 Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleMicrofluidic approaches in microbial ecology
Giovanni Stefano
Ugolini
*a,
Miaoxiao
Wang
bc,
Eleonora
Secchi
a,
Roberto
Pioli
a,
Martin
Ackermann
bcd and
Roman
Stocker
 *a
*a
aDepartment of Civil, Environmental and Geomatic Engineering, Institute of Environmental Engineering, ETH Zurich, Laura-Hezner-Weg 7, 8093 Zurich, Switzerland. E-mail: gugolini@ethz.ch; romanstocker@ethz.ch
bInstitute of Biogeochemistry and Pollutant Dynamics, Department of Environmental Systems Science, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
cDepartment of Environmental Microbiology, Eawag: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology, Duebendorf, Switzerland
dLaboratory of Microbial Systems Ecology, School of Architecture, Civil and Environmental Engineering (ENAC), École Polytechnique Fédéral de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland
First published on 12th February 2024
Abstract
Microbial life is at the heart of many diverse environments and regulates most natural processes, from the functioning of animal organs to the cycling of global carbon. Yet, the study of microbial ecology is often limited by challenges in visualizing microbial processes and replicating the environmental conditions under which they unfold. Microfluidics operates at the characteristic scale at which microorganisms live and perform their functions, thus allowing for the observation and quantification of behaviors such as growth, motility, and responses to external cues, often with greater detail than classical techniques. By enabling a high degree of control in space and time of environmental conditions such as nutrient gradients, pH levels, and fluid flow patterns, microfluidics further provides the opportunity to study microbial processes in conditions that mimic the natural settings harboring microbial life. In this review, we describe how recent applications of microfluidic systems to microbial ecology have enriched our understanding of microbial life and microbial communities. We highlight discoveries enabled by microfluidic approaches ranging from single-cell behaviors to the functioning of multi-cellular communities, and we indicate potential future opportunities to use microfluidics to further advance our understanding of microbial processes and their implications.
1. Microbial life in changing environments
Earth's natural environments, from terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems to animal organs, harbor a rich variety of microbial life. Unseen to the naked eye, microorganisms drive fundamental processes at the global scale by performing functions at microscopic scales, such as decomposing organic matter and thereby regulating the flow of essential elements. The study of microbial ecology is therefore crucial not only for understanding ecosystem functioning and stability, but also for addressing anthropogenic perturbations and tackling pressing environmental challenges.At the heart of microbial ecology lies the complexity of the functions carried out by individual cells and communities. Cells are attracted by organic compounds, through chemotaxis, and transform them through metabolic processes. In addition, they engage in collective behaviors, such as the establishment of inter-species interactions or the formation of multi-cellular architectures, that shape communities whose functions can surpass those of individual cells. These microbial collectives enhance the resilience of microorganisms to physico-chemical stressors and empower them to efficiently exploit diverse ecological niches.
Microbial ecology intertwines processes at the cellular and community level with the heterogeneous nature of the physical environment. Microbial processes are impacted by diverse environmental factors that fluctuate in time and exhibit heterogeneity in space. Patterns in chemical landscapes, fluid flow or surface properties create distinct microenvironments and impact the colonization dynamics and metabolic capabilities of microorganisms. Understanding the life of microorganisms therefore requires a comprehensive approach that integrates data from the cell and community scales with knowledge of how environmental cues act upon both levels.
Most of these processes occur at minute scales that are exquisitely targeted by microfluidic approaches. Microfluidics enables the observation of microbial processes such as growth, division and motility at the single-cell level or community level and provides a means to interrogate and resolve these in both time and space. Moreover, the ability to impose controlled flow patterns, chemical gradients, and spatial confinement, and to vary these precisely within microfluidic channels, provides researchers with unprecedented opportunities to couple the observation of cellular processes with the application of ecologically relevant environmental cues. In this review, we highlight recent advances, methodologies and studies in microbial ecology that have harnessed microfluidics. By addressing multiple scales from single cells to large biofilm architectures, we showcase how microfluidics has significantly expanded the toolbox in the hands of researchers working to advance our understanding of microbial life.
2. Single cells exposed to spatio-temporal heterogeneities
2a. Bacterial responses to temporal fluctuations
In natural and engineered ecosystems, bacteria are often exposed to temporally fluctuating environments, with abiotic conditions such as nutrients, pH, and temperature that can change rapidly through time. For example, bacteria living in the gut experience fluctuations in nutrient availability and pH levels depending on the types and timing of food intake.1 Similarly, marine bacteria in coastal regions experience daily changes in salinity and nutrient availability due to tidal cycles and river runoff.2,3 Understanding microbial responses to such fluctuations is crucial to understanding how bacteria adapt to their environment and regulate global nutrient cycling.4–6 Early studies investigated such responses at the population level7–10 using experiments in which environmental shifts were typically imposed in milliliter-scale flasks or microliter-scale wells. However, different bacterial cells, even within a genetically uniform population, show varied responses to environmental fluctuations, a phenomenon known as phenotypic heterogeneity.11,12 For example, individual cells within a bacterial population respond differently to fluctuating antibiotic pressures, with some cells adopting a physiological state known as “persistence” in which they are insensitive to antibiotics.13,14 To address how different individual bacteria respond to environmental fluctuations and whether the phenotypic heterogeneity among individual cells affects the behavior of the whole population, studies thus need to be designed to achieve measurements at the single-cell level.Single-cell resolution has recently been enabled by the use of microfluidics, which allows the imposition of second-to-minute scale fluctuations and tracking of the response of single cells to these fluctuations with high spatio-temporal resolution.15,16 Microfabricated structures of sizes comparable to those of single bacteria are key to isolating and imaging single cells, while fluidic control allows them to be exposed to environmental fluctuations.17 An important milestone in this regard was the development of a microfluidic device known as the ‘Mother Machine’18 (Fig. 1A). It consists of thousands of parallel, dead-end microchannels in which cells can grow and divide for hundreds of generations, allowing researchers to track the growth of single cells from a given lineage.19,20 The flow of medium through the device can be precisely controlled, enabling rapid switches between different environmental conditions (Fig. 1B). For example, using the Mother Machine one recent study quantified the lag-time distribution of single cells during the transition from starvation to replete nutrient conditions with unprecedented accuracy (Fig. 1C).21 Those measurements showed that the lag time of single cells within a population ranges widely, from 4 h to 20 h. Due to the exponential nature of bacterial growth, population growth after starvation is therefore primarily driven by the cells with the shortest lag time: their progeny will dominate the population numerically before cells with the longest lag time even begin to reproduce. This study offers a typical example where microfluidics enables the quantification of fundamental parameters pertaining to the growth dynamics of bacteria and can help quantify these with unique accuracy due to the large numbers of single cells that can be automatically analyzed in an experiment. Such data can, for example, help untangle how phenotypic heterogeneity among cells affects the population-level response to fluctuations in the environment.
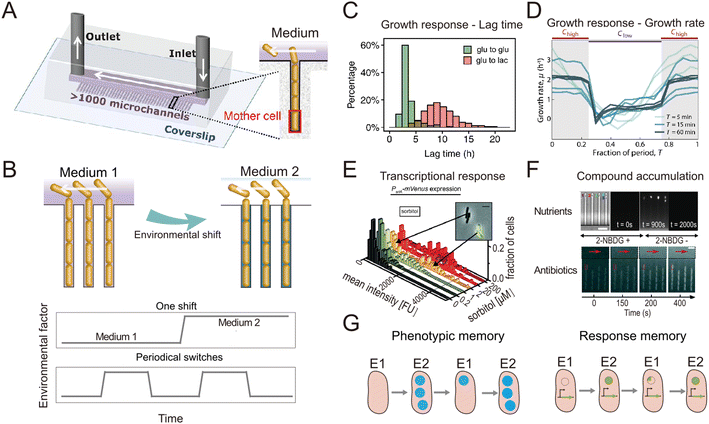 | ||
| Fig. 1 Microfluidic systems used to quantify the response of individual bacteria to environmental fluctuations. (A) Diagram of the Mother Machine microfluidic chip,48 featuring a main channel for cell loading and media flow, and thousands of microchannels hosting single bacteria. Reproduced from ref. 48 with permission from The American Association for the Advancement of Science, copyright 2018. (B) Sketches of the Mother Machine used to mimic a single environmental shift or periodical fluctuations. (C) Quantification of growth responses such as the lag time at single-cell level upon one nutrient switches applied in a Mother Machine. Reproduced from ref. 21 with permission from National Academy of Sciences, copyright 2020. (D) Quantification of growth rates of cells exposed to periodic switches between high and low concentrations of nutrients. Reproduced from ref. 29 with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2021. (E) Transcriptional responses quantified using fluorescent reporters in microfluidics. Reproduced from ref. 31 with permission from Wiley, copyright 2016. (F) Accumulation of auto-fluorescent compounds, such as nutrients39 and antibiotics,40 tracked in a Mother Machine. Reproduced from ref. 39 and 40 with permission from Springer Nature and RSC copyright 2020, 2022. (G) Sketches of the concept of transgeneration cellular memory. Microfluidics enables the dynamic tracking of fluorescence across cell lineages during environmental fluctuations,45,47,49 thus enabling the measurement of transgenerational cellular memory, in which cells in subsequent generations exposed to different environments retain similarities in the level of fluorescence-labeled functional proteins (left panel, blue circles). Similarly, transgenerational memory at the gene expression level (right panel, green circles) can be tracked, where cells maintain similarities in the expression levels of transcriptional reporters. | ||
The nutrient fluctuations that bacteria encounter in nature are often rapid and have complex temporal patterns.5,22–25 They have diverse modalities, including both periodic and non-periodic. For example, the human gut microbiome typically experiences daily periodic nutrient feeding, while soil microbes encounter non-periodic fluctuations depending on factors such as rainfall and nutrient influx.5,26 To study the response of bacteria to such fluctuations, microfluidic tools have been developed to expose bacteria to frequent switches between two environmental conditions (Fig. 1B). For example, a microfluidic platform known as the dMSCC (![[d with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0064_0332.gif) ynamic
ynamic ![[m with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_006d_0332.gif) icrofluidic
icrofluidic ![[s with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0073_0332.gif) ingle-
ingle-![[c with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0063_0332.gif) ell
ell ![[c with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0063_0332.gif) ultivation) enables periodic switches between two media with second-to-minute resolution.27 The dMSCC consists of a microfluidic chip with two inlet channels for two different media, which feed twelve cultivation chamber arrays. During experiments, the system switches the medium dynamically between the two inlets, creating three distinct cultivation zones: two control zones in which the medium remains constant and one switching zone. The flow profiles in the inlet channels are precisely controlled so that the six chamber arrays belonging to the switching zone undergo repeated, software-controlled switching between the two environmental conditions. Using this system to create periodic fluctuations, it has been shown that the cell length and growth rate of Corynebacterium glutamicum cells change with the switching frequency of either nutrient availability27 or pH,28 for switching frequencies ranging from ten seconds to four hours. By providing complete control over the switching pattern, the dMSCC also allows the investigation of cell dynamics under non-periodically changing conditions.27
ultivation) enables periodic switches between two media with second-to-minute resolution.27 The dMSCC consists of a microfluidic chip with two inlet channels for two different media, which feed twelve cultivation chamber arrays. During experiments, the system switches the medium dynamically between the two inlets, creating three distinct cultivation zones: two control zones in which the medium remains constant and one switching zone. The flow profiles in the inlet channels are precisely controlled so that the six chamber arrays belonging to the switching zone undergo repeated, software-controlled switching between the two environmental conditions. Using this system to create periodic fluctuations, it has been shown that the cell length and growth rate of Corynebacterium glutamicum cells change with the switching frequency of either nutrient availability27 or pH,28 for switching frequencies ranging from ten seconds to four hours. By providing complete control over the switching pattern, the dMSCC also allows the investigation of cell dynamics under non-periodically changing conditions.27
A second example is a microfluidic signal generator recently developed to expose surface-attached bacteria to precisely controlled fluctuations between conditions of high and low nutrient concentration, with periods as short as 30 s and as long as 60 min. Automated image analysis with cell segmentation and tracking allowed quantification of single-cell growth rates in Escherichia coli.29 In response to periodic fluctuations, cells adopted a fluctuation-adapted physiology, in which they exhibited a more rapid but reduced-amplitude response to each upshift and downshift in nutrient availability in comparison with cells exposed to only a single shift (Fig. 1D). This fluctuation-adapted physiology likely alleviated the growth costs of constantly modifying their physiology in response to fluctuating conditions. In summary, these studies provide examples of how microfluidic setups can reproduce the fluctuations in resources and environmental conditions that microorganisms encounter in nature, and thus create opportunities to better understand how bacteria respond to these fluctuations at the level of individual cells.
When coupled with fluorescent labeling, microfluidic technologies have also permitted identification of the mechanisms underlying the response of bacteria to environmental fluctuations. We provide two general examples of this. As a first example, when fluorescent proteins are used as transcriptional reporters, single-cell measurements in microfluidic devices enable the direct observation and in situ quantification of gene expression dynamics (Fig. 1D). For instance, the engineering of E. coli cells to express a fluorescent reporter of the araBAD operon and the use of microfluidics to expose the cells to arabinose fluctuations allowed the expression dynamics of arabinose degradation genes to be accurately tracked at the single-cell level.30 Another study combined the quantification of cellular growth dynamics with that of phosphotransferase gene expression31 (Fig. 1E). This work revealed that in a medium containing two sugars as carbon sources, E. coli cells only express genes related to the metabolism of one of the two sugars when both sugars are at high concentrations (known as catabolite repression), but they rapidly switch strategy at low sugar concentrations to use both sugars, adopting a stochastic co-utilization strategy.
As a second example, when compounds of interest are fluorescently labeled, microfluidics enables quantification of the dynamics of their transport and accumulation. To cope with fluctuations, bacteria change the activity of their transport systems to enable the rapid uptake of limiting nutrients32–34 or increase the efflux of antibiotics to reduce toxicity.35–37 To visualize these processes, large polymers can be labeled with fluorescent proteins,38 while smaller molecules can be replaced by fluorescent analogs. For example, 2-NBDG, a fluorescent analog of glucose, was used to investigate the accumulation of glucose within E. coli cells when both nutrients and salinity were depleted.39 In another study, the auto-fluorescence of the antibiotic ofloxacin in combination with microfluidics and time-lapse fluorescence microscopy was used to quantify antibiotic accumulation in individual E. coli cells40 (Fig. 1F). In summary, when reporters of focal genes or metabolites are labeled fluorescently, microfluidics can be used to capture their dynamics, creating opportunities to identify the mechanisms of gene regulation and the metabolic changes governing bacterial responses to environmental fluctuations.
The use of microfluidics has also contributed to our understanding of cellular memory in changing environments. Environmental conditions influence a cell's internal state at later time points and can impact future cellular decision-making. Such history-dependent behavior is known as “cellular memory”, can be maintained over long periods of time and across cell divisions, and potentially improves growth and survival in dynamic environments.41–43 To investigate the mechanisms governing cellular memory in bacteria, the growth and metabolic states of cells must be quantitatively measured over time. Microfluidics not only allows single-cell measurements, but by confining cells in defined space, it also allows full tracking and reconstruction of cell lineages in time-lapse imaging experiments.44 These measurements enable the comparison of phenotypic states of cells throughout lineages and help address questions such as determining the time scales over which cellular states are influenced by past environmental conditions. For example, two types of cellular memory have been identified in the response of E. coli cells to repeated glucose-to-lactose switches.45 First, proteins involved in lactose utilization (Lac proteins) can be transmitted across cell divisions, reducing the lag phase in the transition from glucose to lactose metabolism (Fig. 1G, left panel). This phenomenon was termed phenotypic memory and was revealed by imaging the fluorescence dynamics of labeled Lac proteins within single cells. Second, the pattern of gene expression of the cells persists after transitions, a phenomenon that was termed response memory (Fig. 1G, right panel) and was revealed by analyzing the dynamics of a transcriptional reporter of the focal genes within single cells.
