Statistical thermodynamics of non-stoichiometric ceria and ceria zirconia solid solutions†
Abstract
The thermodynamic redox properties of ceria and ceria zirconia solid solutions are analysed with a new methodology for modelling such systems based on the statistical mechanics of lattice configurations. Experimental thermogravimetric equilibrium data obtained for small non-stoichiometry measurements are combined with literature data to cover a large range of non-stoichiometry (CeO2−δ, δ = 0.001–0.32), temperature (1073–1773 K) and oxygen partial pressure (1–10−13 bar). A dilute species model of defect clusters 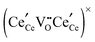 , obeying the law of mass action, was sufficient to describe the system over the whole range of conditions, leading to a simple analytical equation of state for the system. This offers new physical insight into the redox properties of ceria based materials, and the theoretical methods developed should also be of great interest for other materials which exhibit continuous oxygen non-stoichiometry similar to ceria, such as perovskite oxides.
, obeying the law of mass action, was sufficient to describe the system over the whole range of conditions, leading to a simple analytical equation of state for the system. This offers new physical insight into the redox properties of ceria based materials, and the theoretical methods developed should also be of great interest for other materials which exhibit continuous oxygen non-stoichiometry similar to ceria, such as perovskite oxides.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...