Themed collection 2017 PCCP HOT Articles

The generalized maximum hardness principle revisited and applied to solids (Part 2)
Part 2 of this duology is devoted to extended solids, polymorphism and phase diagrams, to which we apply the generalized maximum hardness principle. We illustrate the applicability of the principle to a broad range of phenomena and distinct systems and propose its reformulation.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 30984-31006
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP05027E
The generalized maximum hardness principle revisited and applied to atoms and molecules
Part 1 of this duology is devoted to isolated atoms and molecules, and to chemical reactions between them; we introduce here basic concepts beyond the Generalized Maximum Hardness Principle, and the corresponding Minimum Polarizability Principle, and we illustrate applicability of both principles to a broad range of chemical phenomena and distinct systems in the gas phase.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 30964-30983
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP03101G
Curly arrows, electron flow, and reaction mechanisms from the perspective of the bonding evolution theory
The BET study provides the nature of the reaction mechanism by finding the electronic flow processes along the reaction progress.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 29031-29046
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP06108K
Unveiling universal trends for the energy level alignment in organic/oxide interfaces
Organic/oxide interfaces exhibit an energy-level-alignment universal behaviour when a bias is applied. Coulomb-blockade regime is ruled by the organic electronegativity.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 24412-24420
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP03853D
SAXS on a chip: from dynamics of phase transitions to alignment phenomena at interfaces studied with microfluidic devices
Microfluidic devices allow actuation on the microscale, while in situ SAXS allows visualization of these effects in relevant systems.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23690-23703
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02736B
Synergies in lubrication
In living organisms the aqueous medium is used for providing low friction forces. This is achieved by synergistic actions of different biomolecules that together accomplish a high load bearing capacity and sustain an easily sheared water layer.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23677-23689
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP03517A
Electrosorption at functional interfaces: from molecular-level interactions to electrochemical cell design
This perspective discusses the fundamental processes behind electrosorption at charged interfaces, and highlights advances in electrode design for sustainable technologies in water purification and ion-selective separations.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23570-23584
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02822A
Solid surface vs. liquid surface: nanoarchitectonics, molecular machines, and DNA origami
Comparisons of science and technology between these solid and liquid surfaces would be a good navigation for current-to-future developments.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23658-23676
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02280H
Self-thermophoretic motion of controlled assembled micro-/nanomotors
Controlled assembled micro-/nanomotors are driven in fluid by near infrared light. The behaviour and mechanism of self-thermophoretic motion are reviewed.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23606-23613
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02561K
From force curves to surface nanomechanical properties
Surface science, which spans the fields of chemistry, physics, biology and materials science, requires information to be obtained on the local properties and property variations across a surface.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23642-23657
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02612A
Colloidal diffusion in confined geometries
Colloidal diffusion in confined geometries is analysed at the level of anisotropic pair densities.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23632-23641
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02497E
Unifying hydrotropy under Gibbs phase rule
A rational approach, aiming at constructing a unified theory of hydrotropy, will be presented based upon the first principles of statistical thermodynamics.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23597-23605
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02132A
Multiscale simulations for understanding the evolution and mechanism of hierarchical peptide self-assembly
Multiscale molecular simulations that combine and systematically link several hierarchies can provide insights into the evolution and dynamics of hierarchical peptide self-assembly from the molecular level to the mesoscale.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23614-23631
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP01923H
Near-infrared photochemistry at interfaces based on upconverting nanoparticles
We review near-infrared photochemistry at interfaces based on upconverting nanoparticles, highlight its potential applications, and discuss the challenges.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23585-23596
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP01838J
Limiting the valence: advancements and new perspectives on patchy colloids, soft functionalized nanoparticles and biomolecules
Artistic representation of limited valance units consisting of a soft core (in blue) and a small number of flexible bonding patches (in orange).

