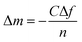Facile immobilization of vascular endothelial growth factor on a tannic acid-functionalized plasma-polymerized allylamine coating rich in quinone groups†
Kaiqin Xiongab,
Pengkai Qiab,
Ying Yangab,
Xiangyang Liab,
Hua Qiuab,
Xin Liab,
Ru Shenab,
Qiufen Tu*ab,
Zhilu Yang*ab and
Nan Huang*ab
aKey Lab of Advanced Technology of Materials of Education Ministry, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, 610031, China. E-mail: zhiluyang1029@126.com; huangnan1956@163.com; Fax: +86 28 87600625
bSchool of Materials Science and Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, 610031, China
First published on 4th February 2016
Abstract
Biomolecules with thiol or amine groups can easily be covalently immobilized onto a substrate equipped with quinone groups in a mild alkali buffer solution based on Schiff base or Michael addition reactions. In this study, we reported a simple two-step approach to creating a functional coating with abundant quinone groups for facile immobilization of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in mild phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4). This approach initially involved the deposition of an amine-bearing plasma-polymerized allylamine (PPAam) coating. Tannic acid (TA) was subsequently used for introducing phenolic hydroxylic hydroxyl/quinone groups. The results of water contact angles (WCAs), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis (XPS) revealed the effective conjugation of TA to PPAam, as well as the immobilization of VEGF to TA-functionalized PPAam (TA-PPAam). The result of a quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCM-D) showed that 158 ± 13 ng cm−2 of VEGF was successfully immobilized onto the TA-PPAam surface. TA-PPAam bound with VEGF significantly enhanced human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) proliferation, indicating the good retention of the bioactivity of VEGF. The TA-PPAam functional coating provided a novel, facile strategy for the covalent immobilization of biomolecules, especially growth factors, under mild reaction conditions.
Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death globally and cause tremendous financial burdens in every country.1 Developments in the field of blood-contacting material production make it possible to provide implantable devices and perform interventional surgery for clinical patients.2 For example, vascular stents or grafts are widely used to treat occluded coronary arteries by expanding the narrowed section of the vessel, and diseased arteries can be replaced to treat narrowed or weakened arteries.3 However, patients who received cardiovascular interventional surgery often exhibit low patency rates and restenosis. This is mainly attributed to limited endothelialization on the surfaces of vascular stents of grafts, which are not able to suppress thrombosis or intimal hyperplasia.4–6To enhance endothelialization of stents or grafts, many strategies have been developed.7–9 One of the most viable approaches is the delivery or immobilization of angiogenic factors to the injured sites to stimulate neovascularization to for promoting endothelium repair.10 Of these angiogenic factors, VEGF is the most potent and widely used key regulator of neovascularization.11 Previous studies have shown that VEGF can stimulate the mobilization and recruitment of endothelial cells, thereby accelerating the differentiation of stem/progenitor cells into endothelial cells.12 Due to the crucial role of VEGF in implant vascularization, numerous strategies and applications have been reported on its conjugation, including non-covalently localized delivery and covalent immobilization on the foreign implants.13,14 Various strategies are available for covalent conjugation of VEGF on different substrates, including traditional methods such as amidation and esterification and more novel techniques such as orthogonal click chemistry or creating an oriented configuration and gradient concentration of growth factors.15 New strategies are continuously emerging; however, the need for developing an optimized system still exists. To obtain a surface with high VEGF concentration and good stability, a novel but facile method to immobilize VEGF onto 316L SS via plasma polymerization technique, using TA molecule as a linker was reported in this work.
TA, a common flavonoid, is a widely utilized polyphenolic hydroxyl found in many products, such as green/black tea, red wine, beer, and fruits.16 It has been reported that these plant polyphenolic hydroxyls display a rich and complex spectrum of physical and chemical properties, and can be used as molecular glue for DNA hydrogel formation, radical scavenging coating, coordination complexes for versatile film or particle engineering, and for the assembly of supermolecules.17–19 TA contains five pyrogallol and five catechol units in one molecule (Fig. 1). Inspired by the high catecholamine content of mussel adhesive proteins and the reactivity with biomolecules of dopamine self-polymerization films, the phenolic hydroxylic groups in TA molecules can be oxidized into quinone, and can react with primary amine groups of multiple categories via Michael addition or Schiff base reaction under mild reaction alkaline conditions.20
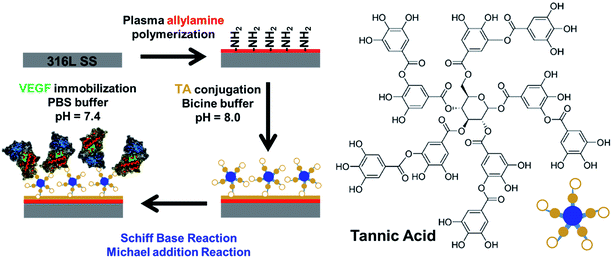 | ||
| Fig. 1 Schematic illustration of the preparation of PPAam coating, the conjugation of TA, and immobilization of VEGF. | ||
Research of optimized and refined plasma-functionalized films for biomedical applications has intensified during the past decade.21,22 The unique advantage of plasma modification is that the surface properties and biocompatibility can be selectively enhanced while the bulk properties remain unchanged.23 The approach reported in this work firstly involves the deposition of PPAam coating onto the 316L SS to introduce the primary amine groups. Subsequently, TA is used to functionalize PPAam for introducing polyphenolic hydroxyl groups. Prior to the immobilization of VEGF, the obtained TA-PPAam is immersed into PBS (pH 7.4), where polyphenolic hydroxyl groups are oxidized to quinone groups. Finally, VEGF is immobilized onto the TA-PPAam (VEGF@TA-PPAam) in PBS (pH 7.4) based on the Schiff base or Michael addition reactions between the quinone of TA-PPAam and the amine groups of VEGF. To evaluate bioactivity, the growth behavior of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) on VEGF@TA-PPAam was analyzed. The results obtained indicated a promising novel strategy to design a VEGF-functionalized surface for biomedical applications.
Experimental section
Preparation of PPAam coating
PPAam was deposited onto mirror-polished 316L SS using inductively coupled plasma excited with external copper band electrodes at a 13.56 MHz pulsed radio frequency. Prior to deposition, the 316L SS substrates were cleaned by Ar plasma sputtering for 5 min under the discharge power of 80 W. After checking up the base pressure kept in 1.0 Pa, 2.5 sccm Ar (2.5 Pa) and a partial pressure of allylamine gas (3.5 Pa) were introduced into the reactor via a needle valve and maintained constant for all of the experiments. The experiments were conducted at 30 W discharge power under the condition of the pulsed duty cycle of 40% (ton = 20 ms, toff = 30 ms) and the bias voltage −80 V. The as-deposited PPAam was then thermally treated at 120 °C under 1.5 × 10−4 Pa to improve the degree of cross-linking, so as to improve its stability.24Covalent immobilization of TA and VEGF
TA was bound to the amine bearing PPAam-coated 316L SS via the Schiff base reaction between the quinone groups of the oxidized TA and the primary amine groups of the PPAam surface. Briefly, 0.1 mg mL−1 TA was dissolved in bicine buffer (pH = 8.0) to transform the phenolic groups into quinone groups. The PPAam-coated 316L SS was then immersed in the aforementioned solution for 24 h at room temperature. After the reaction, TA-PPAam samples were thoroughly washed with PBS and distilled water and then immersed into 500 ng mL−1 of VEGF in PBS buffer (pH = 7.4) for VEGF immobilization. After reacting for 12 h, the samples were washed with PBS, followed by distilled water, and dried under N2 gas. The VEGF-functionalized samples were then used for surface analyses and biological evaluations.Surface characterization
Water contact angles (WCAs) of 316L SS, PPAam, TA-PPAam, and VEGF@TA-PPAam samples were measured by a Krüss DSA 100 Mk2 goniometer (Hamburg, Germany) at room temperature, using a sessile drop of distilled water (5 μL), followed by digital analysis using the circle segment function of DSA 1.8 software. The chemical structures of the specimens were determined by grazing incidence reflection and attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (GATR-FTIR) (Nicolet model 5700) in the range of 4000–400 cm−1. The chemical composition of the specimens were determined using XPS, (Perkin Elmer 16 PC), equipped with a monochromatic Al Kα (1486.6 eV) X-ray source, operated at 12 kV × 15 mA at a pressure of 2 × 10−7 Pa.Real time monitoring immobilization of TA and VEGF by QCM-D
Briefly, AT-cut 5 MHz Au-coated quartz crystal (diameter: 10 mm) modified with PPAam coating (10 nm) was used as a sensor in the QCM-D monitoring of TA and VEGF. Firstly, for the evaluation of TA binding onto PPAam surface, the PPAam-coated sensor was then placed in the QCM-D equipment chamber, and bicine buffer (pH 8.0) was injected continuously at a rate of 50 μL min−1 until the QCM traces maintained steady. Subsequently, 0.1 mg mL−1 of TA per was injected in the same speed. At last, bicine buffer (pH 8.0) was perfused to remove the weak-binding TA. For the VEGF binding measurement, PPAam-coated sensor was further functionalized by TA using the aforementioned treatment. Then, this TA-functionalized sensor quartz crystal was placed in the QCM-D equipment chamber, and PBS (pH 7.4) was injected continuously until the QCM traces maintained steady as well; subsequently, 500 ng of VEGF per 1 mL PBS was injected in the same speed. Finally, PBS (pH 7.4) was perfused to remove the weak-binding VEGF. Besides, we both monitored the immobilization process of VEGF onto PPAam surface and TA modified PPAam surface. When both QCM traces of PPAam and TA-PPAam samples maintained steady, 2% sodium dodecyl sulfonate (SDS) was injected to wash the surface in order to wipe off the weakly adsorbed VEGF. The adsorbed mass (Δm) was calculated using the Sauerbrey equation:where C is a constant that describes the sensitivity of the device to the changes in mass, and n is the overtone number. The mass shift vs. time curve was recorded using QTools software.
