (ECSA) refers to the area which is accessible to protons and electrons. The low ECSA value of Ti4O7 may be due to the low coverage of PFSI on Ti4O7 powder, as PFSI produces paths for protons, or the low electrical conductivity of Ti4O7 powder, as discussed later. The BET surface area of the Ti4O7 powder was reported to be 0.95 m2 g−1, which is two orders of magnitude lower than that of Vulcan XC-72, 250 m2 g−1.34 The low surface area is due to its high synthesis temperature of 1323 K, which induces agglomeration of Ti4O7 powder to yield sub-micrometer to micrometer-sized particles. Fig. 4(d) shows the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of Ti4O7-supported platinum (Pt/Ti4O7) catalysts and commercial carbon-supported platinum catalysts after annealing at 1273 K for 3 h under H2 gas (Pt/XC72-HTT). The bright spots in these images represent Pt particles. Owing to the small surface area of large Ti4O7 powder, the mass fraction of Pt was controlled to 5% w/w to prevent Pt particle coagulation, which is much lower than that in Pt/XC72-HTT, at 30% w/w.35 The 5% w/w Pt/Ti4O7 catalysts displayed a lower cell voltage at any current density in a single cell than 30% w/w Pt/XC72-HTT owing to the smaller ECSA, as shown in Fig. 4(e). Although the initial performance of 5% w/w Pt/Ti4O7 was lower, the stability at high potentials was greater compared with 30% w/w Pt/XC72-HTT, as shown in Fig. 4(f). An MEA with the 5% w/w Pt/Ti4O7 cathode catalyst layer on a titanium gas diffusion layer (Ti-GDL) displayed negligible changes in cell voltages at any current density, even after holding the cell voltage at 1.5 V for 1 h. In contrast, an MEA with 30% w/w Pt/XC72-HTT/Ti-GDL deteriorated to complete loss of ORR activity. The CVs during voltage holding indicate that XC72-HTT was oxidized from 1.2 V. Control experiments using conventional carbon cloth GDLs revealed that even carbon atoms in the GDLs were oxidized at 1.5 V for 1 h, and thus carbon should be eliminated from both catalyst layers and GDLs under harsh conditions without using high-cost potential protecting systems.35 These pioneering studies by Ioroi et al. clearly indicate the advantages of Ti4O7, while revealing challenges for their use in vehicles. The former include the high stability after holding the cell voltage at 1.5 V for 1 h and the latter include low initial cell performance and a low Pt mass fraction in Pt/Ti4O7 due to the large Ti4O7 powder. A strong reductive atmosphere such as pure hydrogen at a high temperature above 1273 K has been required to synthesize Ti4O7 from natural TiO2.33 During high-temperature annealing, the size of the starting material TiO2 increases to form agglomerated Ti4O7 powder, typically of a micrometer order. Indeed, the most widely used commercial Ti4O7, Ebonex® has a size of 3–500 μm.33 A small quantity of Pt particles can readily be deposited on such large Ti4O7 powder, and the resulting catalyst layer thickness may be much larger than that of the current PtCo/C catalyst layers, which is typically ∼10 μm.9 Recent analyses on the MEAs of the latest FCV revealed an anode and cathode catalyst layer thickness of 3.42 and 8.81 μm, respectively.8 A particle size of around 100 nm is needed to increase the surface area of Ti4O7 to an order of at least one hundred m2 g−1 (equivalent to that of conventional carbon black), and thus to increase the mass fraction of Pt without increasing the Pt size to enhance the cell performance. Ioroi et al. later developed a new pulsed ultraviolet (UV) laser irradiation method to synthesize TinO2n−1 particles without using high-temperature annealing. Although the crystal structure was not a single Ti4O7 phase, the BET surface area was successfully increased to 20 m2 g−1 after optimizing the solvent to acetonitrile, in which TiO2 nanoparticles were irradiated using a UV laser.43 Senevirathne et al. developed Ti4O7 nanofiber supports by annealing electrospun TiO2 nanofibers at 1323 K for 6 h under a 50% v/v H2/N2 gas mixture. The BET surface area, 51 m2 g−1 of TiO2 nanofibers, decreased to 6 m2 g−1 of Ti4O7 nanofibers during the annealing process.44 Yao et al. successfully synthesized Ti4O7 nanofiber supports with a BET surface area of 26 m2 g−1 by annealing SiO2-coated TiO2 nanotubes at 1323 K for 4 h under pure H2 gas. The SiO2 shell covering the Ti4O7 fibers was removed using 2% HF solution for 45 h. Although such a multistep method, combined with the use of toxic HF, may increase the cost of synthesis, the size growth and decrease in the surface area during high-temperature annealing were successfully suppressed by the SiO2 shell. The durability of the Ti4O7 fiber-supported Pt
nanoparticles outperformed the durability of commercial Pt/C catalysts against accelerated degradation tests (ADTs), in which the potential was cycled between 0.6 and 1.4 V versus SHE in a half-cell employing 0.5 mol dm−3 H2SO4 solution. The high durability was reported due to (1) highly stable Ti4O7 fiber supports and (2) strong metal-support interactions (SMSIs), as confirmed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The Pt 4f binding energy of the Pt/Ti4O7 fibers shifted lower, and the changes in binding energy during ADTs were smaller compared with those of commercial Pt/C.45 The term SMSI was first introduced by Tauster et al. in 1978 to explain the dramatic changes in the chemisorption properties of Group VIII noble metals on TiO246 and is believed to be the origin of the enhancement in many catalytic properties of supported metal catalysts, including the ORR activity of carbon-free PEFC cathode catalysts.47 As Pt particles can bind to Ti4O7 more strongly than to carbon, Al2O3, and SiO2, they are less mobile on Ti4O7 to suppress Pt particle size growth with increasing temperature compared with Pt/C, Pt/Al2O3, and Pt/SiO2.48,49 Therefore, the durability of Pt/Ti4O7 in PEFC cathodes is expected to exceed that of Pt/C. The SiO2 coating route was also used for the synthesis of particulate Ti4O7 with a BET surface area of 6 m2 g−1 by the Hwang group.50 Although significant efforts have been made to suppress the growth of Ti4O7 support size, the reported BET surface area was below 100 m2 g−1 as mentioned above, and a single-cell performance with Pt/Ti4O7 cathodes comparable to that with their Pt/C counterpart has not been reported until recently. In 2021, we successfully synthesized >2 g of Ti4O7 fine particles with a BET surface area of 172 m2 g−1via an inexpensive carbothermal reduction reaction route, as shown in Fig. 4(g). Pt nanoparticles were highly dispersed on the Ti4O7 particles, and the Pt mass fraction was successfully increased to 30% w/w owing to the high surface area of Ti4O7. The average Pt particle size of the optimized 20% w/w Pt/Ti4O7 determined by a CO pulse method was 4.2 nm, slightly exceeding that of commercial Pt/C, and the single-cell performance with the Pt/Ti4O7 cathode was similar to that of the Pt/C cathode, as shown in Fig. 4(h). The SMSIs between Pt nanoparticles and Ti4O7 supports were observed, as shown in Fig. 4(i). The Ti 2p3/2 peak binding energy shifted to higher binding energy regions after Pt nanoparticles were supported, indicating the decreased electron density of titanium in Pt/Ti4O7 compared with Ti4O7. Pt/Ti4O7 showed a lower Pt 4f7/2 peak binding energy than commercial Pt/C, indicating that the electron density of Pt nanoparticles in Pt/Ti4O7 exceeded that of Pt/C. These Ti 2p and Pt 4f spectra indicate that the electrons from the titanium atoms in Ti4O7 supports were transferred to the platinum atoms in Pt nanoparticles.36 These results are in good agreement with previous oxide-supported platinum catalysts, in which SMSIs are reported to enhance ORR activity.51–53 As the durability against startup/shutdown cannot be evaluated with conventional GDLs utilizing carbon paper or carbon cloth,35 the durability of Pt/Ti4O7 against FCCJ load cycles was evaluated with an MEA utilizing Pt/Ti4O7 in the anode and cathode, as shown in Fig. 4(j). The cell voltage, V, did not change at any current density, j, after 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cycles, indicating that HOR and ORR activity was retained during the cycles. The load cycle durability is among the highest in the state-of-the-art Pt/oxide catalysts, as shown in Table 1. The enhanced cell performance is due to (1) the high surface area which allows an increased Pt mass fraction without increasing the Pt nanoparticle size and (2) the high conductivity, as shown in Fig. 4(k). The conductivity of powders, σ, is determined by bulk and contact resistance, and the latter depends on the morphology, size, and size distributions. In many papers on Pt or Pt-alloy/non-carbon catalysts, only one σ-value of non-carbon supports measured at a specific pressure, P, has been reported. The selected P differs across these papers, and the specific P value is not even described in some papers, making it difficult to compare the reported σ-values of non-carbon supports against each other. Some researchers reported σ at various P values, and the σ values of Ti4O7,36–38 mixed Magnèli-phase TinO2n−1 (4 ≤ n ≤ 6),39 commercial TiO2 (ref. 38) and commercial carbon black38 are compared in Fig. 4(k). The σ-value of fine Ti4O7 particles shown in Fig. 4(g) is high (0.7 S cm−1 from the lowest P of 3 MPa) and exceeds 1 S cm−1 at P ≥ 6 MPa, which is just one order of magnitude lower than that of commercial carbon black used in Pt/C (Ketjen Black EC600JD). The results shown in Fig. 4(h) and (k) suggest that the σ-value of fine Ti4O7 particles was sufficiently high not to restrict cell performance, at least under the conditions used. Li et al. recently synthesized fine Ti4O7 particles using our carbothermal reduction reaction route with some modifications.37 The σ-value reported in our paper36 was well reproduced by Li et al.37 as shown by the open36 and filled circles,37 respectively, in Fig. 4(k). The 172 m2 g−1 BET surface area reported in our paper36 was also well reproduced by Li et al., at 166 m2 g−1.37 Micrometer-sized Ti4O7 synthesized by a conventional method, annealing commercial TiO2 powder under a reductive atmosphere (denoted as Ti4O7-L), resulted in a σ-value five orders of magnitude lower, at P = 3 MPa, two orders of magnitude lower at P = 25 MPa compared with fine Ti4O7 particles. This differing dependence of σ on P may be the result of the difference in size, as shown in Fig. 4(g). As the particle size decreases, the tensile strain increases, distorting the crystal lattice to incorporate oxygen vacancies, which is known to increase the conductivity of oxides.62 Indeed, Raman spectra showed that fine Ti4O7 particles contained a large number of oxygen vacancies on the surface.36 Thus, contact resistance between Ti4O7 particles, which is dominant for σ at low P, is suppressed owing to the high surface conductivity.
000 cycles, indicating that HOR and ORR activity was retained during the cycles. The load cycle durability is among the highest in the state-of-the-art Pt/oxide catalysts, as shown in Table 1. The enhanced cell performance is due to (1) the high surface area which allows an increased Pt mass fraction without increasing the Pt nanoparticle size and (2) the high conductivity, as shown in Fig. 4(k). The conductivity of powders, σ, is determined by bulk and contact resistance, and the latter depends on the morphology, size, and size distributions. In many papers on Pt or Pt-alloy/non-carbon catalysts, only one σ-value of non-carbon supports measured at a specific pressure, P, has been reported. The selected P differs across these papers, and the specific P value is not even described in some papers, making it difficult to compare the reported σ-values of non-carbon supports against each other. Some researchers reported σ at various P values, and the σ values of Ti4O7,36–38 mixed Magnèli-phase TinO2n−1 (4 ≤ n ≤ 6),39 commercial TiO2 (ref. 38) and commercial carbon black38 are compared in Fig. 4(k). The σ-value of fine Ti4O7 particles shown in Fig. 4(g) is high (0.7 S cm−1 from the lowest P of 3 MPa) and exceeds 1 S cm−1 at P ≥ 6 MPa, which is just one order of magnitude lower than that of commercial carbon black used in Pt/C (Ketjen Black EC600JD). The results shown in Fig. 4(h) and (k) suggest that the σ-value of fine Ti4O7 particles was sufficiently high not to restrict cell performance, at least under the conditions used. Li et al. recently synthesized fine Ti4O7 particles using our carbothermal reduction reaction route with some modifications.37 The σ-value reported in our paper36 was well reproduced by Li et al.37 as shown by the open36 and filled circles,37 respectively, in Fig. 4(k). The 172 m2 g−1 BET surface area reported in our paper36 was also well reproduced by Li et al., at 166 m2 g−1.37 Micrometer-sized Ti4O7 synthesized by a conventional method, annealing commercial TiO2 powder under a reductive atmosphere (denoted as Ti4O7-L), resulted in a σ-value five orders of magnitude lower, at P = 3 MPa, two orders of magnitude lower at P = 25 MPa compared with fine Ti4O7 particles. This differing dependence of σ on P may be the result of the difference in size, as shown in Fig. 4(g). As the particle size decreases, the tensile strain increases, distorting the crystal lattice to incorporate oxygen vacancies, which is known to increase the conductivity of oxides.62 Indeed, Raman spectra showed that fine Ti4O7 particles contained a large number of oxygen vacancies on the surface.36 Thus, contact resistance between Ti4O7 particles, which is dominant for σ at low P, is suppressed owing to the high surface conductivity.
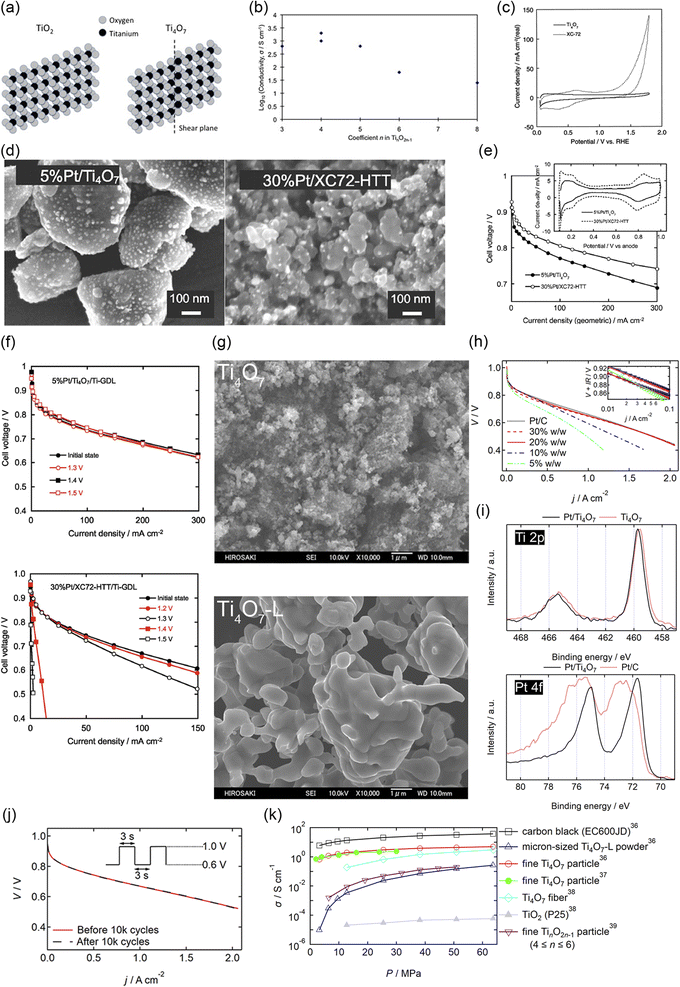 | ||
Fig. 4 (a) Crystal structure of rutile TiO2 and Ti4O7. (b) A conductivity versus n in Magnèli-phase TinO2n−1 curve. Reproduced with permission.33 Copyright 2010, Elsevier. (c) Cyclic voltammograms (CVs) of Ti4O7 and carbon black; Vulcan XC-72 electrodes in membrane electrode assemblies (MEAs) supplied with N2 at a scan rate of 100 mV s−1 at 353 K. The counter electrodes were made with commercial 40% w/w Pt/C and supplied with fully humidified H2 to be a reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE). Therefore, the counter electrode also served as a reference electrode. Reproduced with permission.34 Copyright 2005, Elsevier. (d) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of 5% w/w Pt/Ti4O7 and 30% w/w Pt/C after annealing at 1273 K for 3 h under H2, denoted as 30% w/w Pt/XC72-HTT. (e) Cell voltage versus current density curves for MEAs fabricated using 5% w/w Pt/Ti4O7 and 30% w/w Pt/XC72-HTT in the cathode at 353 K. Platinum loading was set at 0.24 and 0.29 mgPt cm−2 for 5% w/w Pt/Ti4O7 and 30% w/w Pt/XC72-HTT, respectively. The anode and cathode gases were fully humidified H2 and O2, respectively. The inset shows their corresponding CVs. (f) Cell voltage versus current density curves for MEAs fabricated using 5% w/w Pt/Ti4O7 and 30% w/w Pt/XC72-HTT in the cathode catalyst layer formed on a hydrophobic titanium fiber gas diffusion layer (Ti-GDL) before (initial state) and after voltage holding at 1.2–1.5 V for 1 h at 353 K. Reproduced with permission.35 Copyright 2008, The Electrochemical Society. (g) Field emission (FE)-SEM images of (top) fine Ti4O7 particles synthesized via a carbothermal reduction reaction route and (bottom) micrometer-sized Ti4O7 powder synthesized from commercial TiO2 powder (Ti4O7-L). (h) Cell voltage versus current density (V–j) curves of five MEAs fabricated using commercial 46% w/w Pt/C and Pt/Ti4O7 with four different Pt mass fractions, 5%, 10%, 20%, and 30% w/w in the cathode at 353 K. Pt/C was used in the anode of all MEAs and the Pt loading at the anode and cathode was 0.2 and 0.5 mgPt cm−2, respectively. The anode and cathode gases were fully humidified H2 and O2 with 83% relative humidity (RH), respectively. (i) Ti 2p and Pt 4f X-ray photoelectron spectra of the 20% w/w Pt/Ti4O7 catalyst (solid curves). For reference, a Ti 2p spectrum of Ti4O7 and a Pt 4f spectrum of commercial Pt/C are shown by the dashed curves. (j) V–j curves of an MEA fabricated using 20% w/w Pt/Ti4O7 in the anode and cathode before (solid curve) and after (dashed curve) 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 voltage cycles with symmetric rectangular waves (held at 0.6 V for 3 s and then at 1.0 V for 3 s); hereafter referred to as FCCJ load cycles. Pt loading and operating conditions are identical to those of (h). Reproduced with permission.36 Copyright 2021, Royal Society of Chemistry. (k) Powder/particle conductivity versus pressure (σ–P) curves of commercial carbon black, Ketjen Black EC600JD, and micron-sized Ti4O7-L powders shown at the bottom of (g),36 fine Ti4O7 particles,36,37 Ti4O7 fibers, commercial TiO2, P25 particles38 and fine Ti2nO2n−1 (4 ≤ n ≤ 6) particles.39 Reproduced with permission.36–39 Copyright 2021, Royal Society of Chemistry, Copyright 2024, Royal Society of Chemistry, Copyright 2016, Elsevier and Copyright 2011, The Electrochemical Society. 000 voltage cycles with symmetric rectangular waves (held at 0.6 V for 3 s and then at 1.0 V for 3 s); hereafter referred to as FCCJ load cycles. Pt loading and operating conditions are identical to those of (h). Reproduced with permission.36 Copyright 2021, Royal Society of Chemistry. (k) Powder/particle conductivity versus pressure (σ–P) curves of commercial carbon black, Ketjen Black EC600JD, and micron-sized Ti4O7-L powders shown at the bottom of (g),36 fine Ti4O7 particles,36,37 Ti4O7 fibers, commercial TiO2, P25 particles38 and fine Ti2nO2n−1 (4 ≤ n ≤ 6) particles.39 Reproduced with permission.36–39 Copyright 2021, Royal Society of Chemistry, Copyright 2024, Royal Society of Chemistry, Copyright 2016, Elsevier and Copyright 2011, The Electrochemical Society. | ||
| Cathode catalysta | w Pt | m Pt | Back pressurec | Load cycle protocol | T cell | Oxidant | ΔVe | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
a Anode catalysts were commercial Pt/C except for ref. 36, in which 20% w/w Pt/Ti4O7 was used for the anode and cathode.
b Cathode platinum loading in mgPt cm−2.
c Cathode back pressure.
d Cell temperature.
e Decrease in V at j = 1 A cm−2 after 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cycles except for ref. 54, 55, 59 and 61, which used 50 000 cycles except for ref. 54, 55, 59 and 61, which used 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 (assumption, the cycle number was not clearly described in ref. 54) and 5000 cycles, respectively. Ref. 57 and 60 report a decrease in V + IR after 10 000 (assumption, the cycle number was not clearly described in ref. 54) and 5000 cycles, respectively. Ref. 57 and 60 report a decrease in V + IR after 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cycles.
f It was 0.1 MPa without clear descriptions as gauge or absolute pressure in ref. 54.
g N/A, not applicable; RH, relative humidity; VGCF, vapor-grown carbon fiber. 000 cycles.
f It was 0.1 MPa without clear descriptions as gauge or absolute pressure in ref. 54.
g N/A, not applicable; RH, relative humidity; VGCF, vapor-grown carbon fiber.
|
||||||||
| Pt/Ti4O7 | 20% w/w | 0.5 | Ambient pressure | 0.6 V (3 s)–1.0 V (3 s) | 353 K | O2 83% RH | 0 mV | 36 |
| Pt/Ti3O5Mo0.2Si0.4 | 20% w/w | 0.2 | N/Af | 0.6 V–1.0 V at 0.5 V s−1 (triangle waves) | 323 K | O2 100% RH | 16 mV | 54 |
| Pt/TiO2 | 60.4% w/w | 0.4 | 0.27 MPa-absolute | 0.7 V (30 s)–0.9 V (30 s) | 353 K | Air 100% RH | 0.09 V | 55 |
| Pt/Ta0.3Ti0.7O2 | 20% w/w | 0.4 | Ambient pressure | 0.6 V (3 s)–0.95 V (3 s) | 353 K | Air 75% RH | ∼15 mV | 56 |
| Pt/RuO2-TiO2 | 40% w/w | 0.35 | N/A | 0.6 V (3 s)–0.95 V (3 s) | 353 K | Air 100% RH | 0.03 V | 14 |
| Pt/IrO2-TiO2 | 8.9% w/w | 0.45 | 0.15 MPa-absolute | 0.6 V–1.0 V at 50 mV s−1 (triangle waves) | 353 K | Air 100% RH | 0.07 V | 57 |
| O2 100% RH | 0.07 V | |||||||
| Pt/Cu,N-doped TiO2 | 40% w/w | 0.2 | Ambient pressure | 0.6 V–1.0 V at 50 mV s−1 | 348 K | O2 100% RH | 0.07 V | 58 |
| Pt3Co/Sn0.98Nb0.02O2-VGCF | N/A | 0.3 | N/A | 0.6 V (3 s)–1.0 V (3 s) | 353 K | Air 100% RH | 0.09 V | 59 |
| Pt/Nb-doped SnO2 | 18.5% w/w | 0.1 | Ambient pressure | 0.6 V (3 s)–0.94 V (60 s) | 353 K | O2 100% RH | 0.08 V | 60 |
| Pt/Sb-doped SnO2 | 20% w/w | 0.4 | Ambient pressure | 0.6 V (3 s)–0.95 V (3 s) | 353 K | Air 90% RH | 0.20 V | 61 |
Controlling the size to the order of 10 or 100 nm, as well as maintaining phase purity in the crystal structure, is necessary for the use of Ti4O7 as a support for PEFC cathodes. The catalyst mass, which is vital for its use in vehicles, should increase by changing the support from carbon black to Ti4O7 at a lower Pt mass fraction in Pt/Ti4O7 than Pt/C when the Pt loading is kept constant. The Pt mass fraction of a standard Pt/C (TEC10E50E; Tanaka Kikinzoku Kogyo) is 46–48% w/w and that in Pt/Ti4O7 optimized in ref. 36 was 20% w/w. Li et al. succeeded in increasing the Pt mass fraction optimized for use in PEFC anodes to 40% w/w with a smaller Pt particle size (3–4 nm) and narrower size distribution than our work36 by using an ethanol reduction method to deposit Pt nanoparticles on Ti4O7 with a size of 200–300 nm.37 The enlargement of the surface area of Ti4O7 by decreasing its size produces a larger number of sites on which to deposit Pt nanoparticles. A Ti4O7 particle size of approximately 100 nm will be sufficient to produce 46% w/w Pt/Ti4O7, similar to the standard Pt/C. The density of Ti4O7, 4.32 g cm−3,63 is approximately twice as large as that of carbon, 2.2 g cm−3, and thus the volume of Pt/Ti4O7 is lower than that of Pt/C at an identical platinum mass fraction. Therefore, catalyst layer thickness can be reduced by replacing Pt/C with Pt/Ti4O7 at a constant platinum mass fraction and constant platinum loading. Indeed, the thickness of the 40% w/w Pt/Ti4O7 catalyst layer was much lower than that of the 47% w/w Pt/C catalyst layer.37
Another challenge for the widespread use of Ti4O7 is its scalability, and the batch size has not been described in many publications. We have recently reported that simple substitutional vanadium doping increased the batch size of Ti4O7 synthesized via a conventional high-temperature solid-state reaction route to 2 g. Vanadium cations, V4+ and V3+, were dissolved into a Ti4O7 lattice without segregating to form vanadium oxides up to (Ti0.91V0.09)4O7.64 A combination of vanadium doping and the carbothermal reduction reaction may further increase the batch size.
Esfahani et al. utilized Mo-doped Ti3O5 (ref. 65) and Mo, Si-codoped Ti3O5 (ref. 54 and 66) as supports for Pt particles. Although Ti3O5 is less conductive in bulk than Ti4O7,33 their conductivity was enhanced by doping with Mo and Si.66 The term “doping” has been most frequently used to describe the introduction of foreign elements into metal oxides, nitrides, etc., although the precise meaning differs by author. When V4+ substituted for Ti4+ in Ti4O7, the peaks in the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns shifted to higher angles with increasing vanadium doping level as the ionic radius of V4+ is lower than that of Ti4+.64 In this case, the term “doping” is taken to mean substitution. In other cases, foreign elements occupy an interstitial position or form other phases. The term “doping” has even been used without evaluating the crystal structure in some papers. In the current paper, all articles that contributed to the development of carbon-support-free catalysts are reviewed, and the term “doping” is taken to mean any of the cases described above. The Mo, Si-codoped Ti3O5 contains seven phases (Ti3O5, Ti6O, Mo, MoO2, Mo9O26, Si, and SiO2), and the presence of these different phases makes it difficult to clarify the role of each element. However, the reported durability is among the highest in the reported oxide-supported catalysts, as shown in Table 1.