By enabling the tracking of individual cells, microfluidics allows the investigation of differences in the cellular memory among cells in different cell states. For example, Caulobacter crescentus cells may have two different cell states: a motile state (cells are flagellated and can engage in motility) and a sessile state (cells are not flagellated and use a stalk to attach to a surface).46 A recent study used microfluidics to investigate whether C. crescentus cells previously exposed to antibiotics exhibit increased tolerance to future exposures to antibiotics, i.e., whether they would have cellular memory of antibiotic exposure. The cells were first cultured in an antibiotic-free medium and then exposed to a medium containing a low concentration of ampicillin. After switching back to the antibiotic-free condition for a short period, the cells were then subjected to a high concentration of ampicillin. The microfluidic experiments enabled measurements of the division trajectories of cells of the two distinct states (motile and sessile). The results revealed that only the cells in the sessile state possess a cellular memory of antibiotic exposure.47
In all these examples, microfluidics has been used as a platform to mimic some of the diverse environmental fluctuations that bacteria experience in nature or to design temporal changes in environmental cues that would enable the study of specific cellular responses. By integrating transcriptional reporters or labeled metabolites with the tracking of fluorescence dynamics at the single-cell level, microfluidics allows quantification of proxies of the metabolic states of individual cells and analysis of correlations between these states and cell growth and division processes. These approaches can thus yield new insights into how individual bacteria respond to environmental fluctuations by changing their metabolic state, growth or division strategies.
2b. Navigation in spatially heterogeneous environments
Beyond aiding in the study of single-cell responses to temporal fluctuations, microfluidics has been widely used to study microbial responses to the gradients and heterogeneous resource landscapes that characterize most microbial habitats. Many microbial species use spatial navigation and motile responses to spatial gradients as mechanisms for survival. These adaptations allow bacteria to find optimal nutrient and environmental conditions. Examples include the detection and colonization of organic particles sinking in the ocean by heterotrophic bacteria,50 movement through plant structures by pathogens,51 or bacteria navigating through pores in soil to find nutrient hotspots.52 These microscale behaviors have fundamental consequences for macro-scale ecological processes, including nutrient cycling, symbiosis, pathogenesis, and community assembly, and govern the contributions of bacteria to ecosystem functions such as carbon cycling. By enabling the fabrication of fine-scale geometries, allowing precise control over flow and other physico-chemical conditions, and providing access for high resolution, real-time imaging and tracking, microfluidics has revolutionized methods for the observation of microbial navigation responses to spatially heterogeneous distributions of a variety of environmental parameters, including resource and gas concentration, antibiotics, temperature, and fluid velocity.From a microorganism's perspective, natural environments are often heterogeneous chemical landscapes punctuated by hotspots and gradients.53 In the ocean, particles of different sizes and larger organisms such as algae generate gradients of dissolved organic matter.53 On plant surfaces or in the soil, topographical features and fluctuating water availability alter nutrient distributions.54 In the gastrointestinal tract, microorganisms are simultaneously exposed to gradients of oxygen levels and of compounds processed by intestinal cells.55 Many microorganisms can exploit this heterogeneity using chemotaxis, the directed movement toward higher concentrations of nutrients or attractant molecules (or away from noxious substances). The precise control over concentration gradients offered by microfluidic systems has enabled microbial chemotaxis to be characterized in unprecedented detail, providing insights into the life of microbes in heterogeneous landscapes and their impact on the functioning of the ecosystems they inhabit.
Within a microfluidic system, a controlled gradient of an environmental cue can be formed in an observation region where cells are free to move. Live microscopy and cell tracking are then typically applied to identify and quantify chemotaxis (as well as other forms of taxis), as the directed movement of individual cells along the gradient or the accumulation of cells at one end of the gradient. Microfluidic devices for the study of chemotaxis are often based on a source–sink design (Fig. 2A). In such systems, a central channel is used to harbor a suspension of the cells to be studied, while in two flanking channels two solutions are flowed, a source solution with a higher concentration of the compound of interest (e.g., a nutrient) and a sink solution with a lower (or zero) concentration. The regions separating the central observation channel and the flanking channels are fabricated in a manner that allows for the diffusive exchange of solutes, but prevents convective flow and the passage of cells, for example through the use of permeable hydrogels. Diffusion of the compound of interest through these diffusion-permeable walls from the source to the sink then establishes a stable, often linear, concentration gradient in the central channel, where the response of the cells can be studied by video microscopy.
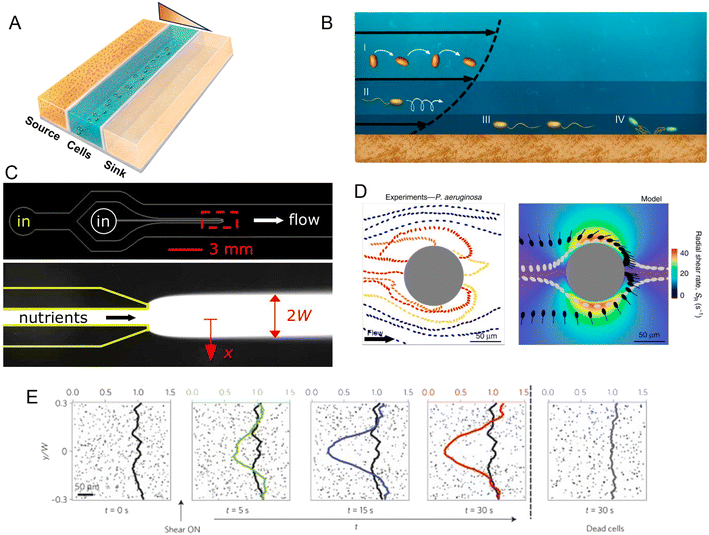 | ||
| Fig. 2 Microfluidic approaches to study the effect of spatial heterogeneity on microorganisms. (A) Schematic of a source–sink device architecture. A central channel containing cells is flanked by two side channels where two different concentrations of a compound are flowed. Permeable side walls block the passage of cells but allow for transport and the formation of a defined (often linear) gradient within the central channel. (B) Effects of flow on bacteria at different locations in the water column: (i and ii) the torque from shear rotates cells or causes them to travel in spiral trajectories; (iii and iv) near a surface, cells can be oriented by shear in the direction opposite to the flow, causing upstream movement, either by flagellar propulsion or via the use of pili.98 (C) A microinjector geometry to study bacterial chemotaxis: a central channel is nested within a larger channel to form a nozzle. Nutrients are flowed through the nozzle to form a plume (red box, lower magnified view) within the larger channel hosting cells. Reproduced from ref. 99 with permission from Wiley, copyright 2008. (D) Distribution of P. aeruginosa flowing around a micropillar. Non-motile cells preferentially attach to the windward side of the pillar, while motile cells are reoriented by shear and preferentially attach to the leeward side. Reproduced from ref. 89 with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2020. (E) Trapping of motile B. subtilis cells by shear. In these time series showing the spatial distribution of motile B. subtilis cells in a laminar flow, motile cells are rapidly depleted from the central low-shear regions when flow is applied, compared to experiments with no flow applied or with flow applied to dead cells. Reproduced from ref. 87 with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2014. | ||
A large body of work using microfluidic systems to generate chemical gradients has helped to reveal fundamental properties of chemotaxis in model strains.56–68 Initial studies using E. coli cells exposed to concentration gradients of serine and aspartate (two important amino acids) of different steepness showed for the first time that the chemotactic drift velocity (i.e., the speed at which bacteria move up the attractant gradient) depends linearly on the gradient of the logarithm of the concentration, rather than on the gradient of the concentration itself.60 This has important ecological implications, as it indicates that cells have evolved to respond more strongly to small changes in the absolute concentration of key resources when these are near depletion (and thus presumably more valuable to cells) than when the concentration is high. Given the finite bandwidth of an organism's response to any sensory signal, this strategy increases the dynamic range of chemotaxis and allows cells to sense and navigate through low-concentration environments.
The response to spatial gradients has also been studied in settings where the gradients themselves change over time. Devices capable of generating chemical gradients with a tunable switching frequency have been used to elucidate how E. coli cells adapt to temporally variable landscapes.67 Below periods of 200 s, the cell's chemotactic response is significantly out of phase and cannot cope with the stimulus as a consequence of the intracellular adaptation dynamics of signaling pathways.
Microfluidic source–sink designs are also applicable to the generation of multi-source conditions and opposing gradients. For example, a source–sink device has been used to challenge E. coli with opposing gradients of serine and aspartate, two strong attractants and ligands of the major chemotactic receptors Tsr and Tar, respectively.69 This work revealed that the chemotactic preference of E. coli depends on the ratio of the expression of the two receptors, which in turn is regulated by the cell concentration in the culture. Other experiments probed the response of E. coli to opposing gradients of an amino-acid attractant (aspartate) and a richer nutrient source (tryptone broth). Cells initially accumulated at the attractant side; however, after a threshold local cell concentration was reached, cells formed an escape band that traveled toward more favorable nutrient conditions.66 By using mutant strains, the competition between Tar and Tsr receptors was found to be responsible for this dynamic behavior.
Alongside fundamental studies on the mechanisms of chemotaxis, microfluidic devices have been developed to mimic ecologically relevant scenarios in which microorganisms experience spatial gradients. This has been achieved for a range of different microbial environments. In the ocean, for example, patchily distributed nutrient sources such as phytoplankton lysates and exudates or the excretions from larger organisms create strong heterogeneity in the distribution of organic matter. Some of this organic matter agglomerates and sinks, creating a vertical flux of particulate organic carbon that is critical for global carbon cycling. However, as they sink, the organic particles are degraded by bacteria, so that understanding how microbes navigate, locate and degrade this organic matter has important implications for the ecology and biogeochemistry of the oceans and the regulation of atmospheric carbon.70 Early microfluidic work employed a microinjector design in which a focused band of nutrients was injected into a microchannel to form a plume and the response of marine bacteria to that plume was tracked as a function of time (Fig. 2C). Using this setup, marine bacteria were shown to perform chemotaxis toward coral mucus components,71–73 lysed algae and organic particle material,74 and phytoplankton exudates.75
More recently, microfluidic experiments using a source–sink approach revealed the existence of distinct bacterial strategies for interacting with microscale ocean patches.76 Two coexisting and closely related groups of strains of Vibrio cyclitrophicus were shown to employ different strategies to exploit ephemeral sources of organic matter. One group of strains (L) had a superior ability to attach to and exploit longer-lasting patches, whereas the other (S) had a superior ability to rapidly respond to new patches. This is an example of a competition–dispersal trade-off, and was uniquely revealed by the source–sink microfluidic approach because the diffusion-permeable wall separating the observation chamber from the source channel acted both as the source of nutrients and as colonization (i.e., attachment) substrate. Interestingly, experiments using standard bulk culture conditions suggest that the L strains would outcompete the S strains, since their swimming speed and chemotactic magnitude were comparable but the L strains were superior in surface attachment. It was the ability of the microfluidic setup with a source–sink design to impose a switch in the direction of the gradient that revealed how the S strains compensated for their inferior attachment abilities through a quicker response time and ability to rapidly migrate toward a new source.
Like the oceans, soils and groundwater are also characterized by microscale heterogeneity in resource distribution that shapes microbial hotspots and thereby governs their contribution to important biogeochemical cycles, such as those of carbon and nitrogen.77 In addition to providing precise control over chemical gradients, microfluidics offers the ability to mimic geometrically complex environments with a resolution from one to hundreds of micrometers, very similar to many pore size ranges found in soils. Devices containing microfabricated arrays of pillars, mimicking soil grains, have been used to show that the chemotactic migration of E. coli has similar characteristic times in porous media compared to obstacle-free environments.64 This was found to be due to the cells reducing their tumbling frequency in response to a more intricate topology. A microfluidic system featuring a region with narrow pores, representing soil, adjacent to a flowing channel has been used to study the chemotaxis of Pseudomonas putida F1 toward toluene, a common hydrocarbon contaminant of groundwater. Chemotaxis was measured by flowing bacteria in the main channel at different flow rates and visualizing their ability to move within the porous network toward trapped toluene droplets. Results show that chemotaxis was only observed at flow velocities below 1 m per day,78 whereas higher flow velocities impeded bacterial chemotactic and swimming capabilities. This type of microfluidic study can inform bioremediation strategies by revealing whether and how different bacteria react to and reach pollutants for a given flow velocity in the groundwater.
Bacterial chemotaxis is further important in establishing symbiotic interactions, in the soils as well as in the oceans, and microfluidics offers an opportunity to investigate the initiation of interactions between symbiotic partners.79 For example, for the case of soils, microfluidic devices have been developed that enable roots of the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana to grow within a microchannel, thereby allowing continuous tracking of their interaction with bacteria through time-lapse microscopy.80 In this way, accumulation of soil-borne Bacillus subtilis was observed toward a specific region of the root, the elongation zone in which root cells grow to extend the root. This accumulation was attributed to chemotaxis, rather than cell division, due to the very short timeframes involved (20 min). In addition, this work revealed that, in a co-inoculation experiment, B. subtilis actively excluded E. coli from the root surface. These represent initial insights into how plants recruit microbes from the soil environment, previously unattainable due to the opacity of the soil that hinders real-time microscopy.
Microbial habitats are characterized by gradients of a variety of other physico-chemical parameters, in addition to nutrients. For instance, microbial communities commonly experience heterogeneity in oxygen levels, such as in the mammalian gut or in soil. While chemotaxis is the best-studied system of microbial navigation, other forms of taxis exist and are often similarly accessible through microfluidic experiments. For example, bacteria are known to move along thermal gradients (thermotaxis) and oxygen gradients (aerotaxis) in order to find optimal growth conditions.81 Microfluidic devices with a source–sink design can be conveniently adapted to generate thermal gradients or gradients in the concentration of a gas. For example, the accumulation and swimming patterns of B. subtilis82 and C. crescentus83 have been studied in controlled oxygen gradients. These experiments demonstrated that, as for chemotaxis,60 aerotaxis also depends linearly on the gradient of the logarithm of the ligand concentration. Experiments using devices that generate a thermal gradient have shown that thermotactic behaviors lead E. coli cells to accumulate toward warmer temperatures (up to 38 °C) and can be explained by the interplay between the Tar and Tsr receptors.84 Indeed, in the presence of serine or aspartate, two chemical ligands of these receptors, the response is modulated and bacteria accumulate at intermediate temperatures (e.g., 30 °C for serine), considered optimal for growth and utilization of these nutrient sources.
In the environment, the fluids in which microorganisms are suspended are rarely at rest. Thus, microorganisms are frequently exposed to fluid flows, from creeping flow in groundwater, to pipe-flow transport in man-made structures and conduits of plant and animal hosts, to turbulence in the oceans. Because flows are very rarely homogeneous, and most often characterized by velocity gradients (e.g., shear), fluid flow represents another source of heterogeneity in microbial habitats. In addition to transporting cells along flow streamlines (like a micrometer-sized passive particle would be transported), flow induces specific additional effects on cell movement, from swimming to adhesion and crawling, depending on whether the cells are located in the bulk of the fluid, near a surface, or attached to a surface (Fig. 2B). Microfluidics offers the opportunity to capture this complexity by allowing precise live-imaging and tracking of cells in highly controlled flow fields and geometries.
In many types of flows, including both near and far from solid surfaces, differences in velocity gradients are usually present, creating regions of low shear (for example, in the center of a conduit like a pipe) and regions of high shear (often closest to surfaces, but also within a turbulent flow). Fluid velocity gradients induce torques on microorganisms suspended in the fluid, and these torques cause the microorganisms to rotate, either at a uniform angular velocity if bacteria are spherical or at a highly non-uniform angular velocity if they are elongated (as all motile bacteria are). These rotations (called ‘Jeffery orbits’) directly affect the direction of movement of motile microorganisms, which in turn results in the accumulation of microorganisms in specific regions of the flow, for example near solid surfaces. Microfluidics is particularly suited to investigate this phenomenon, as it allows both fine control on well-defined flows (and thus velocity gradients and shear rates) and direct imaging of the resulting effects on the microorganisms.
Indeed, microfluidic experiments have provided new insights into the coupling of shear and motility.85–87 For example, experiments have been performed to track the motion of B. subtilis in a precisely controlled laminar flow in a straight microchannel.87 To investigate the effects of different shear rates, the microchannel was designed to have a high aspect ratio (height/width > 1), thus ensuring that the dominant velocity gradients occurred in the plane of observation, the horizontal plane. In these conditions, bacteria swam along nearly undisturbed paths when they were located in the middle of the channel where shear rates were low. In contrast, near the channel sidewalls, high shear rates caused swimming trajectories to loop so that bacteria became trapped there, and ultimately accumulated near the walls (Fig. 2E). Additionally, a modification of that microfluidic device to create an oxygen gradient in the presence of the same shear flow showed that this shear-trapping effect due to fluid velocity gradients can severely hamper bacterial chemotaxis. With the addition of a source–sink design with two flanking channels that generated an oxygen gradient across the main observation channel, experiments demonstrated that the strength of aerotaxis declined with increasing shear rate, i.e., with increasing velocity gradients. This was attributed to the effect of shear in trapping bacteria near the walls of the channel, demonstrating that the chemotactic navigation of bacteria can be overpowered by fluid flow where shear rates are high. This phenomenon is expected to be relevant in many environments, since the shear rates for which it was observed (2.5–10 s −1) are ecologically relevant for many settings, such as the subtidal coastal ocean, groundwater, mammalian reproductive tracts, and catheters.
In the presence of geometries more complex than a straight channel, such as pillar arrays and curved surfaces, the interplay of flow and bacterial motility gives rise to further phenomena that can be ecologically relevant and fruitfully studied using microfluidics. Many natural settings present intricate geometries, such as villi in the gut, pores and grains in soil, or the rough surfaces of plant leaves. In a microfluidic model of a porous medium, mimicked experimentally through a randomly distributed array of circular pillars with different diameters, experiments showed that the transport and distribution of non-motile bacteria followed those expected for passive microscale particles.88 In contrast, motile bacteria displayed a retardation effect: their transport velocity along the mean direction of the flow was systematically lower than that of non-motile cells. This was explained by their use of characteristic behaviors, identified by the tracking of individual cell trajectories, in which bacteria were observed to swim across flow lines, dwell at surfaces and swim upstream. This indicates that motility, even in the presence of fluid flow, significantly increases the chances of cells exploring and making contact with surfaces. While the origins of these behaviors were not investigated in detail, the results demonstrate how the interplay at the microscale between motility and flow has a significant impact on macroscopic transport properties.
The interplay of flow and motility also influences how bacteria interact with curved or rough surfaces. Microfluidic experiments have been used to quantify the behavior and colonization of E. coli and Pseudomona aeruginosa in microchannels containing circular pillars of different diameters.89 At flow velocities up to 3–6 times the bacterial swimming speed (i.e., flow velocities of ∼150–300 μm s−1 for P. aeruginosa), bacteria were reoriented by shear near the curved surface, leading to preferential attachment on the leeward side of the pillar. This is in sharp contrast to the impact of flow on colonization of the pillar by non-motile cells, which attached preferentially on the windward side (Fig. 2D). The same study also reported the preferential colonization of specific regions of sinusoidal or randomly corrugated surfaces, specifically the crests of the surfaces that protrude in the flow, as a result of the same mechanism of reorientation of bacteria by fluid shear. A mathematical model based on these microfluidic experiments successfully predicted the preferential attachment sites on circular, sinusoidal and randomly corrugated surfaces, paving the way to understanding colonization patterns on complex natural surfaces.
Soils are peculiar environments where fluids flow through a porous network and, in so doing, contribute to generating non-uniform chemical landscapes. These two aspects were combined in experiments using a microchannel geometry containing circular or crescent-shaped pillars in which an invading front of a chemoattractant or a chemorepellent was created, to represent the strong chemical gradients that can occur in soil.90 The results revealed that flow through the porous medium was accompanied by the emergence of preferential pathways of rapid flow and areas of fluid stagnation, and that chemotaxis strongly modulated the persistence of bacteria in the low-flow regions of the pore spaces. This pore-scale chemotaxis was found to be the principal determinant of the large-scale bacterial transport through the system.
While studies of swimming motility have dominated work on bacterial chemotaxis, surface motility plays a crucial role in the cascade of events that brings microorganisms from their dispersed, planktonic state to the formation of surface colonies, in ecological scenarios ranging from plant vascular systems to soil particles, from medical devices to tissues and organs. Adhesion and surface motility are also strongly modulated by the ambient flow field. Microfluidic techniques have proved versatile in work to quantify the strength and dynamics of cell surface adhesion in a variety of strains, mutants, surface affinities and flow conditions.91–93 For example, microfluidic experiments have been used to demonstrate the ability of several bacterial strains to twitch upstream in a channel, a mode of locomotion in which pili attach to the surface and then retract to drag the main cell body forward. This behavior is thought to play a role, for instance, in the colonization of vessels within host organisms, from plants (e.g., vascular networks94) to mammals (e.g., the urinary tract95). In experiments using flow chambers mimicking branched conduit networks, P. aeruginosa was found to be able to colonize branches located upstream from an initially colonized branch, in contrast to a mutant unable to express pili. This upstream colonization occurred through cycles of surface attachment, upstream movement by twitching, detachment, movement across streamlines, and surface reattachment. This entire cycle was termed dynamic switching.96 These findings demonstrate that upstream migration via surface motility increases the efficiency of bacterial exploration of flow networks and could thus contribute to their colonization of vessels within host organisms.
The morphology of bacterial cells has also been linked to their ability to adhere to surfaces through the use of microfluidic experiments. Using observations in a microchannel, C. crescentus cells undergoing division on a surface under constant flow were found to have an advantage in colonizing the surface if they possessed a curved shape, compared to straight mutants.97 This finding was rationalized based on the curved shape of the cells, which—in the presence of the shear due to fluid flow—caused cells to bend further toward the surface upon division. The curved shape thus confers cells an advantage for adhesion, as the daughter cell becomes positioned closer to the surface and so is better able to adhere to the surface, in comparison with straight mutants.
3. Two-dimensional microcolonies interacting with the environment
3a. Phenotypic heterogeneity and collective behaviors among cells in clonal microcolonies
Individualism dominates microbial life in many ecological settings, as in water bodies such as lakes or oceans. However, collectivism (i.e., when cells grow or live in close spatial association) can bring advantages for microorganisms, from increased resource acquisition to improved protection against adverse conditions. Collectivism is typically associated with surfaces in nature (e.g., submerged rocks, plants, the gastrointestinal lining, pipe surfaces) and the simplest collective architecture is a two-dimensional microcolony. When a two-dimensional microcolony originates from a single cell, dividing and generating progeny in close association, the colony has a clonal nature and all members share the original genome.Even in clonal microcolonies, however, heterogeneity is present, as individual cells often exhibit phenotypic variation in metabolism, mobility, and growth.11 Phenotypic variation can stem from differences in the local microenvironment12,100 or result from intracellular processes such as stochastic variation in gene expression, molecular interactions, and the segregation of molecules during cell division.11 In addition, bacteria within a clonal population can coordinate individual behaviors to achieve collective behaviors, such as collective growth and migration.101–103 In order to understand how such heterogeneity and coordination affect population growth, it is critical to measure quantities (such as metabolic states) at the single-cell level within the colony.100,104 Such measurements allow quantification of the heterogeneity among individual cells and a link to be made between individual-level behaviors and processes at the level of the population. Here, we outline how the application of microfluidics has advanced our understanding of variation and behavior in surface-associated microbial colonies.
The spatial heterogeneity of gene expression in a clonal microbial population can be directly visualized and measured at the single-cell level.105 Fluorescent proteins acting as transcriptional reporters in key metabolic traits can be analyzed by fluorescence microscopy and serve as proxies for metabolic activity. To visualize and quantify the spatially distributed metabolism of microbial populations and communities, clonal populations can be cultured on agar pads and analyzed by time-lapse microscopy.106–110 However, culture on agar pads only allows a short duration of observation before nutrients are depleted or the growing colonies develop a three-dimensional structure. The use of microfluidics can overcome these limitations,111,112 by creating a stable environment that allows the long-term measurements that are typically required to observe metabolic heterogeneity. For example, heterogeneity in the production of the amino acid valine in Corynebacterium glutamicum only becomes clearly visible around 45 hours after inoculating the cells.113 One microfluidic device, known as the Family Machine (Fig. 2A), has been used to analyze the spatial heterogeneity of gene expression in a clonal microbial population, as well as the ecological consequences of such heterogeneity. In this device, fresh medium is supplied from a main channel to support the growth of bacterial cells within a set of side chambers. The side chambers are fabricated to have a depth similar to the depth of a single cell, forcing cells to form monolayer microcolonies. As a result, cells are accessible for imaging, enabling the tracking of growth and the analysis of metabolic activity at the single-cell level.
Using a Family Machine, recent studies have revealed spatial heterogeneity in many metabolic traits, including amino-acid production,113 exopolysaccharide biosynthesis,114 and antibiotic resistance.115 For example, spatial gradients of nutrients and metabolites emerge through the metabolic activities of microorganisms, and interact with gene regulatory networks to give rise to metabolic interactions within clonal populations. These interactions can contribute to the emergence of a division of labor or niche specialization that benefits the growth of the whole population.116,117 Microfluidic experiments using the Family Machine have shown that such emerging gradients of nutrients and metabolites are among the most important factors causing such differentiation. The device operates by supplying nutrients from the main channel to the side microchambers (Fig. 2A). When nutrients are supplied at high concentrations, the emerging nutrient gradients are not pronounced and do not cause substantially different microenvironments in different regions of the chamber. In contrast, if the supplied nutrient concentration is low, spatial gradients of nutrients can form within each microchamber, with the concentration of externally supplied nutrients being highest at the opening of the chamber and decreasing with distance into the chamber. The Family Machine is therefore a useful tool to understand how microscale gradients of nutrients affect the spatial distribution of metabolic activities in clonal populations and simple communities. Using this approach, experiments have revealed that an E. coli population growing on glucose can differentiate into one subpopulation directly metabolizing glucose and one metabolizing acetate, a byproduct of glucose metabolism, depending on the local nutrient availability.118,119 The two subpopulations establish a metabolic cross-feeding interaction that increases the ability of the whole population to cope with nutrient switches and survive transient exposure to antibiotics.
Microfluidics is also well suited to investigate how bacterial collective behaviors are coordinated and regulated. By growing genetically identical bacterial cells in a Family Machine (Fig. 2A), it is possible to continuously track how individual cells within a population coordinate their growth and organize into colonies.120–123 For example, quantitative analysis of E. coli cells growing in a microfluidic chemostat120 has shown that during the development of colonies, the spatial arrangement of cells is disordered and isotropic initially, but gradually self-organizes into a nematic phase through the alignment of rod-shaped cells. These observations motivated the development of a biomechanical model to quantify collective growth based on equations for local cell density, velocity, and the tensor order parameter.
Chambers in a Family Machine can be designed in different shapes and sizes to determine how bacterial colonies gradually self-organize in response to the structure of their habitat. In this way, experiments have shown that cells can coordinate their orientation, growth, and collective motion according to the shape of the chamber to increase the diffusion of nutrients and waste products within the colonies.124 Several studies have used microfluidic systems to study the transition between solitary growth, where progeny are dispersed into the surroundings, and aggregative growth, where progeny remain in close association and aggregate. When cells of C. crescentus were cultured in a microfluidic chamber, they engaged in solitary growth when a simple monomer (xylose) was supplied as the carbon source.125 However, when the carbon source was switched to a complex polymer (xylan), the cells rapidly changed to a state of collective growth. This shift in the mode of growth arises because in order to metabolize polymers, cells need to secrete enzymes into the extracellular space. The formation of groups enabled cells to collectively accumulate a higher concentration of extracellular enzymes and thus better degrade the polymer. In this study, tracking of cell lineages using the Family Machine enabled quantification of transitions between solitary and collective growth in response to the substrate. Similarly, experiments using the same microfluidic setup to grow Vibrionaceae on another polymer, alginate, revealed that strains with a lower capacity for enzymatic secretion were more likely to engage in collective growth compared to strains that secrete high levels of enzymes when growing on polysaccharides.126
3b. Cross-feeding and competition among cells in genetically diverse microcolonies
In addition to clonal microcolonies, surface-associated environments also harbor multi-species colonies, where genetically different individual cells interact collectively.127–130 These interactions occur in diverse modes, including through the diffusive exchange of compounds and through contact-dependent interactions mediated by specific cell appendages.131,132 However, how microscale factors such as cell positioning, cell motility and cell–cell attachment govern these interactions and how these interactions affect the dynamics and functioning of microbial communities remain unclear.133–135 Many of these questions can be aptly addressed by microfluidic experiments.136,137Microfluidics has been applied to study how microorganisms interact with each other through the exchange of diffusible chemicals. One important factor that governs such interactions is the spatial distance among cells belonging to genetically differentiated populations.138,139 Because metabolites must diffuse across space from producer to receiver, a small cell-to-cell distance generally facilitates the exchange of beneficial metabolites that increase community productivity,140,141 but may also intensify microbial antagonism mediated by biotoxins, potentially destabilizing the community.142,143 Therefore, to understand community dynamics, it is crucial to identify the cell-to-cell distances over which interactions occur.141 This parameter can be measured using microfluidic devices with a specialized design in which different genotypes are spatially segregated in different chambers (Fig. 4A and B). The chambers are separated by small pillars144–146 or a nanoporous membrane,138 to allow the passage of metabolites but not cells. This design facilitates the segregation of cells with different genotypes into distinct regions. It allows straightforward quantification of the average and maximum distances over which metabolic interactions occur.145,146 In this way, it is possible to define a range of distances within which metabolic interactions between genotypes can occur.
Alternatively, two recent studies developed methods to define the interaction range in non-segregated, interacting populations using a Family Machine141,147 (Fig. 4C and D). This work showed that different genotypes typically form cell clusters when growing together in a monolayer in a Family Machine, so that the genotypes are separated into distinct regions of the Family Machine's microchambers (Fig. 4C and D). If one genotype serves as the producer of a molecular signal while the other is the receiver, the interaction range can be quantified as the maximal distance from the boundary of the two genotypes at which the receiver cells still display a fluorescent response to the signal147 (Fig. 4D). In the case of interactions through the exchange of beneficial metabolites, the interaction range can be defined instead by the range within which the number of cells of the interacting partner predominantly determines the growth rate of a focal receiver cell141 (Fig. 4C). Based on these approaches, uniquely enabled by microfluidics, we now know that the interaction range of two bacteria that exchange metabolites (amino acids) is in the range of 3 to 20 μm,141,144 depending on the uptake, leakage, and diffusion of metabolites and on the density of cells. In addition, the interaction range of cell–cell signal communication ranges from 5 to 90 μm,147 contingent on whether the receiver cells sense the signal externally via membrane-bound receptors or internally through irreversible uptake before sensing, and on the rates of signal uptake.
In contrast to this work on metabolic exchange and communication, to date, no studies have used these approaches to define the range of competitive interactions mediated by diffusible inhibitors (e.g., antibiotics, peptides, and protein toxins148). For example, determining the effective range of antibiotics is important to understand how this mode of competition shapes community dynamics.149,150 The competition range has only been investigated at the macrocolony level, at the millimeter scale.151–153 An open area for investigation is the study of the interaction range at the single-cell level, which can be enabled by microfluidics-based approaches like those described above.
