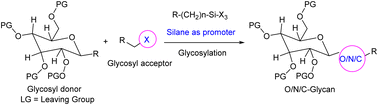
The structural diversity of carbohydrates through glycosylation reactions is the holy grail of carbohydrate chemistry. One or more carbohydrates covalently bonded to another molecule at selective sites by glycosylation/glycoconjugation are often required for better pharmacological activity and their synthesis is apparently more consistent. Selective conjugation of carbohydrates at the –OH group remains a challenge because of the similar reactivity of equivalent polyhydroxyl groups. Eventually a small variety of reagents have been demonstrated to promote site selective glycosylation reactions. Silanes have long provided a leverage in glycosylation reactions since they are easy to install and remove/modify in various synthetic procedures. Regardless of the fact that silanes have proven to be efficient promoters for facile glycoconjugation reactions, a thorough investigation has not been done on this subject. This review discusses the recent application and synthetic usefulness of versatile silanes like trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate (TMSOTf), tert-butyldimethylsilyltrifluoromethanesulphonate (TBSOTf), N-(trimethylsilyl)bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (TMSNTf2), potassium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide (KHMDS), trimethylsilyl perchlorate (TMSClO4), etc. in various site selective glycosylation reactions and also effective methods for the preparation of sugar compounds and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).