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 19847-19868
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP03149A
Vibronic coupling in organic semiconductors for photovoltaics
Ultrafast two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy reveals vibronically-assisted coherent charge transport and separation in organic materials and opens up new perspectives for artificial light-to-current conversion.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 18813-18830
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP03007J
Exploring the chemical kinetics of partially oxidized intermediates by combining experiments, theory, and kinetic modeling
Correlation between aerosol yields and the decomposition of oxidized intermediates during gas phase ozonolysis at different pressures.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 18128-18146
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02759A
Carbon nitrides: synthesis and characterization of a new class of functional materials
We examine the characterization of carbon nitrides and provide a perspective on their functional properties as next-generation materials.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 15613-15638
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02711G
Azaporphyrin phosphorus(V) complexes: synthesis, structure, and modification of optical properties
Azaporphyrinoids, such as phthalocyanines (Pcs), tetraazaporphyrins (TAPs), and tetrabenzotriazacorroles (TBCs), are some of the most well-known and successful artificial dyes and pigments in modern material chemistry.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 15596-15612
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02155K
Tetrel, pnictogen and chalcogen bonds identified in the gas phase before they had names: a systematic look at non-covalent interactions
Tetrel, pnictogen and chalcogen-bonded complexes: old bonds but new names.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 14884-14896
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02518A
Molecular electron acceptors for efficient fullerene-free organic solar cells
Small molecule electron acceptors pairing with wide bandgap or narrow bandgap electron donors are reviewed and discussed for fullerene-free organic solar cells.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 3440-3458
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP07465K
Collective proton transfer in ordinary ice: local environments, temperature dependence and deuteration effects
Ordinary ice at low temperature: what about collective nuclear quantum effects in its chiral six rings?

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 2623-2635
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP05679B
Scalable exfoliation and dispersion of two-dimensional materials – an update
The preparation of dispersions of 2D materials in various solvents, as well as the characterization methods, is critically reviewed.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 921-960
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP06813H
Why do the Togni reagent and some of its derivatives exist in the high-energy hypervalent iodine form? New insight into the origins of their kinetic stability
A scheme for the prediction of the kinetic and thermodynamic stability of Togni-type reagents is presented. The scheme is evaluated based on computations of the isomerization and transition state energies of an array of more than 600 compounds.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 32179-32183
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP05943D
Direct estimation of the transfer integral for photoinduced electron transfer from TD DFT calculations
A simple approach to estimate the electronic coupling for photoinduced charge separation in materials and biomolecules is proposed.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 31007-31010
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP06152H
Electrophilicity of oxalic acid monomer is enhanced in the dimer by intermolecular proton transfer
Excess electron induces proton transfer in the dimer of oxalic acid and leads to formation of very stable anions.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 29760-29766
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP00474E
LK peptide side chain dynamics at interfaces are independent of secondary structure
Real-time observation of the ultrafast motions of leucine side chains within model peptides at the water–air interface with representative folds – α-helix, 310-helix, β-strand – show that interfacial dynamics are mostly determined by surface interactions.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 28507-28511
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP05897G
Interaction with prefibrillar species and amyloid-like fibrils changes the stiffness of lipid bilayers
Prefibrillar species cause a significant reduction in the bending modulus of lipid bilayers, without large-scale morphological disruption.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 27930-27934
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP05339H
Isotope effects on the resonance interactions and vibrational quantum dynamics of fluoroform 12,13CHF3
We report a comparison of the vibrational quantum dynamics based on the analysis of the low energy spectra of 13CHF3 and 12CHF3 from the THz (FIR) range to the ν1 fundamental at high resolution (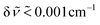 or Doppler limited).
or Doppler limited).

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 26527-26534
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP04762B
Light induced oxidation of an indoline derived system triggered spherical aggregates
A novel indoline assisted InBT system displayed a visible colour transitions from pink to orange to yellow in chloroform owing to the photooxidation of N,N-dimethyl indoline by light irradiation at excitation wavelengths of 320 and 500 nm, which leads to spherical assemblies.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 26535-26539
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP04988A
Light-induced piston nanoengines: ultrafast shuttling of a styryl dye inside cucurbit[7]uril
A proof of principle for an ultrafast molecular shuttle based on the light-operated movement of a styryl dye inside cucurbit[7]uril was described.
