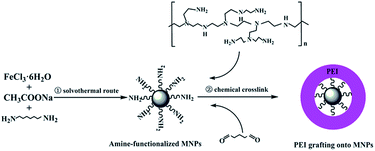
Highly stable and covalently functionalized magnetic nanoparticles by polyethyleneimine for Cr(VI) adsorption in aqueous solution†
Bo Chen‡
,
Xuesong Zhao‡,
Yang Liu,
Bugang Xu and
Xuejun Pan*
Faculty of Environmental Science and Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, Yunnan 650500, PR China. E-mail: xjpan@kmust.edu.cn; Fax: +86-871-65920510; Tel: +86-871-65920510
First published on 26th November 2014
Abstract
In the present work, highly stable magnetic nanoparticles covalently functionalized by polyethyleneimine (PEI), denoted as PEI-MNPs, were prepared based on the glutaraldehyde crosslinking reaction between the aldehyde moiety in glutaraldehyde and the amine groups in both PEI and Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs), and showed strong adsorption affinity to Cr(VI). The successful modification by PEI was confirmed by a series of measurements, such as TEM, XRD, FT-IR, TGA, et al. The time-dependent adsorption experiments indicated that the adsorption of Cr(VI) onto PEI-MNPs finished within 10 min and the adsorption process could be described by the pseudo-second-order kinetics model. The studies on the adsorption of Cr(VI) revealed that the Langmuir adsorption isotherm with the adsorption capacity of 175.76 mg g−1 at 318 K fit the adsorption data. The calculated thermodynamic parameters (ΔG, ΔH, and ΔS) indicated that adsorption of Cr(VI) on PEI-MNPs was spontaneous and exothermic. Furthermore, the stability testing demonstrated that the used adsorbents could be regenerated effectively with 0.5 mol L−1 NaOH solution and no significant loss of adsorption capacity were observed after a run of 20 adsorption–desorption cycles, showing their high stability in extremely acidic and alkaline solution. Most importantly, the obtained PEI-MNPs composite can effectively and selectively absorb Cr(VI) from complex industrial wastewater, indicating that PEI-MNPs could be used as a promising adsorbent for removal of Cr(VI) from real wastewater with high efficiency.
Introduction
Chromium, as a toxic heavy metal, is widely used in industrial applications as a catalyst or a pigment for electroplating leather tannins.1 Cr(III) and Cr(VI) are the two main oxidation states of chromium in aqueous systems. Cr(III) is relatively nontoxic and considered as an essential micronutrient, while Cr(VI) is highly toxic, mutagenic and carcinogenic to living organisms due to its strong oxidizing properties.2–4 Moreover, Cr(VI) poses a serious threat to the ecological environment and human health due to its typical speciation as anionic chromate or dichromate, making it highly mobile in the environment.5,6 Therefore, it is crucial to remove Cr(VI) from a contaminated aqueous solution before their discharge into receiving waters.Various methods have been taken into account for removing of Cr(VI) from wastewater, such as ion-exchange,7 chemical precipitation,8 adsorption,9 liquid–liquid extraction,10 membrane technologies11 and electrochemical treatment.12 Among these methods, adsorption is considered to be an efficient, simple and relatively low-cost approach for Cr(VI) removal. Furthermore, adsorption not only can deal with contaminants but also can recover and recycle them back to industrial processes.13 Up to now, a large number of different solid adsorbents, such as graphene,14 biological substances,15 activated carbon,16 montmorillonite,17 zero-valent iron18 et al. have been adopted to dispose Cr(VI). Compared with traditional materials, Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) as adsorbents have attracted considerable attention in the past several decades owing to their huge specific surface area and easily separation from wastewater with an external magnetic field.19–21
PEI, as a typical water-soluble polyamine, contains a great number of nitrogen atoms of amine groups on its macromolecular chains.22,23 According to the different structures, it can be divided into linear and branched forms. Linear PEI is only composed of secondary amine groups, while branched PEI is consists of primary, secondary and tertiary amine forms.24 Several studies have confirmed that these amine groups have strong adsorption ability to Cr(VI).25–27 Based on the hypothesis that the composites composed of PEI and MNPs combine the magnetic properties of MNPs and the extremely high adsorption capacity of PEI, many efforts have been exerted to explore MNPs modified by PEI (PEI-MNPs). In previously published work, various methods, such as electrostatic interaction,28 self-assembly,29 dispersion polymerization method30 and co-precipitation method,31 have been adopted to prepare PEI-MNPs. However, a lot of primary experimental results in our laboratory demonstrated that the magnetism and stability of the Fe3O4 based nanocomposites were easily affected by the functionalization methods. Therefore, there are some challenges to keeping long-term stability and good performance of magnetic nanoparticles adsorbents.
To overcome the shortcomings in unstable nanostructures, we focus on fabricating highly stable PEI-MNPs via glutaraldehyde crosslinking chemical route at room temperature. The crosslinking reaction is due to the formation of Schiff base between the aldehydes in glutaraldehyde and amine groups in both PEI and Fe3O4 MNPs. It is known that crosslinking of polymers and the formation of covalent bond would enhance the mechanical stability of functional MNPs. Herein, a PEI covalently functionalized MNPs as a model have been synthesized for the first time. It is found that the PEI-MNPs has the ability to capture Cr(VI) in aqueous solution, and the adsorption capacity of Cr(VI) reached 175.76 mg g−1 much higher than that of most MNPs based adsorbents. Importantly, the as-prepared PEI-MNPs adsorbents could be regenerated effectively and recycled at 20 times without significant loss of adsorption capacity, showing their high stability and potential application in removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater.
Experimental details
Materials
All the needed chemicals such as iron chloride hexahydrate, ethylene glycol, 1,6-hexadiamine, sodium acetate anhydrous, glutaraldehyde, sodium hydroxide and potassium dichromate were of analytical reagent grade unless otherwise stated and were all purchased from Aladin. A branched PEI (molecular weight of 25![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000) was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich. The solution pH was adjusted using diluted HCl and NaOH solutions. Magnet was used to separate magnetic adsorbents from the solution.
000) was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich. The solution pH was adjusted using diluted HCl and NaOH solutions. Magnet was used to separate magnetic adsorbents from the solution.
Preparation of amine-functionalized Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (NH2-MNPs)
The synthesis of the amine-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles (NH2-MNPs) was carried out according to the previously reported method with slight modification.32 Firstly, 4 g of sodium acetate anhydrous and 2 g of FeCl3·6H2O were added into 60 mL ethylene glycol, and the mixture was vigorously stirred at 50 °C until the solids were fully dissolved. Secondly, 10 g of 1,6-hexadiamine was dissolved to the resulting solution by continuous stirring. The obtained solution was then transferred into a 100 mL of Teflon lined autoclave and reacted at 200 °C for 8 h. Finally, the resulting NH2-MNPs were fully washed with ultrapure water and ethanol to effectively remove the solvent and unbound 1,6-hexadiamine, and then dried in the refrigeration dryer before characterization and application.Covalent grafting of PEI onto NH2-MNPs (PEI-MNPs)
The PEI covalently functionalized magnetic nanoparticles (PEI-MNPs) was prepared by a crosslinking reaction according to the published report.27 The detailed procedures are as follows. Firstly, 0.2 g of NH2-MNPs was immersed in 50 mL of different concentrations of PEI in methanol for 30 min with ultrasonic irradiation. Then 100 mL 2% (w/v) glutaraldehyde solution was added dropwise to the mixture and mechanically stirred for 30 min at a speed of 300 rpm at room temperature, followed by washing with ultrapure water several times until the supernatant became clear. The washed PEI-MNPs were dried in the desiccator and reserved for following adsorption experiments. The schematic diagram was shown in Fig. 1.Characterization
In order to confirm whether that obtained product was in fact the PEI-MNPs composites, the material was characterized by using various analytical techniques. The FT-IR spectra of the samples were measured on Magna-IR 750 spectrometric analyzer. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analyses were taken on a Bruker D8 Advance X-ray diffractometer with Cu Kα radiation over the angular range from 5° to 80° at room temperature. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and energy dispersive X-ray spectrum (EDX) images of the samples were obtained using a FEI Tecnai G20 microscope. The Zeta potential of samples was determined using Malvern ZEN3600 Zetasizer Nano. Magnetic behaviour was analyzed by a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) at room temperature (MPMS XL-5). Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was performed on a TAQ 600 instrument at a heating rate of 20 °C min−1 in a nitrogen flow from 45 °C to 800 °C. The concentration of Cr(VI) in solution was determined using a UV-vis spectrophotometer (UV-754N Shanghai, China).Batch adsorption experiments
For the investigation of pH, contact time, temperature, and adsorption capacity, batch experiments were carried out in glass conical flasks by shaking at 180 rpm in an air bath shaker. After adsorption, the adsorbents were separated from aqueous solution by a permanent magnet made of Nd–Fe–B. The effect of pH on the adsorption performance was studied over the range from 2 to 12. And NaOH (1 M) and HCl (1 M) solutions were used to adjust the initial solution pH. The time-dependent adsorption behaviour was measured by performing a series of adsorption experiments at three different initial concentrations. The effect of temperature on Cr(VI) adsorption was studied at four different temperatures. The equilibrium adsorption capacity of PEI-MNPs for Cr(VI) can be calculated by the following formula:33
