Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Environmental drivers of monomethylmercury photodegradation along the land-to-ocean aquatic continuum†
Sonja
Gindorf
 a,
Johannes
West
ab,
Andrew
Graham
a,
Johannes
West
ab,
Andrew
Graham
 c and
Sofi
Jonsson
c and
Sofi
Jonsson
 *a
*a
aDepartment of Environmental Science, Stockholm University, Sweden. E-mail: sofi.jonsson@aces.su.se
bScripps Institution of Oceanography, University of California San Diego, USA
cDepartment of Chemistry, Grinnell College, Iowa, USA
First published on 9th January 2025
Abstract
In surface waters, photodegradation is a major abiotic removal pathway of the neurotoxin monomethylmercury (MMHg), acting as a key control on the amounts of MMHg available for biological uptake. Different environmental factors can alter the rate of MMHg photodegradation. However, our understanding of how MMHg photodegradation pathways in complex matrixes along the land-to-ocean aquatic continuum respond to changes in salinity, dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentration and dissolved organic matter (DOM) composition is incomplete. In a set of laboratory experiments combining several artificial and natural waters, we demonstrate that the interplay of DOC concentration, DOM composition, and salinity affects the photodegradation rate of MMHg. The presence of DOM was found to facilitate MMHg photodegradation, but degradation rates were not altered by varying DOC concentrations over two orders of magnitude. We found DOM composition to have a stronger effect on MMHg photodegradation rates than DOC concentration. However, at high DOC levels, where most UV radiation was lost within the first cm of the reaction vessels, lower MMHg photodegradation rates were observed. When moving from terrestrially influenced waters, characterized by a high degree of humification, towards marine conditions with a protein-rich DOM pool, MMHg photodegradation rates increased. In contrast, salinity had a stabilizing effect on MMHg. Hence, especially in systems with low salt and DOC concentrations, changes in either salinity or DOC concentration can impact the photodegradation rates of MMHg.
Environmental significanceThe neurotoxin monomethylmercury (MMHg) poses a concern to human and environmental health due to its biomagnification, especially in aquatic ecosystems. Besides the formation of MMHg, its environmental degradation processes play a key role in controlling the amounts of MMHg available for biological uptake. This work improves our understanding of how the interplay of different environmental drivers affects MMHg photodegradation rates along the land-to-ocean aquatic continuum represented by both, natural and artificial waters. |
1. Introduction
The biomagnification of monomethylmercury (MMHg) in aquatic ecosystems poses a concern to wildlife and human health. In the environment, the availability of MMHg for biological uptake is controlled by its formation and degradation processes, among which photodegradation is a dominant removal pathway within the photic zone.1 However, we still do not fully understand how changes in salinity, dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentration and dissolved organic matter (DOM) quality along the land-to-ocean aquatic continuum alter MMHg photodegradation rates.Anthropogenic emissions of Hg (e.g., from fossil fuel burning) have heavily altered its biogeochemical cycle.2 Once emitted, Hg can be transported over long distances in the atmosphere in its elemental form (Hg0) and deposited e.g., in fresh- or seawater as divalent mercury (HgII) where microbes can methylate the HgII to the neurotoxin MMHg. It was long thought that bacterial methylation was a strictly anoxic process, which led to the understanding that biogenic formation and photochemical degradation of MMHg would occur in separate environments. Today, we know, however, that Hg methylation can also happen in surface waters.3 The concentrations of MMHg in natural waters typically range up to 5 pM in freshwater systems4 and up to 0.5 pM in the open ocean.5 Although lower concentrations of MMHg are expected in marine waters, marine harvested seafood is the main exposure pathway of Hg in many populations.6 Besides its sources, the environmental sinks of MMHg along the land-to-ocean aquatic continuum play a crucial role in determining aqueous MMHg concentrations. Among these sinks, photodegradation has been identified as an especially important abiotic removal pathway in sunlit surface waters.1,7–11 The degradation rate of MMHg through photochemical processes, however, differs among water types as it is influenced not only by the intensity and wavelength distribution of incoming light but also by the properties of the water.8,12,13
DOM is a key property changing along the freshwater to marine aquatic continuum, and both DOM quantity and composition have been shown to play an important role in the photodegradation of MMHg.14–16 Two main reaction pathways for MMHg photodegradation in the presence of DOM are discussed in the literature: direct and indirect photochemical degradation. Direct photochemical degradation of MMHg relies on light absorption by the DOM part of the MMHg–DOM complex. The energy is then transmitted to the Hg atom, and cleavage of the C–Hg bond is facilitated by the weakening of the bond due to the complexation of Hg to reduced sulfur sites on the DOM.17 In a similar way, indirect photochemical degradation of MMHg is believed to be facilitated by the weakening of the Hg–C bond by complexation of MMHg to the DOM, but here, the energy comes from a photochemically produced reactive intermediate (PPRI) instead of an intramolecular transfer of energy.18–21 The production of these PPRI is mainly facilitated by the chromophoric fraction of DOM (CDOM). As CDOM absorbs light, the triplet excited state 3DOM* is formed, which is a PPRI itself and also further involved in the formation, as well as inhibition, of other PPRI, such as carbonate radicals (CO3−˙) and reactive oxygen species (ROS), including hydroxyl (˙OH), singlet oxygen (1O2), and superoxide (O2˙−) radicals.22 Several studies have demonstrated PPRI to play a major role in the photodegradation of MMHg.16,21,23,24
In addition to weakening the Hg–C bond and facilitating the cleavage of the Hg–C bond by directly or indirectly transferring the energy of incoming light, DOM also limits the depth at which incoming light may penetrate the water column. Across natural gradients, both, the concentration and composition of DOM, can differ greatly. Hence, when transitioning from terrestrial to marine waters, changes in DOM concentration and composition accompany a change in light absorption, which has important implications for the wavelength-dependent MMHg photodegradation. While UVB and UVA are much more effective in MMHg degradation than photosynthetically active radiation9,11,25 (PAR; e.g., relative MMHg degradation efficiency ratios PAR![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) UVA
UVA![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) UVB of 1
UVB of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 43
43![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3100,23 and 1
3100,23 and 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 37
37![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 400,
400,![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 26 UV radiation penetrates only the uppermost layer of the water column, whereas PAR can reach deeper down.8,26
26 UV radiation penetrates only the uppermost layer of the water column, whereas PAR can reach deeper down.8,26
Salinity is another water property influencing the photochemical degradation rate of MMHg along the land-to-ocean aquatic continuum. In artificial solutions where salt has been dissolved in purified water,27 and across natural gradients with varying salinity,26 higher salt content has been shown to slow MMHg photodegradation rates. Two main explanations have been provided to explain this effect; potential changes in the chemical complexation of MMHg7,19 and the change in PPRIs produced.28
Despite a large body of research on MMHg photodegradation, it remains challenging to relate MMHg photodegradation rates to changes in environmental factors, such as DOC concentration,12,26 DOM composition,8,14,18,29 salinity,26,27,30 and PPRIs.16,24 The interplay of these different environmental factors may affect MMHg photodegradation along the land-to-ocean aquatic continuum in ways not observed when studying these parameters in isolation. However, little attention has been paid to the broad transect from freshwater to oceanic waters or how DOC concentration and salinity interact with regards to MMHg photodegradation. Here, we test the role of DOM composition and quantity as well as salinity on the photodegradation of MMHg using a wide range of waters characteristic of the whole spectrum from fresh to oceanic waters. In addition, we tested the most prominent environmental parameters driving this gradient, salinity and DOC, in isolation as well as their combined effects. Building on previous work, this study provides new insights into how salinity and DOM affect MMHg photodegradation across terrestrially-influenced to marine waters.
2. Material and methods
2.1 Natural waters
Seawater from the Arctic Ocean (AOW) was collected in September 2018 during the SWEDARCTIC cruise (5 m water depth). The sample was stored frozen at −20 °C until use. Baltic Sea brackish water (BSW) was collected from the shore of Lilla Värtan in the Stockholm Archipelago. The pond water sample (Pond) was collected from Laduviken in Norra Djurgården, Stockholm. BSW and Pond water samples were collected within 24 hours prior to experiments and stored refrigerated at 4 °C until use.2.2 Solutions and standards
The DOC concentrations and FDOM characterization of the working solutions were determined using a TOC analyzer and Horriba aqualog as described below. For use in experiments, the respective volume of working solution was pipetted into the reaction flasks filled with ultrapure water.
CAUTION: DMHg is an extremely toxic and volatile compound that may quickly penetrate regular laboratory gloves.
2.3 Experimental setup
Table S1† gives an overview of the waters used in each of the experiments.The experimental setup in this study was modified from West et al. (2022).34 Custom-made quartz glass bottles were placed in boxes that only allowed light to pass through high-pass filters. The filters have a 50% cut-off at 305 nm, transmitting UV wavelengths in a range close to natural sunlight. The boxes were fixed to a rotating disk (1 rotation per minute) around a stationary xenon UV lamp (Osram SUPRATEC HTC 400-241). The lamp was cooled using an air stream. MM200Hg was added to the samples to concentrations of 1.3–4.3 ng L−1 for all experiments and allowed to equilibrate in the dark for two hours before initiating the experiments. The influence of MMHg concentration on kd MMHg was ruled out as kd MMHg was independent of MMHg concentration over the concentration range of 0.2 to 726 ng L−1 (Fig. S1†). Along with the MM200Hg tracer, 1.3–4.5 ng L−1of DM204Hg was added to the reaction vessels (photochemical degradation of DMHg will be discussed elsewhere). Measurement of in-bottle temperature revealed the sample temperature to be 34.5 °C after the first 30 minutes of light exposure and to reach 54 °C after 220 minutes. In a previous control experiment, we observed no loss of MMHg in dark incubations at 40 °C over the course of 6 hours for several water types (water from the Arctic Ocean, Baltic Sea, a DOC-rich stream, artificial seawater, and ultrapure water).34 As no degradation was observed in control experiments carried out at 40 °C for 6 hours, and the changes in concentration of MMHg over the course of the experiments fits well with the first order kinetic model used, we assume that although the temperature exceeded 40 °C, the temperature did not play a role for the concentrations of MMHg detected.
Upon subsampling, 9.6 mL of the sample was transferred to a subsample vial filled with purified water, internal standards 199HgII, MM201Hg, and DMHg (natural abundance), and 225 μL 2 M acetate buffer. The three internal standards were used to quantify the remaining MM200Hg as well as potential products simultaneously at each timepoint. To preserve the headspace volume, 9.6 mL of sample water without Hg addition was returned to the reactor flasks, which were then quickly closed.
In four different waters (ultrapure water with 35 g L−1 NaCl, AOW, BSW, Pond), the effect of O2 removal was tested. The waters were purged with N2 gas while heated to a boil and cooled to room temperature. Less than 20% of water volume was lost during the heating. The degassed waters were transferred into the reactor flasks under oxygen-free conditions in a glovebox. Before select experiments, the O2 concentrations were measured, and over 90% of O2 was found to have been removed. We tested for the reintroduction of O2 during the experiments and subsampling and found less than 30% O2 compared to the untreated sample concentrations at the end of a 4-sampling point experiments.
