Tsuyoshi Takata and Kazunari Domen
Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 10529-10544
DOI:
10.1039/C7DT00867H,
Perspective
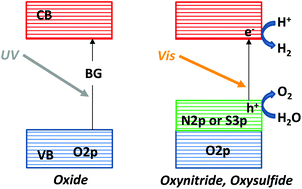
Water splitting via photocatalysis and photoelectrolysis is a potential means to produce clean and renewable hydrogen as a storable high-density energy carrier. At present, the main concern is how to develop semiconductor materials for efficiently converting sunlight energy. The present perspective summarises recent developments in the use of new semiconductors as light-harvesting materials. Specifically, non-oxides, oxynitrides and oxysulfides have been demonstrated to be promising materials for water splitting under visible light. The design of such materials and their application to photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical water splitting are discussed.