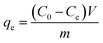 | (1) |
Regeneration and stability of PEI-MNPs
The regeneration and stability of the as-prepared adsorbents were evaluated by checking the cycle number dependence of adsorption capacity for 50 mg L−1 Cr(VI), using the same PEI-MNPs separated from solution by magnet for subsequent cycles. The detailed procedures for regeneration of the used PEI-MNPs adsorbents were as follows. The adsorbent with adsorbed Cr(VI) was dispersed in 30 mL of NaOH solution (0.5 mol L−1) and then sonicated for 10 min. The resultant mixture was separated by external magnetic field and the regenerated adsorbent was washed thoroughly with ultrapure water for subsequent experiment.Results and discussion
Characterization of the adsorbents
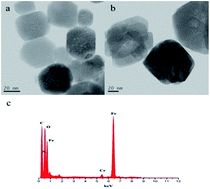
The FT-IR related to the NH2-MNPs and PEI-MNPs were shown in Fig. S1 (ESI†). A strong bond at around 587 cm−1 was observed in both the two materials, and it was assigned to the vibration of the Fe–O bond of Fe3O4.34 For NH2-MNPs, the peaks at 875, 1045, 1465, 1625 and 3450 cm−1 are identified as N–H asymmetric bending vibration, C–N stretching vibration, CH2 bending vibration, N–H symmetric bending vibration and N–H stretching vibration, respectively, which indicated that magnetic nanoparticles were obtained in the presence of 1,6-hexadiamine.32 For PEI-MNPs, the peak near 1625 cm−1 assigned to the presence of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N stretching vibration, which overlapped with original N–H symmetric bending vibration. The peaks at 2865 and 2930 cm−1 attributed to the stretching vibration of CH2 (asymmetric stretching of CH2 at 2930 cm−1, symmetric stretching of CH2 at 2865 cm−1) are present in both two MNPs. The obvious stronger peaks for PEI-MNPs at 2865 and 2930 cm−1 indicated more CH2 were contained in this material. So these results confirmed the introduction of PEI on the surface of NH2-MNPs. The XRD patterns of NH2-MNPs and PEI-MNPs were shown in Fig. S2 (ESI†). As can be seen, six typical peaks of (220), (311), (400), (422), (511) and (440) located at 30.1°, 35.5°, 43.1°, 53.4°, 57.0° and 62.6° matched well with those of Fe3O4.35,36 The results indicated that PEI surface modification did not significantly change the crystal structure of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. The transmission electron microscope (TEM) images of MNPs before and after modification were presented in Fig. 2. As is shown, the PEI coating was formed on the surface of the NH2-MNPs, and the diameter of as-prepared PEI-MNPs (Fig. 2b approximate 60 nm) was clearly larger than that of NH2-MNPs (Fig. 2a with an average particle size of 40 nm). Also, successful grafting of PEI onto MNPs and adsorption of Cr(VI) by PEI-MNPs were verified by EDX analysis (Fig. 2c).
N stretching vibration, which overlapped with original N–H symmetric bending vibration. The peaks at 2865 and 2930 cm−1 attributed to the stretching vibration of CH2 (asymmetric stretching of CH2 at 2930 cm−1, symmetric stretching of CH2 at 2865 cm−1) are present in both two MNPs. The obvious stronger peaks for PEI-MNPs at 2865 and 2930 cm−1 indicated more CH2 were contained in this material. So these results confirmed the introduction of PEI on the surface of NH2-MNPs. The XRD patterns of NH2-MNPs and PEI-MNPs were shown in Fig. S2 (ESI†). As can be seen, six typical peaks of (220), (311), (400), (422), (511) and (440) located at 30.1°, 35.5°, 43.1°, 53.4°, 57.0° and 62.6° matched well with those of Fe3O4.35,36 The results indicated that PEI surface modification did not significantly change the crystal structure of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. The transmission electron microscope (TEM) images of MNPs before and after modification were presented in Fig. 2. As is shown, the PEI coating was formed on the surface of the NH2-MNPs, and the diameter of as-prepared PEI-MNPs (Fig. 2b approximate 60 nm) was clearly larger than that of NH2-MNPs (Fig. 2a with an average particle size of 40 nm). Also, successful grafting of PEI onto MNPs and adsorption of Cr(VI) by PEI-MNPs were verified by EDX analysis (Fig. 2c).
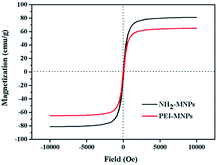
The magnetization curves shown in Fig. 3 revealed that both NH2-MNPs and PEI-MNPs were superparamagnetic. Under a maximum applied magnetic field of 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 Oe, the maximum specific magnetization of NH2-MNPs and PEI-MNPs were about 81.3 and 65.1 emu g−1, respectively. NH2-MNPs showed much higher magnetization values than PEI-MNPs, which is related to the coating of nonmagnetic PEI molecules layer on the surface of NH2-MNPs. Hence, the as-prepared PEI-MNPs composites could be easily separated from aqueous solution under an external magnetic field after the adsorption process due to such high saturation magnetization.
000 Oe, the maximum specific magnetization of NH2-MNPs and PEI-MNPs were about 81.3 and 65.1 emu g−1, respectively. NH2-MNPs showed much higher magnetization values than PEI-MNPs, which is related to the coating of nonmagnetic PEI molecules layer on the surface of NH2-MNPs. Hence, the as-prepared PEI-MNPs composites could be easily separated from aqueous solution under an external magnetic field after the adsorption process due to such high saturation magnetization.
Fig. S3 (ESI†) shows the typical thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) curves of NH2-MNPs and PEI-MNPs at temperature ranging from 45 to 800 °C. It was observed that PEI-MNPs had a total weight loss of nearly 26.2 wt%, and NH2-MNPs had a total weight loss of around 9.3 wt%. The weight loss attributed to physically adsorbed water in the sample (below 200 °C) was about 2.1 wt% for both NH2-MNPs and PEI-MNPs. From the thermogram of NH2-MNPs, it was clear that the loss of 1,6-hexadiamine occurred between 200 and 350 °C, thus the content of 1,6-hexadiamine in NH2-MNPs sample was 7.2 wt%. For PEI-MNPs, the weight loss of 24.1 wt% between 200 and 600 °C was attributed to the thermal decomposition of PEI molecules and the contribution from the 1,6-hexadiamine. It is noteworthy that the weight of NH2-MNPs and PEI-MNPs remained constant when the combustion temperature was above 600 °C, which indicated that iron oxide cannot be easily decomposed at even higher temperatures. On this basis, we can calculated that the contents of 1,6-hexadiamine and PEI in PEI-MNPs were about 7.2 wt% and 16.9 wt%, respectively. Therefore, all the above results demonstrated that PEI molecules have been successfully grafted onto MNPs.
Effect of PEI concentration
The effect of PEI grafting amount on Cr(VI) adsorption capacity of PEI-MNPs was investigated by varying the usage amount of PEI in the preparation procedure. The PEI concentration was studied over the range of 0–90 g L−1. The results in Fig. S4 (ESI†) demonstrated that the Cr(VI) removal efficiency increased with increase of PEI concentration in the range of 0–70 g L−1, and then remained stable when PEI concentration was above 70 g L−1. It is clear that PEI grafting amount played a crucial important role in promoting Cr(VI) adsorption onto PEI-MNPs. Therefore, to achieve effective adsorption of Cr(VI) by PEI-MNPs, the optimum PEI concentration in synthetic procedure of adsorbents was determined to be 70 g L−1.Effect of solution pH
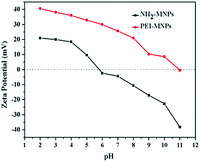
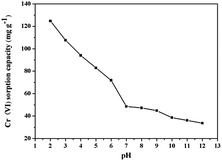
The solution pH is one of the most important factors influencing the adsorption behaviour because it not only governs the surface charge density of the adsorbent, but also determines the metal ionization degree and the metal speciation. The zeta potential of NH2-MNPs and PEI-MNPs shown in Fig. 4 illustrated that the point of zero charge (pHpzc) of NH2-MNPs was found to be about 5.5. By contrast, the pHpzc for the PEI-MNPs was increased to a much higher value of 11.4. The zeta potential of MNPs was significantly increased after modification by PEI, which was due to the protonation of amine groups of PEI molecules on the particle surface.In addition, Cr(VI) generally exists in solution as different forms of oxyanions, i.e. HCrO4−, CrO42− and Cr2O72−.37 For a pH lower than 6.8, HCrO4− is the dominant species of hexavalent chromium, and subsequently HCrO4− is completely shifted to CrO42− at above pH 6.8.31 In present work, the effect of pH on Cr(VI) adsorption over the range of 2.0–12.0 was investigated. As shown in the Fig. 5, the highest Cr(VI) adsorption capacity was observed at pH of 2.0, subsequently, the adsorption decreased sharply in the solution pH range of 3.0–7.0, ultimately, less than 50 mg g−1 Cr(VI) of adsorption capacity was obtained in the alkali solution. Therefore, pH value of 2.0 was an ideal parameter in this work. The influence of solution pH can be tentatively explained by considering the surface charge of the adsorbents and the degree of ionization of the adsorbates. As amine groups on PEI chains are protonated to form the positively charged sites when the solution pH < 11.4, electrostatic interaction occurred between anionic Cr(VI) and protonated sites, leading to the increase of adsorption capacity. Thus, from the viewpoint of electrostatic interaction, lower pH was favourable to the adsorption of anionic Cr(VI). With the increase of pH, the PEI-MNPs surfaces are increasingly deprotonated and the competition from OH− increased, resulting in the weak interaction between Cr(VI) and adsorbents. Furthermore, the predominant form of Cr(VI) changed to CrO42− from HCrO4− at pH > 7. And the adsorption free energy of CrO42− (−2.1 to −0.3 kcal mol−1) is higher than that of HCrO4− (−2.5 to −0.6 kcal mol−1).38 Consequently, CrO42− is less likely adsorbed than HCrO4− at the same concentration. Based on the discussion above, it was concluded that the electrostatic interaction between anionic Cr(VI) and positive charged sites on adsorbents was the predominant adsorption mechanism (Fig. S5 (ESI†)).
Adsorption kinetic studies
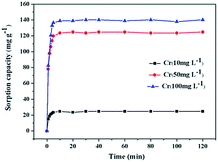
The time-dependent adsorption of Cr(VI) onto PEI-MNPs was investigated at three different initial concentrations (10, 50 and 100 mg L−1). The results in Fig. 6 indicated that the adsorption rate was considerably fast in the first 5 min and the adsorption equilibrium was achieved within 10 min for different initial concentrations, indicating a strong interaction between the adsorbent and adsorbate. To describe the adsorption process, the pseudo-first-order kinetic model (eqn (2)) and pseudo-second-order kinetic model (eqn (3)) have been widely applied to fit the experimental data. The pseudo-second-order model assumes that the rate controlling step is the chemical adsorption or the chemical adsorption step involving valence forces through sharing or exchange of electrons between adsorbent and adsorbate.31,39 The adsorption kinetics were described using following linear form of the model:40
ln(qe − qt) = ln![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) qe − k1t qe − k1t
| (2) |
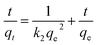 | (3) |
Plotting t/qt against t in Fig. S6 (ESI†) and the parameters related to kinetic process listed in Table 1, indicated that the pseudo-second-order model can better fit adsorption data in view of the higher regression coefficients (R2 > 0.99). As can be seen, the rate constant of pseudo-second-order decreased with the increase of initial Cr(VI) concentration, which is in agreement with previous report.41 Also, the calculated values of qe was very close to that of the experimental values, demonstrating that the adsorption process of Cr(VI) onto PEI-MNPs obeyed the pseudo-second-order model. By contrast, there was a large deviation between the calculated values and the experimental values of adsorption capacity for pseudo-first-order kinetics model. Therefore, the pseudo-first-order kinetics was less likely to explain the rate processes.
| C0 (mg L−1) | qe(exp) | Pseudo-first-order kinetic model | Pseudo-second-order kinetic model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | qe(cal) | R2 | k2 | qe(cal) | R2 | ||
| 10 | 24.75 | 0.56 | 21.43 | 0.986 | 0.114 | 24.75 | 0.999 |
| 50 | 124.14 | 0.58 | 100.58 | 0.987 | 0.027 | 125.00 | 0.999 |
| 100 | 140.26 | 0.73 | 144.60 | 0.981 | 0.025 | 140.84 | 0.999 |
To our knowledge, the electrostatic attraction forces between protonated amine groups and negatively charged Cr(VI) belongs to ionic bond. At the same time, ionic bond involving the electrons sharing between oppositely charged ions is also a type of chemical bonds. Thus, chemisorption is considered to be the rate controlling step in this study and our conclusion is also confirmed by other previous report.42–44
Adsorption isotherms
To evaluate the adsorption behaviour of Cr(VI) on the PEI-MNPs adsorbents, Langmuir and Freundlich equations, two commonly used isotherm models, are used to fit the data of Cr(VI) adsorption on PEI-MNPs over the temperature range of 288–318 K. The Langmuir (eqn (4)) and Freundlich (eqn (5)) models are expressed as follows.45
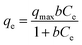 | (4) |
| qe = KFCe1/n | (5) |
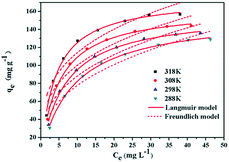
The calculated results based on Langmuir and Freundlich models were listed in Table 2. The Langmuir model presented that the maximum adsorption capacities (qmax) for Cr(VI) by PEI-MNPs increased from 156.37 to 175.76 mg g−1 at the temperature ranging from 288 to 318 K, demonstrating that the adsorption process was an endothermic process. The n value of the Freundlich model was more than 1, suggesting that Cr(VI) adsorption on PEI-MNPs was a favourable adsorption process. The adsorption data were found to be well fitted with the Langmuir model based on the Cr(VI) adsorption isotherm curves shown in Fig. 7 and the correlation coefficients (R2 > 0.99), suggesting the Cr(VI) adsorption onto PEI-MNPs was a monolayer adsorption reaction.
| Temperature (K) | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | qmax (mg g−1) | R2 | KF | n | R2 | |
| 288 | 0.11 | 156.37 | 0.998 | 33.03 | 2.68 | 0.933 |
| 298 | 0.15 | 158.96 | 0.996 | 40.26 | 2.93 | 0.917 |
| 308 | 0.20 | 164.09 | 0.996 | 49.19 | 3.23 | 0.903 |
| 318 | 0.25 | 175.76 | 0.996 | 57.89 | 3.38 | 0.900 |
In addition, the adsorption capacity of PEI-MNPs for Cr(VI) removal was compared with the values for other adsorbents reported in the literature. The results indicate that the maximum adsorption capacity of 175.76 mg g−1 obtained with PEI-MNPs is much higher than most of those obtained with many other adsorbents (Table 3).13,17,46–54 The high adsorption capacity indicated its potential application in Cr(VI) removal from wastewater.
| Adsorbents | Qmax (mg g−1) | References |
|---|---|---|
| γ-Fe2O3 | 15.6 | 13 |
| Magnetite polyethylenimine montmorillonite | 8.8 | 17 |
| Fe3O4/GO | 32.33 | 46 |
| Fe3O4@NiO | 184.2 | 47 |
| CTS/MMT–Fe3O4 | 58.82 | 48 |
| EDA-MPs | 61.35 | 49 |
| DP/MWCNTs | 55.55 | 50 |
| Magnetic carbon nanocomposite fabrics | 3.74 | 51 |
| Zero-valent bimetallic nanoparticles | 55.96 | 52 |
| Magnetic multi-wall carbon nanotubes | 14.28 | 53 |
| Magnetic activated carbon | 2.84 | 53 |
| Amino-functionalized magnetic cellulose | 171.5 | 54 |
| PEI-MNPs | 175.76 | This work |
Adsorption thermodynamic study
Based on adsorption isotherms, thermodynamic studies were undertaken to demonstrate the nature of adsorption of Cr(VI) onto PEI-MNPs adsorbents.55 The following eqn (6) and (7) have been applied to determine the thermodynamic parameters including enthalpy (ΔH), Gibbs free energy (ΔG) and entropy (ΔS).56
ΔG = −RT![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ln ln![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Kd Kd
| (6) |
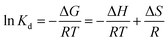 | (7) |
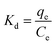 | (8) |
| ΔH (kJ mol−1) | ΔS (J mol−1 K−1) | ΔG (kJ mol−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 288 K | 298 K | 308 K | 318 K | ||
| 9.799 | 42.439 | −2.457 | −2.821 | −3.215 | −3.748 |
The negative values of ΔG suggested that the adsorption process was spontaneous, and the decreasing of ΔG with the growth of temperature indicated that the adsorption was more favourable at high temperatures. The positive values of ΔH confirmed the endothermic process for the adsorption of Cr(VI), consistent with the increase of adsorption capacity as temperature increased. The positive value of ΔS suggested that the increasing randomness between the solid/solution interface during the adsorption process.
Regeneration and stability of PEI-MNPs
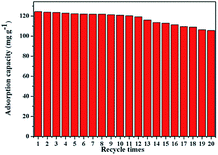
Reusability is one of the most important considerations for adsorbents in the perspective of industrial application. By analyzing the influence of pH on Cr(VI) removal, it was concluded alkaline solution could be effective for desorption of Cr(VI) from PEI-MNPs. Thus, to evaluate the regeneration and stability of the as-prepared PEI-MNPs, different concentrations of NaOH solution were used to treat the used adsorbents. The results demonstrated the concentration of NaOH solution has no significant impact on the desorption efficiency of Cr(VI) (Table S1†). The adsorption–desorption cycles shown in Fig. 8 presented that the used adsorbents could be regenerated easily by 0.5 M NaOH solution, without significant loss in adsorption capacity even after 20 sequential cycles of adsorption–desorption experiments. It was clear that the PEI-MNPs composites were highly stable and suitable for the long-term repetitive adsorption–desorption of Cr(VI), and the as-prepared PEI-MNPs are promising absorbents for the effective removal of Cr(VI) from contaminated waters.Evaluation of PEI-MNPs for real wastewater
To evaluate the practical application of PEI-MNPs in treatment of Cr(VI) contaminated water, an electroplating wastewater with original Cr(VI) of 18.86 mg L−1 was collected from a mechanical and electrical factory. By comparison, a simulated wastewater with the same Cr(VI) concentration as that of real wastewater was also prepared. Under the optimized conditions, both the real and the simulated water samples were subjected to adsorption experiment using as-prepared PEI-MNPs as adsorbent. The results showed that the removal efficiencies of Cr(VI) for real wastewater and simulated wastewater were 92.63% and 98.75%, respectively. It was indicated that the relatively low removal efficiency of Cr(VI) for real wastewater was due to the complexity of the matrix. The co-existing substances such as cations (K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, Pb2+, et al.), anions (Cl−, SO42−, NO3−, HCO3−, et al.) and other organic compounds may compete the active site on PEI-MNPs with Cr(VI), leading to the decrease of removal efficiency of Cr(VI). However, the interference effect of other co-existing substances on removal of Cr(VI) was unobvious, demonstrating that as-prepared PEI-MNPs composite can selectively absorb Cr(VI) from complex industrial wastewater. Thus, the suggested PEI-MNPs could be used as a potential adsorbent for removal of Cr(VI) from industrial wastewater.Conclusion
In this work, MNPs with enhanced stability and excellent regeneration were prepared via simple glutaraldehyde crosslinking method. PEI was covalently grafted to MNPs to fabricate a positively charged adsorbent for effective removal of anionic Cr(VI) mainly by electrostatic interaction between protonated amino groups and negatively charged Cr(VI). A series of measurements including FT-IR, XRD, TEM, TGA, et al. confirmed the successful modification of PEI. Batch adsorption tests by PEI-MNPs indicated that the removal efficiency of Cr(VI) was highly dependent on pH and the optimal adsorption occurred at pH of 2. The pseudo-second-order kinetics and Langmuir isotherm describes well the Cr(VI) adsorption process. Adsorption thermodynamic study suggested that the Cr(VI) adsorption onto PEI-MNPs was a spontaneous and endothermic process. The regeneration and stability testing confirmed the as-prepared PEI-MNPs composites exhibited high stability and good reusability. Most importantly, the obtained PEI-MNPs composite can effectively and selectively adsorb Cr(VI) from complex industrial wastewater, suggesting that PEI-MNPs could be used as a promising adsorbent for removal of Cr(VI) from industrial wastewater.Acknowledgements
Financial supports by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 21307048), Application Fundamental Research Foundation of Yunnan Province, China (Grant no. 2013FB011) and Personnel Training Project Foundation of Kunming University of Science and Technology, China (Grant no. KKSY201322097) are gratefully acknowledged.Notes and references
- N. Fabregat-Cabello, P. Rodriguez-Gonzalez, A. Castillo, J. Malherbe, A. F. Roig-Navarro, S. E. Long and J. I. Garcia Alonso, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2012, 46, 12542–12549 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. G. Tekerlekopoulou, M. Tsiflikiotou, L. Akritidou, A. Viennas, G. Tsiamis, S. Pavlou, K. Bourtzis and D. V. Vayenas, Water Res., 2013, 47, 623–636 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. D. Palmer and P. R. Wittbrodt, Environ. Health Perspect., 1991, 92, 25–40 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Costa and C. B. Klein, Crit. Rev. Toxicol., 2006, 36, 155–163 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Bayramoglu and M. Y. Arica, J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 187, 213–221 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Zhang, M. Zeng, W. Xu, J. Li, J. Li, J. Xu and X. Wang, Dalton Trans., 2013, 42, 7854–7858 RSC.
- Y. Xing, X. Chen and D. Wang, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2007, 41, 1439–1443 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhang, Y. Li, J. Li, G. Sheng, Y. Zhang and X. Zheng, Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 185–186, 243–249 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. S. Ng, X. Wu, X. Yang, Y. Xie, Y. Lu and C. Chen, Bioresour. Technol., 2013, 145, 297–301 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. E. El-Hefny, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2009, 67, 44–49 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. A. Taha, Y. N. Wu, H. Wang and F. Li, J. Environ. Manage., 2012, 112, 10–16 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Velazquez-Peña, I. Linares-Hernández, V. Martínez-Miranda, C. Barrera-Díaz and B. Bilyeu, Fuel, 2013, 110, 12–16 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Wang and I. M. C. Lo, Water Res., 2009, 43, 3727–3734 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhu, S. Wei, H. Gu, S. B. Rapole, Q. Wang, Z. Luo, N. Haldolaarachchige, D. P. Young and Z. Guo, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2012, 46, 977–985 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Bertagnolli, A. Uhart, J. C. Dupin, M. G. da Silva, E. Guibal and J. Desbrieres, Bioresour. Technol., 2014, 164, 264–269 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. R. Espinoza-Quinones, A. N. Modenes, A. S. Camera, G. Stutz, G. Tirao, S. M. Palacio, A. D. Kroumov, A. P. Oliveira and V. L. Alflen, Appl. Radiat. Isot., 2010, 68, 2208–2213 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Larraza, M. Lopez-Gonzalez, T. Corrales and G. Marcelo, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2012, 385, 24–33 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. S. Mak and I. M. C. Lo, Chemosphere, 2011, 84, 234–240 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Dui, G. Zhu and S. Zhou, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5, 10081–10089 CAS.
- I. Akin, G. Arslan, A. Tor, M. Ersoz and Y. Cengeloglu, J. Hazard. Mater., 2012, 235–236, 62–68 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhang, S. Zhai, S. Li, Z. Xiao, Y. Song, Q. An and G. Tian, Chem. Eng. J., 2013, 215–216, 461–471 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Gong and T. Ngai, Langmuir, 2013, 29, 5974–5981 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. W. Won, J. Park, J. Mao and Y. S. Yun, Bioresour. Technol., 2011, 102, 3888–3893 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Wu, J. Jia and S. Luan, Colloids Surf., A, 2011, 384, 180–185 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Wang, Q. Chang, M. Zhang and X. Han, React. Funct. Polym., 2013, 73, 1439–1446 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Owlad, M. K. Aroua and W. M. A. Wan Daud, Bioresour. Technol., 2010, 101, 5098–5103 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Liu and Y. Huang, J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21, 17413–17418 RSC.
- X. Wang, L. Zhou, Y. Ma, X. Li and H. Gu, Nano Res., 2009, 2, 365–372 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Kitamoto, T. Fuchigami and Y. Namiki, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2013, 52, 110–114 CrossRef.
- Y. Pang, G. Zeng, L. Tang, Y. Zhang, Y. Liu, X. Lei, Z. Li, J. Zhang and G. Xie, Desalination, 2011, 281, 278–284 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Pang, G. Zeng, L. Tang, Y. Zhang, Y. Liu, X. Lei, Z. Li, J. Zhang, Z. Liu and Y. Xiong, Chem. Eng. J., 2011, 175, 222–227 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Wang, J. Bao, L. Wang, F. Zhang and Y. Li, Chem.–Eur. J., 2006, 12, 6341–6347 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wang, R. Sun and C. Wang, Colloids Surf., A, 2014, 441, 51–58 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. M. Jiang, T. Yang, Y. H. Wang, H. Z. Lian and X. Hu, Talanta, 2013, 116, 361–367 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Li, L. Fan, M. Sun, H. Qiu, X. Li, H. Duan and C. Luo, Colloids Surf., B, 2013, 107, 76–83 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Stojanovic, M. Otonicar, J. Lee, M. M. Stevanovic, M. P. Hwang, K. H. Lee, J. Choi and D. Uskokovic, Colloids Surf., B, 2013, 109, 236–243 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. J. Jiang, X. Y. Yu, T. Luo, Y. Jia, J. H. Liu and X. J. Huang, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2013, 58, 3142–3149 CrossRef CAS.
- C. H. Weng, J. H. Wang and C. P. Huang, Water Sci. Technol., 1997, 35, 55–62 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Y. Wang, L. Q. Yang, Y. F. Li, Y. Zhang, X. J. Ma and Z. F. Ye, Chem. Eng. J., 2010, 163, 364–372 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Li, X. Li, H. Duan, X. Wang and C. Luo, Dalton Trans., 2014, 8431–8438 RSC.
- Y. Li, B. Gao, T. Wu, D. Sun, X. Lia, B. Wang and F. Lu, Water Res., 2009, 43, 3067–3075 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Cai, L. Tan, J. Yu, M. Jaroniec, X. Liu, B. Cheng and F. Verpoort, Chem. Eng. J., 2014, 239, 207–215 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Wang, W. Liu, T. Wang and J. Ni, Chem. Eng. J., 2013, 225, 153–163 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Guo, B. Dua, Q. Wei, J. Yang, L. Hu, L. Yan and W. Xu, J. Hazard. Mater., 2014, 278, 211–220 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Liu, C. Chen, T. Wen and X. Wang, Dalton Trans., 2014, 7050–7056 RSC.
- M. Liu, T. Wen, X. Wu, C. Chen, J. Hu, J. Li and X. Wang, Dalton Trans., 2013, 14710–14717 RSC.
- S. Zhang, J. Li, T. Wen, J. Xu and X. Wang, RSC Adv., 2013, 3, 2754–2764 RSC.
- D. Chen, W. Li, Y. Wu, Q. Zhu, Z. Lu and G. Du, Chem. Eng. J., 2013, 221, 8–15 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. G. Zhao, H. Y. Shen, S. D. Pan and M. Q. Hu, J. Hazard. Mater., 2010, 182, 295–302 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Kumar, M. O. Ansari and M. A. Barakat, Chem. Eng. J., 2013, 228, 748–755 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhu, H. Gu, J. Guo, M. Chen, H. Wei, Z. Luo, H. A. Colorado, N. Yerra, D. Ding, T. C. Ho, N. Haldolaarachchige, J. Hopper, D. P. Young, Z. Guo and S. Wei, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 2256–2265 CAS.
- K. P. Singh, A. K. Singh, S. Gupta and S. Sinha, Desalination, 2011, 270, 275–284 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. S. Bayazit and Ö. Kerkez, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 2014 DOI:10.1016/j.cherd.2014.02.007.
- X. Sun, L. Yang, Q. Li, J. Zhao, X. Li, X. Wang and H. Liu, Chem. Eng. J., 2014, 241, 175–183 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Kapur and M. K. Mondal, Chem. Eng. J., 2013, 218, 138–146 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. B. Senturk, D. Ozdes, A. Gundogdu, C. Duran and M. Soylak, J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 172, 353–362 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Tables and figures. See DOI: 10.1039/c4ra10602d |
| ‡ These authors contributed to the work equally and should be regarded as co-first authors. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 |