Dynamic kinetic resolution of tert-butyl 4-methyl-3,5-dioxohexanoate through enzymatic reduction
Aiguo Jia, Michael Wolberga, Werner Hummelc, Christian Wandreya and Michael Müller*a
aInstitut für Biotechnologie 2, Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH, 52425, Jülich, Germany.. E-mail: E-mail: mi.mueller@fz-juelich.de
bDepartment of Pharmacy, Shandong Medical University, Jinan, Shandong 250012, China
cInstitut für Enzymtechnologie der Heinrich-Heine
Universität Düsseldorf im Forschungszentrum Jülich
GmbH, 52426, Jülich, Germany
First published on 14th December 2000
Abstract
An entirely new method for the dynamic kinetic resolution of a racemic, 2-methyl substituted, unsymmetrical 1,3-diketone via enzymatic reduction to give an enantiomerically pure compound is introduced.
The dynamic kinetic resolution of α-substituted β-keto esters by chemical1 or biocatalytical2 reduction is particularly useful due to the simultaneous introduction of two stereogenic centres into the molecule in combinationwith a theoretical maximum yield of 100%. Although this method has proven broad applicability in stereoselective synthesis, the corresponding dynamic kinetic resolution of 2-substituted 1,3-diketones is rarely found in the literature.3 Our aim is directed toward extending dynamic kinetic resolution to enantio- and regioselective reduction of alkyl-substituted 3,5-dioxoesters, which would enable the introduction of up to four stereogenic centers by two consecutive reduction steps.
The attempted enantioselective ketone reduction of 3,5-dioxohexanoate esters by chemical methods4 or biotransformation5 usually results in complex mixtures of several stereo- and regioisomeric products with one or both keto groups reduced. We figured out that this difficult transformation can be accomplished by using isolated enzymes to afford optically pure 5-hydroxy-3-oxohexanoates in high yield.6 Herein we wish to report in preliminary form on the first enantio- and regioselective enzymatic reduction of 4-alkyl-3,5-dioxohexanoates resulting in formation of one out of a total of 8 monoreduction and 8 bisreduction products.
tert-Butyl 4-methyl-3,5-dioxohexanoate (1) was prepared by acylation of the bisenolate of tert-butyl 3-oxovalerate with commercially available Weinreb acetamide.7 For the enzymatic reduction recombinant alcohol dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus brevis (recLBADH) was chosen, which has been cloned and overexpressed in E. coli.8 recLBADH exhibits a broad substrate range and considerable stability even towards highly reactive compounds like 6-chloro-3,5-dioxohexanoates.6,8 Cofactor (NADPH) regeneration succeeds via a coupled-substrate process. Propan-2-ol (200 mM) was applied in excess to the reaction mixture as an auxiliary substrate in order to shift the equilibrium of the reaction towards the desired direction (Scheme 1).9
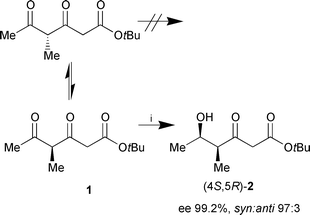 | ||
| Scheme 1 Reagents and conditions: i, 1 (20 mM), propan-2-ol (200 mM), NADP+ (1 mM), pH 6.5, recLBADH (360 U), 23 h, rt (66%). | ||
NMR data of the major product (4S,5R)-2 which was obtained in 66% isolated yield, clearly proved the regioselective monoreduction of the keto group at C-5. Additionally, from GC-MS data of the crude product after derivatisation with (F3CCO)2O, pyridine, no evidence could be found for the reduction of the keto group at C-3. In order to verify the proposed absolute configuration and to enable precise determination of the enantiomeric excess, (4S,5R)-2 was transformed through sodium borohydride reduction into lactone 4via diol (3RS,4S,5R)-3. Lactonisation and dehydration gave the unsaturated lactone (5R,6R)-4 which is known in racemic form10 (Scheme 2).
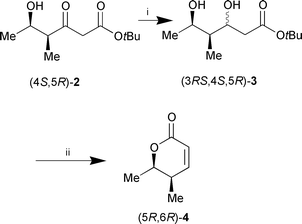 | ||
| Scheme 2 Reagents and conditions: i, NaBH4, EtOH, 0 °C; ii, cat. TsOH, toluene, reflux, 2 h (60% over two steps). | ||
As a standard a racemic 1:1 mixture of syn- and anti-lactonerac-4 was synthesised from keto ester 5 by sodium borohydride reduction, subsequent chain elongation, and, finally, lactone formation as described above (Scheme 3). The four stereoisomers of syn/anti-rac-4, which were formed in equal amounts, can be separated by HPLC on chiral stationary phase (Daicel Chiracel OB).
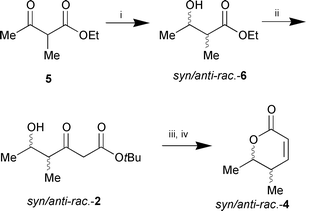 | ||
Scheme 3 Reagents and conditions: i, NaBH4, EtOH,
0 °C (83%); ii, CH2![[double bond, length half m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e006.gif) C(OLi)OtBu, THF,
−30 °C (53%); iii, NaBH4, EtOH, 0 °C;
iv, cat. TsOH, toluene, reflux, 2 h (60% over two steps). C(OLi)OtBu, THF,
−30 °C (53%); iii, NaBH4, EtOH, 0 °C;
iv, cat. TsOH, toluene, reflux, 2 h (60% over two steps). | ||
An authentic sample of the enantiomeric syn-lactone (5S,6S)-4 was synthesised by the same sequence starting from bakers’ yeast reduction of 5via the known11 ethyl (2R,3S)-2-methyl-3-hydroxybutyrate (2R,3S)-6 (Scheme 4).
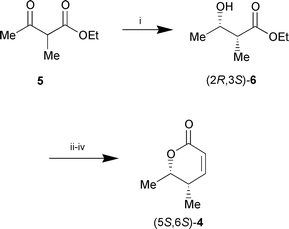 | ||
Scheme 4 Reagents and conditions: i, bakers’ yeast, 10% aq. EtOH,
(50%); ii, CH2![[double bond, length half m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e006.gif) C(OLi)OtBu, THF, −30
°C; iii, NaBH4, EtOH, 0 °C; iv, cat. TsOH,
toluene, reflux, 2 h (53% over three steps). C(OLi)OtBu, THF, −30
°C; iii, NaBH4, EtOH, 0 °C; iv, cat. TsOH,
toluene, reflux, 2 h (53% over three steps). | ||
The spectroscopic data (1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, MS) of (5S,6S)-4 and of (5R,6R)-4, produced via enzymatic (recLBADH) reduction of 1, are identical. Comparison of the CSP-HPLC data of both lactones revealed the (4S,5R)-absolute configuration for the product 2 of the recLBADH reduction. This product is formed in almost enantiomerically pure form (99.2% ee, HPLC data); the diastereomeric ratio of syn∶anti 97∶3 is likewise very high (NMR and HPLC data).
In summary, we have shown the regio- and enantioselective reduction of tert-butyl 4-methyl-3,5-dioxohexanoate via dynamic kinetic resolution to give an almost enantiomerically and diastereomerically pure compound introducing two stereogenic centers can be done efficiently by enzyme-catalysed reduction. This method represents a novel entry into the chemistry of polypropionates based on a biomimetic approach via polyketides. This method should be extendable towards dynamic kinetic resolution of other 2-alkyl-substituted unsymmetrical 1,3-diketones.
Acknowledgements
A. Ji is the recipient of a Chinese Government Fellowship. The skilful technical assistance of Mrs Silke Bode is gratefully acknowledged. We thank the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 380) for financial support.Notes and references
- R. Noyori, M. Tokunaga and M. Kitamura, Bull. Chem. Soc., 1995, 68, 36; and refs. cited therein. Search PubMed.
- H. Stecher and K. Faber, Synthesis, 1997, 1; and refs. cited therein. Search PubMed.