Microfluidic experiments have also been used to investigate how diffusion-mediated interactions govern community dynamics and function in spatially structured environments. By culturing synthetic consortia (i.e., communities of microorganisms artificially engineered for specific functions) that exhibit pre-defined interactions, experiments have been used to investigate how specific modes of interaction determine the dynamics and functions of a community. Synthetic consortia that perform amino acid exchange represent a widely used system to investigate the effects of metabolic exchange on microbial communities.132,154,155 When culturing such a consortium in microfluidic devices, studies have shown that the short interaction range of amino-acid-based interactions limits the community-level productivity141 and that community stability is highly sensitive to perturbations of microbial interaction networks.144 Microfluidics also allows the analysis of the interactions within communities composed of naturally occurring strains to explore the effects of these interactions on community dynamics.156,157 For example, a recent study employed a Mother Machine approach to investigate the dynamics of a marine microbial community composed of two species as their interactions transitioned from positive to negative over time156 (Fig. 3B) This work demonstrated that metabolic interactions between the two species undergo temporal changes, leading to variation in community growth dynamics across ecological time scales.
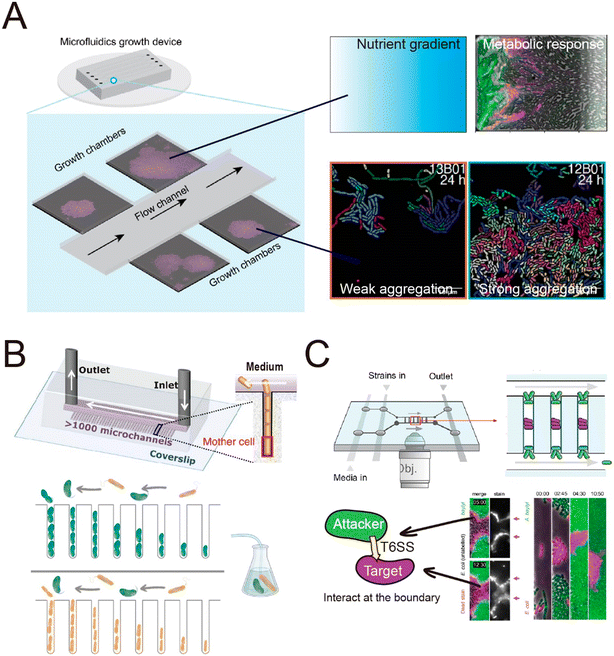 | ||
| Fig. 3 Schematic overview of typical microfluidic systems for studying microbial interactions in clonal populations. (A) Left: A Family Machine, containing one main channel and multiple side microchambers to culture bacteria monolayers. Right: Representative applications of the Family Machine setup including to establish nutrient gradients through the chamber to quantify the resulting metabolic heterogeneity of a population, or to evaluate aggregation behavior of cell populations. (B) The Mother Machine device connected to an external flask hosting a pair of interacting bacteria enables flow of the medium from such interactions to the same strains cultured in the Mother Machine, thus monitoring single-cell growth rates in response to the evolution of the interaction in the flask. Reproduced from ref. 156 with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2023. (C) A Family Machine containing two main channels has been used to investigate contact-dependent interactions.160,161 When this device was used to investigate T6SS-mediated killing,160,161 “target” cells (purple) were inoculated into the center of the chamber, followed by inoculation of “attacker” cells (green) at the edges of the chamber. This spatial arrangement enables time-lapse tracking of the boundary between cells of the two species, where the interaction occurs. Reproduced from ref. 161 with permission from PLOS, copyright 2020. | ||
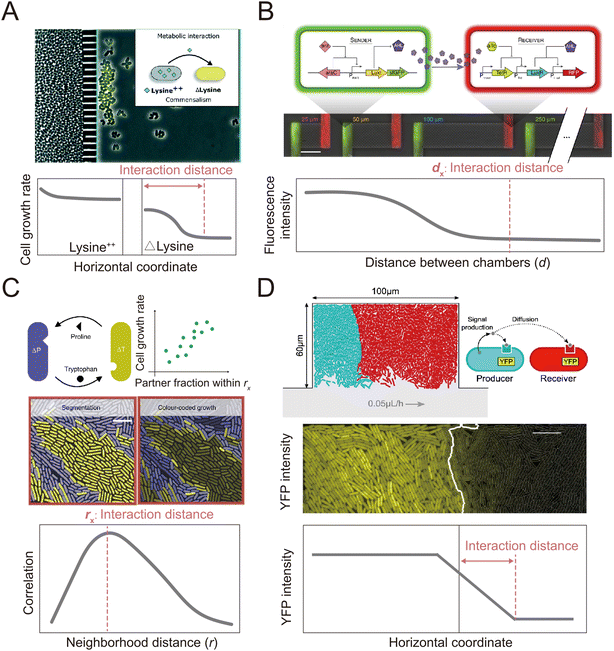 | ||
| Fig. 4 Microfluidic approaches to quantify the interaction distance among microbial cells. (A) Using microfluidics, populations can be spatially isolated within separate chambers using a barrier that prevents the passage of cells while permitting the exchange of compounds.145 In this way, the interaction distance can be quantified by determining the farthest point from the barrier at which cross-fed cells are able to grow. Reproduced from ref. 145 with permission from RSC, copyright 2019. (B) The MISTiC microfluidics design allows direct measurement of how the spatial distance between sender and receiver cell populations affects their interactions mediated by diffusible metabolites, by introducing a diffusion chamber of varying length between the two populations of cells. Reproduced from ref. 144 with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2020. (C and D) Genetically distinct populations often form spatially segregated cell clusters arising from different founder cells within a microfluidic chamber. Cell clusters can be differentiated using fluorescent labeling. (C) In the case of metabolic exchange of amino acids, the interaction range has been quantified by correlating the growth rates of individual focal cells with the fraction of the community within a given neighborhood distance that is constituted by the interacting partner. The interaction range is then defined as the neighborhood distance with maximal correlation coefficient.141 Reproduced from ref. 141 with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2020. (D) In the case of signaling between different cell populations, the interaction range can be quantified as the maximal distance from the boundary at which receiver cells show fluorescent response.147 Reproduced from ref. 147 with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2021. | ||
In addition to helping to elucidate diffusion-mediated interactions, microfluidic studies at the single-cell level have also enabled the investigation of interactions that require direct cell–cell contact.111 In recent studies, single-cell imaging in microfluidics has shown that growth inhibition or cell killing only occurs when the attacker cells are in contact with the target cells, thus providing direct evidence for contact-dependent interactions. For example, microfluidic experiments have indicated that cells of the pathogen Listeria monocytogenes kill gut commensal bacteria in a contact-dependent manner.158 Similarly, Acinetobacter baumannii can use contact-dependent growth inhibition (CDI) systems to kill other bacteria.159 A microfluidic device was developed that allows the identification of the contact site between two interacting bacteria160 (Fig. 3C). In this device, attacker cells are loaded into both the top and the bottom of the observation chamber, while target cells are trapped in between. This setup enables time-lapse tracking of the interface between the two populations where the contact-dependent interaction occurs. Using this device, it has been observed that the attacker cells take up DNA released from target cells while lysing the target cells using type VI secretion systems (T6SS).160 Another study used the same device to investigate the T6SS-mediated killing in dense microcolonies.161 The study showed that T6SSs exhibit heightened effectiveness in competition against other bacteria when the injected effector toxins can swiftly lyse target cells rather than only killing them. This is because target cells tend to accumulate around the attacker when they are killed but not rapidly lysed, forming “corpse barriers” that obstruct subsequent attacks. In order to generalize these findings to behavior in natural habitats, the authors reanalyzed genomic data across 466 bacterial species. Of the 1125 effectors identified in the dataset, 83% were predicted to cause rapid lysis, with 85% of species possessing at least one fast-lysing effector. This analysis supported the notion that the findings from microfluidics are representative of behaviors seen more widely in the environment. Studies using microfluidics have also revealed that contact-dependent competition affects the antibiotic resistance of both attacker and target cells. These experiments showed that cells of an attacker strain, Acinetobacter baylyi, acquired resistance genes from adjacent target cells when performing T6SS-mediated killing.162 In another case, when attacker cells delivered toxins using CDI systems, cells lacking the CdiI protein that provides immunity instead developed into persisters, which have higher levels of antibiotic tolerance.159 In summary, microfluidic devices have successfully enabled observation of the dynamics of both diffusion-mediated and contact-dependent interactions, and thereby increased our understanding of how such interactions shape the assembly and evolution of microbial communities.
4. Three-dimensional biofilms: cells shaping their extracellular surroundings
When cell growth within multicellular colonies is accompanied by the production of structural extracellular substances, the bacterial community becomes a biofilm. Biofilms are aggregates of microorganisms in which cells are embedded in a self-secreted matrix of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).163 The matrix comprises polysaccharides, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids, whose type and abundance depend on the microorganisms, the nutrient availability, and the environmental conditions.164 The matrix forms the scaffold of the biofilm structure, is responsible for adhesion to the surface and for internal cohesion, retains the cells in close proximity, thus favoring interactions, and protects the microbial community from chemical and mechanical insults.165–167 Overall, the presence of the matrix shapes the physico-chemical environment within biofilms. For example, it affects molecular diffusion and, thus, shapes localized chemical gradients and influences the exchange of signaling molecules and metabolites that regulate the communication between cells.168Biofilm formation and structuring are driven by the interplay between biological processes, including growth, motility and EPS matrix production, and physical quantities, such as osmotic pressure and flow shear stress, which depend on the external environment. Moreover, the result of this interplay depends on the biofilm age and size. This makes biofilm development a multiscale process, strongly dependent not only on the bacterial community but also on the physico-chemical conditions of the environment. Consequently, studying biofilm formation and development strongly benefits from technologies that allow for the investigation of different spatial scales, ranging from the single cell to the entire bacterial community, and for the tracking of the multi-day development process of the biofilm under controlled environmental conditions. In this respect, even though flow channels were used in early work on biofilms,169 the advent of microfluidics represented a fundamental innovation in the study of biofilms by providing unprecedented control over physico-chemical conditions during biofilm development and the geometry of the environment, full optical access for imaging and tracking, ease of fabrication, and high parallelization capabilities.170
Among the physical processes that can influence the development of biofilms, ambient fluid flow, along with the shear forces it generates, is nearly ubiquitous in aqueous environments. Flow can control biofilm formation by affecting surface colonization,87,89 bacterial communication,171 nutrient and oxygen supply,172 and the shear forces acting on biofilms173 (Fig. 5A). For example, fluid flow was observed to lead to the formation of bacterial monolayers in high shear conditions, but to a multilayer in low shear conditions.174 Microfluidics has provided insights into the role of fluid forces in shaping the structure and the community composition of surface-attached biofilms. Important results on the interplay between flow shear and community phenotype were obtained in the simple case of a straight channel with planar surfaces exposed to different shear rates and flow magnitudes.175,176 In particular, the precise control over flow in straight microchannels allowed experiments that revealed that, in a population of C. crescentus, high flow rates favor the creation of scattered, dense microcolonies and repress the mixing of clonal lineages, thus affecting the composition of the biofilm community176 (Fig. 5B). A similar microfluidic platform was used to demonstrate that, in early-stage Vibrio cholerae biofilms, cells from highly adhesive strains exposed to flow generate coherent clonal clusters more easily than less adhesive strains.175 Experiments employing controlled flow in straight microfluidic channels have also been used to show that flow governs the spatial organization and composition of biofilm communities by affecting their metabolic interactions. In this case, the study was conducted on the commensal association between two metabolically interacting bacteria: one bacterium that readily metabolizes dextran and a second that can only grow on the metabolite by-products produced by the first. The dextran-metabolizing bacterium localizes upstream in the flow, while the other bacterium localizes downstream, where transported metabolite by-products allow it to produce robust biofilms. Thus, fluid flow contributes to determining the spatial organization of the community by influencing the transport of public goods.177
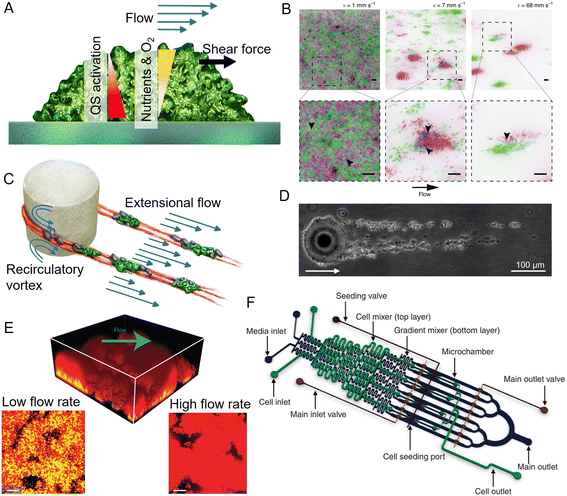 | ||
| Fig. 5 Applications of microfluidics in biofilm research. (A) Surface-attached biofilms in a microfluidic channel can be exposed to a controlled flow, impacting nutrient and oxygen concentration, quorum sensing, and exerting hydrodynamic forces on the superficial layer. (B) Flow modulates cell structuring in surface-attached biofilms. Flow rate determines the cell patterning of two fluorescently labeled C. crescentus populations within a straight microchannel, resulting in limited clonal segregation at a low flow rate (left) and scattered monoclonal colonies at a high flow rate (right). Reproduced from ref. 176 with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2019. (C) Streamers are biofilm filaments surrounded by fluid flow. Secondary flow around the curved surfaces of a pillar causes biomass to accumulate in the midplane, while the downstream flow extrudes it downstream of the pillar. (D) Streamers formed by Sagittula stellata on a single oil droplet in a microfluidic channel. Reproduced from ref. 183 with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2020. (E) Activation of quorum sensing in a thick Staphylococcus aureus biofilm exposed to flow in a microfluidic channel (upper panel). Lower panels: Comparison of the base of biofilms grown at low (left) and high flow rates (right). Quorum sensing is active in yellow cells, inactive in red cells. Reproduced from ref. 200 with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2016. (F) The diffuse mixer microfluidic channel dispenses quorum sensing signaling molecules and two dispersal proteins during biofilm growth. Reproduced from ref. 201 with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2012. | ||
Microfluidics is also uniquely suited to study the diverse morphologies that biofilms display under different environmental conditions. In aqueous environments characterized by fluid flow and obstacles, bacteria can form streamers, filamentous biofilms that grow suspended in the flow178,179 (Fig. 5C). Due to their suspended nature, biofilm streamers impact the local flow field more strongly than their surface-attached counterpart and, consequently, can more strongly affect chemical transport. In natural contexts, streamers are challenging to visualize due to their suspended nature, hampering the study of their ecological impact. Microfluidics has allowed this limitation to be overcome, because with microfluidic devices one can mimic geometrically complex environments and easily create porous structures while retaining control over fluid flow and full optical access. For example, microfluidic experiments have revealed that streamers often form in conduits and porous media and can cause their rapid clogging.180 Furthermore, streamers can also form on micrometric oil droplets or microparticles moving in fluids. In this case, microfluidic microcosms have been used to investigate streamer formation on droplets181–183 (Fig. 5D). Fluid dynamic simulations of the flow around streamers grown in a microfluidic channel have shown that the presence of two parallel 2 mm-long streamers attached to a 50 μm cylinder can cause a 10-fold increase in the hydrodynamic drag.184 The magnitude of the increase depends on the local flow and the streamers' geometry.184 Consequently, observations of the growth of streamers on oil droplets trapped in microfluidic channels have indicated that they would affect the fate of particles moving in the water column by reducing their velocity as they rise or sink, thereby increasing the time available for biotic processes such as bacterial colonization and degradation.185
Microfluidic experiments have revealed that streamer formation is intimately linked to local hydrodynamic conditions and the mechanical properties of the EPS matrix. Biomass accumulation, promoted by recirculatory vortexes around curved surfaces, initiates the formation of a streamer,178,179 while flow extrudes the matrix, thus lengthening and shaping the streamer.184,186 Local hydrodynamic conditions are ultimately controlled by the geometry of the flow domain and flow rate, two parameters that can be easily tuned in microfluidics. By tuning different elements of the geometry of the microchannel, particularly the radius of curvature of the corners of a channel where streamers can nucleate, microfluidic experiments have revealed that the sharper the angle of the corners, the longer and thicker the streamers formed.179 The development of a microfluidic platform in which isolated micropillars acted as nucleation sites for biofilm streamers allowed both the reproducible formation of streamers and the characterization of their biochemical composition, morphology, and rheology in situ, i.e., directly within the microchannel.184 This approach has shown that streamers display viscoelastic behavior, confirming macroscale findings on biofilms from different species and environments.167,187 Furthermore, it demonstrated that the EPS matrix composition controls the mechanical properties and, in turn, the morphology of the streamers that P. aeruginosa forms in the wake of an obstacle.188 Staining with propidium iodide showed that bacterial extracellular DNA is essential for the formation and structural stability of streamers, more so than for surface-attached biofilms, while the polysaccharide component of the EPS controls streamer mechanical properties. In particular, a higher polysaccharide concentration causes matrix stiffening.184,188 Nevertheless, experiments performed in a microfluidic device featuring hundreds of regularly spaced micropillars within a microchannel demonstrated that, while the protruding, suspended nature of streamers impacts their hydrodynamic effect and EPS composition, it does not lead to differentiation of their community composition from that of surface-attached multispecies biofilms.189
Porous structures are widespread in environmental, technological, and medical settings, and in these contexts the growth of biofilms affects transport and influences biochemical reactions. The geometrical layout of microfluidic channels can be easily designed to mimic porous environments through the inclusion of pillars and obstacles to create the desired grain and pore size distributions. For example, the packing and size distribution of sand grains in soil has been reproduced in a microfluidic analog of soil by introducing micropillars of a size matching that of sand grains. This device was then used to study biofilm attachment, growth and pore-scale hydrodynamics.190 This work highlighted how pore clogging is promoted under two different flow scenarios: in low-velocity regions, easily colonized by swimming bacteria, and in high-shear regions, where shear trapping191 promotes bacterial accumulation.
Within porous environments, clogging as a result of biofilm growth creates a feedback loop with further growth, as it redirects nutrient and oxygen transport.192 A new understanding of the clogging dynamics in porous systems has emerged from studying the phenomenon in microfluidic analogs of porous media.193 Such studies revealed that, initially, flow drives biofilm growth.194 However, once the porous system has become clogged, the mature biofilm redirects the flow and, at the same time, is shaped by it.195 For instance, visualization of the microscale clogging dynamics revealed that the interplay between the growth of the biofilm and its flow-driven compression and rupture causes the emergence of preferential flow paths, where most of the fluid flows at high velocities, compared to the mostly stagnant adjacent biofilm areas. When observed over tens of hours, these preferential flow paths repeatedly display sudden spatial rearrangements. These rearrangements, caused by intermittent opening and closing of the flow paths, drastically alter fluid transport in the porous medium193 (and thus ultimately chemical and biological transport).
Experiments conducted in similar microfluidic platforms containing 2D-porous structures showed that the dynamic nature of biofilm growth in porous environments profoundly impacts the bacterial community.194,196 In this study, the use of fluorescently tagged strains allowed localization of community members bearing a particular mutation, while precise control over the flow allowed community composition to be related to the local environmental conditions. For example, while wild-type P. aeruginosa outcompete matrix-deficient mutants, the clogging induced by wild-type cells allows accumulation of the mutants in low-shear regions and thereby favors coexistence of the two strains.196 Similarly, rapidly growing strains clog the pore space that they have colonized and divert the nutrient-carrying flow toward less clogged areas inhabited by slowly growing strains that would otherwise be outcompeted.194 The possibility offered by microfluidics of creating complex but controlled flow domains allowed the discovery of these hydrodynamic interactions and how they shape competition and coexistence within the bacterial community of biofilms.
Local flow conditions also control the transport of the signaling molecules that bacteria use to sense cell density (quorum sensing) and, consequently, regulate biofilm growth.197 In the absence of flow, signaling molecules that diffuse from cells remain in the proximity of cells, thus favoring communication. Conversely, sufficiently strong flows suppress quorum sensing by removing signaling molecules, as shown at the meso-scale198 and microscale.199 Microfluidics has provided insights into the activation of quorum sensing in complex geometries and intermittent flows.200 For example, confocal imaging of thick biofilms revealed that while flow hampers quorum sensing in the biofilm layers close to the flowing fluid, the protective action of the biofilm matrix allows quorum sensing activation in the layers further removed from flow. Similarly, the presence of crevices allows activation of quorum sensing by shielding the biofilm in the crevices from flow and thus reducing the removal of signaling molecules200 (Fig. 5E).
The possibility offered by microfluidics of controlling the chemical environment during biofilm formation has been exploited to study biofilm inhibition and dispersal. During biofilm formation and maturation, quorum sensing signaling molecules can control biofilm development and alter competition within the bacterial community. In this context, microfluidic experiments were used to show how quorum sensing can be exploited to engineer biofilms. Quorum sensing molecules and two different dispersal proteins were used to regulate the rate of biofilm formation and then induce the dispersal of multispecies biofilm grown in a microfluidic channel with a diffuse mixer geometry201 (Fig. 5F). Antibiotics can also be used to manipulate biofilm formation by altering the interactions within the bacterial community. The addition of a concentration of antibiotics below the minimum inhibitory concentration has been used to mimic the cell damage induced by competing strains in mixed-strain biofilms and, consequently, alter the ecological competition between strains.202 The use of fluorescently labeled strains, combined with time-resolved optical visualization and spatially controlled chemical gradients in microfluidic channels, has allowed elucidation of the bacterial population dynamics in time and its correlation with the local antibiotic concentration. This work revealed that bacteria displayed increased biofilm formation in response to ecological competition, simulated by antibiotic stress.202
Not only liquids, but also mixtures of liquids and gases can be flown in microfluidic devices, enabling the study of the effect of the multiphase flows that often occur in microbial habitats. In the context of biofilm research, this feature has been exploited to study the effect of moving air plugs within a flowing liquid on biofilms of different ages grown on the surface of a microfluidic device.203 This work revealed that while isolated surface-attached cells of P. aeruginosa are removed by the passage of an air plug, cells encased within a biofilm matrix remain on the surface and quickly resume growth after the air plug has passed, underscoring the role of the biofilm matrix in conferring protection from mechanical insults.203
To date, microfluidics has made important contributions to the study of biofilm development, allowing researchers to identify the roles played by physico-chemical phenomena in biofilm development and ecology. Additionally, the possibility of controlling fluid transport at the microscale could be further exploited to control bacterial spatial arrangement during the initial stage of biofilm development, namely surface attachment, and to study its impact on long-term biofilm development and properties. In this regard, droplet microfluidics has been applied in approaches that allow the placement of spatially confined colonies onto a channel surface.204 Alternatively, a recently developed patterning technique that exploits the mechanical action of the capillary force exerted by an evaporating droplet allows the placement of bacterial colonies with controlled geometry and composition in a microfluidic channel.205 The application of these bacterial patterning techniques to ecologically relevant questions holds promise in elucidating emergent properties of multispecies biofilms.
5. Concluding remarks
Experimentally probing the behaviors, physiology and interactions of microorganisms in natural settings is a highly challenging endeavor, due to the minute scale at which microbial processes play out and the fluctuating and heterogeneous nature of many microbial habitats. Microfluidic approaches have made a significant contribution toward overcoming these challenges. They provided unique opportunities to mimic in the laboratory many of the biological, physical and chemical conditions that shape the ecology of microorganisms in the environment. At the same time, they enable highly quantitative measurements of microbial responses, often at the single-cell level, including, for example, the highly-resolved analysis of growth, the tracking of motility and chemotaxis, and the spatial quantification of gene expression. From probing the dynamic behavior of single cells to unraveling complex biofilm structures, we have shown how microfluidics has brought more authentic representations of nature to the experimental systems at our disposal to study microbial ecology and vastly greater precision in our ability to quantify microbial processes.While microfluidics offers numerous advantages for the study of microbial ecology, it is important to acknowledge the current challenges and limitations associated with this technology. Microfluidics offers compatibility with a wide array of analytical readouts, from imaging to genomics. However, challenges arise when seeking to apply microfluidics to experiments where a substantial amount of cellular material is required for downstream measurements, such as in protein harvesting and proteomics analyses (e.g., for the analysis of biofilm matrix composition or the study of protein expression in cells). In these cases, the minute scale of the experimental system results in a biomass yield that is often too small. Also, although microfluidic devices are uniquely suited to mimic many features of natural habitats, an accurate reproduction of the full complexity of the physico-chemical cues typical of natural ecosystems remains challenging to achieve, and in some cases may be out of reach. For instance, complex flow regimes like environmentally relevant turbulence remain very challenging or indeed impossible to create using microfluidics, due precisely to the constraints of the small scale of this technology. In addition, microfluidic systems are often designed to create a single physico-chemical cue (e.g., a nutrient gradient or a specific flow pattern) to achieve a mechanistic understanding of its effects on the microbes' ecology, yet in nature such cues are often intertwined and coupled to others. This results in a complexity that remains difficult to reproduce in a controlled manner in an experimental system, microfluidics included.
Microbial communities encountered in natural habitats are characterized by high taxonomical complexity, comprising diverse species belonging to different kingdoms. While it is still technically difficult to simultaneously track a large number of species using microfluidic approaches and to design microsystems for organisms with considerable differences in size, it is intriguing that some microfluidic devices applied to multi-kingdom systems have been reported. These are relevant for ecological settings where bacterial communities are associated with a host organism, because the presence of the host can significantly shape microbial behavior. For instance, the interface between bacteria and the human gut has been a target of extensive microfluidic efforts with the aim of creating so-called gut-on-chips.206–209 Similarly, microfluidic approaches have helped to shed light on the interactions of bacteria with fungi210 and with plant roots.211,212
Microfluidics has not only helped to advance microbial ecology by replicating the physico-chemical aspects of natural habitats in laboratory studies, but has also provided a means to directly probe microbes in the environment through systems designed for in situ measurements. For instance, the in situ chemotaxis assay (ISCA213,214) enables studies of microbial chemotaxis directly in water-based habitats, such as lakes or oceans, by sampling bacteria that swim into small wells pre-loaded with candidate chemoattractants. Such experiments have, for example, demonstrated the consistency between chemotaxis results obtained in laboratory settings and those observed in the natural ocean environment at coastal sites (for instance, chemotaxis to glutamine213 and laminarin215). A similar avenue was pursued for soil habitats, where open porous microsystems were deployed in soil environments to allow colonization and subsequent imaging of soil microorganisms.216 While still developed only for limited microbial processes in a limited set of environments, these in situ measurements demonstrate the applicability of microfluidics to natural environments and have already provided valuable insights into microbial dynamics in their native context, helping to bridge the gap between controlled laboratory studies and real-world ecosystems.
Although there has already been great progress, the synergies between microfluidics and microbial ecology have only begun to be exploited, and we anticipate that many opportunities lie ahead. Even greater precision in the microfluidic realization of microbial environments will come from approaches to generate increasingly complex nutrient landscapes within microfluidic systems, for example, by controlling the spatial and temporal availability of nutrient sources, and from methods to engineer the composition and spatial structure of bacterial communities. Increasingly sophisticated analytical methods are becoming available, such as microscale sensors to probe the physico-chemical environment within biofilms, single-cell gene expression and optogenetics to visualize and manipulate bacterial gene expression, and imaging and analytical approaches to allow long-term tracking. These advances will bring even greater spatial and temporal resolution to our view of both the environment experienced by cells and their responses. The coupling of microfluidic experiments with approaches to probe the chemical composition of the environment and the properties of cells themselves, such as Raman microspectroscopy and NanoSIMS, is a frontier that is only beginning to be explored and holds great promise. Finally, the application of microfluidic approaches directly in the natural environment is starting to enable the analysis of the full diversity of bacterial responses in situ.
The synergy between microfluidics and microbial ecology is inherently and excitingly interdisciplinary. At this interface, it is the joint contributions of engineers, physicists, biologists, chemists and mathematicians that have enabled and will continue to enable the invention of new approaches to mimic or directly probe the natural environments of microorganisms, the quantification of their responses, and the placing of this understanding into the broader context of how microorganisms affect their ecosystem. These advances will ultimately provide a deeper understanding of the mechanisms underlying the interactions of microorganisms with each other and with the environment, and a clearer picture of how the rich tapestry of microbial ecology shapes Earth's ecosystems.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge funding from a Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation Symbiosis in Aquatic Systems Investigator Award (GBMF9197; https://doi.org/10.37807/GBMF9197) to R. S.; Swiss National Science Foundation grant 205321_207488 to R. S.; the Simons Foundation through the Principles of Microbial Ecosystems (PriME) collaboration (grant 542395) to R. S. and M. A.; the Swiss National Science Foundation, National Centre of Competence in Research (NCCR) Microbiomes (No. 51NF40_180575) to R. S. and M. A.; M. W. and M. A. were supported by grant nr. IZLCZ0_206044 from the Sino Swiss Science and Technology Cooperation (SSSTC) Program; M. A. was supported by grant nr. 310030_188642 from the Swiss National Science Foundation; E. S. was supported by the PRIMA grant 179834 from the Swiss National Science Foundation.References
- C. A. Lozupone, J. I. Stombaugh, J. I. Gordon, J. K. Jansson and R. Knight, Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota, Nature, 2012, 489(7415), 220–230 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. M. Martin-Platero, B. Cleary, K. Kauffman, S. P. Preheim, D. J. McGillicuddy, E. J. Alm and M. F. Polz, High resolution time series reveals cohesive but short-lived communities in coastal plankton, Nat. Commun., 2018, 9(1), 266 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Tinta, J. Vojvoda, P. Mozeticč, I. Talaber, M. Vodopivec, F. Malfatti and V. Turk, Bacterial community shift is induced by dynamic environmental parameters in a changing coastal ecosystem (northern Adriatic, northeastern Mediterranean Sea) – a 2-year time-series study, Environ. Microbiol., 2014, 17(10), 3581–3596 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. P. Mancuso, H. Lee, C. I. Abreu, J. Gore and A. S. Khalil, Environmental fluctuations reshape an unexpected diversity-disturbance relationship in a microbial community, eLife, 2021, 10, e67175 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Nguyen, J. Lara-Gutiérrez and R. Stocker, Environmental fluctuations and their effects on microbial communities, populations and individuals, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 2020, 45(4), fuaa068 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Rodríguez-Verdugo, C. Vulin and M. Ackermann, The rate of environmental fluctuations shapes ecological dynamics in a two-species microbial system, Ecol. Lett., 2019, 22(5), 838–846 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. W. Erickson, S. J. Schink, V. Patsalo, J. R. Williamson, U. Gerland and T. Hwa, A global resource allocation strategy governs growth transition kinetics of Escherichia coli, Nature, 2017, 551(7678), 119–123 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Korem Kohanim, D. Levi, G. Jona, B. D. Towbin, A. Bren and U. Alon, A Bacterial Growth Law out of Steady State, Cell Rep., 2018, 23(10), 2891–2900 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Mori, S. Schink, D. W. Erickson, U. Gerland and T. Hwa, Quantifying the benefit of a proteome reserve in fluctuating environments, Nat. Commun., 2017, 8(1), 1225 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Link, T. Fuhrer, L. Gerosa, N. Zamboni and U. Sauer, Real-time metabolome profiling of the metabolic switch between starvation and growth, Nat. Methods, 2015, 12(11), 1091–1097 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Ackermann, A functional perspective on phenotypic heterogeneity in microorganisms, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2015, 13(8), 497–508 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Takhaveev and M. Heinemann, Metabolic heterogeneity in clonal microbial populations, Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 2018, 45, 30–38 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Q. Balaban, J. Merrin, R. Chait, L. Kowalik and S. Leibler, Bacterial persistence as a phenotypic switch, Science, 2004, 305(5690), 1622–1625 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Q. Balaban, S. Helaine, K. Lewis, M. Ackermann, B. Aldridge, D. I. Andersson, M. P. Brynildsen, D. Bumann, A. Camilli, J. J. Collins, C. Dehio, S. Fortune, J. M. Ghigo, W. D. Hardt, A. Harms, M. Heinemann, D. T. Hung, U. Jenal, B. R. Levin, J. Michiels, G. Storz, M. W. Tan, T. Tenson, L. Van Melderen and A. Zinkernagel, Definitions and guidelines for research on antibiotic persistence, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2019, 17(7), 441–448 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Potvin-Trottier, S. Luro and J. Paulsson, Microfluidics and single-cell microscopy to study stochastic processes in bacteria, Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 2018, 43, 186–192 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Leygeber, D. Lindemann, C. C. Sachs, E. Kaganovitch, W. Wiechert, K. Nöh and D. Kohlheyer, Analyzing microbial population heterogeneity—expanding the toolbox of microfluidic single-cell cultivations, J. Mol. Biol., 2019, 431(23), 4569–4588 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Basan, T. Honda, D. Christodoulou, M. Hörl, Y. F. Chang, E. Leoncini, A. Mukherjee, H. Okano, B. R. Taylor, J. M. Silverman, C. Sanchez, J. R. Williamson, J. Paulsson, T. Hwa and U. Sauer, A universal trade-off between growth and lag in fluctuating environments, Nature, 2020, 584(7821), 470–474 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Wang, L. Robert, J. Pelletier, W. L. Dang, F. Taddei, A. Wright and S. Jun, Robust growth of Escherichia coli, Curr. Biol., 2010, 20(12), 1099–1103 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Ollion, M. Elez and L. Robert, High-throughput detection and tracking of cells and intracellular spots in mother machine experiments, Nat. Protoc., 2019, 14(11), 3144–3161 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Smith, J. Metz and S. Pagliara, MMHelper: An automated framework for the analysis of microscopy images acquired with the mother machine, Sci. Rep., 2019, 9(1), 10123 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Moreno-Gámez, D. J. Kiviet, C. Vulin, S. Schlegel, K. Schlegel, G. S. Van Doorn and M. Ackermann, Wide lag time distributions break a trade-off between reproduction and survival in bacteria, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2020, 117(31), 18729–18736 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Fenchel, Microbial behavior in a heterogeneous world, Science, 2002, 296(5570), 1068–1071 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. K. Marchant, S. Ahmerkamp, G. Lavik, H. E. Tegetmeyer, J. Graf, J. M. Klatt, M. Holtappels, E. Walpersdorf and M. M. M. Kuypers, Denitrifying community in coastal sediments performs aerobic and anaerobic respiration simultaneously, ISME J., 2017, 11(8), 1799–1812 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Smriga, V. I. Fernandez, J. G. Mitchell and R. Stocker, Chemotaxis toward phytoplankton drives organic matter partitioning among marine bacteria, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2016, 113(6), 1576–1581 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Cremer, I. Segota, C. Y. Yang, M. Arnoldini, J. T. Sauls, Z. Zhang, E. Gutierreza, A. Groisman and T. Hwa, Effect of flow and peristaltic mixing on bacterial growth in a gut-like channel, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2016, 113(41), 11414–11419 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Kuzyakov and E. Blagodatskaya, Microbial Hotspots and Hot Moments in Soil: Concept & review, Soil Biol. Biochem., 2015, 83, 184–199 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Täuber, C. Golze, P. Ho, E. Von Lieres and A. Grünberger, dMSCC: a microfluidic platform for microbial single-cell cultivation of Corynebacterium glutamicum under dynamic environmental medium conditions, Lab Chip, 2020, 20(23), 4442–4455 RSC.
- S. Täuber, L. Blöbaum, V. F. Wendisch and A. Grünberger, Growth response and recovery of corynebacterium glutamicum colonies on single-cell level upon defined pH stress pulses, Front. Microbiol., 2021, 12, 711893 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Nguyen, V. Fernandez, S. Pontrelli, U. Sauer, M. Ackermann and R. Stocker, A distinct growth physiology enhances bacterial growth under rapid nutrient fluctuations, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12(1), 3662 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Fritz, J. A. Megerle, S. A. Westermayer, D. Brick, R. Heermann, K. Jung, J. O. Rädler and U. Gerland, Single cell kinetics of phenotypic switching in the arabinose utilization system of E. coli, PLoS One, 2014, 9(2), e89532 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. A. Westermayer, G. Fritz, J. Gutiérrez, J. A. Megerle, M. P. S. Weißl, K. Schnetz, U. Gerland and J. O. Rädler, Single-cell characterization of metabolic switching in the sugar phosphotransferase system of Escherichia coli, Mol. Microbiol., 2016, 100(3), 472–485 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Sekar, S. M. Linker, J. Nguyen, A. Grünhagen, R. Stocker and U. Sauer, Bacterial glycogen provides short-term benefits in changing environments, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2020, 86(9), e00049-20 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. You, H. Okano, S. Hui, Z. Zhang, M. Kim, C. W. Gunderson, Y. P. Wang, P. Lenz, D. Yan and T. Hwa, Coordination of bacterial proteome with metabolism by cyclic AMP signalling, Nature, 2013, 500(7462), 301–306 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. D. Towbin, Y. Korem, A. Bren, S. Doron, R. Sorek and U. Alon, Optimality and sub-optimality in a bacterial growth law, Nat. Commun., 2017, 8(1), 14123 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Cama, A. M. Henney and M. Winterhalter, Breaching the Barrier: Quantifying antibiotic permeability across Gram-negative bacterial membranes, J. Mol. Biol., 2019, 431(18), 3531–3546 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Du, Z. Wang, N. R. James, J. E. Voss, E. Klimont, T. Ohene-Agyei, H. Venter, W. Chiu and B. F. Luisi, Structure of the AcrAB–TolC multidrug efflux pump, Nature, 2014, 509(7501), 512–515 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Liu and T. Ferenci, Regulation of porin-mediated outer membrane permeability by nutrient limitation in Escherichia coli, J. Bacteriol., 1998, 180(15), 3917–3922 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Liu, D. Li, X. Yan, Z. Zhang, S. Zheng, J. Zhang, W. Huang, F. Wu, F. Li and G. Q. Chen, Rapid quantification of polyhydroxyalkanoates accumulated in living cells based on green fluorescence protein-labeled phasins: The qPHA method, Biomacromolecules, 2022, 23(10), 4153–4166 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Glover, M. Voliotis, U. Łapińska, B. M. Invergo, D. Soanes, P. O'Neill, K. Moore, N. Nikolic, P. G. Petrov, D. S. Milner, S. Roy, K. Heesom, T. A. Richards, K. Tsaneva-Atanasova and S. Pagliara, Nutrient and salt depletion synergistically boosts glucose metabolism in individual Escherichia coli cells, Commun. Biol., 2022, 5(1), 385 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Cama, M. Voliotis, J. Metz, A. Smith, J. Iannucci, U. F. Keyser, K. Tsaneva-Atanasova and S. Pagliara, Single-cell microfluidics facilitates the rapid quantification of antibiotic accumulation in Gram-negative bacteria, Lab Chip, 2020, 20(15), 2765–2775 RSC.
- T. M. Norman, N. D. Lord, J. Paulsson and R. Losick, Memory and modularity in cell-fate decision making, Nature, 2013, 503(7477), 481–486 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. M. Wolf, L. Fontaine-Bodin, I. Bischofs, G. Price, J. Keasling and A. P. Arkin, Memory in Microbes: Quantifying History-Dependent Behavior in a Bacterium, PLoS One, 2008, 3(2), e1700 CrossRef PubMed.
- V. Lagage and S. Uphoff, Pulses and delays, anticipation and memory: seeing bacterial stress responses from a single-cell perspective, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 2020, 44(5), 565–571 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. B. Lugagne, H. Lin and M. J. Dunlop, DeLTA: Automated cell segmentation, tracking, and lineage reconstruction using deep learning, PLoS Comput. Biol., 2020, 16(4), e1007673 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Lambert and E. Kussel, Memory and fitness optimization of bacteria under fluctuating environments, PLoS Genet., 2014, 10(9), e1004556 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. M. Skerker and M. T. Laub, Cell-cycle progression and the generation of asymmetry in Caulobacter crescentus, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2004, 2(4), 325–337 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Mathis and M. Ackermann, Response of single bacterial cells to stress gives rise to complex history dependence at the population level, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2016, 113(15), 4224–4229 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Robert, J. Ollion, J. Robert, X. Song, I. Matic and M. Elez, Mutation dynamics and fitness effects followed in single cells, Science, 2018, 359(6381), 1283–1286 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Mathis and M. Ackermann, Asymmetric cellular memory in bacteria exposed to antibiotics, BMC Evol. Biol., 2017, 17(1), 73 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Stocker and J. R. Seymour, Ecology and physics of bacterial chemotaxis in the ocean, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2012, 76(4), 792–812 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Y. L. Tsai, M. Oota and S. Sawa, Chemotactic host-finding strategies of plant endoparasites and endophytes, Front. Plant Sci., 2020, 11 DOI:10.3389/fpls.2020.01167.
- S. T. N. Aroney, P. S. Poole and C. Sánchez-Cañizares, Rhizobial chemotaxis and motility systems at work in the soil, Front. Plant Sci., 2021, 12 DOI:10.3389/fpls.2021.725338.
- R. Stocker, Marine microbes see a sea of gradients, Science, 2012, 338(6107), 628–633 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. A. Vorholt, Microbial life in the phyllosphere, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2012, 10(12), 828–840 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. P. Donaldson, S. M. Lee and S. K. Mazmanian, Gut biogeography of the bacterial microbiota, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2015, 14(1), 20–32 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Ahmed, T. S. Shimizu and R. Stocker, Bacterial chemotaxis in linear and nonlinear steady microfluidic gradients, Nano Lett., 2010, 10(9), 3379–3385 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Ahmed and R. Stocker, Experimental verification of the behavioral foundation of bacterial transport parameters using microfluidics, Biophys. J., 2008, 95(9), 4481–4493 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. L. Englert, M. D. Manson and A. Jayaraman, Flow-based microfluidic device for quantifying bacterial chemotaxis in stable, competing gradients, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2009, 75(13), 4557–4564 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Grognot and K. M. Taute, A multiscale 3D chemotaxis assay reveals bacterial navigation mechanisms, Commun. Biol., 2021, 4(1), 669 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. V. Kalinin, L. Jiang, Y. Tu and M. Wu, Logarithmic sensing in Escherichia coli bacterial chemotaxis, Biophys. J., 2009, 96(6), 2439–2448 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Kim, S. H. Kim, S. K. Lee and T. Kim, Microfluidic device for analyzing preferential chemotaxis and chemoreceptor sensitivity of bacterial cells toward carbon sources, Analyst, 2011, 136(16), 3238 RSC.
- M. D. Lazova, T. Ahmed, D. Bellomo, R. Stocker and T. S. Shimizu, Response rescaling in bacterial chemotaxis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2011, 108(33), 13870–13875 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Mao, P. S. Cremer and M. D. Manson, A sensitive, versatile microfluidic assay for bacterial chemotaxis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2003, 100(9), 5449–5454 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Rashid, Z. Long, S. Singh, M. Kohram, H. Vashistha, S. Navlakha, H. Salman, Z. N. Oltvai and Z. Bar-Joseph, Adjustment in tumbling rates improves bacterial chemotaxis on obstacle-laden terrains, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2019, 116(24), 11770–11775 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. M. Salek, F. Carrara, V. Fernandez, J. S. Guasto and R. Stocker, Bacterial chemotaxis in a microfluidic T-maze reveals strong phenotypic heterogeneity in chemotactic sensitivity, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 1877 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Zhang, G. Si, Y. Dong, K. Chen, Q. Ouyang, C. Luo and Y. Tu, Escape band in Escherichia coli chemotaxis in opposing attractant and nutrient gradients, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2019, 116(6), 2253–2258 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Zhu, G. Si, N. Deng, Q. Ouyang, T. Wu, Z. He, L. Jiang, C. Luo and Y. Tu, Frequency-dependent Escherichia coli chemotaxis behavior, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2012, 108(12), 128101 CrossRef PubMed.
- N. Norris, U. Alcolombri, J. M. Keegstra, Y. Yawata, F. Menolascina, E. Frazzoli, N. M. Levine, V. I. Fernandez and R. Stocker, Bacterial chemotaxis to saccharides is governed by a trade-off between sensing and uptake, Biophys. J., 2022, 121(11), 2046–2059 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Kalinin, S. Neumann, V. Sourjik and M. Wu, Responses of Escherichia coli bacteria to two opposing chemoattractant gradients depend on the chemoreceptor ratio, J. Bacteriol., 2010, 192(7), 1796–1800 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. T. H. Nguyen, E. J. Zakem, A. Ebrahimi, J. Schwartzman, T. Caglar, K. Amarnath, U. Alcolombri, F. J. Peaudecerf, T. Hwa, R. Stocker, O. X. Cordero and N. M. Levine, Microbes contribute to setting the ocean carbon flux by altering the fate of sinking particulates, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13(1), 1657 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Gao, M. Garren, K. Penn, V. I. Fernandez, J. R. Seymour, J. R. Thompson, J. B. Raina and R. Stocker, Coral mucus rapidly induces chemokinesis and genome-wide transcriptional shifts toward early pathogenesis in a bacterial coral pathogen, ISME J., 2021, 15(12), 3668–3682 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Garren, K. Son, J. Tout, J. R. Seymour and R. Stocker, Temperature-induced behavioral switches in a bacterial coral pathogen, ISME J., 2015, 10(6), 1363–1372 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Garren, K. Son, J. B. Raina, R. Rusconi, F. Menolascina, O. H. Shapiro, J. Tout, D. G. Bourne, J. R. Seymour and R. Stocker, A bacterial pathogen uses dimethylsulfoniopropionate as a cue to target heat-stressed corals, ISME J., 2013, 8(5), 999–1007 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Stocker, J. R. Seymour, A. Samadani, D. E. Hunt and M. F. Polz, Rapid chemotactic response enables marine bacteria to exploit ephemeral microscale nutrient patches, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2008, 105(11), 4209–4214 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. R. Seymour, T. Ahmed and R. Stocker, Bacterial chemotaxis towards the extracellular products of the toxic phytoplankton Heterosigma akashiwo, J. Plankton Res., 2009, 31(12), 1557–1561 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Yawata, O. X. Cordero, F. Menolascina, J. H. Hehemann, M. F. Polz and R. Stocker, Competition–dispersal tradeoff ecologically differentiates recently speciated marine bacterioplankton populations, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2014, 111(15), 5622–5627 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. G. Falkowski, T. Fenchel and E. F. Delong, The microbial engines that drive earth's biogeochemical cycles, Science, 2008, 320(5879), 1034–1039 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wang, L. M. Lanning and R. M. Ford, Enhanced retention of chemotactic bacteria in a pore network with residual NAPL contamination, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 50(1), 165–172 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. B. Raina, V. Fernandez, B. Lambert, R. Stocker and J. R. Seymour, The role of microbial motility and chemotaxis in symbiosis, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2019, 17(5), 284–294 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Massalha, E. Korenblum, S. Malitsky, O. H. Shapiro and A. Aharoni, Live imaging of root–bacteria interactions in a microfluidics setup, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2017, 114(17), 4549–4554 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. L. Taylor, I. B. Zhulin and M. S. Johnson, Aerotaxis and other energy-sensing behavior in bacteria, Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 1999, 53(1), 103–128 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Menolascina, R. Rusconi, V. I. Fernandez, S. Smriga, Z. Aminzare, E. D. Sontag and R. Stocker, Logarithmic sensing in Bacillus subtilis aerotaxis, npj Syst. Biol. Appl., 2017, 3(1), 16036 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Morse, R. Colin, L. G. Wilson and J. X. Tang, The aerotactic response of caulobacter crescentus, Biophys. J., 2016, 110(9), 2076–2084 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Paulick, V. Jakovljevic, S. Zhang, M. Erickstad, A. Groisman, Y. Meir, W. S. Ryu, N. S. Wingreen and V. Sourjik, Mechanism of bidirectional thermotaxis in Escherichia coli, eLife, 2017, 6, e26607 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. Jing, A. Zöttl, É. Clément and A. Lindner, Chirality-induced bacterial rheotaxis in bulk shear flows, Sci. Adv., 2020, 6(28), eabb2012 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. J. T. M. Mathijssen, N. Figueroa-Morales, G. Junot, É. Clément, A. Lindner and A. Zöttl, Oscillatory surface rheotaxis of swimming E. coli bacteria, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 3434 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Rusconi, J. S. Guasto and R. Stocker, Bacterial transport suppressed by fluid shear, Nat. Phys., 2014, 10(3), 212–217 Search PubMed.
- A. Creppy, E. Clément, C. Douarche, M. V. D'Angelo and H. Auradou, Effect of motility on the transport of bacteria populations through a porous medium, Phys. Rev. Fluids, 2019, 4(1), 013102 Search PubMed.
- E. Secchi, A. Vitale, G. L. Miño, V. Kantsler, L. Eberl, R. Rusconi and R. Stocker, The effect of flow on swimming bacteria controls the initial colonization of curved surfaces, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1), 2851 Search PubMed.
- P. De Anna, A. A. Pahlavan, Y. Yawata, R. Stocker and R. Juanes, Chemotaxis under flow disorder shapes microbial dispersion in porous media, Nat. Phys., 2020, 17(1), 68–73 Search PubMed.
- L. F. Cruz, P. A. Cobine and L. De La Fuente, Calcium increases xylella fastidiosa surface attachment, biofilm formation, and twitching motility, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2012, 78(5), 1321–1331 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Lecuyer, R. Rusconi, Y. Shen, A. Forsyth, H. Vlamakis, R. Kolter and H. A. Stone, Shear stress increases the residence time of adhesion of pseudomonas aeruginosa, Biophys. J., 2011, 100(2), 341–350 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. De La Fuente, E. Montanes, Y. Meng, Y. Li, T. J. Burr, H. C. Hoch and M. Wu, Assessing adhesion forces of type I and type IV pili of xylella fastidiosa bacteria by use of a microfluidic flow chamber, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2007, 73(8), 2690–2696 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Meng, Y. Li, C. D. Galvani, G. Hao, J. N. Turner, T. J. Burr and H. C. Hoch, Upstream migration of xylella fastidiosa via pilus-driven twitching motility, J. Bacteriol., 2005, 187(16), 5560–5567 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. C. Lane, V. Lockatell, G. Monterosso, D. Lamphier, J. Weinert, J. R. Hebel, D. E. Johnson and H. L. T. Mobley, Role of motility in the colonization of uropathogenic Escherichia coli in the urinary tract, Infect. Immun., 2005, 73(11), 7644–7656 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Kannan, Z. Yang, M. K. Kim, H. A. Stone and A. Siryaporn, Dynamic switching enables efficient bacterial colonization in flow, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2018, 115(21), 5438–5443 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Persat, H. A. Stone and Z. Gitai, The curved shape of Caulobacter crescentus enhances surface colonization in flow, Nat. Commun., 2014, 5(1), 3824 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. D. Wheeler, E. Secchi, R. Rusconi and R. Stocker, Not just going with the flow: The effects of fluid flow on bacteria and plankton, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 2019, 35(1), 213–237 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. R. Seymour, T. Ahmed, Marcos and R. Stocker, A microfluidic chemotaxis assay to study microbial behavior in diffusing nutrient patches, Limnol. Oceanogr.: Methods, 2008, 6(9), 477–488 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Schreiber and M. Ackermann, Environmental drivers of metabolic heterogeneity in clonal microbial populations, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 2020, 62, 202–211 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. H. Mattingly and T. Emonet, Collective behavior and nongenetic inheritance allow bacterial populations to adapt to changing environments, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2022, 119(26), e2117377119 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Qin, C. Fei, A. A. Bridges, A. A. Mashruwala, H. A. Stone, N. S. Wingreen and B. L. Bassler, Cell position fates and collective fountain flow in bacterial biofilms revealed by light-sheet microscopy, Science, 2020, 369(6499), 71–77 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Dharanishanthi, A. Orgad, N. Rotem, E. Hagai, J. Kerstnus-Banchik, J. Ben-Ari, T. Harig, S. R. Ravella, S. Schulz and Y. Helman, Bacterial-induced pH shifts link individual cell physiology to macroscale collective behavior, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2021, 118(14), e2014346118 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. R. Evans, C. P. Kempes, A. Price-Whelan and L. E. P. Dietrich, Metabolic heterogeneity and cross-feeding in bacterial multicellular systems, Trends Microbiol., 2020, 28(9), 732–743 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Binder, T. Drepper, K. E. Jaeger, F. Delvigne, W. Wiechert, D. Kohlheyer and A. Grünberger, Homogenizing bacterial cell factories: Analysis and engineering of phenotypic heterogeneity, Metab. Eng., 2017, 42, 145–156 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Bayramoglu, D. Toubiana, S. Van Vliet, R. F. Inglis, N. Shnerb and O. Gillor, Bet-hedging in bacteriocin producing Escherichia coli populations: the single cell perspective, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7(1), 42068 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. K. Lin, D. S. W. Lee, S. McKeithen-Mead, T. Emonet and B. Kazmierczak, A primed subpopulation of bacteria enables rapid expression of the type 3 secretion system in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, mBio, 2021, 12(3), e0083121 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Mortier, S. Van Riet, D. Senovilla Herrero, K. Vanoirbeek and A. Aertsen, High-throughput time-lapse fluorescence microscopy screening for heterogeneously expressed genes in Bacillus Subtilis, Microbiol. Spectrum, 2022, 10(1), e0204521 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Mridha and R. Kümmerli, Coordination of siderophore gene expression among clonal cells of the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Commun. Biol., 2022, 5(1), 545 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Z. Rosenthal, Y. Qi, S. Hormoz, J. Park, S. H. J. Li and M. B. Elowitz, Metabolic interactions between dynamic bacterial subpopulations, eLife, 2018, 7, e33099 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Cooper, L. Tsimring and J. Hasty, Microfluidics-based analysis of contact-dependent bacterial interactions, Bio-Protoc., 2018, 8(16), e2970 CAS.
- N. M. V. Sampaio and M. J. Dunlop, Functional roles of microbial cell-to-cell heterogeneity and emerging technologies for analysis and control, Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 2020, 57, 87–94 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Mustafi, A. Grünberger, R. Mahr, S. Helfrich, K. Nöh, B. Blombach, D. Kohlheyer and J. Frunzke, Application of a Genetically Encoded Biosensor for Live Cell Imaging of L-Valine Production in Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex-Deficient Corynebacterium glutamicum Strains, PLoS One, 2014, 9(1), e85731 CrossRef PubMed.
- J.-P. Schlüter, P. Czuppon, O. Schauer, P. Pfaffelhuber, M. McIntosh and A. Becker, Classification of phenotypic subpopulations in isogenic bacterial cultures by triple promoter probing at single cell level, J. Biotechnol., 2015, 198, 3–14 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Wang, Y. Kang, C. Luo, T. Zhao, L. Liu, X. Jiang, R. Fu, S. An, J. Chen, N. Jiang, L. Ren, Q. Wang, J. Kenneth Baillie, Z. Gao and J. Yu, Heteroresistance at the Single-Cell Level: Adapting to Antibiotic Stress through a Population-Based Strategy and Growth-Controlled Interphenotypic Coordination, mBio, 2014, 5(1), e00942-13 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. van Gestel, H. Vlamakis and R. Kolter, Division of Labor in Biofilms: the Ecology of Cell Differentiation, Microbiol. Spectrum, 2015, 3(2), MB-0002-2014 Search PubMed.
- M. Lyng and Á. T. Kovács, Microbial ecology: Metabolic heterogeneity and the division of labor in multicellular structures, Curr. Biol., 2022, 32(14), R771–R774 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Dal Co, M. Ackermann and S. Van Vliet, Metabolic activity affects the response of single cells to a nutrient switch in structured populations, J. R. Soc., Interface, 2019, 16(156), 20190182 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Dal Co, S. Van Vliet and M. Ackermann, Emergent microscale gradients give rise to metabolic cross-feeding and antibiotic tolerance in clonal bacterial populations, Philos. Trans. R. Soc., B, 2019, 374(1786), 20190080 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Volfson, S. Cookson, J. Hasty and L. S. Tsimring, Biomechanical ordering of dense cell populations, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2008, 105(40), 15346–15351 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. Boyer, W. Mather, O. Mondragón-Palomino, S. Orozco-Fuentes, T. Danino, J. Hasty and L. S. Tsimring, Buckling instability in ordered bacterial colonies, Phys. Biol., 2011, 8(2), 026008 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. Mather, O. Mondragón-Palomino, T. Danino, J. Hasty and L. S. Tsimring, Streaming Instability in Growing Cell Populations, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2010, 104(20), 208101 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Sheats, B. Sclavi, M. C. Lagomarsino, P. Cicuta and K. D. Dorfman, Role of growth rate on the orientational alignment of Escherichia coli in a slit, R. Soc. Open Sci., 2017, 4(6), 170463 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. J. Cho, H. Jönsson, K. Campbell, P. Melke, J. W. Williams, B. Jedynak, A. M. Stevens, A. Groisman and A. Levchenko, Self-Organization in High-Density Bacterial Colonies: Efficient Crowd Control, PLoS Biol., 2007, 5(11), e302 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. G. D'Souza, V. R. Povolo, J. M. Keegstra, R. Stocker and M. Ackermann, Nutrient complexity triggers transitions between solitary and colonial growth in bacterial populations, ISME J., 2021, 15(9), 2614–2626 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. D'Souza, A. Ebrahimi, A. Stubbusch, M. Daniels, J. Keegstra, R. Stocker, O. Cordero and M. Ackermann, Cell aggregation is associated with enzyme secretion strategies in marine polysaccharide-degrading bacteria, ISME J., 2023, 17(5), 703–711 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. C. Flemming, J. Wingender, U. Szewzyk, P. Steinberg, S. A. Rice and S. Kjelleberg, Biofilms: an emergent form of bacterial life, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2016, 14(9), 563–575 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. E. F. Little, C. J. Robinson, S. B. Peterson, K. F. Raffa and J. Handelsman, Rules of Engagement: Interspecies Interactions that Regulate Microbial Communities, Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 2008, 62(1), 375–401 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Mitri and K. Richard Foster, The Genotypic View of Social Interactions in Microbial Communities, Annu. Rev. Genet., 2013, 47(1), 247–273 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. D. Nadell, K. Drescher and K. R. Foster, Spatial structure, cooperation and competition in biofilms, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2016, 14(9), 589–600 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. V. Phelan, W.-T. Liu, K. Pogliano and P. C. Dorrestein, Microbial metabolic exchange—the chemotype-to-phenotype link, Nat. Chem. Biol., 2011, 8(1), 26–35 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. D'Souza, S. Shitut, D. Preussger, G. Yousif, S. Waschina and C. Kost, Ecology and evolution of metabolic cross-feeding interactions in bacteria, Nat. Prod. Rep., 2018, 35(5), 455–488 RSC.
- R. Hatzenpichler, V. Krukenberg, R. L. Spietz and Z. J. Jay, Next-generation physiology approaches to study microbiome function at single cell level, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2020, 18(4), 241–256 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. X. Cordero and M. S. Datta, Microbial interactions and community assembly at microscales, Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 2016, 31, 227–234 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. S. Datta, E. Sliwerska, J. Gore, M. F. Polz and O. X. Cordero, Microbial interactions lead to rapid micro-scale successions on model marine particles, Nat. Commun., 2016, 7(1), 11965 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Burmeister and A. Grünberger, Microfluidic cultivation and analysis tools for interaction studies of microbial co-cultures, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 2020, 62, 106–115 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Rusconi, M. Garren and R. Stocker, Microfluidics Expanding the Frontiers of Microbial Ecology, Annu. Rev. Biophys., 2014, 43(1), 65–91 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. K. Hyun, J. Q. Boedicker, W. C. Jang and R. F. Ismagilov, Defined spatial structure stabilizes a synthetic multispecies bacterial communit, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2008, 105(47), 18188–18193 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. Liu, J. Russel, M. Burmølle, S. J. Sørensen and J. S. Madsen, Micro-scale intermixing: a requisite for stable and synergistic co-establishment in a four-species biofilm, ISME J., 2018, 12(8), 1940–1951 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Wang, X. Chen, Y. Ma, Y.-Q. Tang, D. R. Johnson, Y. Nie and X.-L. Wu, Type IV Pilus Shapes a ‘Bubble-Burst’ Pattern Opposing Spatial Intermixing of Two Interacting Bacterial Populations, Microbiol. Spectrum, 2022, 10(1), e0194421 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Dal Co, S. van Vliet, D. J. Kiviet, S. Schlegel and M. Ackermann, Short-range interactions govern the dynamics and functions of microbial communities, Nat. Ecol. Evol., 2020, 4(3), 366–375 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Durrett and S. Levin, Spatial Aspects of Interspecific Competition, Theor. Popul. Biol., 1998, 53(1), 30–43 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. L. Czárán, R. F. Hoekstra and L. Pagie, Chemical warfare between microbes promotes biodiversity, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2002, 99(2), 786–790 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Gupta, T. D. Ross, M. M. Gomez, J. L. Grant, P. A. Romero and O. S. Venturelli, Investigating the dynamics of microbial consortia in spatially structured environments, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1), 2418 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Burmeister, F. Hilgers, A. Langner, C. Westerwalbesloh, Y. Kerkhoff, N. Tenhaef, T. Drepper, D. Kohlheyer, E. von Lieres, S. Noack and A. Grünberger, A microfluidic co-cultivation platform to investigate microbial interactions at defined microenvironments, Lab Chip, 2019, 19(1), 98–110 RSC.
- E. Osmekhina, C. Jonkergouw, G. Schmidt, F. Jahangiri, V. Jokinen, S. Franssila and M. B. Linder, Controlled communication between physically separated bacterial populations in a microfluidic device, Commun. Biol., 2018, 1(1), 97 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. van Gestel, T. Bareia, B. Tenennbaum, A. Dal Co, P. Guler, N. Aframian, S. Puyesky, I. Grinberg, G. G. D'Souza, Z. Erez, M. Ackermann and A. Eldar, Short-range quorum sensing controls horizontal gene transfer at micron scale in bacterial communities, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12(1), 2324 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. T. Granato, T. A. Meiller-Legrand and K. R. Foster, The Evolution and Ecology of Bacterial Warfare, Curr. Biol., 2019, 29(11), R521–R537 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Kerr, M. A. Riley, M. W. Feldman and B. J. M. Bohannan, Local dispersal promotes biodiversity in a real-life game of rock–paper–scissors, Nature, 2002, 418(6894), 171–174 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Bucci, C. D. Nadell and J. B. Xavier, The Evolution of Bacteriocin Production in Bacterial Biofilms, Am. Nat., 2011, 178(6), E162–E173 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. Gonzalez, A. Sabnis, K. R. Foster and D. A. I. Mavridou, Costs and benefits of provocation in bacterial warfare, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2018, 115(29), 7593–7598 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. T. Granato and K. R. Foster, The Evolution of Mass Cell Suicide in Bacterial Warfare, Curr. Biol., 2020, 30(14), 2836–2843.e3 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. A. I. Mavridou, D. Gonzalez, W. Kim, S. A. West and K. R. Foster, Bacteria Use Collective Behavior to Generate Diverse Combat Strategies, Curr. Biol., 2018, 28(3), 345–355.e4 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Shou, S. Ram and J. M. G. Vilar, Synthetic cooperation in engineered yeast populations, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2007, 104(6), 1877–1882 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. T. Mee, J. J. Collins, G. M. Church and H. H. Wang, Syntrophic exchange in synthetic microbial communities, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2014, 111(20), E2149–E2156 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Daniels, S. van Vliet and M. Ackermann, Changes in interactions over ecological time scales influence single-cell growth dynamics in a metabolically coupled marine microbial community, ISME J., 2023, 17(3), 406–416 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Mohan, C. Sanpitakseree, A. V. Desai, S. E. Sevgen, C. M. Schroeder and P. J. A. Kenis, A microfluidic approach to study the effect of bacterial interactions on antimicrobial susceptibility in polymicrobial cultures, RSC Adv., 2015, 5(44), 35211–35223 RSC.
- J. Meza-Torres, M. Lelek, J. J. Quereda, M. Sachse, G. Manina, D. Ershov, J. Y. Tinevez, L. Radoshevich, C. Maudet, T. Chaze, Q. G. Gianetto, M. Matondo, M. Lecuit, I. Martin-Verstraete, C. Zimmer, H. Bierne, O. Dussurget, P. Cossart, J. Pizarro-Cerdá and S. Listeriolysin, A bacteriocin from Listeria monocytogenes that induces membrane permeabilization in a contact-dependent manner, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2021, 118(40), e2108155118 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Roussin, S. Rabarioelina, L. Cluzeau, J. Cayron, C. Lesterlin, S. P. Salcedo and S. Bigot, Identification of a Contact-Dependent Growth Inhibition (CDI) System That Reduces Biofilm Formation and Host Cell Adhesion of Acinetobacter baumannii DSM30011 Strain, Front. Microbiol., 2019, 10 DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2019.02450.
- L. Lin, P. D. Ringel, A. Vettiger, L. Dürr and M. Basler, DNA Uptake upon T6SS-Dependent Prey Cell Lysis Induces SOS Response and Reduces Fitness of Acinetobacter baylyi, Cell Rep., 2019, 29(6), 1633–1644.e4 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. P. J. Smith, A. Vettiger, J. Winter, T. Ryser, L. E. Comstock, M. Basler and K. R. Foster, The evolution of the type VI secretion system as a disintegration weapon, PLoS Biol., 2020, 18(5), e3000720 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. M. Cooper, L. Tsimring and J. Hasty, Inter-species population dynamics enhance microbial horizontal gene transfer and spread of antibiotic resistance, eLife, 2017, 6, e25950 CrossRef PubMed.
- H.-C. Flemming, J. Wingender, U. Szewzyk, P. Steinberg, S. A. Rice and S. Kjelleberg, Biofilms: an emergent form of bacterial life, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2016, 14(9), 563–575 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Flemming and J. Wingender, The biofilm matrix, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2010, 8(9), 623–633 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. B. Otto, M. Martin, D. Schäfer, R. Hartmann, K. Drescher, S. Brix, A. Dragoš and Á. T. KovÁcs, Privatization of Biofilm Matrix in Structurally Heterogeneous Biofilms, mSystems, 2020, 5(4), e00425-20 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. S. Branda, Å. Vik, L. Friedman and R. Kolter, Biofilms: the matrix revisited, Trends Microbiol., 2005, 13(1), 20–26 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. S. Gloag, S. Fabbri, D. J. Wozniak and P. Stoodley, Biofilm mechanics: Implications in infection and survival, Biofilm, 2020, 2, 100017 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. S. Stewart and M. J. Franklin, Physiological heterogeneity in biofilms, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2008, 6(3), 199–210 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Stoodley, I. Dodds, J. D. Boyle and H. M. Lappin-Scott, Influence of hydrodynamics and nutrients on biofilm structure, J. Appl. Microbiol., 1998, 85(S1), 19S–28S CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Yuan, H. Straub, L. Shishaeva and Q. Ren, Microfluidics for Biofilm Studies, Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem., 2023, 16(1), 139–159 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. K. Kim, F. Ingremeau, A. Zhao, B. L. Bassler and H. A. Stone, Local and global consequences of flow on bacterial quorum sensing, Nat. Microbiol., 2016, 1(1), 15005 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. S. Stewart, Mini-review: Convection around biofilms, Biofouling, 2012, 28(2), 187–198 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Stoodley, Z. Lewandowski, J. D. Boyle and H. M. Lappin-Scott, Structural deformation of bacterial biofilms caused by short-term fluctuations in fluid shear: An in situ investigation of biofilm rheology, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 1999, 65(1), 83–92 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Paul, J. C. Ochoa, Y. Pechaud, Y. Liu and A. Liné, Effect of shear stress and growth conditions on detachment and physical properties of biofilms, Water Resour., 2012, 46(17), 5499–5508 CAS.
- R. Martínez-García, C. D. Nadell, R. Hartmann, K. Drescher and J. A. Bonachela, Cell adhesion and fluid flow jointly initiate genotype spatial distribution in biofilms, PLoS Comput. Biol., 2018, 14(4), e1006094 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Rossy, C. D. Nadell and A. Persat, Cellular advective-diffusion drives the emergence of bacterial surface colonization patterns and heterogeneity, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 2471 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. P. H. Wong, M. Fischer-Stettler, S. C. Zeeman, T. J. Battin and A. Persat, Fluid flow structures gut microbiota biofilm communities by distributing public goods, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2023, 120(25), e2217577120 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Rusconi, S. Lecuyer, L. Guglielmini and H. A. Stone, Laminar flow around corners triggers the formation of biofilm streamers, J. R. Soc., Interface, 2010, 7(50), 1293–1299 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Rusconi, S. Lecuyer, N. Autrusson, L. Guglielmini and H. A. Stone, Secondary Flow as a Mechanism for the Formation of Biofilm Streamers, Biophys. J., 2011, 100(6), 1392–1399 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Biswas, M. Sadrzadeh and A. Kumar, Impact of bacterial streamers on biofouling of microfluidic filtration systems, Biomicrofluidics, 2018, 12(4), 044116 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. R. White, M. Jalali and J. Sheng, A new ecology-on-a-chip microfluidic platform to study interactions of microbes with a rising oil droplet, Sci. Rep., 2019, 9(1), 13737 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. R. White, M. Jalali and J. Sheng, Hydrodynamics of a Rising Oil Droplet With Bacterial Extracellular Polymeric Substance (EPS) Streamers Using a Microfluidic Microcosm, Front. Mar. Sci., 2020, 7 DOI:10.3389/fmars.2020.00294.
- A. R. White, M. Jalali, M. C. Boufadel and J. Sheng, Bacteria forming drag-increasing streamers on a drop implicates complementary fates of rising deep-sea oil droplets, Sci. Rep., 2020, 10(1), 4305 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Savorana, J. Slomka, R. Stocker, R. Rusconi and E. Secchi, A microfluidic platform for characterizing the structure and rheology of biofilm streamers, Soft Matter, 2022, 18(20), 3878–3890 RSC.
- V. Hickl and G. Juarez, Tubulation and dispersion of oil by bacterial growth on droplets, Soft Matter, 2022, 18(37), 7217–7228 RSC.
- S. Das and A. Kumar, Formation and post-formation dynamics of bacterial biofilm streamers as highly viscous liquid jets, Sci. Rep., 2014, 4(1), 7126 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Shaw, M. Winston, C. J. Rupp, I. Klapper and P. Stoodley, Commonality of Elastic Relaxation Times in Biofilms, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2004, 93(9), 098102 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Secchi, G. Savorana, A. Vitale, L. Eberl, R. Stocker and R. Rusconi, The structural role of bacterial eDNA in the formation of biofilm streamers, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2022, 119(12), e2113723119 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Scheidweiler, H. Peter, P. Pramateftaki, P. de Anna and T. J. Battin, Unraveling the biophysical underpinnings to the success of multispecies biofilms in porous environments, ISME J., 2019, 13(7), 1700–1710 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. A. Aufrecht, J. D. Fowlkes, A. N. Bible, J. Morrell-Falvey, M. J. Doktycz and S. T. Retterer, Pore-scale hydrodynamics influence the spatial evolution of bacterial biofilms in a microfluidic porous network, PLoS One, 2019, 14(6), e0218316 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Rusconi, J. S. Guasto and R. Stocker, Bacterial transport suppressed by fluid shear, Nat. Phys., 2014, 10(3), 212–217 Search PubMed.
- W. M. Durham, O. Tranzer, A. Leombruni and R. Stocker, Division by fluid incision: Biofilm patch development in porous media, Phys. Fluids, 2012, 24(9), 091107 Search PubMed.
- D. L. Kurz, E. Secchi, F. J. Carrillo, I. C. Bourg, R. Stocker and J. Jimenez-Martınez, Competition between growth and shear stress drives intermittency in preferential flow paths in porous medium biofilms, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2022, 119(30), e2122202119 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Z. Coyte, H. Tabuteau, E. A. Gaffney, K. R. Foster and W. M. Durham, Microbial competition in porous environments can select against rapid biofilm growth, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2016, 114(2), e1525228113 Search PubMed.
- D. L. Kurz, E. Secchi, R. Stocker and J. Jimenez-Martinez, Morphogenesis of Biofilms in Porous Media and Control on Hydrodynamics, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2023, 57(14), 5666–5677 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. D. Nadell, D. Ricaurte, J. Yan, K. Drescher and B. L. Bassler, Flow environment and matrix structure interact to determine spatial competition in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms, eLife, 2017, 6, e21855 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Mukherjee and B. L. Bassler, Bacterial quorum sensing in complex and dynamically changing environments, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2019, 17(6), 371–382 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. Kirisits, J. J. Margolis, B. L. Purevdorj-Gage, B. Vaughan, D. L. Chopp, P. Stoodley and M. R. Parsek, Influence of the Hydrodynamic Environment on Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms, J. Bacteriol., 2007, 189(22), 8357–8360 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Meyer, J. A. Megerle, C. Kuttler, J. Müller, C. Aguilar, L. Eberl, B. A. Hense and J. O. Rädler, Dynamics of AHL mediated quorum sensing under flow and non-flow conditions, Phys. Biol., 2012, 9(2), 026007 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. K. Kim, F. Ingremeau, A. Zhao, B. L. Bassler and H. A. Stone, Local and global consequences of flow on bacterial quorum sensing, Nat. Microbiol., 2016, 1(1), 15005 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. H. Hong, M. Hegde, J. Kim, X. Wang, A. Jayaraman and T. K. Wood, Synthetic quorum-sensing circuit to control consortial biofilm formation and dispersal in a microfluidic device, Nat. Commun., 2012, 3(1), 613 CrossRef PubMed.
- N. M. Oliveira, E. Martinez-Garcia, J. Xavier, W. M. Durham, R. Kolter, W. Kim and K. R. Foster, Biofilm Formation As a Response to Ecological Competition, PLoS Biol., 2015, 13(7), e1002191 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Jang, R. Rusconi and R. Stocker, Biofilm disruption by an air bubble reveals heterogeneous age-dependent detachment patterns dictated by initial extracellular matrix distribution, npj Biofilms Microbiomes, 2017, 3(1), 6 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Jin, M. Nie, R. Hu, T. Zhao, J. Xu, D. Chen, J. Yun, L. Z. Ma and W. Du, Dynamic Sessile-Droplet Habitats for Controllable Cultivation of Bacterial Biofilm, Small, 2018, 14(22), 1800658 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Pioli, R. Stocker, L. Isa and E. Secchi, Patterning of Microorganisms and Microparticles through Sequential Capillarity-assisted Assembly, J. Visualized Exp., 2021, 177, 1–15 Search PubMed.
- S. Moossavi, M.-C. Arrieta, A. Sanati-Nezhad and F. Bishehsari, Gut-on-chip for ecological and causal human gut microbiome research, Trends Microbiol., 2022, 30(8), 710–721 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. J. Kim, D. Huh, G. Hamilton and D. E. Ingber, Human gut-on-a-chip inhabited by microbial flora that experiences intestinal peristalsis-like motions and flow, Lab Chip, 2012, 12(12), 2165 RSC.
- A. Grassart, V. Malardé, S. Gobba, A. Sartori-Rupp, J. Kerns, K. Karalis, B. Marteyn, P. Sansonetti and N. Sauvonnet, Bioengineered Human Organ-on-Chip Reveals Intestinal Microenvironment and Mechanical Forces Impacting Shigella Infection, Cell Host Microbe, 2019, 26(3), 435–444.e4 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Shah, J. V. Fritz, E. Glaab, M. S. Desai, K. Greenhalgh, A. Frachet, M. Niegowska, M. Estes, C. Jäger, C. Seguin-Devaux, F. Zenhausern and P. Wilmes, A microfluidics-based in vitro model of the gastrointestinal human–microbe interface, Nat. Commun., 2016, 7(1), 11535 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. E. Stanley, M. Stöckli, D. van Swaay, J. Sabotič, P. T. Kallio, M. Künzler, A. J. deMello and M. Aebi, Probing bacterial–fungal interactions at the single cell level, Integr. Biol., 2014, 6(10), 935–945 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Parashar and S. Pandey, Plant-in-chip: Microfluidic system for studying root growth and pathogenic interactions in Arabidopsis, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2011, 98(26), 263703 CrossRef.
- J. A. Aufrecht, C. M. Timm, A. Bible, J. L. Morrell-Falvey, D. A. Pelletier, M. J. Doktycz and S. T. Retterer, Quantifying the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Plant Root Colonization by Beneficial Bacteria in a Microfluidic Habitat, Adv. Biosyst., 2018, 2(6), 1800048 CrossRef.
- E. E. Clerc, J.-B. Raina, B. S. Lambert, J. Seymour and R. Stocker, In Situ Chemotaxis Assay to Examine Microbial Behavior in Aquatic Ecosystems, J. Visualized Exp., 2020,(159) DOI:10.3791/61062.
- B. S. Lambert, J.-B. Raina, V. I. Fernandez, C. Rinke, N. Siboni, F. Rubino, P. Hugenholtz, G. W. Tyson, J. R. Seymour and R. Stocker, A microfluidics-based in situ chemotaxis assay to study the behaviour of aquatic microbial communities, Nat. Microbiol., 2017, 2(10), 1344–1349 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. E. Clerc, J.-B. Raina, J. M. Keegstra, Z. Landry, S. Pontrelli, U. Alcolombri, B. S. Lambert, V. Anelli, F. Vincent, M. Masdeu-Navarro, A. Sichert, F. De Schaetzen, U. Sauer, R. Simó, J.-H. Hehemann, A. Vardi, J. R. Seymour and R. Stocker, Strong chemotaxis by marine bacteria towards polysaccharides is enhanced by the abundant organosulfur compound DMSP, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14(1), 8080 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. M. Mafla-Endara, C. Arellano-Caicedo, K. Aleklett, M. Pucetaite, P. Ohlsson and E. C. Hammer, Microfluidic chips provide visual access to in situ soil ecology, Commun. Biol., 2021, 4(1), 889 CrossRef PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |
