Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCarbon dioxide hydrogenation catalysed by well-defined Mn(I) PNP pincer hydride complexes†
Federica
Bertini
 a,
Mathias
Glatz
a,
Mathias
Glatz
 b,
Nikolaus
Gorgas
b,
Nikolaus
Gorgas
 b,
Berthold
Stöger
b,
Berthold
Stöger
 c,
Maurizio
Peruzzini
c,
Maurizio
Peruzzini
 a,
Luis F.
Veiros
a,
Luis F.
Veiros
 d,
Karl
Kirchner
d,
Karl
Kirchner
 *b and
Luca
Gonsalvi
*b and
Luca
Gonsalvi
 *a
*a
aConsiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR), Istituto di Chimica dei Composti Organometallici (ICCOM), Via Madonna del Piano 10, 50019 Sesto Fiorentino, Firenze, Italy. E-mail: l.gonsalvi@iccom.cnr.it
bInstitute of Applied Synthetic Chemistry, Vienna University of Technology, Getreidemarkt 9/163-AC, A-1060 Wien, Austria. E-mail: karl.kirchner@tuwien.ac.at
cInstitute of Chemical Technologies and Analytics, ViennaUniversity of Technology, Getreidemarkt 9/163-AC, A-1060 Wien, Austria
dCentro de Química Estrutural, Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Av. Rovisco Pais No. 1, 1049-001 Lisbon, Portugal
First published on 4th May 2017
Abstract
The catalytic reduction of carbon dioxide is of great interest for its potential as a hydrogen storage method and to use carbon dioxide as C-1 feedstock. In an effort to replace expensive noble metal-based catalysts with efficient and cheap earth-abundant counterparts, we report the first example of Mn(I)-catalysed hydrogenation of CO2 to HCOOH. The hydride Mn(I) catalyst [Mn(PNPNH-iPr)(H)(CO)2] showed higher stability and activity than its Fe(II) analogue. TONs up to 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 and quantitative yields were obtained after 24 h using DBU as the base at 80 °C and 80 bar total pressure. At catalyst loadings as low as 0.002 mol%, TONs greater than 30
000 and quantitative yields were obtained after 24 h using DBU as the base at 80 °C and 80 bar total pressure. At catalyst loadings as low as 0.002 mol%, TONs greater than 30![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 could be achieved in the presence of LiOTf as the co-catalyst, which are among the highest activities reported for base-metal catalysed CO2 hydrogenations to date.
000 could be achieved in the presence of LiOTf as the co-catalyst, which are among the highest activities reported for base-metal catalysed CO2 hydrogenations to date.
Introduction
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the end product of combustion of organic matter and its increasing concentration in the atmosphere is causing great concerns due to its negative effects on the environment. On the other hand, it can represent a cheap, readily available and abundant carbon feedstock, and its utilisation for the production of value-added chemicals and fuels is a hot topic of research today.1 Among the possible target reactions, the catalytic hydrogenation of CO2 to formic acid (FA) and its derivatives is a subject of increasing interest, as FA is a widely employed commodity chemical and can be used as a hydrogen storage material.2In recent years, a number of efficient homogeneous catalysts for the hydrogenation of CO2 to FA under mild reaction conditions have been developed, most of them based on expensive and rare noble metals such as iridium and ruthenium.3 The replacement of the scarce and expensive noble metals with cheaper, earth abundant, and less toxic first-row transition metals would enhance the sustainability and industrial applicability of these hydrogenation reactions. Recently, iron- and cobalt-based homogeneous catalysts have been reported for this reaction (Scheme 1),4 and in some cases show a catalytic activity comparable to that observed for some noble metal catalysts. Beller and co-workers described Fe(II)- and Co(II)-PP3 catalysts (PP3 = tripodal tetraphosphines) that could reach significantly high turnover numbers (TONs) for CO2 hydrogenation to FA and derivatives.4g,i,j Milstein reported that the PNP pincer complex trans-[Fe(PNP-tBu)(H)2(CO)] promotes the reaction already at a low pressure with TONs up to 788.4h In 2015, Hazari, Bernskoetter and co-workers described the catalytic activity of a library of Fe(PNP) pincer complexes exhibiting very high activities which could be even further enhanced using Lewis acid co-catalysts achieving TONs up to ca. 59![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000. This sets the current state-of-the-art in CO2 hydrogenation to FA with a non-precious, earth-abundant metal catalyst.4b More recently, the beneficial effect of Lewis acid co-catalysts was demonstrated also for related cobalt pincer complexes.4k
000. This sets the current state-of-the-art in CO2 hydrogenation to FA with a non-precious, earth-abundant metal catalyst.4b More recently, the beneficial effect of Lewis acid co-catalysts was demonstrated also for related cobalt pincer complexes.4k
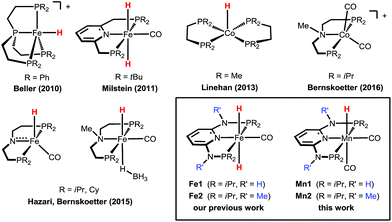 | ||
| Scheme 1 Examples of efficient base-metal catalysts for the hydrogenation of carbon dioxide to formic acid or formate. | ||
Recently,4a we demonstrated the remarkable catalytic activity of the Fe(II) PNP pincer complexes [Fe(PNPNH-iPr)(H)2(CO)] (Fe1) and [Fe(PNPNMe-iPr)(H)2(CO)] (Fe2) for CO2 hydrogenation reaching TONs of up to ca. 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 in the presence of a base with quantitative yields of formate at 80 °C (Scheme 1). Complex Fe2 also exhibited a significant activity even at room temperature affording FA in quantitative yield (TON ca. 1000) in 24 h. Based on these results, we decided to explore the activities of other earth-abundant metal complexes starting with low valent manganese compounds. As yet, in contrast to iron, manganese plays a minor role, despite the fact that manganese, after iron and titanium, is the third most abundant transition metal in the earth’s crust, and ubiquitously available and essentially non-toxic. Reports on homogeneous Mn(I) catalysed reactions only appeared very recently in the literature from the groups of Milstein,5 Beller,6 Kirchner,7 Kempe,8 and Boncella9 and their collaborators.
000 in the presence of a base with quantitative yields of formate at 80 °C (Scheme 1). Complex Fe2 also exhibited a significant activity even at room temperature affording FA in quantitative yield (TON ca. 1000) in 24 h. Based on these results, we decided to explore the activities of other earth-abundant metal complexes starting with low valent manganese compounds. As yet, in contrast to iron, manganese plays a minor role, despite the fact that manganese, after iron and titanium, is the third most abundant transition metal in the earth’s crust, and ubiquitously available and essentially non-toxic. Reports on homogeneous Mn(I) catalysed reactions only appeared very recently in the literature from the groups of Milstein,5 Beller,6 Kirchner,7 Kempe,8 and Boncella9 and their collaborators.
Here, we report the first efficient hydrogenation of CO2 to FA catalysed by the well-defined Mn(I) catalysts [Mn(PNPNH-iPr)(H)(CO)2] (Mn1) and [Mn(PNPNMe-iPr)(H)(CO)2] (Mn2). These complexes are isoelectronic with our previously tested Fe(II) catalysts (Fe1 and Fe2), and Mn1 was shown very recently to be highly active in the dehydrogenative coupling of alcohols and amines to give imines7a as well as in the synthesis of substituted quinolines and pyrimidines.7b
Results and discussion
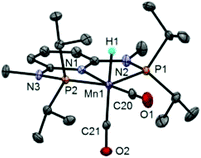
The synthesis of the complexes [Mn(PNPNH-iPr)(H)(CO)2] (Mn1) and [Mn(PNPNMe-iPr)(H)(CO)2] (Mn2) was carried out as recently described by some of us.7a In addition, X-ray quality crystals of Mn2 were grown from toluene/pentane and the corresponding solid state structure was obtained (Fig. 1 and ESI†). The structural data are comparable with those obtained for Mn1,7a with slightly shorter bond distances for Mn1–C20 (1.700 vs. 1.747 Å) and longer distances for Mn1–C21 (1.784 vs. 1.775 Å) and Mn1–H1 (1.80 vs. 1.46 Å).Catalytic CO2 hydrogenation
The catalytic activity of the Mn(I) pincer complexes Mn1 and Mn2 was initially tested in a THF/H2O (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) solvent mixture in the presence of DBU (DBU = 1,8-diazabicycloundec-7-ene) as the base, at 80 °C, under 80 bar total pressure (H2
1) solvent mixture in the presence of DBU (DBU = 1,8-diazabicycloundec-7-ene) as the base, at 80 °C, under 80 bar total pressure (H2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CO2 = 1
CO2 = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), for 24 h.10 Selected results are reported in Table 1. Using a Mn1/DBU ratio of 1
1), for 24 h.10 Selected results are reported in Table 1. Using a Mn1/DBU ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1000, FA was obtained in quantitative yields with respect to DBU (TON = 1000, entry 1). At lower catalyst loadings (Mn1/DBU = 1
1000, FA was obtained in quantitative yields with respect to DBU (TON = 1000, entry 1). At lower catalyst loadings (Mn1/DBU = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10
10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000; [Mn1] = 0.18 μmol mL−1), FA was formed in a 55% yield after 24 h (TON = 5520, entry 2). Notably, under such reaction conditions Mn1 had a superior performance compared to Fe1 and Fe2, which in turn gave the TONs of 2080 and 2750 respectively (entries 3 and 4).
000; [Mn1] = 0.18 μmol mL−1), FA was formed in a 55% yield after 24 h (TON = 5520, entry 2). Notably, under such reaction conditions Mn1 had a superior performance compared to Fe1 and Fe2, which in turn gave the TONs of 2080 and 2750 respectively (entries 3 and 4).
| Entry | Cat | Cat/DBU ratio | Solvent | TONb | Yieldc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
a General reaction conditions: catalyst (0.2–10 μmol), 10 mmol DBU, 5.5 mL solvent, 80 °C, 80 bar total pressure (H2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CO2 = 1 CO2 = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), 24 h.
b TON = (mmol FA)/(mmol catalyst).
c Yield = [(mmol FA)/(mmol DBU)] × 100. The yield of formate was calculated from the integration of the corresponding 1H NMR signal, using DMF as the standard.
d 48 h reaction time. All experiments were repeated at least twice, av. error ca. 6%. 1), 24 h.
b TON = (mmol FA)/(mmol catalyst).
c Yield = [(mmol FA)/(mmol DBU)] × 100. The yield of formate was calculated from the integration of the corresponding 1H NMR signal, using DMF as the standard.
d 48 h reaction time. All experiments were repeated at least twice, av. error ca. 6%.
|
|||||
| 1 | Mn1 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1000 1000 |
THF/H2O | 1000 | >99 |
| 2 | Mn1 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF/H2O | 5520 | 55 |
| 3 | Fe1 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF/H2O | 2080 | 21 |
| 4 | Fe2 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF/H2O | 2750 | 28 |
| 5d | Mn1 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF/H2O | 8600 | 86 |
| 6 | Mn2 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF/H2O | 1010 | 10 |
| 7 | Mn1 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF | 4400 | 44 |
| 8 | Mn2 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF | 420 | 4 |
| 9 | Fe1 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | Fe2 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF | 0 | 0 |
| 11 | Mn1 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF/H2O | 9100 | 16 |
| 12 | Mn1 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
EtOH | 8000 | 80 |
| 13 | Mn2 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
EtOH | 1330 | 13 |
| 14 | Fe1 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
EtOH | 0 | 0 |
| 15 | Fe2 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
EtOH | 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
>99 |
| 16 | Mn3 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF/H2O | 5750 | 58 |
Furthermore, increasing the reaction time for the Mn1 tests to 48 h significantly improved the yield of formate (86%, TON = 8600, entry 5). In contrast, Mn2 showed a lower catalytic activity, affording FA in only a 10% yield with a TON of 1010 after 24 h (entry 6). For 3 h runs under standard conditions, Mn1 gave a TON = 475 (yield = 48%), and Mn2 gave a TON = 96 (yield = 10%). Decreasing the catalyst concentration to 0.036 μmol mL−1 (Mn1/DBU = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50
50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000) afforded FA in a lower yield (16%) but with a significantly increased TON (9100, entry 11), indicating that the catalyst activity strongly depends on the catalyst/DBU ratio.
000) afforded FA in a lower yield (16%) but with a significantly increased TON (9100, entry 11), indicating that the catalyst activity strongly depends on the catalyst/DBU ratio.
The promoting effect of adding H2O (10%) to THF may be attributed to a water-assisted dissociation of the formate ligand resulting from the CO2 insertion into the Mn–H bond under catalytic conditions (see DFT calculations), as well as to an improved stabilization of the FA/DBU adduct due to hydrogen bonding. This is supported by the observation that the FA/DBU adduct is immiscible with THF, but cleanly dissolves in H2O. However, a striking difference between the Mn and Fe catalysts was observed when running the tests in anhydrous THF. Whereas with the Mn(I) complexes FA was formed even in the absence of water, albeit with lower TONs (4400 and 420 for Mn1 and Mn2, entries 7 and 8, respectively), and Fe1 and Fe2 were completely inactive under these conditions (entries 9 and 10). We thus re-examined the solvent effects for the Fe catalysts Fe1 and Fe2.4a
While their catalytic activity in the THF/H2O mixtures is comparable (entries 3 and 4), we observed a substantial difference running the tests in EtOH. In this solvent, the catalytic activity of Fe2 is substantially improved (TON = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000; >99% yield, entry 15), while Fe1 resulted in being totally inactive (0% yield, entry 14), confirming the data previously reported.4a The reason for the latter observation is that for Fe1 EtOH prevents the formation of the key catalytic intermediates [Fe(PNPNH-iPr)(H)2(CO)]. This was not the case for Fe2, which readily affords the corresponding dihydrides in the presence of the base and H2.11b We then studied the effect of EtOH in the hydrogenation of CO2 catalysed by Mn1 and Mn2. To our delight, using EtOH as the solvent improved the catalytic performance of Mn1 (entry 12) significantly, which afforded FA in an 80% yield (TON = 8000). In turn, only a minor improvement was observed for Mn2 (entry 13).
000; >99% yield, entry 15), while Fe1 resulted in being totally inactive (0% yield, entry 14), confirming the data previously reported.4a The reason for the latter observation is that for Fe1 EtOH prevents the formation of the key catalytic intermediates [Fe(PNPNH-iPr)(H)2(CO)]. This was not the case for Fe2, which readily affords the corresponding dihydrides in the presence of the base and H2.11b We then studied the effect of EtOH in the hydrogenation of CO2 catalysed by Mn1 and Mn2. To our delight, using EtOH as the solvent improved the catalytic performance of Mn1 (entry 12) significantly, which afforded FA in an 80% yield (TON = 8000). In turn, only a minor improvement was observed for Mn2 (entry 13).
Effect of LiOTf
In an effort to further improve the Mn-DBU catalytic system, and in line with literature data on other Fe-pincer systems,4b we decided to test the effect of a Lewis acid additive in combination with Mn1, choosing LiOTf as it has previously shown to give the highest promoting effect.4b The results are summarized in Table 2. As previously observed for Fe2,4a the addition of LiOTf only had a minor effect on the catalysis in the presence of Mn1 when the reaction was run in EtOH (entries 1 and 2). In contrast to that, an enhancement effect was observed when using THF/H2O (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) as the solvent mixture. At a catalyst concentration of [Mn1] = 0.18 μmol mL−1 and in the presence of 0.5 mmol of LiOTf (Mn1/DBU = 1
1) as the solvent mixture. At a catalyst concentration of [Mn1] = 0.18 μmol mL−1 and in the presence of 0.5 mmol of LiOTf (Mn1/DBU = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10
10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000; Mn1/LiOTf = 1
000; Mn1/LiOTf = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1000), FA was obtained in quantitative yields within the first 24 h of the reaction (TON = 10
1000), FA was obtained in quantitative yields within the first 24 h of the reaction (TON = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000, entry 3).
000, entry 3).
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) in the presence of LiOTf as the co-catalysta
1) in the presence of LiOTf as the co-catalysta
| Entry | Mn1/DBU ratio | Solvent | LiOTf (mmol) | T (°C) | TONb | Yieldc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
a General reaction conditions: catalyst (0.1–10 μmol), LiOTf (0.5–1.5 mmol), 10 mmol DBU, 5.5 mL solvent, 80 °C, 80 bar total pressure (H2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CO2 = 1 CO2 = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), 24 h.
b TON = (mmol FA)/(mmol catalyst).
c Yield = [(mmol FA)/(mmol DBU)] × 100. The yield of formate was calculated from the integration of the corresponding 1H NMR signal, using DMF as the internal standard.
d 48 h reaction time.
e 72 h reaction time. All experiments were repeated at least twice, av. error ca. 6%. 1), 24 h.
b TON = (mmol FA)/(mmol catalyst).
c Yield = [(mmol FA)/(mmol DBU)] × 100. The yield of formate was calculated from the integration of the corresponding 1H NMR signal, using DMF as the internal standard.
d 48 h reaction time.
e 72 h reaction time. All experiments were repeated at least twice, av. error ca. 6%.
|
||||||
| 1 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
EtOH | 1.0 | 80 | 8700 | 87 |
| 2 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
EtOH | 1.0 | 80 | 5000 | 10 |
| 3 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF/H2O | 0.5 | 80 | 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
>99 |
| 4 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF/H2O | 0.5 | 25 | 1000 | 10 |
| 5 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF/H2O | 0.5 | 80 | 13![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 200 200 |
26 |
| 6 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 100 100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF/H2O | 0.5 | 80 | 14![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 800 800 |
15 |
| 7d | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF/H2O | 0.5 | 80 | 26![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 600 600 |
53 |
| 8 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF/H2O | 1.0 | 80 | 16![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 700 700 |
33 |
| 9 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF/H2O | 1.5 | 80 | 12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 420 420 |
25 |
| 10 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF/H2O | 1.0 | 100 | 31![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 600 600 |
63 |
| 11 | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF/H2O | 1.0 | 115 | 31![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 200 200 |
62 |
| 12e | 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
THF/H2O | 1.0 | 80 | 30![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
60 |
Remarkably, the reaction also proceeds at room temperature, albeit with a TON an order of magnitude lower (TON = 1000, entry 4). Lower catalyst concentrations of 0.036 and 0.018 μmol mL−1 resulted in higher TONs but lower yields (entries 5 and 6). A longer catalytic run (entry 7) indicated that the catalyst remains active for up to 48 h, affording FA with a TON = 26![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 600, a ca. two-fold increase compared to the 24 h catalytic run (entry 5), suggesting a constant reaction rate with an average TOF of ca. 550 h−1. Increasing the LiOTf amount to 1.0 mmol (Mn1/LiOTf = 1
600, a ca. two-fold increase compared to the 24 h catalytic run (entry 5), suggesting a constant reaction rate with an average TOF of ca. 550 h−1. Increasing the LiOTf amount to 1.0 mmol (Mn1/LiOTf = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5000) resulted in an increased TON = 16
5000) resulted in an increased TON = 16![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 700 (entry 8), whereas a further increase to 1.5 mmol gave a slightly decreased TON = 12
700 (entry 8), whereas a further increase to 1.5 mmol gave a slightly decreased TON = 12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 420 (entry 9). As previously suggested,4b such an effect may be attributed to the limited LiOTf solubility in such a solvent mixture.
420 (entry 9). As previously suggested,4b such an effect may be attributed to the limited LiOTf solubility in such a solvent mixture.
The effect of the temperature on the catalysis was tested by increasing it from 80 to 100 °C, which resulted in a ca. 2-fold increase in the TON to 31![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 600 after 24 h (63% yield, entry 10). However, increasing the temperature further to 115 °C resulted in the formation of an unidentified side product (4) in a ca. 25% yield with respect to DBU, along with a yield of formate of ca. 62% (entry 11). Trace amounts of the same by-product (<5%) were also observed at 100 °C. Careful examination of the 1H and 13C{1H} NMR spectra showed new signals (δH = 8.00, δC = 161.7) typical for N-formyl groups, suggesting that N-formylation of DBU occurs as a side reaction at high temperatures (see ESI†). This attribution was confirmed by obtaining the same product independently from the reaction of FA with DBU (1
600 after 24 h (63% yield, entry 10). However, increasing the temperature further to 115 °C resulted in the formation of an unidentified side product (4) in a ca. 25% yield with respect to DBU, along with a yield of formate of ca. 62% (entry 11). Trace amounts of the same by-product (<5%) were also observed at 100 °C. Careful examination of the 1H and 13C{1H} NMR spectra showed new signals (δH = 8.00, δC = 161.7) typical for N-formyl groups, suggesting that N-formylation of DBU occurs as a side reaction at high temperatures (see ESI†). This attribution was confirmed by obtaining the same product independently from the reaction of FA with DBU (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) at 120 °C in THF/H2O (10
1) at 120 °C in THF/H2O (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) in the absence of the catalysts (see details in ESI†). The catalytic tests run at 80 °C with longer reaction times (72 h, entry 12) also gave high TONs of ca. 30
1) in the absence of the catalysts (see details in ESI†). The catalytic tests run at 80 °C with longer reaction times (72 h, entry 12) also gave high TONs of ca. 30![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 (60% formate yield) but in this case no N-formylation of DBU was observed, confirming that this side reaction is triggered by temperature effects.
000 (60% formate yield) but in this case no N-formylation of DBU was observed, confirming that this side reaction is triggered by temperature effects.
Mechanistic studies
Details on the reaction mechanism were obtained for the most active catalytic system, complex Mn1, by a combination of experimental NMR techniques and DFT calculations. The reactivity of complexes Mn1 and Mn2 towards CO2 was initially investigated in a stoichiometric reaction by NMR and IR techniques. When a solution of Mn1 in THF was stirred under an atmosphere of CO2 (1 bar) for ca. 1 min, the immediate formation of the formate complex [Mn(PNPNH-iPr)(CO)2(κ1-O-OC(O)H)] (Mn3) was observed (Scheme 2). The complex precipitated from the solution in essentially quantitative yield (see ESI†). This complex is characterised by a 1H NMR singlet at δ = 8.21 ppm for the proton of the formyl ligand. In the IR spectrum, the characteristic νCO frequencies for the cis-CO and for the formyl carbonyl ligands were observed at 1923, 1842, and 1593 cm−1, respectively. Mn3 could also be obtained by reacting Mn1 with 1 equiv. of HCOOH in THF at room temperature. In the case of Mn2, no reaction was observed with either CO2 or HCOOH under the above conditions. It was possible to prove the reversibility of the CO2 insertion in Mn1 by reacting Mn3 with H2 (70 bar) in the presence of excess DBU at room temperature in THF (Scheme 2), whereas no reaction took place in the absence of base.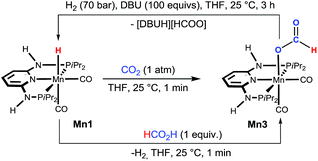 | ||
| Scheme 2 Reaction of Mn1 with CO2 (1 atm) and FA (1 equiv.) to give Mn3. For the former reaction, the reversibility from Mn3 to Mn1 was also demonstrated. | ||
Interestingly, isolated Mn3 was also active in the catalysis, giving comparable activity to Mn1 under the same test conditions (Table 1, entry 16 vs. 2), as expected for a reaction intermediate. The reactivity of Mn1 with CO2 to give the formate complexes is somewhat remarkable, since the isostructural and isoelectronic cationic Fe analogues cis-[Fe(PNPNR-iPr)(CO)2H]+ (Fe3, R = H and Fe4, R = Me) were found to be catalytically inactive for the hydrogenation of ketones and aldehydes,11b as well as in stoichiometric reactions with CO2. We reasoned that this could be related to the electron density around the metal and in particular with the M–H bond. Indeed, the corresponding atomic charges (NPA, see ESI†) were found to be CMn = −0.92/CH = −0.13 in Mn1 and CFe = −0.53/CH = −0.04 in Fe3, showing an electron richer metallic centre and hydride ligand in the case of Mn1 (Scheme 3). Moreover, the M–H bond is weaker in the case of M = Mn as shown by the corresponding Wiberg indices12 (WIMn–H = 0.43, WIFe–H = 0.47), indicating a more reactive hydride for Mn1 than for Fe3. The free energy balances (gas phase) calculated for the reaction of the CO2 insertion into the M–H bond (Scheme 3) corroborate the previous conclusions, including the absence of the reactivity of Mn2 toward CO2 at room temperature.
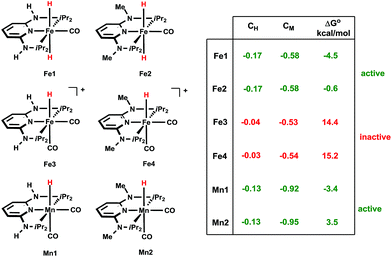 | ||
| Scheme 3 Comparison of NPA charges for the Fe(II) and Mn(I) pincer complexes and computational free energies ΔGo for the CO2 insertion into the metal–H bond to yield the κ1-O formate complexes according to Scheme 2. | ||
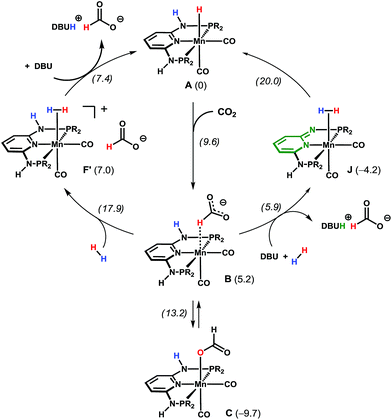
A deeper insight into the reaction mechanism was obtained by DFT calculations.13 Free energy profiles obtained for the entire reaction are presented in the ESI.† An explicit water molecule was considered in the model providing H-bond stabilisation for the intermediates (see ESI†). Two alternative mechanisms were investigated for the most active Mn catalyst Mn1. In the first mechanism (Scheme 4, left and Fig. S9 in ESI†), a purely metal-centred mechanism is considered, i.e. without the participation of the N–H bond of the PNP ligand. This path starts with a nucleophilic attack of the hydride in intermediate A to the carbon dioxide C-atom, in an outer sphere reaction. This affords an intermediate (B) with a formate ligand bound to Mn in a C–H σ-complex, with an accessible barrier of 9.6 kcal mol−1.14B is less stable than the initial reactants (A) by ΔG = 5.2 kcal mol−1. From B, two pathways are possible. Formato ligand isomerisation can be achieved through a transition state with the energy of 13.2 kcal mol−1, yielding a κ1-O formate complex (C, corresponding to isolated Mn3), 9.7 kcal mol−1 more stable than the reagents, representing a resting state of the catalyst. Alternatively, the exchange of the formate in B by one H2 molecule can give a dihydrogen complex (F′), 7.0 kcal mol−1 less stable than the initial reagents (A). The H2 coordination step has the highest energy transition state of the entire mechanism (ΔG≠ = 17.9 kcal mol−1). Finally, the deprotonation of the dihydrogen intermediate F′ (by either formate or DBU) regenerates the initial hydride complex Mn1 while the final product is obtained as [DBUH][HCOO]. Overall, the reaction has a barrier of 27.6 kcal mol−1, considering C as the catalyst resting state, and the entire reaction is thermodynamically favorable with ΔG = −11.2 kcal mol−1.
In the second path investigated (Scheme 4, right and Fig. S10 in ESI†) a bifunctional mechanism with the participation of the N–H bond of the PNP ligand is considered. Here, the first step corresponds to the formation of the Mn-bound formate C–H σ-complex B, as in the previous mechanism. From B, the base (DBU) deprotonates the N–H group of the PNP ligand and releases the formate ion yielding the product as [DBUH][HCOO]. In turn, the so-obtained five-coordinated Mn neutral complex, bearing a formally negative PNP ligand (Fig. S10 in ESI†), readily coordinates to H2 and the resulting Mn(η2-H2) complex (J) is 4.2 kcal mol−1 more stable than the starting species A. Water- (or protic solvent) assisted H–H bond splitting from complex J follows, yielding back the initial catalyst by forming a Mn–H hydride bond and reprotonating the PNP ligand. This last step has a transition as high as 20.0 kcal mol−1, which is the highest of this path. The overall barrier for the reaction is 29.7 kcal mol−1 (with respect to C), which is within 2 kcal mol−1 from the first pathway considered.
We then turned our attention to the effects of the Li additive. We investigated the relative stabilities of the intermediates B and C in the presence of the Li(THF)2+ adducts (Fig. 2 and ESI†) and compared them with the values obtained in the absence of Li. The energy difference between B·Li(THF)2 and C·Li(THF)2 is 11.2 kcal mol−1, i.e., 3.4 kcal mol−1 smaller than the difference between B and C. The increased stabilisation in B·Li(THF)2 may be attributed to the κ2-O,O formate chelation of Li(THF)2+, and will have a promoting effect on the catalysis by favoring the κ1-H formate B over the κ1-O formate resting state C. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first quantification of the Li effect for base-metal catalysed CO2 hydrogenation by DFT calculations.
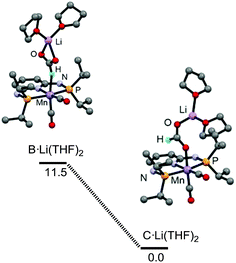 | ||
| Fig. 2 Relative stability (free energy, kcal mol−1) and structures of the intermediates B·Li(THF)2 and C·Li(THF)2. | ||
In summary, both mechanisms described above are competitive with overall barriers within 2 kcal mol−1 of each other. The two pathways feature different roles of the free base (DBU). In the first case, DBU can either react with FA produced from the CO2 hydrogenation yielding [DBUH][HCOO] in an acid–base process, or deprotonate the η2-H2 coordinated ligand, directly forming [DBUH][HCOO]. In the second mechanism, DBU deprotonates the N–H bond of the PNP ligand and forms [DBUH][HCOO] with an uncoordinated formate anion. Based on the results of the catalytic experiments, however, we conclude that the bifunctional pathway must have a major role in the CO2 hydrogenation in the presence of Mn1. In fact, the activity of Mn2, whose PNP structure does not allow for metal–ligand cooperation due to the NMe groups instead of NH groups, is much lower than that of Mn1.
Conclusions
In conclusion, this study has shown for the first time that CO2 catalytic hydrogenation to FA can be achieved with high TONs and yields using well-defined hydrido carbonyl Mn(I) PNP pincer complexes in the presence of an added base (DBU) and a Lewis acid (LiOTf), paving the way for the use of manganese as an earth-abundant and cheap metal for efficient Carbon Dioxide Utilization (CDU). DFT calculations showed that, in the case of the most active catalyst Mn1, the reaction can follow two competing routes, involving either a metal-centred or a ligand-assisted mechanism, based on the possible bifunctional role of the PNPNR ligand when R = H. Further studies are in progress to assess the effects of ligand structural modifications on this reaction and to expand the scope of the catalysts to other challenging CDU processes.Acknowledgements
Financial contributions by the ECRF through the project ENERGYLAB are gratefully acknowledged. This work was also supported by COST Action CM1205 CARISMA (Catalytic Routines for Small Molecule Activation). LFV acknowledges Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia, grant UID/QUI/00100/2013. NG and KK gratefully acknowledge the Financial support by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) (Project No. P29584-N28).Notes and references
- (a) M. Aresta, A. Dibenedetto and E. Quaranta, J. Catal., 2016, 343, 2–45 CrossRef CAS; (b) I. Omae, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2012, 256, 1384–1405 CrossRef CAS; (c) T. Sakakura, J.-C. Choi and H. Yasuda, Chem. Rev., 2007, 107, 2365–2387 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) M. Aresta, in Carbon Dioxide as Chemical Feedstock, ed. M. Aresta, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2010, pp. 1–13 Search PubMed; (e) W.-H. Wang, Y. Himeda, J. T. Muckerman, G. F. Manbeck and E. Fujita, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 12936–12973 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) T. Zell and R. Langer, Recyclable Catalysis, 2015, 2, 87–109 Search PubMed.
- (a) A. K. Singh, S. Singh and A. Kumar, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2016, 6, 12–40 RSC; (b) D. Mellmann, P. Sponholz, H. Junge and M. Beller, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45, 3954–3988 RSC; (c) F. Joo, ChemSusChem, 2008, 1, 805–808 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) S. Enthaler, J. von Langermann and T. Schmidt, Energy Environ. Sci., 2010, 3, 1207–1217 RSC; (e) B. Loges, A. Boddien, F. Gärtner, H. Junge and M. Beller, Top. Catal., 2010, 53, 902–914 CrossRef CAS; (f) J. Klankermayer, S. Wesselbaum, K. Beydoun and W. Leitner, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 7296–7343 CrossRef CAS PubMed (and references therein).
- (a) R. Tanaka, M. Yamashita and K. Nozaki, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 14168–14169 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) T. J. Schmeier, G. E. Dobereiner, R. H. Crabtree and N. Hazari, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 9274–9277 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) S. Moret, P. J. Dyson and G. Laurenczy, Nat. Commun., 2014, 5, 1–7 Search PubMed; (d) J. F. Hull, Y. Himeda, W.-H. Wang, B. Hashiguchi, R. Periana, D. J. Szalda, J. T. Muckerman and E. Fujita, Nat. Chem., 2012, 4, 383–388 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) A. Boddien, C. Federsel, P. Sponholz, D. Mellmann, R. Jackstell, H. Junge, G. Laurenczy and M. Beller, Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5, 8907–8911 RSC; (f) G. A. Filonenko, M. P. Conley, C. Copéret, M. Lutz, E. J. M. Hensen and E. A. Pidko, ACS Catal., 2013, 3, 2522–2526 CrossRef CAS; (g) C. A. Huff and M. S. Sanford, ACS Catal., 2013, 3, 2412–2416 CrossRef CAS; (h) K. Muller, Y. Sun and W. R. Thiel, ChemCatChem, 2013, 5, 1340–1343 CrossRef CAS; (i) G. A. Filonenko, R. Van Putten, E. N. Schulpen, E. J. M. Hensen and E. A. Pidko, ChemCatChem, 2014, 6, 1526–1530 CrossRef CAS; (j) S. F. Hsu, S. Rommel, P. Eversfield, K. Muller, E. Klemm, W. R. Thiel and B. Plietker, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 7074–7078 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) F. Bertini, N. Gorgas, B. Stöger, M. Peruzzini, L. F. Veiros, K. Kirchner and L. Gonsalvi, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 2889–2893 CrossRef CAS; (b) Y. Zhang, A. D. MacIntosh, J. L. Wong, E. A. Bielinski, P. G. Williard, B. Q. Mercado, N. Hazari and W. H. Bernskoetter, Chem. Sci., 2015, 6, 4291–4299 RSC; (c) O. Rivada-Wheelaghan, A. Dauth, G. Leitus, Y. Diskin-Posner and D. Milstein, Inorg. Chem., 2015, 54, 4526–4538 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) F. Zhu, L. Zhu-Ge, G. Yang and S. Zhou, ChemSusChem, 2015, 8, 609–612 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) H. Fong and J. C. Peters, Inorg. Chem., 2015, 54, 5124–5135 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) M. S. Jeletic, M. T. Mock, A. M. Appel and J. C. Linehan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 11533–11536 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) C. Ziebart, C. Federsel, P. Anbarasan, W. Baumann, A. Spannenberg, M. Beller and R. Jackstell, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 20701–20704 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) R. Langer, Y. Diskin-Posner, G. Leitus, L. J. W. Shimon, Y. Ben-David and D. Milstein, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 9948–9952 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) C. Federsel, A. Boddien, R. Jackstell, R. Jennerjahn, P. J. Dyson, R. Scopelliti, G. Laurency and M. Beller, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 9777–9780 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (j) C. Federsel, C. Ziebart, R. Jackstell, W. Baumann and M. Beller, Chem.–Eur. J., 2012, 18, 72–75 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (k) A. Z. Spentzos, C. L. Barnes and W. H. Bernskoetter, Inorg. Chem., 2016, 55, 8225–8233 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Mukherjee, A. Nerush, G. Leitus, L. J. W. Shimon, Y. Ben-David, N. A. E. Jalapa and D. Milstein, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 4298–4301 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) S. Elangovan, C. Topf, S. Fischer, H. Jiao, A. Spannenberg, W. Baumann, R. Ludwig, K. Junge and M. Beller, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 8809–8814 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) M. Perez, S. Elangovan, A. Spannenberg, K. Junge and M. Beller, ChemSusChem, 2017, 10, 83–86 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) S. Elangovan, J. Neumann, J.-B. Sortais, K. Junge, C. Darcel and M. Beller, Nat. Commun., 2016, 7, 12641 CrossRef PubMed; (d) S. Elangovan, M. Garbe, H. Jiao, A. Spannenberg, K. Junge and M. Beller, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 128, 15590–15594 CrossRef.
- (a) M. Mastalir, M. Glatz, N. Gorgas, B. Stöger, E. Pittenauer, G. Allmaier, L. F. Veiros and K. Kirchner, Chem.–Eur. J., 2016, 22, 12316–12320 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) M. Mastalir, M. Glatz, E. Pittenauer, G. Allmaier and K. Kirchner, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 15543–15546 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) F. Kallmeier, T. Irrgang, T. Dietel and R. Kempe, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 11806–11809 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) N. Deibl and R. Kempe, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 1663–1666 CrossRef CAS PubMed (and references therein).
- A. M. Tondreau and J. M. Boncella, Organometallics, 2016, 35, 2049–2052 CrossRef CAS.
- As the hydrogenation of CO2 to FA is a mildly endergonic process, it requires the use of an added base to drive the reaction. Based on our previous work with Fe,4a and screening of base effects in other Fe(PNP) systems,4b we selected DBU as the base of choice for promoting FA production.
- (a) N. Gorgas, B. Stöger, L. F. Veiros and K. Kirchner, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 2664–2672 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) N. Gorgas, B. Stöger, E. Pittenauer, G. Allmaier, L. F. Veiros and K. Kirchner, Organometallics, 2014, 33, 6905–6914 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) B. Bichler, C. Holzhacker, B. Stöger, M. Puchberger, L. F. Veiros and K. Kirchner, Organometallics, 2013, 32, 4114–4121 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Wiberg indices are electronic parameters related to the electron density between atoms. They can be obtained from a natural population analysis and provide an indication of the bond strength. See K. B. Wiberg, Tetrahedron, 1968, 24, 1083 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) R. G. Parr and W. Yang, Density Functional Theory of Atoms and Molecules, Oxford University Press, New York, 1989 Search PubMed; (b) Calculations performed at the PBE0/(SDD, 6-31G**) level using the Gaussian 09 package. All calculations included solvent effects (THF) using the PCM/SMD model. A full account of the computational details and a complete list of references are provided in ESI.†.
- All free energy values are relative to the initial reagent Mn1.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Experimental procedures, NMR and IR spectra, atomic coordinates for DFT optimized structures and computational details, and crystallographic data for 2. CCDC 1520528. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c7sc00209b |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 |