Isolation and culture of HUVECs
A human umbilical cord was cannulated and washed with PBS to remove the blood inside the lumen. The umbilical vein was then filled with 0.1% collagenase II and clamped. After incubation for 12 min at 37 °C, digestion was quenched by adding Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (F12) containing 15% fetal bovine serum (FBS). HUVECs were collected by centrifugation of the digested cell suspension. Harvested primary cells were cultured in a humidified incubator under 5% CO2 at 37 °C, using F12 supplemented with 15% FBS, glutamine, and 20 μg mL−1 endothelial cell growth supplements.Adhesion and proliferation of HUVECs
HUVECs were seeded at a density of 3 × 104 cells per cm2 with 316L SS, PPAam, TA-PPAam, and VEGF@TA-PPAam samples. After incubating for 1 and 3 days, the samples were washed and fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde solutions, followed by staining with rhodamine123, and then immediately examined using a fluorescence microscope (DMRX, Leica, Germany).Proliferation of HUVECs was investigated by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) after incubation for 1 and 3 days. The medium was removed and the samples were washed twice with saline. Subsequently, 350 μL of fresh medium containing 10% CCK-8 solution was added to each sample and incubated at 37 °C for 3 h under standard culture conditions. Then, 200 μL media was transferred to a 96-well plate. The absorbance was measured at 450 nm by a microplate reader. All proliferation experiments were performed in triplicate.
Results and discussion
Limited endothelialization caused by synthetic vascular graft or stent materials often results in undesirable clinical complications such as thrombogenic responses and intimal hyperplasia.25 Surface modification such as immobilization of biomolecules have been demonstrated as a promising approach to address these issues. VEGF is an important angiogenic growth factor that can regulate blood vessel formation by acting as a specific EC surface receptor, and is therefore considered an essential tool for many vascular tissue engineering strategies.12 Fig. 1 shows the schematic of this strategy; based on this strategy, the behavior of HUVECs on VEGF@TA-PPAam films is of particular interest.The results of the WCAs (Fig. 2) indicate the changes in hydrophilicity for each modification step. For the 316L SS, after coating with PPAam, there was a considerable increase in hydrophobicity, most likely due to the co-existence of amino and alkyl groups in the backbone of the cross-linked PPAam film26 The conjugation of TA to the PPAam surface leads to a remarkable increase in hydrophilicity compared to that observed in the unmodified PPAam, because TA is a hydrophilic molecule. The WCA of the VEGF@TA-PPAam sample decreased to 41.2° compared to that of TA-PPAam. This increase in hydrophilicity with the addition of VEGF is a result of the introduction of additional terminal amino and carboxyl groups from the protein molecules.27
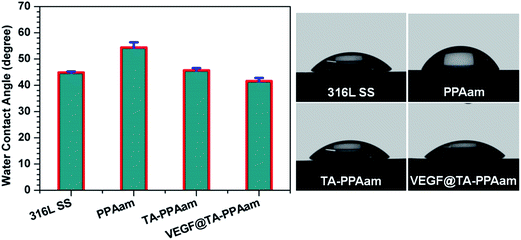 | ||
| Fig. 2 WCA results and images of 316L SS, PPAam, TA-PPAam, and VEGF@TA-PPAam. The data is presented as mean ± SD (n = 6). | ||
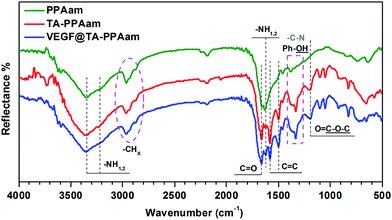
GATR-FTIR analysis was used to confirm PPAam deposition, TA conjugation, and VEGF immobilization, and in an effort to understand the changes of the surface chemical structures. As shown in Fig. 3, the basic features of the allylamine (H2C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH–CH2–NH2) structure were represented in the PPAam coating.24 The –CHx peaks, resulting from the radical chain growth polymerization during the “plasma-off” periods, are observed around 2925 cm−1. Note that the presence of ν–NH stretching vibrations at 3350 cm−1 and 3225 cm−1 revealed the good retention of the primary amine group (–NH2). After immobilization of TA, the peaks that are typical of a pyrogallol backbone were observed, including the –C
CH–CH2–NH2) structure were represented in the PPAam coating.24 The –CHx peaks, resulting from the radical chain growth polymerization during the “plasma-off” periods, are observed around 2925 cm−1. Note that the presence of ν–NH stretching vibrations at 3350 cm−1 and 3225 cm−1 revealed the good retention of the primary amine group (–NH2). After immobilization of TA, the peaks that are typical of a pyrogallol backbone were observed, including the –C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C– peaks, at 1580–1500 cm−1, and the O–C