![Graphical abstract: Light-induced piston nanoengines: ultrafast shuttling of a styryl dye inside cucurbit[7]uril](/nl-be/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C7CP04283C&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2017)
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 25834-25839
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP04283C
Sibling rivalry: intrinsic luminescence from two xanthene dye monoanions, resorufin and fluorescein, provides evidence for excited-state proton transfer in the latter
Excited-state proton transfer in gas-phase fluorescein monoanions results in a broad, featureless emission band and a large Stokes shift compared to resorufin, which shares the same xanthene core structure.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 24440-24444
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP04689H
Defocused dark-field orientation imaging of single gold microrods on synthetic membranes
Defocused scattering patterns allowed us to resolve both in-plane and out-of-plane angles of single AuMRs.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 24453-24457
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP04714B
One-step assembly of multi-layered structures with orthogonally oriented stripe-like patterns on the surface of a capillary tube
Highly-ordered, large-scale stripe patterns could be formed simultaneously on both the inner and outer surfaces of capillary tubes with orthogonal orientations.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23719-23722
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02583A
Coherent quantum scattering of CH4 from Ni(111)
We have measured high-resolution angular distributions of methane scattered from a Ni(111) surface at incident energies between 68.9 meV and 108.6 meV.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 21267-21271
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP04559J
Indirect NMR detection of transient guanosyl radical protonation in neutral aqueous solution
Protonation of a neutral guanosyl radical at the N7 position in neutral aqueous solution has been proved by the TR CIDNP technique.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 21262-21266
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP03797J
A reaction model on the self-assembly process of octahedron-shaped coordination capsules
Master equation was utilized to track the time evolution in a self-assembly process.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 20338-20342
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP03493H
Non-isothermal kinetics of spin crossover
Non-isothermal magnetic studies can be used to estimate the activation energy of cooperative spin transition.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 16955-16959
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP03442C
Electrochemistry of single droplets of inverse (water-in-oil) emulsions
Single water droplet electrochemistry investigated for the first time, reveals the biphasic kinetics of ion transfer within water-in-oil emulsions.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 15662-15666
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP03300A
Fano resonances in the photoinduced H-atom elimination dynamics in the πσ* states of pyrrole
The interference is supported by two distinct dynamical scenarios controlled by two exit channel conical intersections between the πσ* states and the ground electronic state.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 14902-14906
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP01401E
The Rashba effect and indirect electron–hole recombination in hybrid organic–inorganic perovskites
Slow electron–hole recombination, characterized by the bimolecular coefficient k2 in hybrid organic–inorganic perovskites (HOIPs), can be quantitatively accounted for by phonon-assisted processes.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 14907-14912
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02568H
First-principles study of adsorption–desorption kinetics of aqueous V2+/V3+ redox species on graphite in a vanadium redox flow battery
Vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs) represent a promising solution to grid-scale energy storage, and understanding the reactivity of electrode materials is crucial for improving the power density of VRFBs.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 14897-14901
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02350B
Susceptibility contrast by echo shifting in spatially encoded single-scan MRI
By modifying an established hybrid imaging sequence called Rapid Acquisition by Sequential Excitation and Refocusing (RASER) so as to obtain Echo-Shifted RASER sequences, we show how one can tune the contrast due to inhomogeneous Tinh2 decay.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 14210-14213
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP01898C
Intrinsic ferromagnetism and quantum anomalous Hall effect in a CoBr2 monolayer
The electronic, magnetic, and topological properties of a CoBr2 monolayer are studied in the framework of density-functional theory (DFT) combined with tight-binding (TB) modeling in terms of the Wannier basis.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 13432-13437
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02158E
Isomer-dependent fragmentation dynamics of inner-shell photoionized difluoroiodobenzene
The fragmentation dynamics of 2,6- and 3,5-difluoroiodobenzene after iodine 4d inner-shell photoionization with soft X-rays are studied using coincident electron and ion momentum imaging.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 13419-13431
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP01379E
Unzipping and shearing DNA with electrophoresed nanoparticles in hydrogels
Under electric control, nanoparticles are used as electromechanical actuators for releasing DNA from hydrogel by dehybridization.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 13414-13418
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02214J
The shielding cone in spherical aromatic structures: insights from models for spherical 2(N + 1)2 aromatic fullerenes
The shielding cone in spherical aromatic fullerenes is of long-range character and permits multiple orientations.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 12633-12636
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP01870C
High-resolution FTIR spectroscopy of trisulfane HSSSH: a candidate for detecting parity violation in chiral molecules
We present the first analysis of high resolution infrared spectra for trisulfane, a candidate to measure molecular parity violation.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 11738-11743
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP01139C
Cage-like B39+ clusters with the bonding pattern of σ + π double delocalization: new members of the borospherene family
The recently observed cage-like borospherenes D2d B40−/0 and C3/C2 B39− have attracted considerable attention in chemistry and materials science.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 10998-11003
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP00725F
Dissociative and non-dissociative adsorption of O2 on Cu(111) and CuML/Ru(0001) surfaces: adiabaticity takes over
Adiabatic molecular spin-quenching during the approach of O2 to Cu(111) and CuML/Ru(0001) surfaces.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 10217-10221
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP00753A
Anionic and cationic Hofmeister effects are non-additive for guanidinium salts
The interaction of spherical anions and cations with a model amide is additive, except for salts containing the guanidinium cation.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 9724-9728