2.1.1.2 Titanium dioxide-supported catalysts. Titanium dioxide, TiO2, is the most widely studied metal oxide owing to its abundance and potential for use in a number of applications including photocatalysis, photovoltaic cells, gas sensors, and anodes in secondary batteries based on lithium, sodium, potassium, and aluminum ions. TiO2-based materials are also the most studied non-carbon PEFC cathode catalyst supports. The main advantage of TiO2 is its higher surface area compared with Magnèli-phase TinO2n−1, which is due to the lower synthesis temperature because TiO2 does not need to be reduced at high temperatures. In contrast, the principal disadvantage of TiO2 is its lower conductivity, as displayed in Fig. 4(k). The Popov group reported high surface-area TiO2 supports for PEFC cathodes, including mesoporous TiO2 with a BET surface area of 250–266 m2 g−1, which was successfully synthesized via a template-assisted route using Pluronic P123 as a surfactant.55,67 Pt nanoparticles were deposited on high surface-area mesoporous TiO2 to yield high platinum mass fractions of 40% w/w and 60% w/w for Pt particle sizes of 4.2 nm and 5.1 nm, respectively.55 Pt/TiO2 exhibited a single-cell performance comparable to that of commercial Pt/C when the cell voltage exceeded 0.6 V, as shown in Fig. 5(a). At a cell voltage below 0.6 V, Pt/TiO2 displayed even higher current density than Pt/C owing to the thinner catalyst layer, improving mass-transport properties. As the density of TiO2 is approximately twice that of carbon, the Pt/TiO2 catalyst layers were thinner than their Pt/C counterparts (<3 μm).67 Pt/TiO2 exhibited considerably higher durability against cell potential held at 1.2 V compared with Pt/C, as shown in Fig. 5(b). Although these results from the Popov group are encouraging, other researchers have extended their work to use TiO2-carbon composites to further enhance the conductivity of TiO2 supports. Composites of oxides and carbon materials such as carbon black74 and carbon nanotubes (CNTs)75 rely on the conductivity of the carbon materials, which decreases following exposure to high PEFC potentials due to carbon corrosion, as described in Section 1. A more favorable approach than using TiO2-carbon composites is to enhance the conductivity of TiO2 by doping with other cations or anions.
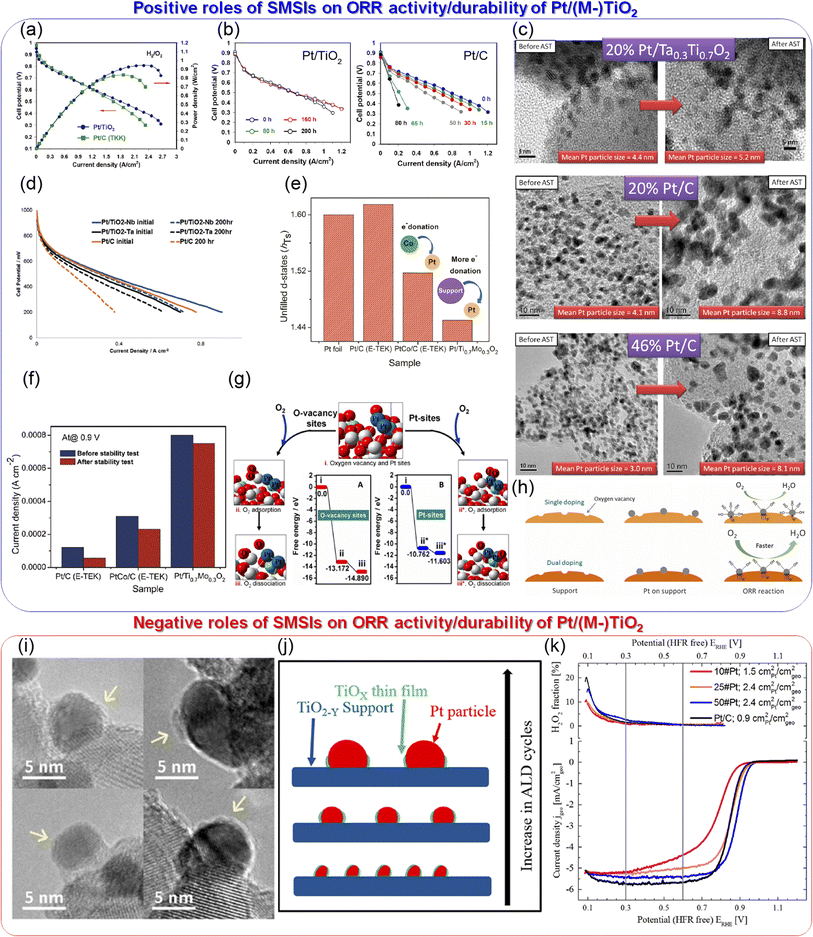 | ||
Fig. 5 (a) Cell potential versus current density curves of MEAs fabricated using Pt/TiO2 and Pt/C in cathodes and Pt/C in anodes at 348 K. The Pt loading was set at 0.5 and 0.4 mgPt cm−2 in the anode and cathode, respectively. The anode and cathode gases were fully humidified H2 and O2, respectively. (b) Cell potential versus current density curves of MEAs fabricated using Pt/TiO2 and Pt/C in cathodes and Pt/C in anodes at 353 K before and after cell potential holding at 1.2 V for various durations. The anode and cathode gases were H2 and O2, respectively, with 50% RH. During potential holding, the cell was supplied with fully humidified H2 and N2 at the anode and cathode, respectively. The Pt loading was set at 0.5 and 0.4 mgPt cm−2 in the anodes and cathodes, respectively. Reproduced with permission.67 Copyright 2009, American Chemical Society. (c) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of 20% w/w Pt/Ta0.3Ti0.7O2, 20% w/w Pt/C, and commercial 46% w/w Pt/C particles before and after 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 voltage cycles between 1.0 and 1.5 V at 0.5 V s−1, hereafter denoted as FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles in a single cell. Reproduced with permission.56 Copyright 2014, American Chemical Society. (d) Cell potential versus current density curves of MEAs fabricated using a phosphoric-acid-doped polybenzimidazole (PBI) membrane, 20% w/w Pt/TiO2-Nb, and 20% w/w Pt/TiO2-Ta in the cathodes and 20% w/w Pt/C in the anodes at 423 K before and after holding the open-circuit potential for 200 h. Pt loading was set at 0.2 and 0.5 mgPt cm−2 in the anodes and cathodes, respectively. Reproduced with permission.68 Copyright 2014, Royal Society of Chemistry. (e) Unfilled d-states of Pt foil, commercial 20% w/w Pt/C, commercial 30% w/w PtCo/C, and 20% w/w Pt/Ti0.7Mo0.3O2 measured using X-ray adsorption near-edge spectroscopy (XANES). (f) Current density of commercial 20% w/w Pt/C, commercial 30% w/w PtCo/C and 20% w/w Pt/Ti0.7Mo0.3O2 at 0.9 V versus SHE in 0.5 mol dm−3 H2SO4 before and after 5000 potential cycles between 0 and 1.1 V at 50 mV s−1. Reproduced with permission.69 Copyright 2011, American Chemical Society. (g) Proposed models of selective oxygen adsorption and the different reaction pathways for oxygen dissociation on the Pt/d-Ti0.9Mo0.1O2 catalyst at (A) the interface between the Pt and oxygen vacancy and (B) the supported Pt surface, where white, red, blue, and light blue spheres represent Ti, oxygen, Pt, and, Mo, respectively. Reproduced with permission.70 Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society. (h) Schematic illustration of Pt loading on single-doped and dual-doped TiO2 supports and the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). Reproduced with permission.71 Copyright 2017, Nature Publishing Group. (i) High-resolution (HR) TEM images of Pt on Pt/TiO2 after reduction under pure H2 at 473 K. Reproduced with permission.72 Copyright 2017, Elsevier. (j) Schematic diagram of the correlation between TiOx film coverage and Pt particle size. The larger the number of Pt atomic layer deposition (ALD) cycles, the larger the Pt particle size, and the smaller the TiOx surface coverage, and vice versa. (k) Rotating ring disk electrode voltammograms of Pt/TiO2−y/C catalysts prepared with ALD and 5% w/w Pt/C as a reference. Roughness factors (in cmPt2/cmgeo2) of the electrodes are shown in the legend. The voltammograms were obtained in the anodic scan direction recorded at 50 mV s−1 and 1600 rpm in O2 saturated 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4. The ring potential was held at 1.2 V versus RHE. Reproduced with permission.73 Copyright 2020, The Electrochemical Society. 000 voltage cycles between 1.0 and 1.5 V at 0.5 V s−1, hereafter denoted as FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles in a single cell. Reproduced with permission.56 Copyright 2014, American Chemical Society. (d) Cell potential versus current density curves of MEAs fabricated using a phosphoric-acid-doped polybenzimidazole (PBI) membrane, 20% w/w Pt/TiO2-Nb, and 20% w/w Pt/TiO2-Ta in the cathodes and 20% w/w Pt/C in the anodes at 423 K before and after holding the open-circuit potential for 200 h. Pt loading was set at 0.2 and 0.5 mgPt cm−2 in the anodes and cathodes, respectively. Reproduced with permission.68 Copyright 2014, Royal Society of Chemistry. (e) Unfilled d-states of Pt foil, commercial 20% w/w Pt/C, commercial 30% w/w PtCo/C, and 20% w/w Pt/Ti0.7Mo0.3O2 measured using X-ray adsorption near-edge spectroscopy (XANES). (f) Current density of commercial 20% w/w Pt/C, commercial 30% w/w PtCo/C and 20% w/w Pt/Ti0.7Mo0.3O2 at 0.9 V versus SHE in 0.5 mol dm−3 H2SO4 before and after 5000 potential cycles between 0 and 1.1 V at 50 mV s−1. Reproduced with permission.69 Copyright 2011, American Chemical Society. (g) Proposed models of selective oxygen adsorption and the different reaction pathways for oxygen dissociation on the Pt/d-Ti0.9Mo0.1O2 catalyst at (A) the interface between the Pt and oxygen vacancy and (B) the supported Pt surface, where white, red, blue, and light blue spheres represent Ti, oxygen, Pt, and, Mo, respectively. Reproduced with permission.70 Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society. (h) Schematic illustration of Pt loading on single-doped and dual-doped TiO2 supports and the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). Reproduced with permission.71 Copyright 2017, Nature Publishing Group. (i) High-resolution (HR) TEM images of Pt on Pt/TiO2 after reduction under pure H2 at 473 K. Reproduced with permission.72 Copyright 2017, Elsevier. (j) Schematic diagram of the correlation between TiOx film coverage and Pt particle size. The larger the number of Pt atomic layer deposition (ALD) cycles, the larger the Pt particle size, and the smaller the TiOx surface coverage, and vice versa. (k) Rotating ring disk electrode voltammograms of Pt/TiO2−y/C catalysts prepared with ALD and 5% w/w Pt/C as a reference. Roughness factors (in cmPt2/cmgeo2) of the electrodes are shown in the legend. The voltammograms were obtained in the anodic scan direction recorded at 50 mV s−1 and 1600 rpm in O2 saturated 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4. The ring potential was held at 1.2 V versus RHE. Reproduced with permission.73 Copyright 2020, The Electrochemical Society. | ||
2.1.1.2.1 Cation-doped titanium dioxide-supported catalysts. Pentavalent cations such as Nb5+, Ta5+, and V5+ are the most studied dopants for TiO2 as a PEFC cathode catalyst support. When pentavalent cations (M5+) substituted for Ti4+ in TiO2, one Ti cation vacancy is created for every four M5+ introduced, or Ti4+ is reduced to Ti3+ for every M5+ introduced to compensate for the charge imbalance caused by M5+ substitution. This introduces shallow donor levels below the conduction band edge of TiO2 and increases the metallic character. The doping of hexavalent cations such as Mo6+ and W6+ into TiO2 has also been researched, and Nb-doped TiO2 has been investigated by many groups since the late 2000s. A higher ORR activity has been reported for Nb-doped TiO2 compared with Pt/C in half-cells employing acidic media,76–79 as well as a higher durability of Nb-doped TiO2 than Pt/C in single cells.80,81 These advantages of Nb-doped TiO2 have been attributed to SMSIs.76,78,79,81 However, the initial single-cell performance of Nb-doped TiO2 remains lower than that of Pt/C,80,81 and careful optimization of some factors is therefore needed. As mentioned in Section 2.1.1.1, each titanium atom in rutile TiO2 coordinates six oxygen atoms to form a TiO6 octahedron. Anatase, another form of TiO2 which is often used as a Pt-catalyst support, also consists of TiO6 octahedra, but differs in the number of shared edges (two for rutile versus four for anatase). Therefore, the coordination number of the titanium atoms in both anatase and rutile TiO2 is 6. The ionic radii of 6-coordinated titanium and its dopants are listed in Table 2.82 The ionic radius of Nb5+ at 64 pm is close to that of Ti4+ (60.5 pm), and thus Nb5+ readily substituted for Ti4+ to increase the doping level. Both the anatase/rutile ratio and Nb-doping level significantly affect the conductivity and BET surface area of Nb-doped TiO2,83 which are critical for the single-cell performance of Pt/Nb-doped TiO2. Most studies on Nb-doped TiO2 have been performed using a single composition, i.e., a single Nb-doping level or sole crystal structure (anatase or rutile). Careful optimization of these material factors mentioned in the previous sentence and catalyst layer structure such as the PFSI to catalyst ratio and the mass fraction of Pt in Pt/Nb-doped TiO2 to control the thickness and pore structure may improve the single-cell performance of MEAs employing Pt/Nb-doped TiO2 catalyst layers.
| Cation | Ionic radius (pm) | Cation | Ionic radius (pm) | Cation | Ionic radius (pm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti4+ | 60.5 | V5+ | 54 | Cr4+ | 55 |
| Nb5+ | 64 | V4+ | 58 | Cr3+ | 61.5 |
| Nb4+ | 68 | Mo6+ | 59 | W6+ | 60 |
| Ta5+ | 64 | Mo5+ | 61 | W5+ | 62 |
| Ta4+ | 68 | Cr5+ | 49 | W4+ | 66 |
Kumar and Ramani introduced Ta-doped TiO2 into PEFC cathodes in the mid-2010s.56,84 The Ta formed solid solutions with TiO2 and shifted peaks in the XRD patterns to lower angles, suggesting that the larger Ta5+ substituted for smaller Ti4+ in TiO2.84 Interestingly, the growth of the TiO2 particle size during annealing at 1123 K for 3 h was inhibited by Ta-doping due to distortion in the crystal lattice. When the composition changed from TiO2 to Ta0.3Ti0.7O2, the mean particle size decreased from 84 nm to 67 nm, and thus the BET surface area increased from 9 m2 g−1 to 26 m2 g−1.84 Pt nanoparticles around 4–5 nm in size were supported on Ta0.3Ti0.7O2 to yield 20% w/w Pt/Ta0.3Ti0.7O2. Although the ECSA and ORR mass activity of 20% w/w Pt/Ta0.3Ti0.7O2 are smaller than those of commercial 46% w/w Pt/C with 3 nm Pt particles in both a half-cell84 and single cell56 owing to the larger Pt particle size, 20% w/w Pt/Ta0.3Ti0.7O2 exhibited much higher durability against 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 DOE load cycles and 10
000 DOE load cycles and 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles than 46% w/w Pt/C in a single cell. During both types of cycles, the growth of Pt particle size in 20% w/w Pt/Ta0.3Ti0.7O2 was suppressed, as shown in Fig. 5(c), with the high durability ascribed to the SMSI between Pt nanoparticles and Ta0.3Ti0.7O2 supports.56 Other researchers following the work of Kumar and Ramani reported that SMSIs were responsible for the higher durability of Pt/Ta-doped TiO2versus commercial Pt/C.68,85 SMSIs in Pt/Ta-doped TiO2 and Pt/Nb-doped TiO2 were also reported to enhance the methanol oxidation reaction at 353 K in direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC) anodes and the ORR at temperatures exceeding that of PEFCs (423 K in polybenzimidazole [PBI] membrane fuel cell cathodes, as shown in Fig. 5(d)).68
000 FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles than 46% w/w Pt/C in a single cell. During both types of cycles, the growth of Pt particle size in 20% w/w Pt/Ta0.3Ti0.7O2 was suppressed, as shown in Fig. 5(c), with the high durability ascribed to the SMSI between Pt nanoparticles and Ta0.3Ti0.7O2 supports.56 Other researchers following the work of Kumar and Ramani reported that SMSIs were responsible for the higher durability of Pt/Ta-doped TiO2versus commercial Pt/C.68,85 SMSIs in Pt/Ta-doped TiO2 and Pt/Nb-doped TiO2 were also reported to enhance the methanol oxidation reaction at 353 K in direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC) anodes and the ORR at temperatures exceeding that of PEFCs (423 K in polybenzimidazole [PBI] membrane fuel cell cathodes, as shown in Fig. 5(d)).68
Vanadium, whose maximum valence is 5+, has attracted less attention than Nb5+ or Ta5+ as a dopant in TiO2. In 2016, Kim et al. reported that SMSIs were responsible for the three-fold higher durability of Pt nanoparticles supported on spherical V-doped TiO2 particles compared to Pt/C in a half-cell.86 Although the half-cell tests were designed with catalyst layers comprising catalysts and carbon black to improve the conductivity, and although the compositions of the catalysts are not described, Kim et al. noted that lattice contraction by substitutional doping of the smaller V5+ for Ti4+ in TiO2 shortened the interatomic Pt–Pt bond length to enhance ORR activity. Table 2 shows that the ionic radii of Nb5+ and Ta5+ are larger than that of Ti4+, and thus the TiO2 lattice is expanded when Nb5+ or Ta5+ substituted for Ti4+. Kim et al. also reported that the ORR activity of Pt/V-doped TiO2 exceeded that of Pt supported on TiO2 doped with larger cations (Pt/Cr-doped TiO2 and Pt/Nb-doped TiO2).86 Later, Noh et al. reported the higher activity and durability of a 6% w/w Pt/V-TiO2 nanotube (V-TNT) compared with conventional 20% w/w Pt/C in a half-cell without adding carbon black in catalyst layers. Similar to the work of Kim et al.,86 they also used Cr-doped and Nb-doped TNT as supports. Among the three 6% w/w Pt/M-TNTs where M = V, Cr, or Nb, Pt/V-TNT displayed the smallest Pt particle size and the highest ORR activity and durability.87 Using single-cell tests, Bharti and Cheruvally reported higher ORR activity and durability of Pt/V-doped TiO2 particle catalysts compared with commercial Pt/C.88
The Hwang group has focused on Mo-doped TiO2 supports. By using a hydrothermal method, fine Ti0.7Mo0.3O2 nanoparticles (8–10 nm in size) with a high BET surface area of 230 m2 g−1 were successfully synthesized. The Mo ions with an average valence of 5.75 were dissolved in a single anatase TiO2 phase. Then 3–4 nm Pt nanoparticles were anchored on Ti0.7Mo0.3O2 using a microwave-assisted polyol method. X-ray adsorption near-edge spectroscopy (XANES) revealed that 20% w/w Pt/Ti0.7Mo0.3O2 displayed a higher electron density around the Pt atoms, and thus a lower d-band vacancy than commercial 20% w/w Pt/C or commercial 30% w/w PtCo/C owing to SMSIs between Pt nanoparticles and Ti0.7Mo0.3O2, as shown in Fig. 5(e). 20% w/w Pt/Ti0.7Mo0.3O2 exhibited the highest initial ORR activity and the highest durability against 5000 potential cycles between 0 and 1.1 V versus RHE in half-cells among the three catalysts, as shown in Fig. 5(f).69 Later, the composition was optimized after introducing oxygen vacancies by H2 annealing to Ti0.9Mo0.1Oy. The oxygen vacancies enhanced the conductivity and ORR activity by facilitating the dissociative adsorption of O2 molecules on the Pt surface, with the proposed ORR model by density functional theory (DFT) calculations shown in Fig. 5(g).70 Rutile TiO2 doped with other cations such as W and Ir and anatase TiO2 doped with W have also been reported to enhance the ORR activity and durability of Pt catalysts in half-cells.89–91
2.1.1.2.2 Cation and anion codoped titanium dioxide-supported catalysts. While anions such as N3− and F− have been doped into TiO2 photocatalysts to decrease the band gap and increase the electrical conductivity, anion-doped TiO2 has seldom been investigated as a support material in PEFCs. The Hwang group developed Nb/Ta- and N-codoped TiO2 particles for use as support materials in PEFC cathodes. These dopants successfully formed a solid solution with the anatase TiO2 crystal structure, and σ at P = 200 MPa and the BET surface area were increased by codoping rather than single-cation doping. Interestingly, Ti K-edge XANES analyses revealed that Pt nanoparticles were selectively deposited on oxygen vacancy sites on Nb/Ta- and N-codoped TiO2 supports compared with Nb/Ta-doped TiO2. The Pt particles deposited on the oxygen vacancy sites were more electronegative and had fewer hydroxyl groups on the surface during the ORR, enhancing the activity as illustrated in Fig. 5(h). Due to SMSIs, both Pt/codoped TiO2 catalysts displayed higher ORR activity and durability against load cycles between 0.6 and 1.0 V at 50 mV s−1 than Pt/C in a half-cell.71 Lee et al. reported N- and C-codoped TiO2-supported Pt catalysts. Abundant oxygen vacancies and lattice disorder defects formed by the N, C-codoping enhanced the magnitude of the SMSIs to achieve high durability against 5000 FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles in a single cell.92 The high durability of Pt/N, C-codoped TiO2 in a half cell was reported by the Bhat group.93 The codoping of Cu and N into TiO2 supports has also been shown to enhance ORR activity compared with Pt/C in a single cell.58
2.1.1.2.3 Mixed oxide-supported catalysts. Besides the substitutional and/or interstitial doping described above, the Ramani group also reported mixed oxide supports in the 2010s. By using a simple wet chemical route and annealing at 723 K in air, a mixture of anatase TiO2 and rutile RuO2 (TRO) supports with a BET surface area of 33 ± 4 m2 g−1 was synthesized. Although the pressure applied for the measurements was not described, the TiO2-RuO2 support particles displayed a high σ of 21 ± 5 S cm−1, which is close to that of carbon black (Vulcan XC-72) at 31 ± 5 S cm−1.94 RuO2 and IrO2 have been used as OER catalysts and are known to exhibit metallic conductivities in the range of 0.01–1 times the conductivities of the parent metals. The conductivities of RuO2 in the [100] and [001] directions at 300 K are 27.7 and 28.0 kS cm−1, respectively, and the average single-crystal conductivity is reported to be 28.4 kS cm−1.95 Therefore, the high σ-value of TRO particles is reasonable. Pt particles around 4–6 nm in size were deposited on TRO, and 40% w/w Pt/TRO exhibited higher durability against the DOE load and startup/shutdown cycles in a single cell compared with commercial 50% w/w Pt/C owing to SMSIs.14 Other important findings from this comprehensive work are that carbon corrosion during startup/shutdown resulted in more severe damage than Pt dissolution during load cycles. In addition, CO2 emissions were observed from the Pt/TRO cathode exit of a single cell. Although the volume of CO2 emissions from the Pt/TRO cathode was one order of magnitude lower than that of Pt/C, the carbon microporous layer of GDLs was oxidized,14 which is consistent with the results of Ioroi et al.,35 suggesting the need to develop carbon-free GDLs. Similarly, Pătru et al. reported that Pt/IrO2-TiO2 exhibited higher durability against load cycles and startup/shutdown cycles in single cells compared with commercial 47% w/w Pt/C due to SMSIs.57 The advantage of both mixed oxide supports is a high conductivity, although a disadvantage is the scarcity of RuO2 and IrO2. The use of these mixed oxide supports inevitably causes an increase in PGM loading.
All of the above-cited studies on TiO2-based supports emphasize the merits of SMSIs for enhancing ORR activity and/or durability in half-cells and single cells. However, contrasting results have been reported since the late 2010s. One disadvantage of SMSIs is the formation of reduced thin titanium oxide (TiO2−x) layers on Pt particles96 that suppress ORR activity. The Hwang group reported that simple annealing of Pt/TiO2 at a low temperature (473 K) induced SMSIs between the Pt nanoparticles and commercial TiO2 particles (P25; a standard photocatalyst with 80% anatase and 20% rutile; Degussa Co.). The Pt particles on TiO2 were covered by thin TiO2−x layers, as shown by the arrows in Fig. 5(i). Electrochemical characterization in a half-cell revealed that the thin TiO2−x layers formed during low-temperature annealing decreased the ORR activity of Pt/TiO2, while the layers were removed by hydrofluoric acid treatment to boost the ORR activity beyond that of the original Pt/TiO2. Similar results were also observed from Pt/Nb-doped TiO2. The thin TiO2−x layers suppressed ORR activity, whereas protons could pass through the layers from CVs.72 Banham et al. suggested Nb and/or Ti dissolution from Nb-doped anatase TiO2 supports and their redeposition on Pt nanoparticles. The ORR activity of Pt/Nb-doped TiO2 decreased significantly during potential cycling between 1.0 and 1.4 V versus RHE in a half-cell employing 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 electrolyte, although its HOR activity did not change. The HOR activity of Pt/Nb-doped TiO2 was also stable after holding the anode voltage at 1.45 V versus the cathode supplied with H2 (i.e., the RHE in a single cell).97 Eckardt et al. reported that Pt/TiO2 and Pt/TiO2-CNT composite catalysts degraded faster than Pt/C during startup/shutdown ADTs in a half-cell and suggested that this was due to the thin TiO2−x layers.98 Stühmeier et al. recently systematically investigated the transport properties of thin TiO2−x layers. The thin TiO2−x layers on Pt particles reduced the ORR, OER, and CO oxidation activity of Pt catalysts, although they did not affect either the HOR activity or the formation of hydrogen underpotential deposition. This indicates that unlike protons and hydrogen, oxygen and oxygenated species could not pass through the layers, making Pt/TiO2 a highly selective HOR catalyst.73,99 The researchers deposited Pt nanoparticles on a reduced TiO2−y film synthesized at 973 K for 2 h under 4% v/v H2/Ar via atomic layer deposition (ALD) and controlled the size of the Pt particles by changing the number of ALD cycles. A schematic diagram of the correlation between the layer coverage and Pt particle size obtained from the electrochemical measurements and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images is shown in Fig. 5(j). Pt particle size increased and the Pt surface area decreased with increasing number of ALD cycles, while ORR activity increased significantly due to the increase in the exposed Pt surface area, as shown in Fig. 5(k). Hornberger et al. reported that a thin oxide layer gradually grew on the Pt particles during potential cycles between 0.6 and 0.95 V versus RHE at 0.1 V s−1 in 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4. The growth of the thin layer due to SMSIs decreased the ECSA and ORR activity of Pt/TRO.100 The controversial effect of SMSIs on the ORR activity and durability of Pt/(M-)TiO2 catalysts needs to be further investigated. In many reports, SMSIs between Pt nanoparticles and TiO2-based supports produce higher ORR activity and durability than conventional Pt/C, although there are exceptions that display lower ORR activity and durability owing to the presence of thin TiO2−x layers on Pt particles, as mentioned above. One of the key factors is Pt particle size, as addressed by Stühmeier et al.73 In previous studies on Pt/TiO2 or Pt/Ti4O7 in which high ORR activity and durability are reported, the Pt particle sizes are larger (mostly above 4 nm) than those of commercial Pt/C. The surface coverage of the thin TiO2−x layers on the Pt particles might be low when the particle size is large, as illustrated in Fig. 5(j). This illustration is a hypothetical model, and discussions around clear high-resolution (HR)-TEM images are needed in future studies.
