Mixed valence that induces superior dielectric properties of CdCu3(Tb1/2Ta1/2)xTi4−xO12 ceramics†
Abstract
The considerable demand for energy and the accelerated growth of the microelectronics sector has prompted extensive research into dielectric materials with high dielectric constants for use in electronic storage devices. In this study, a conventional solid-phase method was used to enhance the dielectric properties of CdCu3Ti4O12 by co-doping Ti sites with Tb and Ta ions. Impressively, the CdCu3(Tb1/2Ta1/2)xTi4−xO12 ceramics exhibit superior dielectric properties with a dielectric constant (ε ∼ 3.21 × 104) and a low loss tangent (tan δ ∼ 0.020) at 1 kHz. In addition, the temperature dependent-coefficient of variation of its dielectric constant (Δε/ε25 °C) is less than ±15% over the temperature range of −13 to 174 °C. The dielectric response is mainly due to intrinsic and extrinsic effects, and the inherent effects may be due to the formation of defect clusters (i.e., 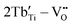 ,
, 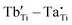 and
and 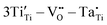 ). While the non-intrinsic effects are caused by the microstructure of the internal barrier layer capacitor, the impedance spectra show the presence of semiconductor grains as well as the huge resistance at the grain boundaries, where the heterogeneous structure causes an increase in grain boundary resistance. This study explores the dielectric response of a new type of giant dielectric ceramics and provides a new candidate for the fabrication of ceramic capacitors.
). While the non-intrinsic effects are caused by the microstructure of the internal barrier layer capacitor, the impedance spectra show the presence of semiconductor grains as well as the huge resistance at the grain boundaries, where the heterogeneous structure causes an increase in grain boundary resistance. This study explores the dielectric response of a new type of giant dielectric ceramics and provides a new candidate for the fabrication of ceramic capacitors.

- This article is part of the themed collection: 2025 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...