Stable pyrano[2,3-b]quinoxalines and pyrano[2,3-g]pteridines related to molybdopterin
Ben
Bradshaw
,
David
Collison
,
C. David
Garner†
and
John A.
Joule
*
Chemistry Department, The University of Manchester, Manchester, UK M13 9PL. E-mail: j.a.joule@man.ac.uk
First published on 18th December 2000
Abstract
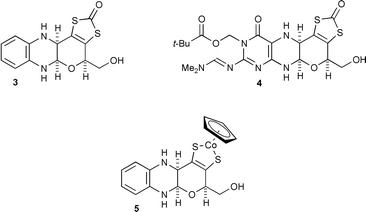
The syntheses of the quinoxaline and pteridine proligands (3 and 4) related to molybdopterin are described and 3 has been characterised complexed via its dithiolene group to a CpCo(III) centre (5). Each of 3–5 has the sensitive hemiaminal unit of molybdopterin, unprotected, verifying its stability in vitro.
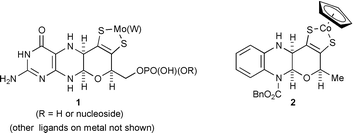
The pioneering studies on representatives of the molybdenum enzymes by Garrett and Rajagopalan1 showed that each contained a prosthetic group that comprises a pteridine carrying a C4-side-chain at pteridine C-6, having two sulfur atoms which ligate molybdenum. A series of X-ray crystallographic determinations on molybdenum and tungsten enzymes2 further clarified the structure of the cofactor and its mode of ligation to Mo and W. Thus, the metals are chelated by an ene-1,2-dithiolate (dithiolene) which is part of a tricyclic system, in which a dihydropyran ring is fused to a partially reduced pteridine, 1. The pterin (2-aminopteridin-4(3H)-one) moiety is generally known as molybdopterin.
We have previously described3 the synthesis of CpCo(III) (where Cp = η5-cyclopentadienyl) complex 2 which involves ligation of the metal by a dithiolene moiety as part of a dihydropyran fused to a partially reduced pyrazine, as in 1. However, 2 differs from 1 in several key respects. Firstly, 2 has a benzene ring instead of a pyrimidine ring; secondly the terminal primary hydroxy (phosphate) is absent; and thirdly, and crucially it retains a urethane at the nitrogen of the hemiaminal unit. It was far from certain that, freed from this protection against possible cleavage of the N–C–O system, the cyclic aminal would be stable, especially during the process of ligand release and complexation to a metal centre. Thus, to assess whether there are any special effects operating in the natural system which maintain the hemiaminal linkage, it was essential that structural analogues of 1 without the urethane be prepared. We describe here the synthesis of just such model compounds, the proligands 3 and 4 and the cobalt complex 5 derived from 3.
We have previously described syntheses of quinoxaline 64 and protected pteridine 10.5 Hydrolysis of the acetal in 6 then reaction of 7 with fluoren-9-ylmethyl chloroformate (Fmoc-Cl), under carefully defined conditions gave a high yield of a 2∶1 mixture of cis6 (the desired) and trans tetracyclic products 8 which could not be separated by chromatography. Reduction of the mixture with sodium cyanoborohydride proceeded stereoselectively producing 9a6 and 9b6 which could be separated. It is notable that there were no problems associated with the presence of a second alcohol group—neither cyclisation to give an oxepino[2,3-b]quinoxaline nor acylation of the primary hydroxy occurred.
Release of the Fmoc nitrogen protection, most efficiently using diethylamine,7 gave the unprotected compound 3which retained the hemiaminal unit. It remained to verify that this sensitive functionality would survive conditions to release the enedithiolate and form a metal complex. This indeed proved to be possible for, using caesium hydroxide for hydrolytic ligand release, with subsequent trapping by reaction with CpCoI2, complex 5 was produced (Scheme 1).
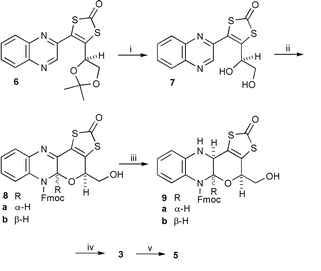 | ||
| Scheme 1 Reagents and conditions: i, TsOH·H2O, MeOH, reflux (92%); ii, Fmoc-Cl, 1,4-dioxane, 35 °C, 14 h (92%); iii, NaB(CN)H3, AcOH, CH2Cl2, MeOH, rt (92%); iv, 9a, Et2NH, THF, rt (80%); v, CsOH, CHCl3, MeOH, rt then Cp(Co)I2 (55%). | ||
A comparable sequence led to the isolation of a pyranopteridine having an unprotected hemiaminal unit. Thus, treatment of pteridine 10 with trifluoroacetic acid allowed selective removal of the acetal protection giving diol 11 then reaction of this with Fmoc-Cl produced a separable mixture of pyran-containing products in which the ratio of cis-12a6 (desired) to trans-12b6 (2∶1) was comparable to that in the quinoxaline series. Conducting the cyclisation reaction at rt produced a more favourable ratio (4∶1) of products but the reaction was much slower, not being complete after 1 week. N-Deprotection of the ‘wrong’ isomer 12b led cleanly back to 11 (incidentally confirming the lability of the N–C–O unit) which could thus be recycled. Cyanoborohydride reduction of the cis isomer proceeded stereoselectively in high yield and removal of the N-8-protection from 13 gave pro-ligand 46 with the hemiaminal unit intact and having the same relative stereochemistry8 as the prosthetic groups in the natural cofactors (Scheme 2).
