DOI:
10.1039/C6RA04862E
(Paper)
RSC Adv., 2016,
6, 60291-60307
Self-assembly Z-scheme heterostructured photocatalyst of Ag2O@Ag-modified bismuth vanadate for efficient photocatalytic degradation of single and dual organic pollutants under visible light irradiation
Received
24th February 2016
, Accepted 10th June 2016
First published on 13th June 2016
Abstract
Novel Ag2O@Ag-modified BiVO4 composites with highly efficient visible light photocatalytic activity were synthesized by a facile pH-mediated chemical precipitation method accompanied by a self-built Z-scheme heterojunction under visible light irradiation in this study. X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier transform infrared spectrometry (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV-vis DRS) analysis and electrochemical measurements demonstrated that an acicular sheaf-like heterojunction was formed. Rhodamine B (RhB), methylene blue (MB) and their mixture were selected as the target pollutants to evaluate the enhanced photocatalytic activities of the as-prepared composites. Compared with pure BiVO4 and Ag2O, Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4 had a high photocatalytic activity because of the efficient separation of electron–hole pairs in the heterojunction construction. The composites with an initial Ag2O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 mass ratio of 1
BiVO4 mass ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 exhibited the highest degradation efficiency for dye. Experimental results indicated that single RhB or MB could be degraded completely within a short irradiation time (15 min for 10 mg L−1 RhB, 48 min for 20 mg L−1 MB), but there was obviously competition with the active species, resulting in a decrease of the degradation rate for both dyes. Regardless of the suppression effect, a relatively higher photocatalytic performance was also achieved for the dye mixture. Several parameters, including initial dye concentration, calcination temperature, initial pH and mineralization ability are discussed in detail. The kinetics study suggested that photocatalytic degradation processes for single or complex dye were well described by first-order kinetics. Due to the generated Ag–Ag2O self-stability structure, these acicular sheaf-like three-dimensional heterojunction photocatalysts were fairly stable and there was no obvious loss of photocatalytic activity after four consecutive cycles.
10 exhibited the highest degradation efficiency for dye. Experimental results indicated that single RhB or MB could be degraded completely within a short irradiation time (15 min for 10 mg L−1 RhB, 48 min for 20 mg L−1 MB), but there was obviously competition with the active species, resulting in a decrease of the degradation rate for both dyes. Regardless of the suppression effect, a relatively higher photocatalytic performance was also achieved for the dye mixture. Several parameters, including initial dye concentration, calcination temperature, initial pH and mineralization ability are discussed in detail. The kinetics study suggested that photocatalytic degradation processes for single or complex dye were well described by first-order kinetics. Due to the generated Ag–Ag2O self-stability structure, these acicular sheaf-like three-dimensional heterojunction photocatalysts were fairly stable and there was no obvious loss of photocatalytic activity after four consecutive cycles.
1. Introduction
With the development of modern industry, synthetic dyes are being widely used in various textiles, printing, dyeing and food industries. Colourful dyes have enriched our lives but there also exists a potential hazard to human health and inhabitation for economic development due to the formation of cytotoxic and carcinogenic intermediates.1,2 Recently, advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) have been widely applied in the degradation of these hard-to-treat pollutants. As a promising AOP technology, photocatalysis has gained increasing attention in organic wastewater treatment owing to its high degradation efficiency, low-cost, and long-term stability compared with other conventional treatment methods.3–5 Generally, there are two approaches to improve the photoactivity of single semiconductor catalysts: (i) increasing the adsorption capacity of the catalyst for dye molecules and (ii) heterojunction formation, doping and vacancy generation in the photocatalytic system.6–8 Heterogeneous photocatalytic oxidation (HCO) using semiconductors has attracted considerable interest in air and water purification on account of its strong oxidation power, moderate operation temperature, and green chemistry-related procedures.9–12 In response to the further exploration of photocatalytic technology, a large number of new-type photocatalysts has been discovered and applied in the degradation of organic pollutants, especially heterostructured visible light-driven (VLD) photocatalysts.13
In recent years monoclinic BiVO4 with a band gap of about 2.4 eV has aroused researchers’ interest, because of its sufficient photocatalytic response and good stability against photocorrosion under visible light irradiation.14,15 By now, significant efforts have been devoted to achieve the controllable synthesis of BiVO4 hierarchical nanostructures, improving the photocatalytic performance especially under visible light irradiation.16 However, the photocatalytic activity of pure BiVO4 for water splitting and pollutant degradation is still not satisfactory, attributed to its weak surface absorption ability and migration difficulty of photogenerated electron–hole pairs. In order to solve the above existing problems, BiVO4 was combined with a semiconductor to form an appropriate band position.17 There are many successful cases such as Cu2O/BiVO4,18 BiVO4/TiO2,19 BiVO4/BiOCl,20 BiVO4/Bi2S3,21 and so on, but it seems to be considerably necessary to find more suitable semiconductors and study the photocatalytic activity and intrinsic mechanism more deeply. Ag2O is a p-type semiconductor with a direct band gap of about 1.2 eV, which possesses the ability to absorb a large part of visible light.22 According to previous reports, Ag2O was effectively used as a sensitizer to regulate the light response of relatively wide band gap semiconductors and improve the corresponding visible light photocatalytic activities, such as Ag2O/TiO2,23 Ag2O/BaTiO3,24 Ag2O/Bi2WO6,25 and so forth. The well matched overlapping band structures were successfully built due to the introduction of Ag2O, resulting in effective interface transfer of photogenerated electrons and holes. Taking the applicable energy band gap of Ag2O and BiVO4 into consideration, it is reasonable to construct a p–n heterojunction with the appropriate valence band and conduction band. In addition, it has been documented that the loaded Ag2O could be effectively transformed into a stable Ag2O/Ag structure in the photodecomposition of organic pollutants under illumination.26 Both Ag2O and the formed noble metal Ag could act as traps to capture photogenerated electrons, which were beneficial to the efficient separation of electron–hole pairs in the photocatalytic system.27
Herein, a highly efficient VLD heterogeneous photocatalyst, Ag2O/BiVO4 was firstly synthesized by a simple chemical precipitation method, followed by a self-built Z-scheme photocatalyst Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4 under visible light irradiation. RhB, MB and RhB + MB were used as the target pollutants to evaluate the photocatalytic activities of the Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4 heterojunctions. The influence of initial dye concentration, calcination temperature, and initial pH, and a kinetics study for both single and mixed dye degradation were investigated in detail. A possible reaction mechanism for the improved photocatalytic activities was discussed thoroughly and distinctly presented as graphs coupled with equations.
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemical materials
Bismuth nitrate pentahydrate (Bi(NO3)3·5H2O), ammonium metavanadate (NH4VO3), silver nitrate (AgNO3), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), glacial acetic acid (CH3COOH), aqueous ammonia (NH3·H2O) and ethanol were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. Rhodamine B (RhB, cationic dye) and methylene blue (MB, cationic dye) and their mixture were chosen as the target substances to evaluate the photocatalytic activity of the as-prepared samples. The structural formulae of RhB and MB are illustrated in Scheme 1. All chemicals were analytical reagent grade, commercially available and used without additional purification or treatment. Deionized water was used as the solvent throughout the experiment.
 |
| | Scheme 1 Structural formula of model pollutants: rhodamine B (RhB) and methylene blue (MB). | |
2.2. Preparation of 3D sheaf-shaped BiVO4
The typical preparation procedure of 3D sheaf-shaped BiVO4 was as follows: 2 mmol Bi(NO3)3·5H2O was firstly dissolved in a 50 mL mixed solution (v(C2H5OH)/v(CH3COOH)/v(H2O) = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3), and the formed solution was named as solution A. Simultaneously, 2 mmol NH4VO3 was dispersed in a 20 mL ammonia solution (v(NH3·H2O)/v(H2O) = 3
3), and the formed solution was named as solution A. Simultaneously, 2 mmol NH4VO3 was dispersed in a 20 mL ammonia solution (v(NH3·H2O)/v(H2O) = 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), and the solution was marked as solution B. After constant stirring for 20 min, solution B was added into solution A drop by drop and the pH was adjusted to 7.0 by NH3·H2O. Afterwards the obtained mixture was aged at 80 °C for 3 h under water bath conditions. After naturally cooling down, the yellow precipitate was collected by filtering and washing with deionized water and ethanol several times to remove the residual ions and surfactants in the products. At last, the products were dried at 80 °C in air for 8 h.
1), and the solution was marked as solution B. After constant stirring for 20 min, solution B was added into solution A drop by drop and the pH was adjusted to 7.0 by NH3·H2O. Afterwards the obtained mixture was aged at 80 °C for 3 h under water bath conditions. After naturally cooling down, the yellow precipitate was collected by filtering and washing with deionized water and ethanol several times to remove the residual ions and surfactants in the products. At last, the products were dried at 80 °C in air for 8 h.
2.3. Preparation of Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunctions
Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunctions were fabricated by a pH-mediated chemical precipitation method. Typically, 0.2 g of BiVO4 was added into 50 mL deionized water and ultrasonicated for 30 min to achieve a homogeneous dispersion. The desired amount of AgNO3 was added into the above solution and stirred at room temperature for 30 min in a dark place. The weight ratios of Ag2O/BiVO4 were controlled to be 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, 1
1, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5, 1
5, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 and 1
10 and 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20. Then NaOH (1 M) aqueous solution was adopted to adjust the pH of the suspensions to be about 12.5, and the dispersion was continuously stirred for 2 h at room temperature. Finally, the obtained dark brown Ag2O/BiVO4 was thoroughly washed with deionized water three times and dried at 60 °C for 8 h. The series of samples was labelled as Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
20. Then NaOH (1 M) aqueous solution was adopted to adjust the pH of the suspensions to be about 12.5, and the dispersion was continuously stirred for 2 h at room temperature. Finally, the obtained dark brown Ag2O/BiVO4 was thoroughly washed with deionized water three times and dried at 60 °C for 8 h. The series of samples was labelled as Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
1), Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5), Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
5), Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10), and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10), and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20), respectively. As a reference, pure Ag2O nanoparticles were synthesized from AgNO3 and NaOH aqueous solution by the above-mentioned precipitation method without adding BiVO4. Furthermore, the prepared samples were calcined at 60 °C, 100 °C, 200 °C and 300 °C for 1 h with a heating rate of 2 °C min−1, and named as 60 °C/1 h, 100 °C/1 h, 200 °C/1 h and 300 °C/1 h. A brief description of the preparation process is illustrated in Scheme 2.
20), respectively. As a reference, pure Ag2O nanoparticles were synthesized from AgNO3 and NaOH aqueous solution by the above-mentioned precipitation method without adding BiVO4. Furthermore, the prepared samples were calcined at 60 °C, 100 °C, 200 °C and 300 °C for 1 h with a heating rate of 2 °C min−1, and named as 60 °C/1 h, 100 °C/1 h, 200 °C/1 h and 300 °C/1 h. A brief description of the preparation process is illustrated in Scheme 2.
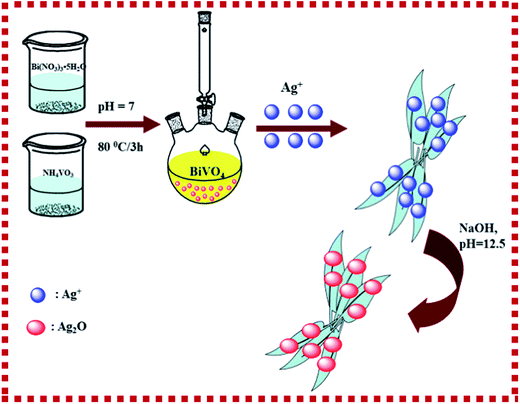 |
| | Scheme 2 The schematic diagram of the formation process of Ag2O/BiVO4 fabricated by a facile pH-mediated chemical precipitation method. | |
2.4. Characterizations
The phase compositions of the as-prepared samples were measured on a Rigaku D/max 2500v/pc X-ray diffractometer with Cu Kα radiation at a scan rate of 0.1° 2θ s−1. The working voltage and the applied current of the diffraction were 40 kV and 40 mA, respectively. FTIR spectra were collected on an IR Prestige-21 spectrometer (Shimadzu, Japan) at room temperature by the standard KBr disk method. Morphological analysis was performed using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM, Hitachi S-4800) with 5.0 kV scanning voltages. The TEM analyses were conducted using transmission electron microscopy (TEM, FEI Tecnai G20) at an accelerating voltage of 200 kV. The UV-vis absorption spectra were obtained on a UV-vis spectrometer (Shimadza UV-4100) in the range of 300–700 nm, using BaSO4 as the reference. The XPS measurements were carried out on a Thermo ESCALAB 250XI spectrometer with an Al Kα source. The total organic carbon (TOC) assays were tested using a Shimadzu TOC-VCPH analyzer. Photoluminescence (PL) measurements were monitored using a transient fluorescence spectrometer (Edinburgh FLsp920 full functional state). Photocurrent–time (PT) measurement was acquired using a conventional three-electrode electrochemical cell with a working electrode, a platinum wire counter electrode and a saturated calomel electrode (SCE) as the reference electrode. The working electrode was immersed in a sodium sulfate electrolyte solution (0.5 M) and illuminated under visible light. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was carried out on a potential Autolab PGSTAT-30 equipped with a frequency analyzer module using a three-electrode system in 0.5 M Na2SO4 solution. The electrochemical experimental results were all recorded with a CHI 660B electrochemical system.