2.1.1.3 Tin dioxide-supported catalysts. Owing to its abundance and high stability in PEFC cathodes, SnO2 is one of the most studied supports in this field. The Sasaki group has been developing SnO2 supports since 2009. SnO2 particles with a size of the order of several tens of nanometers and a BET surface area of approximately 20 m2 g−1 were synthesized via a coprecipitation route. Compared with previous studies on Pt/titanium suboxide and Pt/titanium oxide-based catalysts, smaller Pt nanoparticles with a diameter of 3 nm were successfully deposited on SnO2 at a Pt mass fraction of 20% w/w. The 20% w/w Pt/SnO2 maintained a higher ECSA than 20% w/w Pt/C synthesized by the authors after 10
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 potential cycles between 0.6 and 0.9 or 1.3 V versus RHE at 0.1 V s−1 in 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4. In addition, the single-cell performance of 20% w/w Pt/SnO2 was comparable to that of 20% w/w Pt/C, as shown in Fig. 6(a). Similar to reports on Pt/TiO2 from the Popov group,67 the Pt/SnO2 catalyst layer was thinner than its Pt/C counterpart, and displayed lower mass-transport resistance.101 Later, the Sasaki group doped Nb5+ and Sb5+ into SnO2 to enhance conductivity, which was maximized at a composition of Sn0.98Nb0.02O2. The agglomeration of SnO2 particles was suppressed by Nb-doping to increase the BET surface to around 50 m2 g−1, and the optimized 20% w/w Pt/Sn0.98Nb0.02O2 displayed a larger ECSA than 20% w/w Pt/C after 10
000 potential cycles between 0.6 and 0.9 or 1.3 V versus RHE at 0.1 V s−1 in 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4. In addition, the single-cell performance of 20% w/w Pt/SnO2 was comparable to that of 20% w/w Pt/C, as shown in Fig. 6(a). Similar to reports on Pt/TiO2 from the Popov group,67 the Pt/SnO2 catalyst layer was thinner than its Pt/C counterpart, and displayed lower mass-transport resistance.101 Later, the Sasaki group doped Nb5+ and Sb5+ into SnO2 to enhance conductivity, which was maximized at a composition of Sn0.98Nb0.02O2. The agglomeration of SnO2 particles was suppressed by Nb-doping to increase the BET surface to around 50 m2 g−1, and the optimized 20% w/w Pt/Sn0.98Nb0.02O2 displayed a larger ECSA than 20% w/w Pt/C after 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 rectangular wave potential cycles between 0.9 and 1.3 V versus RHE (held for 30 s at each potential) in 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4. Inductively coupled plasma (ICP) atomic emission spectroscopy analyses on the 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 electrolyte solution after the durability tests indicate that the amount of Sn and Nb dissolved from 20% w/w Pt/Sn0.98Nb0.02O2 was negligible, while nearly 60% of the Pt was dissolved. The authors concluded that the fraction of dissolved Pt increased with the ECSA, regardless of the support material type.107 To enhance the conductivity of catalyst layers utilizing optimized Sn0.98Nb0.02O2, which is two orders of magnitude lower than that of carbon black, they then prepared composite supports of vapor-grown carbon fiber (VGCF) and Sn0.98Nb0.02O2. Various platinum alloy (PtCo, Pt3Co, Pt4Co, and Pt3Ni) nanoparticles were then supported on the composite supports. The optimized Pt3Co/Sn0.98Nb0.02O2/VGCF catalyst survived after 400
000 rectangular wave potential cycles between 0.9 and 1.3 V versus RHE (held for 30 s at each potential) in 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4. Inductively coupled plasma (ICP) atomic emission spectroscopy analyses on the 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 electrolyte solution after the durability tests indicate that the amount of Sn and Nb dissolved from 20% w/w Pt/Sn0.98Nb0.02O2 was negligible, while nearly 60% of the Pt was dissolved. The authors concluded that the fraction of dissolved Pt increased with the ECSA, regardless of the support material type.107 To enhance the conductivity of catalyst layers utilizing optimized Sn0.98Nb0.02O2, which is two orders of magnitude lower than that of carbon black, they then prepared composite supports of vapor-grown carbon fiber (VGCF) and Sn0.98Nb0.02O2. Various platinum alloy (PtCo, Pt3Co, Pt4Co, and Pt3Ni) nanoparticles were then supported on the composite supports. The optimized Pt3Co/Sn0.98Nb0.02O2/VGCF catalyst survived after 400![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 FCCJ load cycles and 60
000 FCCJ load cycles and 60![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles in a single cell. However, the decreases in cell performance and increases in catalyst particle size during these two ADTs were not negligible.59 Kakinuma et al. have devoted significant effort to improving SnO2 conductivity and the cell performance of SnO2-based catalyst layers. By using a flame combustion route, nano-sized M-doped SnO2 (M = Sb, Nb, Ta) particles with a unique fused aggregate structure were successfully synthesized as supports for Pt or Pt-alloy catalysts. The structure of these materials is similar to that of conventional carbon black used in PEFCs,108 and the pore structure strongly affects their conductivity. The diameter of the Pt particle was successfully controlled to 3.0 nm with a nearly monodispersed diameter, as shown in Fig. 6(b). Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) analyses revealed that the Pt surface was encapsulated with an amorphous Sn0.96Sb0.04O2−δ layer with several nanometers in thickness, owing to SMSIs. This is similar to a number of previous reports on TiO2-based supports. The layer was successfully removed by annealing Pt/Sn0.96Sb0.04O2−δ at 573 K under 1% v/v H2/N2, as shown in Fig. 6(c). The resulting surface layer-free 19.8% w/w Pt/Sn0.96Sb0.04O2−δ displayed high durability against rectangular potential cycles between 0.9 and 1.3 V versus RHE (held for 30 s at each potential) in 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4. Interestingly, the ECSA increased from 50 to 60.2 m2 g−1 when the cycle number increased from 0 to 1000, and then decreased slightly to 58 m2 g−1 after 5000 cycles, which still exceeds that before cycling. The SMSIs between the Pt nanoparticles and Sn0.96Sb0.04O2−δ supports suppressed Pt migration or dissolution to maintain the monodisperse distribution of Pt nanoparticle size (mean Pt particle size after the 5000 potential cycles was 3.2 nm, which is almost the same as that before cycling).102 Later, the single-cell performance was optimized using careful CV measurements and support solubility measurements with ICP. When the potential was lower than 0.4 V, a small amount of Sn was dissolved and deposited on the Pt nanoparticle surface to inhibit the ORR process. Preconditioning before measurement significantly affected the single-cell performance, as shown in Fig. 6(d). When the cathode 12.3% w/w Pt/Sn0.96Sb0.04O2−δ or 10.0% w/w Pt/Sn0.96Nb0.04O2−δ catalyst layers were preconditioned at 0.1 V for 24 h before measurement, their current densities were lower than that of the standard 47.9% w/w Pt/CB at cell voltages lower than 0.7 V. However, Pt/Sn0.96Sb0.04O2−δ and Pt/Sn0.96Nb0.04O2−δ catalyst layers outperformed their Pt/CB counterpart when the cathode potential was maintained above 0.4 V, as the dissolution/deposition of Sn species from the support was suppressed.103 The aggregate structure of the supports was later controlled to enhance conductivity, as shown in Fig. 6(e). Kakinuma et al. evaluated the level of necking between Sn0.96Nb0.04O2−δ particles using the “necking index” (NI), defined as the ratio of the BET surface area to the surface area of the sphere, calculated by assuming that the diameter is equal to the mean crystallite size as determined from the XRD pattern. Isolated spheres are expected when NI = 1, and developed necking structures are expected as the NI decreases below 1. Apparent conductivity, defined as σ at P = 19 MPa, increased with decreasing NI for two different types of dependence: the route from B to D and B to E via C. The authors attributed the source of the two different routes to the pore structure. The apparent conductivity increased consistently with the volume of the primary pores, which are formed between the aggregated Sn0.96Nb0.04O2−δ particles and defined as pores below 30 nm in diameter.104 These findings by Kakinuma et al. are truly original and all their studies are among the most meticulous in related literature.
000 FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles in a single cell. However, the decreases in cell performance and increases in catalyst particle size during these two ADTs were not negligible.59 Kakinuma et al. have devoted significant effort to improving SnO2 conductivity and the cell performance of SnO2-based catalyst layers. By using a flame combustion route, nano-sized M-doped SnO2 (M = Sb, Nb, Ta) particles with a unique fused aggregate structure were successfully synthesized as supports for Pt or Pt-alloy catalysts. The structure of these materials is similar to that of conventional carbon black used in PEFCs,108 and the pore structure strongly affects their conductivity. The diameter of the Pt particle was successfully controlled to 3.0 nm with a nearly monodispersed diameter, as shown in Fig. 6(b). Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) analyses revealed that the Pt surface was encapsulated with an amorphous Sn0.96Sb0.04O2−δ layer with several nanometers in thickness, owing to SMSIs. This is similar to a number of previous reports on TiO2-based supports. The layer was successfully removed by annealing Pt/Sn0.96Sb0.04O2−δ at 573 K under 1% v/v H2/N2, as shown in Fig. 6(c). The resulting surface layer-free 19.8% w/w Pt/Sn0.96Sb0.04O2−δ displayed high durability against rectangular potential cycles between 0.9 and 1.3 V versus RHE (held for 30 s at each potential) in 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4. Interestingly, the ECSA increased from 50 to 60.2 m2 g−1 when the cycle number increased from 0 to 1000, and then decreased slightly to 58 m2 g−1 after 5000 cycles, which still exceeds that before cycling. The SMSIs between the Pt nanoparticles and Sn0.96Sb0.04O2−δ supports suppressed Pt migration or dissolution to maintain the monodisperse distribution of Pt nanoparticle size (mean Pt particle size after the 5000 potential cycles was 3.2 nm, which is almost the same as that before cycling).102 Later, the single-cell performance was optimized using careful CV measurements and support solubility measurements with ICP. When the potential was lower than 0.4 V, a small amount of Sn was dissolved and deposited on the Pt nanoparticle surface to inhibit the ORR process. Preconditioning before measurement significantly affected the single-cell performance, as shown in Fig. 6(d). When the cathode 12.3% w/w Pt/Sn0.96Sb0.04O2−δ or 10.0% w/w Pt/Sn0.96Nb0.04O2−δ catalyst layers were preconditioned at 0.1 V for 24 h before measurement, their current densities were lower than that of the standard 47.9% w/w Pt/CB at cell voltages lower than 0.7 V. However, Pt/Sn0.96Sb0.04O2−δ and Pt/Sn0.96Nb0.04O2−δ catalyst layers outperformed their Pt/CB counterpart when the cathode potential was maintained above 0.4 V, as the dissolution/deposition of Sn species from the support was suppressed.103 The aggregate structure of the supports was later controlled to enhance conductivity, as shown in Fig. 6(e). Kakinuma et al. evaluated the level of necking between Sn0.96Nb0.04O2−δ particles using the “necking index” (NI), defined as the ratio of the BET surface area to the surface area of the sphere, calculated by assuming that the diameter is equal to the mean crystallite size as determined from the XRD pattern. Isolated spheres are expected when NI = 1, and developed necking structures are expected as the NI decreases below 1. Apparent conductivity, defined as σ at P = 19 MPa, increased with decreasing NI for two different types of dependence: the route from B to D and B to E via C. The authors attributed the source of the two different routes to the pore structure. The apparent conductivity increased consistently with the volume of the primary pores, which are formed between the aggregated Sn0.96Nb0.04O2−δ particles and defined as pores below 30 nm in diameter.104 These findings by Kakinuma et al. are truly original and all their studies are among the most meticulous in related literature.
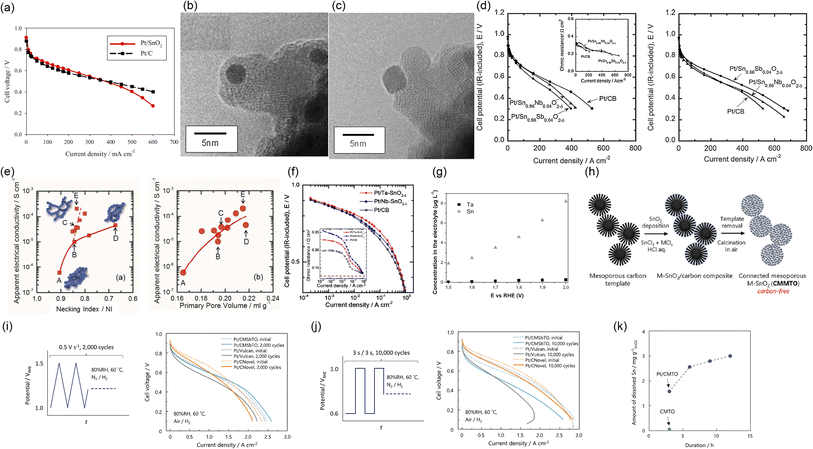 | ||
Fig. 6 (a) Cell voltage versus current density curves of MEAs fabricated using 20% w/w Pt/SnO2 and 20% w/w Pt/C in the cathode at 353 K. The anode and cathode gases were almost fully humidified H2 and air, respectively. Commercial 46% w/w Pt/C catalysts were used in the anode. The cathode and anode platinum loadings were set at 0.6 and 0.4 mgPt cm−2, respectively. Reproduced with permission.101 Copyright 2009, The Electrochemical Society. In situ environmental TEM images of Pt/Sn0.96Sb0.04O2−δ (b) before and (c) after annealing at 573 K under 1% v/v H2/N2. Reproduced with permission.102 Copyright 2011, Elsevier. (d) Cell potential versus current density curves of MEAs fabricated using three different catalysts (10% w/w Pt/Sn0.96Nb0.04O2−δ, 12.3% w/w Pt/Sn0.96Sb0.04O2−δ, and commercial 47.9% w/w Pt/CB) in the cathode at 353 K. Commercial 47.9% w/w Pt/CB catalysts were used in the anode. The cathode and anode platinum loadings were set at 0.2 and 0.5 mgPt cm−2, respectively. The anode and cathode gases were H2 and air, respectively, at 53% RH. Each catalyst layer was (left) preconditioned at 0.1 V for 24 h and (right) maintained above 0.4 V. Reproduced with permission.103 Copyright 2013, Elsevier. (e) (left) Apparent electrical conductivity versus necking index (NI) curves and (right) apparent electrical conductivity versus primary pore volume curve of Sn0.96Nb0.04O2−δ. Reproduced with permission.104 Copyright 2014, Royal Society of Chemistry. (f) Cell potential versus current density curves of MEAs fabricated using three different cathode catalysts (15.8% w/w Pt/Ta-SnO2−δ, 15.3% w/w Pt/Nb-SnO2−δ, and commercial 46–48% w/w Pt/CB) at 353 K. The inset shows cell resistance versus current density curves. Commercial Pt/CB catalysts were used in the anode. The cathode and anode platinum loadings were set at 0.06 ± 0.002 and 0.5 ± 0.05 mgPt cm−2, respectively. The anode and cathode gases were H2 and air, respectively at 53% RH. Reproduced with permission.105 Copyright 2015, Elsevier. (g) Sn and Ta concentrations dissolved from Ta-doped SnO2 in 0.5 mol dm−3 H2SO4 electrolyte solution versus potential curves at 353 K. The potential was held for 4 h. Reproduced with permission.51 Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society. (h) Synthesis scheme of connected mesoporous M-doped tin oxide (CMMTO). (i) (left) Potential versus time curve of the used FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles and (right) cell voltage versus current density curves of MEAs fabricated using three different cathode catalysts (20% w/w Pt/CMSbTO, commercial 30% w/w Pt/Vulcan, and 30% w/w Pt/Cnovel) before (dashed lines) and after (solid lines) 2000 FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles at 333 K. Commercial Pt/C catalysts were used in the anode. The cathode and anode platinum loadings were set at 0.1 and 0.05 mgPt cm−2, respectively. The anode and cathode gases were H2 and air, respectively, at 80% RH. (j) (left) Potential versus time curve of the used FCCJ load cycles and (right) cell voltage versus current density curves of MEAs fabricated using the three different cathode catalysts used in (i) before (dashed lines) and after (solid lines) 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 FCCJ load cycles at 333 K. Other conditions were identical to those used in (i). (k) Cumulative amount of dissolved Sn from the connected mesoporous tin oxide (CMTO) and Pt/CMTO versus the dissolution test duration in 1 M HClO4 at 333 K with H2 bubbling. Reproduced with permission.106 Copyright 2024, American Chemical Society. 000 FCCJ load cycles at 333 K. Other conditions were identical to those used in (i). (k) Cumulative amount of dissolved Sn from the connected mesoporous tin oxide (CMTO) and Pt/CMTO versus the dissolution test duration in 1 M HClO4 at 333 K with H2 bubbling. Reproduced with permission.106 Copyright 2024, American Chemical Society. | ||
The controlled fused aggregate structure was then applied to Ta-doped SnO2 supports. Ta-SnO2 displayed apparent conductivity approximately 40 times higher than that of Nb-SnO2 due to the higher carrier concentration, with a similar aggregate structure. In addition, the ORR activity of Pt/Ta-doped SnO2 exceeded that of Pt/Nb-SnO2 and commercial Pt/C in a single cell, as shown in Fig. 6(f).105 To the best of the author's knowledge, the cathode Pt loading in Fig. 6(f) (0.06 ± 0.002 mgPt cm−2) is the lowest among the MEAs utilizing Pt/non-carbon supported catalysts reported to date. The development of Nb/Ta-doped SnO2-supported Pt,60,109,110 PtCo,111 and PtCoSn112 catalysts continues to the present day, with other groups also focusing on such Sb/Nb/Ta-doped SnO2 supports. For example, Cavaliere et al. developed Sb/Nb/Ta-doped SnO2 nanofiber supports via an electrospinning route.51,53,113–115 Careful optimization of the doping level was performed on these supports, and all Pt/M-doped SnO2 catalysts displayed higher durability than Pt/C in half-cells51,53,114 and in single cells114 owing to SMSIs. The researchers concluded that Ta-doped SnO2 is the best support for Pt nanoparticles among the three candidates, simultaneously showing higher conductivity than Nb-doped SnO2 and higher stability than Sb-doped SnO2.51 Nonetheless, Ta and Sn were found to dissolve from the optimal Ta-doped SnO2 in 0.5 mol dm−3 H2SO4 solution, with the quantity of both elements increasing with potential, as shown in Fig. 6(g).51 Although little of the element was dissolved (less than 0.1% w/w) and the potential holding time was relatively long (4 h), these findings suggest that M-doped SnO2 is more stable in PEFC cathodes than the anode counterparts at potentials exceeding 1.5 V (where PEFC anodes face H2 starvation) (Fig. 6(g)). This is particularly true when combined with the results from Kakinuma et al., in which Sn dissolved at potentials lower than 0.4 V.103 Many other groups have followed these pioneering studies utilizing Sb/Nb/Ta-doped SnO2 supports.61,116–119
Several new strategies have been reported recently. In 2024, Inaba et al. developed unique connected mesoporous M-doped SnO2 supports using a mesoporous carbon template, and the scheme is shown in Fig. 6(h).106 Mesoporous carbon supports enhance PEFC performance by reducing the amount of Pt poisoned by the sulfonic group of PFSI and reduce oxygen-transport resistance through the PFSI,120 and are used in FCVs.121 A carbon-free mesoporous SnO2 support with a single mesopore size has also been developed,118,122 although the effect of pore size on performance has not been clarified. The impact of the pore size was negligible in a half-cell employing liquid electrolyte but significant in a single cell, owing to the difference in mass-transport properties. Inaba et al. optimized parameters such as the pore size of connected mesoporous Sb-doped SnO2 (CMSbTO) at 7.3 nm for single-cell performance and Sb-doping at around 6 at% for conductivity.106 From the four tested dopants (Sb, Nb, Ta, and W), they selected Sb as its conductivity was the highest. The optimized Pt/CMSbTO exhibited superior single-cell performance compared with Pt supported on nonporous solid-core Sb-doped SnO2, solid-core carbon (Vulcan) and mesoporous carbon (Cnovel) supports under dry conditions (i.e., when H2 and air gases with 30% RH were supplied to the anode and cathode), owing to the hydrophilic surface of CMSbTO. When these gases were supplied with 80% RH, Pt/Cnovel exhibited the best cell performance, although this initial high performance deteriorated significantly over 2000 FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles in contrast to the minimal changes in Pt/CMSbTO performance observed, as shown in Fig. 6(i). This indicates the superior durability of Pt/CMSbTO. Interestingly, the higher durability of Pt/CMSbTO over Pt/Cnovel or Pt/Vulcan was not observed over 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 FCCJ load cycles, as shown in Fig. 6(j). One reason for this is the stability of Pt/CMSbTO at low potentials, where Sn ions leach from the CMSbTO support and significantly increase in quantity due to the presence of Pt, as shown in Fig. 6(k).106 Kakinuma et al.103 and Jalalpoor et al.118 reported the dissolution of Sn and Sb ions from Sb-doped SnO2 at low potential, respectively. The selection of other dopants103,105 may affect the amount of Sn or dopant dissolution. The formation of an SnS2/SnO2 heterojunction123 and oxygen vacancies in SnO2 (ref. 124) was recently reported to enhance the ORR activity in a half-cell and durability against FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles in a single cell, respectively. A combination of the three new strategies mentioned in this paragraph may drive the practical application of SnO2-based supports in PEFC cathodes.
000 FCCJ load cycles, as shown in Fig. 6(j). One reason for this is the stability of Pt/CMSbTO at low potentials, where Sn ions leach from the CMSbTO support and significantly increase in quantity due to the presence of Pt, as shown in Fig. 6(k).106 Kakinuma et al.103 and Jalalpoor et al.118 reported the dissolution of Sn and Sb ions from Sb-doped SnO2 at low potential, respectively. The selection of other dopants103,105 may affect the amount of Sn or dopant dissolution. The formation of an SnS2/SnO2 heterojunction123 and oxygen vacancies in SnO2 (ref. 124) was recently reported to enhance the ORR activity in a half-cell and durability against FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles in a single cell, respectively. A combination of the three new strategies mentioned in this paragraph may drive the practical application of SnO2-based supports in PEFC cathodes.
2.1.1.4 Other oxide (WO3, In2O3, ZrO2, Ta2O5, SiO2, and CeO2)-supported catalysts. Compared with Ti- and Sn-based oxides, less attention has been paid to other oxides due to issues around their natural abundance, cost, stability, and conductivity. For example, from the studies on WO3 supports,125–129 the higher stability of Pt/WO3 compared with Pt/C has been confirmed in a half-cell employing 0.5 mol dm−3 H2SO4,127 while the dissolution of W species from Pt/WO3 in 0.05 mol dm−3 H2SO4 has also been reported.125 Raghuveer and Viswanathan replaced W6+ in WO3 with Ti4+ to improve the stability of WO3. However, stability was enhanced only at a low Ti4+ substitution level, and Ti4+ was not stable in the WO3 framework at a high substitution level.126 Liu et al. investigated the source of the degradation of Pt/WO3 in a half-cell and reported that it was tied directly to the formation of water-soluble hydrogen tungsten bronze (HxWO3) on the support surface, which facilitated the detachment of Pt nanoparticles.128 The properties of HxWO3 reported by Liu et al.128 are unsuitable for use as a support for Pt nanoparticles. However, HxWO3 was later used in PEFC anodes to diminish the reverse currents shown in Fig. 1 and thus keep the cathode potential below a theoretical potential during the startup/shutdown, as described in Section 2.2. In contrast, Kumar et al. reported highly stable interconnected Pt nanoparticles supported on WO3 nanorods used in the anode and cathode of a single cell. The cell containing a 20% w/w Pt/WO3 catalyst remained almost constant after holding the cell voltage at 0.40 V for 6 h. The higher durability of Pt/WO3 against startup/shutdown cycles in a half-cell compared with commercial Pt/C was also reported. Furthermore, the ECSA of Pt/WO3 in the MEA was 3.4 times larger than that of commercial Pt/C at a Pt loading of 0.5 mgPt cm−2.129 These contrasting durability results from different groups question the potential of Pt/WO3 in PEFCs. It is key to investigate the effects of WO3 morphology, crystallinity, exposed Pt facet, Pt particle size, and Pt loading on the durability of Pt/WO3 in order to clarify the source of the controversial results reported to date.
Indium tin oxide (ITO), doped In2O3 formed by substituting In3+ with Sn4+, is a well-known and commercially available transparent conducting oxide.130 Chhina et al. reported a Pt/ITO catalyst for use in PEFC cathodes. Pt/ITO displayed higher durability than Pt/C in a half-cell, although the shape of the CVs during 100 potential cycles between 0.6 and 1.8 V versus SHE was not stable.131 Later, Liu and Mustain developed highly durable Pt/ITO catalysts. Their 22% w/w Pt/ITO displayed negligible changes in rotating disk electrode (RDE) voltammograms and CVs during 1000 potential cycles between 0.0 and 1.4 V versus RHE in 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4. However, TEM analyses revealed several small pores formed on the ITO surface during the potential cycles due to the corrosion and dissolution of the surface Sn. Furthermore, the valence of the surviving Sn surface decreased significantly (the Sn4+ content decreased from 91% to 28% and the Sn2+ content increased from 9% to 72% during the potential cycles). Although these changes did not affect the ECSA or ORR activity in a half-cell employing acidic electrolyte solution,132 they may significantly decrease the single-cell performance, as leached cations can decrease the proton conductivity of the PFSI via ion exchange and/or catalyst poisoning. The Strasser group investigated the degradation pathways of Pt/ITO during load cycles and startup/shutdown cycles using an in situ scanning flow cell coupled with ICP mass spectroscopy and in situ X-ray techniques. Pt, Sn, and In metals dissolved on first contact between the catalyst layer and 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 electrolyte under open-circuit potential conditions. Sn and In also dissolved consistently during activation cycles between 0.05 and 1.0 V versus RHE and load cycles between 0.6 and 0.95 V versus RHE at 0.1 V s−1. The Sn dissolution was greater than the In dissolution in both the load cycles and FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles. Although SMSIs between Pt nanoparticles and ITO suppressed Pt dissolution compared with Pt/C, Pt surface modification due to In and accumulation of Sn was proposed as the source of activity loss during the load cycles.133 Recently, Cheng et al. developed a Pt–In alloy nanocluster catalyst supported on In2O3 (Pt–In/In2O3) using a hydrothermal route. The Pt–In alloy and a single Pt metal nanocluster were synthesized on In2O3 by controlling the atmosphere during hydrothermal synthesis to H2 and N2, respectively. A number of Pt–In nanoclusters with an average diameter of 3.4 nm connected with each other on the In2O3 nanoparticles to give a high σ of 15.4 S cm−1 at P = 20 MPa for 42% w/w Pt–In/In2O3 nanoparticles. This is almost the same as that of commercial 46% w/w Pt/C (22.0 S cm−1) and is three orders of magnitude higher than that of In2O3 supports (1.02 × 10−2 S cm−1). Although a small amount of In dissolution from Pt–In nanoclusters was suggested by post-TEM and XRD analyses, 42% w/w Pt–In/In2O3 exhibited little degradation during load cycles between 0.6 and 1.0 V versus RHE at 0.1 V s−1 or during startup/shutdown cycles between 1.0 and 1.6 V at 0.1 V s−1 in 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 solution. This was superior to commercial 46% w/w Pt/C due to the alloying effect and SMSIs.134
Previous studies from Lv et al.31 and Sasaki et al.26 (Fig. 3) suggest that ZrO2, Ta2O5, Nb2O5, and SiO2 are likely to be highly stable in PEFC cathodes, although they are all white in color and insulating, which is an unfavourable characteristic for a support material in PEFCs. Therefore, carbon materials have been used to achieve conductivity for these oxide-based catalyst layers.135–140 The Ota group reported a carbon-free sulfonated ZrO2-supported Pt (Pt/S-ZrO2) catalyst with unique behavior in PEFC cathodes. Commercially available S-ZrO2 is ZrO2 modified by sulfonation to offer high proton conductivity. The researchers synthesized 53% w/w Pt/S-ZrO2 catalysts from commercial S-ZrO2 powder and H2PtCl6·6H2O solution using an ultrasonic spray pyrolysis route. The single-cell performance of the 53% w/w Pt/S-ZrO2 cathode exceeded that of its commercial 46% w/w Pt/C counterpart in the absence of PFSI in the catalyst layers, although the trend was reversed in the presence of PFSI indicating that S-ZrO2 provides proton conductivity in the catalyst layer, allowing S-ZrO2 to decrease the PFSI content.141 Kakinuma et al. recently applied their flame combustion route to synthesize a new non-carbon support, Gd-doped CeO2. Gd-doping was used to enhance the conductivity of CeO2 and Pt nanorods oriented along the (1 1 1) facets of the Gd-doped CeO2. Scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM)-EDS analyses revealed PtCe alloy formation at the Pt and Gd-doped CeO2 interface. The Pt/Gd-doped CeO2 exhibited higher ORR activity and durability against 5000 FCCJ load cycles compared with commercial 46% w/w Pt/C in a half-cell employing 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4. DFT calculations indicated that the source of the high activity and durability was the exposure of Pt(1 1 1) facets and the oxygen-vacancy-mediated interfacial PtCe alloying.142
Most non-carbon oxide supports in PEFC cathodes developed to date have been Ti- and Sn-based oxides owing to their high stability, natural abundance, and high conductivity. In particular, the conductivity of the stoichiometric forms of these oxides (TiO2 and SnO2) can be greatly enhanced by cation doping, as described in Sections 2.1.1.2 and 2.1.1.3. Titanium suboxides also display metallic conductivity. Some of the oxide-supported Pt/Pt-alloy catalysts display excellent activity and durability in both a half-cell and a single cell after removal of any surface layers formed due to SMSIs. The mechanism to enhance the ORR activity of Pt/oxide catalysts by SMSIs has been described as follows. An electron transfer (donation) from the metal of the oxide to Pt causes a decrease in Pt d-band vacancy to downshift the Pt d-band center relative to the Fermi level. Consequently, the interaction between Pt and the oxygenated intermediates formed during the ORR (O, OH, or HO2 shown in eqn 2(b–d)) decreases to facilitate enhanced ORR activity. The four-electron (4e−) ORR in acidic media (eqn (2)) has been assumed to proceed via the elementary steps shown below:
| O2 + * → O2* | (2a) |
| O2* + H+ + e− → HO2* | (2b) |
| HO2* + H+ + e− → H2O + O* | (2c) |
| O* + H+ + e− → HO* | (2d) |
| HO* + H+ + e− → H2O + * | (2e) |
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Nb = 1
Nb = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 6.6 in atomic ratio)/CSCNT) because the interaction between Pt and the oxygenated intermediates formed during the ORR (eqn 2(b–d)) decreases to facilitate enhanced ORR activity. Then ORR activity decreased with further decreasing d-band center to (q) (Pt/WOx/CSCNT), as weak binding between Pt and the ORR intermediates lowered their coverage on the Pt surface.145 The so-called volcano-type dependence of ORR activity on the Pt d-band center has attracted the attention of researchers in this field, and the durability of the optimized Pt/TiNbOx catalyst after removing the carbon support, CSCNT, is also of interest.
6.6 in atomic ratio)/CSCNT) because the interaction between Pt and the oxygenated intermediates formed during the ORR (eqn 2(b–d)) decreases to facilitate enhanced ORR activity. Then ORR activity decreased with further decreasing d-band center to (q) (Pt/WOx/CSCNT), as weak binding between Pt and the ORR intermediates lowered their coverage on the Pt surface.145 The so-called volcano-type dependence of ORR activity on the Pt d-band center has attracted the attention of researchers in this field, and the durability of the optimized Pt/TiNbOx catalyst after removing the carbon support, CSCNT, is also of interest.
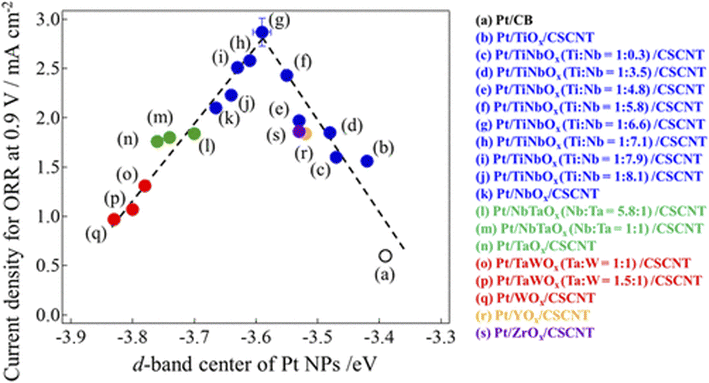 | ||
| Fig. 7 Current density for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) at 0.9 V versus the d-band center of Pt nanoparticle curve. Reproduced with permission.145 Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society. | ||
Another important point when selecting the oxide support is the leaching of metals and/or dopant metals from oxides as this significantly affects the durability, particularly in a single cell, as described in Sections 2.1.1.3 and 2.1.1.4. Although the leaching of Ti from TiO2 and TinO2n−1 is not described in Sections 2.1.1.1 and 2.1.1.2, it has previously been reported and its effect is discussed later in Section 2.2.3.
2.1.2.1 Titanium nitride-supported catalysts. Some nitride materials are known to display a high conductivity and are thus expected to have use as supports in PEFC cathodes. The most studied nitride for PEFC cathodes is TiN, which is a well-known metallic nitride with a conductivity value of 4.6 × 104 S cm−1, which is 17 orders of magnitude greater than that of a TiO2 semiconductor.42 Earlier studies by Avasarala et al. reported the potential146 and drawbacks147 of TiN as a support for PEFC cathodes. They used commercial TiN nanoparticles with a surface area of 40–55 m2 g−1 as supports, and then created supported Pt nanoparticles with an average diameter of 2 nm via a polyol route. In their initial 2009 work, 20% w/w Pt/TiN exhibited a higher ORR activity and a higher ECSA in a half-cell employing 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 at 333 K than commercial 20% w/w Pt/C, due to SMSIs. XPS analyses revealed that the surface was a mixture of TiN and TiO2, while the TiN content increased with Ar+ sputtering time to expose the bulk.146 A thin surface oxygen-rich oxynitride layer is known to be naturally formed by air moisture.148 The conductivity of the thin surface layer was lower than that of bulk TiN,42 although the impact on the initial ORR activity was negligible.146 Later, in their second work in 2010, Avasarala et al. electrochemically treated TiN nanoparticles by cycling the potential between 0 and 1.2 V versus RHE at 50 mV s−1 for 16 h in 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 at 333 K. Although the surface oxynitride layers were not transformed to a pure TiO2 layer to maintain the oxynitride surface after 2 years of air exposure, the layer changed significantly during the 16 h-potential cycles, as revealed by XPS analyses. The high surface TiN content of the as-received TiN particles decreased to less than half (31.5% to 14.3%) after the potential cycles, while the oxide and oxynitride contents increased. Furthermore, dissolution was suggested by the XPS analyses, and the decrease in the ECSA of 20% w/w Pt/TiN during potential cycling was ascribed to the passivation nature of TiN.147 Kakinuma et al. synthesized TiN nanoparticle supports using the radio-frequency plasma method to exhibit a high σ (850 S cm−1) when compressed at 60% relative density.149 Although the exact P value at 60% relative density is not clear, the reported σ of 850 S cm−1 is the highest among those reviewed in this paper. The resulting 19.5% w/w Pt/TiN displayed much higher durability against startup/shutdown cycles between 0.9 and 1.3 V (rectangular wave, held at 30 s at each potential) compared with commercial 47.9% w/w Pt/C and commercial 46.1% w/w Pt/graphitized carbon black. The TiN supports were crystallized in a nearly perfect cubic form, with the difference in durability between the findings of Avasarala et al.147 and Kakinuma et al. ascribed to the degree of crystallization.149 It is noted that the surface of Pt/TiN was covered with a thin (<1 nm) amorphous layer, similar to Pt/(M)-TiO2 and Pt/Sn0.96Sb0.04O2−δ, which could be removed by treating with hydrofluoric acid.149 The presence of the surface amorphous layer on Pt in Pt/TiN indirectly suggests the presence of SMSIs between Pt and TiN, as reported for Pt/oxide catalysts. The ECSA of Pt/TiN was later enhanced by adding acetylene black powder to achieve an agglomerate structure in the half-cell150 and a practical single cell with a large geometrical catalyst layer area of 196 cm2.151 The cell performance was also improved by adding acetylene black.151 Seifitokaldani and Savadogo reported the use of TiO2 and TiN mixture supports to maximize the benefits of TiO2 stability and TiN conductivity.152
Since these first studies reported from the late 2000s to early 2010s, significant efforts have been made to control the morphology of TiN supports to improve their mass-transport properties. The Sung group reported scaffold-like TiN nanotube supports via an alkaline hydrothermal route. The concept was to reduce the contact resistance between TiN nanoparticles by using TiN nanotubes (NTs), as shown in Fig. 8(a). The σ-value of the TiN NTs was 118.73 S cm−1 at P = 5 tons cm−2, which is 28 times higher than that of TiN nanoparticles (4.17 S cm−1). 19.2% w/w Pt/TiN NTs displayed a higher activity than 19.7% w/w Pt/TiN nanoparticles and commercial 20% w/w Pt/C in a half-cell employing 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 due to SMSIs. Both XPS Pt 4f and XANES Pt L3 edge analyses suggested electron transfer from Ti to Pt, similar to most Pt/TiO2 catalysts. Further, the durability against 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 potential cycles between 0.6 and 1.2 V versus RHE also outperformed that of Pt/C, as shown in Fig. 8(b). XPS Ti 2p and XANES Ti K-edge analyses revealed that these spectra did not change during the durability test, indicating a stable TiN surface due to SMSIs.153 The hydrothermal route is an attractive pathway to control the morphology of nanomaterials at low temperatures, typically below 473 K, and maintain a high surface area compared with a traditional solid-state reaction route, which needs a high synthesis temperature. The solvothermal route belongs to the family of hydrothermal routes and has also been used to synthesize TiN NT supports. When Pan et al. deposited 3.75 nm Pt nanoparticles on solvothermally synthesized TiN NTs with a BET surface area of 136 m2 g−1, 20% w/w Pt/TiN NTs showed superior ORR activity and durability compared with commercial 20% w/w Pt/C in a half-cell. Further, the TiN NTs themselves exhibited ORR activity without Pt to act as a co-catalyst to directly strengthen the ORR activity of Pt/TiN NTs.156 Nan et al. developed Ni-doped TiN NTs via a solvothermal route. Randomly oriented and interconnected nanosheets with a thickness of ∼13 nm were formed on NTs with a diameter of ∼930 nm, and Pt nanoparticles were formed on Ti0.9Ni0.1N, as shown in Fig. 8(c) and (d). The ORR activity and durability in the half-cell decreased in the following order: Pt/Ti0.9Ni0.1N NTs > Pt/TiN NTs > commercial Pt/C, as shown in Fig. 8(e) and (f). However, the XPS Pt 4f peak binding energy displayed the opposite trend (Pt/Ti0.9Ni0.1N NTs < Pt/TiN NTs < commercial Pt/C). The source of the higher ORR activity and durability of Pt/Ti0.9Ni0.1N NTs compared with Pt/TiN NTs was ascribed to the electron transfer from Ni to Pt to downshift the d-band center and thus weaken the Pt-oxygenated species interactions (i.e., SMSIs). Furthermore, hollow and porous structures were reported to enhance the activity by introducing efficient mass-transport properties.154 In a half-cell employing a liquid electrolyte, the mass (O2 molecules and protons) transport resistance is not large compared with that in a single cell employing a solid electrolyte, PFSI. Vertically aligned TiN nanorod array-supported PtPdCo alloy nanoparticles (PtPdCo/TiN) were used in a single cell by Jiang et al.157 Vertically aligned organic whiskers, which are called nanostructured thin films (NSTFs)158 and CNTs159, have been used as supports to enhance the mass-transport properties of Pt-based catalyst layers since the 2000s. In particular, the Pt/NSTF catalyst layers are only 0.27 μm thick, while the thin catalyst layer is free from PFSI.158 Similar to the previous study, Jiang et al. prepared vertically aligned TiN arrays with a thickness of 1.2 μm and formed thin PtPdCo/TiN catalyst layers directly on the surface of carbon paper without using PFSI. Water management to avoid water flooding in the thin catalyst layer remained necessary to enhance the cell performance.157 Similar ordered catalyst layer structures have been investigated by other groups.160 Besides controlling the morphology of TiN, doping other metals into TiN or alloying Pt with other metal(s) has also been utilized to enhance the ORR activity and durability of Pt/TiN. Xiao et al. reported Ti0.9Co0.1N particles as supports for Pt nanoparticles and evaluated the ORR activity and durability in a half-cell.161 Their results were very similar to the results for Ti0.9Ni0.1N NTs as reported by Nan et al.,154 confirming the positive roles of
SMSIs between Co and Pt nanoparticles. The Adzic group coated thin Pt layers (∼0.11 nm) on TiNiN nanoparticles with a Ti-to-Ni atomic ratio of 19
000 potential cycles between 0.6 and 1.2 V versus RHE also outperformed that of Pt/C, as shown in Fig. 8(b). XPS Ti 2p and XANES Ti K-edge analyses revealed that these spectra did not change during the durability test, indicating a stable TiN surface due to SMSIs.153 The hydrothermal route is an attractive pathway to control the morphology of nanomaterials at low temperatures, typically below 473 K, and maintain a high surface area compared with a traditional solid-state reaction route, which needs a high synthesis temperature. The solvothermal route belongs to the family of hydrothermal routes and has also been used to synthesize TiN NT supports. When Pan et al. deposited 3.75 nm Pt nanoparticles on solvothermally synthesized TiN NTs with a BET surface area of 136 m2 g−1, 20% w/w Pt/TiN NTs showed superior ORR activity and durability compared with commercial 20% w/w Pt/C in a half-cell. Further, the TiN NTs themselves exhibited ORR activity without Pt to act as a co-catalyst to directly strengthen the ORR activity of Pt/TiN NTs.156 Nan et al. developed Ni-doped TiN NTs via a solvothermal route. Randomly oriented and interconnected nanosheets with a thickness of ∼13 nm were formed on NTs with a diameter of ∼930 nm, and Pt nanoparticles were formed on Ti0.9Ni0.1N, as shown in Fig. 8(c) and (d). The ORR activity and durability in the half-cell decreased in the following order: Pt/Ti0.9Ni0.1N NTs > Pt/TiN NTs > commercial Pt/C, as shown in Fig. 8(e) and (f). However, the XPS Pt 4f peak binding energy displayed the opposite trend (Pt/Ti0.9Ni0.1N NTs < Pt/TiN NTs < commercial Pt/C). The source of the higher ORR activity and durability of Pt/Ti0.9Ni0.1N NTs compared with Pt/TiN NTs was ascribed to the electron transfer from Ni to Pt to downshift the d-band center and thus weaken the Pt-oxygenated species interactions (i.e., SMSIs). Furthermore, hollow and porous structures were reported to enhance the activity by introducing efficient mass-transport properties.154 In a half-cell employing a liquid electrolyte, the mass (O2 molecules and protons) transport resistance is not large compared with that in a single cell employing a solid electrolyte, PFSI. Vertically aligned TiN nanorod array-supported PtPdCo alloy nanoparticles (PtPdCo/TiN) were used in a single cell by Jiang et al.157 Vertically aligned organic whiskers, which are called nanostructured thin films (NSTFs)158 and CNTs159, have been used as supports to enhance the mass-transport properties of Pt-based catalyst layers since the 2000s. In particular, the Pt/NSTF catalyst layers are only 0.27 μm thick, while the thin catalyst layer is free from PFSI.158 Similar to the previous study, Jiang et al. prepared vertically aligned TiN arrays with a thickness of 1.2 μm and formed thin PtPdCo/TiN catalyst layers directly on the surface of carbon paper without using PFSI. Water management to avoid water flooding in the thin catalyst layer remained necessary to enhance the cell performance.157 Similar ordered catalyst layer structures have been investigated by other groups.160 Besides controlling the morphology of TiN, doping other metals into TiN or alloying Pt with other metal(s) has also been utilized to enhance the ORR activity and durability of Pt/TiN. Xiao et al. reported Ti0.9Co0.1N particles as supports for Pt nanoparticles and evaluated the ORR activity and durability in a half-cell.161 Their results were very similar to the results for Ti0.9Ni0.1N NTs as reported by Nan et al.,154 confirming the positive roles of
SMSIs between Co and Pt nanoparticles. The Adzic group coated thin Pt layers (∼0.11 nm) on TiNiN nanoparticles with a Ti-to-Ni atomic ratio of 19![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 (TiNiN@Pt) using a pulse deposition route.162 Similar to the work by Nan et al.,154 the activity and durability trend was as follows: TiNiN@Pt > TiN@Pt > commercial Pt/C. However, the trend in XPS Pt 4f binding energy differed from that of Nan et al.154 (TiNiN@Pt < commercial Pt/C < TiN@Pt), and Adzic et al. reported that electrons were transferred from Ni to Pt in TiNiN@Pt but from Pt to Ti or N in TiN@Pt. The downshift of the Pt d-band center was suggested as the source of the high activity of TiNiN@Pt, while the source for the superior activity of TiN@Pt compared to Pt/C was not clear.162 A unique combination of the Pt-alloy reported by Cui et al. and the mesoporous TiN via Zn-evaporation reported by Goodenough et al. produced a highly active and durable Fe3Pt/Ti0.5Cr0.5N. The ORR mass activity in a half-cell was five times higher than that of Pt/C owing to the well-ordered Fe3Pt catalyst, while the durability against FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles was enhanced by the anti-corrosion nature of the Ti0.5Cr0.5N support. Ti0.5Cr0.5N was also chemically stable after soaking in 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 solution for 2 weeks, with no change in the XRD pattern. However, 6.5% and 26.8% of Fe leached from ordered and disordered Fe3Pt/C catalysts, respectively, after 2 weeks of soaking.163 Fe is known to catalyze the decomposition of H2O2 byproducts formed during the ORR (eqn (6)), to produce hydroxyl or hydroperoxyl radicals,164,165 which degrade PFSI in catalyst layers and PFSI membranes.166 Leached cations also readily exchange for H+ in the sulfate group of PFSI to decrease the single-cell performance via decreased proton conductivity compared with the performance in a half-cell employing liquid electrolyte solution with abundant protons.106 Measures to suppress Fe-leaching during the operation of PEFCs (e.g., washing soluble Fe away using acidic solution prior to use) may be necessary for Fe3Pt/Ti0.5Cr0.5N. Matsui et al. investigated the stability of PtCu alloy catalysts formed on commercial TiN particles (PtCu/TiN) in PEFC cathodes. The ECSA maintained 70% of the initial value after 80
1 (TiNiN@Pt) using a pulse deposition route.162 Similar to the work by Nan et al.,154 the activity and durability trend was as follows: TiNiN@Pt > TiN@Pt > commercial Pt/C. However, the trend in XPS Pt 4f binding energy differed from that of Nan et al.154 (TiNiN@Pt < commercial Pt/C < TiN@Pt), and Adzic et al. reported that electrons were transferred from Ni to Pt in TiNiN@Pt but from Pt to Ti or N in TiN@Pt. The downshift of the Pt d-band center was suggested as the source of the high activity of TiNiN@Pt, while the source for the superior activity of TiN@Pt compared to Pt/C was not clear.162 A unique combination of the Pt-alloy reported by Cui et al. and the mesoporous TiN via Zn-evaporation reported by Goodenough et al. produced a highly active and durable Fe3Pt/Ti0.5Cr0.5N. The ORR mass activity in a half-cell was five times higher than that of Pt/C owing to the well-ordered Fe3Pt catalyst, while the durability against FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles was enhanced by the anti-corrosion nature of the Ti0.5Cr0.5N support. Ti0.5Cr0.5N was also chemically stable after soaking in 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 solution for 2 weeks, with no change in the XRD pattern. However, 6.5% and 26.8% of Fe leached from ordered and disordered Fe3Pt/C catalysts, respectively, after 2 weeks of soaking.163 Fe is known to catalyze the decomposition of H2O2 byproducts formed during the ORR (eqn (6)), to produce hydroxyl or hydroperoxyl radicals,164,165 which degrade PFSI in catalyst layers and PFSI membranes.166 Leached cations also readily exchange for H+ in the sulfate group of PFSI to decrease the single-cell performance via decreased proton conductivity compared with the performance in a half-cell employing liquid electrolyte solution with abundant protons.106 Measures to suppress Fe-leaching during the operation of PEFCs (e.g., washing soluble Fe away using acidic solution prior to use) may be necessary for Fe3Pt/Ti0.5Cr0.5N. Matsui et al. investigated the stability of PtCu alloy catalysts formed on commercial TiN particles (PtCu/TiN) in PEFC cathodes. The ECSA maintained 70% of the initial value after 80![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 FCCJ load cycles in a single cell, as shown in Fig. 8(g). Operando Pt LIII-edge and Cu K-edge XANES analyses revealed that Pt oxidation was suppressed, judging from the smaller difference between the height of the white line at 1.0 V and that at 0.4 V compared with Pt/C. In contrast, some Cu2+ species in the as-prepared PtCu/TiN were lost after incorporation in MEAs, and most of the Cu was found in the metallic state in the conditioned MEA as shown in Fig. 8(h). Changes in the PtCu alloy composition were observed after 80
000 FCCJ load cycles in a single cell, as shown in Fig. 8(g). Operando Pt LIII-edge and Cu K-edge XANES analyses revealed that Pt oxidation was suppressed, judging from the smaller difference between the height of the white line at 1.0 V and that at 0.4 V compared with Pt/C. In contrast, some Cu2+ species in the as-prepared PtCu/TiN were lost after incorporation in MEAs, and most of the Cu was found in the metallic state in the conditioned MEA as shown in Fig. 8(h). Changes in the PtCu alloy composition were observed after 80![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cycles, although the size was kept almost constant according to the ex situ XRD/TEM analyses shown in Fig. 8(i). Furthermore, the TiN peaks in the XRD pattern exhibited no change during the 80
000 cycles, although the size was kept almost constant according to the ex situ XRD/TEM analyses shown in Fig. 8(i). Furthermore, the TiN peaks in the XRD pattern exhibited no change during the 80![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cycles, suggesting the high durability of TiN supports against the load cycles.155 The results from different researchers indicate that once the surface oxynitride layers are formed on TiN, they prevent further oxidation of TiN, at least below 1 V, in PEFC cathodes. The coverage of the surface oxynitride layer is key for durability, particularly as 31.5% of surface TiN (68.5% of oxynitride layer coverage) reported by Avasarala et al.147 seems too high to cause degradation. The surface composition is also discussed in Section 3.
000 cycles, suggesting the high durability of TiN supports against the load cycles.155 The results from different researchers indicate that once the surface oxynitride layers are formed on TiN, they prevent further oxidation of TiN, at least below 1 V, in PEFC cathodes. The coverage of the surface oxynitride layer is key for durability, particularly as 31.5% of surface TiN (68.5% of oxynitride layer coverage) reported by Avasarala et al.147 seems too high to cause degradation. The surface composition is also discussed in Section 3.
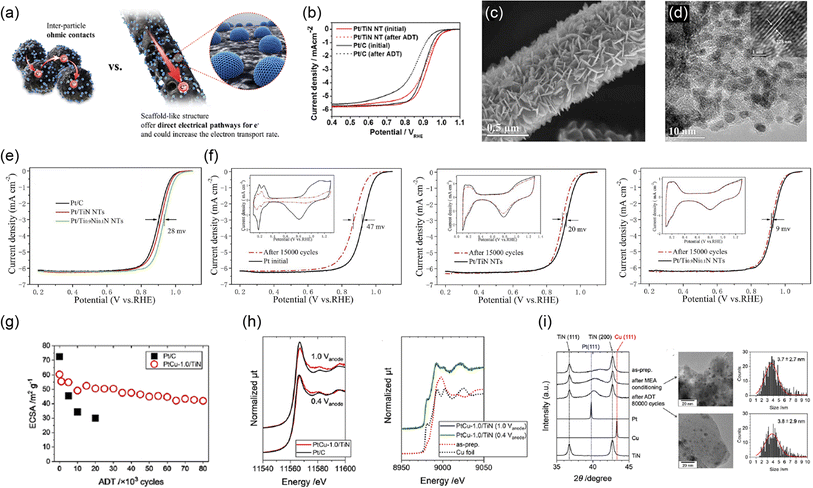 | ||
Fig. 8 (a) Schematic images of Pt/TiN nanoparticles and Pt/TiN nanotubes (NTs). (b) Rotating disk electrode (RDE) voltammograms of Pt/TiN NT and commercial Pt/C catalysts before and after an accelerated degradation test (ADT) (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 potential cycles between 0.6 and 1.2 V at 50 mV s−1). Reproduced with permission.153 Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society. (c) SEM and (d) TEM images of the Pt/Ti0.9Ni0.1N NTs. The inset of (d) shows the HR-TEM image. (e) RDE voltammograms of Pt/C, Pt/TiN NTs, and Pt/Ti0.9Ni0.1N NTs. (f) RDE voltammograms of (left) Pt/C, (center) Pt/TiN NTs, and (right) Pt/Ti0.9Ni0.1N NTs before (solid curves) and after (dashed curves) an ADT (15 000 potential cycles between 0.6 and 1.2 V at 50 mV s−1). Reproduced with permission.153 Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society. (c) SEM and (d) TEM images of the Pt/Ti0.9Ni0.1N NTs. The inset of (d) shows the HR-TEM image. (e) RDE voltammograms of Pt/C, Pt/TiN NTs, and Pt/Ti0.9Ni0.1N NTs. (f) RDE voltammograms of (left) Pt/C, (center) Pt/TiN NTs, and (right) Pt/Ti0.9Ni0.1N NTs before (solid curves) and after (dashed curves) an ADT (15![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 potential cycles between 0.6 and 1.2 V at 50 mV s−1). The inset shows their corresponding CVs. Reproduced with permission.154 Copyright 2018, Royal Society of Chemistry. (g) Electrochemically active surface area (ECSA) versus FCCJ load cycle number curves of MEAs fabricated using two different cathode catalysts (commercial 50% w/w Pt/C and 20% w/w PtCu-1.0/TiN), in which PtCu-1.0 indicates the atomic ratio of Cu to Pt = 1. Commercial 50% w/w Pt/C catalysts were used in the anode. The cathode and anode platinum loadings were set at 0.11 and 0.5 mgPt cm−2, respectively, and the cathode catalyst layer contained 30% w/w carbon black, Ketjen Black. The anode and cathode gases were H2 and 20% v/v O2/N2, respectively, at 93% RH and the cell temperature was kept at 353 K. (h) (left) Operando Pt LIII-edge XANES spectra of the MEAs with PtCu-1.0/TiN (red) and Pt/C (black) cathodes at 0.4 and 1.0 V cell voltages. The data were captured in transmission mode. (right) Operando Cu K-edge XANES spectra of the MEA with the PtCu-1.0/TiN cathode at a cell voltage of 1.0 V (blue) and 0.4 V (green) with those of as-prepared PtCu-1.0/TiN (powder, red dotted line) and Cu foil (black dotted line) as a reference. The data of samples were taken in X-ray fluorescence mode. In the MEAs used for operando XANES measurements, commercial 50% w/w Pd/C was used instead of Pt/C in the anode at a Pd loading of 0.5 mgPd cm−2. (i) (left) XRD patterns of PtCu-1.0/TiN collected from the cathode catalyst layer of the used MEA. The as-prepared catalyst (powder), after MEA conditioning and after an ADT with 80 000 potential cycles between 0.6 and 1.2 V at 50 mV s−1). The inset shows their corresponding CVs. Reproduced with permission.154 Copyright 2018, Royal Society of Chemistry. (g) Electrochemically active surface area (ECSA) versus FCCJ load cycle number curves of MEAs fabricated using two different cathode catalysts (commercial 50% w/w Pt/C and 20% w/w PtCu-1.0/TiN), in which PtCu-1.0 indicates the atomic ratio of Cu to Pt = 1. Commercial 50% w/w Pt/C catalysts were used in the anode. The cathode and anode platinum loadings were set at 0.11 and 0.5 mgPt cm−2, respectively, and the cathode catalyst layer contained 30% w/w carbon black, Ketjen Black. The anode and cathode gases were H2 and 20% v/v O2/N2, respectively, at 93% RH and the cell temperature was kept at 353 K. (h) (left) Operando Pt LIII-edge XANES spectra of the MEAs with PtCu-1.0/TiN (red) and Pt/C (black) cathodes at 0.4 and 1.0 V cell voltages. The data were captured in transmission mode. (right) Operando Cu K-edge XANES spectra of the MEA with the PtCu-1.0/TiN cathode at a cell voltage of 1.0 V (blue) and 0.4 V (green) with those of as-prepared PtCu-1.0/TiN (powder, red dotted line) and Cu foil (black dotted line) as a reference. The data of samples were taken in X-ray fluorescence mode. In the MEAs used for operando XANES measurements, commercial 50% w/w Pd/C was used instead of Pt/C in the anode at a Pd loading of 0.5 mgPd cm−2. (i) (left) XRD patterns of PtCu-1.0/TiN collected from the cathode catalyst layer of the used MEA. The as-prepared catalyst (powder), after MEA conditioning and after an ADT with 80![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 FCCJ load cycles. XRD reference profiles of Pt (ICSD180981) and Cu (ICSD180109) from the ICSD database are presented. (right) TEM images with the particle size distributions of the PtCu-1.0/TiN catalyst collected from the cathode catalyst layer of the used MEA after the conditioning and after an ADT with 80 000 FCCJ load cycles. XRD reference profiles of Pt (ICSD180981) and Cu (ICSD180109) from the ICSD database are presented. (right) TEM images with the particle size distributions of the PtCu-1.0/TiN catalyst collected from the cathode catalyst layer of the used MEA after the conditioning and after an ADT with 80![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 FCCJ load cycles. The red line in the particle size distribution shows Gaussian fitting to estimate the average particle size. Reproduced with permission.155 Copyright 2024, Royal Society of Chemistry. 000 FCCJ load cycles. The red line in the particle size distribution shows Gaussian fitting to estimate the average particle size. Reproduced with permission.155 Copyright 2024, Royal Society of Chemistry. | ||
2.1.2.2 Other nitride (WN, VN, BN)-supported catalysts. Compared with TiN, other nitrides have attracted less attention, mainly due to their poorer conductivity and stability. Tungsten nitride (WN) and vanadium nitride (VN) have been used as supports by forming composites with carbon materials to enhance their conductivity.167,168 Tsai et al. recently coated VN thin films on TaC as a composite support for Pt nanoparticles, as the bulk conductivity of TaC is the highest among the transition metal carbides. However, the single-cell performance of the optimized 2.82% w/w Pt/VN@TaC cathode was lower than that of commercial Pt/C. Although the power density per platinum mass of the Pt/VN@TaC cathode exceeded that of commercial Pt/C owing to the low Pt loading caused by the low Pt mass fraction, an increase in the Pt mass fraction is necessary for practical use, and ADT results are not reported.169 Recently, porous boron nitrides (p-BNs) have been used as supports for Pt nanoparticles without using carbon materials.170 The hexagonal structure of these materials is similar to that of graphite, and the inertness makes them suitable as support materials. BN has been used as a catalyst itself and as a support material for Au catalysts, although the ORR activity remains only moderate.171,172 Li et al. deposited Pt nanoparticles with an average diameter of 2.45 nm onto the edge of micropores in micro-sized rod-like p-BNs. They reported that BN is polar with an electron-deficient B-site that accepts electrons from Pt and an electron-rich N-site that donates electrons to Pt. This allows an electron donation-back process, which strengthens the SMSIs according to DFT calculation results, XPS, and electrochemical analyses with a half-cell configuration.170
2.2 Anode catalysts
As shown in Fig. 2, the anode potential increases above that of the cathode to reverse the cell voltage during H2 starvation if no system-level measures have been taken. Catalysts tolerant to cell reversal are known as reversal tolerant anode (RTA) catalysts, and they have been developed to avoid damage at high potentials. Unlike the widely used startup/shutdown and load cycle protocols for evaluating the durability of supports and the catalyst, respectively, at the cathode,16,17 no protocol for cell reversal has yet been standardized, and the tested potential and duration at the potential differ in different publications. Therefore, a precise comparison of the reported durability results is not possible in this subsection. Furthermore RTA, ORR-inactive anodes have been reported to avoid high cathode potentials during startup/shutdown, as this effect is caused by anode ORR catalysis, as shown in Fig. 1. In this subsection, RTA catalysts and ORR-inactive anodes are reviewed.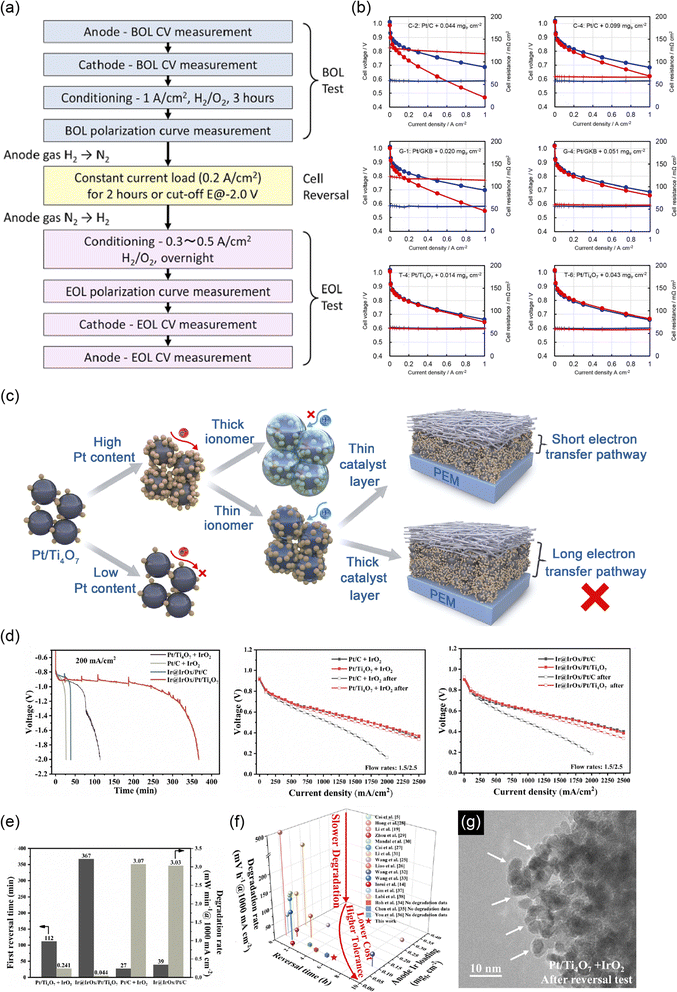 | ||
| Fig. 9 (a) Evaluation protocol of reversal tolerant anodes (RTAs) at the beginning of life (BoL), at cell reversal, and at the end of life (EoL). (b) Cell voltage (●) and cell resistance (+) versus current density curves of MEAs at the BoL and EoL with (top) Pt/C, (middle) Pt/GKB (graphitized Ketjen Black), and (bottom) Pt/Ti4O7 anode catalyst layers mixed with Ir black. All three RTAs were evaluated at the two different Ir loadings shown in the legend. Commercial Pt/C catalysts were used for all cathodes. The anode and cathode Pt loadings were 0.10 ± 0.02 and 0.50 ± 0.05 mgPt cm−2, respectively. The anode and cathode were supplied with fully humidified H2 and O2, respectively, to evaluate the cell performance and the cell temperature was set at 353 K. Reproduced with permission.175 Copyright 2020, Elsevier. (c) Schematic image of the optimization of the Pt/Ti4O7 catalyst and the anode catalyst layer for the cell performance. (d) (left) Cell voltage versus time curves of MEAs with four anode catalyst layers, Pt/Ti4O7 + IrO2, Pt/C + IrO2, Ir@IrOx/Pt/C, and Ir@IrOx/Pt/Ti4O7 during cell reversal. (center) Cell voltage versus current density curves of MEAs with two anode catalyst layers, Pt/Ti4O7 + IrO2 and Pt/C + IrO2, before and after cell reversal. (right) Cell voltage versus current density curves of MEAs with two anode catalyst layers, Ir@IrOx/Pt/C and Ir@IrOx/Pt/Ti4O7, before and after cell reversal. The cathode for all MEAs was commercial Pt/C. The anode and cathode Pt loadings were set at 0.1 and 0.4 mgPt cm−2, respectively. The Ir loading was set at 0.05 mgIr cm−2. The anode and cathode were supplied with fully humidified H2 and air, respectively, to evaluate the cell performance, and the cell temperature was set at 353 K. (e) First reversal time and degradation in the maximum power density of the four RTAs shown in (d). (f) Comparison of the anode Ir loading, first reversal time, and degradation date of RTAs reported in the literature. (g) TEM image of Pt/Ti4O7 + IrO2 anode catalysts after cell reversal. Reproduced with permission.37 Copyright 2024, Royal Society of Chemistry. | ||
In addition to the physical mixing used in these recent studies,175,176 in 2024, Li et al. synthesized Pt and core–shell structured Ir@IrOx on fine Ti4O7 particles.37 The Ti4O7 supports were synthesized via a modified version of the carbothermal reduction reaction reported by our group,36 to yield a BET surface area of 166 m2 g−1; then 3–4 nm Pt nanoparticles were deposited on Ti4O7via ethanol reduction route. Next, the Pt mass fraction in Pt/Ti4O7, PFSI mass fraction in the anode catalyst layers, and Pt loading at the anodes were carefully optimized to 40% w/w, 4% w/w, and 0.1 mgPt cm−2, respectively, to yield a single-cell performance matching that of a commercial Pt/C anode. The schematic diagram for this process is shown in Fig. 9(c). Ir@IrOx OER catalysts were then supported on the optimized 40% w/w Pt/Ti4O7via a hydrothermal route. At an Ir loading of 0.05 mgIr cm−2, the Ir@IrOx/Pt/Ti4O7 anode catalysts exhibited considerably greater tolerance to cell reversal than Ir@IrOx/Pt/C, a physical mixture of Pt/Ti4O7 + IrO2 and Pt/C + IrO2, as shown in Fig. 9(d) and (e). Cell reversal was performed using the protocol shown in the middle of Fig. 9(a), modified to include the use of air as an oxidant at the cathode and the removal of a set reversal time limit. The results shown in Fig. 9(d) and (e) clearly indicate two important aspects: (i) compared to the physical mixture, depositing Pt and Ir@IrOx nanoparticles on Ti4O7 supports produces much higher reversal tolerance in the anodes and (ii) Ti4O7 is considerably more tolerant to cell reversal than carbon black. Considering the results in Fig. 9(d) and the results of Li et al. for Pt/C + IrOx/Ti4O7 RTA,176 we can see that considerably higher Ir loading is necessary for Pt/C than for carbon-support-free Ti4O7 supports in the anodes. The Ir@IrOx/Pt/Ti4O7 anode cell reversal time, defined as the time to reach a cell voltage of −2.0 V during cell reversal, of 367 min was compared with other values reported to date, as shown in Fig. 9(f). The Ir loading used by Li et al.37 was 3.6 times higher than that used by Ioroi and Yasuda, and it is noted that the 2 h cell reversal cut-off time (shown as a red circle in Fig. 9(f) against “Ioroi et al. [14]”) was not the cell reversal time defined by Li et al., not sufficient to reach a cell voltage of −2.0 V.175 Although the reversal tolerance of the Ir@IrOx/Pt/Ti4O7 anode is high, some degradation in cell performance after cell reversal can be seen in Fig. 9(d). The source was investigated using several techniques. A TEM image of the Pt/Ti4O7 + IrO2 anode after the cell reversal test is shown in Fig. 9(g). The Pt nanoparticles were encapsulated by a thin layer of TiOx due to SMSIs, as indicated by the white arrows. Combined with the electrochemical impedance spectra and CVs after cell reversal and XPS analyses, it was concluded that Ti4O7 is stable and that the thin layer on the Pt nanoparticles is permeable to protons and H2 and does not affect HOR activity. However, the formation of the thin TiOx layer oxidizes the Pt surface, which impedes the electron transfer to degrade cell performance.37 These results indicate that the combination of the two pathways mentioned at the beginning of this subsection (the use of Ir-based OER catalysts and non-carbon supports) significantly suppresses damage due to cell reversal. However, Ir is an extremely expensive and scarce metal, with a 2021–2023 price approximately five times higher than that of Pt.177 Non-Ir catalysts have been reported to exhibit higher OER activity and durability than IrO2 in alkaline media; although, as with non-Pt ORR catalysts, they are not active or durable in acidic counterparts. Therefore, attempts have been made to reduce Ir loading in RTAs through means such as the use of IrO2/RuO2 composite,178,179 PtRu alloy,180,181 and Co-doped PtRu alloy182 OER catalysts, with the support of carbon black or graphitized carbon black. Furthermore, the effects of the crystallinity, preferred orientation of IrOx,183 and microstructure of IrOx,184 on cell reversal performance have been reported. When (1) these modified composite or alloy OER catalysts178–182 are supported on Pt/Ti4O7 or other Pt/oxides and/or (2) properties of IrOx183,184 in Ir@IrOx/Pt/Ti4O7 without carbon supports are tuned, the Ir loading may be reduced. Two-dimensional transition metal carbides, known as MXenes, with a composition of Ti3C2Tz were recently used as supports for Pt particles in PEFC anodes, where Tz is the surface terminal group (typically –O, –OH, or –F). Cell reversal tests were performed using the protocol shown in Fig. 9(a), and the tolerance to 2 h of cell reversal was improved by Ta-doping in the composition (Ti0.95Ta0.05)3C2Tz. The single-cell performance with a Pt/(Ti0.95Ta0.05)3C2Tz anode was moderate, although it did not significantly degrade after the 2 h reversal without OER catalysts. Although the mechanism for the durability enhancement was not clearly described and the stability of the Ta-dopants has not been shown,185 the metal doping used in cathode non-carbon supports can be applied to non-carbon anode supports other than MXenes.
2.2.2.1 Thin layers on Pt surfaces. Most research into suppressing cathode damage during startup/shutdown by novel anodes has adopted this approach. The thin layers required are formed via several pathways in order to inhibit O2 transport, suppressing the ORR on Pt and allowing proton and H2 permeation to achieve the HOR. The Marković group attached a self-assembled monolayer of calix[4]arene molecules on a Pt (1 1 1) surface without any loss in HOR activity but with significantly reduced ORR activity in a half-cell employing 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4. From the CVs, the Pt surface coverage was well controlled and at the maximum, 98% of the Pt (1 1 1) surface was covered by calix[4]arene, while the remaining 2% Pt surface was sufficient to maintain the original HOR activity of uncovered Pt (1 1 1). The ORR activity of Pt (1 1 1) decreased with increasing surface coverage, with no limiting current plateau. Instead, a certain amount of H2O2 was produced via a two-electron reaction (eqn (6)) after the coverage.186 Later, Marković et al. applied a self-assembled monolayer of calix[4]arene to commercial Pt/C and commercial Pt/NSTF catalysts, and the HOR selectivity was confirmed in a half-cell.187 The self-assembled monolayer approach was also reported by Yun et al., who attached dodecanethiol on the surface of commercial Pt/C. The HOR-selective Pt/C + dodecanethiol anode exhibited less loss in cell performance than the Pt/C anode after 10 startup/shutdown cycles in a single cell.188 The startup/shutdown cycle protocol for a single cell with HOR-selective anodes used by Yu et al.188 and other researchers189–191 involved injecting air into the anodes to produce H2/air front (interface between Region A and B at anode in Fig. 1) instead of the widely used potential cycles between 1.0 and 1.5 V versus RHE as recommended by FCCJ/DOE. This was because the anode potential was suppressed owing to the decreased ORR activity at the anode and did not increase to 1.5 V. As described in Section 2.1.1.2, thin TiOx layers on Pt nanoparticles in Pt/TiOx formed by SMSIs also inhibit O2 transport, while protons and H2 can pass through, making Pt/TiOx a selective HOR catalyst in a half-cell.73,99 Stühmeier et al. evaluated the startup/shutdown durability of Pt/TiOx/C, where C is carbon black Vulcan XC-72R, in a single-cell anode. Fig. 10(a) shows a cross-sectional SEM image and corresponding EDS line scan profile of a MEA with a 13.0% w/w Pt/TiOx/C anode and commercial 45.6% w/w Pt/C cathode. The image depicts the MEA after the initial cell performance evaluation. A number of Ti ions dissolved to permeate the membrane and were deposited at the cathode, with an EDS signal intensity slightly exceeding the background level. The dissolved Ti ions decreased the cell performance due to decreasing proton conductivity in both catalyst layers and the membrane, for example. Furthermore, the HOR selectivity of Pt/TiOx/C was moderate, and only slightly higher than that of Pt/C in a single cell. However, the Pt/TiOx/C anode nevertheless mitigates the degradation of the Pt/C cathode during startup/shutdown in a single cell to a greater extent than Pt/C, as shown in Fig. 10(b). The proposed mechanism by Stühmeier et al. is a pseudo-capacitance effect due to the reversible spillover of the adsorbed hydrogen atoms from Pt onto TiOx supports.189 The careful and systematic studies on Pt/TiOx/C conducted by Stühmeier et al.73,99,189 suggest the importance of the degree of HOR selectivity and Ti dissolution. Although the ORR activity of Pt/TiOx/C is suppressed by the presence of thin TiOx surface layers, it is still non-negligible, as shown in Fig. 5(k). Jang et al. reported less ORR active, and thus more HOR selective, catalysts that avoid leaching of cations by encapsulating Pt nanoparticles on carbon black with graphitized carbons to block O2, while H2 and protons pass through the shell.190 They selected a graphitized carbon “molecular sieve” because the organic molecules reported in previous papers186–188 may become detached during long-term operation.190 The carbon molecular sieve layers originating from a Pt acetylacetonate precursor successfully covered the Pt nanoparticles to suppress size and ORR activity in a half-cell, even after high-temperature annealing. The ORR activity increased dramatically after 3000 potential cycles between 0.05 and 1.05 V versus RHE in 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4, indicating the detachment of carbon molecular sieve layers that were not annealed or annealed at a low temperature (873 K). However, the ORR activity during the 3000 cycles did not increase when the catalyst was annealed at 1173 K to increase the degree of graphitization of the carbon molecular sieve layers. The graphitized carbon molecular sieve layers successfully blocked O2-transport, while H2 and protons could permeate through to exhibit high HOR selectivity in both a half-cell and a single cell (Fig. 10(c)). The MEA with HOR-selective carbon-encapsulated Pt anodes displayed a negligible change in single-cell performance, in contrast to conventional Pt/C anodes which were severely degraded after 10 simulated startup/shutdown cycles.190 All anode Pt catalysts based on the thin layer approach utilized carbon supports. The damage caused by startup/shutdown was suppressed by these anode catalysts, although the carbon supports at the anode will be oxidized during cell reversal. Similar to the cathode, the removal of carbon supports from these anode catalysts is of interest.
 | ||
| Fig. 10 (a) (left) Cross-sectional SEM image of an MEA with a Pt/TiOx/C anode after initial cell performance characterization and (right) the corresponding EDS line profile of Ti depicted in purple. (b) Cell potential versus current density (Ecell − igeo) curves of MEAs with three different anodes (commercial 19.8% w/w Pt/C at high and low Pt loading, Pt/CHL, and Pt/CLL, respectively) and 13.0% w/w Pt/TiOx/C at 353 K. The anode Pt loading in Pt/CHL and Pt/TiOx/C was set at 45 ± 5 μgPt cm−2 and that in Pt/CLL was set at one-third that of Pt/CHL (15 ± 2 μgPt cm−2). In all MEAs, the cathode catalysts were commercial 45.6% w/w Pt/C with 0.40 ± 0.04 mgPt cm−2 Pt loading. The anode and cathode were supplied with H2 and O2, respectively, with 90% RH. The corresponding high frequency resistance of each cell was also shown as a function of igeo at the bottom. Reproduced with permission.189 Copyright 2023, Elsevier. (c) Cell voltage versus current density curves of MEAs fabricated using two different anode catalysts, (top) commercial 20% w/w Pt/C and (bottom) 20% w/w Pt@C/C 900; carbon black-supported Pt nanoparticles encapsulated in nanoporous carbon shells annealed at 1173 K; before and after 1, 5 and 10 simulated startup/shutdown cycles. In both MEAs, the cathode catalysts were commercial 20% w/w Pt/C, and the Pt loading was 0.2 mgPt cm−2 in the anode and cathode. The anode and cathode were supplied with humidified H2 and air, respectively, and the cell temperature was maintained at 343 K. Reproduced with permission.190 Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society. (d) (top) Cell resistance versus time curves of MEAs with two different Pt/Ti0.9Ta0.1O2−δ anodes (solid line) and Pt/GCB (dashed line) measured at 338 K with humidified (348 K dew point) H2, N2, and air. (bottom) IR-free cell voltage versus current density curves of MEAs with two different Ti0.9Ta0.1O2−δ anodes (circles) and Pt/GCB (triangles) at 338 K. In all MEAs, commercial Pt/GCB was used at the cathode. The anode and cathode Pt loading was set at 0.1 mgPt cm−2 and 0.3 mgPt cm−2, respectively. The anode and cathode were supplied with fully humidified H2 and air, respectively. The utilization of H2 and O2 in air was set at 70% and 40%, respectively. For both MEAs, open and solid symbols represent the curves before and after 1000 air/air startup cycles. The inset shows the cross-sectional SEM images of the Pt/GCB cathode regions; (i) MEA with the Pt/GCB anode before 1000 startup cycles and MEAs after the cycles with (ii) the Pt/Ti0.9Ta0.1O2−δ anode and (iii) the Pt/GCB anode. Reproduced with permission.191 Copyright 2015, Elsevier. (e) (top) Schematic image of an MEA for a hybrid PEFC with a WO3/CNT-based multifunctional anode. The cell functions through reactions (i) and (ii), whereby electrons and protons proceed through pathway 1. The WO3 layer serves as a rapid-response hydrogen reservoir, storing and releasing electrons and protons based on reaction (iii) through pathways 2 and 3, respectively. The WO3 layer also serves as an O2 scavenger invading the anodes through reaction (iv) and as a regulator for the hydrogen-disassociation reaction (i). (bottom) Retention of the peak power density of the three control cells and a hybrid cell after three different ADTs. H2 starvation tests were performed by switching the H2 supply to a N2 flow to a control cell and hybrid cell while operating under a constant current density of 0.2 A cm−2. The cell voltage was recorded during the measurement, and each cycle lasted for 10 s after switching to a N2 flow. Acceleration tests were conducted by oscillating the current output of a control cell and the hybrid cell between 50 and 1000 mA cm−2, with a holding time of 120 and 30 s, respectively. Startup tests were performed using the following steps: both cells were kept at an open-circuit voltage (OCV) supplied with H2 and O2 at the anode and cathode, respectively. The gas for the anodes was switched from H2 to N2 (30 mL min−1) for 10 s to purge the anode compartment. Then, 1 cm3 of air was injected into the anodes, and the equilibrium OCV of the cells was recorded. The cells were then maintained at a constant voltage of 0.8 V for a period of 20 s. The hybrid cell was used throughout all three tests (red line). For the control-cell testing (black line), one cell was used for each test. The anode and cathode Pt loading was set at 0.05 mgPt cm−2 and 0.40 mgPt cm−2, respectively. The anode and cathode were supplied with fully humidified H2 and O2, respectively, to record cell voltage versus current density curves, and the single cell was maintained at 323 K. Reproduced with permission.192 Copyright 2020, Nature Publishing Group. | ||
2.2.2.2 Control of support conductivity during operation. Shintani et al. switched the conductivity of Ta-doped TiO2 (Ti0.9Ta0.1O2−δ) supports between high under H2 and low under an air atmosphere in the anode, respectively, to impede the ORR at startup/shutdown and to promote the HOR under normal operation. The concept is to suppress electron transport from the Ti0.9Ta0.1O2−δ support to the Pt-catalyst surface by decreasing the conductivity of Ti0.9Ta0.1O2−δ only in the presence of O2 contaminants during startup/shutdown, thus maintaining Ti0.9Ta0.1O2−δ conductivity and HOR activity on Pt in the presence of H2 gas during normal anode operation. Consistent with the known decrease in the conductivity of conducting oxide nanoparticles in an oxidizing atmosphere, the resistance of a cell with a Pt/Ti0.9Ta0.1O2−δ anode was one order of magnitude higher in air than in H2, as shown in Fig. 10(d). The Pt/Ti0.9Ta0.1O2−δ anode exhibited higher durability against 1000 simulated startup cycles than graphitized carbon black-supported platinum (Pt/GCB), as shown in Fig. 10(d). The detachment of carbon supports due to corrosion at the Pt/GCB cathode was successfully suppressed by the Pt/Ti0.9Ta0.1O2−δ anode, as shown in the inset.191
2.2.2.3 Small Pt clusters. Luo et al. reported an HOR-selective Pt/TiN catalyst with extremely low Pt mass fractions. Small Pt clusters, which are not visible on the TEM image, were deposited on TiN. The Pt clusters lacked ordered facets and were mostly in an unsaturated coordination environment to display low ORR activity and high HOR activity in a half-cell. The difference in ORR and HOR activity on Pt/TiN was attributed to differences in O2 and H2 bond types, which are sensitive to the coordination environment of Pt.193 Kanai et al.194 reported HOR-selective catalysts based on atomic Pt supported on covalent triazine frameworks and carbon black composites (Pt/CTF). In both studies, the Pt mass fractions were one or two orders of magnitude lower than those of commercial Pt/C (0.29–1.46% w/w for Pt/TiN193 and 2.8% w/w for Pt/CTF).194 Such low Pt mass fractions can increase the thickness of the anode catalyst layers in MEAs. The effect of Pt loading at anode catalyst layers in MEAs on thickness and HOR performance is of interest.
2.2.2.4 Use of non-Pt anode catalysts with HOR selectivity. To date, this concept has been reported solely by Ioroi and Yasuda. They suggested that Ir/Ti4O7 anodes suppress damage at the cathodes during startup/shutdown due to the high HOR activity of Ir, which is just 2.6 times lower than that of Pt, and its insufficient ORR activity, which is substantially lower than that of Pt. The reported RTA performance of the Ir/Ti4O7 catalyst was high and similar to that of the Pt/Ti4O7 + Ir black catalyst shown in Fig. 9(b).175 The startup/shutdown durability of MEAs with an Ir/Ti4O7 anode and Pt/C or PtCo/C cathode is of particular interest. Although many non-Pt cathode ORR catalysts have already been reported, few non-Pt anode HOR catalysts have been described. Examples include WC and bimetallic carbides (NiWC, CoMoC, MoWC, and CoWC) supported on carbon black, as reported by the Nagai group in the late 2000s,195–197 carbon-encapsulated Ni nanocrystals reported by Haslam et al. in 2011,198 nickel-diphosphine complexes on multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) published by several groups since 2011,199,200 and hafnium oxynitride thin films described by the Koel group in 2019.201 The carbide anode catalyst series described by Nagai et al. suffered from low single-cell performance to display a power density that was one order of magnitude lower than that of the Pt/C anode.195–197 This suggests that the low HOR activity changed the rate-determining step from the ORR at the cathodes to the HOR at the anodes due to the carbide anodes. Furthermore, the stability of these carbides in PEFCs remains unclear. Haslam et al. evaluated the HOR activity of their Ni catalysts under the atypical conditions of 0.27 V versus SHE in a strongly acidic medium (1.5 mol dm−3 H2SO4).198 Metallic nickel is not ORR active, although it can readily leach out in acidic media if the protected carbon shell is absent. The HOR activity of a nickel-diphosphine complex catalyst was evaluated under typical conditions in a common electrolyte, 0.5 mol dm−3 H2SO4.199,200 The superior CO tolerance of MEAs compared with commercial Pt/C is another attractive point.199 The hafnium oxynitride HOR catalysts described by the Koel group201 have also been reported as ORR catalysts in acidic media after being supported on carbon black.202 Although they are highly stable in acidic media, it is necessary to decrease ORR activity through precise control of the surface composition202 and crystallinity,203 as they are both dominant factors for the ORR activity of hafnium oxynitride catalysts. The PGM-free HOR catalysts reviewed in this paragraph rely on carbon supports to confer conductivity in the catalyst layer. However, their durability has not been evaluated in a single cell. The non-Pt, PGM catalyst, Ir/Ti4O7, is carbon-support-free and therefore durable against cell reversal, as experimentally confirmed in a single cell.175 Its potential to suppress cathode degradation during startup/shutdown makes it more attractive than other non-Pt HOR catalysts, at least at this stage.
2.2.2.5 Multifunctional layer between a conventional anode catalyst layer and a GDL. Apart from the selective HOR catalyst approach, Shen et al. introduced a new concept, as shown in Fig. 10(e). A “hydrogen storage layer” formed from a WO3/CNT composite was sandwiched between the Pt/C catalyst layer and GDL to form a multifunctional anode that suppresses damage at the anode and cathode during H2 starvation and startup/shutdown, respectively. The supplied H2 molecules pass through the hydrogen storage layer to generate protons and electrons at the Pt/C layer, some of which react with WO3 in the storage layer to form HxWO3via eqn (iii) in Fig. 10(e). When starved of H2, HxWO3 releases protons and electrons to suppress the OER and COR at the adjacent Pt/C layer. When the anode is subjected to air contamination during startup/shutdown, HxWO3 reacts with O2 in the air to form WO3 and H2O, via eqn (iv) in Fig. 10(e). The single cell with and without the multifunctional WO3/CNT layer-inserted anode (denoted as a hybrid cell and a control cell, respectively) displays interesting results. WO3 did not affect the initial single-cell performance, while it significantly increased the durability, as shown in Fig. 10(e). The durability against H2 starvation was evaluated at a constant current density of 0.2 A cm−2 and persisted for 10 s after switching the anode gas from H2 to N2. The hybrid cell exhibited negligible reduction in peak power density, while the control cell lost ∼47% of the initial value after two rounds of H2 starvation tests. The hybrid cell also displayed higher durability against the original simulated acceleration cycles and startup cycles as HxWO3 quickly scavenged O2 molecules in contaminated anodes. The WO3 material cost was estimated to be <$50 per unit for a mid-sedan-type FCV sold by Toyota (MIRAI).192
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ti atomic ratio, from 2
Ti atomic ratio, from 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8 to 6
8 to 6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4, and then increased with further increases in the ratio to 8
4, and then increased with further increases in the ratio to 8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2. At a ratio of 2
2. At a ratio of 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8, a single anatase TiO2 phase was formed with minor rutile TaO2 at 4
8, a single anatase TiO2 phase was formed with minor rutile TaO2 at 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 6. At a ratio of 6
6. At a ratio of 6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4, a Ta2O5/TaO2/TiO2 mixture was formed, followed by a single Ta2O5 phase at a ratio of 8
4, a Ta2O5/TaO2/TiO2 mixture was formed, followed by a single Ta2O5 phase at a ratio of 8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2. The high Ta content in the optimized Ta
2. The high Ta content in the optimized Ta![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ti ratio of 6
Ti ratio of 6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4 greatly exceeds that in the Ta-doped TiO2 supports reviewed in Sections 2.1.1.2 and 2.2.2.2, which ranged from 1
4 greatly exceeds that in the Ta-doped TiO2 supports reviewed in Sections 2.1.1.2 and 2.2.2.2, which ranged from 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 9 (ref. 191) to 3
9 (ref. 191) to 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 7.56 The three mixed phases in the Ta-TiO2 described by Xie et al. have not been reported and clearly also differ from the TiO2 supports used by Zhang et al.204 Zhang et al. concluded that efforts should be directed toward corrosion-resistant oxides as alternatives to Ti oxides, without noting the exact material to be developed.204 The results of Xie et al. on PGM-free catalysts205 suggest the presence of stable-support alternatives to pure Ti oxides for use as Pt supports, at least at a cell temperature of 353 K.
7.56 The three mixed phases in the Ta-TiO2 described by Xie et al. have not been reported and clearly also differ from the TiO2 supports used by Zhang et al.204 Zhang et al. concluded that efforts should be directed toward corrosion-resistant oxides as alternatives to Ti oxides, without noting the exact material to be developed.204 The results of Xie et al. on PGM-free catalysts205 suggest the presence of stable-support alternatives to pure Ti oxides for use as Pt supports, at least at a cell temperature of 353 K.
 | ||
Fig. 11 Fluoride release rate (FRR) versus OCV time curves of MEAs fabricated using a mixture of commercial 20% w/w Pt/C and TiO2 at the (a) anode and (b) cathode. The Pt loading was set at a constant 0.05 mgPt cm−2, while four different TiO2 loadings, 0, 0.33, 1.32, and 5.28 μgTiO2 cm−2, were used, denoted as No TiO2, 1×, 4×, and 16×, respectively. Commercial 30% PtCo/C with 0.1 mgPt cm−2 Pt loading was used at the cathode and anode in (a) and (b), respectively. The anode and cathode were supplied with H2 and air, respectively, at 25% RH, and the absolute back pressure was 0.15 MPa for both electrodes. The cell temperature was set at 383 K. Reproduced with permission.204 Copyright 2021, The Electrochemical Society. (c) Stem–Volmer plots obtained using 6-carboxy fluorescein (6CFL) dye in the radical solution containing Fenton's reagent and Fe–N–C or Ta-TiOx/KB as a function of the H2O2 radical quencher concentration. (d) Cell voltage versus current density curves of MEAs with Fe–N–C and Fe–N–C + 8% w/w Ta-TiOx/KB cathodes before and after 20 voltage cycles between 0.85 V and 0.40 V (ADT). During the ADT, the cell voltage was held at 0.85 V for 5 min and 0.40 V for 55 min per unit cycle, and the cell was maintained at 353 K and supplied with H2 and air at the anode and cathode, respectively. The cathode catalyst loading was set at 6.0 mg cm−2. In all MEAs, the anode was commercial 46.5% w/w Pt/C with 0.2 mgPt cm−2 Pt loading. The anode and cathode were supplied with fully humidified H2 and O2, and the cell temperature was set at 353 K. (e) (top) RDE voltammograms and (bottom) H2O2 yield versus potential curves of (left) Fe–N–C and Fe–N–C + 10% w/w Ta-TiOx/KB, (center) Fe–N–C, and (right) Fe–N–C + 10% w/w Ta-TiOx/KB before and after 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 potential cycles between 0.6 and 1.0 at 20 mV s−1. The scans were performed under an O2 atmosphere using a rotation speed of 900 rpm and a staircase potential step of 25 mV at intervals of 25 s in 0.5 mol dm−3 H2SO4. Reproduced with permission.205 Copyright 2022, Nature Publishing Group. 000 potential cycles between 0.6 and 1.0 at 20 mV s−1. The scans were performed under an O2 atmosphere using a rotation speed of 900 rpm and a staircase potential step of 25 mV at intervals of 25 s in 0.5 mol dm−3 H2SO4. Reproduced with permission.205 Copyright 2022, Nature Publishing Group. | ||
3 Carbon-support-free non-platinum catalysts
The high loading of expensive and scarce Pt catalysts and the low durability of carbon supports are the major motivators to seek cathode materials utilizing neither Pt catalysts nor carbon supports. Conductive PGMs or their oxides can be used as carbon-support-free non-Pt catalysts, including the porous IrO2 catalysts used by Takasu et al.,206 although Ir is extremely scarce in nature and much more expensive than Pt.177 This section focuses on carbon-support-free non-PGM catalysts, which may be considered the ultimate catalysts. Because of the high potential and oxidative acidic environment of PEFC cathodes, as mentioned in Section 1, only two viable non-PGM catalyst types have been reported in the last two decades. Researchers in the PGM-free catalyst community have tended to develop the so-called M/N/C catalysts, which are graphitic carbons with abundant defects doped with N and one or two metals (M), typically Fe,207–212 Co,213 or Mn.214 The highest activity reported to date has been seen with Fe/N/C catalysts, although durability remains an issue, as reported in the literature.210 The formation of carbon dioxide by the oxidation of carbon species in Fe/N/C208,210 and Co/N/C213 has been experimentally verified, even at potentials below 1.0 V,208,210,213 and is regarded as one of the pivotal causes of the degradation of M/N/C catalysts. To minimize carbon oxidation, a recent standardized protocol for evaluating the activity of M/N/C catalysts has limited the upper potential to 0.925 V,212 which is lower than that for automotive carbon-supported platinum–cobalt catalysts (1.0 V (ref. 16) or 0.95 V (ref. 17)). The equilibrium potential in eqn (4) is 0.207 V versus SHE and the reaction rate in eqn (4) is accelerated at high potentials. Thus, even when M/N/C catalysts are used, system-level measures used for protecting the carbon black of the PtCo/C catalysts (as mentioned in Section 1) remain necessary. However, the practical use of M/N/C as a cathode catalyst in FCVs has attracted skepticism from industry due to the previously described durability issues and the greater catalyst loading requirement, which leads to a thicker catalyst layer compared with conventional PtCo/C catalysts.215,216 Another type of non-PGM catalyst, oxides/oxynitrides containing group IV or V metals, has attracted fewer researchers in this community compared with M/N/C, owing to the moderate ORR activity and difficulty in evaluating the activity, even in a half-cell. However, this type of catalyst can eliminate the use of carbon supports, as the active sites are hosted in oxide/oxynitride, unlike M/N/C catalysts where the active sites are assumed to be M-coordinated with N atoms located at the edge of graphitic carbon supports.207–214 Oxide-based catalysts were first reported by the Ota group in the mid-2000s. In their initial work, WC was investigated as a non-PGM catalyst because of its similar electronic structure to Pt. However, the WC was found to be unstable in acidic media and required passivation to WO3. The WC was stabilized by adding Ta, a group V metal.217 Since then, Ota et al. focused on binary oxides containing group IV and V metals as ORR catalysts. The chemical stability in 0.1 mol dm−3 H2SO4 solution analyzed by ICP spectroscopy revealed a small amount of leached metal from ZrO2,218 TiO2,219 N-doped ZrO2,220 or Ta3N5 with oxidized surface Ta2O5.221 Later, we also reported a small Hf leaching amount in monoclinic HfO2 and Hf2ON2 after 2 days of leaching tests in an identical solution.202 These chemical stabilities are a particular benefit of this type of oxide/oxynitride catalyst. The disadvantage of this type of catalyst, however, is the difficulty in evaluating its ORR activity, as displayed in Fig. 12(a). The Ota group synthesized ZrO2 powder catalysts via a sol–gel route, followed by annealing under a reductive atmosphere, and evaluated their ORR activity in a half-cell.222 The four curves shown in Fig. 12(a) clearly differ from each other, even though they all originate from an identical catalyst with different catalyst layers due to mixing with different carbon black materials and different carbon black contents in order to achieve conductivity in the catalyst layer. These results indicate that the optimization of the catalyst layer structure is necessary, even for screening active oxide/oxynitride catalysts. Because the surface area and particle size of the catalysts differ and depend substantially on the route and conditions of synthesis, such optimization is necessary for every catalyst. This is a time-consuming process. Therefore, some researchers synthesized oxide/oxynitride catalysts on conductive carbon materials such as carbon black,202,203,225,231,232 CNTs,223,233 reduced graphene oxide,234,235 and carbon nanocages.236 One of the carbon-supported oxynitride catalysts, N-doped ZrO2 on MWCNTs (N-ZrO2/MWCNTs), exhibited a single-cell performance comparable to that of Fe/N/C, as shown by curve 1 in Fig. 12(b).223 This finding attracted the attention of the pioneers of Fe/N/C catalysts, the Dodelet group.237 However, the single-cell performance was not stable for 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 FCCJ load cycles and even at a constant j = 0.1 A cm−2, as shown in Fig. 12(c) and (d), respectively.223 One reason could be the oxidation of the carbon supports, making oxide/oxynitride catalysts free from carbon supports an attractive option. However, when group IV or V oxide/oxynitride catalysts were used as catalysts without carbon supports, the current was too low even in a half-cell. Indeed, until the mid-2010s, the reported geometrical current density was only at the μA cm−2 level in practical potential regions above 0.6 V versus RHE.218–221,238 Although the conductivity of oxide supports for Pt particles can be enhanced by metal doping, as described in Sections 2.1.1.2 and 2.1.1.3, their conductivity is not sufficient to evaluate ORR activity without Pt. This is because the σ-value of oxide supports is in general enhanced by 2–4 order of magnitude after depositing Pt particles, as the introduction of conductive Pt enhances the σ of catalyst particles.105 Because TiN offers an excellent σ without Pt,149,156 we have recently focused on conductive nitride, TiN, to produce carbon-support-free, non-PGM catalysts. The first catalyst was obtained via the pyrolysis of a hydrothermally synthesized Ti4O7 fiber, TiF4, and a urea precursor mixture prepared in HCl solution.38 Unfortunately, the Ti4O7 fiber oxidized during the pyrolysis to form insulating rutile TiO2, whereas TiF4-derived TiN produced ORR active sites on the oxidized surface, of which the majority was nitrogen-substituted TiO2, as revealed by the control experiment shown in Fig. 12(e).224 The geometrical current density in a practical potential range (>0.6 V versus RHE) in a half-cell was three orders of magnitude higher than that of previous carbon-support-free catalysts.218–221,238 Several control experimental results, including the one shown in Fig. 12(e), revealed that carbon residues from the urea precursor were not the source of the ORR activity or conductivity of this catalyst.38,224 However, the conductivity was insufficient to use carbon black in the cathode catalyst layer to obtain single-cell performance, as shown by curve 2 in Fig. 12(b).38 The ORR activity increased with N content, which substituted for O in the surface TiO2 lattice, while the surface TiN content was simultaneously maintained below 20%.38,224 The surface TiN was also unstable, which decreased the activity as illustrated in Fig. 12(f).225 This is consistent with the work of Avasarala et al., in which 31.5% of surface TiN content was unstable.147 When the TiN surface was covered with nitrogen-substituted TiO2 layers to decrease the surface TiN content, there was no change in surface chemical states during the ORR, as revealed by post-XPS analyses.224 An oxygen vacancy is created when two oxygen atoms in the TiO2 lattice are substituted by two nitrogen atoms to compensate for the charge imbalance due to the nitrogen substitution. An oxygen vacancy is one possible site for the adsorption of O2 molecules, which is the first step for the ORR, eqn (2a). Indeed, the Lyubinetsky group reported the dissociative adsorption of O2 molecules on bridging oxygen vacancies on the (1 1 0) plane of rutile TiO2 at room temperature using in situ scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) in 2008.239 One of the oxygen atoms of O2 filled one oxygen vacancy, while the other was deposited on a five-fold titanium atom next to the vacancy. Two years later, Lyubinetsky et al. presented a subsequent model on the same rutile (1 1 0) plane and used STM and DFT calculations to show that O2 molecules adsorbed on the titanium rows, while the charge from the oxygen vacancy promoted the dissociation of O2 molecules.240 The dissociative adsorption of O2 molecules on the (1 1 0) plane of rutile TiO2 with an oxygen vacancy was also reported using STM by Wendt et al., although the proposed source of charge to promote O2 dissociation differed.241 These thought-provoking studies provide valuable context for the discussion of the ORR active sites on our N-TiO2-covered TiN. The material reported in the aforementioned studies was N-free TiO2, and STM experiments were conducted in an ultra-high-vacuum system free from protons,239–241 which was different from the acidic media where the ORR activity of N-TiO2 was evaluated. It is difficult to conduct similar STM experiments under realistic PEFC conditions in the presence of acidic PFSI electrolytes. Nonetheless, oxygen vacancies in rutile N-TiO2 were revealed to produce ORR active sites through a low-temperature annealing process combined with Raman, XPS, and electrochemical analyses.242 Although the bulk of this catalyst was the metallic character of the conductive TiN, the surface TiO2 layers should have much lower conductivity than the bulk. We recently doped cationic phosphorous onto surface N-TiO2 layers to enhance surface conductivity by introducing an electron donor, P5+.227,243 P5+ was doped into the bulk and surface to more than double the ORR mass activity in a half-cell without changing the number of oxygen vacancies in surface rutile TiO2 layers on S-TiN (S is from the TiOSO4 precursor) formed by N-doping. The enhanced mass activity was also greater than that of N-ZrO2/MWCNT.243 The MEA with an N, P-TiO2/S-TiN cathode exhibited a single-cell performance significantly improved compared with that of P-free N-TiO2/TiN, and even higher than that of the previous best carbon-supported oxynitride catalyst, N-ZrO2/MWCNT at V ≥ 0.6 V (the operating range of FCVs16,17), as shown by curve 3 in Fig. 12(b). Furthermore, the j at V = 0.9 V from N, P-TiO2/S-TiN without back pressure exceeded that of N-ZrO2/MWCNT with high back pressures, as shown in the inset. These results could be due to the synergetic effects of (1) the higher ORR activity of N, P-TiO2/S-TiN than the other two catalysts and (2) improved mass-transport properties owing to the smaller particle size of N, P-TiO2/S-TiN than N-TiO2/TiN, as the aggregation during high-temperature synthesis was suppressed by P-doping.243 Nonetheless, all V–j curves were obtained after mixing carbon black with the catalyst particles to induce conductivity in the catalyst layer. The σ of N, P-TiO2/S-TiN is sufficient without using carbon black in a half-cell; however, it is insufficient in a thicker catalyst layer in a single cell, which produces a current density three orders of magnitude higher than that of the catalyst layer in a half-cell.
000 FCCJ load cycles and even at a constant j = 0.1 A cm−2, as shown in Fig. 12(c) and (d), respectively.223 One reason could be the oxidation of the carbon supports, making oxide/oxynitride catalysts free from carbon supports an attractive option. However, when group IV or V oxide/oxynitride catalysts were used as catalysts without carbon supports, the current was too low even in a half-cell. Indeed, until the mid-2010s, the reported geometrical current density was only at the μA cm−2 level in practical potential regions above 0.6 V versus RHE.218–221,238 Although the conductivity of oxide supports for Pt particles can be enhanced by metal doping, as described in Sections 2.1.1.2 and 2.1.1.3, their conductivity is not sufficient to evaluate ORR activity without Pt. This is because the σ-value of oxide supports is in general enhanced by 2–4 order of magnitude after depositing Pt particles, as the introduction of conductive Pt enhances the σ of catalyst particles.105 Because TiN offers an excellent σ without Pt,149,156 we have recently focused on conductive nitride, TiN, to produce carbon-support-free, non-PGM catalysts. The first catalyst was obtained via the pyrolysis of a hydrothermally synthesized Ti4O7 fiber, TiF4, and a urea precursor mixture prepared in HCl solution.38 Unfortunately, the Ti4O7 fiber oxidized during the pyrolysis to form insulating rutile TiO2, whereas TiF4-derived TiN produced ORR active sites on the oxidized surface, of which the majority was nitrogen-substituted TiO2, as revealed by the control experiment shown in Fig. 12(e).224 The geometrical current density in a practical potential range (>0.6 V versus RHE) in a half-cell was three orders of magnitude higher than that of previous carbon-support-free catalysts.218–221,238 Several control experimental results, including the one shown in Fig. 12(e), revealed that carbon residues from the urea precursor were not the source of the ORR activity or conductivity of this catalyst.38,224 However, the conductivity was insufficient to use carbon black in the cathode catalyst layer to obtain single-cell performance, as shown by curve 2 in Fig. 12(b).38 The ORR activity increased with N content, which substituted for O in the surface TiO2 lattice, while the surface TiN content was simultaneously maintained below 20%.38,224 The surface TiN was also unstable, which decreased the activity as illustrated in Fig. 12(f).225 This is consistent with the work of Avasarala et al., in which 31.5% of surface TiN content was unstable.147 When the TiN surface was covered with nitrogen-substituted TiO2 layers to decrease the surface TiN content, there was no change in surface chemical states during the ORR, as revealed by post-XPS analyses.224 An oxygen vacancy is created when two oxygen atoms in the TiO2 lattice are substituted by two nitrogen atoms to compensate for the charge imbalance due to the nitrogen substitution. An oxygen vacancy is one possible site for the adsorption of O2 molecules, which is the first step for the ORR, eqn (2a). Indeed, the Lyubinetsky group reported the dissociative adsorption of O2 molecules on bridging oxygen vacancies on the (1 1 0) plane of rutile TiO2 at room temperature using in situ scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) in 2008.239 One of the oxygen atoms of O2 filled one oxygen vacancy, while the other was deposited on a five-fold titanium atom next to the vacancy. Two years later, Lyubinetsky et al. presented a subsequent model on the same rutile (1 1 0) plane and used STM and DFT calculations to show that O2 molecules adsorbed on the titanium rows, while the charge from the oxygen vacancy promoted the dissociation of O2 molecules.240 The dissociative adsorption of O2 molecules on the (1 1 0) plane of rutile TiO2 with an oxygen vacancy was also reported using STM by Wendt et al., although the proposed source of charge to promote O2 dissociation differed.241 These thought-provoking studies provide valuable context for the discussion of the ORR active sites on our N-TiO2-covered TiN. The material reported in the aforementioned studies was N-free TiO2, and STM experiments were conducted in an ultra-high-vacuum system free from protons,239–241 which was different from the acidic media where the ORR activity of N-TiO2 was evaluated. It is difficult to conduct similar STM experiments under realistic PEFC conditions in the presence of acidic PFSI electrolytes. Nonetheless, oxygen vacancies in rutile N-TiO2 were revealed to produce ORR active sites through a low-temperature annealing process combined with Raman, XPS, and electrochemical analyses.242 Although the bulk of this catalyst was the metallic character of the conductive TiN, the surface TiO2 layers should have much lower conductivity than the bulk. We recently doped cationic phosphorous onto surface N-TiO2 layers to enhance surface conductivity by introducing an electron donor, P5+.227,243 P5+ was doped into the bulk and surface to more than double the ORR mass activity in a half-cell without changing the number of oxygen vacancies in surface rutile TiO2 layers on S-TiN (S is from the TiOSO4 precursor) formed by N-doping. The enhanced mass activity was also greater than that of N-ZrO2/MWCNT.243 The MEA with an N, P-TiO2/S-TiN cathode exhibited a single-cell performance significantly improved compared with that of P-free N-TiO2/TiN, and even higher than that of the previous best carbon-supported oxynitride catalyst, N-ZrO2/MWCNT at V ≥ 0.6 V (the operating range of FCVs16,17), as shown by curve 3 in Fig. 12(b). Furthermore, the j at V = 0.9 V from N, P-TiO2/S-TiN without back pressure exceeded that of N-ZrO2/MWCNT with high back pressures, as shown in the inset. These results could be due to the synergetic effects of (1) the higher ORR activity of N, P-TiO2/S-TiN than the other two catalysts and (2) improved mass-transport properties owing to the smaller particle size of N, P-TiO2/S-TiN than N-TiO2/TiN, as the aggregation during high-temperature synthesis was suppressed by P-doping.243 Nonetheless, all V–j curves were obtained after mixing carbon black with the catalyst particles to induce conductivity in the catalyst layer. The σ of N, P-TiO2/S-TiN is sufficient without using carbon black in a half-cell; however, it is insufficient in a thicker catalyst layer in a single cell, which produces a current density three orders of magnitude higher than that of the catalyst layer in a half-cell.
 | ||
| Fig. 12 (a) ORR mass activity versus potential (iORR − E) curves of a ZrO2 catalyst for four different catalyst layers in 0.1 mol dm−3 H2SO4 without rotation. The catalyst layers were formed by mixing the ZrO2 catalyst with two different carbon black materials, Ketjen Black EC300J (KB) or acetylene black (AB). The mass fraction of KB was set constant at 10% w/w, whereas that of AB was set at 10, 20, and 30% w/w. Reproduced with permission.222 Copyright 2011, The Electrochemical Society of Japan. (b) V–j curves of MEAs for three different catalysts at the cathode, (1) N-ZrO2/MWCNT, (2) N-TiO2 (shell)/TiN (core), and (3) N, P-TiO2 (shell)/S-TiN (core) at 353 K. The cathode catalyst loadings, m, were 10, 4.7, and 5.8 mg cm−2, respectively, for MEAs 1, 2, and 3. In all MEAs, the anode was commercial 46% w/w Pt/C with 0.3 mgPt cm−2 Pt loading. The anode and cathode were supplied with fully humidified H2 with 0.2 MPa (gauge) and O2 with 0.3 MPa (gauge) back pressures, respectively. MEA 3 was also operated without back pressure at the anode and cathode, and is labeled as 4. The inset shows j at V = 0.9 V from the four curves. Reproduced with permission.38,223 Copyright 2016, Elsevier, Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society. (c) A normalized j at V = 0.6 V versus FCCJ load cycle number (j j0−1|V=0.6 V − N) curve and (d) a cell voltage versus time held at 0.1 A cm−2 (V|j=0.1 A cm2 − th) curves of MEAs with the N-ZrO2/MWCNT cathode catalyst. m was 8.3 and 8.9 mg cm−2 for (c) and (d), respectively. Reproduced with permission.223 Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society. (e) RDE voltammograms of two N-TiO2 catalysts synthesized by mixing urea and one of the two titanium sources, Ti4O7 and TiF4, in 1.0 mol dm−3 HCl solution, followed by pyrolysis at 1123 K. The scans were performed under N2 and O2 atmospheres, with a rotation speed of 1500 rpm and a scan rate of −5 mV s−1 (cathodic) in 0.1 mol dm−3 H2SO4. Reproduced with permission.224 Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society. (f) A schematic image of N-TiO2 catalysts and the ORR active site. Reproduced with permission.225 Copyright 2016, Royal Society of Chemistry. (g) Kinetic current density and number of electrons transferred per unit O2 molecule versus the work function curves (jk − Ф and n − Ф curves, respectively) derived from the RDE voltammograms of four N, M-TiO2/S-TiN catalysts, where M = Zr, Nb, Ni, and V. (h) Two reaction pathways for the ORR on conventional catalysts. Reproduced with permission.226 Copyright 2022, Royal Society of Chemistry. (i) RDE voltammograms of N, P-TiO2/S-TiN, N, Zr-TiO2/S-TiN, and N, P, S-TiO2/S-TiN catalysts before (solid curves) and after (dashed curves) 5000 FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles; the protocol is shown in the inset. Reproduced with permission.227–229 Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society, Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society, Copyright 2024, Royal Society of Chemistry. (j) X-ray photoelectron spectra of the N, P, S-TiO2/S-TiN catalyst before (solid curves) and after (dashed curves) 5000 FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles. The N, P, S-TiO2/S-TiN catalyst after 5000 cycles contains Nafion PFSI in the catalyst layer. Reproduced with permission.229 Copyright 2024, Royal Society of Chemistry. (k) Cell voltage and power density versus current density curves of an MEA fabricated using Ti0.8Co0.2N at m = 4 mg cm−2 and commercial 60% w/w Pt/C catalysts at 0.1 mgPt cm−2 in the cathode and anode, respectively, at 343 K. The anode and cathode were supplied with fully humidified H2 and air, respectively. Reproduced with permission.230 Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society. | ||
On the N-TiO2/TiN and N, P-TiO2/S-TiN catalysts, the ORR proceeded via two- (2e−) and four-electron (4e−) pathways, described by eqn (6) and (2), respectively.224,227,243 We recently revealed that ORR selectivity can be enhanced in the 4e− pathway by tuning the work function, Ф, of N-TiO2/S-TiN via metal doping, as shown in Fig. 12(g).226,228Ф is the difference in the potential energy of an electron between the vacuum and Fermi levels, which corresponds to the minimum energy required to extract an electron from a solid surface. Therefore, 4e− selectivity (i.e., the number of electrons transferred per unit O2 molecule, n) increases with decreasing magnitude of Ф. The 2e− ORR in acidic media has been assumed to proceed via the following three elementary steps:143,144
| O2 + * → O2* | (6a) |
| O2* + H+ + e− → HO2* | (6b) |
| HO2* + H+ + e− → H2O2 + * | (6c) |
In the 4e− and 2e− ORR processes shown in Fig. 12(h), a peroxy-intermediate, HO2, is produced (eqn (2b) and (6b)). The electron-donating ability from the active site expressed by * and the strength of binding between HO2 and * are key factors in determining n. When the magnitude of Ф is too small, the catalyst-HO2 intermediate interaction becomes stronger and ultimately slows the ORR process. Besides this interaction between the HO2 intermediate and the catalyst, the smaller the Ф, the more negative the potential at which the ORR proceeds.244 This could be one reason for the decrease in ORR selectivity with Ф. The Ф was decreased (i.e., the Fermi level of TiN was upshifted by doping foreign metals) in the following order: Nb > Zr > V > Ni. Either Zr or Nb was close to optimum tuning of the Fermi level to donate electrons to O2 molecules but not to bind strongly with the reaction intermediate at the potential where the ORR proceeds. Rutile TiO2 has been investigated as a catalyst for the OER, which is the reverse reaction of the ORR. García-Mota et al. investigated the binding energy of HO2 and * of the (1 1 0) plane on various metal-doped rutile TiO2 catalysts using first principles DFT calculations.245 Although zirconium was not included in their study, niobium, nickel and vanadium were investigated as dopants. The binding energy increased in the order of Nb < V < Ni.245 This trend is the reverse of n shown in Fig. 12(g), suggesting that strong *–HO2 interactions inhibited the breaking of O–O bonds in the HO2 intermediate to favor the 2e− ORR, to produce H2O2.
As these TiN-based catalysts are free from carbon supports, a high durability against startup/shutdown cycles is expected. Fig. 12(i) shows the RDE voltammograms of these catalysts before and after 5000 FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles. Unfortunately, N, P-TiO2/S-TiN catalysts significantly decrease the ORR activity measured by a half-wave potential (E1/2, i.e., the potential at which half of the limiting current density is obtained) by 0.08 V after the 5000 cycles. During the cycles, both N and P atoms were removed from the surface, as revealed by XPS analyses.227 The N, Zr-codoped TiO2/S-TiN with an optimized composition was more durable against the 5000 FCCJ startup/shutdown cycles, decreasing the ΔE1/2 by half that of N, P-TiO2/S-TiN (0.04 V), owing to the high selectivity toward the 4e− ORR.228 We recently enhanced the startup/shutdown durability further using a new catalyst, N, P, S-tridoped TiO2 supported on S-TiN, to successfully reduce ΔE1/2 to 0.02 V without diminishing the limiting current plateau. This result is among the highest of any PGM-free catalysts. Anatase and rutile TiO2 hetero-phase junctions formed in the N, P, S-TiO2/S-TiN catalyst promoted ORR activity, and the surface anionic dopants were not removed during the 5000 cycles to maintain activity, as shown in Fig. 12(j).229 The stabilization of the cationic P5+ dopant, whose binding energy is 134–135 eV, is the remaining challenge in terms of diminishing ΔE1/2. Although this non-PGM catalyst type is rarely studied by this community, other researchers have recently focused on TiN. For example, Tian et al. synthesized Ti0.8Co0.2N catalysts via a combination of a solvothermal route and NH3 annealing. The catalysts were evaluated in a single-cell cathode without adding carbon black to the catalyst layer, as shown in Fig. 12(k).230 Control experiments to evaluate the contribution of possible Co/N/C species in catalysts and the durability of the carbon black-free catalyst layers will be of interest.
4 Possibility of carbon-support-free catalyst use in future vehicles
In order to achieve conductivity in the catalyst layer, carbon-support-free non-PGM catalysts are limited to TiN-based cathode catalysts. The low current density of carbon support-free oxide/oxynitride catalysts arising from the low conductivity has been improved using TiN to the order of mA cm−2 in a half-cell; however, the enhanced conductivity is still insufficient to add carbon black in a single-cell catalyst layer in most cases. The durability in a single cell has therefore seldom been evaluated, and it is therefore too early to discuss the possibility of using this approach in future FCVs.Carbon-support-free Pt-based catalysts have been developed extensively in PEFC anodes and cathodes in the last two decades, although they retain several challenges with respect to their use in FCVs.
(1) Pt loading
As mentioned in Section 1, the target of ∼6 gPGM per mid-sedan FCV9 is comparable to the amount of PGMs per gasoline-fueled LDV,11 and needs to be achieved to make PEFC-powered passenger vehicles affordable and widespread. The target has been set with 0.0625 gPGM kW−1 PGM usage per unit power and 1 W cm−2 power density, which correspond to 0.0125 and 0.05 mgPGM cm−2 PGM loading at the anode and cathode catalyst layers, respectively.9 Considering the currently available PtCo/C cathode and Pt/C anode catalysts, the target PGM loading values can be assumed to be equal to the Pt loading. The Pt loading used in Pt/non-carbon cathode catalyst layers has been much higher than the target of 0.05 mgPt cm−2 in general, as listed in Table 1 and seen in the captions for Fig. 4–11. Rare exceptions include Pt/Ta-SnO2−δ and Pt/Nb-SnO2−δ cathode catalysts with a Pt loading of 0.06 ± 0.002 mgPt cm−2,105 which is close to the target value. Although the advantage of these Pt/oxide catalysts in terms of durability should be taken into account in the comparison with the currently available PtCo/C catalysts, a decrease in Pt loading to the target level without decreasing cell performance is needed for widespread use in FCVs. It will be highly challenging for Pt/non-carbon catalysts, as Pt nanoparticles enhance the conductivity of non-carbons by 2–4 orders of magnitude105 to exceed the proton conductivity of PFSI, and thus prevent electron transport from being the rate-determining step. As illustrated in Fig. 9(c), when it is necessary to have Pt particles that are connected or in close proximity to each other to improve conductivity in the catalyst layer, lowering the Pt content (i.e., reducing Pt loading) is difficult without compromising cell performance. Indeed, 0.1 mgPt cm−2 Pt loading was necessary for the Pt/Ti4O7 anode, and the cell performance decreased significantly when the anode Pt loading was decreased to 0.05 mgPt cm−2.37 This indicates that electron transport restricted the cell performance of MEAs with the Pt/Ti4O7 anode, despite the faster HOR kinetics on Pt than the ORR counterparts. When standard 47% w/w Pt/C catalysts were used in anode catalyst layers and the anode Pt loading was decreased from 0.40 to 0.05 mgPt cm−2, the drop in the cell voltage at a current density of 1 A cm−2 was negligible, in the order of 10 mV.246 The effect of anode Pt loading on the cell performance of MEAs with a Pt/Ti4O7 (ref. 37) anode (significant) and Pt/C246 anode (negligible) clearly differed, as mentioned above, when the loading was decreased to 0.05 mgPt cm−2, which is four times higher than the target value. The σ-value of some non-carbon supports does not restrict the single-cell performance when they are used as supports for Pt catalysts to levels similar to that of Pt/C, at least when the Pt loading exceeded the target value. Further increases in the σ of non-carbon supports to the order of 10 S cm−1 in any P range shown in Fig. 4(k) by, for example, controlling the morphology104 will be necessary. It will be particularly important for use as cathode catalyst supports owing to the slow ORR kinetics and thicker catalyst layer compared with anode counterparts. Theoretically, less than 0.01 mgPt cm−2 cathode Pt loading with power density maintained above 1 W cm−2 is expected by optimizing the O2 and proton transport properties when electron transport across the catalyst layer is sufficiently fast.247 Furthermore, the control of the Pt mass fraction in Pt/non-carbon catalysts will be of particular importance. In most catalysts reviewed in this paper, this was set at around 20% w/w Pt/non-carbon. A support particle size of ∼100 nm, which is smaller than that of most non-carbon supports, will be necessary to increase the Pt mass fraction beyond 20% w/w without an increased Pt nanoparticle size penalty. In addition, a lower Pt mass fraction in Pt/non-carbon catalysts leads to a higher catalyst mass and thicker catalyst layer compared with conventional Pt/C. These properties are unsuitable for use in vehicles. In future studies, cell performance with Pt/non-carbon catalysts at (i) target low Pt loading (0.05 and 0.0125 mgPt cm−2 at the cathode and anode, respectively) and (ii) a high Pt mass fraction (above 40% w/w) will attract significant attention. Although unsupported Pt-alloy anode248 and cathode249 catalysts are beyond the scope of this paper, the evaluation of their performance at (i) will also be of interest.
(2) Metal leaching
To date, no complete non-carbon supports which do not leach in the catalyst layer have been reported. Metals used in non-carbon supports leach as cations to some extent when their chemical stability is evaluated, as reviewed in Section 2. The leached cations exchange H+ in the sulfate groups in PFSI catalyst layers and membranes to decrease the proton conductivity or catalyze the Fenton reaction in some cases. Cation-doped SnO2 is one of the most widely studied non-carbon supports, where the aim of doping was mainly to increase σ. Substantial leaching of the doped cations and Sn at potentials lower than 0.4 V (ref. 103) and higher than 1.5 V has also been reported.51 These systems are therefore more suited for use in cathodes than anodes due to their higher stability in the cathode potential window.103,106 Similarly, the selection of the potential window is necessary when considering other non-carbon supports that are less studied than SnO2-based materials. Another widely studied non-carbon support, TiO2 and Ti4O7, also leaches, while recent results on the radical scavenging properties of Ta-TiOx reported by Xie et al.205 suggest the potential to suppress leaching by Ta-doping or controlling the crystal structure. Doping Ta into effective Ti4O7-based RTAs with an evaluation of the amount of leaching will be of interest.
(3) Scalability
The difficulty in scaling up the batch size of non-carbon supports has seldom been reported, even though many researchers face this issue, even in a laboratory. The solid-state reaction route is a simple, easy, and well-known method suited to the mass production of inorganic supports, although most studies reviewed in this paper utilized other routes to increase the surface area. Hydrothermal routes are also suited for mass production without increasing the synthesis temperature to the level of a solid-state reaction route and have been used to synthesize non-carbon supports for PEFCs; however, the batch size is frequently not reported. Examples of studies reporting the batch size include 10 g of Sn0.96Sb0.04O2−δ particle supports synthesized with a flame combustion route,102 2 g of Ti4O7 synthesized via a carbothermal reduction reaction route,36 and 2 g of (Ti0.91V0.09)4O7 produced by a solid-state reaction.64 There should be considerable interest both in the batch size itself and difficulties for increasing it. For example, vanadium doping increased the batch size of Ti4O7, although excessive amounts of vanadium dopants formed a Ti2O3 phase rather than the target Ti4O7.64
(4) Carbon-free microporous layers and GDLs
As shown by Ioroi's early work on Pt/Ti4O7 cathodes35 and Ramani's work on Pt/TRO cathodes,14 conventional carbon-based microporous layers on GDLs and/or GDLs themselves are oxidized at high potential, complicating the evaluation of Pt/non-carbon catalyst durability. Although carbon papers have been used as GDLs in the latest FCVs produced by multiple companies,121,250 the use of carbon-free GDLs should be the focus of research in academia to help understand the phenomena in Pt/non-carbon catalyst layers at high potentials.
For carbon-supported Pt251–253 and X–Pt core–shell (X = Ni, Cu, Pd, Co, Ag, Au)254 nanoparticle catalysts, theoretical modeling has been performed to clarify their degradation mechanisms. Particularly, the diameter of Pt in Pt/C252 and the thickness of the Pt shell in X–Pt/C254 significantly affected the dissolution rate of Pt and the resulting ECSA after ADTs. Similar theoretical modeling studies on Pt/non-carbon or Pt-alloy/non-carbon catalysts with various degrees of SMSIs and various amounts of leached metals from the supports are expected.
5 Conclusions
Carbon-support-free Pt/Pt-alloy and non-Pt catalysts for use in PEFCs are reviewed in this paper. Particular attention is placed on automotive PEFCs, where lower Pt loading, lower catalyst mass, and a lower cost of materials and operations are required compared with currently available Pt/C anode and PtCo/C cathode catalysts to allow their widespread use in LDVs/MDVs/HDVs. Binary and nonbinary oxides show potential as alternative stable supports to state-of-the-art carbon black, reducing the system cost to protect carbon black from corrosion in anodes and cathodes. Their conductivity, more than six orders of magnitude lower than that of carbon black, has been increased by different routes including foreign metal doping and the formation of suboxides. Binary and ternary nitrides have also been developed, although their variety is limited compared with oxide supports for TiN-based materials, owing to the poorer particle conductivity and stability of other nitrides.Over the last two decades, more effort has been devoted to developing cathode supports than their anode counterparts. Various non-carbon supports have been developed and they display a single-cell performance similar to that of commercial Pt/C catalysts under some conditions. Examples of Pt-based catalysts that have shown this performance and even higher durability at the cathode during startup/shutdown cycles include Magnèli-phase Ti4O7, metal-doped TiO2, and metal-doped-SnO2-supported catalysts. Pt/Ti4O7 also exhibited higher durability against cell reversal at the anode than Pt/C. The excellent activity and durability of these systems are mostly ascribed to SMSIs between Pt particles and metals in the oxide supports, although the mechanism around the d-band center is still under debate. Cathode carbon corrosion during the startup/shutdown is caused by the ORR at the Pt-catalyst anode and has been suppressed by a new approach within the last decade. Anode ORR catalysis has been suppressed by developing HOR-selective catalysts, leveling off the conductivity of supports by using contaminated O2 molecules, and by using a multifunctional hydrogen reservoir layer to capture contaminated O2. Carbon-support-free non-PGM catalysts have been developed only for the cathode sides, where a larger PGM loading is needed compared with the anode counterparts. Such ultimate catalysts are attractive but limited to TiN-based materials owing to the conductivity of other candidates. Oxide materials can be used as supports for Pt particles as the conductivity of the Pt/oxide catalyst is conferred by the Pt particles, whereas the conductivity of the supports themselves is too low to evaluate ORR activity, even in a half-cell. Few single-cell results with TiN-based non-PGM cathodes have been reported to date, and the catalysts were mixed with carbon black in the catalyst layer to obtain more than 1 A cm−2 current density. This is because conductivity is still insufficient for use in a single cell as the current density is three orders of magnitude larger than that in a half-cell. Recent N, P, S-tridoped TiO2 catalysts supported on S-doped TiN are durable against startup/shutdown cycles in a half-cell, although conductivity issues still need to be overcome.
Remaining challenges for the use of carbon-support-free Pt catalysts in future FCVs include reduction in Pt loading, suppression of leaching metals from supports, and scalability. Even state-of-the-art Pt/oxide catalysts rely on the conductivity of Pt particles, and thus decreasing the MEA Pt loading to the target set for the widespread use of FCVs (0.0625 mgPt cm−2, corresponding to 0.0125 and 0.05 mgPt cm−2 at the anode and cathode, respectively) is highly challenging at this stage. When the pressure applied to supports is <10 MPa, the conductivity required for non-carbon supports to meet the stringent Pt loading target will be similar to that of currently available carbon black (of the order of 10 S cm−1). Metal leaching from supports seriously degrades cell performance via a decrease in proton conductivity, with ion exchange of sulfonate groups in PFSI catalyst layers and PFSI membranes, and even the production of radicals. Recently developed Ta-TiOx radical scavengers are potential supports to overcome the issue. The scalability of non-carbon supports, which has seldom been reported in the literature, is particularly important for use in FCVs, and further description of this aspect is needed. Pioneering studies have revealed that carbon in microporous layers on GDLs and that in GDLs are oxidized at high potential to form CO2. Non-carbon GDLs are required to precisely evaluate the tolerance of non-carbon supports in catalyst layers against high potential. Overall, the development of non-carbon materials after factoring these challenges/issues may position these materials at a level close to that needed for practical use in FCVs.
Data availability
No primary research results, software or code has been included in this paper.Author contributions
Mitsuharu Chisaka: conceptualization, writing – original draft, writing – review & editing, and funding acquisition.Conflicts of interest
The author declares no competing financial interests.Acknowledgements
I acknowledge Dr Hiroyuki Morioka, Mr Hirokazu Muramoto, Prof. Akimitsu Ishihara, Prof. Ken-ichiro Ota, and Prof. Hirofumi Daiguji for their fruitful discussions on non-Pt catalysts. I also thank Prof. Tatsuya Takeguchi for his collaboration with Pt catalysts. This work was partially supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research, Grant Numbers JP23H01347, JP23K26042 from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) in Japan and a grant from the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), Japan.References
- U. S. EPA, Sources of Greenhouse Gas Emissions, https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/sources-greenhouse-gas-emissions, last accessed on Apr. 16, 2024 Search PubMed.
- K. L. Fleming, A. L. Brown, L. Fulton and M. Miller, Curr. Sustainable/Renewable Energy Rep., 2021, 8, 180 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Jia, Z. Jiang, Q. Wang, B. Xu and M. Xiao, Transport Policy, 2023, 135, 21 CrossRef.
- https://ww2.arb.ca.gov/news/california-approves-groundbreaking-regulation-accelerates-deployment-heavy-duty-zevs-protect, last accessed on Apr. 16, 2024.
- https://ww2.arb.ca.gov/news/california-transitioning-all-electric-public-bus-fleet-2040, last accessed on Apr. 16, 2024.
- O. Gröger, H. A. Gasteiger and J. P. Suchsland, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2015, 162, A2605 CrossRef.
- D. A. Cullen, K. C. Neyerlin, R. K. Ahluwalia, R. Mukundan, K. L. More, R. L. Borup, A. Z. Weber, D. J. Myers and A. Kusoglu, Nat. Energy, 2021, 6, 462 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Nakamichi, Nikkei Electron., 2022, 6, 73 Search PubMed.
- A. Kongkanand and M. F. Mathias, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2016, 7, 1127 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. M. Whiston, I. L. Azevedo, S. Litster, K. S. Whitefoot, C. Samaras and J. F. Whitacre, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2019, 116, 4899 CrossRef CAS.
- U.S. Department of Energy and Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, Program Record 16006, Platinum Group Metals (P.G.M.) for light-Duty vehicles, https://www.hydrogen.energy.gov/pdfs/16006_pgm_light_duty_vehicles.pdf, last accessed on Apr. 16, 2024 Search PubMed.
- C. A. Reiser, L. Bregoli, T. W. Patterson, J. S. Yi, J. D. Yang, M. L. Perry and T. D. Jarvi, Electrochem. Solid State Lett., 2005, 8, A273 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Linse, G. G. Scherer, A. Wokaun and L. Gubler, J. Power Sources, 2012, 219, 240 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Parrondo, T. Han, E. Niangar, C. Wang, N. Dale, K. Adjemian and V. Ramani, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2014, 111, 45 CrossRef CAS.
- U. Eberle, B. Müller and R. von Helmolt, Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5, 8780 RSC.
- A. Ohma, K. Shinohara, A. Iiyama, T. Yoshida and A. Daimaru, ECS Trans., 2011, 41, 775 CrossRef CAS.
- U.S. Department of Energy and Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Technology Office, Fuel Cell Technologies Office Multi-year Research, Development, and Demonstration Plan, updated in, 2016, https://www.energy.gov/sites/prod/files/2016/10/f33/fcto_myrdd_fuel_cells.pdf, last accessed on Apr. 16, 2024 Search PubMed.
- C. Song, Y. Tang, J. L. Zhang, J. Zhang, H. Wang, J. Shen, S. McDermid, J. Li and P. Kozak, Electrochim. Acta, 2007, 52, 2552 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Taniguchi, T. Akita, K. Yasuda and Y. Miyazaki, J. Power Sources, 2004, 130, 42 CrossRef CAS.
- S. D. Knights, K. M. Colbow, J. St-Pierre and D. P. Wilkinson, J. Power Sources, 2004, 127, 127 CrossRef CAS.
- K. H. Lim, W. H. Lee, Y. Jeong and H. Kim, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2017, 164, F1580 CrossRef CAS.
- W. R. R. Baumgartner, E. Wallnöfer, T. Schaffer, V. Hacker, V. Peinecke and P. Prenninger, ECS Trans., 2006, 3, 811 CrossRef CAS.
- C. W. Roh, H. E. Kim, J. Choi, J. Lim and H. Lee, J. Power Sources, 2019, 443, 227270 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Lü, Z. Liu, C. Wang, Z. Mao and M. Zhang, Int. J. Energy Res., 2011, 35, 24 CrossRef.
- T. Arai, O. Takashi, K. Amemiya and T. Takahashi, SAE Int. J. Alt. Power, 2017, 6, 145 CrossRef.
- K. Sasaki, F. Takasaki, Z. Noda, S. Hayashi, Y. Shiratori and K. Ito, ECS Trans., 2010, 33, 473 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Ioroi, Z. Siroma, S. Yamazaki and K. Yasuda, Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9, 1801284 CrossRef.
- S. J. Percival, J. E. Dick and A. J. Bard, Anal. Chem., 2017, 89, 3087 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Inoue, A. Nakazawa and M. Umeda, J. Power Sources, 2011, 196, 4579 CrossRef CAS; Y. Sugawara, T. Okayasu, A. P. Yadav, A. Nishikata and T. Tsuru, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2012, 159, F779 CrossRef.
- Z. Wang, Y. R. Zheng, I. Chorkendorff and J. K. Nørskov, ACS Energy Lett., 2020, 5, 2905 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Lv, N. Cheng, T. Peng, M. Pan and S. Mu, J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 1135 RSC.
- Y. Li, S. Song, H. Kim, K. Nomoto, H. Kim, X. Sun, S. Hori, K. Suzuki, N. Matsui, M. Hirayama, T. Mizoguchi, T. Saito, T. Kamiyama and R. Kanno, Science, 2023, 381, 50 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. C. Walsh and R. G. A. Wills, Electrochim. Acta, 2010, 55, 6342 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Ioroi, Z. Siroma, N. Fujiwara, S. Yamazaki and K. Yasuda, Electrochem. Commun., 2005, 7, 183 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Ioroi, H. Senoh, S. Yamazaki, Z. Siroma, N. Fujiwara and K. Yasuda, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2008, 155, B321 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Chisaka, W. Nagano, B. Delgertsetseg and T. Takeguchi, Chem. Commun., 2021, 57, 12772 RSC.
- Z. Li, Y. Mu, Q. Zhang, H. Huang, X. Wei, L. Yang, G. Wang, T. Zhao, G. Wu and L. Zeng, Energy Environ. Sci., 2024, 17, 1580 RSC.
- M. Chisaka, Y. Ando, Y. Yamamoto and N. Itagaki, Electrochim. Acta, 2016, 214, 165 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Ioroi, T. Akita, S. Yamazaki, Z. Siroma, N. Fujiwara and K. Yasuda, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2011, 158, C329 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Andersson and A. Magnéli, Naturwissenschaften, 1956, 43, 495 CrossRef CAS.
- R. F. Bartholomew and D. R. Frankl, Phys. Rev., 1969, 187, 828 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Cardarelli, in Properties of Pure Ceramics in Materials Handbook: A Concise Desktop Reference, ed. F. Cardarelli, Springer-Verlag, London, 2nd edn, 2008, ch. 10, p. 660–667 Search PubMed.
- T. Ioroi, H. Kageyama, T. Akita and K. Yasuda, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2010, 12, 7529 RSC.
- K. Senevirathne, R. Hui, S. Campbell, S. Ye and J. Zhang, Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 59, 538 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Yao, F. Li, X. Li and D. Xia, J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 16560 RSC.
- S. J. Tauster, S. C. Fung and R. L. Garten, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1978, 100, 170 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Dong, Y. Liu, Z. Lv, C. Wang, W. Yang and B. Wang, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2023, 11, 23106 RSC.
- R. T. K. Baker, E. B. Prestridge and R. L. Garten, J. Catal., 1979, 56, 390 CrossRef CAS.
- R. T. K. Baker, E. B. Prestridge and R. L. Garten, J. Catal., 1979, 59, 293 CrossRef CAS.
- A. D. Duma, Y. C. Wu, W. N. Su, C. J. Pan, M. C. Tsai, H. M. Chen, J. F. Lee, H. S. Sheu, V. T. T. Ho and B. J. Hwang, ChemCatChem, 2018, 10, 1155 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Jiménez-Morales, F. Haidar, S. Cavaliere, D. Jones and J. Rozière, ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 10399 CrossRef.
- C. J. Pan, M. C. Tsai, W. N. Su, J. Rick, N. G. Akalework, A. K. Agegnehu, S. Y. Cheng and B. J. Hwang, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., 2017, 74, 154 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Jiménez-Morales, S. Cavaliere, D. Jones and J. Rozière, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2018, 20, 8765 RSC.
- R. A. M. Esfahani and E. B. Easton, Appl. Catal., B, 2020, 268, 118743 CrossRef.
- S. Y. Huang, P. Ganesan and B. N. Popov, Appl. Catal., B, 2011, 102, 71 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Kumar and V. Ramani, ACS Catal., 2014, 4, 1516 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Pătru, A. Rabis, S. E. Temmel, R. Kotz and T. J. Schmidt, Catal. Today, 2016, 262, 161 CrossRef.
- P. Dhanasekaran, S. V. Selvaganesh and S. D. Bhat, New J. Chem., 2017, 41, 13012 RSC.
- S. Matsumoto, M. Nagamine, Z. Noda, J. Matsuda, S. M. Lyth, A. Hayashi and K. Sasaki, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2018, 165, F1164 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Takei, R. Kobayashi, Y. Mizushita, Y. Hiramitsu, K. Kakinuma and M. Uchida, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2018, 165, F1300 CrossRef CAS.
- C. He, X. Wang, S. Sankarasubramanian, A. Yadav, K. Bhattacharyya, X. Liang and V. Ramani, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 3, 5774 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zhang, Y. Wang, Y. Zhang, J. Song, Y. Si, J. Yan, C. Ma, Y. T. Liu, J. Yu and B. Ding, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 23252 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Marezio and P. D. Dernier, J. Solid State Chem., 1970, 3, 340 CrossRef.
- M. Chisaka, W. Nagano, S. Takahashi, B. Delgertsetseg, H. Wakita and T. Takeguchi, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2023, 934, 117308 CrossRef CAS.
- R. A. M. Esfahani, S. K. Vankova, A. H. A. M. Videla and S. Specchia, Appl. Catal., B, 2017, 201, 419 CrossRef.
- R. A. M. Esfahani, I. I. Ebralidze, S. Specchia and E. B. Easton, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6, 14805 RSC.
- S. Y. Huang, P. Ganesan, S. Park and B. N. Popov, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 13898 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Liu, X. Wu and K. Scott, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014, 4, 3891 RSC.
- V. T. T. Ho, C. J. Pan, J. Rick, W. N. Su and B. J. Hwang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 11716 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. C. Tsai, T. T. Nguyen, N. G. Akalework, C. J. Pan, J. Rick, Y. F. Liao, W. N. Su and B. J. Hwang, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 6551 CrossRef CAS.
- B. J. Hsieh, M. C. Tsai, C. J. Pan, W. N. Su, J. Rick, J. F. Lee, Y. W. Yang and B. J. Hwang, NPG Asia Mater., 2017, 9, e403 CrossRef CAS.
- B. J. Hsieh, M. C. Tsai, C. J. Pan, W. N. Su, J. Rick, H. L. Chou, J. F. Lee and B. J. Hwang, Electrochim. Acta, 2017, 224, 452 CrossRef CAS.
- T. N. Geppert, M. Bosund, M. Putkonen, B. M. Stühmeier, A. T. Pasanen, P. Heikkilä, H. A. Gasteiger and H. A. El-Sayed, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2020, 167, 084517 CrossRef CAS.
- S. von Kraemer, K. Wikander, G. Lindbergh, A. Lundblad and A. E. C. Palmqvist, J. Power Sources, 2008, 180, 185 CrossRef CAS.
- N. G. Akalework, C. J. Pan, W. N. Su, J. Rick, M. C. Tsai, J. F. Lee, J. M. Lin, L. D. Tsai and B. J. Hwang, J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 20977 RSC.
- K. W. Park and K. S. Seol, Electrochem. Commun., 2007, 9, 2256 CrossRef CAS.
- T. B. Do, M. Cai, M. S. Ruthkosky and T. E. Moylan, Electrochim. Acta, 2010, 55, 8013 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Chevallier, A. Bauer, S. Cavaliere, R. Hui, J. Rozière and D. J. Jones, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2012, 4, 1752 CrossRef CAS.
- J. H. Kim, G. Kwon, H. Lim, C. Zhu, H. You and Y. T. Kim, J. Power Sources, 2016, 320, 188 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Y. Huang, P. Ganesan and B. N. Popov, Appl. Catal., B, 2010, 96, 224 CrossRef CAS.
- C. He, S. Sankarasubramanian, I. Matanovic, P. Atanassov and V. Ramani, ChemSusChem, 2019, 12, 3468 CrossRef CAS.
- R. D. Shannon, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. A: Found. Crystallogr., 1976, 32, 751 CrossRef.
- Y. Ma, T. Nagai, Y. Inoue, K. Ikegami, Y. Kuroda, K. Matsuzawa, T. W. Napporn, Y. Liu, S. Mitsushima and A. Ishihara, Mater. Des., 2021, 203, 109623 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Kumar and V. Ramani, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2013, 160, F1207 CrossRef CAS.
- M. T. Anwar, X. Yan, S. Shen, N. Husnain, F. Zhu, L. Luo and J. Zhang, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42, 30750 CrossRef CAS.
- J. H. Kim, G. Kwon, H. Lim, C. Zhu, H. You and Y. T. Kim, J. Power Sources, 2016, 320, 188 CrossRef CAS.
- K. J. Noh, H. Im, C. Lim, M. G. Jang, I. Nam and J. W. Han, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 427, 131568 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Bharti and G. Cheruvally, J. Power Sources, 2017, 363, 413 CrossRef CAS.
- C. V. Subban, Q. Zhou, A. Hu, T. E. Moylan, F. T. Wagner and F. J. DiSalvo, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 17531 CrossRef CAS.
- A. V. Nguyen, T. T. Huynh, H. Q. Pham, V. T. T. Thi Phan, S. T. Nguyen and V. T. T. Ho, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44, 2361 CrossRef CAS.
- T. M. Phan, K. Im and J. Kim, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2023, 611, 155740 CrossRef.
- E. Lee, C. Park, D. W. Lee, G. Lee, H. Y. Park, J. H. Jang, H. J. Kim, Y. E. Sung, Y. Tak and S. J. Yoo, ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 12080 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Dhanasekaran, S. V. Selvaganesh and S. D. Bhat, J. Power Sources, 2016, 304, 360 CrossRef CAS.
- C. P. Lo, G. Wang, A. Kumar and V. Ramani, Appl. Catal., B, 2013, 140–141, 133 CrossRef CAS.
- W. D. Ryden, A. W. Lawson and C. C. Sartain, Phys. Rev. B: Solid State, 1970, 1, 1494 CrossRef.
- S. J. Tauster, Acc. Chem. Res., 1987, 20, 389 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Banham, S. Ye, A. O'Toole, A. Lemke and E. Eisenbraun, Nano Energy, 2016, 27, 157 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Eckardt, C. Gebauer, Z. Jusys, M. Wassner, N. Hüsing and R. J. Behm, J. Power Sources, 2018, 400, 580 CrossRef CAS.
- B. M. Stühmeier, S. Selve, M. U. M. Patel, T. N. Geppert, H. A. Gasteiger and H. A. El-Sayed, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2019, 2, 5534 CrossRef.
- E. Hornberger, A. Bergmann, H. Schmies, S. Kühl, G. Wang, J. Drnec, D. J. S. Sandbeck, V. Ramani, S. Cherevko, K. J. J. Mayrhofer and P. Strasser, ACS Catal., 2018, 8, 9675 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Masao, S. Noda, F. Takasaki, K. Ito and K. Sasaki, Electrochem. Solid State Lett., 2009, 12, B119 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Kakinuma, M. Uchida, T. Kamino, H. Uchida and M. Watanabe, Electrochim. Acta, 2011, 56, 2881 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Kakinuma, Y. Chino, Y. Senoo, M. Uchida, T. Kamino, H. Uchida, S. Deki and M. Watanabe, Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 110, 316 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Senoo, K. Kakinuma, M. Uchida, H. Uchida, S. Deki and M. Watanabe, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 32180 RSC.
- Y. Senoo, K. Taniguchi, K. Kakinuma, M. Uchida, H. Uchida, S. Deki and M. Watanabe, Electrochem. Commun., 2015, 51, 37 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Inaba, R. Murase, T. Takeshita, K. Yano, S. Kosaka, N. Takahashi, N. Isomura, K. Oh-Ishi, W. Yoshimune, K. Tsuchiya, T. Nobukawa and K. Kodama, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2024, 16, 10295 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Takasaki, S. Matsuie, Y. Takabatake, Z. Noda, A. Hayashi, Y. Shiratori, K. Ito and K. Sasaki, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2011, 158, B1270 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Uchida, Y. Fukuoka, Y. Sugawara, N. Eda and A. Ohta, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1996, 143, 2245 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Kakinuma, R. Kobayashi, A. Iiyama and M. Uchida, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2018, 165, J3083 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Shi, T. Tano, D. A. Tryk, A. Iiyama, M. Uchida and K. Kakinuma, ACS Catal., 2021, 11, 5222 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Kakinuma, M. Hayashi, T. Hashimoto, A. Iiyama and M. Uchida, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 3, 6922 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Shi, T. Hashimoto, D. A. Tryk, T. Tano, A. Iiyama, M. Uchida and K. Kakinuma, Electrochim. Acta, 2021, 390, 138894 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Cavaliere, S. Subianto, I. Savych, M. Tillard, D. J. Jones and J. Rozière, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117, 18298 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Cavaliere, I. Jiménez-Morales, G. Ercolano, I. Savych, D. Jones and J. Rozière, ChemElectroChem, 2015, 2, 1966 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Jiménez-Morales, S. Cavaliere, M. Dupont, D. Jones and J. Rozière, Sustainable Energy Fuels, 2019, 3, 1526 RSC.
- G. Cognard, G. Ozouf, C. Beauger, G. Berthomé, D. Riassetto, L. Dubau, R. Chattot, M. Chatenet and F. Maillard, Appl. Catal., B, 2017, 201, 381 CrossRef CAS.
- C. He, S. Sankarasubramanian, A. Ells, J. Parrondo, C. C. Gumeci, M. Kodali, I. Matanovic, A. K. Yadav, K. Bhattacharyya, N. Dale, P. Atanassov and V. K. Ramani, ACS Catal., 2021, 11, 7006 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Jalalpoor, D. Göhl, P. Paciok, M. Heggen, J. Knossalla, I. Radev, V. Peinecke, C. Weidenthaler, K. J. J. Mayrhofer, M. Ledendecker and F. Schüth, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2021, 168, 024502 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Ozouf, G. Cognard, F. Maillard, M. Chatenet, L. Guétaz, M. Heitzmann, P. A. Jacques and C. Beauger, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2018, 165, F3036 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Yarlagadda, M. K. Carpenter, T. E. Moylan, R. S. Kukreja, R. Koestner, W. Gu, L. Thompson and A. Kongkanand, ACS Energy Lett., 2018, 3, 618 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Yoshizumi, H. Kubo and M. Okumura, SAE Tech. Pap. Ser., 2021 DOI:10.4271/2021-01-0740.
- P. Zhang, S. Y. Huang and B. N. Popov, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2010, 157, B1163 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Lin, J. Liu, S. Li, J. Liang, X. Liu, L. Xie, G. Lu, J. Han, Y. Huang and Q. Li, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2023, 33, 2211638 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Li, J. Liu, J. Liang, Z. Lin, X. Liu, Y. Chen, G. Lu, C. Wang, P. Wei, J. Han, Y. Huang, G. Wu and Q. Li, Appl. Catal., B, 2023, 320, 122017 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Y. Chen and A. C. C. Tseung, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1996, 143, 2703 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Raghuveer and B. Viswanathan, J. Power Sources, 2005, 144, 1 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Chhina, S. Campbell and O. Kesler, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2007, 154, B533 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liu, S. Shrestha and W. E. Mustain, ACS Catal., 2012, 2, 456 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Kumar, S. N. Bhange, R. Soni and S. Kurungot, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 3, 1908 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Minami, Thin Solid Films, 2008, 516, 5822 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Chhina, S. Campbell and O. Kesler, J. Power Sources, 2006, 161, 893 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liu and W. E. Mustain, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 530 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Schmies, A. Bergmann, J. Drnec, G. Wang, D. Teschner, S. Kühl, D. J. S. Sandbeck, S. Cherevko, M. Gocyla, M. Shviro, M. Heggen, V. Ramani, R. E. Dunin-Borkowski, K. J. J. Mayrhofer and P. Strasser, Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8, 1701663 CrossRef.
- Y. Cheng, X. Zhao, Y. Yu, L. Chen, T. Cheng, J. Huang, Y. Liu, M. Harada, A. Ishihara and Y. Wang, J. Power Sources, 2020, 446, 227332 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Guo, L. Cheng, X. Gao, J. Xu, C. Chen, P. Liu, D. He, L. Tian, J. Song, H. Zhou and Y. Wu, ACS Catal., 2023, 13, 5397 CrossRef CAS.
- O. A. Baturina, Y. Garsany, T. J. Zega, R. M. Stroud, T. Schull and K. E. Swider-Lyons, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2008, 155, B1314 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Gao, Z. Zhang, M. Dou and F. Wang, ACS Catal., 2019, 9, 3278 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Jia, S. Ghoshal, J. Li, W. Liang, G. Meng, H. Che, S. Zhang, Z. F. Ma and S. Mukerjee, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 7893 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Xu, J. Yang, E. Liu, Q. Jia, G. M. Veith, G. Nair, S. DiPietro, K. Sun, J. Chen, P. Pietrasz, Z. Lu, M. Jagner, K. K. Gath, S. Mukerjee and J. R. Waldecker, J. Power Sources, 2020, 451, 227709 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Takenaka, H. Matsumori, K. Nakagawa, H. Matsune, E. Tanabe and M. Kishida, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111, 15133 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Suzuki, A. Ishihara, S. Mitsushima, N. Kamiya and K. Ota, Electrochem. Solid State Lett., 2007, 10, B105 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Shi, T. Tano, D. A. Tryk, A. Iiyama, M. Uchida, Y. Kuwauchi, A. Masuda and K. Kakinuma, J. Catal., 2022, 407, 300 CrossRef CAS.
- J. K. Nørskov, J. Rossmeisl, A. Logadottir, L. Lindqvist, J. R. Kitchin, T. Bligaard and H. Jónsson, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 17886 CrossRef.
- S. Siahrostami, S. J. Villegas, A. H. B. Mostaghimi, S. Back, A. B. Farimani, H. Wang, K. A. Persson and J. Montoya, ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 7495 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Ando, T. Gunji, T. Tanabe, I. Fukano, H. D. Abruña, J. Wu, T. Ohsaka and F. Matsumoto, ACS Catal., 2021, 11, 9317 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Avasarala, T. Murray, W. Li and P. Haldar, J. Mater. Chem., 2009, 19, 1803 RSC.
- B. Avasarala and P. Haldar, Electrochim. Acta, 2010, 55, 9024 CrossRef CAS.
- N. C. Saha and H. G. Tompkins, J. Appl. Phys., 1992, 72, 3072 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Kakinuma, Y. Wakasugi, M. Uchida, T. Kamino, H. Uchida and M. Watanabe, Electrochemistry, 2011, 79, 399 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Kakinuma, Y. Wakasugi, M. Uchida, T. Kamino, H. Uchida, S. Deki and M. Watanabe, Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 77, 279 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Shintani, K. Kakinuma, H. Uchida, M. Watanabe and M. Uchida, J. Power Sources, 2015, 280, 593 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Seifitokaldani and O. Savadogo, Electrochim. Acta, 2015, 167, 237 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Shin, H. Kim, D. Y. Chung, J. M. Yoo, S. Weon, W. Choi and Y. E. Sung, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 3914 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Nan, D. Dang and X. L. Tian, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6, 6065 RSC.
- H. Matsui, A. Shoji, C. Chen, X. Zhao, T. Uruga and M. Tada, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2024, 14, 1501 RSC.
- Z. Pan, Y. Xiao, Z. Fu, G. Zhan, S. Wu, C. Xiao, G. Hu and Z. Wei, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 13966 RSC.
- S. Jiang, B. Yi, H. Zhang, W. Song, Y. Bai, H. Yu and Z. Shao, ChemElectroChem, 2016, 3, 734 CrossRef CAS.
- M. K. Debe, A. K. Schmoeckel, G. D. Vernstrom and R. Atanasoski, J. Power Sources, 2006, 161, 1002 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Li, X. Wang, Z. Chen, M. Waje and Y. Yan, Langmuir, 2005, 21, 9386 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Perego, G. Giuffredi, P. Mazzolini, M. Colombo, R. Brescia, M. Prato, D. C. Sabarirajan, I. V. Zenyuk, F. Bossola, V. D. Santo, A. Casalegno and F. D. Fonzo, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2019, 2, 1911 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Xiao, G. Zhan, Z. Fu, Z. Pan, C. Xiao, S. Wu, C. Chen, G. Hu and Z. Wei, J. Power Sources, 2015, 284, 296 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Tian, J. Luo, H. Nan, H. Zou, R. Chen, T. Shu, X. Li, Y. Li, H. Song, S. Liao and R. R. Adzic, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 1575 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Liu, L. Du, G. Fu, Z. Cui, Y. Li, D. Dang, X. Gao, Q. Zheng and J. B. Goodenough, Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9, 1803040 CrossRef.
- C. Walling, Acc. Chem. Res., 1975, 8, 125 CrossRef CAS.
- I. A. Salem, M. El-Maazawi and A. B. Zaki, Int. J. Chem. Kinet., 2000, 32, 643 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Kinumoto, M. Inaba, Y. Nakayama, K. Ogata, R. Umebayashi, A. Tasaka, Y. Iriyama, T. Abe and Z. Ogumi, J. Power Sources, 2006, 158, 1222 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Jing, L. Luo, S. Yin, F. Huang, Y. Jia, Y. Wei, Z. Sun and Y. Zhao, Appl. Catal., B, 2014, 147, 897 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Yin, L. Wang, C. Tian, T. Tan, G. Mu, L. Zhao and H. Fu, Chem.–Eur. J., 2013, 19, 13979 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. C. Tsai, T. K. Chin, W. S. Liu and T. P. Perng, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 3, 11610 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Li, L. Li, X. Yu, X. Wu, Z. Xie, X. Wang, Z. Lu, X. Zhang, Y. Huang and X. Yang, Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 399, 125827 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Uosaki, G. Elumalai, H. Noguchi, T. Masuda, A. Lyalin, A. Nakayama and T. Taketsugu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 6542 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Elumalai, H. Noguchi, A. Lyalin, T. Taketsugu and K. Uosaki, Electrochem. Commun., 2016, 66, 53 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Dou, M. Hou, H. Zhang, G. Li, W. Lu, Z. Wei, Z. Shao and B. Yi, ChemSusChem, 2012, 5, 945 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Dou, M. Hou, D. Liang, W. Lu, Z. Shao and B. Yi, Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 92, 468 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Ioroi and K. Yasuda, J. Power Sources, 2020, 450, 227656 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Li, W. Song, G. Jiang, Y. Yang, H. Yu, Z. Shao, F. Duan and Y. Yang, Front. Energy, 2022, 16, 852 CrossRef.
- U.S. Geological Survey, Mineral Commodity Summaries, 2024, p. 136, DOI:10.3133/mcs2024.
- X. Zhou, H. Ji, B. Li and C. Zhang, ACS Omega, 2020, 5, 10099 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Wang, X. Zhou, B. Li, D. Yang, H. Lv, Q. Xiao, P. Ming, X. Wei and C. Zhang, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45, 8930 CrossRef CAS.
- E. You, M. Min, S. A. Jin, T. Kim and C. Pak, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2018, 165, F3094 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Y. Kim, S. W. Lee and C. Pak, J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2020, 85, 87 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Li, L. Zhao, X. Du, W. Gao, C. Zhang, H. Chen, X. He, C. Wang and Z. Mao, Chem. Eng. J., 2023, 461, 141823 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Liao, S. Zaman, Y. Wang, M. Yang, L. Yang, M. Chen and H. Wang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2023, 15, 4092 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Wang, Y. Jiang, J. Liao, Z. Li, T. Zhao and L. Zeng, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14, 56867 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Favelukis, S. Chakrabartty, V. Kumar, S. H. Kim, A. El-Zoka, M. Krämer, D. Raabe, B. Gault, N. Eliaz, A. Natan, M. Sokol and B. A. Rosen, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2024, 34, 2309749 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Genorio, D. Strmcnik, R. Subbaraman, D. Tripkovic, G. Karapetrov, V. R. Stamenkovic, S. Pejovnik and N. M. Marković, Nat. Mater., 2010, 9, 998 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Genorio, R. Subbaraman, D. Strmcnik, D. Tripkovic, V. R. Stamenkovic and N. M. Markovic, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 5468 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. W. Yun, S. A. Park, T. J. Kim, J. H. Kim, G. W. Pak and Y. T. Kim, ChemSusChem, 2017, 10, 489 CrossRef CAS.
- B. M. Stühmeier, A. M. Damjanović, K. Rodewald and H. A. Gasteiger, J. Power Sources, 2023, 558, 232572 CrossRef.
- J. Jang, M. Sharma, D. Choi, Y. S. Kang, Y. Kim, J. Min, H. Sung, N. Jung and S. J. Yoo, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 27735 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Shintani, Y. Kojima, K. Kakinuma, M. Watanabe and M. Uchida, J. Power Sources, 2015, 294, 292 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Shen, J. Liu, H. B. Wu, P. Xu, F. Liu, C. Tongsh, K. Jiao, J. Li, M. Liu, M. Cai, J. P. Lemmon, G. Soloveichik, H. Li, J. Zhu and Y. Lu, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 1191 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Luo, H. Tang, X. Tian, S. Hou, X. Li, L. Du and S. Liao, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 3530 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Kamai, K. Kamiya, K. Hashimoto and S. Nakanishi, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 13184 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Nagai, M. Yoshida and H. Tominaga, Electrochim. Acta, 2007, 52, 5430 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Izhar and M. Nagai, J. Power Sources, 2008, 182, 52 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Izhar, M. Yoshida and M. Nagai, Electrochim. Acta, 2009, 54, 1255 CrossRef CAS.
- G. E. Haslam, X. Y. Chin and G. T. Burstein, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011, 13, 12968 RSC.
- P. D. Tran, A. Le Goff, J. Heidkamp, B. Jousselme, N. Guillet, S. Palacin, H. Dau, M. Fontecave and V. Artero, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 1371 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. N. Huan, R. T. Jane, A. Benayad, L. Guetaz, P. D. Tran and V. Artero, Energy Environ. Sci., 2016, 9, 940 RSC.
- X. Yang, F. Zhao, Y. W. Yeh, R. S. Selinsky, Z. Chen, N. Yao, C. G. Tully, Y. Ju and B. E. Koel, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 1543 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Chisaka, T. Iijima, T. Yaguchi and Y. Sakurai, Electrochim. Acta, 2011, 56, 4581 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Chisaka, Y. Suzuki, T. Iijima and Y. Sakurai, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115, 20610 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhang, F. Coms and S. Kumaraguru, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2021, 168, 024520 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Xie, X. Xie, G. Hu, V. Prabhakaran, S. Saha, L. Gonzalez-Lopez, A. H. Phakatkar, M. Hong, M. Wu, R. Shahbazian-Yassar, V. Ramani, M. I. Al-Sheikhly, D. Jiang, Y. Shao and L. Hu, Nat. Energy, 2022, 7, 281 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Takasu, H. Fukunaga, H. S. Yang, T. Ohashi, M. Suzuki and W. Sugimoto, Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 105, 224 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Proietti, F. Jaouen, M. Lefèvre, N. Larouche, J. Tian, J. Herranz and J. P. Dodelet, Nat. Commun., 2011, 2, 416 CrossRef.
- C. H. Choi, C. Baldizzone, J. P. Grote, A. K. Schuppert, F. Jaouen and K. J. J. Mayrhofer, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 12753 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Strickland, E. Miner, Q. Jia, U. Tylus, N. Ramaswamy, W. Liang, M. T. Sougrati, F. Jaouen and S. Mukerjee, Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 7343 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Shao, J. P. Dodelet, G. Wu and P. Zelenay, Adv. Mater., 2019, 31, 1807615 CrossRef.
- X. Zhao, X. Yang, M. Wang, S. Hwang, S. Karakalos, M. Chen, Z. Qiao, L. Wang, B. Liu, Q. Ma, D. A. Cullen, D. Su, H. Yang, H. Y. Zang, Z. Feng and G. Wu, Appl. Catal., B, 2020, 279, 119400 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Zhang, L. Osmieri, J. H. Park, H. T. Chung, D. A. Cullen, K. C. Neyerlin, D. J. Myers and P. Zelenay, Nat. Catal., 2022, 5, 455 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Xie, C. He, B. Li, Y. He, D. A. Cullen, E. C. Wegener, A. J. Kropf, U. Martinez, Y. Cheng, M. H. Engelhard, M. E. Bowden, M. Song, T. Lemmon, X. S. Li, Z. Nie, J. Liu, D. J. Myers, P. Zelenay, G. Wang, G. Wu, V. Ramani and Y. Shao, Nat. Catal., 2020, 3, 1044 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Chen, X. Li, F. Yang, B. Li, T. Stracensky, S. Karakalos, S. Mukerjee, Q. Jia, D. Su, G. Wang, G. Wu and H. Xu, ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 10523 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Gottesfeld, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2022, 169, 124518 CrossRef.
- K. Kodama, T. Nagai, A. Kuwaki, R. Jinnouchi and Y. Morimoto, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2021, 16, 140 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Lee, A. Ishihara, S. Mitsushima, N. Kamiya and K. Ota, Electrochim. Acta, 2004, 49, 3479 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liu, A. Ishihara, S. Mitsushima, N. Kamiya and K. Ota, Electrochem. Solid State Lett., 2005, 8, A400 CrossRef CAS.
- J. H. Kim, A. Ishihara, S. Mitsushima, N. Kamiya and K. Ota, Electrochim. Acta, 2007, 52, 2492 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Doi, A. Ishihara, S. Mitsushima, N. Kamiya and K. Ota, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2007, 154, B362 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Ishihara, S. Doi, S. Mitsushima and K. Ota, Electrochim. Acta, 2008, 53, 5442 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Ukita, A. Ishihara, Y. Ohgi, K. Matsuzawa, S. Mitsushima and K. Ota, Electrochemistry, 2011, 79, 340 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Chisaka, A. Ishihara, H. Morioka, T. Nagai, S. Yin, Y. Ohgi, K. Matsuzawa, S. Mitsushima and K. I. Ota, ACS Omega, 2017, 2, 678 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Chisaka, Y. Yamamoto, N. Itagaki and Y. Hattori, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2018, 1, 211 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Chisaka, Y. Ando and N. Itagaki, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4, 2501 RSC.
- M. Chisaka, T. Abe, R. Xiang, S. Maruyama and H. Daiguji, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022, 24, 29328 RSC.
- M. Chisaka, R. Xiang, S. Maruyama and H. Daiguji, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 3, 9866 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Chisaka, R. Xiang, S. Maruyama and H. Daiguji, Energy Fuels, 2022, 36, 539 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Chisaka, J. A. Shamim, W. L. Hsu and H. Daiguji, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2024, 12, 11277 RSC.
- X. L. Tian, L. Wang, B. Chi, Y. Xu, S. Zaman, K. Qi, H. Liu, S. Liao and B. Y. Xia, ACS Catal., 2018, 8, 8970 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Liu, H. M. Zhang, M. R. Wang, H. X. Zhong and J. Chen, J. Power Sources, 2007, 172, 503 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Seo, D. H. Anjum, K. Takanabe, J. Kubota and K. Domen, Electrochim. Acta, 2014, 149, 76 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Chisaka, A. Ishihara, N. Uehara, M. Matsumoto, H. Imai and K. Ota, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3, 16414 RSC.
- M. Chisaka and H. Muramoto, ChemElectroChem, 2014, 1, 544 CrossRef.
- G. Zhang, D. Sebastián, X. Zhang, Q. Wei, C. Lo Vecchio, J. Zhang, V. Baglio, W. Wang, S. Sun, A. S. Aricò and A. C. Tavares, Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 10, 2000075 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Sun, Q. Wu, R. Che, Y. Bu, Y. Jiang, Y. Li, L. Yang, X. Wang and Z. Hu, ACS Catal., 2015, 5, 1857 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Chenitz, U. I. Kramm, M. Lefèvre, V. Glibin, G. Zhang, S. Sun and J. P. Dodelet, Energy Environ. Sci., 2018, 11, 365 RSC.
- C. Gebauer, J. Fischer, M. Wassner, T. Diemant, J. Bansmann, N. Hüsing and R. J. Behm, Electrochim. Acta, 2014, 146, 335 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Du, Z. Dohnálek and I. Lyubinetsky, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 2649 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Du, N. A. Deskins, Z. Zhang, Z. Dohnálek, M. Dupuis and I. Lyubinetsky, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2010, 12, 6337 RSC.
- S. Wendt, P. T. Sprunger, E. Lira, G. K. H. Madsen, Z. Li, J. Ø. Hansen, J. Matthiesen, A. Blekinge-Rasmussen, E. Laegsgaard, B. Hammer and F. Besenbacher, Science, 2008, 320, 1755 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Chisaka, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2018, 20, 15613 RSC.
- M. Chisaka and H. Morioka, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2019, 9, 611 RSC.
- S. Trasatti, Pure Appl. Chem., 1986, 58, 955 CrossRef CAS.
- M. García-Mota, A. Vojvodic, H. Metiu, I. C. Man, H. Y. Su, J. Rossmeisl and J. K. Nørskov, ChemCatChem, 2011, 3, 1607 CrossRef.
- H. A. Gasteiger, J. E. Panels and S. G. Yan, J. Power Sources, 2004, 127, 162 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Chisaka and H. Daiguji, Electrochem. Commun., 2006, 8, 1304 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Henning, R. Shimizu, J. Herranz, L. Kühn, A. Eychmüller, M. Uchida, K. Kakinuma and T. J. Schmidt, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2018, 165, F3001 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Tamaki, H. Kuroki, S. Ogura, T. Fuchigami, Y. Kitamoto and T. Yamaguchi, Energy Environ. Sci., 2015, 8, 3545 RSC.
- P. von Tettau, S. Sterlepper, P. Mauermann, M. Wick, S. Tinz, M. Jesser, M. Walters and S. Pischinger, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 52, 1127 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Goswami, A. N. Mistry, J. Grunewald, T. F. Fuller and P. P. Mukherjee, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2020, 167, 084519 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Goswami, J. B. Grunewald, T. F. Fuller and P. P. Mukherjee, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022, 10, 15101 RSC.
- N. Goswami, J. B. Grunewald, T. F. Fuller and P. P. Mukherjee, Electrochim. Acta, 2024, 486, 144143 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Goswami, K. Chen, X. Wang, J. S. Spendelow, R. L. Borup and P. P. Mukherjee, Chem. Eng. J., 2024, 484, 149672 CrossRef CAS.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |
