Single electron transfer catalysis by diphenylthiourea under visible light photoredox conditions†
Abstract
Herein, we report diphenylthiourea (DPTU) as a potent photocatalyst, which in its deprotonated state can promote reductive bond cleavage in aryl bromide substrates. An easy deprotonation of the DPTU molecule using a strong base KOtBu and subsequent photoexcitation makes it a fairly strong reductant that promotes single electron transfer (SET). The excited-state potential for the deprotonated thiourea was calculated to be 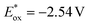 vs. SCE which is promising for the reductive cleavage of strong aryl bromide bonds. Leveraging on the reductive capacity of the DPTU anion, an aryl radical was generated under blue light excitation and it was employed in isoindolinone and oxindole formation and C–C cross-coupling reactions. Interestingly, the deprotonated form of DPTU was crystallized in the presence of a crown ether and catalysis was conducted with the isolable crystalline material to substantiate the role of putative anionic species in photocatalysis. The fate of DPTU after electron transfer was also traced to reveal that multiple species in reaction solution helped to build sufficient concentration of aryl radicals.
vs. SCE which is promising for the reductive cleavage of strong aryl bromide bonds. Leveraging on the reductive capacity of the DPTU anion, an aryl radical was generated under blue light excitation and it was employed in isoindolinone and oxindole formation and C–C cross-coupling reactions. Interestingly, the deprotonated form of DPTU was crystallized in the presence of a crown ether and catalysis was conducted with the isolable crystalline material to substantiate the role of putative anionic species in photocatalysis. The fate of DPTU after electron transfer was also traced to reveal that multiple species in reaction solution helped to build sufficient concentration of aryl radicals.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...