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP00790F
Prediction of strong O–H/M hydrogen bonding between water and square-planar Ir and Rh complexes
The very strong O–H/M interaction between a water molecule and a neutral square-planar complex (−9.83 kcal mol−1) is calculated using a quantum chemical method.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 8657-8660
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP08796E
Quantitative assessment of kosmotropicity of hydrated ionic liquids by nuclear magnetic resonance
The NMR chemical shift variation of H2O varied with the component ion and reflected the kosmotropicity quantitatively in hydrated ionic liquids.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 8148-8151
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP07463D
Light-driven rotary molecular motors without point chirality: a minimal design
Despite lacking a stereocenter, light-driven cyclohexenylidene-pyrrolinium molecular motors achieve unidirectional rotary motion through the asymmetry afforded by the puckered cyclohexenylidene.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 6952-6956
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP08484B
Interfacial defects induced electronic property transformation at perovskite SrVO3/SrTiO3 and LaCrO3/SrTiO3 heterointerfaces
Unravelling the atomic structure and chemical species of interfacial defects is critical to understanding the origin of interfacial properties in many heterojunctions.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 6945-6951
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP07691B
Alpha-tocopherol inhibits pore formation in oxidized bilayers
Alpha-tocopherols (α-toc; vitamin E) play a crucial role in protecting biological membranes from free radicals.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 5699-5704
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP08051K
Understanding the connection between conformational changes of peptides and equilibrium thermal fluctuations
A novel computational method to analyze jointly the vibrational fluctuations and the conformational dynamics of peptides and proteins in water at equilibrium.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 3459-3463
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP06776J
Mechanism and kinetics of the electrocatalytic reaction responsible for the high cost of hydrogen fuel cells
Free energy barrier as a function of applied potential for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction (ORR) on Pt(111) surface.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 2666-2673
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP08055C
Reaching the ideal glass transition by aging polymer films
By aging, we draw glassy polymer films to a thermodynamic state, the ideal glass, with the entropy of the crystal.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 961-965
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP07139B
Escape of anions from geminate recombination in THF due to charge delocalization
Geminate recombination of 24 radical anions (M˙−) with solvated protons (RH2+) was studied in tetrahydrofuran (THF) with pulse radiolysis.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 32272-32285
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP05880B
The cohesive energy of superheavy element copernicium determined from accurate relativistic coupled-cluster theory
The cohesive energy of bulk copernicium is accurately determined using the incremental method within a relativistic coupled-cluster approach.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 32286-32295
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP07203A
Infrared spectroscopy of hydrated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon cations: naphthalene+–water
The combination of infrared spectroscopy and quantum chemical calculations unravels the salient properties of the bifurcated CH⋯O ionic hydrogen bond typical for the PAH+–H2O interaction.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 32262-32271
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP06893J
Theoretical exploration of the potential applications of Sc-based MXenes
Herein, we systematically explored the electronic properties of Sc-based MXenes via first-principles calculations, with the aim to extend their applicability.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 32253-32261
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP06224A
Control of chemical chaos through medium viscosity in a batch ferroin-catalysed Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction
A macroscopic parameter, such as medium viscosity, can be used to fine tune chemical chaos in a reaction–diffusion–convection system.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 32235-32241
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP06601E
Detection of the electronic structure of iron-(III)-oxo oligomers forming in aqueous solutions
The electronic structure of the small iron-oxo oligomers forming in iron-(III) aqueous solutions is determined from liquid jet photoelectron spectroscopy.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 32226-32234
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP06945F
Solvent effects on excitation energies obtained using the state-specific TD-DFT method with a polarizable continuum model based on constrained equilibrium thermodynamics
Nonequilibrium solvation effects need to be treated properly in the study of electronic absorption processes of solutes since solvent polarization is not in equilibrium with the excited-state charge density of the solute.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 32242-32252
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP05673G
A look at the density functional theory zoo with the advanced GMTKN55 database for general main group thermochemistry, kinetics and noncovalent interactions
We present the updated and extended GMTKN55 benchmark database for more accurate and extensive energetic evaluation of density functionals and other electronic structure methods with detailed guidelines for method users.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 32184-32215
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP04913G
Unimolecular decay strongly limits the atmospheric impact of Criegee intermediates
The stabilized Criegee intermediates formed from large, biogenic VOC often have multiple unimolecular decay channels with high rate coefficients.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 31599-31612
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP05541B
Electronic structure and dynamics of torsion-locked photoactive yellow protein chromophores
Anion photoelectron spectroscopy and computational chemistry study of the role of torsional motions in the electronic relaxation of PYP chromophores.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 31572-31580
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP06950B
Investigations on structural determination of semi-transition-metal borides
The present calculations show a series of semi-transition-metal borides with the long-assumed I4/mcm symmetry are dynamically unstable and I4/m structure is predicted to be both energetically and dynamically stable by freezing the unstable phonon mode.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 31592-31598
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP06550G
About this collection
Welcome to our online rolling collection of the hottest work published in PCCP. Here we feature all the 2017 PCCP articles highlighted as HOT by the handling editor or our referees. Congratulations to all the authors whose articles are featured.