Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCo-doping effect of Mn2+ on fluorescence thermostability of Ca-α-sialon:Eu2+ phosphors
Jia Ni abc,
Qian Liu*ab,
Zhenzhen Zhouab and
Guanghui Liuab
abc,
Qian Liu*ab,
Zhenzhen Zhouab and
Guanghui Liuab
aState Key Laboratory of High Performance Ceramics and Superfine Microstructure, Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1295 Dingxi Road, Shanghai, 200050, China. E-mail: qianliu@mail.sic.ac.cn
bShanghai Materials Genome Institute, 99 Shangda Road, Shanghai 200444, China
cUniversity of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19A Yuquan Road, Beijing 100049, China
First published on 1st September 2017
Abstract
To reveal transition metal manganese ion (Mn2+) co-doping influence on Ca-α-sialon:Eu2+ phosphors, Mn2+ and europium ion (Eu2+) co-doped Ca-α-sialon phosphors were synthesized using a solid state reaction at 1600 °C under an ambient nitrogen atmosphere, and the effects of the co-dopant Mn2+ on the fluorescence thermostability of Ca-α-sialon:Eu2+ phosphors were systematically investigated. With increasing Mn2+ concentration, X-ray diffraction analysis shows a phase-pure host Ca-α-sialon structure and unit cell shrinkage (or a tighter structure). The photoluminescence spectra of all samples, with or without Mn2+ co-doping, exhibit a strong yellow emission. For the energy transfer between Mn2+ and Eu2+, the emission intensity is strongest when the co-doping concentration of Mn2+ is 0.02 molar and the CIE chromaticity index of the strongest emission composition is (0.474, 0.513) with a high internal quantum efficiency of 72.4%. Importantly, the fluorescence thermal quenching behavior of the as-prepared phosphors is remarkable and is over 80% of the initial emission intensity tested at room temperature, at a higher temperature of 275 °C. The major energy transition mechanism between co-dopants Mn2+ and Eu2+ during the heating process was deduced and considered to be a non-radiative energy transfer and phonon-assisted tunneling. Using further calculations, the thermal activation energy, ΔE, is 0.28 eV. In consequence, Mn2+ and Eu2+ co-doped Ca-α-sialon is an attractive and competitive phosphor candidate for applications in white light emitting diodes.
1. Introduction
In the 1970s, α-sialon was first found and promised to be useful as a structural material, which stemmed from its solid solution feature of strong covalent silicon nitride (Si3N4).1,2 By 2002, the research teams of Hintzen et al.3 and Xie et al.4 not only proposed that α-sialon could be applied to phosphor as a consolidus host material but also demonstrated its excellent luminescence properties, such as high thermal stability, high efficiency and a friendly environment.In past decade, α-sialon, as a good silicon-based oxynitride host material has been attracting much attention and has been widely studied. The chemical formula of α-sialon is Mm/vSi12−(m+n)Alm+nOnN16−n (where v is the valence of the M ion). In this composition, M consists of a compensation cation (calcium (Ca2+), lithium (Li+), magnesium (Mg2+), strontium (Sr3+), and so on)5–7 and most rare earth metals (europium (Eu2+), cerium (Ce3+), terbium (Tb3+), and so on).4,7,8 The changes of the m and n values represent the quantity of (Si–N) bonds, (Al–N) bonds and (Al–O) bonds in M-α-sialon.9–11 The ratio of these bonds exerts effects on the luminescence properties. In the previously mentioned systematic research, Eu2+ and Ce3+ doped Ca-α-sialon possess better luminescence properties. In a Ca-α-sialon host, activator Eu2+ and Ce3+ is 5d–4f transitions with a strong nephelauxetic effect and large ligand field splitting, showing a typical broad yellow and green emission with high thermal stability. They could keep ∼70% of the initial emission intensity when the temperature reached 300 °C, and this was far better than results obtained using yttrium aluminium garnet (YAG):Ce3+.12 Besides the wider emission wavelength range and high thermal stability, compared with other oxide and oxynitride phosphors (e.g., BaSi3O4N2,13 BaMgAl10O17,14 and so on), Eu2+ or Ce3+ doped Ca-α-sialon possesses a high external quantum efficiency (QE) of about 40%.15,16 Furthermore, relative to nitride phosphors CaAlSiN3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 17 which have complex requirements to prepare, Ca-α-sialon phosphor is easier to prepare.
17 which have complex requirements to prepare, Ca-α-sialon phosphor is easier to prepare.
Currently, to achieve better luminescence properties of phosphors and low utilization of expensive rare earth elements, manganese (Mn2+) used as a sensitizer was introduced in to many host materials co-doped with Eu2+ and this has been studied extensively.18–21 It has been reported that the energy transfer between Mn2+ and Eu2+ is efficient with several phosphors, such as Mg2Al4Si5O18 and apatite-type fluorophosphate phosphors, and this could improve the emission intensity and influence the emission wavelength to red shift. Also, it has been determined from the previously mentioned papers that the energy transfer between the sensitizer Mn2+ and the activator Eu2+ is proportional to the spectral overlap between the emission band of the sensitizer and the excitation band of the acceptor. In accordance with the previous studies, the energy transfer between Eu2+ and Mn2+ in Ca-α-sialon is attributed to the resonance transfer under excitation in a room temperature (RT) environment.22 However, much work is still needed to explore the Mn2+/Eu2+ co-doped Ca-α-sialon to enrich the understanding of scientific recognition and to understand its practical applications.
In this research, Mn2+ and Eu2+ co-doped Ca-α-sialon was successfully prepared using a solid-state reaction. The effects of co-doped Mn2+ on the luminescence properties and especially on the thermal quenching behavior were investigated in detail. Furthermore, the energy transfer phenomenon between Eu2+ and Mn2+ under high temperature conditions was also considered and a non-radiative energy transfer and phonon-assisted tunneling mechanism was deduced.
2. Experimental procedures
2.1 Synthesis of Ca-α-sialon:Eu2+,Mn2+ phosphors
The phosphors with the compositions of Ca0.92−xSi9Al3ON15:0.08Eu2+,xMn2+ (x = 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 mol%) were prepared using a traditional high temperature solid-state reaction method, with a fixed and optimal Eu2+ doping content of 0.08 mol based on previous research, and these were used to find out the Mn2+ co-doping influence on Ca-α-sialon:Eu2+ phosphors. The starting materials were α-Si3N4 (SN-E10, Ube Industries, Japan), aluminum nitride (AlN, Grade A, Starck Industries, Germany), calcium carbonate (≥99.90%, AR, Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd, China), europium(III) oxide (99.99%, Shanghai Yuelong New Materials Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) and manganese(II) carbonate (CP, Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd, China). After mixing and grinding the powders thoroughly in an agate mortar for two h, the powdered mixture was put into BN crucibles, loaded in a graphite furnace, and finally calcined at 1600 °C for 4 h under a 0.8 L min−1 nitrogen (N2) flow. The as-prepared powders were cooled down to RT in the furnace and ground finely again to obtain the final powders for further analysis.2.2 Characterization
The products of synthesized powders were identified using X-ray powder diffraction (XRD, D8 ADVANCE, Bruker, Germany) with CuKα radiation (λ = 0.1541 nm). Photoluminescence (PL) spectra and temperature dependent luminescence properties (from 25 °C to 275 °C) were performed on a fluorescence spectrometer (F-4600, Hitachi, Japan) with a 150 W xenon lamp. The QE spectra were measured by using the integrated sphere on the time resolved and steady state fluorescence spectrophotometer (FLS980, Edinburgh Instruments, UK). The decay curves of the lifetime values were also recorded on the FLS 980 with a μF2 tunable microsecond flashlight (Edinburgh Instruments, UK), using a 450 W xenon lamp as excitation source, with pulsed light, measured under a fixed wavelength of 570 nm emission and 375 nm excitation, simultaneously, combined with a time correlated single photon counting card and specialty software (Fluoracle, Edinburgh Instruments) to analyze and draw the decay curves.3. Results and discussion
3.1 Phase composition of Ca-α-sialon:Eu2+,Mn2+ phosphors
XRD patterns of Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+,xMn2+ phosphors are shown in Fig. 1a, with a standard reference pattern of Ca-α-sialon at the bottom. The intense and sharp crystal diffraction peaks indicate that all the samples agreed well with the structure of Ca-α-sialon (JCPDS 33-0261) and no visible impurity phases were detected. Compared with the phosphors without dopant Mn2+, the diffraction peaks in the selected 2θ region from 33° to 36° gradually shift to higher 2θ angles with increasing Mn2+ concentration (seen in Fig. 1b), which is because of the lattice shrinking caused by smaller Mn2+ ions (0.067 nm ionic radius) substituting for larger Ca2+ ions (0.10 nm ionic radius). The previous experimental results show that the transition metal cation, Mn2+, has been co-doped into the Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+ lattices.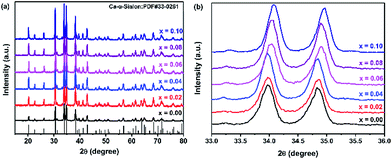 | ||
| Fig. 1 (a) XRD patterns of Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+,xMn2+ phosphors with various Mn2+ concentrations (x = 0.00–0.10); (b) magnified regions of the XRD patterns in the 2θ range of 33–36°. | ||
3.2 Photoluminescence properties of Ca-α-sialon:Eu2+,Mn2+ phosphors
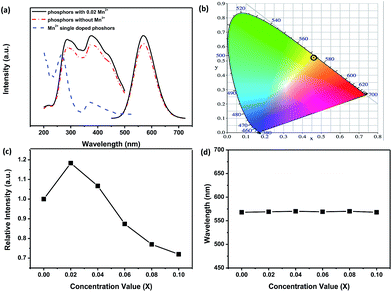
The excitation and emission PL spectra of two representative phosphors of Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+, and Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+,0.02Mn2+ are shown in Fig. 2a. The spectra of both excitation and emission for the Mn2+ doped sample are identical to the spectra of the sample without Mn2+ dopant. The excitation spectra present two broad bands with maxima at ∼287 nm and ∼375 nm. The band of ∼287 nm is attributed to the absorption of the Ca-α-sialon host lattice,23 whereas the band of ∼375 nm originates from the 4f7 → 4f65d electron transition of Eu2+. The emission spectra only show one broad band and its center peak around ∼570 nm is attributed to the energy transfer from the 4f65d excited state to the 4f7 ground state of the Eu2+ rare earth ions.23 The increased excitation spectrum of Ca-α-sialon:0.02Mn2+ is also illustrated in Fig. 2a, and shows an obvious overlap between the emission spectrum of Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+ and the excitation spectrum of Ca-α-sialon:0.02Mn2+, indicating the energy transfer interaction between Eu2+ and Mn2+. In Fig. 2b, the Commission International de I'Éclairage (CIE) chromaticity diagrams of the two phosphors, Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+, and Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+,0.02Mn2+, excited under 375 nm blue light are shown. The CIE chromaticity index for Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+ is (0.473, 0.514) and for Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+,0.02Mn2+ is (0.474, 0.513). It gives a distinct visual that the CIE chromaticity index of these two phosphors are very close and both of them belong to typical yellow phosphors which can be coupled to blue light-emitting diode (LED) chips for generating white light. Meanwhile, the internal QE of phosphors under 375 nm excitation were measured and calculated using the following expression:24,25
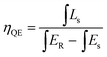 | (1) |
| Rc = 2(3V/4πNxc)1/3 | (2) |
Using eqn (2), V is the volume of the unit cell of Ca-α-sialon (304.8 Å3), N is the number of Z ions in the single unit cell (1), and xc is the stoichiometric doping composition sum of the Eu2+ concentration of 0.08 and the Mn2+ critical concentration of 0.02 (assumed from Fig. 2c). Therefore, the calculated Rc is 17.98 Å. If the doping concentration of Mn2+ increases to 0.06 and 0.10, the value of R becomes smaller (16.08 Å and 14.78 Å, respectively). Therefore, with the further increase of Mn2+ content beyond 0.02 (after the second dot in the curve as shown in Fig. 2c), the critical distance Rc or the distance between the Mn2+ and Eu2+ decreases, resulting in an enhanced energy transfer interaction and the final concentration quenching of emission or emission intensity decline. It should be noted that the added Mn2+ composition is volatile to some extent during the high temperature calcination of phosphors, and the real content of Mn2+ in the prepared phosphors is below the stoichiometric composition and then the calculated critical distance Rc is rather smaller. Furthermore, based on the calculated Rc (more than 5–8 Å), the energy transfer model between Eu2+ and Mn2+ can be deduced as being multipolar interactions following Dexter's principle. In Fig. 2d, the emission peak positions of the Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+ phosphors with different Mn2+ concentrations are tiny, and fluctuate around 570 nm and have no distinct emission shift. Therefore, the appropriate co-doping of Mn2+ with Eu2+ in the Ca-α-sialon host material can enhance the emission intensity and the internal QE as well, but does not induce the red shift of the emission at RT.
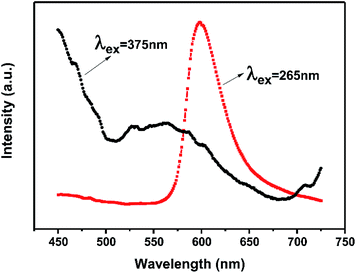
In general, the 4T1(4G) → 6A1(6S) transition of Mn2+ within the 3d shell strongly depends on lattice vibration and crystal field strength. In previous studies, the emission spectra of Mn2+ shows a broad green emission band in oxide hosts with tetrahedral coordination, whereas it emits orange to red light with octahedral coordination. Whereas, because of the strong nephelauxetic effect, it can also give red light (∼600 nm) with tetrahedral coordination in AlN and AlON nitride hosts.19,28,29 Furthermore, the dopant Mn2+ in Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+ is expected to substitute for Ca2+ sites which are coordinated by seven (O, N) anions at three different M–(O, N) distances.8,30,31 Theoretically speaking, the introduction Mn2+ in Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+ can result in a red shift of the emission wavelength. However, in these experiments, the dopant Mn2+ in Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+ only enhances the luminescence intensity observed from the spectra (Fig. 2c and d), and obvious emission shift is absent. It was supposed that 4T1 → 6A1 d–d electron transition of Mn2+ is spin and parity-forbidden, compared to the 4f → 5d transition of Eu2+, therefore, the emission intensity of the Mn2+ ion singly doped phosphor is far weaker than that of the Eu2+ ion in many host materials,32 as is the situation in the Ca-α-sialon host. In addition, the excitation wavelength of longer than the 375 nm selected in the experiments is probably not an appropriate excitation wavelength for Mn2+ emitting in Ca-α-sialon, and this is supported by the curves shown in Fig. 3, which show a stronger emission of Mn2+ centered at ∼600 nm under excitation of wavelengths shorter than 265 nm, rather than under excitation of a longer wavelength of 375 nm.
3.3 Thermal quenching behaviors of Ca-α-sialon:Eu2+,Mn2+ phosphors
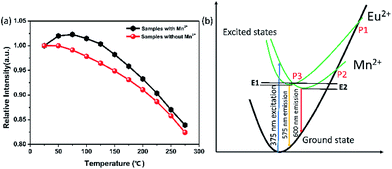
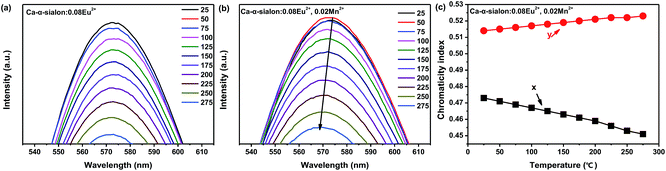
In this research, the temperature dependent luminescent intensity of Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+ with (x = 0.02) and without Mn2+ was measured at a wider temperature range from RT (25 °C) to 275 °C and the results are shown in Fig. 4a. Because of the thermal quenching, the trend of the PL intensity trends to decline. The thermal quenching is ascribed to the non-radiative energy transfer and expressed in the schematic configuration coordinate diagram of Eu2+ and Mn2+ electrons in Ca-α-sialon lattice to describe the energy transfer process, as shown in Fig. 4b. In the configuration coordinate diagram, the lower parabola (black line) and higher two parabolas (green lines) represent the total energy of the ground state and excited states of Eu2+ and Mn2+, respectively. In general, the electrons jump from the bottom of the ground state (black) to the Eu2+ and Mn2+ excited states (green) under 375 nm excitation, then the excited electrons partly release energy by radiative transition directly and vertically from the bottom of two excited states of Eu2+ and Mn2+ parabolas (green) to the bottom of the ground state (black) accompanied by yellow (575 nm) and red (600 nm) light emission. When heating the samples, except in the previously described process, part of the electrons obtains much more energy and reaches the high cross points P1 and P2 via the Eu2+ and Mn2+ parabola (green) and then transits to the bottom of the ground state via the ground state parabola (black). This is the non-radiative energy transfer and it is the major energy transfer during the whole heating process, and as a result, the luminescence intensity is gradually weakened. From Fig. 4a, it is worth noting that the introduction of Mn2+ enhances rather than weakens the emission intensity of the phosphor at temperatures lower than 125 °C. From another perspective, the enhanced emission intensity should be considered as the phonon-assisted tunneling effect. At relatively low heating temperatures (<125 °C), by absorbing the extra heat energy, part of the heat excited electrons (also called phonons) move from the bottom of the low energy excited states (Mn2+, green parabola) to the high energy excited states (Eu2+, green parabola) via the cross point P3,33 and finally release the obtained energy by radiatively emitting light. Consequently, the emission intensity enhancement occurs at relatively low heating temperatures by the phonon-assisted tunneling effect caused by the heating excitation. If the heating temperature increases further to high levels, the electrons could gain more energy and reach the high cross points, P1 and P2, via the Eu2+ and Mn2+ parabola (green) and then transit to the bottom of the ground state via the ground state parabola (black). This is described as non-radiative energy transfer or thermal quenching.From the measured spectra, illustrated in Fig. 5a and b, the emission peak wavelengths of Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+,0.02Mn2+ shift from the long wavelength of 573 nm to the short wavelength of 567 nm with the increase of the heating temperatures, while the emission peak wavelengths of the single doped Ca-α-sialon:0.02Mn2+ remain almost unchanged at around 573 nm. Otherwise, the slight decrease of the x values and the increase of y values in the chromaticity index, indicated in both Fig. 5c and Table 1, show more direct evidence of the emission blue-shift behavior of Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+,0.02Mn2+ with the increase in temperature. It has to be noted that this blue-shift of emission is caused partially by phonon-assisted tunneling.33,34 From Fig. 4b, it can be seen that at first, although the energy barrier, E1, can be overcome, it is higher than E2, so the low energy emission of Mn2+ plays the major role in the reaction. When the temperature rises to a higher level, the thermal quenching energy goes over the E2 barrier and the high energy emission of Eu2+ gradually becomes dominant. Furthermore, in Table 1, the CIE chromaticity coordinate index of Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+,0.02Mn2+ phosphor, shift from (0.473, 0.514) at 25 °C to (0.451, 0.523) at 275 °C. This tiny displacement reveals the strong color stability of the co-doped phosphor.
| Temperature (°C) | Chromaticity index x | Chromaticity index y |
|---|---|---|
| 25 | 0.473 | 0.514 |
| 50 | 0.471 | 0.515 |
| 75 | 0.469 | 0.516 |
| 100 | 0.467 | 0.517 |
| 125 | 0.465 | 0.518 |
| 150 | 0.463 | 0.519 |
| 175 | 0.461 | 0.520 |
| 200 | 0.459 | 0.521 |
| 225 | 0.456 | 0.522 |
| 250 | 0.453 | 0.522 |
| 275 | 0.451 | 0.523 |
However, in practical applications, phosphors are packed with LED chips when applied in solid-state lighting and the heat generated by LED chips always affects the emission intensity of phosphors during the service time. In terms of the LED industry standard, 150 °C is regarded as the working temperature for a high power white-LED (W-LED). For this standard, thermal stability under 150 °C becomes one of the crucial phosphor parameters. When the temperature reaches 150 °C, the emission intensity of Ca-α-sialon with (x = 0.02) and without Mn2+ maintains 98% and 94% of the initial intensity (RT), respectively, (see Fig. 4a), indicating that both of them have an excellent resistibility to thermal quenching and have a good thermal stability. As the working temperature rises to 275 °C, the emission loss of these two phosphors is less than 20% of the initial intensity (RT) and in thermal quenching behavior of the phosphors with Mn2+ co-doping are little better. To better understand the temperature dependence of the PL, the thermal activation energy for thermal quenching has been calculated according to the Arrhenius equation:35,36
I0/I(T) = 1 + A![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) exp(−ΔE/KBT) exp(−ΔE/KBT)
| (3) |
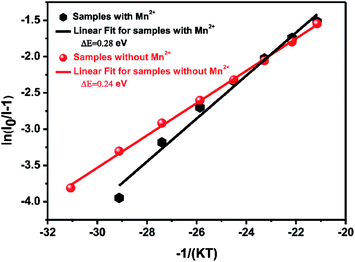 | ||
| Fig. 6 Activation energy ΔE of thermal quenching of Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+ with (x = 0.02) and without Mn2+ phosphors. | ||
3.4 Fluorescence decay
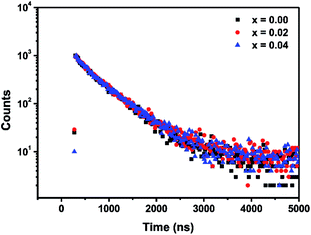
Fig. 7 shows the decay curves for three samples: single doped Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+, co-doped samples Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+,0.02Mn2+ and Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+,0.04Mn2+, measured simultaneously with a fixed emission wavelength of 570 nm and excitation wavelength of 375 nm. All the experimental values can be fitted using the double-exponential equation:
I(t) = A1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) exp(−t/τ1) + A2 exp(−t/τ1) + A2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) exp(−t/τ2) exp(−t/τ2)
| (4) |
In eqn (4), I is the luminescence intensity, A1 and A2 are constants, t is the testing time, τ1 and τ2 are the shorter and longer decay times calculated using eqn (4). According to eqn (4) and using computerized fitting, the τ1 and τ2 results for the three samples are listed in Table 2. Furthermore, the average lifetime constant (τ) can be estimated as follows:
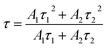 | (5) |
| Doping content | τ1 (ns) | τ2 (ns) | τ (ns) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (0.08Eu2+) | 156.5 | 553.8 | 515.1 |
| (0.08Eu2+,0.02Mn2+) | 237.4 | 584.0 | 521.9 |
| (0.08Eu2+,0.04Mn2+) | 151.7 | 562.3 | 519.4 |
It is found that the average decay time of the sample with single Eu2+ doping is a little faster than that of the co-doped samples with 0.02 and 0.04 Mn2+ addition. In addition, the double-exponential decay indicates the existence of two relaxation processes. The fast decay components (τ1) are defined by the PL intensity decay, whereas the slow decay components possibly result from the luminescence caused by defects of phosphors on the surface and inside.38
4. Conclusions
In summary, Mn2+ and Eu2+ co-activated Ca-α-sialon phosphors were prepared using a conventional high temperature solid-state reaction method. The prepared phosphors display intense yellow emission centered at 570 nm under 375 nm excitation and the optimal doping concentration of Mn2+ is x = 0.02 molar for all the Ca-α-sialon:0.08Eu2+,xMn2+ compositions. Compared to Eu2+ single doped Ca-α-sialon, the increase of emission intensity indicates that additional energy transfer occurs between Eu2+ and Mn2+ during the luminescence process in the co-doped phosphors. The effective energy transfer leads to a good resistance behavior to thermal quenching. At 150 °C it can maintain 98% of the initial emission intensity (measured at RT), and its emission intensity remains at over 80% when the temperature rises to 275 °C. Based on the calculation results, the thermal activation energy ΔE (0.28 eV) of the co-doped phosphors is larger than that of phosphor without Mn2+. All the results show that the co-dopant Mn2+ plays a promoting role in the resistance to thermal quenching of the Ca-α-sialon:Eu2+ phosphors.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
The Authors wish to thank the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFB0700204 and 2016YFB0701004) and the Research Program of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission Foundation (Grant No. 14DZ2261203, 14ZR1445400, and 16ZR1441100), for their financial supports.Notes and references
- K. H. Jack and W. I. Wilson, Nature, Phys. Sci., 1972, 238, 28–29 CrossRef.
- Y. Oyama and O. Kamigait, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 1971, 10, 1637 CrossRef CAS.
- J. W. H. van Krevel, J. W. T. van Rutten, H. Mandal, H. T. Hintzen and R. Metselaar, J. Solid State Chem., 2002, 165, 19–24 CrossRef CAS.
- R.-J. Xie, M. Mitomo, K. Uheda, F.-F. Xu and Y. Akimune, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2002, 85, 1229–1234 CrossRef CAS.
- R.-J. Xie, N. Hirosaki, M. Mitomo, K. Sakuma and N. Kimura, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2006, 89, 241103 CrossRef.
- S. Hampshire, H. K. Park, D. P. Thompson and K. H. Jack, Nature, 1978, 274, 880–882 CrossRef CAS.
- R. J. Xie, N. Hirosaki, M. Mitomo, K. Uheda, T. Suehiro, X. Xu, Y. Yamamoto and T. Sekiguchi, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 9490–9494 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Shen, M. Nygren and U. Halenius, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1997, 16, 263–266 CrossRef CAS.
- R.-J. Xie, N. Hirosaki, M. Mitomo, T. Suehiro, X. Xu and H. Tanaka, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2005, 88, 2883–2888 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Liu, R.-J. Xie, N. Hirosaki, T. Takeda, J. Li and X. Sun, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2009, 92, 2668–2673 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Shioi, N. Hirosaki, R.-J. Xie, T. Takeda and Y. Q. Li, J. Alloys Compd., 2010, 504, 579–584 CrossRef CAS.
- R.-J. Xie and N. Hirosaki, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater., 2007, 8, 588–600 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Huang, Y. Zhou, W. Xu, K. Wang, Z. Liu and M. Hong, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 653, 148–155 CrossRef CAS.
- K.-B. Kim, Y.-I. Kim, H.-G. Chun, T.-Y. Cho, J.-S. Jung and J.-G. Kang, Chem. Mater., 2002, 14, 5045–5052 CrossRef CAS.
- R.-J. Xie, N. Hirosaki, M. Mitomo, K. Takahashi and K. Sakuma, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2006, 88(10), 101104 CrossRef.
- L. Liu, X. Zhou, R.-J. Xie and Q. Huang, Chin. Sci. Bull., 2012, 58, 708–712 CrossRef.
- B. Dierre, T. Takeda, T. Sekiguchi, T. Suehiro, K. Takahashi, Y. Yamamoto, R.-J. Xie and N. Hirosaki, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater., 2013, 14, 064201 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Chen, Y. Liu, M. Fang and Z. Huang, Inorg. Chem., 2014, 53, 11396–11403 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. J. Wang, R. J. Xie, B. Dierre, T. Takeda, T. Suehiro, N. Hirosaki, T. Sekiguchi, H. Li and Z. Sun, Dalton Trans., 2014, 43, 6120–6127 RSC.
- N. Guo, C. Jia, J. Li, Y. Zhao, R. Ouyang, W. Lü and A. Setlur, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2015, 98, 1162–1168 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Miao, Z. Xia, J. Zhang and Q. Liu, Inorg. Chem., 2014, 53, 10386–10393 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y.-q. Zhang, X.-j. Liu, Z.-r. Huang, J. Chen and Y. Yang, J. Lumin., 2012, 132, 2561–2565 CrossRef CAS.
- R.-J. Xie, N. Hirosaki, K. Sakuma, Y. Yamamoto and M. Mitomo, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, 84, 5404–5406 CrossRef CAS.
- W. A. Thornton, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1969, 116, 286–298 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Ohkubo and T. Shigeta, Journal of the Illuminating Engineering Institute of Japan, 1999, 83, 87–93 CrossRef.
- G. Blasse and A. Bril, Philips Res. Rep., 1968, 23, 201–206 CAS.
- G. Blasse and W. Wanamaker, Philips Res. Rep., 1968, 23, 189 CAS.
- B. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Wen, F. Zhang, G. Zhu and J. Zhang, Mater. Lett., 2012, 75, 137–139 CrossRef CAS.
- R.-J. Xie, N. Hirosaki, X.-J. Liu, T. Takeda and H.-L. Li, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, 92, 201905 CrossRef.
- F. Izumi, M. Mitomo and J. Suzuki, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1982, 1, 533–535 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Z. Cao and R. Metselaar, Chem. Mater., 1991, 3, 242–252 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Guo, L. Liao, L. Mei and H. Liu, J. Solid State Chem., 2015, 232, 102–107 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Zhou, Q. Wang and Y. Jin, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2015, 3, 11151–11162 RSC.
- S. J. Gwak, P. Arunkumar and W. B. Im, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118, 2686–2692 CAS.
- S. Bhushan and M. V. Chukichev, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1988, 7, 319–321 CrossRef CAS.
- R.-J. Xie, N. Hirosaki, N. Kimura, K. Sakuma and M. Mitomo, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2007, 90, 191101 CrossRef.
- C.-C. Chung and J.-H. Jean, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2010, 123, 13–15 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Zhou, S. Deng, C. Rong, Q. Xie, S. Lian, J. Zhang, C. Li and L. Yu, RSC Adv., 2013, 3, 16781 RSC.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 |