C– peaks, at 1580–1500 cm−1, and the O–C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O peak at 1690 cm−1; the significantly enhanced peaks at 1380–1300 cm−1 reveals the existence of Ph–OH and maybe suggests the Schiff base reaction between the phenolic hydroxylic of TA and the primary amine groups on the PPAam. Other characteristic peak observed at 1051 cm−1 (O
O peak at 1690 cm−1; the significantly enhanced peaks at 1380–1300 cm−1 reveals the existence of Ph–OH and maybe suggests the Schiff base reaction between the phenolic hydroxylic of TA and the primary amine groups on the PPAam. Other characteristic peak observed at 1051 cm−1 (O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C–O–C) correlate with TA further confirm its conjugation.
C–O–C) correlate with TA further confirm its conjugation.
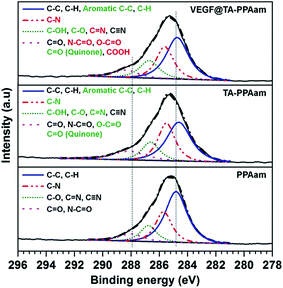
The surface chemical compositions of samples after each surface modification step were determined by XPS (Table 1), and the XPS survey spectrum was shown in Fig. S1.† The analysis of survey wide-scan survey spectrum reveals that all the samples consist of carbon, nitrogen and oxygen. PPAam the VEGF@TA-PPAam showed a considerable difference in surface chemical compositions when compared to the PPAam. An increase content of oxygen was detected for each modification: 8.9% for PPAam, 13.1% for TA-PPAam, and 15.8% for VEGF@TA-PPAam. Conversely, a reduced content of nitrogen was observed for each modification: 14.0% for PPAam samples, 10.6% for TA-PPAam, and 9.8% for VEGF@TA-PPAam. In addition, the C 1s high resolution XPS spectra of PPAam, TA-PPAam and VEGF@TA-PPAam were generated (Fig. 4). The C 1s high-resolution spectra revealed at least four overlapped peaks.28 The peak at 284.8 eV was assigned to C–C and C–H bonds, which was used as a reference point to determine that all the spectra had shifted. A second peak at 285.7 eV corresponds to C–N bond. The third component of C 1s was shifted by approximately 2.0 eV, and was assigned mainly to C–O, C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N and C
N and C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N groups. A fourth peak at 287.9 eV possibly corresponds to C
N groups. A fourth peak at 287.9 eV possibly corresponds to C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O and N–C
O and N–C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bonds. The immobilization of TA resulted in a significant change to the C 1s spectra. As shown in Fig. 4, the introduction of C
O bonds. The immobilization of TA resulted in a significant change to the C 1s spectra. As shown in Fig. 4, the introduction of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C and C
C and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C–H (aromatic C–C, C–H) in TA led to a visible shift of shoulder toward low binding energy, fitted to a component at 284.6 eV and the introduction of quinone (C
C–H (aromatic C–C, C–H) in TA led to a visible shift of shoulder toward low binding energy, fitted to a component at 284.6 eV and the introduction of quinone (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) and O–C
O) and O–C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O in TA resulted in a visible shift of shoulder toward high binding energy, fitted to a component at 288.2 eV. After VEGF immobilization, the further change that was observed was a shift of the peak at 288.4 eV, most likely due to the introduction of carboxyl groups (–COOH) and N–C
O in TA resulted in a visible shift of shoulder toward high binding energy, fitted to a component at 288.2 eV. After VEGF immobilization, the further change that was observed was a shift of the peak at 288.4 eV, most likely due to the introduction of carboxyl groups (–COOH) and N–C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O in VEGF. The N 1s and O 1s high-resolution spectra further confirmed the TA and VEGF immobilization. TA immobilization on PPAam led to a shift of shoulder toward high binding energy, fitted to a component at 399.9 eV, VEGF conjugation on TA-PPAam surface produced the further shift of peak toward the higher binding energy, fitted to a component at 400.0 eV (Fig. S2A†), which suggested that the Michael addition and Schiff base reactions occurred between the primary amine groups of PPAam and VEGF and the quinone groups derived from TA oxidization in alkali reaction buffer.29 The peaks at 532.3 and 533.4 eV in O 1s high-resolution spectrum of PPAam shifted to high binding energy after TA and VEGF immobilization (Fig. S2B†), further confirming the successful immobilization of TA and VEGF.
O in VEGF. The N 1s and O 1s high-resolution spectra further confirmed the TA and VEGF immobilization. TA immobilization on PPAam led to a shift of shoulder toward high binding energy, fitted to a component at 399.9 eV, VEGF conjugation on TA-PPAam surface produced the further shift of peak toward the higher binding energy, fitted to a component at 400.0 eV (Fig. S2A†), which suggested that the Michael addition and Schiff base reactions occurred between the primary amine groups of PPAam and VEGF and the quinone groups derived from TA oxidization in alkali reaction buffer.29 The peaks at 532.3 and 533.4 eV in O 1s high-resolution spectrum of PPAam shifted to high binding energy after TA and VEGF immobilization (Fig. S2B†), further confirming the successful immobilization of TA and VEGF.
| Sample | % C | % N | % O |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPAam | 77.1 | 14.0 | 8.9 |
| TA-PPAam | 76.3 | 10.6 | 13.1 |
| VEGF@TA-PPAam | 74.4 | 9.8 | 15.8 |
Although WCA, GATR-FTIR, and XPS results provide supporting evidence of the successful immobilization of VEGF, quantitation analysis is essential for evaluating the conjugation. The development of QCM for use in liquids allowed the measurement of interactions at the sensor–solution interface, facilitating applications in a range of biomedical analytical fields. Further advances soon provided an ability to measure not only the mass adsorbed via changes in the frequency but also the viscoelastic properties of the adhered layer using the dissipation factor D according to the Sauerbrey equation.30,31 Thereafter, the ability to measure the mass and the viscoelastic properties of adsorbed materials in their native, hydrated states, quickly saw the technique applied to the study of biological systems, including protein and cellular interactions.
Exposure to a 500 ng mL−1 VEGF solution resulted in a decrease in frequency, corresponding to a mass increase due to molecule attachment as well as chemical binding for both control PPAam and TA-PPAam coated sensors. After equilibration, the sensors were subjected to thorough in situ rinsing and washing steps, first with PBS, then with concentrated SDS (10%) and finally, with PBS again. Analysis of the frequency trace throughout these washing steps revealed the advantages of modified TA molecule in the protein binding behavior since the SDS could remove the physically adsorbed VEGF only on TA-PPAam surfaces. The mass of PPAam coated sensors decreased in a sharp after SDS wash and PBS rinse recovering completely their initial values, which reveals that all adsorbed protein had been washed off the sensor surface. On the other hand, no mass change was observed for TA-PPAam coated sensors, which suggests that irreversible attachment indicative for covalent VEGF binding occurs on the TA-PPAam films, as opposed to the reversible physisorption of VEGF observed on PPAam surfaces. The average amount of VEGF covalently bound to TA-PPAam plasma film was estimated using the Sauerbrey equation and found to be 165 ng cm−2 (Fig. 5).32
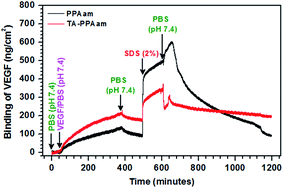 | ||
| Fig. 5 QCM-D analysis of the covalent immobilization of VEGF to the TA-PPAam and PPAam films followed by rigorous washing processes. | ||
TA and VEGF immobilization onto the PPAam and TA-PPAam surface was also monitored in real-time by QCM-D at room temperature, respectively due to the long-term process of these two reactions. Fig. S3† shows the mass shift vs. time curve of TA and VEGF immobilization and the subsequent buffer cleaning. It could be found out that the curve that reflected the reaction process kept unchanged after 20 hours. Therefore, we set the reaction time as 24 hours in order to get tannic acid saturating conjugated onto PPAam. It seems that the grafting reaction is a long process since the covalently conjugation between TA and PPAam (Fig. S3A†). Unlike physical adsorption of TA on other surfaces via majority of hydrogen bonds,33 the QCM curve reflected the physical and chemical binding kinetics of TA. Both physical deposition and chemical immobilization happened on PPAam surfaces. Thus, the strong binding amount of TA was estimated with about 300 ng cm−2. Also, the results show that the mass of VEGF that was bound to PPAam gradually increased with an increased in reaction time. After immobilization for about 500 min, 158 ± 13 ng cm−2 of VEGF was effectively immobilized onto the TA-PPAam surface, which is almost the same as the measured before (Fig. S3B†). Both of these two processes could be demonstrated by the covalent binding via Schiff base reactions.34
VEGF is a key regulator of angiogenesis and vasculogenesis. Thus, it has been a popular choice for a range of biomaterials. Immobilized VEGF has been used in the development of advanced tissue scaffolds and was shown to have a greater angiogenic effect than repeated doses of soluble VEGF.35 Many techniques to immobilize VEGF onto the surface of a biomaterial are available, such as electrostatic binding, physical loading, and covalent immobilization.36 Of these, covalent immobilization offers an advantage over other techniques since it enhances the stability and persistence of VEGF, thus reducing the amount of VEGF required and ensuring the effects are localized within the implant site, rather than the surrounding tissue.37 For example, carbodiimide chemistry has been extensively studied for the chemical coupling of biomolecules to the material surface. This chemical coupling reaction occurs with several side reactions such as hydrolysis of the activated VEGF or intermolecular coupling between several VEGF molecules. These side reactions often lead to changes in conformation, loss of bioactivity, and reduction of yield.38 Polydopamine coating, which has phenolic hydroxyl and quinone functional groups capable of covalent coupling to nucleophiles, was used to immobilize as low as 26 ± 2.5 ng cm−2 of VEGF.39 Our group also constructed a dopamine coating that was rich in quinone groups via thermal oxidation, resulting in a VEGF density of 78.5 ng cm−2.40 Applying mussel-inspired chemistry, we deposited gallic acid (GA), the degradable unit of TA, onto a PPAam surface, which resulted in 120 ng cm−2 of immobilized VEGF.41 More quinone groups are exposed on gallate ester-rich TA when phenolic hydroxylic groups are oxidized under alkaline conditions. VEGF can therefore be easily immobilized onto the surface of TA-PPAam in PBS, based on the Schiff base and Michael addition reactions between the quinone of TA-PPAam and the amine groups of VEGF.42 Using this strategy, a stable and large amount of VEGF can be successfully conjugated onto a material surface.
The biological activity of immobilized VEGF plays a dominant role in the neovascularization or re-endothelialization of an implant in vivo, and impinges upon different aspects of cardiovascular homeostasis by regulating multiple endothelial biological functions.43 HUVEC adhesion and proliferation were therefore evaluated to determine the biological activity of VEGF bound to the TA-PPAam surface. As shown in Fig. 6, the amount of adhered HUVECs on PPAam-modified surfaces was greater than that for 316L SS, most likely due to the introduction in aqueous cell culture medium.26 The immobilization of TA on PPAam surface further enhanced HUVEC adhesion and proliferation. This may be attributed to the increased adsorption of serum proteins from the cell culture medium in their native structures due to the presence of quinone groups on the TA-PPAam surface.35 The fastest proliferation of HUVECs was observed for VEGF@TA-PPAam samples. The VEGF immobilization leads to a significant enhancement in HUVEC adhesion and proliferation, indicating substantial retention of VEGF bioactivity. To observe the morphology of the cells that grown on different samples, rhodamine123 was used to stain the cellular matrix (Fig. 7). After 2 h of culture, the HUVECs on VEGF@TA-PPAam surfaces were more elongated and had a unidirectional shape. TA-PPAam showed better HUVEC affinity than did PPAam samples during the first 2 h of incubation, while 316L SS presented the least amount of cells. Furthermore, HUVECs on VEGF@TA-PPAam surfaces presented elliptical, cobblestone, and polygonal morphologies, and had a polarized shape, indicating that cytoskeleton development correlates with CCK-8 test results for the first and third culture days. These results indicate the facilitation of a migrational traction force, which would ultimately lead to a faster re-endothelialization rate.
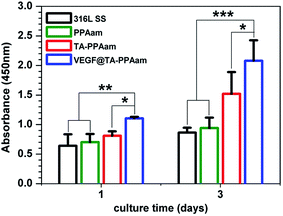 | ||
| Fig. 6 HUVEC proliferation on 316L SS, PPAam, TA-PPAam, and VEGF@TA-PPAam. Data is presented as mean ± SD and analyzed using a one-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. | ||
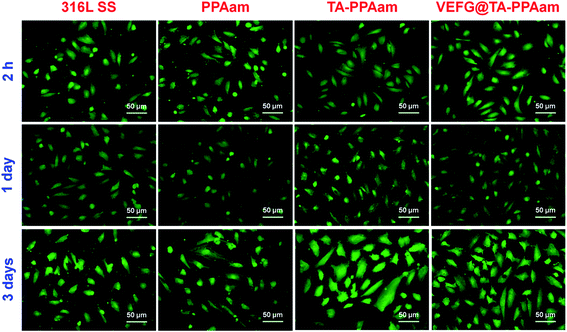 | ||
| Fig. 7 Rhodamine123 staining of HUVECs cultured on 316L SS, PPAam, TA-PPAam, and VEGF@TA-PPAam samples which were collected randomly for 12 images of each sample. | ||
The use of TA, one of the most well-known plant-derived polyphenolic hydroxyls, has been reported in the construction of multifunctional coatings in material-independent surface chemistry.44 TA-functionalized substrates do not present observable cytotoxicity to mammalian cells.17 In addition, the presence of ester bonds and a high number of catechol/pyrogallol groups (ten moieties per TA) could selectively promote the adhesion and proliferation of HUVECs, which we have previously demonstrated on both of our GA loading coatings and GA immobilized surfaces.45 In this study, TA immobilization provides quinone-functionalized biointerfaces, which have multiple beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system. Recent studies indicate that these polyphenolic hydroxyls could lead to the activation of endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) by phosphorylation at Ser1177. The subsequent endothelium-dependent relaxation of porcine coronary artery rings depends on the activation of the redox-sensitive PI3-kinase/Akt-dependent pathway.46 Therefore, the TA-PPAam functional coating also presents the ability to enhance HUVEC adhesion and proliferation. TA protects the endothelium against redox behavior and radical attack, and acts as a linker between VEGF and substrates.47 Large amounts of VEGF could be immobilized through the Michael addition or Schiff base reaction owing to its phenolic hydroxylic/quinone groups. The endothelium-rich microenvironment may contribute to the synergetic effect of TA and VEGF. Therefore, future work will focus on the investigation of endothelial cell growth for PPAam surfaces modified with various amounts of TA and VEGF, and the effect of TA and VEGF-functionalized surfaces on the expressed functions of HUVECs.
Conclusion
We have demonstrated a facile strategy to immobilize VEGF by using covalent coupling onto a TA-functionalized PPAam surface. The process of VEGF immobilization was performed in PBS solution at the physiological pH value, and the bioactivity of cell growth was assessed. TA and VEGF functionalized surfaces significantly enhanced HUVEC adhesion and proliferation. The quinone-bearing TA-functionalized coating has potential for use as a multifunctional coating for surface modification of biomaterials, as it provides excellent biocompatibility and secondary reactivity with biomolecules. This functional coating not only provides a facile strategy for the covalent immobilization of biomolecules under mild reaction conditions, but can also be adapted for a wide range of materials without the need for surface pretreatment.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project 81271701, 31570957, 81501596 and Key Program 81330031).References
- P. A. Heidenreich, J. G. Trogdon, O. A. Khavjou, J. Butler, K. Dracup, M. D. Ezekowitz, E. A. Finkelstein, Y. Hong, S. C. Johnston, A. Khera, D. M. Lloyd-Jones, S. A. Nelson, G. Nichol, D. Orenstein, P. W. F. Wilson and Y. J. Woo, Circulation, 2011, 123, 933 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Qi, M. F. Maitz and N. Huang, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2013, 233, 80 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Fontaine, Fresno. Calif. Vascular stent, US Pat., US005314472A, 1994, 5, 24.
- A. T. Ong, E. P. McFadden, E. Regar, P. P. de jaeqere, R. T. van Domburg and P. W. Serruys, J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 2005, 45, 2088 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- U. Sigwart, J. Puel, V. Mirkovitch, F. Joffre and L. Kappenberqer, N. Engl. J. Med., 1987, 316, 701 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. D. Mel, C. Bolvin, M. Edirisinghe, G. Hamilton and A. M. Seifalian, Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther., 2008, 6, 1259 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Avci-Adali, A. Paul, G. Ziemer and H. P. Wendel, Biomaterials, 2008, 29, 3936 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Avci-Adali, G. Ziemer and H. P. Wendel, Biotechnol. Adv., 2010, 28, 119 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Qi, S. Chen, T. Liu, J. Chen, Z. Yang, Y. Weng, J. Chen, J. Wang, M. F. Maitz and N. Huang, Biointerphases, 2014, 9, 1 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. P. Richardson, M. C. Peters, A. B. Ennett and D. J. Mooney, Nat. Biotechnol., 2001, 19, 1029 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Jin, Y. Zhu, Y. Sun, X. O. Mao, L. Xie and D. A. Greenberg, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2002, 99, 11946 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Rouwkema, N. C. Rivron and C. A. van Blitterswijk, Trends Biotechnol., 2008, 26, 434 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. B. Wissink, R. Beernink, A. A. Poot, G. H. M. Engbers, T. Beugeling, W. G. Van Aken and J. Feijen, J. Controlled Release, 2000, 64, 103 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. H. Shen, M. S. Shoichet and M. Radisic, Acta Biomater., 2008, 4, 477 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Hajimiri, S. Shahverdi, G. Kamalinia and R. Dinarvand, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part A, 2015, 103, 819 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Hong, J. Yeom, I. T. Song, S. M. Kang and H. Lee, Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 1, 1400113 Search PubMed.
- T. S. Sileika, D. G. Barrett, R. Zhang, K. H. A. Lau and P. B. Messersmith, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 10766 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Ejima, J. J. Richardson, K. Liang, J. P. Best, M. P. van Koeverden, G. K. Such, J. W. Cui and F. Caruso, Science, 2013, 341, 154 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Shin, J. H. Ryu, J. P. Park, K. Kim, J. W. Yang and H. Lee, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2015, 25, 1270 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Lee, S. M. Dellatore, W. M. Miller and P. B. Messersmith, Science, 2007, 318, 426 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Desmet, R. Morent, N. D. Geyter, C. Leys, E. Schacht and P. Dubruel, Biomacromolecules, 2009, 10, 2351 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. M. Goddard and J. H. Hotchkiss, Prog. Polym. Sci., 2007, 32, 698 CrossRef CAS.
- P. K. Chu, J. Y. Chen, L. P. Wang and N. Huang, Mater. Sci. Eng., R, 2002, 36, 143 CrossRef.
- Z. Yang, X. Wang, J. Wang, Y. Yao, H. Sun and N. Huang, Plasma Processes Polym., 2009, 6, 498 CrossRef CAS.
- A. J. Melchiorri, N. Hibino, T. Yi, Y. U. Lee, T. Suqiura, S. Tara, T. Shinoka, C. Breuer and J. P. Fisher, Biomacromolecules, 2014, 16, 437 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Qi, W. Yan, Y. Yang, Y. Li, Y. Fan, J. Chen, Z. Yang, Q. Tu and N. Huang, Colloids Surf., B, 2015, 126, 70 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Yang, Q. Tu, J. Wang and N. Huang, Biomaterials, 2012, 33, 6615 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Truica-Marasescu and M. R. Wertheimer, Plasma Processes Polym., 2008, 5, 44 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Chen, X. Li, Z. Yang, S. Zhou, R. Luo, M. F. Maitz, Y. Zhao, J. Wang, K. Xiong and N. Huang, Colloids Surf., B, 2014, 113, 125 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. J. Molino, M. J. Higgins, P. C. Innis, R. M. Kapsa and G. G. Wallace, Langmuir, 2012, 28, 8433 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Zhu, Z. Wang, A. Zhao, N. Huang, H. Chen, S. Zhou and X. Xie, Colloids Surf., B, 2014, 116, 459 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. N. Ramiasa, A. A. Cavallaro, A. Mierczynska, S. N. Christo, J. M. Gleadle, J. D. Hayball and K. Vasilev, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 4279 RSC.
- V. Ball and F. Meyer, Colloids Surf., A, 2016, 491, 12 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Atacan and M. Özacar, Colloids Surf., B, 2015, 128, 227–236 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. H. Ku and C. B. Park, Biomaterials, 2010, 31, 9431 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Hu, K. G. Neoh, J. Zhang, E. T. Kang and W. Wang, Biomaterials, 2012, 33, 8082 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. M. Shin, Y. B. Lee, S. J. Kim, J. K. Kang, J. C. Park, W. Jang and H. Shin, Biomacromolecules, 2012, 13, 2020 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. G. Guex, D. Hegemann, M. N. Giraud, H. T. Tevaearai, A. M. Popa, R. M. Rossi and G. Fortunato, Colloids Surf., B, 2014, 123, 724 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. K. Poh, Z. Shi, T. Y. Lim, K. G. Neoh and W. Wang, Biomaterials, 2010, 31, 1578 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Luo, L. Tang, J. Wang, Y. Zhao, Q. Tu, Y. Weng and N. Huang, Colloids Surf., B, 2013, 106, 66 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Yang, J. Wu, X. Wang, J. Wang and N. Huang, Plasma Processes Polym., 2012, 9, 718 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Yang, Y. Yang, W. Yan, Q. Tu, J. Wang and N. Huang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5, 10495 CAS.
- N. Ferrara and T. Davis-Smyth, Endocr. Rev., 1997, 18, 4 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. G. Barrett, T. S. Sileika and P. B. Messersmith, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 7265 RSC.
- Z. Yang, K. Xiong, P. Qi, Y. Yang, Q. Tu, J. Wang and N. Huang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6, 2647 CAS.
- L. Ziberna, J. H. Kim, C. Auger, S. Passamonti and V. Schini-Kerth, Food Funct., 2013, 4, 1452 CAS.
- W. Ma and Y. T. Long, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 30 RSC.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c5ra25917g |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |