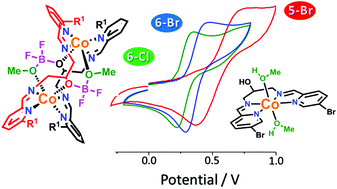
Three new tetradentate imine ligands, HLHBr, HLClH and HLBrH (HLR1R2) were synthesised by 2 : 1 condensation of the appropriately n-halo substituted pyridine-2-carboxaldehyde (5-bromo-4a, 6-bromo-4b or 6-chloro-4c) with 1,3-diaminopropan-2-ol (5). Reactions of each of these three ligands with one equivalent of cobalt(II) tetrafluoroborate resulted in the formation of three N4O2 coordinated cobalt(II) complexes: the anticipated mononuclear complex [CoII(HLHBr)(MeOH)2](BF4)2 (1), and two unexpected dinuclear complexes, [CoII2(LBrH-BF2OMe)]2(BF4)2 (2) and [CoII2(LClH-BF2OMe)]2(BF4)2 (3). Dinuclear 2 and 3 result from complexation of cobalt(II) to the ligands derived from the sterically demanding 6-halo substituted pyridine-2-carboxaldehydes (4b and 4c) undergoing rearrangement, reacting with MeOH and a BF4 anion, resulting in a pair of borate ester bridges between the two cobalt(II) centres. A similar type of rearrangement is proposed for the PF6 analogues. Cyclic voltammetry in acetonitrile reveals that cobalt(II) complexes 1–3 undergo a quasi-reversible oxidation: Em = 0.57, 0.38 and 0.29 V vs. 0.01 AgNO3/Ag, respectively. The observed Em value is tuned by the ligand, with the 6-chloro-substituent leading to the lowest Em value being observed for the corresponding cobalt complex, 3, rather than for either of the complexes of the n-bromo-substituted ligands (n = 6 or 5), 2 and 1.