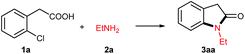Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Copper powder-catalyzed chelation-assisted cascade reaction of o-chloroarylacetic acids with amines under solvent- and ligand-free conditions: synthesis of oxindoles†
Jiang-Sheng Li *,
Guo-Qin Chen,
Qian Yang,
Zhi-Wei Li,
Ci-Zhi Liu and
Peng-Mian Huang
*,
Guo-Qin Chen,
Qian Yang,
Zhi-Wei Li,
Ci-Zhi Liu and
Peng-Mian Huang
Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Materials Protection for Electric Power and Transportation, School of Chemistry and Biological Engineering, Changsha University of Science & Technology, Changsha 410114, P. R. China. E-mail: jsli@csust.edu.cn; Fax: +86-731-85258733
First published on 21st September 2017
Abstract
An efficient method to construct oxindole scaffolds from o-chloroarylacetic acids/esters with amines has been explored. This cascade protocol involves the in situ generation of o-aminoarylacetic acid derivatives by the copper powder catalyzed and weak O-chelation assisted Ullmann amination of unactivated C–Cl bonds under air, and solvent-/ligand-free conditions followed by annulative N-acylation.
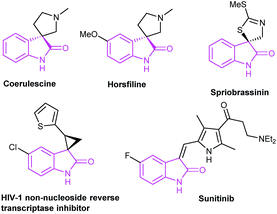
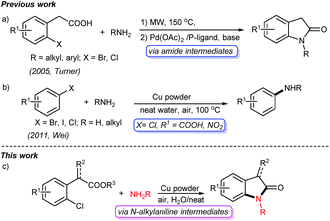
Oxindoles are privileged heterocycles prevalent in naturally occurring products and pharmacologically active compounds (Fig. 1),1 and they also serve as important precursors in drug design and organic synthesis.1b Over the past few decades, an array of efficient methods have been developed to access oxindoles. Basically, these methods involve the derivatization of three types of starting materials: anilide derivatives,2 isatins2g,3 or indoles,2g,4 and arylacetic acid derivatives.2g,5 One of the most remarkable features is the pre-installation of a nitrogen-containing functional group on the precursors. Among them, the use of anilide derivatives is predominate in contemporary organic synthetic methodologies, whereas arylacetic acid derivatives are far less used. The methods documented include the nitro reduction/intramolecular cyclization of o-nitrophenylacetic acid,2g the intramolecular oxidative amidation of N-acetoxy-2-phenylacetamides,2g and the intramolecular Ullmann-type N-arylation of o-halophenylacetamides.2g,5 The former two limit to the preparation of free NH oxindoles. The latter provides a powerful strategy for the construction of oxindoles functionalized at N-, C3-positions. For instance, Turner's group has reported the access to oxindoles via sequential amide formation/palladium-catalyzed intramolecular amidation in two steps (Scheme 1a),5 wherein the expensive noble metal catalyst, toxic phosphine ligand, and strong base are required besides the high temperature of 150 °C. To our knowledge, the direct construction of oxindole scaffold by the introduction of amino group to the benzene ring of o-haloarylacetic acids, especially o-chloroarylacetic acids, is yet unexplored.
Copper catalyzed Ullmann-type reaction of arylic C-halo bonds has emerged as a fundamental tool for C–N bond formation in academic and industrial fields.6 These protocols usually require ligands, and in particular hardly avoid using organic solvents such as DMSO, DMF, and NMP. Later on, Wei reported a copper powder catalyzed amination of aromatic C-halo bonds without ligands in water,7 which allows efficient access to C–N bonds from C–I, C–Br bonds, and some C–Cl bonds (Scheme 1b). However, the substrates without electron-withdrawing groups (e.g. chlorobenzene and p-chloroanisole) are inert in such a transformation. Consequently, the transformation of simple arylic C–Cl bonds remains a challenge.6a
In the realm of C–H activation, a carboxyl group acts as an effective directing group to promote coupling reactions by weak O-coordination with the metal centers of catalysts.8 Yu reported some elegant transformations of arylacetic acids C–H bonds directed by carboxyl groups.8b–i We speculated that the COOH group will also facilitate copper powder catalyzed Ullmann amination through the activation of C–Cl bond, and then subsequent intramolecular cyclization will give oxindole scaffolds. Following our continuous interest in the synthesis of heterocycles,9 herein, we present a facile and efficient cascade protocol for the construction of oxindole derivatives from readily available o-chlorophenylacetic acids with amines catalyzed by copper powder under air and neat conditions (Scheme 1c).
o-Chlorophenylacetic acid 1a and ethylamine 2a were chosen as prototype substrates for this cascade reaction (Table 1). The reaction proceeded smoothly in water with a small amount of air sealed in the tube when copper powder (10 mol%) was used as the catalyst in the absence of any additive, and the cyclized product oxindole 3aa was obtained in 77% yield (entry 1). This positive result suggested that the carboxyl group tethered at ortho position did facilitate the C–Cl Ullmann reaction via ortho chelating effect,10 just like acting as a directing group in C–H activation. Reducing the water volume, the 2a equivalent or the catalyst loading resulted in lower efficiency (entries 2, 3, 6). Prolonging the reaction time or elevating the reaction temperature enhanced the yield while shortening the time or lowering the temperature diminished the efficiency (entries 4 vs. 5, 7 vs. 8). It is worthwhile to note that the activated copper powder delivered a comparable yield of 78% (entry 9). Interestingly, the higher yield of 85% resulted under solvent-free condition (entry 10). As expected, no reaction occurred under N2 atmosphere (entry 11), which further confirmed that the small amount of O2 is essential in the copper powder catalyzed transformation as pointed out by Wei.7 Other copper sources such as cuprous salts (CuCl, CuBr) or oxide (Cu2O) could also catalyze this cascade reaction under N2 atmosphere, providing the similar yields (entries 12–14). The cupric species (CuCl2·2H2O, CuO) were ineffective in water and N2 systems (entries 14 & 15). Intriguingly, they could trigger the current transformation with less efficacy (58% & 65%) under the solvent-free and N2 conditions.11 These results revealed that the catalytically active species is Cu(I).7 Thus, the optimum conditions for this cascade reaction were summarized as follows: 1a (2 mmol), 2a (10 mmol), Cu powder (10 mol%) all sealed in a 15 mL reaction tube under air atmosphere, stirring at 100 °C for 16 h, affording N-ethyl indolin-2-one 3aa in 85% yield.
| Entry | Cat. (mol%) | Temp. (oC) | Time (h) | Yieldb (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Reaction conditions: 1a (2 mmol), 2a (10 mmol), Cu powder or other copper catalyst, H2O (2 mL, not degassed) added to a 15 mL sealed tube under air atmosphere, 100 °C unless otherwise stated.b Isolated yields.c H2O (1 mL, not degassed).d 3 equiv. of 2a.e Cu powder activated by I2 in acetone.f Without water.g Under N2. N. R. means no reaction. | ||||
| 1 | Cu (10) | 100 | 16 | 77 |
| 2c | Cu (10) | 100 | 16 | 70 |
| 3d | Cu (10) | 100 | 16 | 66 |
| 4 | Cu (10) | 100 | 12 | 73 |
| 5 | Cu (10) | 100 | 24 | 82 |
| 6 | Cu (5) | 100 | 16 | 66 |
| 7 | Cu (10) | 80 | 16 | 67 |
| 8 | Cu (10) | 120 | 16 | 80 |
| 9e | Cu (10) | 100 | 16 | 78 |
| 10f | Cu (10) | 100 | 16 | 85 |
| 11f,g | Cu (10) | 100 | 16 | N. R. |
| 12g | CuCl (10) | 100 | 16 | 67 |
| 13g | CuBr (10) | 100 | 16 | 67 |
| 14g | Cu2O (5) | 100 | 16 | 80 |
| 15g | CuO (10) | 100 | 16 | N. R. |
| 16g | CuCl2 (10) | 100 | 16 | Trace |
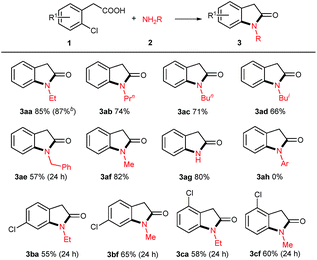
With the optimized reaction conditions in hand, we set out to investigate the scope of amines 2 for this copper powder catalyzed C–Cl amination and the results are compiled in Table 2. In general, all the tested aliphatic primary amines are effective substrates with o-chlorophenylacetic acid 1a, providing the corresponding 3-unsubstituted oxindoles in moderate to good yields (entries 3aa–3af). The amines with longer chains gave relatively lower yields (3aa, 3ab, 3ac). The straight-chain amine 2c was preferred over the branched-chain one 2d. Benzyl amine 2e delivered the desired product only in 57% yield when the reaction time was fixed at 24 h (3ae). Noteworthy, aqueous methyl amine 2f afforded oxindole 3af in 82% yield, and aqueous ammonium gave free NH oxindole 3ag in 80% yield. Besides, the o-bromophenylacetic acid instead of 1a generated a comparable yield of 87%.
When aromatic amines were used instead, for example, aniline, o/p-toluidines, o/p-anisidines, and p-chloroaniline, no obvious N-arylated oxindoles were observed (3ah), even in the case of strong nucleophilic p-anisidine, but their corresponding amides 4ah were verified based on NMR and MS analysis (please see ESI†). The additional bases (e.g. NaOH 2.0 equiv., t-BuONa 2.0 equiv.) could not trigger Ullmann-type C–N bond formation, even in higher temperature (120 °C or 130 °C). This failure might be ascribed to the weaker nucleophilicity of aromatic amines than that of aliphatic amines.
When 2,4-dichlorophenylacetic acid 1b and 2,6-dichlorophenylacetic acid 1c were used in this transformation, their corresponding oxindoles were obtained. It is worth noting that in the former case the Ullmann-type amination reaction occurred selectively at the ortho C–Cl bond of carboxylates (3ba & 3bf). In both cases, no sequential Ullmann-type amination process re-occurred at the other C–Cl bond. These results suggested that the tethered carboxyl group presumably plays an essential role in this cascade reaction. Besides, it should be noted that further oxidation products such as 3-hydroxyloxindoles or isatins were not observed although oxindole C3–H bonds are very reactive to O2 in all the cases of the aforementioned 3-unsubstituted oxindoles.
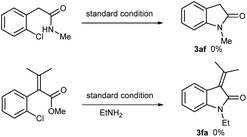
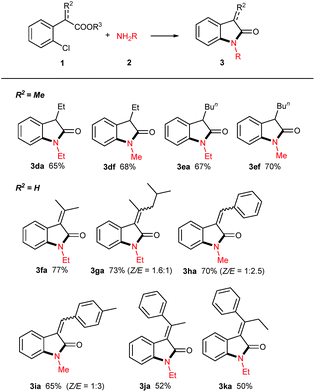
The synthesis of 3-monosubstituted oxindoles remains a challenge. Because 3-unsubstituted oxindoles are reactive enough to alkylation, sequential double alkylation usually occurs. Normally, they are produced via post-functionalization, for example, by the condensation of 3-unsubstituted indolin-2-ones with carbonyl compounds followed by reduction. As such, we attended to extend this cascade reaction to the synthesis of 3-monosubstituted oxindoles. Delightedly, 2-alkylated o-chlorophenylacetic acid esters can be smoothly converted into 3-alkylated oxindoles in moderate yields (3da, 3df, 3ea, 3ef, Table 3). In these cases, it is not necessary to use the acetic acids as precursor. Additionally, the use of 2-(2-chlorophenyl)acrylic acids 1f–k were attempted, and the desired 3-methyleneindolin-2-ones were furnished in acceptable yields (3fa–3ka). In the cases of 1g–I, the products were mixtures of Z/E isomers, which can readily be isolated by preparative thin-layer chromatography. Interestingly, as for the acids 1j & 1k, only the E-isomers were isolated in yields of 52% & 50%, respectively. The configurations of all the isomers were assigned based on the documented reports including the results of Studer.12 Noteworthy, no aza-Michael adducts resulted under standard conditions, although 3fa–ka, especially 3ha and 3ia, are good Michael acceptors.
| a Reaction conditions: 1 (2 mmol), 2 (10 mmol), Cu powder (10 mol%) in a 15 mL sealed tube, 100 °C for 24 h. Isolated yields based on the substrates 1. Z/E ratios were calculated from the isolated isomer yields. |
|---|
 |
After the investigation of amines, their analogues hydrazines or hydroxylamine were attempted (Scheme 2). Interestingly, aqueous hydrazine 2i is an effective coupling partner, and its desired product N-amino oxindole 3ai was obtained in 70% yield after 24 h of reaction. However, N-phenyl hydrazine 2j gave a negative result. Hydroxylamine hydrochloride 2k was used, even in combination with equivalent base (e.g. NaOH, Et3N), and no product was detected except with the starting acid 1a recovered.
To explore the application possibility of this chemistry in industry or organic synthesis, the scale-up experiment was carried out. When 10 mmol of 1a was used to react with ethylamine 2a in a 48 mL sealed tube under the standard conditions, the reaction proceeded smoothly, providing 80% yield of 3aa with a small amount of 1a detected after 16 h.
To gain an insight into the mechanism of this cascade reaction, simple experiments were carried out to unveil the cascade process. When methyl 2-chlorophenylacetamide was used as cyclization precursor under the standard conditions, intramolecular cyclization to indolin-2-one did not occur with the amide almost fully recovered (Scheme 3). This result excluded the possibility of a sequential amide formation/intramolecular Ullmann-type N-arylation process. When the ester of 1f reacted with ethylamine 2a, no reaction also occurred. This suggests that the existence of benzyl C–H, which enables the formation of an enolate, is essential for the esters to realize the present cascade reaction.
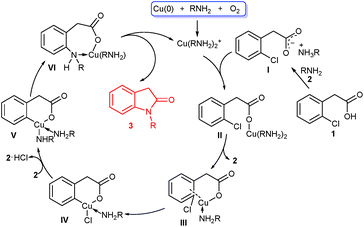
Based on our experimental results and previous reports,6,7,10 a tentative mechanism was proposed in Scheme 4. Initially, Cu(0) powder is oxidized to Cu(I) species such as Cu(RNH2)2+ in the presence of a small amount of O2 and amines via a complicated process. Reaction of the acetic acid 1 with amine 2 affords the ammonium carboxylate I,13 which exchanges with Cu(RNH2)2+ to generate the cuprous carboxylate II. Intramolecular ligand exchange of II produces coordinated III along with the release of amine 2, and further oxidative addition of III furnishes IV. Then IV undergoes chloride/amine ligand exchange with the aid of second amine 2 to form V, followed by reductive elimination to generate coordinated VI. Finally, intramolecular cyclization of VI forms the target product 3 and reactive Cu(I) species.
Conclusions
We have disclosed a ligand- and solvent-free catalytic approach to access oxindoles from o-chloroarylacetic acids with amines using copper powder via one pot sequential Ullmann type amination, and annulative N-acylation. The ortho chelating effect of a carboxyl/ester group and the presence of a small amount of O2 both play essential roles in the C–Cl activation and catalytic activity of copper powder. In view of its efficiency and operational simplicity, this cascade protocol will find its wide application in academic and industrial fields relating to the oxindole chemistry.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21202010), Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (16B003), Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2017JJ2275 & 2015JJ3012), the Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Materials Protection for Electric Power and Transportation (2015CL05), Changsha University of Science & Technology, P. R. China.References
- (a) A. Millemaggi and R. J. K. Taylor, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2010, 4527 CrossRef CAS; (b) M. Kaur, M. Singh, N. Chadha and O. Silakari, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2016, 123, 858 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) J. E. M. N. Klein and R. J. K. Taylor, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2011, 6821 CrossRef CAS; (b) J.-R. Chen, X.-Y. Yu and W.-J. Xiao, Synthesis, 2015, 47, 604 CrossRef CAS; (c) W. Ji, Y. A. Liu and X. Liao, Angew. Chem., 2016, 128, 13480 CrossRef; (d) J. Lv, D. Zhang-Negrerie, J. Deng, Y. Du and K. Zhao, J. Org. Chem., 2014, 79, 1111 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) S. I. Son, W. K. Lee, J. Choi and H.-J. Ha, Green Chem., 2015, 17, 3306 RSC; (f) P. Patel and G. Borah, Chem. Commun., 2017, 53, 443 RSC; (g) J. Bergman, in Chapter One – Oxindoles, ed. F. V. S. Eric and A. R. Christopher, Academic Press, 2015, vol. 117, pp. 1–81 Search PubMed.
- (a) J.-L. Han and C.-H. Chang, Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 2322 RSC; (b) D. Cheng, F. Ling, C. Zheng and C. Ma, Org. Lett., 2016, 18, 2435 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) N. Xu, D.-W. Gu, J. Zi, X.-Y. Wu and X.-X. Guo, Org. Lett., 2016, 18, 2439 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) R. Moradi, G. M. Ziarani and N. Lashgari, ARKIVOC, 2017, 148 CAS; (e) P. Qian, J.-H. Su, Y. Wang, M. Bi, Z. Zha and Z. Wang, J. Org. Chem., 2017, 82, 6434 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) X. Jiang, J. Yang, F. Zhang, P. Yu, P. Yi, Y. Sun and Y. Wang, Org. Lett., 2016, 18, 3154 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) X. Jiang, F. Zhang, J. Yang, P. Yu, P. Yi, Y. Sun and Y. Wang, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2016, 358, 3938 CrossRef CAS; (c) L. Liu and Z. Wang, Green Chem., 2017, 19, 2076 RSC.
- R. R. Poondra and N. J. Turner, Org. Lett., 2005, 7, 863 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) F. Monnier and M. Taillefer, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2009, 48, 6954 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) C. Sambiagio, S. P. Marsden, A. J. Blacker and P. C. McGowan, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 3525 RSC.
- J. Jiao, X. R. Zhang, N. H. Chang, J. Wang, J. F. Wei, X. Y. Shi and Z. G. Chen, J. Org. Chem., 2011, 76, 1180 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) R. Giri and J.-Q. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 14082 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) D.-H. Wang, T.-S. Mei and J.-Q. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 17676 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) K. M. Engle, D.-H. Wang and J.-Q. Yu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 6169 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) B.-F. Shi, Y.-H. Zhang, J. K. Lam, D.-H. Wang and J.-Q. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 460 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) D.-H. Wang, K. M. Engle, B.-F. Shi and J.-Q. Yu, Science, 2010, 327, 315 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) K. M. Engle, P. S. Thuy-Boun, M. Dang and J.-Q. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 18183 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) P. S. Thuy-Boun, G. Villa, D. Dang, P. Richardson, S. Su and J.-Q. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 17508 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) N. Dastbaravardeh, T. Toba, M. E. Farmer and J.-Q. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 9877 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) K. M. Engle, D.-H. Wang and J.-Q. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 14137 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (j) K.-J. Xiao, L. Chu and J.-Q. Yu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 2856 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (k) S. Li, G.-J. Deng, F. Yin, C.-J. Li and H. Gong, Org. Chem. Front., 2017, 4, 417 RSC; (l) Y. Wang, J.-Y. Gu and Z.-J. Shi, Org. Lett., 2017, 19, 1326 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (m) Y.-Q. Zhu, Y. Liu, H. N. Wang, W. B. Liu and C.-J. Li, Org. Chem. Front., 2016, 3, 971 RSC; (n) Q. Jiang, C. Zhu, H. Zhao and W. Su, Chem.–Asian J., 2016, 11, 356 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (o) R. Mei, C. Zhu and L. Ackermann, Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 13171 RSC; (p) A. Biafora, T. Krause, D. Hackenberger, F. Belitz and L. J. Gooßen, Angew. Chem., 2016, 128, 14972 CrossRef; (q) X.-Y. Shi, A. Renzetti, S. Kundu and C.-J. Li, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2014, 356, 723 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) J.-S. Li, D.-M. Fu, Y. Xue, Z.-W. Li, D.-L. Li, Y.-D. Da, F. Yang, L. Zhang, C.-H. Lu and G. Li, Tetrahedron, 2015, 71, 2748 CrossRef CAS; (b) J.-S. Li, F.-F. Cai, Z.-W. Li, W.-D. Liu, J. Simpson, Y. Xue, H.-L. Pang, P.-M. Huang, Z. Cao and D.-L. Li, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 474 RSC; (c) J.-S. Li, Y. Xue, Z.-W. Li, W.-D. Liu, C.-H. Lu and P.-X. Zhao, Synlett, 2013, 24, 2003 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Cai, B. Zou and D. Ma, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2006, 45, 1276 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Under neat condition, the Cu(II) species might be reduced by an aliphatic amine to in situ generate the Cu(I) ones. See: R. D. Patil and S. Adimurthy, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2011, 353, 1695 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) A. Teichert, K. Jantos, K. Harms and A. Studer, Org. Lett., 2004, 6, 3477 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) X.-N. Wang, Y.-Y. Zhang and S. Ye, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2010, 352, 1892 CrossRef CAS; (c) S. Tang, P. Peng, P. Zhong and J.-H. Li, J. Org. Chem., 2008, 73, 5476 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) T.-S. Jiang, R.-Y. Tang, X.-G. Zhang, X.-H. Li and J.-H. Li, J. Org. Chem., 2009, 74, 8834 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- In the case of the esters 1d & 1e, their corresponding enolates I′ could be formed as the intermediates
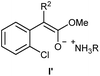 .
.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Detailed experimental procedures and copies of NMR spectra are included. See DOI: 10.1039/c7ra08123e |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 |