Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleFabrication of cefotaxime sodium-functionalized gold nanoclusters for the detection of copper ions in Chinese herbal medicines†
Cunling Ye‡
*a,
Yuanfei Wanga,
Shen Wanga and
Zhike Wang‡ *b
*b
aSchool of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang, Henan 453007, China. E-mail: ycl@htu.cn
bSchool of Environment, Henan Key Laboratory for Environmental Pollution Control, Key Laboratory for Yellow River and Huai River Water Environment and Pollution Control, Ministry of Education, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang, Henan 453007, China. E-mail: wzk@htu.cn
First published on 11th February 2019
Abstract
Antibiotic-based gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) are a good sensing platform for specific recognition; however, the related studies are few. Herein, a simple and facile strategy was proposed for the fabrication of bright blue fluorescent AuNCs through the degradation product (DCTX) of cefotaxime sodium that induced the reduction of HAuCl4. Various analytical techniques were applied to characterize the prepared AuNCs@DCTX. AuNCs@DCTX exhibited a strong emission peak centered at 420 nm and a quantum yield of 11.8%. Furthermore, an aggregation-induced fluorescence quenching mode endowed the AuNCs@DCTX probe with good specificity and sensitivity for Cu2+ detection. The proposed probe had a linear range of 0.01–40 μM, a precision with a relative standard deviation of 1.2% (n = 8), and a detection limit of 8 nM (signal/noise = 3). Interestingly, the probe could be reused through switching the “off” and “on” states by the addition of Cu2+ and EDTA. The practicality of the sensing platform was investigated for the determination of Cu2+ in four Chinese herbal medicines (CHMs), and the results were in accordance with those obtained by the FAAS method. This study has provided an alternate way for the fabrication of thiolate-protected AuNCs for sensing applications.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, Chinese herbal medicines (CHMs) have gained extensive attention due to their long-standing clinical applications, reliable therapeutic efficacy and less secondary effects as compared to synthetic pharmaceuticals.1 Since CHMs readily assimilate heavy metallic elements through their roots, one of the major concerns in the usage of CHMs is the issue of safety related to the presence of some heavy metal elements, including copper (Cu), at high concentrations.2,3 Since the toxicity and bioavailability of Cu in humans depend on its concentration, trace amounts of copper in CHMs should be regularly determined for the protection of public health.4,5The available traditional techniques, such as atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS),6 inductively coupled plasma atomic emission/mass spectrometry (ICP-AES/ICP-MS),7 capillary electrophoresis,2 and electrochemical methods,8 have been used to detect copper ions in various sample matrices. However, most of these techniques suffer from one or more limitations such as requirement of sophisticated and expensive instruments and well-trained operators as well as time consumption, which limit their widespread applications in routine copper ion detection.9 Moreover, CHMs have matrix effects and low copper levels that fall below the limit of quantification of many techniques. Compared to the abovementioned techniques, the fluorescence method is more favorable because of its low-cost, good selectivity, low detection limit and real-time monitoring with a fast response.10–14
Recently, fluorescent metal nanoclusters, including gold nanoclusters (AuNCs), silver nanoclusters (AgNCs) and copper nanoclusters (CuNCs), have gained significant attention for application in analytical sensors.15–21 AuNCs, which consist of several to a few hundred Au atoms with a typical size less than 2 nm, comparable to the Fermi wavelength of the electrons, have gained significant interest in chemical, biological, and environmental analysis due to their distinct advantages of simple preparation, extraordinary stability, satisfying luminescence quantum yield (QY), and biocompatibility.22 To date, some different kinds of ligands or templates (e.g., DNA, peptides, proteins, dendrimers, polymers, small thiol molecules, etc.) have been used to guide the synthesis of the AuNCs.15,22–24 Specifically, thiolate-protected AuNCs exhibit attractive features such as ultra-small hydrodynamic diameters, excellent photostability and modifiable surface properties and act as probes for the detection of H2O2, glucose, pyrophosphate, trypsin activity, Ag+, Cr3+, Cu2+, Fe3+, Hg2+, Pb2+, NO2−, and S2−.25–27
As is known, some antibiotics contain a variety of functional groups, which allow them to provide multiple interactions (e.g., electrostatic, hydrophobic, dipole–dipole, π–π interactions, hydrogen bonding, etc.) with the target compounds.28 Therefore, some antibiotic-type stationary phases have been developed for enantioseparation.29 This suggests that AuNCs, prepared in the presence of commercial antibiotics serving as both reductants and ligands, can have the ability to capture the analytes through multiple interactions. However, few studies have been focussed on the preparation of antibiotic-based fluorescent AuNCs for sensing applications.30 Cefotaxime sodium (CTX), the third generation of cephalosporin against Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria,31 contains nitrogen, sulphur and oxygen like many efficient ligands or templates of AuNCs. Interestingly, CTX in an alkaline medium can be entirely degraded into an equal mole of a reducing sulfhydryl compound (DCTX) in a boiling water bath.32 Thus, we believe that DCTX can be used as both a reductant and a capping ligand for the generation of DCTX-capped AuNCs (AuNCs@DCTX). Herein, water-soluble AuNCs@DCTX with a bright blue luminescence at 420 nm were fabricated via a facile one-pot synthesis using DCTX as the reducing and capping ligand. Furthermore, the fluorescence of the AuNCs@DCTX could be selectively quenched by Cu2+ on the basis of a mechanism involving particle aggregation-induced fluorescence quenching through the coordination of Cu2+ with –NH2 and –COOH on the surface of AuNCs@DCTX. Since the degree of quenching of AuNCs@DCTX is directly related to the concentration of Cu2+, we have investigated the feasibility of using this probe for the detection of Cu2+ in CHMs. Moreover, the fluorescence response could be reversibly switched between the “off” and “on” states by the addition of Cu2+ and EDTA; this clearly benefitted our understanding of the fluorescence quenching mechanisms. This study provides a new route for the synthesis of thiolate-protected AuNCs for the quantitative analysis of heavy metal ions in CHMs.
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents and chemicals
Unless otherwise stated, all reagents were of analytical grade, obtained from commercial suppliers and used without further purification. HAuCl4·4H2O, cefotaxime sodium, Cu(NO3)2·3H2O, NaCl, NaOH and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt (EDTA) were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. Other metal salts were purchased from Tianjin De'en Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. The Pur-A-Lyzer™ Mega 1000 dialysis kit (1 kDa) was acquired from Shanghai Biotechnology Engineering Co., Ltd. All detection experiments were performed in a 0.1 M NaH2PO4–Na2HPO4 buffer (pH = 7.0). Ultra-pure water (18.2 MΩ) was used throughout the experiments.2.2. Apparatus
Fluorescence spectra were obtained using the FP-6500 spectrofluorometer (JASCO, Japan). Fourier transform Infrared spectra (FTIR) were acquired over the range 600–4000 cm−1 using the Tensor 27 FTIR spectrometer (Bruker, Germany), equipped with a germanium-attenuated total reflection (ATR) accessory. The size and morphologies of the as-synthesized samples were investigated via high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) using the JEOL JEM-2010 electron microscope (JEOL, Japan) at the acceleration voltage of 200 kV. Flame atomic absorption spectrometry (Perkin-Elmer, AA700) with an air-acetylene flame was used as the classical reference method to determine Cu2+ in CHMs, and the wavelength was set to 324.8 nm with a spectral slit-width of 0.7 nm and a lamp current of 15 mA. The model T6 UV/Vis spectrophotometer (Beijing Purkinje General Instrument Co., Beijing, China) was used to obtained the absorption spectra. The pH-3C digital pH meter (Shanghai Leici Instrument Factory, Shanghai, China) was used for pH adjustment.2.3. Preparation of AuNCs@DCTX
AuNCs@DCTX was synthesized according to the following procedure. At first, 2.5 mM DCTX aqueous solution was obtained using a previously reported method.32 Then, DCTX (2.5 mM, 7 mL) was rapidly added to boiling HAuCl4 (5 mM, 14 mL) under vigorous stirring for 4 h. After being cooled down to room temperature, the solution was filtered using a 0.45 μm PTFE filter membrane to remove larger particles. Subsequently, AuNCs@DCTX was further purified using a dialysis membrane (MWCO: 1 kDa) to remove any residual unreacted species. The final AuNCs@DCTX was stored at 4 °C for further use. Herein, the concentration of the prepared AuNCs@DCTX was denoted as 1X.2.4. Selectivity measurement
To evaluate the specificity of AuNCs@DCTX for Cu2+, various competitive metal ions, including Zn2+, Al3+, Ni2+, Co2+, Pb2+, Cr3+, Cd2+, Mn2+, Mg2+, K+, Bi3+, Ba2+, Ca2+, Fe3+ and Hg2+ (800 μL, 100 μM), were separately mixed with 300 μL of AuNCs@DCTX and 200 μL of pH 7.0 phosphate buffer solution (PBS). The mixture solution was made up to 4.0 mL with ultra-pure water and then maintained at 30 °C for 40 min. Moreover, the selectivity was tested by mixing the abovementioned metal ions in the presence of Cu2+ under identical conditions. The fluorescence response of AuNCs@DCTX was obtained with excitation at 321 nm.2.5. Fluorescence detection of Cu2+
For Cu2+ determination, 300 μL of the prepared AuNCs@DCTX (1X) was mixed with 200 μL of pH 7.0 PBS and a certain amount of Cu2+ at final concentrations ranging from 0.01 μM to 40 μM, and the final volume was adjusted to 4.0 mL. After incubation at 30 °C for 40 min, the fluorescence spectra were obtained with excitation at 321 nm (slit width: excitation, 10 nm; emission, 10 nm). Then, the calibration curve for Cu2+ was constructed based on the quenched factor (F0/F), where F and F0 are the maximum fluorescence signals of AuNCs@DCTX in the presence and absence of Cu2+, respectively. All experiments were performed in triplicate.2.6. Analysis of CHMs
Poria, alisma, licorice and salvia were acquired from a local drugstore. A digestion method with an acid mixture of HNO3 and HClO4 was used for sample preparation.33 In brief, the four samples were washed with ultrapure water and dried at 60 °C until a constant weight was achieved. The dried samples were finely ground using an agate mortar and sieved through a 60-mesh sieve. Each powder sample (0.5 g) was accurately weighed into a beaker with a watch-glass, followed by the addition of 10 mL of HNO3. The mixture was allowed to stand overnight at room temperature. The next day, after the addition of 10 mL of HNO3 and 5 mL of HClO4, the digestion was slowly carried out on an electric hot plate until the formed transparent solution was evaporated to near dryness followed by cooling at room temperature. After this, the residue was transferred to a 25.0 mL volumetric flask and adjusted to a nearly neutral pH with 2 M NaOH before the volume was adjusted with ultrapure water. The resulting solution was used for the determination of Cu2+ by the proposed fluorescence method and flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS).3. Results and discussion
3.1. Synthesis and characterization of AuNCs@DCTX
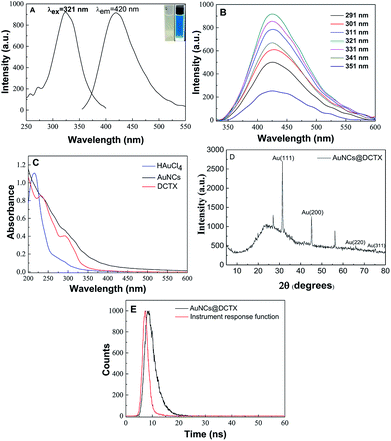
AuNCs@DCTX was prepared via a one-pot synthesis, in which DCTX played a dual role as a capping agent and a reducing agent due to its numerous functional groups such as a thiol group, a heterocyclic amine, an amine group and a carboxyl group. That is, in the synthesis process, Au(III) in HAuCl4 was reduced to Au(I) by –SH of DCTX, followed by the coordination of Au(I) with the thiol group to form Au(I)–thiolate complexes. Subsequently, a portion of Au(I) was further immediately reduced to Au(0) atoms by the heterocyclic nitrogen atom of DCTX in a boiling aqueous solution, and the Au(0) atoms were sequestrated by the Au(I)–thiolate complexes.26,27,32,33 The process was very simple as pH adjustment and addition of other templates or reducing agents were not required. The related synthesis parameters, including the molar ratio of HAuCl4 to DCTX, the reaction temperature and the reaction time, were optimized (Fig. S1†). As shown in Fig. S1(D),† the obtained AuNCs@DCTX exhibited a strong fluorescence emission at 420 nm, whereas the fluorescence of DCTX could be ignored (no peak intensity) under the same conditions; this demonstrated that the obtained fluorescence originated from the gold core of AuNCs@DCTX. To further confirm the formation of AuNCs@DCTX, the HRTEM image was obtained. Fig. 1A shows that the prepared AuNCs@DCTX has a spherical shape and uniform size distribution with an average diameter of around 2.03 nm (Fig. S2†). The selected area electron diffraction pattern (Fig. 1B) also provided evidence for the crystalline nature of AuNCs@DCTX. Therefore, these evidences verified that ultra-small AuNCs@DCTX was successfully prepared using the proposed approach.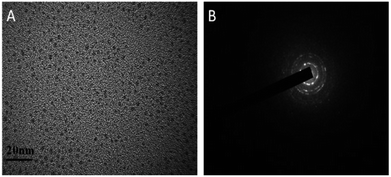 | ||
| Fig. 1 An HRTEM image (A) and the selected electron diffraction pattern (B) of the prepared AuNCs@DCTX (scale bar = 20 nm). | ||
The prepared AuNCs@DCTX is inherently water soluble because some hydrophilic groups such as –COOH and –NH2 are included in the DCTX structures. In addition, the stability of AuNCs@DCTX was systematically investigated. As shown in Fig. S3(A),† 98.9% of the initial value of the fluorescence intensity of AuNCs@DCTX was maintained after storage of AuNCs@DCTX in the dark at 4 °C for three months; this demonstrated that AuNCs@DCTX exhibited excellent storage photostability. As depicted in Fig. S3(B),† there was no obvious change in the fluorescence intensity of AuNCs@DCTX in the pH range of 2.0–7.0. The fluorescence intensities of AuNCs@DCTX were not obviously affected upon varying the NaCl concentration from 5 mM to 200 mM, as shown in Fig. S3(C).† Furthermore, Fig. S3(D)† displays that the fluorescence intensities of AuNCs@DCTX are preserved at 91.7% after 80 min of illumination at 365 nm. In brief, these experimental results indicated that the prepared AuNCs@DCTX had ultra-high stability, providing great potential for their practical application.
Optical properties of the as-synthesized AuNCs@DCTX are presented in Fig. 2. As shown in Fig. 2A, AuNCs@DCTX has maximum excitation and emission peaks at 321 and 420 nm, respectively. As shown in the inset of Fig. 2A, the AuNCs@DCTX solution is pale yellow under visible light; on the other hand, it emits strong bright blue fluorescence under 365 nm UV light irradiation. Moreover, the fluorescence emission peaks showed almost no shift over a wide excitation wavelength range of 291–351 nm (Fig. 2B); this indicated that the observed optical signal was a real fluorescence signal from the relaxed states rather than the scattering effects.34 This may be attributed to the uniform size of AuNCs@DCTX, which is well supported by its HRTEM image.35 Fig. 2C displays the UV-vis absorption spectra of AuNCs@DCTX, HAuCl4 and DCTX, and there is no characteristic surface plasmon resonance absorption peak of gold nanoparticles near 520 nm; this suggests that most of the particles are smaller than 2.5 nm; this is evidence for the existence of AuNCs.30,36 The quantum yield (Φ) of AuNCs@DCTX in an aqueous solution is 11.8% at 321 nm, with quinine sulfate (0.1 mol L−1 H2SO4, Φref = 0.54) as the reference based on the slope method (Fig. S4†); this value is higher than those of most of the previously developed thiol-protected AuNCs.26,37–39 The stronger fluorescence of AuNCs@DCTX could be ascribed to the more electron-rich groups (e.g., –NH2 and –COOH) in DCTX directly donating the delocalized electron to the gold core via surface interactions.40 Moreover, as shown in Fig. S5,† the fluorescence intensity of AuNCs@DCTX at 420 nm displayed a 69.1% decrease upon introducing NaBH4 at the concentration of 1 mM; this indicated that the electronic structures Au(0) and Au(I) of Au coexisted in AuNCs@DCTX.39 The XRD pattern of AuNCs@DCTX in Fig. 2D demonstrates sharp peaks at 31.5° and 45.1° corresponding to the (111) and (200) lattice planes of AuNCs@DCTX, respectively. The other two characteristic peaks at 65.9° and 75.4° were labeled as the (220) and (311) diffractions of face-centered cubic (fcc) gold (JCPDS 75-2870).41,42 Fig. 2E shows the fluorescence decay profile of AuNCs@DCTX, and it can be fitted with a biexponential profile with the two components 2.380 ns and 6.061 ns (χ2 = 1.040). FTIR spectroscopy was also used to characterize AuNCs@DCTX. As shown in Fig. S6,† the peaks at 1657 cm−1 and 1562 cm−1 were attributed to the asymmetric stretching vibrations of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O and N–H of DCTX, respectively; however, the DCTX-functionalized AuNCs led to a small blue shift of the corresponding peaks because of the interaction of DCTX with Au.41 Interestingly, the FTIR spectrum of AuNCs@DCTX was very similar to that of DCTX; this indicated that DCTX was successfully immobilized on the surface of AuNCs.43
O and N–H of DCTX, respectively; however, the DCTX-functionalized AuNCs led to a small blue shift of the corresponding peaks because of the interaction of DCTX with Au.41 Interestingly, the FTIR spectrum of AuNCs@DCTX was very similar to that of DCTX; this indicated that DCTX was successfully immobilized on the surface of AuNCs.43
3.2. Detection of Cu2+using AuNCs@DCTX
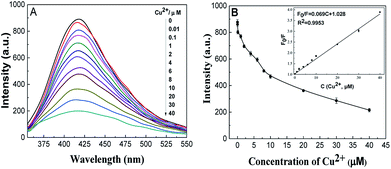
To obtain a sensitive response towards Cu2+, several related factors, including the pH, the volume of AuNCs@DCTX, the reaction temperature and the incubation time, were optimized via a univariate method. Fig. 3A shows the effect of pH on the relative fluorescence intensity F0/F (F0 and F refer to the fluorescence intensity of AuNCs@DCTX at 420 nm before and after the addition of Cu2+, respectively) in PBS. It could be observed that the value of F0/F increased upon increasing the pH of the developed system from 2.0 to 7.0 and then slightly decreased in the pH range of 7.0–9.0. The reasons for this could be two-fold: first, a low pH increased the degree of amino group protonation of AuNCs@DCTX, and second, the carboxyl group of AuNCs@DCTX mainly existed as –COOH rather than –COO− at a low pH, thus weakening the complexation between Cu2+ and AuNCs@DCTX. Therefore, a pH of 7.0 was adopted for further study. The effect of the volume of AuNCs@DCTX (1X) on the fluorescence quenching efficiency is depicted in Fig. 3B. It was found that 300 μL of AuNCs@DCTX was appropriate for the detection of Cu2+. The volume of AuNCs@DCTX over 300 μL resulted in a low fluorescence quenching efficiency due to the self-quenching effect. However, when the volume of AuNCs@DCTX was below 300 μL, the limited number of fluorescence molecules in the sensor system resulted in a low fluorescence quenching efficiency. As a result, the volume of 300 μL of AuNCs@DCTX was selected. Fig. 3C shows the effect of the reaction temperature on the F0/F value of the proposed system. The results indicated that the reaction temperature had little impact on the fluorescence quenching efficiency in the tested range from 25 to 65 °C. Considering the facile operation, a temperature of 30 °C was selected. As shown in Fig. 3D, the fluorescence quenching efficiency reached an optimum value when the reaction time was 40 min. Thus, 40 min was selected as the reaction time hereinafter.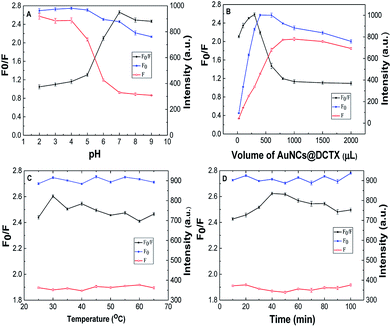 | ||
| Fig. 3 The effects of pH (A), volume of AuNCs@DCTX (B), reaction temperature (C) and incubation time (D) on the relative fluorescence intensity of the AuNCs@DCTX-Cu2+ system. | ||
As per the design, Cu2+ can significantly affect the fluorescence of AuNCs@DCTX. Under the optimum conditions, a plot of the fluorescence quenching efficiency of AuNCs@DCTX versus the concentration of Cu2+ is presented in Fig. 4A. As depicted in Fig. 4B, a linear response between F0/F and Cu2+ concentration was observed over the range of 0.01–40 μM, and the corresponding linear equation was F0/F = 0.069C + 1.028 (C is the concentration of Cu2+ in μM) with a correlation coefficient of R2 = 0.9953. The relative standard deviation (RSD), determined by 8 repetitive measurements of 20 μM Cu2+, was 1.2%. The limit of detection (LOD), based on a signal to noise ratio of 3, was 8 nM, which was lower than the maximum level (32 μM) of Cu2+ in drinking water defined by the World Health Organization.46 As shown in Table 1, the performances of AuNCs@DCTX as a Cu2+ sensor were compared with those of other nanocluster-based fluorescence probes, and it was found that the proposed sensor was highly sensitive for Cu2+ detection.38,39,44–50
| Probe | Ligands/reductant | Φ | Linear range (μM) | LOD | Sample | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a DTT, dithiothreitol; BSA, bovine serum albumin; GSH, L-glutathione; HEPES, 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid; hPEI, hyperbranched polyethyleneimine; AA, ascorbic acid. | ||||||
| AuNCs@DTT | DTT | 2.09% | 0–60 | 80 nM | Human serum | 38 |
| Met-AuNC | Methionine | 2.8% | 0.05–8 | 7.9 nM | Soil | 39 |
| AuNCs | BSA | — | 100 μM to 50 mM | 50 μM | Live cells | 44 |
| GS-Au NCs | GSH | — | 0.100–6.25 | 86 nM | — | 45 |
| AuNCs | Riboflavin/GSH | — | 0–30 | 0.9 μM | — | 46 |
| AuNCs | DNA/HEPES | — | 0.01–10 | 10 nM | Human serum, water | 47 |
| Lys-AuNCs | Lysozyme | — | 0.04–0.4 | 9 nM | Water | 48 |
| AuNCs | Sn(II)/citrate | — | 0.5–70 | 0.38 μM | Water | 49 |
| hPEI-Cu NCs | hPEI/AA | 7.9% | 0.022–8.8 | 8.9 nM | Water | 50 |
| AuNCs@DCTX | DCTX | 11.8% | 0.01–40 | 8 nM | CHMs | This work |
The selectivity of AuNCs@DCTX towards Cu2+ was evaluated by measuring the fluorescence response of AuNCs@DCTX after adding 20 μM of different common metal cations (Zn2+, Al3+, Ni2+, Co2+, Pb2+, Cr3+, Cd2+, Mn2+, Mg2+, K+, Bi3+, Ba2+, Ca2+, Fe3+ and Hg2+) without and with 20 μM Cu2+, separately. Fig. 5 shows that other metal cations results in negligible or minor changes in fluorescence as compared to Cu2+; this indicates that the prepared AuNCs@DCTX probe possesses high selectivity towards Cu2+.
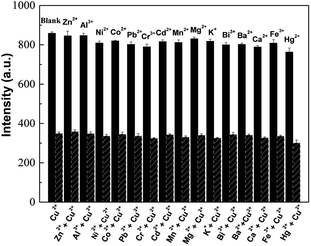 | ||
| Fig. 5 Selectivity of AuNCs@DCTX towards 20 μM Cu2+ and 20 μM of other common metal cations under the optimum conditions. | ||
3.3. Possible fluorescence quenching mechanism
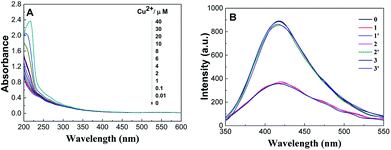
As is well-known, Cu2+ ions with paramagnetic properties are prone to quench the fluorescence of metal nanoclusters due to their strong affinity to some functional groups present on the surface of metal nanoclusters.39,44,51 We rationalize that DCTX as the capping and reducing agent contains some amino and carboxyl groups and is a high-affinity chelating agent towards Cu2+ ions like glutathione;45 thus, it would lead to fluorescence quenching of AuNCs@DCTX in the presence of Cu2+ ions. We explored the practicality of the as-prepared AuNCs@DCTX system for the detection of Cu2+. Interestingly, it was observed that the fluorescence of AuNCs@DCTX was selectively quenched by Cu2+. This phenomenon of fluorescence quenching might be due to a high possibility of aggregation of nanoclusters via complexation between the Cu2+ ions and the amino and carboxyl groups of DCTX grafted on the surface of AuNCs; this blocked the effective Au–S charge transfer process at the interface of AuNCs@DCTX, and the fluorescence of AuNCs@DCTX was quenched.52,53 As expected, the HRTEM image, as shown in Fig. 6A, revealed that the average diameter of particles increased to around 5.02 nm in the presence of Cu2+ ions (Fig. S7†), and the selected area electron diffraction pattern, as shown in Fig. 6B, verified the crystalline nature of the AuNCs@DCTX-Cu2+ system. As depicted in Fig. 7A, a distinct peak appeared in the UV-vis absorption spectra of the AuNCs@DCTX-Cu2+ system when the concentration of the quenching Cu2+ was above 10 μM. Furthermore, the absorption peak was red-shifted with an increase in the concentration of Cu2+. This could be another evidence of the coordination between Cu2+ and AuNCs@DCTX. However, the absence of a surface plasmon absorption peak at around 520 nm further ruled out the possibility of gold nanoparticle formation. To further elucidate the sensing mechanism, a strong chelator, EDTA, was added to the system to compete with AuNCs@DCTX for Cu2+. Fig. 7B shows that after quenching by Cu2+, the fluorescence intensity of AuNCs@DCTX can be reversibly recovered after adding EDTA at [EDTA]≈[Cu2+]. Preliminary experiments indicated that EDTA had no influence on the fluorescence intensity of AuNCs@DCTX in the absence of Cu2+ under the same conditions. The recovery of the fluorescence of AuNCs@DCTX stemmed from the formation of the Cu2+–EDTA complex, allowing the release of AuNCs@DCTX. The reversibility further confirmed that AuNCs@DCTX aggregation was induced by complexation between Cu2+ and the functional groups of DCTX of AuNCs@DCTX.44 Moreover, after three cycles, the fluorescence intensity of AuNCs@DCTX was still maintained at 96.3% of the initial value; this indicated that the as-prepared AuNCs@DCTX as a probe could be reusable.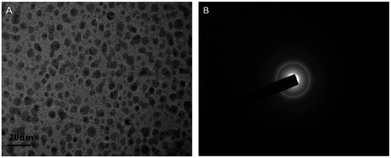 | ||
| Fig. 6 The HRTEM image (A) and the selected electron diffraction pattern (B) of the prepared AuNCs@DCTX after adding Cu2+ in PBS (scale bar = 20 nm). | ||
To further explore the fluorescence quenching mechanism, the quenching process was fitted by the Stern–Volmer equation:54
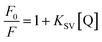 | (1) |
| KSV = Kqτ0 | (2) |
3.4. Determination of Cu2+ in CHMs
The practicality of AuNCs@DCTX was investigated by determining Cu2+ in four CHMs i.e. licorice, alisma, salvia and poria. We found that iron in these four CHMs, which was about 5–20 times as abundant as copper, would interfere with the determination of Cu2+. Accordingly, a certain amount of NaF, as a complexing agent for Fe3+, was added to the AuNCs@DCTX-Cu2+ system, and the analytical results of Cu2+ in the four CHMs were obtained, as listed in Table S1.† Moreover, these four CHMs were analyzed by the FAAS. As shown in Table S1,† our results with an absolute value of the relative error less than 8.6% were similar to those obtained by the reference FAAS method. The consistent analytical results confirmed the reliability of the AuNCs@DCTX-based method for the determination of Cu2+ in CHM samples.4. Conclusions
Herein, we successfully prepared water-soluble AuNCs@DCTX via a one-pot approach using the degradation product of CTX as the capping and reducing agent. The synthesis process was simple and environmentally friendly. Due to the high colloidal stability and multifunctional groups, the AuNCs@DCTX probe had acceptable selectivity for the detection of Cu2+ through aggregation-induced fluorescence quenching. Further applications were confirmed by the analysis of licorice, alisma, salvia and poria in the presence of NaF, and the results obtained via our study were in agreement with those determined by the FAAS method; this demonstrated that the proposed probe had great potential for the determination of Cu2+ in complicated samples.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
The financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21107022), the Key Scientific Research Project of Higher Education of Henan Province of China (No. 18A150034) and the Natural Science Foundation of Henan province of China (No. 182300410257) is gratefully acknowledged.Notes and references
- H. Huo, Y. Liu, W. Liu, J. Sun, Q. Zhang, Y. Zhao, J. Zheng, P. Tu, Y. Song and J. Li, J. Chromatogr. A, 2018, 1558, 37–49 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Meng, Y. Wei, H. Lu, X. Zhou, J. Liu, G. Li and J. Hou, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2013, 24, 506–508 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Ting, Y. Chow and W. Tan, J. Tradit. Chin. Med., 2013, 33, 119–124 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. M. Memon, E. Yilmaz and M. Soylak, Talanta, 2017, 174, 645–651 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Liu, J. Qin, X. Dou, M. Yang and X. Sun, Chin. Herb. Med., 2018, 10, 117–136 CrossRef.
- M. T. F. Teodoro, F. d. S. Dias, D. G. da Silva, M. A. Bezerra, A. F. Dantas, L. S. G. Teixeira and A. L. C. Pereira, Microchem. J., 2017, 132, 351–357 CrossRef CAS.
- G. P. C. Rao, K. Seshaiah, Y. K. Rao and M. C. Wang, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2006, 54, 2868–2872 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. A. Deshmukh, H. K. Patil, G. A. Bodkhe, M. Yasuzawa, P. Koinkar, A. Ramanaviciene, M. D. Shirsat and A. Ramanavicius, Sens. Actuators, B, 2018, 260, 331–338 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Zhan, H. Xu, W. Zhang, X. Zhan, Y. Wu, L. Wang and P. Zhou, Talanta, 2015, 142, 176–182 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Sun, Y. Li, Q. Niu, T. Li and Y. Liu, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2018, 195, 142–147 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. R. Bhamore, S. Jha, T. J. Park and S. K. Kailasa, Sens. Actuators, B, 2018, 277, 47–54 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Wang, J. Yu, X. Wang, L. Wang, B. Li, D. Shen, Q. Kang and L. Chen, Microchim. Acta, 2018, 185, 420 CrossRef PubMed.
- N. Wang, Y. Liu, Y. Li, Q. Liu and M. Xie, Sens. Actuators, B, 2018, 255, 78–86 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Qi, B. Li, X. Wang, Z. Zhang, Z. Wang, J. Han and L. Chen, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 251, 224–233 CrossRef CAS.
- M. H. Ibrahim, W. Gao, M. Saqib, S. A. Kitte, F. Wu and G. Xu, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2017, 95, 8–14 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. Ding, L. Guan, J. Han, R. Mangala and Z. Luo, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 250, 364–371 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Hu, X. Mao, X. Zhang and Y. Huang, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 247, 312–318 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Hu, T. Liu, Y. Zhuang, W. Wang, Y. Li, W. Fan and Y. Huang, TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem., 2016, 77, 66–75 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Zhang and E. Wang, Nano Today, 2014, 9, 132–157 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wu, Z. Zhang, J. Li, H. You, Y. Li and L. Chen, Sens. Actuators, B, 2015, 211, 507–514 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Ding, S. Wang, J. Li and L. Chen, TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem., 2016, 82, 175 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Chen, C. Wang, Z. Yuan and H. Chang, Anal. Chem., 2014, 87, 216–229 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Luo, J. Di, L. Li, Y. Tu and J. Yan, Talanta, 2018, 187, 231–236 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Liu, X. Wang, Y. Wang, J. Li, D. Shen, Q. Kang and L. Chen, Sens. Actuators, B, 2018, 262, 810–817 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Chen, A. P. Periasamy, S. G. Harroun, W. Wu and H. Chang, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2016, 320–321, 129–138 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Jiang, P. Gao, Y. Zhang, G. Zhang, Y. Zhou, C. Dong and S. Shuang, Talanta, 2017, 174, 44–51 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Zhao, C. Chen, J. Zhao, J. Sun and X. Yang, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 247, 392–399 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Ding, Y. Liu, R. Cong and J. Wang, Talanta, 2004, 62, 997–1003 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Jiang, Y. Li, M. Pelzer, M. J. Cannon, C. Randlett, H. Junga, X. Jiang and Q. C. Ji, J. Chromatogr. A, 2008, 1192, 230–238 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Yu, Z. Zhu, H. Wang, L. Li, F. Fu, Y. Song and E. Song, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2017, 91, 143–148 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Bagheri Gh, A. Yosefi rad, M. Rezvani and S. Roshanzamir, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2012, 89, 317–321 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Wu, Y. Zhang, W. Zhao and Q. Li, J. Chin. Chem. Soc., 2008, 55, 550–556 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Liu, S. Dong and L. Han, Chin. J. Spectrosc. Lab., 2007, 24, 31–33 Search PubMed.
- H. Deng, F. Wang, X. Shi, H. Peng, A. Liu, X. Xia and W. Chen, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2016, 83, 1–8 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Huang, H. Li, J. Feng, H. Feng, A. Wang and Z. Qian, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 241, 292–297 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Liu, M. Li, Y. Xia and X. Ren, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9, 120–126 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Xu, H. Yang, K. Zhao, J. Li, L. Mei, Y. Xie and A. Deng, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 11343–11348 RSC.
- H. Ding, C. Liang, K. Sun, H. Wang, J. K. Hiltunen, Z. Chen and J. Shen, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2014, 59, 216–220 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Deng, L. Zhang, S. He, A. Liu, G. Li, X. Lin, X. Xia and W. Chen, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2015, 65, 397–403 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Wu and R. Jin, Nano Lett., 2010, 10, 2568–2573 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Tian, W. Zhao, L. Li, Y. Tong, G. Peng and Y. Li, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 240, 114–124 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Xu, X. Feng, T. Gao, R. Wang, Y. Mao, J. Lin, X. Yu and X. Luo, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2017, 958, 22–29 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Yang, Z. Jia, Z. Tan, H. Xu, N. Luo and X. Liao, Food Control, 2016, 70, 286–292 CrossRef CAS.
- C. V. Durgadas, C. P. Sharmaa and K. Sreenivasan, Analyst, 2011, 136, 933–940 RSC.
- G. Zhang, Y. Li, J. Xu, C. Zhang, S. Shuang, C. Dong and M. M. F. Choi, Sens. Actuators, B, 2013, 183, 583–588 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zhang, H. Le, X. Jiang, S. Guo, H. Yu and B. Ye, Talanta, 2013, 117, 399–404 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Qing, H. Bu, X. He, D. He, B. Zhou, H. Sun, R. Jia, W. Ma and K. Wang, Anal. Methods, 2017, 9, 6222–6227 RSC.
- K. Shanmugaraj and M. Ilanchelian, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 54518–54524 RSC.
- S. Chen, Y. Kuang, P. Zhang, Y. Huang, A. Wen, X. Zeng, R. Feng, H. Nie, X. Jiang and Y. Long, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 253, 283–291 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Liu, J. Qi, C. Hu, L. Zhang, W. Song, R. Liang and J. Qiu, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2015, 895, 95–103 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Li, J. Feng, P. Huang and F. Wu, New J. Chem., 2017, 41, 12930–12936 RSC.
- J. S. Anjali Devi, S. Salini, A. H. Anulekshmi, G. L. Praveen and G. Sony, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 246, 943–951 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Chen, X. Tu and X. Guo, Chem. Commun., 2009, 1736–1738 RSC.
- H. Jia, C. Feng and C. Tian, Anal. Sci., 2018, 34, 1079–1083 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Mehrzad-Samarin, F. Faridbod and M. R. Ganjali, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2019, 206, 430–436 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Wu, Z. Chen, G. Huang and X. Liu, Sens. Actuators, A, 2014, 205, 72–78 CrossRef CAS.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c8ra09987a |
| ‡ The authors contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 |