- S. Tsuboi, E. Nishiyama, H. Furutani, M. Utaka and A. Takeda, J. Org. Chem., 1987, 52, 1359 CrossRef CAS; T. Fujisawa, B. I. Mobele and M. Shimizu, Tetrahedron Lett., 1992, 33, 5567 CrossRef CAS; T. Zelinski, A. Liese, C. Wandrey and M.-R. Kula, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 1999, 10, 1681 CrossRef CAS cf. R. Hayakawa and M. Shimizu, Synlett, 1999, 1298; (α-substituted β-ketoaldehyde)..
- V. Blandin, J.-F. Carpentier and A. Mortreux, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 1999, 3421 CrossRef CAS; L. Shao, H. Kawano, M. Saburi and Y. Uchida, Tetrahedron, 1993, 49, 1997 CrossRef CAS N. Sayo, T. Saito, H. Kumobayashi, S. Akutagawa, R. Noyori and H. Takaya, (Takasago International Corp.), Eur. Pat. Appl. EP 297,752, 1989 [Chem. Abstr., 1989, 111, 114745n]..
- R. N. Patel, A. Banerjee, C. G. McNamee, D. Brzozowski, R. L. Hanson and L. J. Szarka, Enzyme Microb. Technol., 1993, 15, 1014 CrossRef CAS M. Uko, H. Azuma, T. Sakai, S. Tsuboi (Mitsubishi Kasei Corp.), Jpn. Kokai Tokkyo Koho JP 03-48,641, 1991 [Chem Abs. 1991, 115, 28713b]..
- M. Wolberg, W. Hummel, C. Wandrey and M. Müller, Angew. Chem., in press. Search PubMed.
- S. Nahm and S. M. Weinreb, Tetrahedron Lett., 1981, 22, 3815 CrossRef CAS cf. J.-F. Lavallée, C. Spino, R. Ruel, K. T. Hogan and P. Deslongchamps, Can. J. Chem., 1992, 70, 1406 CAS cf. K. B. Mullah and J. K. Sutherland, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1992, 1237 RSC.
- B. Riebel, PhD thesis, University of Düsseldorf, 1996..
- Enzymatic transformation: A solution of recLBADHwas prepared by mechanically disrupting wet cells of recombinant E. coli strain recADH-HB101+.8 One unit (U) enzyme activity is defined as the amount of recLBADH that catalyses the oxidation of 1 μmol NADPH per minute when incubated with acetophenone (10 mM) and NADPH (0.25 mM) at 25 °C and pH 6.5 (100 mM phosphate buffer, 1 mM MgCl2). In a round bottom flask, a solution of diketo ester 1 (0.53 g, 2.5 mmol) in propan-2-ol (1.9 mL, 25 mmol) was added to 120 mL phosphate buffer (100 mM, pH 6.5) containing 1 mM MgSO4, and the mixture was ultrasonicated for 1 minute. The reaction was started by addition of NADP+ (105 mg, 120 μmol; FLUKA Nr. 93210, 90%) and recLBADH (360 U). After slowly stirring for 23 h at ambient temperature, 20 g NaCl were added and the solution was extracted with ethyl acetate three times. The combined organic phases were dried over MgSO4 and evaporated. The crude product was purified by flash chromatography (silica, ethyl acetate isohexane 40/60 (v/v)), yielding 0.35 g (66%) hydroxyketo ester (4S,5R)-2 as a colourless oil..
- M. A. Adams, A. J. Duggan, J. Smolanoff and J. Meinwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1979, 101, 5364 CrossRef CAS; T. M. Willson, P. Kocienski, K. Jarowicki, K. Isaac, A. Faller, S. F. Campbell and J. Bordner, Tetrahedron, 1990, 46, 1757 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Akita, A. Furuichi, H. Koshiji, K. Horikoshi and T. Oishi, Chem. Pharm. Bull., 1983, 31, 4376 Search PubMed; G. Fráter, U. Müller and W. Günther, Tetrahedron, 1984, 40, 1269 CrossRef CAS; K. Nakamura, T. Miyai, A. Nagar, S. Oka and A. Ohno, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 1989, 62, 1179 CAS; W.-R. Shieh and C. J. Sih, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 1993, 4, 1259 CrossRef CAS.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2001 |