2.4 Analytical methods
2.5 Data processing
Hg species concentrations were quantified using internal standards (199HgII, MM201Hg) and signal deconvolution.36 Under the assumption that photodegradation follows pseudo-first-order kinetics, kd MMHg was calculated as the slope from ln([MM200Hg]t) as a function of time t (per day), following eqn (1):| [MM200Hg]t = [MM200Hg]0e−kd MMHgt | (1) |
Different DOM fluorescence indices were computed using the dreem toolbox Version 0.6.4 for Matlab. The fluorescence Index represents the ratio of the emission intensities at 470 nm and 520 nm at 370 nm excitation.37 The freshness index is calculated from the emission intensity at 380 nm divided by the maximum emission intensity between 420 and 435 nm at an excitation wavelength of 310 nm.38 The humification index is defined as the area under the emission spectra from 435 to 480 nm divided by the emission peak area from 300 to 345 nm plus the peak area of 435 to 480 nm, all at an excitation of 254 nm.39 The biological index is calculated as the emission intensity at 380 nm divided by the emission intensity at 430 nm at 310 nm excitation wavelength.40
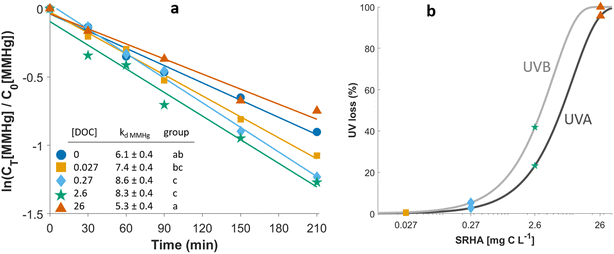
The relative loss of actinic flux (total amount of UV lost along the 6 cm long reaction flask) was calculated using the relative distribution of different UV wavelengths from the UV lamp (provided by the manufacturer (Osram SUPRATEC HTC 400-241)) and UV absorbance measurements for the different waters (5 nm increments). For SRHA, the relative loss of actinic flux was modeled by predicting the absorbance of UV radiation at a specific wavelength from the absorbance measured at 0.026, 0.26, 2.7 and 27 mg C L−1 of SRHA (Fig. 1b).
Statistical analysis to test for significant differences between treatments was performed in Matlab (version 2023a) using the aoctool for ANOVA analysis and multcompare function for post hoc tests.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) K) of 5.4 for MMHgCl,41 and 16.1 to 17.4 for MMHg-DOC (aq.) together with the concentrations of thiols (calculated as 0.15% × DOC), MMHg, and Cl.42,43
K) of 5.4 for MMHgCl,41 and 16.1 to 17.4 for MMHg-DOC (aq.) together with the concentrations of thiols (calculated as 0.15% × DOC), MMHg, and Cl.42,43
3. Results and discussion
We observed a decline in MMHg concentrations over the course of the experiments across all treatments (Fig. 1, 2 and S1–S12†). As no demethylation of MMHg was observed in dark controls over 6 hours at comparable temperatures for a collection of natural and artificial waters,34 we attribute the MMHg demethylation in our experiments to photochemical processes. For our different waters, the sum of recovered tracer (MM200Hg + 200HgII) ranges from 32 to 116% at the last time point (67 ± 18%, relative to T0) (Table S1†). The experiments and sampling protocols were designed to avoid loss of volatile Hg species (Hg0 and DMHg), and only trace levels (<5% of our tracer) was found as Hg0 at the end of our experiments (estimation based on the peak for Hg0 and internal standard used for quantification of DMHg). The lower recovery observed for some of our waters is thus more likely attributed to the adsorption of Hg to the reaction flask walls. Recoveries show a matrix effect, with poor results primarily in DOM-rich waters. In the same flasks, recoveries for the DMHg tracer were consistently good (57–97% at the last timepoint averaged per treatment), despite substantial degradation of DMHg to MMHg, suggesting that low MMHg tracer recoveries result from poor HgII recovery, not MMHg adsorption to flask walls.3.1 Role of DOC concentration
To study the impact of DOC concentration isolated from other drivers, we compared the rate of MMHg photodegradation in ultrapure water containing 0 to 26 mg C L−1 of SRHA (Fig. 1a & S3†). We observed the highest photodegradation rates in the treatments with low to intermediate concentrations of SRHA (0.027 to 2.6 mg C L−1), demonstrating that DOC concentration plays an important role in MMHg photodegradation. Significantly slower rates of MMHg degradation were measured in the solution with the highest concentration of SRHA (27 mg C L−1) and the ultrapure water without SRHA addition.Many studies have previously demonstrated low or no effect of DOC concentration on the photodegradation rate of MMHg (e.g., DOC ranges tested: 0.8–4.6,8 5–30,29 8.5–36.3,14 and 1.5–11.3 (ref. 26) mg C L−1). In line with these previous findings, our study supports that over a wide range (2 orders of magnitude; 0.027–2.6 mg C L−1), DOC concentration does not affect MMHg degradation rates. By combining the relative contribution of different wavelengths of our UV lamp and the measured absorbance of all waters used in this study, we estimate the integrated actinic flux relative to incoming UV radiation (Table S2,†Fig. 1b). Despite a partial loss of UV radiation at 2.6 mg C L−1 (50 and 30% for UVB and UVA, respectively, throughout the 6 cm long reaction flask), the kd MMHg was not statistically different from the kd MMHg determined at lower concentrations of SRHA (where less than 7 and 4% of UVB and UVA, respectively, was lost). These findings agree with those of Black et al. (2012),26 who only observed small changes in MMHg photodegradation rates over DOC concentrations ranging from 1.5 to 11.3 mg C L−1, despite notable loss in the absorption of light (52% of UVB and 30% of UVA along the optical pathway at DOC concentration of 11.3 mg C L−1). These observations align with earlier ideas that DOC concentration does not affect MMHg photochemical degradation as long as sufficient thiol groups are available to complex MMHg (and supporting the intramolecular charge transfer from 3DOM* to the Hg–C bond).21 At our highest concentration of SRHA (27 mg C L−1), most of the UV radiation (97 and 53% of UVB and UVA, respectively) was lost in the first cm of the reaction flasks optical pathway (total length of 6 cm), suggesting that absence of UV radiation in a significant fraction of the water inside each flask during the experiment resulted in lower kd MMHg. Additionally, this inhibiting effect of high DOM levels on MMHg photodegradation may be explained by excess DOM diluting the fraction of photosensitized DOM associated with MMHg. This may also co-occur with an increased rate of PPRI quenching induced by DOM, in agreement with the findings of Klapstein et al. (2018),12 who observed a negative linear relationship between DOC concentration and photodegradation (DOC range: 3.9–16.4 mg C L−1). In natural systems, DOC controls the depth at which light of different wavelengths penetrates. Hence, DOC concentration may control the depth at which photochemical degradation occurs throughout a water column. However, our results suggest that the photodegradation rate cannot simply be assumed to follow changes in the UV radiation with depth.