2.5. Evaluation of visible light photocatalytic activity
The photocatalytic degradation of RhB, MB as well as their mixtures under visible light irradiation was adopted to evaluate the photocatalytic activities of the as-prepared Ag2O/BiVO4 samples. A 300 W Xe lamp with a cut-off filter (λ > 420 nm) was used as the light source and the average light intensity striking the surface of the reaction solution was about 100 mW cm2. Briefly, 0.03 g of photocatalyst was added to a 50 mL aqueous solution of RhB (10 mg L−1), MB (20 mg L−1), RhB + MB (5 mg L−1 + 10 mg L−1) or RhB + MB (10 mg L−1 + 20 mg L−1). Before illumination, the suspension was constantly stirred for 30 min in the dark to achieve the adsorption–desorption equilibrium. Afterwards, the mixture was exposed to visible light irradiation with magnetic stirring. At given time intervals, 2.5 mL of the suspension was periodically collected and analyzed after centrifugation. The concentrations of RhB and MB were determined by monitoring the absorbance at ca. 554 nm and 664 nm, respectively.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Characterization of the as-prepared photocatalysts
3.1.1 XRD analysis. The crystallographic structure and phase purity of the as-obtained samples were examined by XRD analysis. Fig. 1A shows the XRD patterns of Ag2O/BiVO4 heterostructures with different weight ratios of Ag2O. All of the diffraction peaks for BiVO4 could be indexed as the body-centered monoclinic phase of BiVO4 (JCPDS File No. 14-0688).28,29 The major characteristic XRD peaks of pure BiVO4 and Ag2O/BiVO4 heterostructures detected at 2θ values of 18.67°, 28.82°, 30.55°, 34.49°, 35.22°, 39.78°, 42.46°, 45.43°, 46.71°, 49.96°, 53.32°, 55.27° and 59.26° could be indexed as (110), (011), (121), (040), (200), (002), (211), (051), (231), (240), (202), (161), (321) and (123) respectively. The diffraction peaks at 2θ values of 26.77°, 32.79°, 38.11°, 55.02° and 65.56° belong to the (110), (111), (200), (220) and (311) planes of cubic Ag2O with JCPDS File No. 41-1104.25 The XRD patterns of the Ag2O/BiVO4 composites possessed the characteristic peaks of both Ag2O and BiVO4 crystalline phases. From Fig. 1A, the intensity of the diffraction peaks of Ag2O in the composites becomes weaker and the level of weakening was in accordance with the reduction of Ag2O dosage. A high degree of crystallinity was achieved and there was no detectable peaks ascribable to the impurities, implying that a high purity of Ag2O and BiVO4 was obtained. Furthermore, the XRD pattern comparison of the fresh and used Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) composite is given in Fig. 1B; the crystal structure of the catalyst remained unchanged, and only a small peak of metallic Ag was discovered in the used samples. The XRD pattern of the first cycle was similar to that of the fourth cycle, confirming the stable construction of a Ag–Ag2O bridge in the composite and leading to a stable Z-scheme photocatalyst Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4.
10) composite is given in Fig. 1B; the crystal structure of the catalyst remained unchanged, and only a small peak of metallic Ag was discovered in the used samples. The XRD pattern of the first cycle was similar to that of the fourth cycle, confirming the stable construction of a Ag–Ag2O bridge in the composite and leading to a stable Z-scheme photocatalyst Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4.
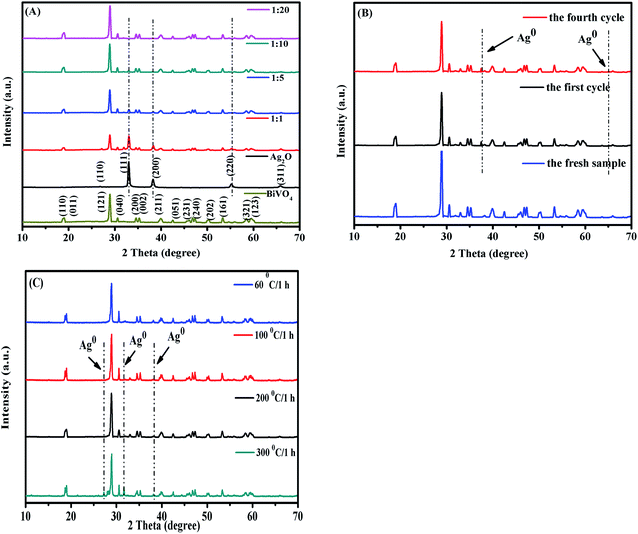 |
| | Fig. 1 XRD patterns of pure BiVO4, pure Ag2O and Ag2O/BiVO4 composite photocatalysts with different weight ratios (A), XRD patterns of the fresh and used Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) (B), and XRD patterns at different calcination temperatures (C). 10) (B), and XRD patterns at different calcination temperatures (C). | |
3.1.2 SEM and TEM analysis. The representative SEM images of the as-prepared BiVO4, Ag2O and Ag2O/BiVO4 composites are presented in Fig. 2. Fig. 2A and B show the morphology of Ag2O obtained by the precipitation method and the corresponding sizes were about 100–500 nm. Both BiVO4 and Ag2O/BiVO4 are presented as 3D acicular sheaf-shaped structures (Fig. 2C–F). Pure BiVO4 had uniform size and shape distributions. For the Ag2O/BiVO4 composite, the general sheaf-shaped morphology could be also observed, while the surfaces of the catalysts were rough providing numerous nucleation sites for the growth of Ag2O. Fig. 2F shows clearly that Ag2O nanoparticles dispersed homogeneously on the surface of BiVO4. The co-existence of Ag2O and BiVO4 in the forming heterojunction structure is proven by the TEM images for pure BiVO4 (Fig. 3A and C) and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) (Fig. 3B, D and E). As depicted in Fig. 3A–D, BiVO4 should be responsible for the emergence of a sheaf-like structure, and a large amount of small nanoparticles on the surface of the Ag2O/BiVO4 composite should be Ag2O. Fig. 3F is a representative HRTEM image of Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) (Fig. 3B, D and E). As depicted in Fig. 3A–D, BiVO4 should be responsible for the emergence of a sheaf-like structure, and a large amount of small nanoparticles on the surface of the Ag2O/BiVO4 composite should be Ag2O. Fig. 3F is a representative HRTEM image of Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10); the clear lattice fringes present are indicative of high crystallinity. The interplanar spacings of 0.475 nm and 0.309 nm are clearly observed, which should correspond to the (110) and (121) crystallographic planes of BiVO4 (JCPDS File No. 14-0688). The d-spacing measured to be 0.272 nm was in good consistency with the lattice spacing (111) of cubic Ag2O (JCPDS File No. 41-1104).
10); the clear lattice fringes present are indicative of high crystallinity. The interplanar spacings of 0.475 nm and 0.309 nm are clearly observed, which should correspond to the (110) and (121) crystallographic planes of BiVO4 (JCPDS File No. 14-0688). The d-spacing measured to be 0.272 nm was in good consistency with the lattice spacing (111) of cubic Ag2O (JCPDS File No. 41-1104).
 |
| | Fig. 2 SEM images of the samples: pure BiVO4 (A and B), pure Ag2O (C and D), and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) (E and F). 10) (E and F). | |
 |
| | Fig. 3 TEM images of the samples: BiVO4 (A and C) and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) (B, D and E), and HRTEM image of Ag2O/BiVO4 (1 10) (B, D and E), and HRTEM image of Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) (F). 10) (F). | |
3.1.3 FTIR and XPS analysis. The components of the as-prepared composite catalysts were confirmed by FTIR analysis. Fig. 4A shows the FTIR spectra of the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterostructures with different weight ratios of Ag2O. For pure Ag2O, two bands at 3410 and 1671 cm−1 could be ascribed to O–H stretching and deformation vibration of physisorbed and/or chemisorbed water molecules,27 while the peak at 1380 cm−1 [F–Ag] belongs to the H–O–H bending vibration of the absorbed water molecules on the surface.30 The band at about 600 cm−1 could be assigned to Ag–O, which was achieved by analysis with Ag2O and the Ag2O/BiVO4 composites.27 The intensity of Ag–O in the Ag2O/BiVO4 composites became weaker accompanied with the reduction of the Ag2O content. Moreover, the broad band at 700–850 cm−1 for both the pure BiVO4 and Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunctions [F–Bi] is considered as the bending vibration of VO43−.31
 |
| | Fig. 4 FTIR spectra of the samples: pure BiVO4, pure Ag2O and Ag2O/BiVO4 composites (A); XPS spectra of Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) (B–F). (Additional information: in Fig. 4A, a–f represented for Ag2O/BiVO4 (1 10) (B–F). (Additional information: in Fig. 4A, a–f represented for Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20), Ag2O/BiVO4 (1 20), Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10), Ag2O/BiVO4 (1 10), Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5), Ag2O/BiVO4 (1 5), Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), pure BiVO4 and Ag2O, respectively.) 1), pure BiVO4 and Ag2O, respectively.) | |
XPS measurements were carried out to analyze the surface chemical states and the bonding modality among the atoms of the Ag2O/BiVO4 composites. Fig. 4B shows the XPS survey spectra of pure BiVO4 and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10). The co-existence of C, Bi, V and O elements for pure BiVO4 could be observed, while another Ag element was discovered in Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10). The co-existence of C, Bi, V and O elements for pure BiVO4 could be observed, while another Ag element was discovered in Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) without any other impurities. The emergence of C (the peak at 284.57 eV) could be assigned to the adventitious hydrocarbon from the XPS instrument itself.20 The peaks located at 159.44 eV and 164.68 eV belong to Bi 4f7/2 and Bi 4f5/2, respectively (Fig. 4C).32 Two main peaks appearing at the binding energies of 517.02 eV and 524.18 eV correspond to V 2p1/2 and V 2p3/2, respectively (Fig. 4D).33 Typical O 1s spectra of pure BiVO4 and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) without any other impurities. The emergence of C (the peak at 284.57 eV) could be assigned to the adventitious hydrocarbon from the XPS instrument itself.20 The peaks located at 159.44 eV and 164.68 eV belong to Bi 4f7/2 and Bi 4f5/2, respectively (Fig. 4C).32 Two main peaks appearing at the binding energies of 517.02 eV and 524.18 eV correspond to V 2p1/2 and V 2p3/2, respectively (Fig. 4D).33 Typical O 1s spectra of pure BiVO4 and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) exhibit the predominant characteristic peaks at 530.2 eV (Fig. 4E). The peaks at 368.1 eV and 374.1 eV in Ag2O (1
10) exhibit the predominant characteristic peaks at 530.2 eV (Fig. 4E). The peaks at 368.1 eV and 374.1 eV in Ag2O (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) revealed the presence of Ag+, which are homologous to the Ag 3d5/2 and Ag 3d3/2 binding energies (Fig. 4F). This suggests the existence of a Ag2O phase in the composite, which is in good agreement with the XRD and FTIR analysis.
10) revealed the presence of Ag+, which are homologous to the Ag 3d5/2 and Ag 3d3/2 binding energies (Fig. 4F). This suggests the existence of a Ag2O phase in the composite, which is in good agreement with the XRD and FTIR analysis.
3.1.4 UV-vis analysis. The UV-vis diffuse absorption spectra of the as-prepared samples were measured using a spectrophotometer, as shown in Fig. 5. As for the pure BiVO4 composite, only the band gap absorption with an absorption edge at ca. 517 nm could be observed. Accompanied by the introduction of Ag2O nanoparticles, the obtained Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunction exhibited a broader visible light absorption in the range of 500–700 nm and the intensity strengthened with the increase of the Ag2O content. The optical band gap for semiconductor photocatalysts could be estimated using the following equation:13,19| | |
(Ahv) = α(hv − Eg)n/2
| (1) |
where α, v, Eg and A are the absorption coefficient, light frequency, band gap energy, and a constant, respectively. n is determined by the type of optical transition of a semiconductor (n = 1 for direct transition and n = 4 for indirect transition). The n value for pure BiVO4 is 4, and the corresponding energy band gap was measured and estimated to be about 2.4 eV.
 |
| | Fig. 5 UV spectra of pure BiVO4, pure Ag2O and Ag2O/BiVO4 composites (A), and plot of (Ahv)2 versus hv for pure BiVO4 (B). | |
3.2. Photocatalytic activity study
3.2.1 Effect of Ag2O content. The photocatalytic activities of the as-synthesized samples were evaluated through the decomposition of RhB, MB and RhB + MB under visible light irradiation. Fig. 6A and B show the photodegradation of RhB (10 mg L−1) and MB (20 mg L−1), respectively with different weight ratios of Ag2O to BiVO4. It could be perceived that there was a slight loss in the dye concentration after 30 min treatment in the dark, verifying the weak absorption ability of the catalysts for the dye. The photocatalytic performance of pure BiVO4 was poor while it was greatly enhanced with the introduction of Ag2O. RhB and MB were completely decolourized in 15 and 48 min by Ag2O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10), while for pure BiVO4 only 12.9% of RhB and 7.3% of MB could be degraded within the same irradiation time. However, different weight ratios of Ag2O to BiVO4 showed different degradation rates for RhB and MB, which were in the order of Ag2O
10), while for pure BiVO4 only 12.9% of RhB and 7.3% of MB could be degraded within the same irradiation time. However, different weight ratios of Ag2O to BiVO4 showed different degradation rates for RhB and MB, which were in the order of Ag2O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) > Ag2O
10) > Ag2O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5) > Ag2O > Ag2O
5) > Ag2O > Ag2O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20) > Ag2O
20) > Ag2O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) > BiVO4. So the optimized weight ratio of Ag2O in the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterostructures should be 1
1) > BiVO4. So the optimized weight ratio of Ag2O in the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterostructures should be 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10. These results suggested that a feasible mass ratio of Ag2O in the constructed heterojunction was good for the enhancement of photoactivity. Excess Ag2O deposited on the BiVO4 surface would increase the recombination rate of photogenerated electron–hole pairs, leading to a poorer degradation efficiency. Wan and Zhang also found that excess AgI deposited on the surface of Bi2SiO5 would decrease the photocatalytic activities of Bi2SiO5/AgI nanoplates.12
10. These results suggested that a feasible mass ratio of Ag2O in the constructed heterojunction was good for the enhancement of photoactivity. Excess Ag2O deposited on the BiVO4 surface would increase the recombination rate of photogenerated electron–hole pairs, leading to a poorer degradation efficiency. Wan and Zhang also found that excess AgI deposited on the surface of Bi2SiO5 would decrease the photocatalytic activities of Bi2SiO5/AgI nanoplates.12
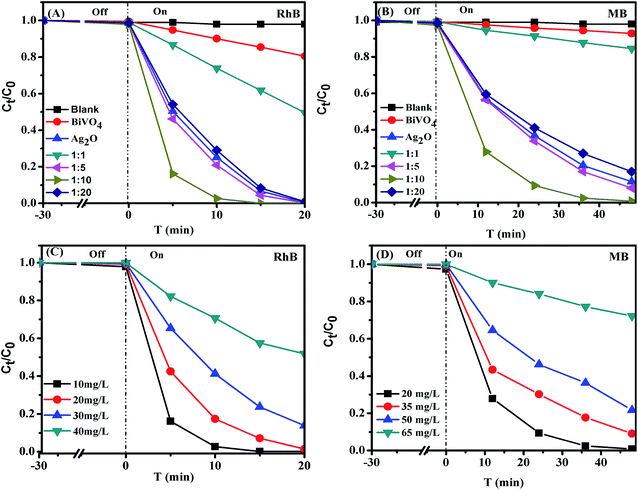 |
| | Fig. 6 Photodegradation of RhB and MB over Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) composite with different weight ratios (A and B) (experimental conditions: initial RhB concentration: 10 mg L−1, initial MB concentration: 20 mg L−1, pH = 6.3, m/V = 0.600 g L−1, visible light: λ > 420 nm) and initial dye concentrations (C and D) (experimental conditions: pH = 6.3, m/V = 0.600 g L−1, visible light: λ > 420 nm). 10) composite with different weight ratios (A and B) (experimental conditions: initial RhB concentration: 10 mg L−1, initial MB concentration: 20 mg L−1, pH = 6.3, m/V = 0.600 g L−1, visible light: λ > 420 nm) and initial dye concentrations (C and D) (experimental conditions: pH = 6.3, m/V = 0.600 g L−1, visible light: λ > 420 nm). | |
3.2.2 Effect of initial dye concentration. Fig. 6C and D display the RhB and MB degradation with different initial dye concentrations using Ag2O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10). As shown in Fig. 6C, the RhB degradation efficiency decreased with the increase of initial dye concentration in the investigated range (10 to 40 mg L−1). When the initial RhB concentration was below 30 mg L−1, the degradation efficiency maintained a high level (over 90%), but observably declined to 42.1% at 40 mg L−1. A similar variation also appeared in the MB photocatalytic degradation process (Fig. 6D). Higher initial pollutant concentrations could affect the light penetration through the solution in the photocatalytic process.34 The reduced light penetration at a high initial concentration solution resulted in less arrival of photons to the catalyst surface. Meanwhile dye molecules and the produced intermediates tended to compete with each other for initial absorption and catalytic sites on the Ag2O/BiVO4 surface. Many studies validated that the dye degradation process was restricted for the formed intermediates during the photocatalytic oxidation process.35,36 So more production of intermediates in the photocatalytic process would in turn aggravate the competitive adsorption on the catalyst surface between the dye compound and intermediates under high dye concentration conditions.
10). As shown in Fig. 6C, the RhB degradation efficiency decreased with the increase of initial dye concentration in the investigated range (10 to 40 mg L−1). When the initial RhB concentration was below 30 mg L−1, the degradation efficiency maintained a high level (over 90%), but observably declined to 42.1% at 40 mg L−1. A similar variation also appeared in the MB photocatalytic degradation process (Fig. 6D). Higher initial pollutant concentrations could affect the light penetration through the solution in the photocatalytic process.34 The reduced light penetration at a high initial concentration solution resulted in less arrival of photons to the catalyst surface. Meanwhile dye molecules and the produced intermediates tended to compete with each other for initial absorption and catalytic sites on the Ag2O/BiVO4 surface. Many studies validated that the dye degradation process was restricted for the formed intermediates during the photocatalytic oxidation process.35,36 So more production of intermediates in the photocatalytic process would in turn aggravate the competitive adsorption on the catalyst surface between the dye compound and intermediates under high dye concentration conditions.
3.2.3 Effect of different calcination temperatures. The effect of calcination temperature on the photocatalytic activity of the as-prepared Ag2O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) was investigated and the results are exhibited in Fig. 7A and B. With the calcination temperature increasing from 60 to 200 °C, the photocatalytic activity of the as-prepared Ag2O
10) was investigated and the results are exhibited in Fig. 7A and B. With the calcination temperature increasing from 60 to 200 °C, the photocatalytic activity of the as-prepared Ag2O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) for the decomposition of dye deteriorated. The degradation efficiency of RhB and MB was only 25.8% and 15.2% when the calcination temperature went up to 300 °C. The reason should be attributed to the destruction of the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunction structure. Yu et al. found that Ag2O in Ag2O/Bi2WO6 decomposed to form Ag nanoparticles at a calcination temperature of 450 °C.25 The XRD patterns of Ag2O
10) for the decomposition of dye deteriorated. The degradation efficiency of RhB and MB was only 25.8% and 15.2% when the calcination temperature went up to 300 °C. The reason should be attributed to the destruction of the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunction structure. Yu et al. found that Ag2O in Ag2O/Bi2WO6 decomposed to form Ag nanoparticles at a calcination temperature of 450 °C.25 The XRD patterns of Ag2O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) calcined at 300 °C also demonstrate that almost all of the Ag2O was decomposed and formed metallic Ag (Fig. 1C). Ag-modified BiVO4 exhibited a slightly better photocatalytic performance than that of pure BiVO4, because the electron–hole separation rate was also improved by introducing metallic Ag.25 The excessive Ag0 would lower the photocatalytic activity of Ag2O/BiVO4. In order to maintain the 3D sheaf-like heterojunctions of Ag2O/BiVO4, the calcination temperature should be controlled at a relatively lower level.
10) calcined at 300 °C also demonstrate that almost all of the Ag2O was decomposed and formed metallic Ag (Fig. 1C). Ag-modified BiVO4 exhibited a slightly better photocatalytic performance than that of pure BiVO4, because the electron–hole separation rate was also improved by introducing metallic Ag.25 The excessive Ag0 would lower the photocatalytic activity of Ag2O/BiVO4. In order to maintain the 3D sheaf-like heterojunctions of Ag2O/BiVO4, the calcination temperature should be controlled at a relatively lower level.
 |
| | Fig. 7 Photodegradation of RhB and MB over Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) composite with different calcination temperatures (A and B) (experimental conditions: initial RhB concentration: 10 mg L−1, initial MB concentration: 20 mg L−1, pH = 6.3, m/V = 0.600 g L−1, visible light: λ > 420 nm), and with different initial pH (experimental conditions: initial RhB concentration: 10 mg L−1, initial MB concentration: 20 mg L−1, m/V = 0.600 g L−1, visible light: λ > 420 nm). 10) composite with different calcination temperatures (A and B) (experimental conditions: initial RhB concentration: 10 mg L−1, initial MB concentration: 20 mg L−1, pH = 6.3, m/V = 0.600 g L−1, visible light: λ > 420 nm), and with different initial pH (experimental conditions: initial RhB concentration: 10 mg L−1, initial MB concentration: 20 mg L−1, m/V = 0.600 g L−1, visible light: λ > 420 nm). | |
3.2.4 Effect of initial pH. The initial pH is an important parameter for controlling the photocatalytic process. As displayed in Fig. 7C and D, a series of pH was controlled by NaOH (0.1 M) or HNO3 (0.1 M) to investigate the effect of initial pH in the photocatalytic process. The highest photodegradation efficiencies of RhB and MB could be achieved at an initial pH of 6.3. The pH of an aqueous medium can influence the photocatalytic process through absorption between dyes and the catalyst surface and redox processes of photocatalysts. The optimum photodegradation efficiencies of RhB and MB appeared at nearly neutral, and the photocatalytic activity was depressed under strong acid and alkali conditions, especially in an acidic environment. When the initial pH was below 6, the surface charge of the as-prepared catalysts became increasingly positive as the pH decreased resulting in increasingly stronger electrostatic repulsion with dye molecules. However with an initial pH of 8–10, the negatively charged photocatalyst surface prevented the sorption of hydroxide ions, thus reducing the formation of hydroxyl radicals and the photo-oxidation efficiency.18,29 Herein, the optimum pH value for both RhB and MB degradation was 6.3.
3.2.5 Degradation and mineralization of mixed dyes. It is well known that real-world wastewater from dye industries usually is various organic dye mixtures.37,38 Thus it is meaningful to investigate the superior photocatalytic performance of the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunction for mixed dye wastewater. The experiments were carried out in RhB (5 mg L−1) + MB (10 mg L−1) and RhB (10 mg L−1) + MB (20 mg L−1) aqueous solution in the presence of Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10). Compared with single RhB or MB degradation, the degradation efficiencies of a mixture of dyes descended to some extent. As exhibited in Fig. 8A and B, RhB and MB were completely degraded in 20 and 48 min, respectively, while in Fig. 8C and D, we could find that MB achieved a high decomposition rate in both mixed dye solutions and the RhB degradation was significantly hindered, especially at high initial concentrations. As displayed in Fig. 8E, the degradation rate of MB was much faster than that of RhB, which could be explained by the fact that MB possessed better affinity to the catalyst than RhB did, and good absorption resulted in the promotion of dye photodegradation. There is usually a competition mode between two cationic dyes in the photodegradation process of a mixture of dyes, which also was proven in the visible light-driven degradation of RhB and MB catalyzed by InVO4–BiVO4 and its supported noble metal nanoparticles.39 Total organic carbon (TOC) analysis is an efficient way to evaluate the degradation degree of organic dyes, which requires a long irradiation time.40 Fig. 8F presents the TOC removal in single and mixed dye degradation. The TOC removal for single RhB and MB degradation reached 90.2% and 93.2%. However, the corresponding values for mixed dyes obviously decreased and the TOC removal for the RhB (10 mg L−1) + MB (20 mg L−1) solution was only 32.5%, which should be attributed to the high initial dye concentration. The above information suggested that the TOC removal in single dye degradation was more thorough than that in the mixture of dyes. Meanwhile, it could be noticed that although the whole degradation time in RhB (5 mg L−1) + MB (10 mg L−1) solution was longer than that of any single dye, the final TOC removal could reach 88.2% and was desirable. The relatively high TOC removal was acquired in both single and mixed dye degradation, confirming that the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunction possessed a preferable mineralization ability.
10). Compared with single RhB or MB degradation, the degradation efficiencies of a mixture of dyes descended to some extent. As exhibited in Fig. 8A and B, RhB and MB were completely degraded in 20 and 48 min, respectively, while in Fig. 8C and D, we could find that MB achieved a high decomposition rate in both mixed dye solutions and the RhB degradation was significantly hindered, especially at high initial concentrations. As displayed in Fig. 8E, the degradation rate of MB was much faster than that of RhB, which could be explained by the fact that MB possessed better affinity to the catalyst than RhB did, and good absorption resulted in the promotion of dye photodegradation. There is usually a competition mode between two cationic dyes in the photodegradation process of a mixture of dyes, which also was proven in the visible light-driven degradation of RhB and MB catalyzed by InVO4–BiVO4 and its supported noble metal nanoparticles.39 Total organic carbon (TOC) analysis is an efficient way to evaluate the degradation degree of organic dyes, which requires a long irradiation time.40 Fig. 8F presents the TOC removal in single and mixed dye degradation. The TOC removal for single RhB and MB degradation reached 90.2% and 93.2%. However, the corresponding values for mixed dyes obviously decreased and the TOC removal for the RhB (10 mg L−1) + MB (20 mg L−1) solution was only 32.5%, which should be attributed to the high initial dye concentration. The above information suggested that the TOC removal in single dye degradation was more thorough than that in the mixture of dyes. Meanwhile, it could be noticed that although the whole degradation time in RhB (5 mg L−1) + MB (10 mg L−1) solution was longer than that of any single dye, the final TOC removal could reach 88.2% and was desirable. The relatively high TOC removal was acquired in both single and mixed dye degradation, confirming that the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunction possessed a preferable mineralization ability.
 |
| | Fig. 8 The temporal absorption spectrum changes of RhB (A), MB (B), and RhB + MB (C and D) aqueous solutions, and the photodegradation of RhB + MB mixture (E) and TOC removal (F) in the presence of the Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) composite under visible light irradiation. 10) composite under visible light irradiation. | |
3.3. Photocatalytic reaction kinetics
Moreover, the photocatalytic decomposition of RhB, MB and RhB + MB in this study followed the pseudo-first-order kinetics model. The rate constant (kapp) could be calculated by the following equation:41where C0 and Ct are the concentration of the dye at time 0 and t, respectively (mg L−1), and kapp represents the rate constant (min−1). The kinetic plots of the different samples are displayed in Fig. 9A–C. The corresponding plots of −ln(Ct/C0) ∼ t exhibited a good linearity. Table 1 summarizes the kinetic parameters of the samples occurring in the photocatalytic process. High correlation coefficients (R2 > 0.98) indicated that the dye photodegradation catalyzed by Ag2O/BiVO4 followed a pseudo-first-order reaction. Based on the rate constant (kapp), the photocatalytic performance of BiVO4 was greatly enhanced with the introduction of Ag2O, in which Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) presented the highest photocatalytic activity. The corresponding kapp was 0.5208 and 0.1008 min−1 for RhB and MB degradation, which was 49/2.5 and 72/2.2 times higher than that of pure BiVO4 and Ag2O, respectively. This result demonstrated the advantage of building 3D Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunctions. Furthermore, compared with the single dye degradation, the value of kapp for RhB (or MB) deceased to 0.0222 (0.0684) and 0.0038 (0.0432) min−1 in RhB (5 mg L−1) + MB (10 mg L−1) and RhB (10 mg L−1) + MB (20 mg L−1) solutions. Obviously, RhB degradation was more affected than MB in the mixed dye solution. This phenomenon further revealed that a competitive mode existed in the multi-component dye photodegradation process. The discrepancy in the absorption ability between RhB and MB and the advantages of good absorption served as a promoter for dye degradation.39
10) presented the highest photocatalytic activity. The corresponding kapp was 0.5208 and 0.1008 min−1 for RhB and MB degradation, which was 49/2.5 and 72/2.2 times higher than that of pure BiVO4 and Ag2O, respectively. This result demonstrated the advantage of building 3D Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunctions. Furthermore, compared with the single dye degradation, the value of kapp for RhB (or MB) deceased to 0.0222 (0.0684) and 0.0038 (0.0432) min−1 in RhB (5 mg L−1) + MB (10 mg L−1) and RhB (10 mg L−1) + MB (20 mg L−1) solutions. Obviously, RhB degradation was more affected than MB in the mixed dye solution. This phenomenon further revealed that a competitive mode existed in the multi-component dye photodegradation process. The discrepancy in the absorption ability between RhB and MB and the advantages of good absorption served as a promoter for dye degradation.39
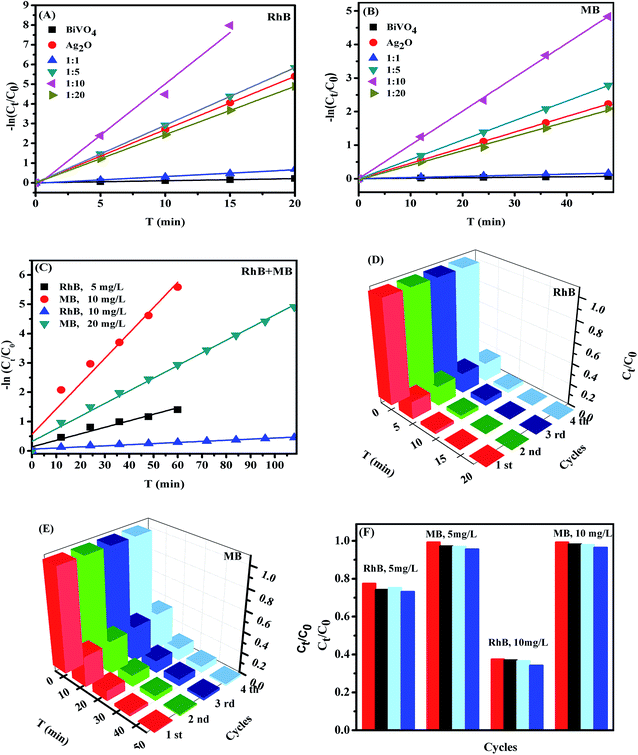 |
| | Fig. 9 Kinetic plots and the recycling efficiencies for dye degradation: RhB (A and D), MB (B and E), and RhB + MB (C and F). | |
Table 1 Correlation coefficients and rate constants for the degradation of dyes in the different photocatalytic systems
| Catalyst |
RhB |
MB |
| kapp (min−1) |
R2 |
kapp (min−1) |
R2 |
| For the degradation of RhB + MB (5 mg L−1 + 5 mg L−1). For the degradation of RhB + MB (10 mg L−1 + 10 mg L−1). |
| BiVO4 |
0.0106 |
0.9982 |
0.0014 |
0.9958 |
| Ag2O |
0.2101 |
0.9986 |
0.0465 |
0.9969 |
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
0.0344 |
0.9879 |
0.0039 |
0.9905 |
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5 5 |
0.2931 |
0.9901 |
0.0579 |
0.9904 |
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10 |
0.5208 |
0.9806 |
0.1008 |
0.9899 |
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10a 10a |
0.0222 |
0.9801 |
0.0684 |
0.9821 |
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10b 10b |
0.0038 |
0.9821 |
0.0432 |
0.9919 |
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20 20 |
0.2448 |
0.9901 |
0.0433 |
0.9958 |
3.4. Recyclability and reusability of the photocatalysts
In addition, the stability and recyclability of the photocatalysts are also crucial issues in their practical applications. The photodegradation of RhB, MB and RhB + MB using Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) was investigated for four consecutive runs under identical experimental conditions. As shown in Fig. 9D–F, after four successive cycles, the photocatalytic activity for both single and mixed organic dye degradation had no obvious loss. The XPS spectra of the fresh and used Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) was investigated for four consecutive runs under identical experimental conditions. As shown in Fig. 9D–F, after four successive cycles, the photocatalytic activity for both single and mixed organic dye degradation had no obvious loss. The XPS spectra of the fresh and used Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) (Fig. 10A and B) reveal that there were two peaks at 374.1 eV and 368.1 eV, which belonged to Ag+ in the composite. Another two peaks appeared at 373.2 eV and 367.3 eV which could be attributed to metallic Ag (Ag0 (ref. 10 and 33)), which is in accordance with the description in the XRD analysis. The used samples for the first and fourth cycle presented a similar structure and intensity in their XRD patterns, confirming the desirable stability of the as-prepared Z-scheme photocatalyst. The above-mentioned information indicates the excellent reusability performance longevity of Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4 under visible light irradiation, which makes it a promising candidate in practical composite wastewater treatment.
10) (Fig. 10A and B) reveal that there were two peaks at 374.1 eV and 368.1 eV, which belonged to Ag+ in the composite. Another two peaks appeared at 373.2 eV and 367.3 eV which could be attributed to metallic Ag (Ag0 (ref. 10 and 33)), which is in accordance with the description in the XRD analysis. The used samples for the first and fourth cycle presented a similar structure and intensity in their XRD patterns, confirming the desirable stability of the as-prepared Z-scheme photocatalyst. The above-mentioned information indicates the excellent reusability performance longevity of Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4 under visible light irradiation, which makes it a promising candidate in practical composite wastewater treatment.
 |
| | Fig. 10 The XPS spectra of the fresh and used Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) (A and B) and the effects of different scavengers on the degradation of RhB (C) and MB (D) over Ag2O/BiVO4 (1 10) (A and B) and the effects of different scavengers on the degradation of RhB (C) and MB (D) over Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) under visible light irradiation. 10) under visible light irradiation. | |
3.5. Photocatalytic mechanism
It is generally recognized that photo-induced reactive species including trapped holes (h+), hydroxyl radicals (˙OH) and superoxide radicals (˙O2−) are expected to be involved in the photocatalytic process. In order to reveal the photocatalytic mechanism more clearly, the main oxidative species produced in the photocatalytic process were detected through trapping experiments using benzoquinone (BQ), triethanolamine (TEOA) and isopropanol (IPA) as the scavengers of ˙O2−,42 h+,43 and ˙OH,44 respectively. The results are illustrated in Fig. 10C and D and Table 2, and the degradation efficiency of RhB or MB was hardly inhibited with the addition of IPA, implying that ˙OH was not mainly produced in the photocatalytic system of Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4. On the contrary, the degradation efficiencies of RhB changed from 99.80% to 3.12% and 26.55% in the presence of TEOA and BQ, respectively. The same variation happened in MB degradation, and the whole degradation process was almost inhibited and the decomposition rate remarkably decreased with the addition of TEOA and BQ. It could be elucidated that ˙O2− and h+ were the dominant active species generated in the photocatalytic process, which should be responsible for the highly enhanced photocatalytic performance for dye degradation.
Table 2 Degradation efficiencies of RhB or MB in the presence of different scavenger
| Scavenger |
RhB |
MB |
| Initial |
Final |
Initial |
Final |
| No scavenger |
99.80% |
99.80% |
99.52% |
99.51% |
| IPA |
99.80% |
99.51% |
99.51% |
96.32% |
| BQ |
99.80% |
26.55% |
99.51% |
11.68% |
| TEOA |
99.80% |
3.12% |
99.51% |
1.59% |
The possible transfer routes of photo-excited electrons and holes were employed to explain the enhanced photocatalytic activity based on the conduction band (CB) and valence band (VB) potentials of Ag2O and BiVO4. The band energy (CB and VB) positions of each semiconductor could be calculated by Mulliken electronegativity theory as exemplified below:19,33
where
X is the electronegativity of the semiconductor,
Ec is the energy of free electrons on the hydrogen scale (∼4.5 eV), and the CB and VB potentials of Ag
2O are approximately +0.2 eV and +1.4 eV, respectively.
25 The CB and VB potentials of BiVO
4 are estimated to be +0.46 eV and +2.86 eV, respectively.
It is generally acknowledged that the photocatalytic reaction is completed by the collection of efficient charge carrier trapping, migration and transfer. A low PL intensity is indicative of a high separation efficiency of electron–hole pairs, in other words, a good photocatalyst should have a minimum electron–hole recombination. The corresponding PL spectra of BiVO4, Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) are clearly revealed in Fig. 11A. From Fig. 11A, the PL intensity of the Ag2O/BiVO4 composites is significantly reduced as compared to that of pure BiVO4, implying a lower recombination feasibility of free charges in the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterostructures. Moreover, the lower PL intensity achieved by the fresh Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
1) are clearly revealed in Fig. 11A. From Fig. 11A, the PL intensity of the Ag2O/BiVO4 composites is significantly reduced as compared to that of pure BiVO4, implying a lower recombination feasibility of free charges in the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterostructures. Moreover, the lower PL intensity achieved by the fresh Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) composite suggested that photo-induced electron–hole recombination processes were truly hindered. Notably, the used Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) composite suggested that photo-induced electron–hole recombination processes were truly hindered. Notably, the used Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) (self-built Z-scheme photocatalyst Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4) exhibited the lowest recombination probability of electron–hole pairs, which could be assigned to the formed metallic Ag, further indicating that a Z-scheme system was constructed under visible light.
10) (self-built Z-scheme photocatalyst Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4) exhibited the lowest recombination probability of electron–hole pairs, which could be assigned to the formed metallic Ag, further indicating that a Z-scheme system was constructed under visible light.
 |
| | Fig. 11 The PL spectra (A), PT spectra (B) and EIS analysis (C and D) of the samples: BiVO4, Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1 10) and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). 1). | |
The effect of the Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) composite on the separation efficiency of electron–hole pairs was investigated by photocurrent–time (PT) experiments, as demonstrated in Fig. 11B. The transient photocurrent responses of pure BiVO4, Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) composite on the separation efficiency of electron–hole pairs was investigated by photocurrent–time (PT) experiments, as demonstrated in Fig. 11B. The transient photocurrent responses of pure BiVO4, Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) were recorded for several on–off cycles under visible light irradiation. For pure BiVO4, a small amount of photocurrent was generated while for Ag2O/BiVO4 composites, a significantly enhanced photocurrent intensity was detected. Especially, Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
1) were recorded for several on–off cycles under visible light irradiation. For pure BiVO4, a small amount of photocurrent was generated while for Ag2O/BiVO4 composites, a significantly enhanced photocurrent intensity was detected. Especially, Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) possessed the highest current intensity, suggesting more efficient separation of the photogenerated electron–hole pairs over Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) possessed the highest current intensity, suggesting more efficient separation of the photogenerated electron–hole pairs over Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10). Meanwhile, the above photocurrent order was in good agreement with the result of the photocatalytic activity. The results indicated that there existed good energy band matching in the formation of Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunctions, due to highly efficient electron–hole separation at the interface.
10). Meanwhile, the above photocurrent order was in good agreement with the result of the photocatalytic activity. The results indicated that there existed good energy band matching in the formation of Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunctions, due to highly efficient electron–hole separation at the interface.
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was employed to signify the transfer and migration processes of the photo-excited electron–hole pairs in the photodegradation process. Based on previous studies,45,46 the corresponding radius of the arc reflects the interfacial layer resistance at the electrode surface, and a smaller arc radius indicates higher efficiency in charge transfer. Under the same light irradiation conditions (Fig. 11C), the diameter of the arc radius of the Ag2O/BiVO4 composites was much smaller than that of pure BiVO4. In particular, for Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10), the smallest arc radius was acquired, indicating the highest separation of photogenerated carriers over Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10), the smallest arc radius was acquired, indicating the highest separation of photogenerated carriers over Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10). Moreover, the EIS measurements of Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10). Moreover, the EIS measurements of Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) which were either under light irradiation or dark conditions were also investigated for the produced photogenerated carriers. As displayed in Fig. 11D, a smaller arc radius was achieved for Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) which were either under light irradiation or dark conditions were also investigated for the produced photogenerated carriers. As displayed in Fig. 11D, a smaller arc radius was achieved for Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) under light irradiation, which further verifies the more efficient generation of photogenerated carriers over Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) under light irradiation, which further verifies the more efficient generation of photogenerated carriers over Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10). In all, the formed p–n heterojunction facilitated migration of charge carriers among the constructed Ag2O/BiVO4 systems.
10). In all, the formed p–n heterojunction facilitated migration of charge carriers among the constructed Ag2O/BiVO4 systems.
Based on the above results and analysis, the possible mechanism, energy bands and charge separation of the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterostructures are proposed as illustrated in Scheme 3. Both BiVO4 and Ag2O could be excited under visible light illumination and produced photogenerated electrons and holes. Since the conduction band (CB) position of Ag2O was lower than that of BiVO4, the photogenerated electrons on the CB of Ag2O could directly transfer to the CB of BiVO4. Consequently, the accumulated electrons in the CB of BiVO4 could capture the dissolved O2 and induce it to form ˙O2−. Subsequently, dye molecules can be degraded by an oxidation reaction with the formed ˙O2− on the catalyst surface. Meanwhile, the corresponding valence band (VB) position of BiVO4 is more negative than that of Ag2O, and the photogenerated holes on the VB of BiVO4 could spontaneously migrate to the VB of Ag2O.14,25 The holes on the VB of Ag2O could directly degrade the organic compounds under visible light irradiation. The photo-excited electrons were mainly collected by BiVO4 and holes were accumulated by Ag2O, which were finally consumed by the photo-oxidation process. Unlike the conventional mechanism for a two-phase heterojunction under visible light irradiation, the generated metallic Ag immediately constructed a cross-linking bridge for two semiconductors,27 thus a novel Z-scheme heterostructured photocatalyst Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4 was constructed. Similar results have also been confirmed by previous reports, where a Z-scheme system could be generated in Ag compound-based photocatalysts.47 For instance, He et al. discovered that a small amount of metallic Ag could be formed under visible light irradiation and a Z-scheme mechanism would work in the Ag3PO4/g-C3N4 hybrid due to their matching band gaps and positions of Ag3PO4 and g-C3N4.48 The recombination of electrons from BiVO4 and holes from the VB of Ag2O on the Ag surface may strongly increase the electron–hole lifetime in each material. This could bring about the activation of two substrates towards electron-rich and electron-deficient intermediates, respectively, therefore the recombination process of electron–hole pairs could be hampered leading to effective charge separation. The high reducing electrons located on the CB bottom of Ag2O will react with molecular oxygen to form ˙O2− that could further oxidize dyes. Simultaneously, the holes situated in the VB of BiVO4 will photocatalytically oxidize dyes directly due to a high positive potential of the EVB of BiVO4. The holes could also oxidize water molecules to form ˙OH active species (E0 for ˙OH/OH− = 2.38 eV vs. NHE). But the slight amount of the formation of ˙OH active species only participated in the photocatalytic degradation of dyes. The well-matched overlapping band structures and closely contacting interfaces between BiVO4 and Ag2O as well as the high-speed separation of the photogenerated electron–hole pairs across the interconnection of the constructed Z-scheme heterojunction were of utmost importance for the enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation.
 |
| | Scheme 3 A schematic illustration of the photocatalytic mechanism of dye degradation over Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4 composite photocatalysts under visible light irradiation. | |
The primary reactive species of Ag2O/BiVO4 could be summarized as follows:
| | |
Ag2O + hv → Ag2O (h+) + Ag2O (e−)
| (5) |
| | |
BiVO4 + hv → BiVO4 (h+) + BiVO4 (e−)
| (6) |
| | |
Ag2O (e−) + BiVO4 → Ag2O + BiVO4 (e−)
| (7) |
| | |
BiVO4 (h+) + Ag2O → BiVO4 + Ag2O (h+)
| (8) |
| | |
BiVO4 (e−) + O2 → BiVO4 + ˙O2−
| (9) |
| | |
˙O2− + organic pollutant → CO2 + H2O
| (10) |
| | |
h+ + organic pollutant → CO2 + H2O
| (11) |
The major reactions for when metallic Ag is produced in the photocatalytic process are listed as below:
| | |
Ag2O + hv → Ag2O (h+) + Ag2O (e−)
| (12) |
| | |
BiVO4 + hv → BiVO4 (h+) + BiVO4 (e−)
| (13) |
| | |
BiVO4 (e−) + Ag → Ag (e−) + BiVO4
| (14) |
| | |
Ag2O (h+) + Ag → Ag (h+) + Ag2O
| (15) |
| | |
Ag2O (e−) + O2 → ˙O2− + Ag2O
| (17) |
| | |
˙O2− + h+ + organic pollutant → CO2 + H2O
| (18) |
4. Conclusions
In summary, Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4 heterostructures were prepared using a facile pH-mediated chemical precipitation method along with a self-built Z-scheme under visible light. The as-synthesized samples exhibited much superior photocatalytic activities compared to pure Ag2O and BiVO4 in the degradation of single organic dye (RhB or MB) and multi-component organic dyes (RhB + MB). The optimum weight ratio of Ag2O in the Ag2O/BiVO4 composite was found to be 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 under identical experimental conditions. The effect of initial dye concentration, calcination temperature, and initial pH on the photodegradation of dye TOC removal was investigated in detail. Both the single and mixed dye degradation matched well with first-order kinetics reactions. The p–n 3D acicular sheaf-shaped heterojunction combined with the Ag–Ag2O self-stability structure ensured the excellent photocatalytic activity, mineralization ability and high stability. The superior photoelectric properties of the Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4 heterostructures ensured a promising application in energy conservation. A Z-scheme charge transfer mechanism in the constructed heterojunction was presumed and interpreted in detail. This work may provide a research strategy to design more heterojunction photocatalysts in the visible light degradation of dye wastewater, with further extension to multiple contaminant treatment.
10 under identical experimental conditions. The effect of initial dye concentration, calcination temperature, and initial pH on the photodegradation of dye TOC removal was investigated in detail. Both the single and mixed dye degradation matched well with first-order kinetics reactions. The p–n 3D acicular sheaf-shaped heterojunction combined with the Ag–Ag2O self-stability structure ensured the excellent photocatalytic activity, mineralization ability and high stability. The superior photoelectric properties of the Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4 heterostructures ensured a promising application in energy conservation. A Z-scheme charge transfer mechanism in the constructed heterojunction was presumed and interpreted in detail. This work may provide a research strategy to design more heterojunction photocatalysts in the visible light degradation of dye wastewater, with further extension to multiple contaminant treatment.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No. 51278175, 51378188, 51478170) and Doctoral Fund of Ministry of Education of China (20130161120021).
References
- A. A. Ahmad, B. H. Hameed and N. Aziz, Adsorption of direct dye on palm ash: Kinetic and equilibrium modeling, J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, 141, 70–76 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. C. Hsiao, T. F. Wu, Y. S. Wang, C. C. Hu and C. Huang, Evaluating the sensitizing effect on the photocatalytic decoloration of dyes using anatase-TiO2, Appl. Catal., B, 2014, 148, 250–257 CrossRef.
- B. O. O’Regan and M. Gratzel, A Low-cost, High-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films, Nature, 1991, 353, 737–740 CrossRef.
- X. Chen and S. S. Mao, Titanium Dioxide Nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications, Chem. Rev., 2007, 107, 2891–2959 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Tong, S. Ouyang, Y. Bi, N. Umezawa, M. Oshikiri and J. Ye, Nano-photocatalytic materials: possibilities and challenges, Adv. Mater., 2012, 24, 229–251 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Kudo and Y. Miseki, Heterogeneous photocatalyst materials for water splitting, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38, 253–278 RSC.
- Y. Y. Bu and Z. Y. Chen, Role of polyaniline on the photocatalytic degradation and stability performance of the polyaniline/silver/silver phosphate composite under visible light, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6, 17589–17598 Search PubMed.
- V. Vaiano, O. Sacco, D. Sannino and P. Ciambelli, Nanostructured N-doped TiO2 coated on glass spheres for the photocatalytic removal of organic dyes under UV or visible light irradiation, Appl. Catal., B, 2015, 170–171, 153–161 CrossRef CAS.
- M. S. A. S. Shah, A. R. Park, K. Zhang, J. H. Park and P. J. Yoo, Green synthesis of biphasic TiO2-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites with highly enhanced photocatalytic activity, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2012, 4, 3893–3901 Search PubMed.
- M. R. Elahifard, S. Rahimnejad, S. Haghighi and M. R. Gholami, Apatite-coated Ag/AgBr/TiO2 visible-light photocatalyst for destruction of bacteria, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 9552–9553 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Hu, X. X. Hu, L. S. Wang, J. H. Qu and A. M. Wang, Visible-light-induced photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous AgI/TiO2 dispersion, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2006, 40, 7903–7907 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Wan and G. K. Zhang, Synthesis and facet-dependent enhanced photocatalytic activity of Bi2SiO5/AgI nanoplate photocatalysts, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3, 16737–16745 RSC.
- Z. M. Yang, G. F. Huang and W. Q. Huang, Novel Ag3PO4/CeO2 composite with high efficiency and stability for photocatalytic applications, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 1750–1756 RSC.
- N. C. Castillo, A. Heel, T. Graule and C. Pulgarin, Flame-assisted synthesis of nanoscale, amorphous and crystalline, spherical BiVO4 with visible-light photocatalytic activity, Appl. Catal., B, 2010, 95, 335–347 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Wang, C. J. Li, J. Y. Ji, Y. J. Wei, P. Zhang, S. P. Wang, X. B. Fan and J. L. Gong, reduced graphene oxide (rGO)/BiVO4 composites with maximized interfacial coupling for visible light photocatalysis, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2014, 2, 2253–2258 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Y. Dong, J. L. Feng, Y. K. Li, L. M. Hu, M. L. Liu and Y. F. Wang, Shape-controlled synthesis of BiVO4 hierarchical structures with unique natural-sunlight-driven photocatalytic activity, Appl. Catal., B, 2014, 152–153, 413–424 CrossRef CAS.
- K. M. Ji, J. G. Deng, H. J. Zang, J. H. Han, H. Arandiyan and H. X. Dai, Fabrication and high photocatalytic performance of noble metal nanoparticles supported on 3DOM InVO4-BiVO4 for the visible-light-driven degradation of rhodamine B and methylene blue, Appl. Catal., B, 2015, 165, 285–295 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Yuan, L. Chen, M. Xiong, J. He, S. L. Luo and C. T. Au, Shuang-Feng Yin, Cu2O/BiVO4 heterostructures: synthesis and application in simultaneous photocatalytic oxidation of organic dyes and reduction of Cr(VI) under visible light, Chem. Eng. J., 2014, 255, 394–402 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Hu, D. Z. Li, Y. Zheng, W. Chen, Y. H. He, Y. Shao, X. Z. Fu and G. C. Xiao, BiVO4/TiO2 nanocrystalline heterostructure: A wide spectrum responsive photocatalyst towards the highly efficient decomposition of gaseous benzene, Appl. Catal., B, 2011, 104, 30–36 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Q. He, Y. Q. Shi, C. Gao, L. N. Wen, J. M. Chen and S. Song, BiOCl/BiVO4 p–n heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible-light irradiation, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118, 389–398 CrossRef CAS.
- X. H. Gao, H. B. Wu, L. X. Zheng, Y. J. Zhong, Y. Hu and X. W. Lou, Formation of mesoporous heterostructured BiVO4/Bi2S3 hollow giscoids with enhanced photoactivity, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 5917–5921 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. X. Hu, C. Hu and R. Wang, Enhanced solar photodegradation of toxic pollutants by long-lived electrons in Ag-Ag2O nanocomposites, Appl. Catal., B, 2015, 176–177, 637–645 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Sarkar, C. K. Ghosh, S. Mukherjee and K. K. Chattopadhyay, Three dimensional Ag2O/TiO2 type-II (p–n) nanoheterojunctions for superior photocatalytic activity, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5, 331–337 Search PubMed.
- H. D. Li, Y. H. Sang, S. J. Chang, X. Huang, Y. Zhang, R. S. Yang, H. D. Jiang, H. Liu and Z. L. Wang, Enhanced ferroelectric-nanocrystal-based hybrid photocatalysis by ultrasonic-wave-generated piezophototronic effect, Nano Lett., 2015, 15, 2372–2379 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. G. Yu, R. Liu, X. F. Wang, P. P. Wang and J. G. Yu, Enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity of Bi2WO6 nanoparticles by Ag2O cocatalyst, Appl. Catal., B, 2012, 111–112, 326–333 CrossRef CAS.
- C. B. Liu, C. H. Cao, X. B. Luo and S. L. Luo, Ag-bridged Ag2O nanowire network/TiO2 nanotube array p–n heterojunction as a highly efficient and stable visible light photocatalyst., J. Hazard. Mater., 2015, 285, 319–324 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Xu, L. Han and S. J. Dong, Facile fabrication of highly efficient g-C3N4/Ag2O heterostructured photocatalysts with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5, 12533–12540 Search PubMed.
- E. Aguilera-Ruiz, U. M. García-Pérez and M. de la Garza-Galván, Efficiency of Cu2O/BiVO4 particles prepared with a new soft procedure on the degradation of dyes under visible-light irradiation, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 328, 361–367 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Martínez-de la Cruz and U. G. Pérez, Photocatalytic properties of BiVO4 prepared by the co-precipitation method: degradation of rhodamine B and possible reaction mechanisms under visible irradiation, Mater. Res. Bull., 2010, 45(2), 135–141 CrossRef.
- S. Kumar, T. Surendar, A. Baruah and V. Shanker, Synthesis of a novel and stable g-C3N4-Ag3PO4 hybrid nanocomposite photocatalyst and study of the photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1, 5333–5340 RSC.
- S. Y. Dong, Y. R. Cui, Y. F. Wang, Y. K. Li, L. M. Hu, J. Y. Sun and J. H. Sun, Designing three-dimensional acicular sheaf shaped BiVO4/reduced graphene oxide composites for efficient sunlight-driven photocatalytic degradation of dye wastewater, Chem. Eng. J., 2014, 249, 102–110 CrossRef CAS.
- C. D. Lv, G. Chen, J. X. Sun, Y. S. Zhou, S. Fan and C. M. Zhang, Realizing nanosized interfacial contact via constructing BiVO4/Bi4V2O11 element-copied heterojunction nanofibres for superior photocatalytic properties, Appl. Catal., B, 2015, 179, 54–60 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Y. Li, Y. J. Sun, B. Cai, S. Y. Gan, D. X. Han, L. Niu and T. S. Wu, Hierarchically Z-scheme photocatalyst of Ag@AgCl decorated on BiVO4 (040) with enhancing photoelectrochemical and photocatalytic performance, Appl. Catal., B, 2015, 170–171, 206–214 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Pelaez, N. T. Nolan, S. C. Pillai, M. K. Seery, P. Falaras, A. G. Kontos, P. S. M. Dunlop, J. W. J. Hamilton, J. A. Byrne, K. O’Shea, M. H. Entezari and D. D. Dionysiou, A review on the visible light active titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental applications, Appl. Catal., B, 2012, 125, 331–349 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Rezaei and A. Habibi-Yangjeh, Simple and large scale refluxing method for preparation of Ce-doped ZnO nanostructures as highly efficient photocatalyst, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 265, 591–596 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Wang, X. Z. Yuan, Y. Wu, G. M. Zeng, X. H. Chen, L. J. Leng and H. Li, Synthesis and applications of novel graphitic carbon nitride/metal-organic frameworks mesoporous photocatalyst for dyes removal, Appl. Catal., B, 2015, 174, 445–454 CrossRef.
- M. A. M. Salleh, D. K. Mahmoud, W. A. W. A. Karim and A. Idris, Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: a comprehensive review, Desalination, 2011, 280, 1–13 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Chen, S. F. Yin, S. L. Luo, R. Huang, Q. Zhang, T. Hong and C. T. Au, Bi2O2CO3/BiOI photocatalysts with heterojunctions highly efficient for visible-light treatment of dye-containing wastewater, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2012, 51, 6760–6768 CrossRef CAS.
- K. M. Ji, J. G. Deng, H. J. Zang, J. H. Han, H. Arandiyan and H. X. Dai, Fabrication and high photocatalytic performance of noble metal nanoparticles supported on 3DOM InVO4-BiVO4 for the visible-light-driven degradation of rhodamine B and methylene blue, Appl. Catal., B, 2015, 165, 285–295 CrossRef CAS.
- X. X. Yao and X. H. Liu, One-pot synthesis of Ag/AgCl@SiO2 core-shell plasmonic photocatalyst in natural geothermal water for efficient photocatalysis under visible light, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2014, 393, 30–38 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Chen, Q. Yang, C. G. Niu, X. M. Li and C. Zhang, Enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity and mechanism of ZSH nanocubes modified with AgI nanoparticles, Catal. Commun., 2016, 73, 1–6 CrossRef CAS.
- L. H. Yu, W. Chen, D. Z. Li, J. B. Wang, Y. Shao, M. He, P. Wang and X. Z. Zheng, Inhibition of photocorrosion and photoactivity enhancement for ZnO via specific hollow ZnO core/ZnS shell structure, Appl. Catal., B, 2015, 164, 453–461 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Chen, Q. Yang, C. G. Niu, X. M. Li, C. Zhang and G. M. Zeng, Plasmonic photocatalyst Ag@AgCl/ZSH: Synthesis, characterization and enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activities in the decomposition of dyes and phenol, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 63152–63164 RSC.
- Y. M. He, L. H. Zhang, B. T. Teng and M. H. Fan, New Application of Z-Scheme Ag3PO4/g-C3N4 Composite in Converting CO2 to Fuel, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49, 649–656 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. J. Bai, L. Wang and Y. F. Zhu, Visible photocatalytic activity enhancement of ZnWO4 by graphene hybridization, ACS Catal., 2012, 2, 2769–2778 CrossRef CAS.
- C. S. Pan, D. Li, X. G. Ma, Y. Chen and Y. F. Zhu, Effects of distortion of PO4 tetrahedron on the photocatalytic performancesof BiPO4, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2011, 1, 1399–2140 Search PubMed.
- Z. H. Chen, W. L. Wang, Z. G. Zhang and X. L. Fang, High-efficiency visible-light-driven Ag3PO4/AgI photocatalysts: Z-Scheme photocatalytic mechanism for their enhanced photocatalytic activity, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117, 19346–19352 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. M. He, L. H. Zhang, B. T. Teng and M. H. Fan, New application of Z-Scheme Ag3PO4/g-C3N4 composite in converting CO2 to fuel, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49, 649–656 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
|
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |
Click here to see how this site uses Cookies. View our privacy policy here. ![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 mass ratio of 1
BiVO4 mass ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 exhibited the highest degradation efficiency for dye. Experimental results indicated that single RhB or MB could be degraded completely within a short irradiation time (15 min for 10 mg L−1 RhB, 48 min for 20 mg L−1 MB), but there was obviously competition with the active species, resulting in a decrease of the degradation rate for both dyes. Regardless of the suppression effect, a relatively higher photocatalytic performance was also achieved for the dye mixture. Several parameters, including initial dye concentration, calcination temperature, initial pH and mineralization ability are discussed in detail. The kinetics study suggested that photocatalytic degradation processes for single or complex dye were well described by first-order kinetics. Due to the generated Ag–Ag2O self-stability structure, these acicular sheaf-like three-dimensional heterojunction photocatalysts were fairly stable and there was no obvious loss of photocatalytic activity after four consecutive cycles.
10 exhibited the highest degradation efficiency for dye. Experimental results indicated that single RhB or MB could be degraded completely within a short irradiation time (15 min for 10 mg L−1 RhB, 48 min for 20 mg L−1 MB), but there was obviously competition with the active species, resulting in a decrease of the degradation rate for both dyes. Regardless of the suppression effect, a relatively higher photocatalytic performance was also achieved for the dye mixture. Several parameters, including initial dye concentration, calcination temperature, initial pH and mineralization ability are discussed in detail. The kinetics study suggested that photocatalytic degradation processes for single or complex dye were well described by first-order kinetics. Due to the generated Ag–Ag2O self-stability structure, these acicular sheaf-like three-dimensional heterojunction photocatalysts were fairly stable and there was no obvious loss of photocatalytic activity after four consecutive cycles.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3), and the formed solution was named as solution A. Simultaneously, 2 mmol NH4VO3 was dispersed in a 20 mL ammonia solution (v(NH3·H2O)/v(H2O) = 3
3), and the formed solution was named as solution A. Simultaneously, 2 mmol NH4VO3 was dispersed in a 20 mL ammonia solution (v(NH3·H2O)/v(H2O) = 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), and the solution was marked as solution B. After constant stirring for 20 min, solution B was added into solution A drop by drop and the pH was adjusted to 7.0 by NH3·H2O. Afterwards the obtained mixture was aged at 80 °C for 3 h under water bath conditions. After naturally cooling down, the yellow precipitate was collected by filtering and washing with deionized water and ethanol several times to remove the residual ions and surfactants in the products. At last, the products were dried at 80 °C in air for 8 h.
1), and the solution was marked as solution B. After constant stirring for 20 min, solution B was added into solution A drop by drop and the pH was adjusted to 7.0 by NH3·H2O. Afterwards the obtained mixture was aged at 80 °C for 3 h under water bath conditions. After naturally cooling down, the yellow precipitate was collected by filtering and washing with deionized water and ethanol several times to remove the residual ions and surfactants in the products. At last, the products were dried at 80 °C in air for 8 h.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, 1
1, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5, 1
5, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 and 1
10 and 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20. Then NaOH (1 M) aqueous solution was adopted to adjust the pH of the suspensions to be about 12.5, and the dispersion was continuously stirred for 2 h at room temperature. Finally, the obtained dark brown Ag2O/BiVO4 was thoroughly washed with deionized water three times and dried at 60 °C for 8 h. The series of samples was labelled as Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
20. Then NaOH (1 M) aqueous solution was adopted to adjust the pH of the suspensions to be about 12.5, and the dispersion was continuously stirred for 2 h at room temperature. Finally, the obtained dark brown Ag2O/BiVO4 was thoroughly washed with deionized water three times and dried at 60 °C for 8 h. The series of samples was labelled as Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
1), Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5), Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
5), Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10), and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10), and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20), respectively. As a reference, pure Ag2O nanoparticles were synthesized from AgNO3 and NaOH aqueous solution by the above-mentioned precipitation method without adding BiVO4. Furthermore, the prepared samples were calcined at 60 °C, 100 °C, 200 °C and 300 °C for 1 h with a heating rate of 2 °C min−1, and named as 60 °C/1 h, 100 °C/1 h, 200 °C/1 h and 300 °C/1 h. A brief description of the preparation process is illustrated in Scheme 2.
20), respectively. As a reference, pure Ag2O nanoparticles were synthesized from AgNO3 and NaOH aqueous solution by the above-mentioned precipitation method without adding BiVO4. Furthermore, the prepared samples were calcined at 60 °C, 100 °C, 200 °C and 300 °C for 1 h with a heating rate of 2 °C min−1, and named as 60 °C/1 h, 100 °C/1 h, 200 °C/1 h and 300 °C/1 h. A brief description of the preparation process is illustrated in Scheme 2.

![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) composite is given in Fig. 1B; the crystal structure of the catalyst remained unchanged, and only a small peak of metallic Ag was discovered in the used samples. The XRD pattern of the first cycle was similar to that of the fourth cycle, confirming the stable construction of a Ag–Ag2O bridge in the composite and leading to a stable Z-scheme photocatalyst Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4.
10) composite is given in Fig. 1B; the crystal structure of the catalyst remained unchanged, and only a small peak of metallic Ag was discovered in the used samples. The XRD pattern of the first cycle was similar to that of the fourth cycle, confirming the stable construction of a Ag–Ag2O bridge in the composite and leading to a stable Z-scheme photocatalyst Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) (Fig. 3B, D and E). As depicted in Fig. 3A–D, BiVO4 should be responsible for the emergence of a sheaf-like structure, and a large amount of small nanoparticles on the surface of the Ag2O/BiVO4 composite should be Ag2O. Fig. 3F is a representative HRTEM image of Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) (Fig. 3B, D and E). As depicted in Fig. 3A–D, BiVO4 should be responsible for the emergence of a sheaf-like structure, and a large amount of small nanoparticles on the surface of the Ag2O/BiVO4 composite should be Ag2O. Fig. 3F is a representative HRTEM image of Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10); the clear lattice fringes present are indicative of high crystallinity. The interplanar spacings of 0.475 nm and 0.309 nm are clearly observed, which should correspond to the (110) and (121) crystallographic planes of BiVO4 (JCPDS File No. 14-0688). The d-spacing measured to be 0.272 nm was in good consistency with the lattice spacing (111) of cubic Ag2O (JCPDS File No. 41-1104).
10); the clear lattice fringes present are indicative of high crystallinity. The interplanar spacings of 0.475 nm and 0.309 nm are clearly observed, which should correspond to the (110) and (121) crystallographic planes of BiVO4 (JCPDS File No. 14-0688). The d-spacing measured to be 0.272 nm was in good consistency with the lattice spacing (111) of cubic Ag2O (JCPDS File No. 41-1104).

![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) (E and F).
10) (E and F).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10). The co-existence of C, Bi, V and O elements for pure BiVO4 could be observed, while another Ag element was discovered in Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10). The co-existence of C, Bi, V and O elements for pure BiVO4 could be observed, while another Ag element was discovered in Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) without any other impurities. The emergence of C (the peak at 284.57 eV) could be assigned to the adventitious hydrocarbon from the XPS instrument itself.20 The peaks located at 159.44 eV and 164.68 eV belong to Bi 4f7/2 and Bi 4f5/2, respectively (Fig. 4C).32 Two main peaks appearing at the binding energies of 517.02 eV and 524.18 eV correspond to V 2p1/2 and V 2p3/2, respectively (Fig. 4D).33 Typical O 1s spectra of pure BiVO4 and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) without any other impurities. The emergence of C (the peak at 284.57 eV) could be assigned to the adventitious hydrocarbon from the XPS instrument itself.20 The peaks located at 159.44 eV and 164.68 eV belong to Bi 4f7/2 and Bi 4f5/2, respectively (Fig. 4C).32 Two main peaks appearing at the binding energies of 517.02 eV and 524.18 eV correspond to V 2p1/2 and V 2p3/2, respectively (Fig. 4D).33 Typical O 1s spectra of pure BiVO4 and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) exhibit the predominant characteristic peaks at 530.2 eV (Fig. 4E). The peaks at 368.1 eV and 374.1 eV in Ag2O (1
10) exhibit the predominant characteristic peaks at 530.2 eV (Fig. 4E). The peaks at 368.1 eV and 374.1 eV in Ag2O (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) revealed the presence of Ag+, which are homologous to the Ag 3d5/2 and Ag 3d3/2 binding energies (Fig. 4F). This suggests the existence of a Ag2O phase in the composite, which is in good agreement with the XRD and FTIR analysis.
10) revealed the presence of Ag+, which are homologous to the Ag 3d5/2 and Ag 3d3/2 binding energies (Fig. 4F). This suggests the existence of a Ag2O phase in the composite, which is in good agreement with the XRD and FTIR analysis.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10), while for pure BiVO4 only 12.9% of RhB and 7.3% of MB could be degraded within the same irradiation time. However, different weight ratios of Ag2O to BiVO4 showed different degradation rates for RhB and MB, which were in the order of Ag2O
10), while for pure BiVO4 only 12.9% of RhB and 7.3% of MB could be degraded within the same irradiation time. However, different weight ratios of Ag2O to BiVO4 showed different degradation rates for RhB and MB, which were in the order of Ag2O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) > Ag2O
10) > Ag2O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5) > Ag2O > Ag2O
5) > Ag2O > Ag2O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20) > Ag2O
20) > Ag2O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) > BiVO4. So the optimized weight ratio of Ag2O in the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterostructures should be 1
1) > BiVO4. So the optimized weight ratio of Ag2O in the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterostructures should be 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10. These results suggested that a feasible mass ratio of Ag2O in the constructed heterojunction was good for the enhancement of photoactivity. Excess Ag2O deposited on the BiVO4 surface would increase the recombination rate of photogenerated electron–hole pairs, leading to a poorer degradation efficiency. Wan and Zhang also found that excess AgI deposited on the surface of Bi2SiO5 would decrease the photocatalytic activities of Bi2SiO5/AgI nanoplates.12
10. These results suggested that a feasible mass ratio of Ag2O in the constructed heterojunction was good for the enhancement of photoactivity. Excess Ag2O deposited on the BiVO4 surface would increase the recombination rate of photogenerated electron–hole pairs, leading to a poorer degradation efficiency. Wan and Zhang also found that excess AgI deposited on the surface of Bi2SiO5 would decrease the photocatalytic activities of Bi2SiO5/AgI nanoplates.12
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10). As shown in Fig. 6C, the RhB degradation efficiency decreased with the increase of initial dye concentration in the investigated range (10 to 40 mg L−1). When the initial RhB concentration was below 30 mg L−1, the degradation efficiency maintained a high level (over 90%), but observably declined to 42.1% at 40 mg L−1. A similar variation also appeared in the MB photocatalytic degradation process (Fig. 6D). Higher initial pollutant concentrations could affect the light penetration through the solution in the photocatalytic process.34 The reduced light penetration at a high initial concentration solution resulted in less arrival of photons to the catalyst surface. Meanwhile dye molecules and the produced intermediates tended to compete with each other for initial absorption and catalytic sites on the Ag2O/BiVO4 surface. Many studies validated that the dye degradation process was restricted for the formed intermediates during the photocatalytic oxidation process.35,36 So more production of intermediates in the photocatalytic process would in turn aggravate the competitive adsorption on the catalyst surface between the dye compound and intermediates under high dye concentration conditions.
10). As shown in Fig. 6C, the RhB degradation efficiency decreased with the increase of initial dye concentration in the investigated range (10 to 40 mg L−1). When the initial RhB concentration was below 30 mg L−1, the degradation efficiency maintained a high level (over 90%), but observably declined to 42.1% at 40 mg L−1. A similar variation also appeared in the MB photocatalytic degradation process (Fig. 6D). Higher initial pollutant concentrations could affect the light penetration through the solution in the photocatalytic process.34 The reduced light penetration at a high initial concentration solution resulted in less arrival of photons to the catalyst surface. Meanwhile dye molecules and the produced intermediates tended to compete with each other for initial absorption and catalytic sites on the Ag2O/BiVO4 surface. Many studies validated that the dye degradation process was restricted for the formed intermediates during the photocatalytic oxidation process.35,36 So more production of intermediates in the photocatalytic process would in turn aggravate the competitive adsorption on the catalyst surface between the dye compound and intermediates under high dye concentration conditions.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) was investigated and the results are exhibited in Fig. 7A and B. With the calcination temperature increasing from 60 to 200 °C, the photocatalytic activity of the as-prepared Ag2O
10) was investigated and the results are exhibited in Fig. 7A and B. With the calcination temperature increasing from 60 to 200 °C, the photocatalytic activity of the as-prepared Ag2O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) for the decomposition of dye deteriorated. The degradation efficiency of RhB and MB was only 25.8% and 15.2% when the calcination temperature went up to 300 °C. The reason should be attributed to the destruction of the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunction structure. Yu et al. found that Ag2O in Ag2O/Bi2WO6 decomposed to form Ag nanoparticles at a calcination temperature of 450 °C.25 The XRD patterns of Ag2O
10) for the decomposition of dye deteriorated. The degradation efficiency of RhB and MB was only 25.8% and 15.2% when the calcination temperature went up to 300 °C. The reason should be attributed to the destruction of the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunction structure. Yu et al. found that Ag2O in Ag2O/Bi2WO6 decomposed to form Ag nanoparticles at a calcination temperature of 450 °C.25 The XRD patterns of Ag2O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) BiVO4 (1
BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) calcined at 300 °C also demonstrate that almost all of the Ag2O was decomposed and formed metallic Ag (Fig. 1C). Ag-modified BiVO4 exhibited a slightly better photocatalytic performance than that of pure BiVO4, because the electron–hole separation rate was also improved by introducing metallic Ag.25 The excessive Ag0 would lower the photocatalytic activity of Ag2O/BiVO4. In order to maintain the 3D sheaf-like heterojunctions of Ag2O/BiVO4, the calcination temperature should be controlled at a relatively lower level.
10) calcined at 300 °C also demonstrate that almost all of the Ag2O was decomposed and formed metallic Ag (Fig. 1C). Ag-modified BiVO4 exhibited a slightly better photocatalytic performance than that of pure BiVO4, because the electron–hole separation rate was also improved by introducing metallic Ag.25 The excessive Ag0 would lower the photocatalytic activity of Ag2O/BiVO4. In order to maintain the 3D sheaf-like heterojunctions of Ag2O/BiVO4, the calcination temperature should be controlled at a relatively lower level.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10). Compared with single RhB or MB degradation, the degradation efficiencies of a mixture of dyes descended to some extent. As exhibited in Fig. 8A and B, RhB and MB were completely degraded in 20 and 48 min, respectively, while in Fig. 8C and D, we could find that MB achieved a high decomposition rate in both mixed dye solutions and the RhB degradation was significantly hindered, especially at high initial concentrations. As displayed in Fig. 8E, the degradation rate of MB was much faster than that of RhB, which could be explained by the fact that MB possessed better affinity to the catalyst than RhB did, and good absorption resulted in the promotion of dye photodegradation. There is usually a competition mode between two cationic dyes in the photodegradation process of a mixture of dyes, which also was proven in the visible light-driven degradation of RhB and MB catalyzed by InVO4–BiVO4 and its supported noble metal nanoparticles.39 Total organic carbon (TOC) analysis is an efficient way to evaluate the degradation degree of organic dyes, which requires a long irradiation time.40 Fig. 8F presents the TOC removal in single and mixed dye degradation. The TOC removal for single RhB and MB degradation reached 90.2% and 93.2%. However, the corresponding values for mixed dyes obviously decreased and the TOC removal for the RhB (10 mg L−1) + MB (20 mg L−1) solution was only 32.5%, which should be attributed to the high initial dye concentration. The above information suggested that the TOC removal in single dye degradation was more thorough than that in the mixture of dyes. Meanwhile, it could be noticed that although the whole degradation time in RhB (5 mg L−1) + MB (10 mg L−1) solution was longer than that of any single dye, the final TOC removal could reach 88.2% and was desirable. The relatively high TOC removal was acquired in both single and mixed dye degradation, confirming that the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunction possessed a preferable mineralization ability.
10). Compared with single RhB or MB degradation, the degradation efficiencies of a mixture of dyes descended to some extent. As exhibited in Fig. 8A and B, RhB and MB were completely degraded in 20 and 48 min, respectively, while in Fig. 8C and D, we could find that MB achieved a high decomposition rate in both mixed dye solutions and the RhB degradation was significantly hindered, especially at high initial concentrations. As displayed in Fig. 8E, the degradation rate of MB was much faster than that of RhB, which could be explained by the fact that MB possessed better affinity to the catalyst than RhB did, and good absorption resulted in the promotion of dye photodegradation. There is usually a competition mode between two cationic dyes in the photodegradation process of a mixture of dyes, which also was proven in the visible light-driven degradation of RhB and MB catalyzed by InVO4–BiVO4 and its supported noble metal nanoparticles.39 Total organic carbon (TOC) analysis is an efficient way to evaluate the degradation degree of organic dyes, which requires a long irradiation time.40 Fig. 8F presents the TOC removal in single and mixed dye degradation. The TOC removal for single RhB and MB degradation reached 90.2% and 93.2%. However, the corresponding values for mixed dyes obviously decreased and the TOC removal for the RhB (10 mg L−1) + MB (20 mg L−1) solution was only 32.5%, which should be attributed to the high initial dye concentration. The above information suggested that the TOC removal in single dye degradation was more thorough than that in the mixture of dyes. Meanwhile, it could be noticed that although the whole degradation time in RhB (5 mg L−1) + MB (10 mg L−1) solution was longer than that of any single dye, the final TOC removal could reach 88.2% and was desirable. The relatively high TOC removal was acquired in both single and mixed dye degradation, confirming that the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunction possessed a preferable mineralization ability.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) presented the highest photocatalytic activity. The corresponding kapp was 0.5208 and 0.1008 min−1 for RhB and MB degradation, which was 49/2.5 and 72/2.2 times higher than that of pure BiVO4 and Ag2O, respectively. This result demonstrated the advantage of building 3D Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunctions. Furthermore, compared with the single dye degradation, the value of kapp for RhB (or MB) deceased to 0.0222 (0.0684) and 0.0038 (0.0432) min−1 in RhB (5 mg L−1) + MB (10 mg L−1) and RhB (10 mg L−1) + MB (20 mg L−1) solutions. Obviously, RhB degradation was more affected than MB in the mixed dye solution. This phenomenon further revealed that a competitive mode existed in the multi-component dye photodegradation process. The discrepancy in the absorption ability between RhB and MB and the advantages of good absorption served as a promoter for dye degradation.39
10) presented the highest photocatalytic activity. The corresponding kapp was 0.5208 and 0.1008 min−1 for RhB and MB degradation, which was 49/2.5 and 72/2.2 times higher than that of pure BiVO4 and Ag2O, respectively. This result demonstrated the advantage of building 3D Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunctions. Furthermore, compared with the single dye degradation, the value of kapp for RhB (or MB) deceased to 0.0222 (0.0684) and 0.0038 (0.0432) min−1 in RhB (5 mg L−1) + MB (10 mg L−1) and RhB (10 mg L−1) + MB (20 mg L−1) solutions. Obviously, RhB degradation was more affected than MB in the mixed dye solution. This phenomenon further revealed that a competitive mode existed in the multi-component dye photodegradation process. The discrepancy in the absorption ability between RhB and MB and the advantages of good absorption served as a promoter for dye degradation.39

![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5
5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10
10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10a
10a![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10b
10b![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20
20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) was investigated for four consecutive runs under identical experimental conditions. As shown in Fig. 9D–F, after four successive cycles, the photocatalytic activity for both single and mixed organic dye degradation had no obvious loss. The XPS spectra of the fresh and used Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) was investigated for four consecutive runs under identical experimental conditions. As shown in Fig. 9D–F, after four successive cycles, the photocatalytic activity for both single and mixed organic dye degradation had no obvious loss. The XPS spectra of the fresh and used Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) (Fig. 10A and B) reveal that there were two peaks at 374.1 eV and 368.1 eV, which belonged to Ag+ in the composite. Another two peaks appeared at 373.2 eV and 367.3 eV which could be attributed to metallic Ag (Ag0 (ref. 10 and 33)), which is in accordance with the description in the XRD analysis. The used samples for the first and fourth cycle presented a similar structure and intensity in their XRD patterns, confirming the desirable stability of the as-prepared Z-scheme photocatalyst. The above-mentioned information indicates the excellent reusability performance longevity of Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4 under visible light irradiation, which makes it a promising candidate in practical composite wastewater treatment.
10) (Fig. 10A and B) reveal that there were two peaks at 374.1 eV and 368.1 eV, which belonged to Ag+ in the composite. Another two peaks appeared at 373.2 eV and 367.3 eV which could be attributed to metallic Ag (Ag0 (ref. 10 and 33)), which is in accordance with the description in the XRD analysis. The used samples for the first and fourth cycle presented a similar structure and intensity in their XRD patterns, confirming the desirable stability of the as-prepared Z-scheme photocatalyst. The above-mentioned information indicates the excellent reusability performance longevity of Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4 under visible light irradiation, which makes it a promising candidate in practical composite wastewater treatment.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) are clearly revealed in Fig. 11A. From Fig. 11A, the PL intensity of the Ag2O/BiVO4 composites is significantly reduced as compared to that of pure BiVO4, implying a lower recombination feasibility of free charges in the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterostructures. Moreover, the lower PL intensity achieved by the fresh Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
1) are clearly revealed in Fig. 11A. From Fig. 11A, the PL intensity of the Ag2O/BiVO4 composites is significantly reduced as compared to that of pure BiVO4, implying a lower recombination feasibility of free charges in the Ag2O/BiVO4 heterostructures. Moreover, the lower PL intensity achieved by the fresh Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) composite suggested that photo-induced electron–hole recombination processes were truly hindered. Notably, the used Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) composite suggested that photo-induced electron–hole recombination processes were truly hindered. Notably, the used Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) (self-built Z-scheme photocatalyst Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4) exhibited the lowest recombination probability of electron–hole pairs, which could be assigned to the formed metallic Ag, further indicating that a Z-scheme system was constructed under visible light.
10) (self-built Z-scheme photocatalyst Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4) exhibited the lowest recombination probability of electron–hole pairs, which could be assigned to the formed metallic Ag, further indicating that a Z-scheme system was constructed under visible light.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1).
1).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) composite on the separation efficiency of electron–hole pairs was investigated by photocurrent–time (PT) experiments, as demonstrated in Fig. 11B. The transient photocurrent responses of pure BiVO4, Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) composite on the separation efficiency of electron–hole pairs was investigated by photocurrent–time (PT) experiments, as demonstrated in Fig. 11B. The transient photocurrent responses of pure BiVO4, Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) and Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) were recorded for several on–off cycles under visible light irradiation. For pure BiVO4, a small amount of photocurrent was generated while for Ag2O/BiVO4 composites, a significantly enhanced photocurrent intensity was detected. Especially, Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
1) were recorded for several on–off cycles under visible light irradiation. For pure BiVO4, a small amount of photocurrent was generated while for Ag2O/BiVO4 composites, a significantly enhanced photocurrent intensity was detected. Especially, Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) possessed the highest current intensity, suggesting more efficient separation of the photogenerated electron–hole pairs over Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) possessed the highest current intensity, suggesting more efficient separation of the photogenerated electron–hole pairs over Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10). Meanwhile, the above photocurrent order was in good agreement with the result of the photocatalytic activity. The results indicated that there existed good energy band matching in the formation of Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunctions, due to highly efficient electron–hole separation at the interface.
10). Meanwhile, the above photocurrent order was in good agreement with the result of the photocatalytic activity. The results indicated that there existed good energy band matching in the formation of Ag2O/BiVO4 heterojunctions, due to highly efficient electron–hole separation at the interface.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10), the smallest arc radius was acquired, indicating the highest separation of photogenerated carriers over Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10), the smallest arc radius was acquired, indicating the highest separation of photogenerated carriers over Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10). Moreover, the EIS measurements of Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10). Moreover, the EIS measurements of Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) which were either under light irradiation or dark conditions were also investigated for the produced photogenerated carriers. As displayed in Fig. 11D, a smaller arc radius was achieved for Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) which were either under light irradiation or dark conditions were also investigated for the produced photogenerated carriers. As displayed in Fig. 11D, a smaller arc radius was achieved for Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) under light irradiation, which further verifies the more efficient generation of photogenerated carriers over Ag2O/BiVO4 (1
10) under light irradiation, which further verifies the more efficient generation of photogenerated carriers over Ag2O/BiVO4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10). In all, the formed p–n heterojunction facilitated migration of charge carriers among the constructed Ag2O/BiVO4 systems.
10). In all, the formed p–n heterojunction facilitated migration of charge carriers among the constructed Ag2O/BiVO4 systems.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 under identical experimental conditions. The effect of initial dye concentration, calcination temperature, and initial pH on the photodegradation of dye TOC removal was investigated in detail. Both the single and mixed dye degradation matched well with first-order kinetics reactions. The p–n 3D acicular sheaf-shaped heterojunction combined with the Ag–Ag2O self-stability structure ensured the excellent photocatalytic activity, mineralization ability and high stability. The superior photoelectric properties of the Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4 heterostructures ensured a promising application in energy conservation. A Z-scheme charge transfer mechanism in the constructed heterojunction was presumed and interpreted in detail. This work may provide a research strategy to design more heterojunction photocatalysts in the visible light degradation of dye wastewater, with further extension to multiple contaminant treatment.
10 under identical experimental conditions. The effect of initial dye concentration, calcination temperature, and initial pH on the photodegradation of dye TOC removal was investigated in detail. Both the single and mixed dye degradation matched well with first-order kinetics reactions. The p–n 3D acicular sheaf-shaped heterojunction combined with the Ag–Ag2O self-stability structure ensured the excellent photocatalytic activity, mineralization ability and high stability. The superior photoelectric properties of the Ag2O@Ag@BiVO4 heterostructures ensured a promising application in energy conservation. A Z-scheme charge transfer mechanism in the constructed heterojunction was presumed and interpreted in detail. This work may provide a research strategy to design more heterojunction photocatalysts in the visible light degradation of dye wastewater, with further extension to multiple contaminant treatment.









