A single hydrogen bond that tunes flavin redox reactivity and activates it for modification†
Abstract
Electron bifurcation produces high-energy products based on less energetic reagents. This feat enables biological systems to exploit abundant mediocre fuel to drive vital but demanding reactions, including nitrogen fixation and CO2 capture. Thus, there is great interest in understanding principles that can be portable to man-made devices. Bifurcating electron transfer flavoproteins (Bf ETFs) employ two flavins with contrasting reactivities to acquire pairs of electrons from a modest reductant, NADH. The bifurcating flavin then dispatches the electrons individually to a high and a low reduction midpoint potential (E°) acceptor, the latter of which captures most of the energy. Maximum efficiency requires that only one electron accesses the exergonic path that will ‘pay for’ the production of the low-E° product. It is therefore critical that one of the flavins, the ‘electron transfer’ (ET) flavin, is tuned to execute single-electron (1e−) chemistry only. To learn how, and extract fundamental principles, we systematically altered interactions with the ET-flavin O2 position. Removal of a single hydrogen bond (H-bond) disfavored the formation of the flavin anionic semiquinone (ASQ) relative to the oxidized (OX) state, lowering 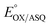 by 150 mV and retuning the flavin's tendency for 1e−vs. 2e− reactivity. This was achieved by replacing conserved His 290 with Phe, while also replacing the supporting Tyr 279 with Ile. Although this variant binds oxidized FADs at 90% the WT level, the ASQ state of the ET-flavin is not stable in the absence of H290's H-bond, and dissociates, in contrast to the WT. Removal of this H-bond also altered the ET-flavin's covalent chemistry. While the WT ETF accumulates modified flavins whose formation is believed to rely on an anionic paraquinone methide intermediate, the FADs of the H-bond lacking variant remain unchanged over weeks. Hence the variant that destabilizes the anionic semiquinone also suppresses the anionic intermediate in flavin modification, verifying electronic similarities between these two species. These correlations suggest that the H-bond that stabilizes the crucial flavin ASQ also promotes flavin modification. The two effects may indeed be inseparable, as a Jekyll and Hydrogen bond.
by 150 mV and retuning the flavin's tendency for 1e−vs. 2e− reactivity. This was achieved by replacing conserved His 290 with Phe, while also replacing the supporting Tyr 279 with Ile. Although this variant binds oxidized FADs at 90% the WT level, the ASQ state of the ET-flavin is not stable in the absence of H290's H-bond, and dissociates, in contrast to the WT. Removal of this H-bond also altered the ET-flavin's covalent chemistry. While the WT ETF accumulates modified flavins whose formation is believed to rely on an anionic paraquinone methide intermediate, the FADs of the H-bond lacking variant remain unchanged over weeks. Hence the variant that destabilizes the anionic semiquinone also suppresses the anionic intermediate in flavin modification, verifying electronic similarities between these two species. These correlations suggest that the H-bond that stabilizes the crucial flavin ASQ also promotes flavin modification. The two effects may indeed be inseparable, as a Jekyll and Hydrogen bond.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...