3.2 Role of salinity
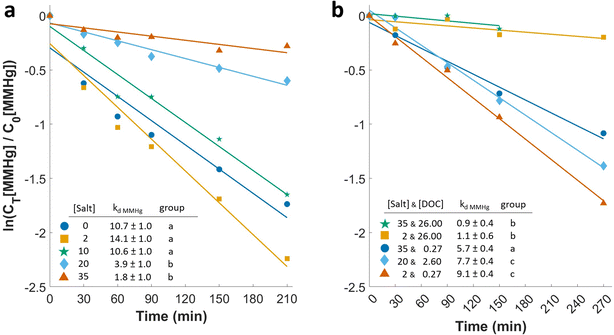
The land-to-ocean aquatic continuum is characterized by a large gradient in salinity. In our experiment exploring the role of salinity in the absence of DOM, we observed significantly higher kd MMHg at lower salinity (0–10 g L−1 of NaCl) than at higher salinities (20 and 35 g L−1 NaCl; p < 0.001, Fig. 2a & S4†). This aligns with previous reports of salinity having a photostabilizing effect on MMHg. For instance, Sun et al. (2013)27 observed slower MMHg degradation in salt solutions compared to water without salt. The same study showed no differences in MMHg degradation when varying the type of chloride salts used (KCl, NaCl, and MgCl2), illustrating that Cl− is the key driver rather than the cation.In all natural waters, DOM is present; hence, the effect of changes in Cl− concentrations on kd MMHg needs to be studied in combination with DOM. We investigated the combined effect of these parameters on MMHg photodegradation in solutions with different concentrations of SRHA (0.27, 2.6, or 27 mg C L−1) and NaCl (2, 20, or 35 g L−1) (Fig. 2b & S5†). The highest rates of MMHg photodegradation were measured for treatments with low and medium DOC and salt concentrations (0.27 mg C L−1, 2 g L−1 NaCl and 2.6 mg C L−1, 20 g L−1 NaCl, respectively). We observed lower kd MMHg in the low DOC-high salt solution (0.27 mg C L−1, 35 g L−1 NaCl). MMHg photodegradation was slowest in the high DOC treatments, regardless of the salt concentration (27 mg C L−1, 2 or 35 g L−1 NaCl).
The decrease of kd MMHg with a salt concentration in the low DOC treatments (a 37% decrease in kd MMHg when increasing NaCl from 2 to 35 g L−1) reveals that salinity can slow down MMHg photodegradation when DOM is limited. A negative effect of salinity on the photochemical degradation rates of MMHg in the presence of DOM has previously been observed by Black et al. (2012),26 who conducted experiments with three different DOM extracts combined in different proportions with artificial sea salt (1.5 to 11 mg C L−1 of DOC and 5 to 25 g L−1 of salt). For all of their DOM extracts, and regardless of DOC concentration, an increase in salinity from 5 to 25 resulted in a decrease in the kd MMHg, on average ∼20%. In contrast, Di Mento and Mason (2017)8 observed an 8% increase in kd MMHg when raising the Cl− concentration from ∼0.3 to 330 mM (corresponding to a salinity of around 20 g L−1) in water collected from Shetucket River (DOC concentration of ca. 2 mg C L−1).
Chemical speciation of MMHg has previously been discussed as a potential explanation for the lower photochemical degradation rates observed in coastal and marine waters. For example, Zhang & Hsu-Kim (2010)19 interpreted lower photochemical degradation rates of MMHg in marine water to be related to complexation with Cl−, compared to MMHg complexed to DOM ligands. Recently revised thermodynamic stability constants for Hg-DOM complexes support, however, that DOM is also the main complexing agent for Hg in most marine waters.41 This was also true for our systems testing the effect of salinity in the presence of SRHA (thermodynamic speciation model results presented in Table S3†), as well as for similar experiments conducted by Black et al. (2012).26 Instead, the reduced photochemical degradation rates observed at higher salinities in the presence of DOM may relate to the PPRIs present at these conditions. For instance, DOM-chloride interactions may facilitate the photochemical production of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2),44 a precursor for ˙OH.45 Chloride may also react with both ˙OH and 3DOM* to create chlorine radicals.46 Our results of MMHg photostabilization at higher Cl− may thus be explained by e.g., the depletion of 3DOM* by Cl− at higher salinity.
Being a key precursor for ROS as well as an important agent for quenching 3DOM*, O2 plays a crucial role in controlling the formation and steady-state concentrations of PPRIs in natural waters.47 To explore the role of O2 on MMHg photodegradation, we carried out a set of experiments where oxygen-depleted waters were compared to untreated controls (Fig. S6–S10†). Tested waters include ultrapure water with 35 g L−1 NaCl and natural waters representing a gradient along the land-to-ocean continuum: pond (DOC: 14 mg C L−1, salinity of 0.6‰), BSW (DOC: 8.1 mg C L−1, salinity of 2.3‰) and AOW (DOC: 2.3 mg L−1, salinity of 31‰). While we saw no effect in the Pond and brackish water, we found opposing trends in the 35 g L−1 NaCl water (decrease in kd MMHg with O2 removal) and AOW (enhanced kd MMHg with O2 removal) (Fig. S10†). While the identities of the ROS and mechanisms cannot be fully constrained from the available data, the observed differences may be related to different PPRIs dominating in the different waters. In the two salt-rich waters, we can expect halogen radicals to play a more important role, which further affect the concentrations of other PPRIs (e.g. scavenging of ˙OH).46 In oligotrophic waters, ˙OH has been shown to facilitate MMHg photodegradation.48 That deoxygenation did not affect kd MMHg in the Pond and BSW samples may hint that direct absorption dominates the photodegradation process in these waters, as previously suggested for other terrestrially influenced waters.16,49
3.3 Role of DOM source
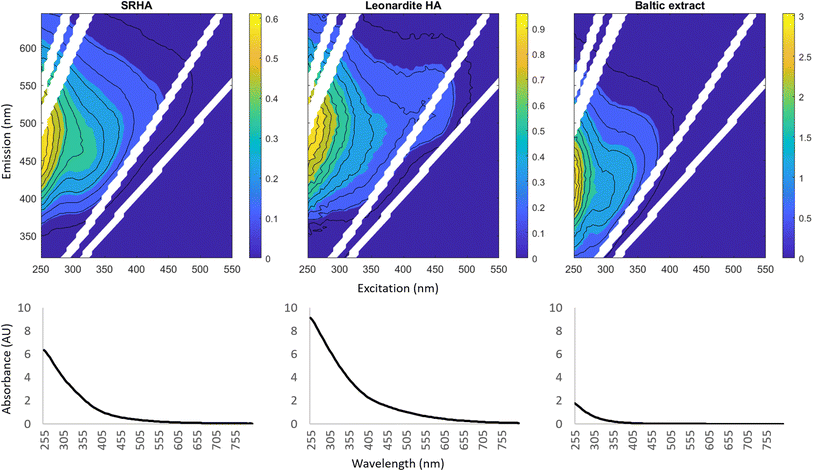
We tested the effect of different DOM sources on MMHg photodegradation rates using two commercially available DOM extracts (SRHA and LHA) and DOM we extracted from Baltic Sea water (BS-DOM). To distinguish concentration and composition-derived effects, solutions containing the different extracts were prepared to a concentration of 2.6 mg C L−1. The comparison was done in two sets of experiments with SRHA compared to the BS-DOM (Fig. S11†) in the first set and LHA in the second (Fig. S12†). Combined, these two sets revealed the following order for the photochemical degradation rates of MMHg: kd MMHg BS-DOM > kd MMHg SRHA ∼ kd MMHg LHA (Fig. S11 and S12†). Although the order of kd MMHg among these three waters is in agreement with differences in UV light attenuation (9.5, 48, and 65% loss for UVB and 2.9, 27, and 44% loss for UVB for the BS-DOM, SRHA, and LHA waters, respectively; Table S2†), the attenuation of light does not appear to explain the faster kd MMHg observed for BS-DOM. We base this argument on the fact that the level of UV attenuation in the BS-DOM treatment is comparable to that in the SRHA treatment at 0.27 mg C L−1 (around 6–10% loss of UVB and 3% loss of UVA throughout the 6 cm long reaction vessel, Table S2†). Yet, we observed 2.6 times higher kd MMHg in the BS-DOM compared to the SRHA solution (at 0.27 mg C L−1) despite comparable UV loss. In contrast, we do not find differences in the kd MMHg among the SRHA solutions over two orders of magnitude of DOC concentration (0.027–2.6 mg C L−1). Altogether, this suggests that the differences in light attenuation alone cannot explain the order of kd MMHg observed for the BS-DOM, SRHA, and LHA waters, and that the properties of DOM influence MMHg photodegradation.Characterization of the DOM extracts with fluorescence and absorbance measurements revealed distinct differences between SHRA, LHA and BS-DOM. The fluorescence emission excitation matrices (Fig. 3) show that in contrast to fulvic and humic acid-dominated SRHA and LHA, the BS-DOM extends far into protein-like fluorescence (as indicated by the signals in the lower UV region). These patterns are also demonstrated when comparing indices calculated from pre-defined fluorescence peaks (Table S4, further discussion in ESI (Section S1†)). Based on these distinctions, we find that kd MMHg decreases among the three DOM extracts from the least to the most humified: BS-DOM > SRHA > LHA. Our observations are in line with earlier work from Kim et al. (2018)30 who observed higher kd MMHg when a DOM extract primarily consisting of microbial DOM (Pony Lake fulvic acid) was added to artificial estuarine water in comparison to when terrestrially derived humic- or fulvic acids (SRHA and SRFA) were used. Higher kd MMHg have also been observed for SRFA in comparison to SRHA by Kim and Zoh (2013),18 although this was not observed by Kim et al. (2018)30 who compared the same extracts. It is possible that the source of the water impacted these differences, as Kim et al. (2018)30 dissolved the DOM in artificial estuarine water, while Kim and Zoh (2013)18 used purified water. Water chemistry, including trace elements and salt constituents can alter the formation and quenching of the PPRI44,46,50,51 and thus the photodegradation of MMHg in natural waters. Kim et al. (2018)30 also attribute the accelerated rates of MMHg degradation in microbial DOM compared to SRFA to PPRIs, as microbial DOM typically results in higher steady-state concentrations of 1O2 and 3DOM*.52–54 Recent work in the field of DOM photochemistry has revealed that based on the source and humification state of DOM, two different photochemical processes occur: photo-humification of protein-rich DOM and photo-bleaching of humic substances. These two processes can occur simultaneously in the water column and affect the reactivity and PPRI interactions of the respective DOM. While in photo-humification 3DOM* is the dominant PPRI involved, ROS are the most critical species in photo-bleaching.55 Hence, we hypothesize 3DOM* to be an important driver for higher kd MMHg in the BS-DOM solution compared to the waters with the two humic acid extracts.
3.4 Environmental drivers of MMHg photodegradation along the land-to-ocean continuum
Building on previous work, we here further advance our understanding of the role that different environmental drivers play in the photochemical degradation of MMHg along the terrestrial freshwater to marine aquatic continuum (Fig. 4). In all of the presented experiments, photochemical degradation was studied using radiation from a UV lamp (further described in West et al. 2022).34 Although the lamp simulates solar radiation based on the emitted wavelength spectra, the rates reported are not necessarily representative of the rates expected under natural sunlight. However, we demonstrated in one of our previous studies that our experimental setup is appropriate for mechanistic studies of photochemical degradation of methylated Hg species by comparing the results to experiments in natural sunlight.34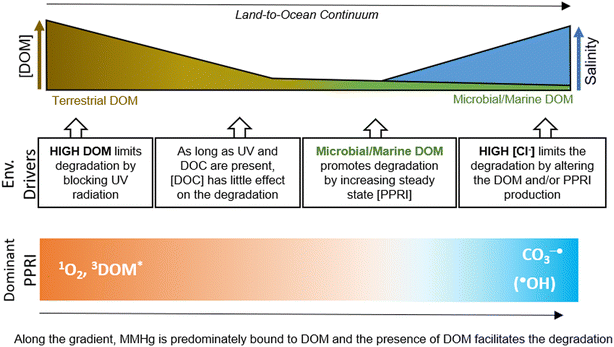 | ||
| Fig. 4 Conceptional illustration of environmental drivers (Env. Drivers) altering the photochemical degradation rates of MMHg along the land (left) to ocean (right) continuum with changes in DOM concentration, quality and salinity (top), environmental drivers (middle) and dominant photochemically produced reactive intermediates (PPRIs) (bottom) along the gradient presented as expected based on Vähätalo et al. (2022).50 | ||
In line with earlier work, our data supports DOM to play a central role in the photochemical degradation of MMHg in natural waters. At high DOC concentrations, where almost all UV radiation is lost due to light attenuation, the shielding of incoming light limits the demethylation rate. However, at lower DOC concentrations, DOM facilitates the photochemical degradation of MMHg. As long as the loss of UV radiation is low or moderate (in our experiment, around 50% for UVB), increasing DOC concentration does not appear to affect the kd MMHg. Along the gradient from terrestrial to marine systems, the transition from a humic-like, highly degraded DOM pool to a more labile, protein-rich DOM pool promotes photodegradation of MMHg. While the properties of humic-like DOM in terrestrial systems may impact MMHg photodegradation, the effect of DOM composition is small compared to when transitioning from humic-like terrestrially derived to aquatic in situ produced DOM. In marine systems, where low concentrations of DOC are expected, photo-humification of protein-rich DOM may facilitate the photochemical degradation of MMHg. Although the salinity typically does not alter the chemical speciation of MMHg (as it remains complexed to DOM), increased salt concentrations lower the rate of MMHg photodegradation. We suggest that our experiments testing the effects of salinity and DOM represent a shift in dominant PPRI from CO3−˙ and ˙OH in the high saline–low DOC (or no DOM) waters to 1O2 and 3DOM* in the DOC-rich waters (Fig. 4).50 Overall, MMHg photodegradation is driven by a complex interplay of environmental drivers, including DOC concentration, DOM composition, and salinity, and when isolating these drivers, the effects they express when combined may be missed. Our results support, along with previous studies, that in systems with low to intermediate salt and DOC concentrations, changes in one of the two can alter the kd MMHg. This might have especially relevant implications for the management of estuarine and coastal regions, which are also the areas expected to change most drastically due to land use and climate change when it comes to input of terrestrial DOM and Hg. For instance, browning of coastal waters, may result in a more humic-like DOM pool, which also may result in lower MMHg degradation rates. While browning of freshwaters may not necessarily alter the net photochemical degradation of MMHg, it could have a significant impact in clear lakes by reducing the depths of UV light penetration.56
Data availability
The data supporting this article have been included as part of the ESI.†Author contributions
SG: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, validation, visualization, writing – original draft, writing – review & editing. JW: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, validation, visualization, writing – review & editing. AG: conceptualization, writing – review & editing. SJ: conceptualization, funding acquisition, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, resources, supervision, validation, writing – original draft, writing – review & editing.Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the EU H2020 (Grant No. 860497), the Swedish Research Council (2017-05275 to S. J.), and Stockholm University. Seawater was collected with financial and logistical support from the Swedish Polar Research Secretariat (Arctic Ocean) and the Stockholm University Baltic Sea Centre (to S. G.).References
- P. Sellers, C. A. Kelly, J. W. M. Rudd and A. R. MacHutchon, Photodegradation of methylmercury in lakes, Nature, 1996, 380, 694–697 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Outridge, F. Wang, R. Mason, S. Guerrero and L. Heimbürger-Boavida, Updated Global and Oceanic Mercury Budgets for the United Nations Global Mercury Assessment 2018, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2018, 52(20), 11466–11477 CAS.
- M. Monperrus, E. Tessier, D. Amouroux, A. Leynaert, P. Huonnic and O. F. X. Donard, Mercury methylation, demethylation and reduction rates in coastal and marine surface waters of the Mediterranean Sea, Mar. Chem., 2007, 107, 49–63 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Gojkovic, A. Skrobonja, C. Funk, I. Garbayo and C. Vílchez, The Role of Microalgae in the Biogeochemical Cycling of Methylmercury (MeHg) in Aquatic Environments, Phycology, 2022, 2, 344–362 CrossRef.
- B. Gworek, O. Bemowska-Kałabun, M. Kijeńska and J. Wrzosek-Jakubowska, Mercury in Marine and Oceanic Waters—a Review, Water, Air, Soil Pollut., 2016, 227, 371 CrossRef.