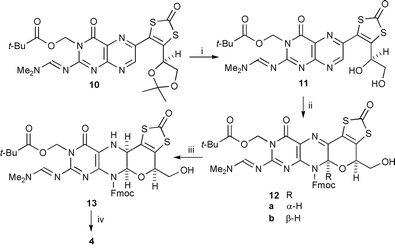 | ||
| Scheme 2 Reagents and conditions: i, TFA, CH2Cl2, 0 °C→rt (90%); ii, Fmoc-Cl, 1,4-dioxane, H2O, 35 °C, 14 h (84%); iii, 11a, NaB(CN)H3, AcOH, CH2Cl2, MeOH, rt (92%); iv, Et2NH, THF, rt (85%). | ||
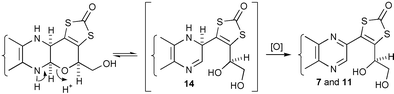
Both 3 and 4 are relatively stable compounds. However, after several weeks at rt, and without protection from moisture or oxygen, each reverted to the corresponding ring opened diol, 7 and 11. This must involve reversible proton-catalysed cleavage of the N–C–O system revealing dihydro-systems 14 and then irreversible aerial oxidation (Scheme 3). The stabilities of the pyranoquinoxalines and pyranopteridine established in this work make it unlikely that any special properties of the enzyme environment need to be invoked to explain the tricyclic form of molybdopterin found in all the crystal structure determinations,2 save that it must be protected from oxidation. The proton-catalysed cleavage of the N–C–O system, which we have suggested9 may be intimately involved with catalysis at the metal centre, can now be studied in vitro with the compounds described herein. We shall be reporting on such studies in due course.
 | ||
| Scheme 3 | ||
Acknowledgements
We thank the EPSRC for post-graduate (B. B.) and post-doctoral (B. B.) support for this work.Notes and references
- For a leading reference see R. M. Garrett and K. V. Rajagopalan, J. Biol. Chem., 1996, 271, 7387 CrossRef CAS.
- M. K. Chan, S. Mukund, A. Kletzin, M. W. W. Adams and D. C. Rees, Science, 1995, 267, 1463 CAS; M. J. Romão, M. Archer, I. Moura, J. J. G. Moura, J. LeGall, E. Engh, M. Schneider, P. Hof and R. Huber, Science, 1995, 270, 1170 CAS; H. Schindelin, C. Kisker, J. Hilton, K. V. Rajagopalan and D. C. Rees, Science, 1996, 272, 1615 CrossRef CAS; F. Schneider, J. Löwe, R. Huber, H. Schindelin, C. Kisker and J. Knäblein, J. Mol. Biol., 1996, 263, 53 CrossRef CAS; R. Huber, P. Hof, R. O. Duarte, J. J. G. Moura, I. Moura, M.-Y. Liu. J. Legall, R. Hille, M. Archer and M. Romão, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1996, 93, 8846 CrossRef CAS; J. C. Boyington, V. Sladishev, S. V. Khangulov, T. C. Stadtman and P. D. Sun, Science, 1997, 275, 1305 CrossRef CAS; J. Knäblein, H. Dobbeck, S. Ehlert and F. Schneider, Biol. Chem., 1997, 378, 293 Search PubMed; C. Kisker, H. Schindelin, A. Pacheco, W. A. Wehbi, R. M. Garrett, K. V. Rajagopalan, J. H. Enemark and D. C. Rees, Cell, 1997, 91, 973 CrossRef CAS; M. Czjzek, J.-P. Dos Santos, J. Pommier, G. Giordano, V. Méjean and R. Haser, J. Mol. Biol., 1998, 284, 435 CrossRef CAS; A. S. McAlpine, A. G. McEwan and S. Bailey, J. Mol. Biol., 1998, 275, 613 CrossRef CAS; J. M. Dias, M. E. Than, A. Humm, R. Huber, G. P. Bourenkov, H. D. Bartunik, S. Bursakov, J. Calvete, J. Caldeira, C. Carneiro, J. J. G. Moura, I. Moura and M. J. Romão, Structure, 1999, 7, 65 CrossRef CAS; H. Dobbek, L. Gremer, O. Meyer and R. Huber, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1999, 96, 8884 CrossRef CAS; H.-K. Li, C. Temple, K. V. Rajagopalan and H. Schindelin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2000, 122, 7673 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Bradshaw, A. Dinsmore, C. D. Garner and J. A. Joule, Chem. Commun., 1998, 417 RSC.
- A. Dinsmore, C. D. Garner and J. A. Joule, Tetrahedron, 1998, 54, 3291 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Dinsmore, C. D. Garner and J. A. Joule, Tetrahedron, 1998, 54, 9559 CrossRef CAS.
- In each case, relative stereochemistry was determined by NOE experiments involving the hydrogen atoms at the pyran/pyrazine ring junction and at the hydroxymethyl-bearing carbon..
- M. Ueki, N. Nishigaki, H. Aoki, T. Tsurusaki and T. Katoh, Chem. Lett., 1993, 721 CAS; K. C. Nicolau, C. W. Hummel, M. Nakada, K. Shibayama, E. N. Pitsinos, H. Saimoto, Y. Mizuno, K. Baldenuius and A. L. Smith, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1993, 115, 7625 CrossRef CAS.
- D. C. Rees, Y. Hu, C. Kisker and H. Schindelin, J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans., 1997, 3909 RSC.
- S. P. Greatbanks, I. H. Hillier, C. D. Garner and J. A. Joule, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 1997, 1529 RSC.
Footnote |
| † Present address: School of Chemistry, University of Nottingham, University Park, Nottingham, UK NG7 2RD. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2001 |