Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Identification of “sarsasapogenin-aglyconed” timosaponins as novel Aβ-lowering modulators of amyloid precursor protein processing†
Lai-King
Sy
a,
Chun-Nam
Lok
a,
Juan-Yu
Wang
a,
Yungen
Liu
a,
Lu
Cheng
a,
Pui-Ki
Wan
a,
Chi-Ting
Leung
a,
Bei
Cao
a,
Wai-Lun
Kwong
a,
Raymond Chuen-Chung
Chang
b and
Chi-Ming
Che
*a
aDepartment of Chemistry, The University of Hong Kong, Chemical Biology Centre, 8/F., The Hong Kong Jockey Club Building for Interdisciplinary Research, 5, Sassoon Road, Pokfulam, Hong Kong, China. E-mail: cmche@hku.hk; Fax: +852-28571586; Tel: +852-28592154
bNeurodegenerative Diseases Laboratory, School of Biomedical Sciences, LKS Faculty of Medicine, Research Centre of Heart, Brain and Hormone, and Healthy Aging, LKS Faculty of Medicine, State Key Laboratory of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, The University of Hong Kong, China
First published on 22nd January 2016
Abstract
The inhibition of amyloid β (Aβ) peptide production is a key approach in the development of therapeutics for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD). We have identified that timosaponins consisting of sarsasapogenin (SSG) as the aglycone can effectively lower the production of Aβ peptides and stimulate neurite outgrowth in neuronal cell cultures. Structure–activity relationship studies revealed that the cis-fused AB ring, 3β-configuration, spiroketal F-ring and 25S-configuration of SSG are the essential structural features responsible for the Aβ-lowering effects and neurite-stimulatory activity. New synthetic derivatives that retain the SSG scaffold also exhibited an Aβ lowering effect. Treatment of cells with timosaponins led to modulation of amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing through the suppression of β-cleavage and preferential lowering of the production of the 42-amino acid Aβ species (Aβ42) without affecting another γ-secretase substrate. The SSG and “SSG-aglyconed” timosaponins also penetrated brain tissue and lowered brain Aβ42 levels in mice. Our studies demonstrate that timosaponins represent a unique class of steroidal saponins that may be useful for the development of AD therapeutics.
Introduction
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder that starts with a decline in short-term memory and progresses to the loss of cognition and executive functions. The pathology of AD is characterized by synaptic loss, neuronal death, frequent deposition of phosphorylated tau proteins and Aβ aggregation within the brain.1 Although the underlying cause of AD is complex, the accumulation of Aβ within the brain appears to play a pivotal role in the onset and progression of the disease.2Aβ is generated from the proteolysis of amyloid precursor protein (APP) during aging or in subjects with an inherited cause of AD.3 APP is a transmembrane protein whose proteolysis is mediated by α-, β- and γ-secretases that cleave APP at specific sites.3 The amyloidogenic process first involves the cleavage of APP to create a c-terminal fragment (CTF), known as β-CTF, which is subsequently cleaved by a multiprotein γ-secretase complex to produce different lengths of Aβ peptides such as Aβ38, Aβ40 and Aβ42. Genetic and mechanistic data strongly suggest that the accumulation of amyloidogenic Aβ42 peptide results in the formation of toxic oligomers and/or fibrils. Accordingly, Aβ42-lowering compounds that target the β- and/or γ-cleavage processes represent a promising strategy for therapeutic intervention in AD.4,5 γ-Secretase inhibitors (GSI) initially emerged as effective Aβ-lowering agents, but the side effects resulting from non-specific inhibition of other vital γ-secretase substrates, such as Notch, have complicated the development of these inhibitors.6 With evidence for the more specific role of Aβ42 in amyloidogenesis, current approaches to AD drug development are focused on γ-secretase modulators (GSM) that preferentially lower Aβ42 without affecting the action of γ-secretase on general APP processing and the cleavage of other substrates.7 Modulation of β-secretase is also considered to be a viable strategy for lowering Aβ production.8 A mutation in APP that hinders β-cleavage and lowers the production of Aβ by 40% was demonstrated to be protective against AD and age-related cognitive decline,9 supporting the idea that a moderate reduction of Aβ in humans is favourable for AD treatment or prevention.
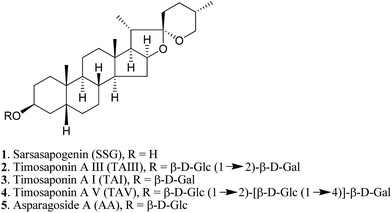
Natural products provide opportunities for the development of anti-AD pharmaceuticals (ESI Table S1†). For example, green tea polyphenols, ginsenosides and resveratrol have all been shown to exhibit promising anti-amyloidogenic effects.10–12 In the course of studying the pharmacological properties of medicinal saponins from natural products, we found that timosaponins consisting of sarsasapogenin (SSG, 1) (Fig. 1) as the aglycone, including timosaponin A III (TAIII, 2) isolated from the rhizome of Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bge. (Liliaceae), could effectively lower Aβ production. We have previously identified TAIII's anti-cancer and autophagy-inducing properties.13,14 Oral administration of SSG, TAIII and other timosaponins were shown to improve memory dysfunction in animal models of dementia15–18 despite the chemical structural differences between these compounds. Total saponins from Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bge. were reported to ameliorate diabetes-associated cognitive decline in rats and mediate Aβ decreases in brain.19 In the present study, we show that SSG (1) and other timosaponins (2–5, Fig. 1) specifically exhibit Aβ-lowering activities and their actions are akin to GSM,7 which preferentially lowers Aβ42 peptide production. We propose a model by which the timosaponins may bind to the steroid binding site of APP,20 possibly modulating the APP secretase properties. Importantly, SSG and several timosaponins showed brain penetration and Aβ42-diminishing activities in vivo.
Results and discussion
Synthesis of timosaponins, SSG analogues and SSG derivatives
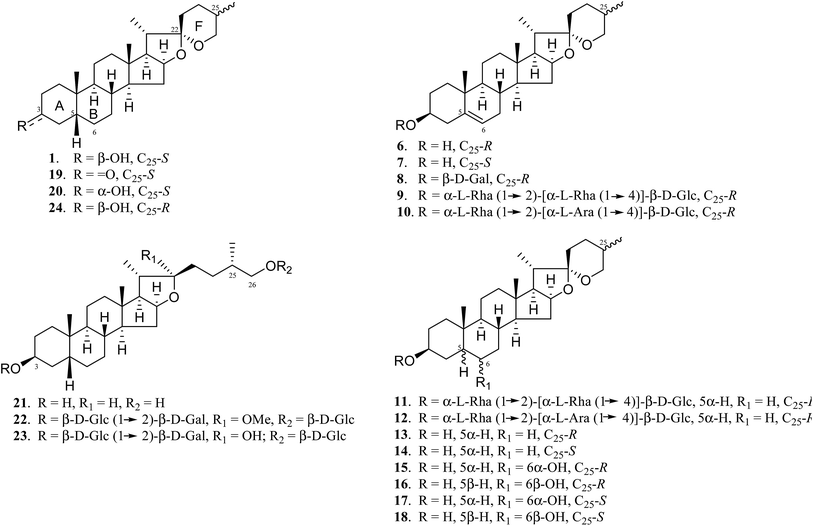
A. asphodeloides is a medicinal herb that is rich in structurally closely related timosaponins whose isolation and purification are exceptionally difficult.17 Chemical synthesis, on the other hand, is a feasible strategy to obtain timosaponins that are of low natural abundance or commercially unavailable. Preparation of steroidal timosaponins (2–5) (Fig. 1) with different sugar lengths was achieved by reacting aglycone 1 with different glycosyl donors (ESI Fig. S1–S3†).The chemical structure of the aglycone SSG (1) is rather unique in naturally-occurring sapogenins due to its structural characteristics, including a cis-fused AB ring (or 5β-configuration), 3β-configuration, spiroketal F-ring and 25S-configuration.21 In this study, a series of SSG analogues (6–24) (Fig. 2) differing in these structural features were employed to study the structure–activity relationship (SAR) in the Aβ-lowering activities. The linkage of AB rings in steroidal sapogenins can be cis-, trans- or Δ5-double bonded. Δ5-Double bonded diosgenin (6) and yamogenin (7) were studied in addition to “diosgenin-aglyconed” saponins, including synthesized capsicoside A3 (8) (ESI Fig. S4†), dioscin (9) and polyphyllin D (10). Hydrogenation of saponins 9 and 10 generated AB ring trans-fused dihydrodioscin (11) and dihydropolyphyllin D (12), respectively (ESI Fig. S5†). Similarly, hydrogenation of 6 and 7 produced AB ring trans-fused tigogenin (13) and neotigogenin (14), respectively (ESI Fig. S6†). Functionalization at Δ5 of 6 or Δ5 of 7 led to production of a pair of isomers for each compound: 5α-H, 6α-OH diosgenin (15), 5β-H, 6β-OH diosgenin (16) and 5α-H, 6α-OH yamogenin (17), 5β-H, 6β-OH yamogenin (18) (ESI Fig. S7†).22 The hydration products 15 and 17 are AB ring trans-fused, while the new compounds 16 and 18 are AB ring cis-fused.
Compound 1 has a secondary β-OH at C3. Oxidation of 1 to sarsasapogenone (19) followed by reduction gave episarsasapogenin (20) (ESI Fig. S8†).23
SSG 1 has heterocyclic rings E and F fixed at C22 in which the F-spiroketal ring appears to be a crucial moiety in bioactive saponins21 (Fig. 2). Reductive cleavage of the F-ring in 1 gave dihydrosarsasapogenin (dSSG, 21) with a terminal OH group24 (ESI Fig. S9†). Timosaponin B I (TBI, 22) and timosaponin B II (TBII, 23) are two examples of “dSSG-aglyconed” saponins with two sugar chains substituted at C3 and C26. The contribution of the C25S-configuration of 1 in decreasing Aβ42 was also investigated by comparing the activity of compound 16 and its epimer, smilagenin (24), both of which have a C25R-configuration.
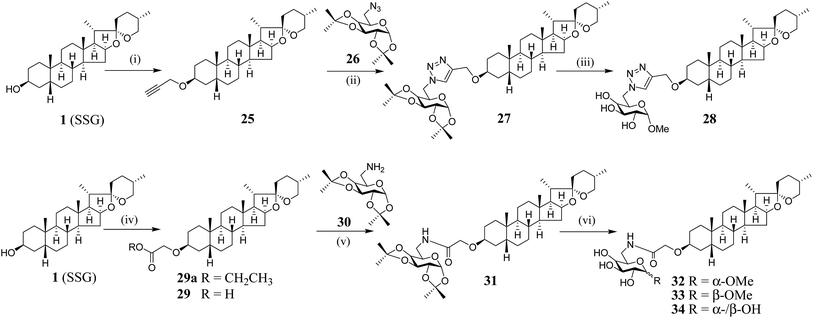
We have synthesized new SSG derivatives (28–29, 32–34) in an attempt to modify the biological activity and/or bioavailability (Fig. 3).25,26 Reaction of 1 with propargyl bromide yielded 25, containing a propargyl group, which can be linked to other moieties or probes via click chemistry. By reacting 25 with acetonide-protected α-galactose azide (26), via Cu(I)-catalysed click chemistry, triazole SSG (27) was obtained. Removing the acetonide protecting groups of 27 yielded α-OMe triazole SSG (28) (ESI Fig. S10†). The relatively harsh reaction conditions (strong base NaH and long reaction time) used in the preparation of 25 was also attempted for the preparation of carboxylate ethereal SSG (29a) by reacting compound 1 with methyl bromoacetate, but without success. Compound 1 was then reacted with diazoacetate, in the presence of Rh2(OAc)4 as a catalyst, to obtain 29a in good yield via carbene insertion under mild conditions. Hydroxylation of the carboxylate 29a in alkaline conditions, followed by neutralization, produced the ethereal SSG (29) (ESI Fig. S11†). The carboxylic acid of 29 serves as a useful linkage for coupling with other moieties under mild conditions. Reaction of 29 with acetonide-protected α-galactose amine (30) gave amide SSG (31). The acetonide protecting groups of 31 were then removed by acid hydrolysis to yield α-OMe SSG (32), β-OMe SSG (33) and a mixture of α- and β-OH SSG (34) (ESI Fig. S12†).
Aβ42-lowering activities
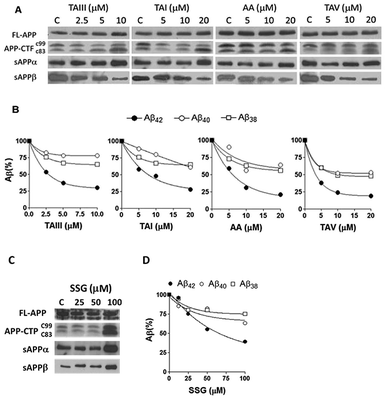
Using Neuro-2A neuroblastoma cells stably transfected with APP with the AD-linked Swedish mutation (N2A-APPswe) as a cell culture model of Aβ production,27 it was found that the SSG 1 treatment modestly decreases Aβ42 production with an IC50 of 53 μM (Table 1). Treatment with timosaponins (2–5) markedly lowered Aβ42 production when compared to the aglycone SSG. SSG analogue 18, in addition to the newly synthesized SSG derivatives 28–29 and 32–34, also showed slight to moderate improvement in Aβ42-lowering activity when compared to 1 (Table 1). In rat primary cortical neuronal cultures, which produce and secrete low levels of Aβ, chronic exposure to compounds 1–3 also resulted in a moderate diminishment of Aβ42 levels in the medium (Table 2).| Compound | IC50 (μM) | Compound | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSG (1) | 53.0 ± 9.0 | 5α-H, 6α-OH yamogenin (17) | >100 |
| TAIII (2) | 2.3 ± 0.2 | 5β-H, 6β-OH yamogenin (18) | 45.0 ± 4.0 |
| TAI (3) | 6.1 ± 2.8 | Sarsasapogenone (19) | 50.0 ± 5.0 |
| TAV (4) | 4.2 ± 1.2 | Episarsasapogenin (20) | >100 |
| AA (5) | 6.0 ± 1.4 | Dihydrosarsasapogenin (21) | >100 |
| Diosgenin (6) | >100 | Timosaponin B I (22) | >100 |
| Yamogenin (7) | >100 | Timosaponin B II (23) | >100 |
| Capsicoside A3 (8) | >100 | Smilagenin (24) | >100 |
| Tigogenin (13) | >100 | α-OMe triazole SSG (28) | 6.5 ± 2.1 |
| Neotigogenin (14) | >100 | Ethereal SSG (29) | 27.0 ± 8.0 |
| 5α-H, 6α-OH diosgenin (15) | >100 | α-OMe SSG (32) | 7.2 ± 2.2 |
| 5β-H, 6β-OH diosgenin (16) | >100 | β-OMe SSG (33) | 9.3 ± 3.5 |
| α-, β-OH SSG (34) | 7.3 ± 4.0 |
| Compound | Aβ42 reduction (%) |
|---|---|
| SSG (1) (5 μM) | 25 ± 4 |
| TAIII (2) (5 μM) | 42 ± 9 |
| TAI (3) (10 μM) | 28 ± 5 |
Structure–activity relationship
Timosaponins 2–4 are galactosyl derived and exhibit prominent Aβ42-level reducing effects. Asparagoside A (AA, 5), a glucosyl-derived timosaponin (Fig. 1), shows a comparable Aβ42-lowering effect (IC50 = ∼6.0 μM) to galactosyl 3 (IC50 = ∼6.1 μM), revealing that the nature of the monosaccharide coupled to aglycone 1 has a negligible effect on Aβ42 levels.
The aforementioned enhancement in lowering Aβ42 production by the sugar chains in timosaponins has not been observed in the steroidal aglycone diosgenin 6 and its galactosyl product 8 (Table 1). Taken together with the insignificant Aβ42-lowering effects exhibited by diosgenyl saponins (data not shown) 9 and 10 (Δ5 double bond) and their corresponding hydrogenated products 11 and 12 (both AB trans-fused rings), it is suggested that aglycone 1 is critical in lowering Aβ42 production. The structural features associated with 1, including the AB-fused ring and the F-ring, were subjected to investigation and the findings are discussed below.
Compound 19, with a ketone functionality at C3, showed a comparable effect to 1 in Aβ42 lowering, while compound 20, with a C3 α-OH, was inactive (Table 1), implying that the 3α-configuration is unfavourable for Aβ42 lowering.
Smilagenin 24 and 6β-OH substituted 16 were ineffective in lowering Aβ42 (Fig. 2 and Table 1). Thus, one may envisage that the 25S-configuration in 1 is one of the vital structural factors contributing to the compound's Aβ-lowering activities.
Collectively, the SSG moiety is essential for Aβ42-lowering activity. Notably, the Aβ42-lowering effect of SSG is significantly enhanced when the compound is glycosylated at C3 to obtain timosaponins 2–5 or carboxylated at C3 to obtain SSG derivatives 28–29 and 32–34 (Fig. 1, 3 and Table 1). It is suggested that chemical modification at the C3 position of 1 is an appealing approach for the generation of versatile SSG derivatives with anti-amyloidogenic effects and thus timosaponins herein represent a class of interesting saponins noteworthy of further investigation related to Aβ42-lowering activities.
Biochemical mechanisms
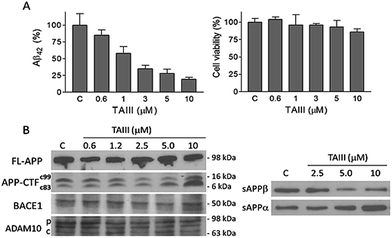
We also studied the effect of SSG on the Aβ production and APP processing (Fig. 5C & D). The Aβ-lowering activity of SSG was weaker than those of timosaponins generally. Treatment of N2A-APPswe cells with SSG at 50 μM and 100 μM for 18 h caused a decrease in Aβ42 by 55% and 40%, respectively. Interestingly, treatment of cells with SSG at 100 μM increased both α-CTF and β-CTF expression with marked increase in the sAPPα levels. There was no change in β-secretase activity in the protein extracts from SSG-treated cells compared to that from untreated cells. Though the mechanism accounting for the difference between timosaponins and SSG in APP processing remains to be elucidated, it was concluded that the sugar moiety appears to play a role in modifying the effects of the timosaponins on APP processing.
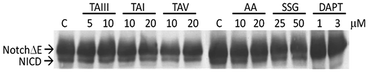
GSM are expected to selectively act on the APP complexes, without inhibiting the cleavage activity of γ-secretase on other physiological substrates.6,7 To further investigate the specificity of the impact of timosaponins on γ-secretase-mediated protein processing, the effects of timosaponins on the γ-secretase-mediated cleavage of the transmembrane receptor Notch1 were examined (Fig. 6). γ-Secretase-catalysed cleavage of Notch releases the Notch intracellular domain (NICD), which regulates developmental gene transcription.32 In cells expressing a Notch1 variant containing transmembrane and intracellular domains (NotchΔE), the NICD is constitutively present due to γ-secretase activity (Fig. 6). Treatment of cells with a γ-secretase inhibitor DAPT completely blocked the production of NICD, while treatment of cells with timosaponins at concentrations that effectively lower Aβ levels did not affect NICD levels. Thus, the timosaponins selectively interfere with Aβ production without altering Notch1 processing.
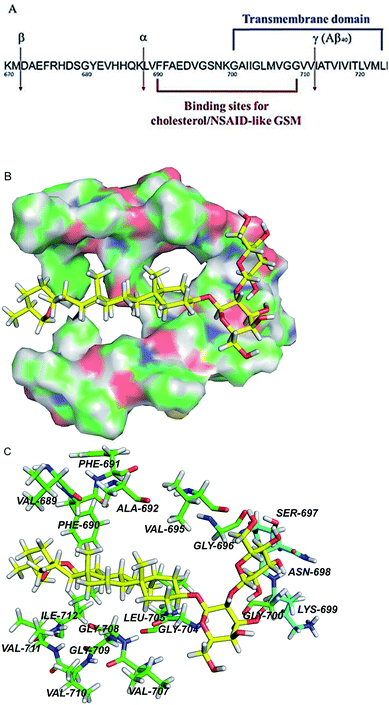 | ||
| Fig. 8 APP transmembrane domain as a potential molecular target of timosaponins. (A) An overview of the portion of APP that is cleaved by α-, β-, and γ-secretases. Also shown are the juxtamembrane and transmembrane regions harbouring binding sites for NASID-like GSM34 and cholesterol.20 Numbering is according to the full length of APP770. (B) QM/MM calculations of TAIII binding to the transmembrane domain of APP. The surface representation of the transmembrane region of APP, showing the calculated binding pose of TAIII. (C) The hydrophobic residues and polar residues around TAIII are portrayed with stick display mode. Carbon atoms of hydrophobic residues are highlighted in green and carbon atoms of polar residues are highlighted in light blue. TAIII is represented by sticks with the carbon atoms in yellow. Colour code: carbon (yellow, green or light blue), nitrogen (dark blue), oxygen (red), and hydrogen (white). | ||
Conclusion
The timosaponins investigated in the current study are preferentially able to lower Aβ42 production and stimulate neurite outgrowth, largely due to the presence of the effective aglycone SSG 1. They contain structural features including a cis-fused AB ring, 3β-configuration and an intact F-spiroketal ring with a 25S-configuration. These characteristics are indispensable structural requirements for the compound's dual properties. The Aβ-lowering activities of “SSG-aglyconed” timosaponins are generally associated with decreases in β-cleavage and/or increases in α-cleavage of APP. These are accompanied by a preferential reduction of Aβ42 levels without affecting the processing of other γ-secretase substrates, resembling the action of GSM. Thus, the “SSG-aglyconed” timosaponins are novel agents that modulate APP processing and subsequently lower Aβ production. We have also shown here that some timosaponins and SSG exhibit Aβ-lowering activities in vivo. It is envisaged that, when properly modified and formulated, timosaponins will be intriguing compounds for the development of AD therapeutics.Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Prof. Yifan Han for providing the N2A-APPswe cells and Prof. Raphael Kopan for the Notch1 plasmid. We thank Mr Chi-Fai Lau and Dr Fuli Liu for technical assistance, as well as Dr Congying Zhou and Dr Jiesheng Huang for editing the manuscript. This study is supported by funding from the Innovative Technology Committee ITF-Tier III project (ITS/149/12), the Hong Kong Jockey Club Charities Trust for the project of R&D Laboratory for Testing of Chinese Medicines, the special equipment grant (SEG HKU02) from the University Grants Committee and Chinese Medicines Information and Research Section of the Department of Health, HKSAR China.Notes and references
- C. Ballard, S. Gauthier, A. Corbett, C. Brayne, D. Aarsland and E. Jones, Lancet, 2011, 377, 1019–1031 CrossRef.
- J. Hardy and D. J. Selkoe, Science, 2002, 297, 353–356 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. J. O'Brien and P. C. Wong, Annu. Rev. Neurosci., 2011, 34, 185–204 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Weggen, J. L. Eriksen, P. Das, S. A. Sagi, R. Wang, C. U. Pietrzik, K. A. Findlay, T. E. Smith, M. P. Murphy, T. Bulter, D. E. Kang, N. Marquez-Sterling, T. E. Golde and E. H. Koo, Nature, 2001, 414, 212–216 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Z. Kounnas, A. M. Danks, S. Cheng, C. Tyree, E. Ackerman, X. Zhang, K. Ahn, P. Nguyen, D. Comer, L. Mao, C. Yu, D. Pleynet, P. J. Digregorio, G. Velicelebi, K. A. Stauderman, W. T. Comer, W. C. Mobley, Y.-M. Li, S. S. Sisodia, R. E. Tanzi and S. L. Wagner, Neuron, 2010, 67, 769–780 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Lundkvist and J. Naslund, Curr. Opin. Pharmacol., 2007, 7, 112–118 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. S. Wolfe, Adv. Pharmacol., 2012, 64, 127–153 CAS.
- A. K. Ghosh, M. Brindisi and J. Tang, J. Neurochem., 2012, 120(1), 71–83 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Jonsson, J. K. Atwal, S. Steinberg, J. Snaedal, P. V. Jonsson, S. Bjornsson, H. Stefansson, P. Sulem, D. Gudbjartsson, J. Maloney, K. Hoyte, A. Gustafson, Y. Liu, Y. Lu, T. Bhangale, R. R. Graham, J. Huttenlocher, G. Bjornsdottir, O. A. Andreassen, E. G. Jonsson, A. Palotie, T. W. Behrens, O. T. Magnusson, A. Kong, U. Thorsteinsdottir, R. J. Watts and K. Stefansson, Nature, 2012, 488, 96–99 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Rezai-Zadeh, D. Shytle, N. Sun, T. Mori, H. Hou, D. Jeanniton, J. Ehrhart, K. Townsend, J. Zeng, D. Morgan, J. Hardy, T. Town and J. Tan, J. Neurosci., 2005, 25, 8807–8814 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Chen, E. A. Eckman and C. B. Eckman, FASEB J., 2006, 20, 1269–1271 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Vingtdeux, L. Giliberto, H. Zhao, P. Chandakkar, Q. Wu, J. E. Simon, E. M. Janle, J. Lobo, M. G. Ferruzzi, P. Davies and P. Marambaud, J. Biol. Chem., 2010, 285, 9100–9113 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L.-K. Sy, S.-C. Yan, C.-N. Lok, R. Y.-K. Man and C.-M. Che, Cancer Res., 2008, 68, 10229–10237 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C.-N. Lok, L.-K. Sy, F.-L. Liu and C.-M. Che, J. Biol. Chem., 2011, 286, 31684–31696 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Xia, Y. Hu, I. Rubin, J. Brostoff, B. Whittle, W. Wang and P. Gunning, US Pat., 6 812 213 B2, 2004.
- B. Lee, K. Jung and D.-H. Kim, Pharmacol., Biochem. Behav., 2009, 93, 121–127 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Hu, Z. Xia, Q. Sun, A. Orsi and D. Rees, Brain Res., 2005, 1060, 26–39 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T.-J. Li, Y. Qiu, P.-Y. Yang, Y.-C. Rui and W.-S. Chen, Neurosci. Lett., 2007, 421, 147–151 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. W. Liu, X. Zhu, Q. Lu, J. Y. Wang, W. Li, Y. Q. Wei and X. X. Yin, J. Ethnopharmacol., 2012, 139, 194–200 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. J. Barrett, Y. Song, W. D. Van Horn, E. J. Hustedt, J. M. Schafer, A. Hadziselimovic, A. J. Beel and C. R. Sanders, Science, 2012, 336, 1168–1171 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) T. K. Devon and A. I. Scott, Handbook of naturally occurring compounds, vol. II. Terpenes, Academic Press, NY, 1972, pp. 401–411 Search PubMed; (b) Y.-M. Hu, Z.-L. Yu and W.-F. Fong, J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2011, 21, 582–589 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) M. A. Iglesias-Arteaga, R. P. Gill, C. S. P. Martinez and F. C. Manchado, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 2001, 261–266 RSC; (b) M. A. Iglesias Arteaga, R. P. Gil, V. L. Lara, C. S. P. Martinez, F. C. Manchado, A. R. Perez and L. P. Rios, Synth. Commun., 1998, 28, 1381–1386 CrossRef; (c) M. A. Iglesias Arteaga, R. P. Gil, V. L. Lara, F. C. Manchado and C. S. P. Martinez, Synth. Commun., 1998, 28, 75–81 CrossRef; (d) S. Yahara, T. Yamashita, N. Nozawa and T. Nohara, Phytochemistry, 1996, 43, 1069–1074 CrossRef CAS.
- S. K. Upadhyay, C. C. Creech, K. L. Bowdy, E. D. Stevens, B. S. Jursic and D. M. Neumann, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2011, 21, 2826–2831 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. L. Eliel, V. G. Badding and M. N. Rerick, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1962, 84, 2371–2377 CrossRef CAS.
- H. van de Waterbeemd, G. Camenish, G. Folkers, J. R. Chretien and O. A. Raevsky, J. Drug Targeting, 1998, 6, 151–165 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Atkinson, S. Cole, C. Green and H. van de Waterbeemd, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2003, 13, 719–722 CrossRef.
- G. Thinakaran, D. B. Teplow, R. Siman, B. Greenberg and S. S. Sisodia, J. Biol. Chem., 1996, 271, 9390–9397 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Hur, P. Lee, E. Moon, I. Kang, S.-H. Kim, M.-S. Oh and S.-Y. Kim, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 2009, 620, 9–15 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Pajouhesh and G. R. Lenz, Neurotherapeutics, 2005, 2, 541–553 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. P. Vincken, L. Heng, A. de Groot and H. Gruppen, Phytochemistry, 2007, 68, 275–297 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. F. Huang, L. Shang, P. Liu, M. Q. Zhang, S. Chen, D. Chen, C. L. Fan, H. Wang and K. Xiong, BMC Complementary Altern. Med., 2012, 12, 189 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. H. Schroeter, J. A. Kisslinger and R. Kopan, Nature, 1998, 393, 382–386 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. L. Young-Pearse, A. C. Chen, R. Chang, C. Marquez and D. J. Selkoe, Neural Dev., 2008, 3(15), 1–13 Search PubMed.
- D. H. Small, H. L. Clarris, T. G. Williamson, G. Reed, B. Key, S. S. Mok, K. Beyreuther, C. L. Masters and V. Nurcombe, J. Alzheimer's Dis., 1999, 1, 275–285 CAS.
- T. L. Kukar, T. B. Ladd, M. A. Bann, P. C. Fraering, R. Narlawar, G. M. Maharvi, B. Healy, R. Chapman, A. T. Welzel, R. W. Price, B. Moore, V. Rangachari, B. Cusack, J. Eriksen, K. Jansen-West, C. Verbeeck, D. Yager, C. Eckman, W. Ye, S. Sagi, B. A. Cottrell, J. Torpey, T. L. Rosenberry, A. Fauq, M. S. Wolfe, B. Schmidt, D. M. Walsh, E. H. Koo and T. E. Golde, Nature, 2008, 453, 925–929 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Kienlen-Campard, B. Tasiaux, J. Van Hees, M. Li, S. Huysseune, T. Sato, J. Z. Fei, S. Aimoto, P. J. Courtoy, S. O. Smith, S. N. Constantinescu and J. N. Octave, J. Biol. Chem., 2008, 283, 7733–7744 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. A. Sagi, C. B. Lessard, K. D. Winden, H. Maruyama, J. C. Koo, S. Weggen, T. L. Kukar, T. E. Golde and E. H. Koo, J. Biol. Chem., 2011, 286, 39794–39803 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. I. Jung, T. B. Ladd, T. Kukar, A. R. Price, B. D. Moore, E. H. Koo, T. E. Golde and K. M. Felsenstein, FASEB J., 2013, 27, 3775–3785 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. K. Burg, H. S. Grimm, T. L. Rothhaar, S. Grösgen, B. Hundsdörfer, V. J. Haupenthal, V. C. Zimmer, J. Mett, O. Weingärtner, U. Laufs, L. M. Broersen, H. Tanila, T. Vanmierlo, D. Lütjohann, T. Hartmann and M. O. Grimm, J. Neurosci., 2013, 33, 16072–16087 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Aureli, A. Gritti, R. Bassi, N. Loberto, A. Ricca, V. Chigorno, A. Prinetti and S. Sonnino, Neurochem. Res., 2012, 37, 1344–1354 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: ESI includes experimental procedures for biology and chemistry experiments, synthetic figures, NMR data and mass spectroscopic analysis. See DOI: 10.1039/c5sc02377g |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |

![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
: