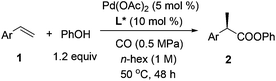Palladium-catalyzed regio- and enantioselective hydroesterification of aryl olefins with CO gas†
Jingfu
Li
 a,
Wenlong
Ren
a,
Jie
Dai
a and
Yian
Shi
*ab
a,
Wenlong
Ren
a,
Jie
Dai
a and
Yian
Shi
*ab
aState Key Laboratory of Coordination Chemistry, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
bDepartment of Chemistry, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado 80523, USA. E-mail: Yian.Shi@colostate.edu
First published on 18th September 2017
Abstract
An effective Pd-catalyzed regio- and enantioselective hydroesterification of aryl olefins with CO gas is described. A variety of phenyl 2-arylpropanoates can be obtained in good yields with high b/l ratios and ees.
Introduction
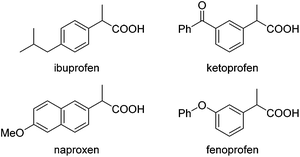
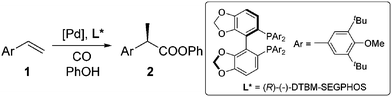
Carboxylic acids and esters are a class of important compounds for pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, and organic synthesis. For example, 2-arylpropanoic acids such as ibuprofen, naproxen, ketoprofen, and fenoprofen are highly effective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents (Fig. 1).1 Asymmetric hydrocarboxylation and hydroesterification of olefins would provide attractive approaches to optically active acids and esters (Scheme 1). During the last few decades, a variety of such processes have been reported with various degrees of success.2–4 In general, the main challenge is to achieve high regio- and enantioselectivity simultaneously. Recently, we reported an asymmetric hydroesterification of aryl olefins with phenyl formate to give optically active phenyl 2-arylpropanoates in generally high regio- and enantioselectivity.5 During our mechanistic studies, it was found that such a process was also feasible with CO gas. While various CO surrogates have been developed to avoid handling toxic CO gas,6 in many cases, the use of CO gas is still more cost-effective particularly for a large scale reaction process, which prompted us to further investigate and optimize the aforementioned CO-based asymmetric hydroesterification (Scheme 2). Herein, we wish to report our studies on this subject.Results and discussion
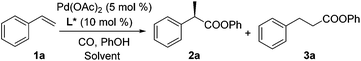
Styrene (1a) was used as the test substrate for the initial studies. The asymmetric hydroesterification was first investigated with different pressures of CO in the presence of 5 mol% Pd(OAc)2, 10 mol% (R)-(−)-DTBM-SEGPHOS,7 and PhOH (1.2 equiv.) in n-hexane at 50 °C (Table 1, entries 1–9). The reaction yield increased significantly (from 43 to 87%) as the CO pressure was reduced from 4.0 to 0.1 MPa. Generally, a high b/l ratio and enantioselectivity were obtained at different pressures of CO with 3.0 to 0.3 MPa being optimal. Among the solvents examined (Table 1, entries 5 and 10–16), n-hexane gave the best yield, b/l ratio, and enantioselectivity. It was notable that ester 2a was also formed in a reasonable yield (53%) with a high b/l ratio and ee when the reaction was carried out in water (Table 1, entry 16). The b/l ratio and ee decreased as the reaction temperature increased while the yield might increase in some cases (Table 1, entries 17–19 vs. entry 5).| Entry | CO (MPa) | Solvent | Temp (°C) | Yieldb (%) (2a![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3a)c 3a)c |
ee (%) (2a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
a The reactions were carried out with styrene (1a) (0.50 mmol), Pd(OAc)2 (0.025 mmol), (R)-(−)-DTBM-SEGPHOS (0.050 mmol), CO, PhOH (0.60 mmol), and solvent (0.50 mL) for 48 h.
b The yield was determined from a crude reaction mixture by 1H NMR with 1-methoxy-4-methylbenzene as an internal standard.
c The ratio of 2a![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3a was determined by 1H NMR analysis of the crude reaction mixture. 3a was determined by 1H NMR analysis of the crude reaction mixture.
|
|||||
| 1 | 4.0 | n-Hex | 50 | 43 (16![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
95 |
| 2 | 3.0 | n-Hex | 50 | 45 (22![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
96 |
| 3 | 2.0 | n-Hex | 50 | 53 (26![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
97 |
| 4 | 1.0 | n-Hex | 50 | 71 (23![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
97 |
| 5 | 0.5 | n-Hex | 50 | 77 (25![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
97 |
| 6 | 0.4 | n-Hex | 50 | 76 (24![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
97 |
| 7 | 0.3 | n-Hex | 50 | 79 (25![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
96 |
| 8 | 0.2 | n-Hex | 50 | 81 (13![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
96 |
| 9 | 0.1 | n-Hex | 50 | 87 (9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
94 |
| 10 | 0.5 | None | 50 | 37 (5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
93 |
| 11 | 0.5 | Tol | 50 | 35 (8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
97 |
| 12 | 0.5 | MEK | 50 | Trace | — |
| 13 | 0.5 | THF | 50 | — | — |
| 14 | 0.5 | EtOAc | 50 | Trace | — |
| 15 | 0.5 | DMF | 50 | — | — |
| 16 | 0.5 | H2O | 50 | 53 (20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
95 |
| 17 | 0.5 | n-Hex | 60 | 95 (15![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
95 |
| 18 | 0.5 | n-Hex | 70 | 91 (9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
92 |
| 19 | 0.5 | n-Hex | 80 | 71 (5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
85 |
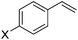
The substrate scope for the asymmetric hydroesterification reaction was investigated with the optimized reaction conditions [5 mol% Pd(OAc)2, 10 mol% (R)-(−)-DTBM-SEGPHOS, CO (0.50 MPa), and PhOH (1.2 equiv.) in n-hexane (0.50 mL) at 50 °C]. As shown in Table 2, the reaction process can be extended to a variety of aryl olefins. Ester 2a was isolated in 72% yield with >20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 b/l ratio and 97% ee (Table 2, entry 1). With para-substituted styrenes, the corresponding 2-arylpropanoates were obtained in 72–88% yield and 92–96% ee with the b/l ratio ranging from 16
1 b/l ratio and 97% ee (Table 2, entry 1). With para-substituted styrenes, the corresponding 2-arylpropanoates were obtained in 72–88% yield and 92–96% ee with the b/l ratio ranging from 16![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 to >20
1 to >20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 (Table 2, entries 2–8). The substrates can bear various substituents including OMe, alkyl, phenyl, Cl, and F groups. meta-Substituted styrenes were also effective for the reaction process. The branched esters were isolated in 84–95% yield and 89–96% ee with >20
1 (Table 2, entries 2–8). The substrates can bear various substituents including OMe, alkyl, phenyl, Cl, and F groups. meta-Substituted styrenes were also effective for the reaction process. The branched esters were isolated in 84–95% yield and 89–96% ee with >20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
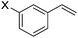
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 b/l ratio (Table 2, entries 9–11). Poorer results were obtained with ortho-methylstyrene, likely due to the steric effect of the Me group (Table 2, entry 12). The asymmetric hydroesterification process was also effective for di-substituted styrenes, giving the corresponding esters in 50–89% yield and 87–93% ee with 7
1 b/l ratio (Table 2, entries 9–11). Poorer results were obtained with ortho-methylstyrene, likely due to the steric effect of the Me group (Table 2, entry 12). The asymmetric hydroesterification process was also effective for di-substituted styrenes, giving the corresponding esters in 50–89% yield and 87–93% ee with 7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 to >20
1 to >20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 b/l ratio (Table 2, entries 13–15). Heteroaryl olefins such as 2-vinylpyridine, 1-vinylimidazole and aliphatic alkenes such as allyltrimethylsilane and 4-pentenyl acetate were not effective substrates under the current reaction conditions.
1 b/l ratio (Table 2, entries 13–15). Heteroaryl olefins such as 2-vinylpyridine, 1-vinylimidazole and aliphatic alkenes such as allyltrimethylsilane and 4-pentenyl acetate were not effective substrates under the current reaction conditions.
| Entry | Substrate (1) | Yieldb (%) (b![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) l)c l)c |
eed (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| a The reactions were carried out with olefin (1) (0.50 mmol), Pd(OAc)2 (0.025 mmol), (R)-(−)-DTBM-SEGPHOS (0.050 mmol), CO (0.50 MPa), PhOH (0.60 mmol), and n-hexane (0.50 mL) at 50 °C for 48 h. b Isolated yield. c The b/l ratio was determined by 1H NMR analysis of the crude reaction mixture. d For entries 1, 3, and 7, the absolute configurations were determined by comparing the optical rotations with the reported values.5,8 For entries 2, 4–6, and 8–15, the absolute configurations were tentatively assigned by analogy. | |||
|
|||
| 1 | X = H, 1a | 72 (>20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
97 |
| 2 | X = OMe, 1b | 84 (16![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
95 |
| 3 | X = iBu, 1c | 73 (>20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
95 |
| 4 | X = tBu, 1d | 80 (20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
92 |
| 5 | X = Me, 1e | 72 (16![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
95 |
| 6 | X = Ph, 1f | 84 (>20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
96 |
| 7 | X = Cl, 1g | 88 (>20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
95 |
| 8 | X = F, 1h | 82 (>20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
95 |
|
|||
| 9 | X = OMe, 1i | 95 (>20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
95 |
| 10 | X = Me, 1j | 84 (>20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
96 |
| 11 | X = Cl, 1k | 88 (>20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
89 |
| 12 |
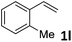
|
49 (5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
89 |
| 13 |
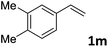
|
87 (14![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
91 |
| 14 |
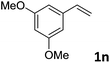
|
89 (>20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
93 |
| 15 |
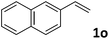
|
50 (7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
87 |
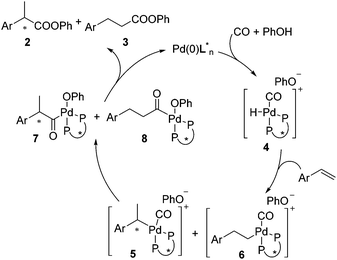
A precise reaction mechanism is not fully understood at this moment and requires further study. A plausible hydroesterification catalytic cycle is proposed in Scheme 3. Complex 4 generated from Pd(0), CO, and PhOH hydropalladated the olefin to give complexes 5 and 6, which were converted into acylpalladium complexes 7 and 8 after migratory insertion. Upon reductive elimination, 7 and 8 were transformed to the esters with 2 being favoured.
Conclusions
In summary, we have developed an efficient Pd-catalyzed regio- and enantioselective hydroesterification of aryl olefins with CO gas under mild reaction conditions, giving a wide variety of phenyl 2-arylpropanoates in good yield with a high b/l ratio and ee. The reaction process is operationally simple and provides a potentially useful method for the synthesis of optically active 2-arylpropanoates and their derivatives. The development of more effective catalytic systems with a broad substrate scope is currently being pursued.Experimental
General methods
All commercially available reagents were used without further purification unless otherwise stated. All solvents used for the reaction were purified with a solvent purification system. Column chromatography was performed on silica gel (200–300 mesh). 1H NMR spectra were recorded on a 400 MHz NMR spectrometer and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on a 100 MHz NMR spectrometer. IR spectra were recorded on a FT-IR spectrometer. Melting points were uncorrected. (R)-(−)-DTBM-SEGPHOS was purchased from a commercial supplier. Olefins 1a, 1b, 1d–l, and 1o were purchased from commercial suppliers. Olefins 1c, 1m, and 1n were prepared from the corresponding aldehydes via the Wittig reaction.9aRepresentative procedure for hydroesterification (Table 2, entry 1)
To a mixture of Pd(OAc)2 (0.0056 g, 0.025 mmol), (R)-(−)-DTBM-SEGPHOS (0.059 g, 0.050 mmol), PhOH (0.0564 g, 0.60 mmol), and n-hexane (0.50 mL) in a high pressure reactor (12.0 mL) was added styrene (1a) (0.0521 g, 0.50 mmol) via a syringe. The reactor was purged with CO three times to remove the air, filled with CO gas (0.5 MPa), and tightly sealed. The reaction mixture was stirred at 50 °C for 48 h, cooled to rt, and purified by flash chromatography (silica gel, eluent: petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 100/1) to give compound 2a as a colorless oil (0.0815 g, 72% yield, 97% ee).2a.5,8a,9b Colorless oil; [α]D20 = −93.7 (c 0.50, CHCl3) (97% ee); IR (film) 1749, 1487 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.45–7.27 (m, 7H), 7.23–7.16 (m, 1H), 7.03–6.96 (m, 2 H), 3.97 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 1.62 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.3, 151.0, 140.3, 129.6, 129.0, 127.8, 127.6, 126.0, 121.6, 45.9, 18.8; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C15H15O2 (M + H): 227.1067; found: 227.1066.
2b.5,9 Colorless oil; [α]D20 = −83.2 (c 0.54, CHCl3) (95% ee); IR (film) 1749, 1507 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.37–7.29 (m, 4H), 7.23–7.16 (m, 1H), 7.02–6.96 (m, 2H), 6.94–6.87 (m, 2H), 3.91 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 3.82 (s, 3H), 1.59 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.5, 159.1, 151.1, 132.3, 129.5, 128.8, 125.9, 121.6, 114.4, 55.5, 45.0, 18.8; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C16H16NaO3 (M + Na): 279.0992; found: 279.0990.
2c.5,9b Colorless oil; [α]D20 = −76.0 (c 0.51, CHCl3) (95% ee); IR (film) 1753, 1491 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.39–7.27 (m, 4H), 7.23–7.17 (m, 1H), 7.17–7.11 (m, 2H), 7.03–6.96 (m, 2H), 3.95 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.48 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.95–1.81 (m, 1H), 1.61 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H), 0.93 (s, 3H), 0.91 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.5, 151.1, 141.0, 137.5, 129.7, 129.5, 127.4, 125.9, 121.6, 45.5, 45.3, 30.4, 22.6, 18.7; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C19H23O2 (M + H): 283.1693; found: 283.1690.
2d. White solid; mp. 49–51 °C; [α]D20 = −72.2 (c 0.92, CHCl3) (92% ee); IR (film) 1745, 1487 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.43–7.36 (m, 2H), 7.36–7.31 (m, 4H), 7.24–7.17 (m, 1H), 7.06–7.00 (m, 2H), 3.96 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 1.62 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H), 1.35 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.4, 151.1, 150.4, 137.2, 129.5, 127.4, 125.9, 121.6, 45.4, 34.7, 31.6, 18.8; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C19H23O2 (M + H): 283.1693; found: 283.1691.
2e.5 Colorless oil; [α]D20 = −89.9 (c 1.05, CHCl3) (95% ee); IR (film) 1753, 1487 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38–7.28 (m, 4H), 7.23–7.16 (m, 3H), 7.04–6.97 (m, 2H), 3.94 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 2.37 (s, 3H), 1.61 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.4, 151.1, 137.3, 137.2, 129.7, 129.5, 127.6, 125.9, 121.6, 45.4, 21.3, 18.8; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C16H16NaO2 (M + Na): 263.1043; found: 263.1037.
2f.5,9b White solid; mp. 74–76 °C; [α]D20 = −84.2 (c 0.68, CHCl3) (96% ee); IR (film) 1740, 1478 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.63–7.56 (m, 4H), 7.50–7.39 (m, 4H), 7.38–7.29 (m, 3H), 7.24–7.15 (m, 1H), 7.05–6.98 (m, 2H), 4.00 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 1.65 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.2, 151.0, 140.9, 140.5, 139.3, 129.5, 129.0, 128.2, 127.7, 127.5, 127.3, 126.0, 121.6, 45.5, 18.7; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C21H19O2 (M + H): 303.1380; found: 303.1376.
2g.5,9b Colorless oil; [α]D20 = −79.4 (c 0.63, CHCl3) (95% ee); IR (film) 1752, 1490 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38–7.31 (m, 6H), 7.24–7.17 (m, 1H), 7.01–6.95 (m, 2H), 3.94 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 1.61 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 172.9, 150.9, 138.7, 133.5, 129.6, 129.2, 126.1, 121.5, 45.3, 18.7; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C15H1335ClNaO2 (M + Na): 283.0496; found: 283.0494.
2h.5 Colorless oil; [α]D20 = −79.3 (c 0.59, CHCl3) (95% ee); IR (film) 1753, 1507 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.42–7.31 (m, 4H), 7.24–7.17 (m, 1H), 7.10–7.02 (m, 2H), 7.02–6.95 (m, 2H), 3.96 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 1.61 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.1, 162.3 (d, J = 244.0 Hz), 151.0, 136.0 (d, J = 4.0 Hz), 129.6, 129.4 (d, J = 8.0 Hz), 126.1, 121.5, 115.9 (d, J = 21.0 Hz), 45.1, 18.8; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C15H13FNaO2 (M + Na): 267.0792; found: 267.0793.
2i.5,9b Colorless oil; [α]D20 = −75.7 (c 0.61, CHCl3) (95% ee); IR (film) 1753, 1489 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38–7.24 (m, 3H), 7.23–7.16 (m, 1H), 7.03–6.93 (m, 4H), 6.84 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 3.94 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 3.82 (s, 3H), 1.61 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.1, 160.1, 151.0, 141.8, 130.0, 129.5, 126.0, 121.6, 120.1, 113.5, 112.9, 55.5, 45.9, 18.7; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C16H16NaO3 (M + Na): 279.0992; found: 279.0994.
2j.5,9b Colorless oil; [α]D20 = −87.8 (c 0.54, CHCl3) (96% ee); IR (film) 1752, 1486 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.37–7.29 (m, 2H), 7.29–7.23 (m, 1H), 7.22–7.15 (m, 3H), 7.14–7.08 (m, 1H), 7.02–6.96 (m, 2H), 3.92 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.37 (s, 3H), 1.60 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.4, 151.0, 140.2, 138.7, 129.5, 128.9, 128.5, 128.3, 125.9, 124.7, 121.6, 45.8, 21.7, 18.8; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C16H17O2 (M + H): 241.1223; found: 241.1219.
2k.5 Colorless oil; [α]D20 = −69.2 (c 0.58, CHCl3) (89% ee); IR (film) 1749, 1487 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.43–7.39 (m, 1H), 7.38–7.31 (m, 2H), 7.31–7.27 (m, 3H), 7.24–7.18 (m, 1H), 7.03–6.97 (m, 2H), 3.94 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 1.62 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 172.7, 150.9, 142.1, 134.8, 130.3, 129.6, 128.1, 127.9, 126.1, 126.0, 121.5, 45.6, 18.6; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C15H1335ClNaO2 (M + Na): 283.0496; found: 283.0498.
2l.5,9b Colorless oil; [α]D20 = −92.7 (c 0.22, CHCl3) (89% ee); IR (film) 1752, 1486 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38–7.29 (m, 3H), 7.26–7.16 (m, 4H), 7.01–6.96 (m, 2H), 4.20 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.45 (s, 3H), 1.58 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.6, 151.0, 138.9, 135.9, 130.9, 129.5, 127.4, 126.8, 126.7, 125.9, 121.6, 41.7, 19.9, 18.1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C16H17O2 (M + H): 241.1223; found: 241.1218.
2m.5,9b Colorless oil; [α]D20 = −86.3 (c 0.48, CHCl3) (91% ee); IR (film) 1752, 1490 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38–7.31 (m, 2H), 7.23–7.17 (m, 2H), 7.17–7.13 (m, 2H), 7.04–6.99 (m, 2H), 3.91 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.29 (s, 3H), 2.27 (s, 3H), 1.60 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.5, 151.1, 137.8, 137.2, 135.9, 130.2, 129.5, 129.0, 125.9, 125.0, 121.6, 45.4, 20.1, 19.6, 18.9; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C17H18NaO2 (M + Na): 277.1199; found: 277.1194.
2n. Colorless oil; [α]D20 = −65.8 (c 0.61, CHCl3) (93% ee); IR (film) 1753, 1454 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38–7.31 (m, 2H), 7.23–7.17 (m, 1H), 7.04–6.98 (m, 2H), 6.56 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 2H), 6.40 (t, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 3.89 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 3.81 (s, 6H), 1.60 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.0, 161.2, 151.0, 142.5, 129.5, 126.0, 121.6, 105.9, 99.5, 55.6, 46.0, 18.7; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C17H18NaO4 (M + Na): 309.1097; found: 309.1093.
2o.9b White solid; mp. 60–61 °C; [α]D20 = −89.4 (c 0.90, CHCl3) (87% ee); IR (film) 1745, 1491 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.90–7.82 (m, 4H), 7.55 (dd, J = 8.5, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.53–7.45 (m, 2H), 7.37–7.29 (m, 2H), 7.22–7.16 (m, 1H), 7.02–6.96 (m, 2H), 4.14 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 1.71 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.3, 151.0, 137.7, 133.7, 132.9, 129.6, 128.8, 128.1, 127.9, 126.54, 126.48, 126.2, 126.0, 125.8, 121.6, 46.0, 18.7; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C19H16NaO2 (M + Na): 299.1043; found: 299.1045.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21632005, 21472083) and Nanjing University for the financial support.Notes and references
- For leading references on nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, see: (a) F. D. Hart, Drugs, 1975, 9, 321 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) G. Thomas and M. D. Kantor, Pharmacotherapy, 1986, 6, 93 CrossRef; (c) P. J. Harrington and E. Lodewijk, Org. Process Res. Dev., 1997, 1, 72 CrossRef CAS; (d) J. M. Lehmann, J. M. Lenhard, B. B. Oliver, G. M. Ringold and S. A. Kliewer, J. Biol. Chem., 1997, 272, 3406 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For leading reviews on asymmetric hydroesterification, see: (a) C. Godard, B. K. Muñoz, A. Ruiz and C. Claver, Dalton Trans., 2008, 853 RSC; (b) C. Godard, B. F. Perandones, A. Gual and C. Claver, in Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry II, ed. J. Reedijk and K. Poeppelmeier, Elsevier Ltd, 2nd edn, 2013, pp. 383–411 Search PubMed.
- For leading references on the Pd-catalyzed asymmetric intermolecular hydroesterification of olefins with CO gas, see: (a) G. Consiglio, Helv. Chim. Acta, 1976, 59, 124 CrossRef CAS; (b) T. Hayashi, M. Tanaka and I. Ogata, Tetrahedron Lett., 1978, 41, 3925 CrossRef; (c) G. Cometti and G. P. Chiusoli, J. Organomet. Chem., 1982, 236, C31 CrossRef CAS; (d) G. Chelucci, M. A. Cabras, C. Botteghi and M. Marchetti, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 1994, 5, 299 CrossRef CAS; (e) H. Zhou, S. Lu, J. Hou, J. Chen, H. Fu and H. Wang, Chem. Lett., 1996, 339 CrossRef CAS; (f) H. Zhou, J. Hou, J. Cheng, S. Lu, H. Fu and H. Wang, J. Organomet. Chem., 1997, 543, 227 CrossRef CAS; (g) S. Oi, M. Nomura, T. Aiko and Y. Inoue, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 1997, 115, 289 CrossRef CAS; (h) K. Nozaki, M. L. Kantam, T. Horiuchi and H. Takaya, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 1997, 118, 247 CrossRef; (i) L. Wang, W. H. Kwok, A. S. C. Chan, T. Tu, X. Hou and L. Dai, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 2003, 14, 2291 CrossRef CAS; (j) Y. Kawashima, K. Okano, K. Nozaki and T. Hiyama, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 2004, 77, 347 CrossRef CAS; (k) B. Muñoz, A. Marinetti, A. Ruiz, S. Castillon and C. Claver, Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2005, 8, 1113 CrossRef; (l) E. Guiu, M. Caporali, B. Muñoz, C. Müller, M. Lutz, A. L. Spek, C. Claver and P. W. N. M. van Leeuwen, Organometallics, 2006, 25, 3102 CrossRef CAS; (m) C. Godard, A. Ruiz and C. Claver, Helv. Chim. Acta, 2006, 89, 1610 CrossRef CAS; (n) B. K. Muñoz, C. Godard, A. Marinetti, A. Ruiz, J. Benet-Buchholz and C. Claver, Dalton Trans., 2007, 5524 RSC.
- For leading references on the Pd-catalyzed asymmetric hydroxycarbonylation of olefins with CO gas, see: (a) C. Botteghi, G. Consiglio and P. Pino, Chimia, 1973, 27, 477 CAS; (b) G. Consiglio, J. Organomet. Chem., 1977, 132, C26 CrossRef CAS; (c) Y. Becker, A. Eisenstadt and J. K. Stille, J. Org. Chem., 1980, 45, 2145 CrossRef CAS; (d) H. Alper and N. Hamel, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1990, 112, 2803 CrossRef CAS; (e) M. D. Miquel-Serrano, A. Aghmiz, M. Diéguez, A. M. Masdeu-Bultó, C. Claver and D. Sinou, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 1999, 10, 4463 CrossRef CAS; (f) I. del Río, N. Ruiz, C. Claver, L. A. van der Veen and P. W. N. M. van Leeuwen, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2000, 161, 39 CrossRef; (g) T. M. Konrad, J. A. Fuentes, A. M. Z. Slawin and M. L. Clarke, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 9197 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) T. M. Konard, J. T. Durrani, C. J. Cobley and M. L. Clarke, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 3306 RSC; (i) J. A. Fuentes, J. T. Durrani, S. M. Leckie, L. Crawford, M. Bühl and M. L. Clarke, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2016, 6, 7477 RSC.
- J. Li, W. Chang, W. Ren, J. Dai and Y. Shi, Org. Lett., 2016, 18, 5456 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For leading reviews with CO surrogates, see: (a) G. Jenner, Appl. Catal., A, 1995, 121, 25 CrossRef CAS; (b) T. Morimoto and K. Kakiuchi, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2004, 43, 5580 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) L. Wu, Q. Liu, R. Jackstell and M. Beller, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 6310 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) H. Konishi and K. Manabe, Synlett, 2014, 1971 CAS; (e) B. Liu, F. Hu and B.-F. Shi, ACS Catal., 2015, 5, 1863 CrossRef CAS.
- For leading references on (R)-(−)-DTBM-SEGPHOS, see: (a) B. H. Lipshutz, A. Lower and K. Noson, Org. Lett., 2002, 4, 4045 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) B. H. Lipshutz, K. Noson, W. Chrisman and A. Lower, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 8779 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) J. Mao, F. Liu, M. Wang, L. Wu, B. Zheng, S. Liu, J. Zhong, Q. Bian and P. J. Walsh, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 17662 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) K. Dong, Y. Li, Z. Wang and K. Ding, Org. Chem. Front., 2014, 1, 155 RSC.
- (a) H. Konishi, T. Ueda, T. Muto and K. Manabe, Org. Lett., 2012, 14, 4722 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) W. Ren, W. Chang, Y. Wang, J. Li and Y. Shi, Org. Lett., 2015, 17, 3544 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/C7QO00622E |
| This journal is © the Partner Organisations 2018 |