- C. T. Driscoll, R. P. Mason, H. M. Chan, D. J. Jacob and N. Pirrone, Mercury as a global pollutant: Sources, pathways, and effects, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2013, 47, 4967–4983 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Luo, Q. Cheng and X. Pan, Photochemical behaviors of mercury (Hg) species in aquatic systems: a systematic review on reaction process, mechanism, and influencing factor, Sci. Total Environ., 2020, 720, 137540 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. P. DiMento and R. P. Mason, Factors controlling the photochemical degradation of methylmercury in coastal and oceanic waters, Mar. Chem., 2017, 196, 116–125 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Li, X. Han and Y. Li, Mechanism of methylmercury photodegradation in the yellow sea and East China Sea: dominant pathways, and role of sunlight spectrum and dissolved organic matter, Water Res., 2024, 251, 121112 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. R. Hammerschmidt and W. F. Fitzgerald, Photodecomposition of methylmercury in an arctic Alaskan lake, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2006, 40, 1212–1216 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Li, Y. Mao, G. Liu, G. Tachiev, D. Roelant, X. Feng and Y. Cai, Degradation of methylmercury and its effects on mercury distribution and cycling in the Florida everglades, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2010, 44, 6661–6666 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. J. Klapstein, S. E. Ziegler and N. J. O'Driscoll, Methylmercury photodemethylation is inhibited in lakes with high dissolved organic matter, Environ. Pollut., 2018, 232, 392–401 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Sun, D. Wang, W. Mao, S. Zhao and C. Zhang, Photodegradation of methylmercury in Jialing River of Chongqing, China, J. Environ. Sci., 2015, 32, 8–14 CrossRef CAS.
- J. A. Fleck, G. Gill, B. A. Bergamaschi, T. E. C. Kraus, B. D. Downing and C. N. Alpers, Concurrent photolytic degradation of aqueous methylmercury and dissolved organic matter, Sci. Total Environ., 2014, 484, 263–275 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Zhang, Y. Yin, Y. Li, Y. Cai and J. Liu, Critical role of natural organic matter in photodegradation of methylmercury in water: molecular weight and interactive effects with other environmental factors, Sci. Total Environ., 2017, 578, 535–541 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Tai, Y. Li, Y. Yin, L. J. Scinto, G. Jiang and Y. Cai, Methylmercury photodegradation in surface water of the Florida everglades: importance of dissolved organic matter-methylmercury complexation, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2014, 48, 7333–7340 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Kim, J. Yang, Y. Lee, G. Lee, W. Lee and S. Han, Contribution of dissolved organic matter to the photolysis of methylmercury in estuarine water, Mar. Chem., 2018, 207, 13–20 CrossRef CAS.
- M. K. Kim and K. D. Zoh, Effects of natural water constituents on the photo-decomposition of methylmercury and the role of hydroxyl radical, Sci. Total Environ., 2013, 449, 95–101 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Zhang and H. Hsu-Kim, Photolytic degradation of methylmercury enhanced by binding to natural organic ligands, Nat. Geosci., 2010, 3, 473–476 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Suda, M. Suda and K. Hirayama, Degradation of methyl and ethyl mercury by singlet oxygen generated from sea water exposed to sunlight or ultraviolet light, Arch. Toxicol., 1993, 67, 365–368 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Qian, X. Yin, H. Lin, B. Rao, S. C. Brooks, L. Liang and B. Gu, Why Dissolved Organic Matter Enhances Photodegradation of Methylmercury, Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett., 2014, 1, 426–431 CrossRef CAS.
- K. McNeill and S. Canonica, Triplet state dissolved organic matter in aquatic photochemistry: reaction mechanisms, substrate scope, and photophysical properties, Environ. Sci.:Processes Impacts, 2016, 18, 1381–1399 RSC.
- C. Fernández-Gómez, A. Drott, E. Björn, S. Díez, J. M. Bayona, S. Tesfalidet, A. Lindfors and U. Skyllberg, Towards universal wavelength-specific photodegradation rate constants for methyl mercury in humic waters, exemplified by a boreal lake-wetland gradient, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2013, 47, 6279–6287 CrossRef.
- X. Han, Y. Li, D. Li and C. Liu, Role of Free Radicals/Reactive Oxygen Species in MeHg Photodegradation: Importance of Utilizing Appropriate Scavengers, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2017, 51, 3784–3793 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Lehnherr and V. L. St, Louis, Importance of ultraviolet radiation in the photodemethylation of methylmercury in freshwater ecosystems, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2009, 43, 5692–5698 CrossRef CAS.
- F. J. Black, B. A. Poulin and A. R. Flegal, Factors controlling the abiotic photo-degradation of monomethylmercury in surface waters, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2012, 84, 492–507 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Sun, D. Wang, Y. Zhang, W. Mao, T. Zhang, M. Ma and C. Zhang, Photo-degradation of monomethylmercury in the presence of chloride ion, Chemosphere, 2013, 91, 1471–1476 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Tang, Z. Cui, Y. Bai and R. Su, Indirect photodegradation of sulfathiazole and sulfamerazine: influence of the CDOM components and seawater factors (salinity, pH, nitrate and bicarbonate), Sci. Total Environ., 2021, 750, 141762 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. D. Jeremiason, J. C. Portner, G. R. Aiken, A. J. Hiranaka, M. T. Dvorak, K. T. Tran and D. E. Latch, Photoreduction of Hg(II) and photodemethylation of methylmercury: the key role of thiol sites on dissolved organic matter, Environ. Sci.:Processes Impacts, 2015, 17, 1892–1903 RSC.
- J. Kim, J. Yang, Y. Lee, G. Lee, W. Lee and S. Han, Contribution of dissolved organic matter to the photolysis of methylmercury in estuarine water, Mar. Chem., 2018, 207, 13–20 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Dittmar, B. Koch, N. Hertkorn and G. Kattner, A simple and efficient method for the solid-phase extraction of dissolved organic matter (SPE-DOM) from seawater, Limnol. Oceanogr.:Methods, 2008, 6, 230–235 CrossRef CAS.
- J. P. Snell, I. I. Stewart, R. E. Sturgeon and W. Frech, Species specific isotope dilution calibration for determination of mercury species by gas chromatography coupled to inductively coupled plasma- or furnace atomisation plasma ionisation-mass spectrometry, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2000, 15, 1540–1545 RSC.
- J. West, D. Babi, A. Azaroff and S. Jonsson, Dimethylmercury in natural waters—analytical and experimental considerations, Limnol. Oceanogr.:Methods, 2023, 21, 837–846 Search PubMed.
- J. West, S. Gindorf and S. Jonsson, Photochemical Degradation of Dimethylmercury in Natural Waters, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2022, 56, 5920–5928 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. West, A. M. Graham, V. Liem-Nguyen and S. Jonsson, Dimethylmercury degradation by dissolved sulfide and mackinawite, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2020, 54, 13731–13738 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Qvarnström and W. Frech, Mercury species transformations during sample pre-treatment of biological tissues studied by HPLC-ICP-MS, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2002, 17, 1486–1491 RSC.
- N. Maie, K. J. Parish, A. Watanabe, H. Knicker, R. Benner, T. Abe, K. Kaiser and R. Jaffé, Chemical characteristics of dissolved organic nitrogen in an oligotrophic subtropical coastal ecosystem, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2006, 70, 4491–4506 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Parlanti, K. Wörz, L. Geoffroy and M. Lamotte, Dissolved organic matter fluorescence spectroscopy as a tool to estimate biological activity in a coastal zone submitted to anthropogenic inputs, Org. Geochem., 2000, 31, 1765–1781 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Ohno, Fluorescence inner-filtering correction for determining the humification index of dissolved organic matter, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2002, 36, 742–746 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Huguet, L. Vacher, S. Relexans, S. Saubusse, J. M. Froidefond and E. Parlanti, Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary, Org. Geochem., 2009, 40, 706–719 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Seelen, V. Liem-Nguyen, U. Wünsch, Z. Baumann, R. Mason, U. Skyllberg and E. Björn, Dissolved organic matter thiol concentrations determine methylmercury bioavailability across the terrestrial-marine aquatic continuum, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14, 6728 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Liem-Nguyen, U. Skyllberg and E. Björn, Thermodynamic Modeling of the Solubility and Chemical Speciation of Mercury and Methylmercury Driven by Organic Thiols and Micromolar Sulfide Concentrations in Boreal Wetland Soils, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2017, 51, 3678–3686 CrossRef CAS.
- U. Skyllberg, Competition among thiols and inorganic sulfides and polysulfides for Hg and MeHg in wetland soils and sediments under suboxic conditions: illumination of controversies and implications for MeHg net production, J. Geophys. Res.:Biogeosci., 2008, 113, 1–14 Search PubMed.
- C. L. Osburn, D. W. O'Sullivan and T. J. Boyd, Increases in the longwave photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in coastal waters, Limnol. Oceanogr., 2009, 54, 145–159 CrossRef.
- A. V. Vähätalo, Light, Photolytic Reactivity and Chemical Products, Encycl. Inl. Waters, 2009, 761–773 Search PubMed.
- K. Zhang and K. M. Parker, Halogen Radical Oxidants in Natural and Engineered Aquatic Systems, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2018, 52, 9579–9594 CrossRef CAS.
- W. A. Noyes, in Proceedings of the International Congress of Radiation Research, Burlington, Vermont, U. S. A., August 11–15, 1958, 1959, vol. 1, pp. 164–176 Search PubMed.
- C. R. Hammerschmidt and W. F. Fitzgerald, Iron-mediated photochemical decomposition of methylmercury in an arctic Alaskan Lake, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2010, 44, 6138–6143 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Lotfi-Kalahroodi, M. Le Bechec, E. Tessier, T. Pigot and D. Amouroux, Influence of oxygen, UV light and reactive dissolved organic matter on the photodemethylation and photoreduction of monomethylmercury in model freshwater, Chemosphere, 2023, 330, 138675 Search PubMed.
- A. V Vähätalo, L. Carena, D. Vione and E. Science, Photochemical Reactions in Inland Waters, Elsevier Inc., 2nd edn, 2022 Search PubMed.
- L. T. Stirchak, K. J. Moor, K. McNeill and D. J. Donaldson, Differences in photochemistry between seawater and freshwater for two natural organic matter samples, Environ. Sci.:Processes Impacts, 2019, 21, 28–39 RSC.
- C. M. Sharpless and N. V. Blough, The importance of charge-transfer interactions in determining chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) optical and photochemical properties, Environ. Sci.:Processes Impacts, 2014, 16, 654–671 RSC.
- M. Grandbois, D. E. Latch and K. Mcneill, Microheterogeneous concentrations of singlet oxygen in natural organic matter isolate solutions, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2008, 42, 9184–9190 CrossRef CAS.
- A. C. Maizel and C. K. Remucal, Molecular Composition and Photochemical Reactivity of Size-Fractionated Dissolved Organic Matter, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2017, 51, 2113–2123 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. A. Li, Q. Wang, H. Ma, X. Cao, Y. Song, F. Cui and A. J. Tanentzap, Photochemical processes transform dissolved organic matter differently depending on its initial composition, Sci. Total Environ., 2024, 923, 171465 CrossRef CAS.
- C. E. Williamson, E. P. Overholt, R. M. Pilla, T. H. Leach, J. A. Brentrup, L. B. Knoll, E. M. Mette and R. E. Moeller, Ecological consequences of long-term browning in lakes, Sci. Rep., 2015, 5, 1–10 Search PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4em00636d |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |