Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
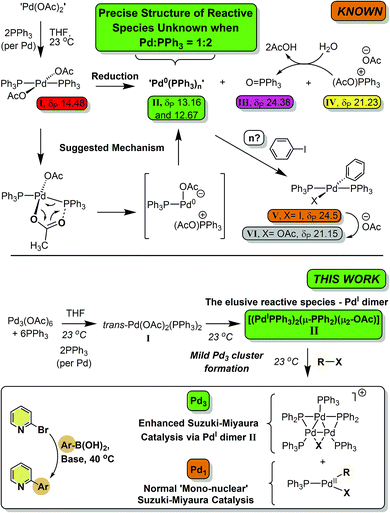
The ubiquitous cross-coupling catalyst system ‘Pd(OAc)2’/2PPh3 forms a unique dinuclear PdI complex: an important entry point into catalytically competent cyclic Pd3 clusters†
Neil W. J.
Scott
 a,
Mark J.
Ford
b,
Christoph
Schotes
c,
Rachel R.
Parker
a,
Mark J.
Ford
b,
Christoph
Schotes
c,
Rachel R.
Parker
 a,
Adrian C.
Whitwood
a,
Adrian C.
Whitwood
 a and
Ian J. S.
Fairlamb
a and
Ian J. S.
Fairlamb
 *a
*a
aDepartment of Chemistry, University of York, Heslington, York, North Yorkshire YO10 5DD, UK. E-mail: ian.fairlamb@york.ac.uk
bBayer Aktiengesellschaft, Crop Science Division, Industriepark Höchst G836, 65926 Frankfurt am Main, Germany
cBayer AG, Crop Science Division, Building A729, 415, 41539 Dormagen, Germany
First published on 12th July 2019
Abstract
Palladium(II) acetate ‘Pd(OAc)2’/nPPh3 is a ubiquitous precatalyst system for cross-coupling reactions. It is widely accepted that reduction of in situ generated trans-[Pd(OAc)2(PPh3)2] affords [Pd0(PPh3)n] and/or [Pd0(PPh3)2(OAc)]− species which undergo oxidative addition reactions with organohalides – the first committed step in cross-coupling catalytic cycles. In this paper we report for the first time that reaction of Pd3(OAc)6 with 6 equivalents of PPh3 (i.e. a Pd/PPh3 ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2) affords a novel dinuclear PdI complex [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2] as the major product, the elusive species resisting characterization until now. While unstable, the dinuclear PdI complex reacts with CH2Cl2, p-fluoroiodobenzene or 2-bromopyridine to afford Pd3 cluster complexes containing bridging halide ligands, i.e. [Pd3(X)(PPh2)2(PPh3)3]X, carrying an overall 4/3 oxidation state (at Pd). Use of 2-bromopyridine was critical in understanding that a putative 14-electron mononuclear ‘PdII(R)(X)(PPh3)’ is released on forming [Pd3(X)(PPh2)2(PPh3)3]X clusters from [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2]. Altering the Pd/PPh3 ratio to 1
2) affords a novel dinuclear PdI complex [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2] as the major product, the elusive species resisting characterization until now. While unstable, the dinuclear PdI complex reacts with CH2Cl2, p-fluoroiodobenzene or 2-bromopyridine to afford Pd3 cluster complexes containing bridging halide ligands, i.e. [Pd3(X)(PPh2)2(PPh3)3]X, carrying an overall 4/3 oxidation state (at Pd). Use of 2-bromopyridine was critical in understanding that a putative 14-electron mononuclear ‘PdII(R)(X)(PPh3)’ is released on forming [Pd3(X)(PPh2)2(PPh3)3]X clusters from [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2]. Altering the Pd/PPh3 ratio to 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4 forms Pd0(PPh3)3 quantitatively. In an exemplar Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction, the importance of the ‘Pd(OAc)2’/nPPh3 ratio is demonstrated; catalytic efficacy is significantly enhanced when n = 2. Employing ‘Pd(OAc)2’/PPh3 in a 1
4 forms Pd0(PPh3)3 quantitatively. In an exemplar Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction, the importance of the ‘Pd(OAc)2’/nPPh3 ratio is demonstrated; catalytic efficacy is significantly enhanced when n = 2. Employing ‘Pd(OAc)2’/PPh3 in a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 ratio leads to the generation of [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2] which upon reaction with organohalides (i.e. substrate) forms a reactive Pd3 cluster species. These higher nuclearity species are the cross-coupling catalyst species, when employing a ‘Pd(OAc)2’/PPh3 of 1
2 ratio leads to the generation of [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2] which upon reaction with organohalides (i.e. substrate) forms a reactive Pd3 cluster species. These higher nuclearity species are the cross-coupling catalyst species, when employing a ‘Pd(OAc)2’/PPh3 of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2, for which there are profound implications for understanding downstream product selectivities and chemo-, regio- and stereoselectivities, particularly when employing PPh3 as the ligand.
2, for which there are profound implications for understanding downstream product selectivities and chemo-, regio- and stereoselectivities, particularly when employing PPh3 as the ligand.
Introduction
Palladium(II) acetate ‘Pd(OAc)2’ is commonly used in combination with tertiary phosphine ligands, e.g. PPh3, to generate active catalyst species for an eclectic array of cross-coupling reactions,1 where it is universally accepted that ‘Pd0(PPh3)n’ species are formed.2 Such species enter into oxidative reactions with organohalides, e.g. iodobenzene to generate trans-[Pd(I)(Ph)(PPh3)2].3 Considerable and notable efforts have been made by Amatore and Jutand4 to understand how varying the ‘Pd(OAc)2’/nPPh3 ratio affects the generation of reduced palladium species in both THF and DMF. Following extensive NMR spectroscopic and electrochemical measurements, conclusions were drawn implicating phosphine-induced reduction of ‘Pd(OAc)2’/nPPh3 mixtures, via trans-[Pd(OAc)2(PPh3)2], by an intramolecular process (independent of phosphine concentration, once the latter complex is formed).4 The global findings from Amatore and Jutand are detailed in Scheme 1, showing the key intermediate species observed by 31P NMR spectroscopic studies. Comparisons of these data were made with complexes generated from [Pd(PPh3)4] in the presence of n-Bu4NOAc,4a under electrochemical conditions. The conclusions were that ‘Pd0(PPh3)n’ species are generated in situ from the reaction of Pd(OAc)2’/2PPh3 mixtures.4a Later studies showed that increasing the Pd/PPh3 ratio to 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 and above led to the clean generation of [Pd0(PPh3)n(OAc)]− species (n = 2 or 3), with O
3 and above led to the clean generation of [Pd0(PPh3)n(OAc)]− species (n = 2 or 3), with O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) PPh3 being a key side product, i.e. formed during the formal PdII → Pd0 reduction process.4b,c Both ‘Pd0(PPh3)2’ and [Pd0(PPh3)2(OAc)]− species react by oxidative addition with organohalides.
PPh3 being a key side product, i.e. formed during the formal PdII → Pd0 reduction process.4b,c Both ‘Pd0(PPh3)2’ and [Pd0(PPh3)2(OAc)]− species react by oxidative addition with organohalides.
 | ||
Scheme 1 Reactions of ‘Pd(OAc)2’ with PPh3 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 ratio). 31P NMR spectral data are taken from ref. 4a. 2 ratio). 31P NMR spectral data are taken from ref. 4a. | ||
Later, Kollár et al. examined the reaction of ‘Pd(OAc)2’/nPPh3 in DMF,5 amongst other phosphines, concluding that ‘Pd0(PPh3)n’ species are formed under ambient reaction conditions. Taken together these studies suggest that a Pd/PPh3 ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 is necessary for satisfactory catalytic cross-coupling performance.
3 is necessary for satisfactory catalytic cross-coupling performance.
Over the last 20 years we have regularly debated the differences in cross-coupling catalyst system performance on changing the Pd/PPh3 ratio from 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 to 1
2 to 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3.6 When papers are reported employing a Pd/PPh3 ratio of 1
3.6 When papers are reported employing a Pd/PPh3 ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 we have asked the why, as 1
2 we have asked the why, as 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 would be ideal based on the outcomes of previous studies;4 in other words, optimal conditions for forming catalytically active [Pd0(PPh3)n(OAc)]− species requires ≥3 equivalents of PPh3 per Pd, “not 2 equivalents”, when ‘Pd(OAc)2’ is used as the initial PdII precatalyst.
3 would be ideal based on the outcomes of previous studies;4 in other words, optimal conditions for forming catalytically active [Pd0(PPh3)n(OAc)]− species requires ≥3 equivalents of PPh3 per Pd, “not 2 equivalents”, when ‘Pd(OAc)2’ is used as the initial PdII precatalyst.
A superb recent example is found in the high-throughput automated reaction screening study conducted by a team from Pfizer,7 where a Pd/PPh3 ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 was used for 480 Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling (SMCC) reactions, involving changes in solvent and base, against relatively minor changes in substrate structure, correlated alongside many other phosphine ligands (over 5760 reactions in total). Cronin et al. further applied a machine learning algorithm based on the product percentage yields.8 With such important developments being made in automation, reaction optimization and machine learning,9 knowing precisely the reactive Pd species, formed under working reaction conditions, has never been more important. Thus, herein we report that the reaction of Pd3(OAc)6 with 6 equivalents of PPh3 (Pd
2 was used for 480 Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling (SMCC) reactions, involving changes in solvent and base, against relatively minor changes in substrate structure, correlated alongside many other phosphine ligands (over 5760 reactions in total). Cronin et al. further applied a machine learning algorithm based on the product percentage yields.8 With such important developments being made in automation, reaction optimization and machine learning,9 knowing precisely the reactive Pd species, formed under working reaction conditions, has never been more important. Thus, herein we report that the reaction of Pd3(OAc)6 with 6 equivalents of PPh3 (Pd![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) PPh3, 1
PPh3, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
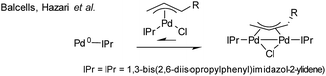
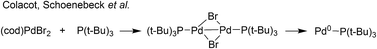
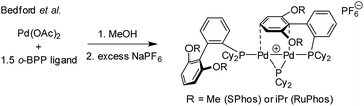
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2), in both THF and DMF, generates a well-defined [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2] complex II. The formation of this unusual species adds to the mechanistic debate concerning the activation pathways for Pd(II) precatalysts, particularly papers reported by: (a) Balcells and Hazari10a showing formation of PdI dimers with NHC ligands and bridging allyl and chloride ligands (eqn (1)); (b) Colacot and Schoenebeck10b showing formation of PdI dimers with phosphines and bridging bromide ligands (eqn (2)); (c) Bedford10c showing SPhos activation on reaction with Pd(OAc)2 (eqn (3)); (d) Jutand and Grimaud10d showing XPhos reactions with Pd(OAc)2 leading to a proposed PdI dimer (eqn (4)).
2), in both THF and DMF, generates a well-defined [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2] complex II. The formation of this unusual species adds to the mechanistic debate concerning the activation pathways for Pd(II) precatalysts, particularly papers reported by: (a) Balcells and Hazari10a showing formation of PdI dimers with NHC ligands and bridging allyl and chloride ligands (eqn (1)); (b) Colacot and Schoenebeck10b showing formation of PdI dimers with phosphines and bridging bromide ligands (eqn (2)); (c) Bedford10c showing SPhos activation on reaction with Pd(OAc)2 (eqn (3)); (d) Jutand and Grimaud10d showing XPhos reactions with Pd(OAc)2 leading to a proposed PdI dimer (eqn (4)).
The stability and reactivity of these PdI dimers appear to be critical in understanding the delivery of active ‘L–Pd0’ species, a process dependent on L/Pd ratios and additives. From our study we find that [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2] II, exhibits unique reactivity toward organohalides, e.g. CH2Cl21a, p-fluoro-iodobenzene 1b and 2-bromopyridine 1c, which affords Pd3 cluster species, namely [Pd3(X)(μ-PPh2)2(PPh3)3]X VII (later referred to as Pd3X·X, where X = Cl, Br, I or OAc). Our results naturally connect to a recent report showing that Pd3Cl·Cl is a highly active catalyst for SMCC reactions, including the activation of substrates containing harder to activate C–Cl bonds.11Pd3Cl·Cl invokes an unusual switch in cross-coupling steps from oxidative addition then transmetallation to transmetallation and then oxidative addition.11
 | (1) |
 | (2) |
 | (3) |
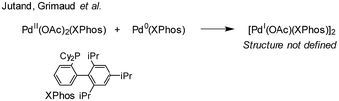 | (4) |
Results and discussion
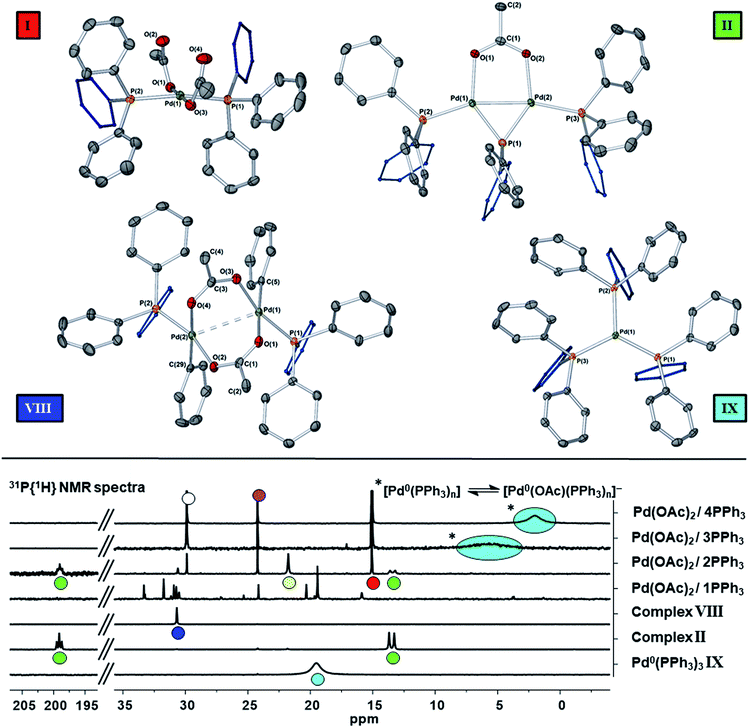
The reaction of ultra-pure Pd3(OAc)6 (>99% purity) with PPh3, in varying ratios, in THF-d8 were conducted at room temperature (25 °C) and monitored by 1H and 31P NMR spectroscopic analysis (where [Pd] = 20 mM; T = 298 K, external reference = 85% H3PO4 in H2O). A wide spectral window (−50 to +250 ppm) was required to allow full characterization of the array of phosphorus signals and associated species formed under these reaction conditions (Fig. 1 and 2).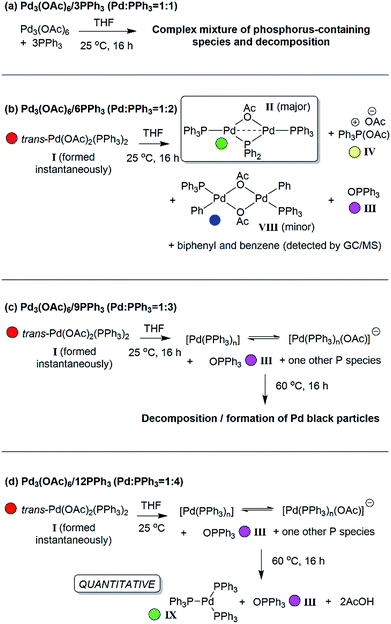 | ||
Fig. 1 The room temperature formation of dinuclear PdII complexes from trans-Pd(OAc)2(PPh3)2 in THF. (a) Ratio of Pd![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) PPh3 = 1 PPh3 = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; (b) ratio of Pd 1; (b) ratio of Pd![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) PPh3 = 1 PPh3 = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2; (c) ratio of Pd 2; (c) ratio of Pd![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) PPh3 = 1 PPh3 = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3; (d) ratio of Pd 3; (d) ratio of Pd![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) PPh3 = 1 PPh3 = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4. The Pd0 species Pd0(PPh3)3IX and [Pd0(PPh3)3OAc]−IX′ are indicated by cyan circles (appearing as coincident signals by 31P NMR spectroscopic analysis when present together – compare top two 31P NMR spectra in Fig. 2 with the authentic sample of Pd0(PPh3)3IX, bottom spectrum, Fig. 2). 4. The Pd0 species Pd0(PPh3)3IX and [Pd0(PPh3)3OAc]−IX′ are indicated by cyan circles (appearing as coincident signals by 31P NMR spectroscopic analysis when present together – compare top two 31P NMR spectra in Fig. 2 with the authentic sample of Pd0(PPh3)3IX, bottom spectrum, Fig. 2). | ||
Where the ratio of Pd![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) PPh3 was 1
PPh3 was 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, degradation of Pd3(OAc)6, leading to the formation of large perfectly spherical Pd particles (sized ∼0.1–0.4 μm, by TEM) and many P-containing species (by 31P NMR) was observed (Fig. 1(a)). Alteration of the Pd/PPh3 ratio to 1
1, degradation of Pd3(OAc)6, leading to the formation of large perfectly spherical Pd particles (sized ∼0.1–0.4 μm, by TEM) and many P-containing species (by 31P NMR) was observed (Fig. 1(a)). Alteration of the Pd/PPh3 ratio to 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 (Fig. 1(b)) led to the formation of a major new phosphorus-containing species at δ 199.01 (t, 1P) and δ 13.41 (d, 2P), with a 2JPP coupling constant of 83.5 Hz (i.e. an AX2 type spin system). The high 31P chemical shift of δ 199.01 indicates that the PPh3 ligand has been activated by P–C bond-cleavage to give a bridging phosphido-group at Pd, with concomitant loss of ‘C6H5’. The 1H NMR spectrum shows a methyl resonance at δ 2.08 (s, 3H), due to a bridging acetoxy ligand, which balances with aromatic proton integrals (40H). Running the reaction at lower Pd3(OAc)6 concentration (between 3 and 20 mM) allowed this species to be isolated in a form that could be crystallized. X-ray diffraction analysis of dark red single crystals of this species confirmed its structure as [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2] II, possessing both bridging μ2-acetoxy and μ-phosphido ligands and terminal-capping PPh3 ligands. Complex II is a diamagnetic species. The Pd–Pd bond distance was found to be 2.5958(3) Å, which is in-keeping with other dinuclear PdI complexes with bridging μ-acetoxy ligands known in the literature (typical Pd–Pd distances 2.532 to 2.711 Å), and shorter than a related structure, [Pd2(η3-allyl)(μ-OC(O)i-Bu)(PPh3)2] where the Pd⋯Pd bond distance equals 2.6267(3).12
2 (Fig. 1(b)) led to the formation of a major new phosphorus-containing species at δ 199.01 (t, 1P) and δ 13.41 (d, 2P), with a 2JPP coupling constant of 83.5 Hz (i.e. an AX2 type spin system). The high 31P chemical shift of δ 199.01 indicates that the PPh3 ligand has been activated by P–C bond-cleavage to give a bridging phosphido-group at Pd, with concomitant loss of ‘C6H5’. The 1H NMR spectrum shows a methyl resonance at δ 2.08 (s, 3H), due to a bridging acetoxy ligand, which balances with aromatic proton integrals (40H). Running the reaction at lower Pd3(OAc)6 concentration (between 3 and 20 mM) allowed this species to be isolated in a form that could be crystallized. X-ray diffraction analysis of dark red single crystals of this species confirmed its structure as [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2] II, possessing both bridging μ2-acetoxy and μ-phosphido ligands and terminal-capping PPh3 ligands. Complex II is a diamagnetic species. The Pd–Pd bond distance was found to be 2.5958(3) Å, which is in-keeping with other dinuclear PdI complexes with bridging μ-acetoxy ligands known in the literature (typical Pd–Pd distances 2.532 to 2.711 Å), and shorter than a related structure, [Pd2(η3-allyl)(μ-OC(O)i-Bu)(PPh3)2] where the Pd⋯Pd bond distance equals 2.6267(3).12
A scaled-up synthesis of II was found possible from Pd3(OAc)6/6PPh3, formed in 31% yield (note: some Pd is lost as large particles during its preparation), which was fully characterized. Interestingly, the LIFDI-MS data showed that the dinuclear PdI complex was present in solution (M+˙ = m/z 982, with the correct isotopic distribution). The reference 31P NMR spectrum for purified II is given in Fig. 2 (externally-referenced to H3PO4). GC-MS analysis of the crude reaction mixture containing II indicated that benzene and biphenyl were present, the former most likely derived from protonation of ‘Pd–Ph’ species by adventitious water/AcOH and the latter by reductive elimination. Acetoxybenzene, a possible reductive elimination product, was not detected by GC-MS analysis. These species are accompanied by O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) PPh3III, [Ph3P(OAc)]X IV and another dinuclear PdII species VIII, the latter only in minor amounts. Complex VIII was previously reported as a major product of a reaction of ‘Pd(OAc)2’ with 2 equivalents of PPh3 on heating in methanol (41% yield).13 It is worth noting that complex II is stable in dry THF solutions over 12 hours, which allows for its spectroscopic characterization, but decomposition is seen after ca. 5 days at 22–25 °C.
PPh3III, [Ph3P(OAc)]X IV and another dinuclear PdII species VIII, the latter only in minor amounts. Complex VIII was previously reported as a major product of a reaction of ‘Pd(OAc)2’ with 2 equivalents of PPh3 on heating in methanol (41% yield).13 It is worth noting that complex II is stable in dry THF solutions over 12 hours, which allows for its spectroscopic characterization, but decomposition is seen after ca. 5 days at 22–25 °C.
On changing the Pd/PPh3 ratio to 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 complex II was not formed, simply a broad resonance at δ 5.71 (FWHM ca. 550 Hz) characterized as Pd0(PPh3)n/[Pd0(PPh3)n(OAc)]P(OAc)Ph3 (n = 1, 2 or 3), see Fig. 1(c). The chemical shift alters with time, with concomitant formation of O
3 complex II was not formed, simply a broad resonance at δ 5.71 (FWHM ca. 550 Hz) characterized as Pd0(PPh3)n/[Pd0(PPh3)n(OAc)]P(OAc)Ph3 (n = 1, 2 or 3), see Fig. 1(c). The chemical shift alters with time, with concomitant formation of O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) PPh3, by hydrolysis of [Ph3P(OAc)]X IV, yielding AcOH also. Heating this mixture to 60 °C, over 16 h, eventually ended in decomposition to form large Pd black particles. Indeed, similar 31P NMR spectra were seen on changing the Pd/PPh3 ratio to 1
PPh3, by hydrolysis of [Ph3P(OAc)]X IV, yielding AcOH also. Heating this mixture to 60 °C, over 16 h, eventually ended in decomposition to form large Pd black particles. Indeed, similar 31P NMR spectra were seen on changing the Pd/PPh3 ratio to 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4, see Fig. 1(d), leading to a mixture of Pd0(PPh3)3IX and [Pd0(OAc)(PPh3)3]−IX′. At the same Pd/PPh3 ratio, subsequent heating to 60 °C resulted in clean conversion of II into Pd0(PPh3)3 (IX), O
4, see Fig. 1(d), leading to a mixture of Pd0(PPh3)3IX and [Pd0(OAc)(PPh3)3]−IX′. At the same Pd/PPh3 ratio, subsequent heating to 60 °C resulted in clean conversion of II into Pd0(PPh3)3 (IX), O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) PPh3 (III) and 2AcOH, quantitatively, as shown by both 31P and 1H NMR spectra. Layering this solution with hexane, after t = 16 h, led to the formation of yellow-orange crystals, which were found suitable for X-ray diffraction, establishing the compound as Pd0(PPh3)3 (IX) (Fig. 2). It is worthy of note that Pd0(PPh3)3IX is a relatively stable Pd0 complex in the solid-state (note: discoloration is noted in air after ∼1 day).
PPh3 (III) and 2AcOH, quantitatively, as shown by both 31P and 1H NMR spectra. Layering this solution with hexane, after t = 16 h, led to the formation of yellow-orange crystals, which were found suitable for X-ray diffraction, establishing the compound as Pd0(PPh3)3 (IX) (Fig. 2). It is worthy of note that Pd0(PPh3)3IX is a relatively stable Pd0 complex in the solid-state (note: discoloration is noted in air after ∼1 day).
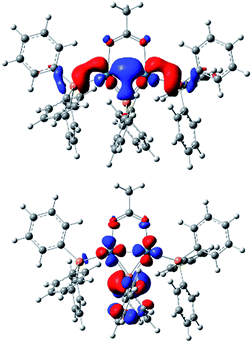
Computational studies using DFT calculations with [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2] II at the B3LYP/DEF2SVP-D3 level of theory. The calculations reveal a short Pd–Pd bond (2.58 Å), supporting its diamagnetic properties. The HOMO resides primarily on the Pd–Pd centers, whereas the LUMO can be found over the phosphide and Pd–Pd centers (Fig. 3). The HOMO/LUMO provide potential clues about the underlying reactivity of [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2] toward other species such as electrophiles and nucleophiles.
We believe that the mechanism for formation of II is different to the PdI dimer stabilised by a bridging arene, as reported by Bedford.10c In the latter case a sequential reaction in methanol was used, followed by treatment with a non-coordinating anion leaves a suitably-disposed arene to stabilise the cationic PdI dimer species, though Pd–π–arene interactions. In II acetate takes on that role.
Reactivity of II towards organohalides
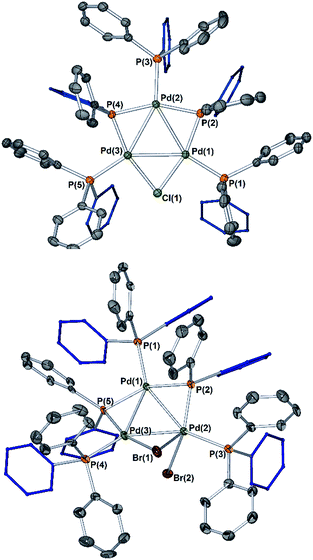
The reaction of [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2] II with CH2Cl21a (∼10-fold excess) occurred at room temperature to afford a new Pd species, which was identified as [Pd3(Cl)(PPh2)2(PPh3)3]OAc Pd3Cl·OAc by ESI studies (+ve mode, detected by the [M − OAc]+ ion) (Fig. 4).14 Real-time reaction monitoring by 31P NMR spectroscopic analysis showed that Pd3Cl·OAc formed over several hours at the expense of II. The data for Pd3Cl·OAc closely matches the data obtained from the independent synthesis of [Pd3(Cl)(μ-PPh2)2(PPh3)3]Cl Pd3Cl·Cl, starting from PdCl2(PPh3)2 in aniline under H2(g) at 90 °C, for which an X-ray structure of a single crystal was determined (Fig. 5).15 We were unable to trace the ‘CH2Cl’ fragment derived from CH2Cl2, ‘Pd(PPh3)1’ and acetate anion required to balance the overall chemical reaction. However, balance of overall charge and mass allows one to postulate a putative 14-electronic PdII species Xa. Similarly, reaction of II with p-fluoro-iodobenzene 1b afforded [Pd3(I)(μ-PPh2)2(PPh3)4]OAc Pd3I·OAc, as shown by 31P NMR and ESI data (as the [M − OAc]+ ion), which degraded rapidly to form Pd black. As with the reaction of II with CH2Cl21a, the ‘p-F-C6H4-’ fragment derived from 1b, ‘Pd(PPh3)1’ and OAc anion could not be fully traced (PdII species Xb is postulated).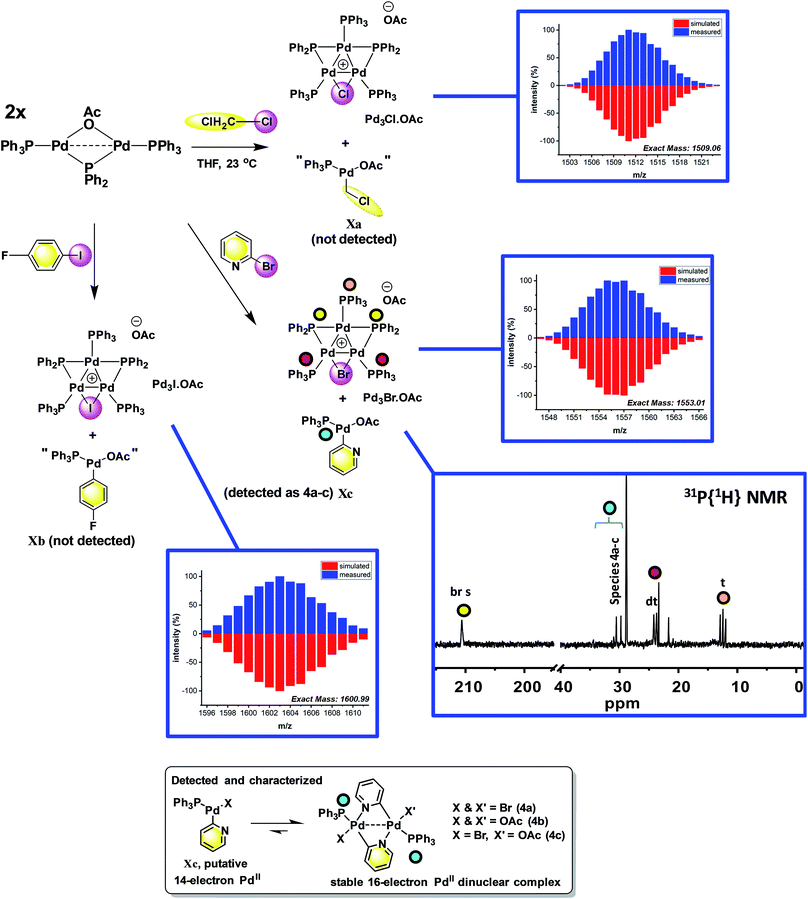 | ||
| Fig. 4 Reactions of dinuclear PdI complex II with organohalides (1a–c), leading to formation of Pd3 clusters Pd3X·OAc. The X anions in these clusters are likely acetate (mass balance is formally correct using acetate for all Pd species formed), although mixtures of different anions cannot be ruled out for species generated in situ. The MS ions are all observed by ESI (+ve mode) as molecular cations, the data for which is presented (measured – in blue; simulated – in red). The 31P{1H} NMR spectrum for species generated from the reaction of 2-bromopyridine 1c with II illustrates the formation of Pd3Br·OAc and species 4a–c (note a cut//in the 31P NMR spectrum is made between 40 and 190 ppm, due to the wide spectral range, for ease of viewing – full 31P NMR spectra are shown in the ESI†). | ||
To reveal whether putative 14-electron PdII species were formed in the reactions of II with organohalides (R-X) we hypothesized that a reaction with 2-bromopyridine 1c would enable characterization by the stabilization conferred by N-coordination from the pyridine ring, leading to formation of a stable 16-electron dinuclear PdII species (i.e.4a–c, Fig. 4).
To verify findings concerning formation of [Pd3(Br)(μ-PPh2)2(PPh3)3]OAc (Pd3Br·OAc) vide supra, a closely related sample was prepared by treatment of [Pd3(Cl)(μ-PPh2)2(PPh3)3]Cl (Pd3Cl·Cl) with excess KBr in CH2Cl2, giving [Pd3(Br)(μ-PPh2)2(PPh3)3]Br (Pd3Br·Br).16 The latter material possessed identical 31P NMR and MS data to that seen for Pd3Br·OAc from the reaction of II with 2-bromopyridine 1c. A reasonable single crystal X-ray diffraction structure for Pd3Br·Br was further determined (Fig. 5). Whilst a detailed comparison between Pd3Cl·Cl and Pd3Br·Br cannot be made (R1 factors for Pd3Cl·Cl = 3.58% and Pd3Br·Br = 7.04%), there are striking structural differences that necessitate additional comment. The cyclic 6-membered ‘Pd–P–Pd–Cl–Pd–P’ fragment is essentially flat in Pd3Cl·Cl, leaving the second chloride anion as non-coordinating. However, in Pd3Br·Br we see something quite different – the cyclic 6-membered ‘Pd–P–Pd–Br–Pd–P’ fragment is highly twisted, which is associated with an interacting second bromide anion.
It is tempting to draw an analogy here to a bromonium ion interacting with a bromide anion (i.e. reactions of alkenes with bromide proceeding via bromonium ion intermediates). The structural differences between Pd3Cl·Cl and Pd3Br·Br suggest that they could be distinctly different in how they operate in catalysis.
The relevance of our findings concerning reaction of II with organohalides requires contextualisation with the results recently reported by Schoenebeck and co-workers.17 It has been shown that [Pd(μ-I)P(t-Bu)3]2 reacts with PHPh2 (slight excess relative to the PdI dimer) in toluene at room temperature to give a Pd3 cluster containing three bridging phosphide ligands (Fig. 6). Subsequent reaction with an aryl halide then delivers a Pd3-type cluster containing a bridging iodide ligand, similar to the Pd3X·X clusters vide supra. The pathways to these Pd3 clusters are not the same. Complex II reacts directly with organohalides to give Pd3X·X clusters (where X = Cl, Br or I), i.e. additional phosphine is not necessary at this point. Indeed, if additional PPh3 (2 equiv.) is reacted with II (1 equiv.) in THF at room temperature we see the generation of Pd(PPh3)n species (where n = 3, this species was detected by LIFDI-MS, see ESI†). This finding is in-keeping with what was observed when Pd3(OAc)6 was reacted with nine equivalents of PPh3 (i.e. Pd/PPh3 ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3, Fig. 2). We expect that Pd0 complexes are generated from disproportionation of the PdI dinuclear complex II, upon addition of PR3, akin to the observations reported by Schoenebeck and Colacot.10b
3, Fig. 2). We expect that Pd0 complexes are generated from disproportionation of the PdI dinuclear complex II, upon addition of PR3, akin to the observations reported by Schoenebeck and Colacot.10b
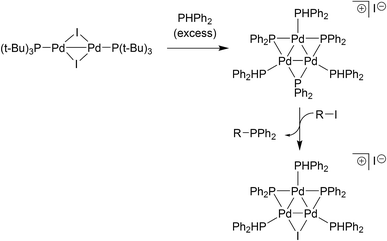 | ||
| Fig. 6 Schoenebeck's findings17 on the formation of a Pd3-type cluster from an electron-rich PdI dimer species. | ||
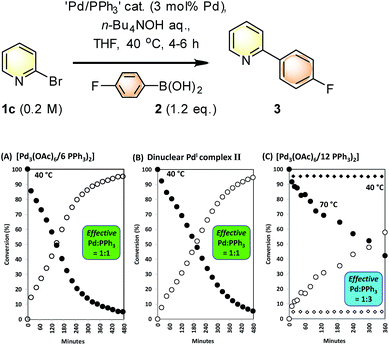
Importance of our findings in an exemplar SMCC reaction
To better understand the importance of the ‘Pd(OAc)2’/nPPh3 ratio in catalysis, the cross-coupling of 2-bromopyridine 1c with p-fluorophenylboronic acid 2 to give 2-arylpyridine 3 was examined,6b using 1 M n-Bu4NOH as the base, in a THF/water mixture (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, v/v) at 40 °C. We carefully selected 1 M n-Bu4NOH as the base, drawing on the recent findings concerning the importance of both the hydroxide anion and cation-type in SMCCs.18 Also pertinent to mention is that our SMCC reaction is homogeneous, i.e. not biphasic, simplifying the discussion concerning which phase the Pd catalyst and organoboron species reside in. Furthermore, operationally NMR spectroscopic analysis in operando was made feasible by use of aqueous n-Bu4NOH in THF.
1, v/v) at 40 °C. We carefully selected 1 M n-Bu4NOH as the base, drawing on the recent findings concerning the importance of both the hydroxide anion and cation-type in SMCCs.18 Also pertinent to mention is that our SMCC reaction is homogeneous, i.e. not biphasic, simplifying the discussion concerning which phase the Pd catalyst and organoboron species reside in. Furthermore, operationally NMR spectroscopic analysis in operando was made feasible by use of aqueous n-Bu4NOH in THF.
SMCC reactions of 1c + 2 → 3 were monitored in operando by 1H NMR spectroscopic analysis, allowing pre-stirred mixtures of ‘Pd3(OAc)6’/nPPh3 (n = 6 and 12, i.e. Pd/PPh3 = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 or 1
2 or 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4 respectively) to be compared in THF against a reaction mediated by [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2] II. The kinetic profiles for the appearance of 3, with concomitant disappearance of 1c (pseudo-zero order in 1c), are shown in Fig. 6. The kinetic profile for the reaction mediated by Pd3(OAc)6/6PPh3 (1
4 respectively) to be compared in THF against a reaction mediated by [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2] II. The kinetic profiles for the appearance of 3, with concomitant disappearance of 1c (pseudo-zero order in 1c), are shown in Fig. 6. The kinetic profile for the reaction mediated by Pd3(OAc)6/6PPh3 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2, Pd/PPh3) indicates that the reaction is efficient at 40 °C {Fig. 7(A)} – there is an exotherm during initial catalyst turnover (ca. 4 turnovers) which is associated with full dissolution of aqueous 1 M n-Bu4NOH (into THF – overall concentration equals 0.5 M n-Bu4NOH). The same reaction mediated by II showed a similar kinetic curve {Fig. 7(B)}, confirming the catalytic competency of this key species isolated earlier. Furthermore, no Pd particles were visibly seen to form during catalysis (the solution appearing completely homogeneous).
2, Pd/PPh3) indicates that the reaction is efficient at 40 °C {Fig. 7(A)} – there is an exotherm during initial catalyst turnover (ca. 4 turnovers) which is associated with full dissolution of aqueous 1 M n-Bu4NOH (into THF – overall concentration equals 0.5 M n-Bu4NOH). The same reaction mediated by II showed a similar kinetic curve {Fig. 7(B)}, confirming the catalytic competency of this key species isolated earlier. Furthermore, no Pd particles were visibly seen to form during catalysis (the solution appearing completely homogeneous).
Altering the Pd3(OAc)6/12PPh3 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4, Pd/PPh3) led to a poor catalyst system for reaction 1c + 2 → 3 at 40 °C {Fig. 7(C), curves illustrated by diamonds}. This catalyst system exhibited higher catalyst efficacy at 70 °C. Thus, additional phosphine slows down catalysis in the reaction of 1c + 2 → 3, at 40 °C, which is an outcome consistent with our previous studies on SMCCs involving 1c.6b
4, Pd/PPh3) led to a poor catalyst system for reaction 1c + 2 → 3 at 40 °C {Fig. 7(C), curves illustrated by diamonds}. This catalyst system exhibited higher catalyst efficacy at 70 °C. Thus, additional phosphine slows down catalysis in the reaction of 1c + 2 → 3, at 40 °C, which is an outcome consistent with our previous studies on SMCCs involving 1c.6b
With the finding that [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2] II reacts with 2-bromopyridine 1c to give [Pd3(Br)(μ-PPh2)2(PPh3)3]OAc (Pd3Br·OAc) and [Pd(X/X′)(N,C2-pyr)(PPh3)]2 (4a–c), additional catalytic experiments were devised to test the importance of such species in the SMCC reaction 1c + 2 → 3 (Fig. 8). Two control experiments, with different Pd catalysts, were conducted: (a) to establish the catalytic competency of Pd3Br·Br;19 (b) to assess the catalytic activity of [Pd(Br)(N,C2-pyr)(PPh3)]24a, under comparable reaction conditions. The reaction of 1c + 2 → 3, mediated by Pd3Br·Br (1 mol%, giving 1 mol% active Pd – the cluster being treated as a well-defined catalyst species11) gave 3 with full conversion after ca. 7.5 h at 40 °C (Fig. 8). The same reaction mediated by an authentic sample of 4a (0.5 mol% giving 1 mol% active Pd6b) gave 3 with 32% conversion after ca. 7.5 h. These control experiments establish that Pd3Br·Br is a significantly more active catalysis species than 4a. Thus, when generated in situ, we expect Pd3Br+ species to play a more dominant role in terms of the overall catalyst efficacy vide infra.
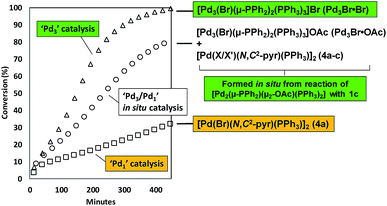 | ||
| Fig. 8 Overlay of kinetic curves for the SMCC reaction of 1c + 2 → 3, mediated by Pd3Br·Br (1 mol%), 4a (0.5 mol%) and II (1.5 mol%, generating Pd3Br·OAc, 4a–cin situ); other reaction conditions identical to Fig. 6. Reactions were monitored by 1H NMR spectroscopic analysis in a J. Young's NMR tube (spinning). | ||
With the kinetic profiles for the SMCC reaction of 1c + 2 → 3, mediated by either Pd3Br·Br or 4a, established, we could then qualitatively compare the catalytic activity mediated by Pd3Br·OAc and [Pd(X/X′)(N,C2-pyr)(PPh3)]2 (4a–c) species, formed in situ from the reaction of II with 1c.20 The observed catalyst activity sits between the high reactivity of Pd3Br·Br and comparatively lower activity of [Pd(Br)(N,C2-pyr)(PPh3)]24a.
Conclusion
In conclusion we have demonstrated that reaction of Pd3(OAc)6 with 6 equivalents of PPh3, that is in a Pd/PPh3 ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2, gives an intriguing dinuclear PdI complex, [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2], II. Species II is relatively unstable, but characterizable, and we propose it is this species that Amatore and Jutand detected in their early studies, which resisted characterization at that time.4a An important discovery was the finding that II reacts relatively cleanly with the organohalides, CH2Cl2 (1a), p-fluoroiodobenzene (1b) and 2-bromopyridine (1c) to afford Pd3 cluster complexes containing bridging halide ligands, i.e. [Pd3(X)(PPh2)2(PPh3)3]X, carrying an overall 4/3 oxidation state. Use of 2-bromopyridine 1c was critical in understanding that a putative 14-electron mononuclear ‘PdII(R)(X)(PPh3)’ is released on forming [Pd3(X)(PPh2)2(PPh3)3]X clusters from II. Altering the Pd/PPh3 ratio from 1
2, gives an intriguing dinuclear PdI complex, [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2], II. Species II is relatively unstable, but characterizable, and we propose it is this species that Amatore and Jutand detected in their early studies, which resisted characterization at that time.4a An important discovery was the finding that II reacts relatively cleanly with the organohalides, CH2Cl2 (1a), p-fluoroiodobenzene (1b) and 2-bromopyridine (1c) to afford Pd3 cluster complexes containing bridging halide ligands, i.e. [Pd3(X)(PPh2)2(PPh3)3]X, carrying an overall 4/3 oxidation state. Use of 2-bromopyridine 1c was critical in understanding that a putative 14-electron mononuclear ‘PdII(R)(X)(PPh3)’ is released on forming [Pd3(X)(PPh2)2(PPh3)3]X clusters from II. Altering the Pd/PPh3 ratio from 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 to 1
2 to 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4 forms Pd0(PPh3)3 quantitatively, generally in-keeping with Amatore's and Jutand's original studies.4 It has been established further that the Pd/PPh3 ratios are important in an exemplar SMCC reaction, Pd/PPh3 ratio Pd/PPh3 reaction, 1c + 2 → 3. Near identical catalytic efficacy was seen for a reaction mediated by either 1Pd(OAc)2/2PPh3 or II, whereas the 1Pd(OAc)2/4PPh3 catalyst system was significantly less effective, requiring a higher temperature (70 rather than 40 °C) for reasonable conversion to product 3 to be observed.
4 forms Pd0(PPh3)3 quantitatively, generally in-keeping with Amatore's and Jutand's original studies.4 It has been established further that the Pd/PPh3 ratios are important in an exemplar SMCC reaction, Pd/PPh3 ratio Pd/PPh3 reaction, 1c + 2 → 3. Near identical catalytic efficacy was seen for a reaction mediated by either 1Pd(OAc)2/2PPh3 or II, whereas the 1Pd(OAc)2/4PPh3 catalyst system was significantly less effective, requiring a higher temperature (70 rather than 40 °C) for reasonable conversion to product 3 to be observed.
An important take home message from our study is that where [Pd2(μ-PPh2)(μ2-OAc)(PPh3)2] II can form, i.e. when a ratio of Pd/PPh3 ratio is 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 employed in catalysis, reactions with organohalides (common starting materials for cross-coupling catalysis) afford catalytically competent Pd3 cluster complexes in situ, in addition to other known PdII species (i.e. oxidative addition products). If the relative amount of PPh3 ligand to Pd is low, then Pd clustering tends to occur, to afford either particles (where Pd/PPh3 = 1
2 employed in catalysis, reactions with organohalides (common starting materials for cross-coupling catalysis) afford catalytically competent Pd3 cluster complexes in situ, in addition to other known PdII species (i.e. oxidative addition products). If the relative amount of PPh3 ligand to Pd is low, then Pd clustering tends to occur, to afford either particles (where Pd/PPh3 = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), or ‘ligated clusters’, whereas well-defined dimers and trimers are formed where Pd/PPh3 = 1
1), or ‘ligated clusters’, whereas well-defined dimers and trimers are formed where Pd/PPh3 = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 (the major finding of this study) and when there is enough PPh3 ligand around, mono-nuclear Pd0(PPh3)n, i.e. n > 2, can be stabilised, aligning with a general understanding of ligated Pd0 species in text book mechanisms.
2 (the major finding of this study) and when there is enough PPh3 ligand around, mono-nuclear Pd0(PPh3)n, i.e. n > 2, can be stabilised, aligning with a general understanding of ligated Pd0 species in text book mechanisms.
Understanding how [Pd3(X)(μ-PPh2)2(PPh3)3]X clusters activate aryl/heteroaryl halides and organometallic coupling partners, e.g. aryl boronic acids,11 will no doubt be important going-forwards, which will enable their catalytic properties to be fully delineated and exploited in chemical synthesis. To emphasize this point further, similar Pd3-type clusters have been studied by Maestri and Malacria in catalysis, particularly hydrogenation.21 Our results, taken together with contributions made by others, show that Pd3-clusters are ripe for exploitation in applied catalysis.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
The project was funded by Bayer AG (PhD studentship to NWJS). We thank the University of York for supporting NMR spectrometers & X-ray equipment, and EPSRC for NMR upgrades (EP/K039660/1). We are grateful to Professor Robin N. Perutz and Dr Jason M. Lynam for many useful discussions regarding this research.Notes and references
- (a) K. C. Nicolaou, P. G. Bulger and D. Sarlah, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2005, 44, 4442–4489 CrossRef CAS; (b) C. Torborg and M. Beller, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2009, 351, 3027–3043 CrossRef CAS; (c) W. A. Carole and T. J. Colacot, Chem.–Eur. J., 2016, 22, 7686–7695 CrossRef CAS; (d) I. J. S. Fairlamb, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 10415–10427 CrossRef CAS; (e) P. Devendar, R.-Y. Qu, W.-M. Kang, B. He and G.-F. Yang, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2018, 66, 8914–8934 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) T. A. Stromnova, V. S. Sergienko, A. V. Kisin, M. A. Porai-Koshits and I. I. Moiseev, Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR, Div. Chem. Sci., 1987, 36, 821–824 CrossRef; (b) V. S. Sergienko and M. A. Porai-Koshits, J. Struct. Chem., 1988, 28, 548–552 CrossRef.
- J. A. Labinger, Organometallics, 2015, 34, 4784–4795 CrossRef CAS.
- In the original publication it was shown that trans-Pd(OAc)2(PPh3)2 forms an unstable Pd(0) species – excess PPh3 was required to form oxidative addition products of the type trans-Pd(I)Ph(PPh3)2 by reaction of Pd(PPh3)2 with PhI, see: (a) C. Amatore, A. Jutand and M. A. M'Barki, Organometallics, 1992, 11, 3009–3013 CrossRef CAS. The subsequent study employed higher PPh3/Pd(OAc)2 ratios, see: (b) C. Amatore, E. Carre, A. Jutand and M. A. M'Barki, Organometallics, 1995, 14, 1818–1826 CrossRef CAS. For the reactions of acetate anion with Pd(PPh3)4, see: (c) C. Amatore, E. Carre, A. Jutand, M. A. M'Barki and G. Meyer, Organometallics, 1995, 14, 5605–5614 CrossRef CAS. The global findings by Amatore and Jutand led to the proposal of anionic Pd intermediates playing a critical role in cross-coupling catalysis, see: (d) C. Amatore and A. Jutand, Acc. Chem. Res., 2000, 33, 314–321 Search PubMed.
- The reaction of Pd(OAc)2 with 2PPh3 was reported, leading to the proposal that a Pd0(PPh3)n species was formed, see: Z. Csákai, R. Skoda-Földes and L. Kollár, Inorg. Chim. Acta, 1999, 286, 93–97 CrossRef.
- The Pd/L ratio is important for effective cross-coupling catalysis, see:
(a) U. Christmann and R. Vilar, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2005, 44, 366–374 CrossRef CAS. The effect of the Pd/PPh3 was also previously examined by us, see:
(b) Suzuki–Miyaura cross-couplings, see: A. Beeby, S. Bettington, I. J. S. Fairlamb, A. E. Goeta, A. R. Kapdi, E. H. Niemela and A. L. A. Thompson, New J. Chem., 2004, 28, 600–605 RSC. A ratio of Pd(OAc)2/PAr3 of 1
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 was found optimal for SMCC reactions involving purines, see:
(c) T. E. Storr, J. A. Strohmeier, C. G. Baumann and I. J. S. Fairlamb, Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 6470–6472 RSC.
2 was found optimal for SMCC reactions involving purines, see:
(c) T. E. Storr, J. A. Strohmeier, C. G. Baumann and I. J. S. Fairlamb, Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 6470–6472 RSC. - D. Perera, J. W. Tucker, S. Brahmbhatt, C. J. Helal, A. Chong, W. Farrell, P. Richardson and N. W. Sachs, Science, 2018, 359, 429–434 CrossRef CAS.
- J. M. Granda, L. Donina, V. Dragone, D.-L. Long and L. Cronin, Nature, 2018, 559, 377–381 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) S. V. Ley, D. E. Fitzpatrick, R. J. Ingham and R. M. Myers, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 3449–3464 CrossRef CAS; (b) M. Trobe and M. D. Burke, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 4192–4214 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) D. P. Hruszkewycz, D. Balcells, L. M. Guard, N. Hazari and M. Tilset, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 7300–7316 CrossRef CAS; (b) C. C. C. Johansson Seechurn, T. Sperger, T. G. Scrase, F. Schoenebeck and T. J. Colacot, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 5194–5200 CrossRef CAS; (c) M. Montgomery, H. M. O'Brien, C. Méndez-Gálvez, C. R. Bromfield, J. P. M. Roberts, A. M. Winnicka, A. Horner, D. Elorriaga, H. A. Sparkes and R. B. Bedford, Dalton Trans., 2019, 48, 3539–3542 RSC; (d) S. Wagschal, L. A. Perego, A. Simon, A. Franco-Espejo, C. Tocqueville, J. Albaneze-Walker, A. Jutand and L. Grimaud, Chem.–Eur. J., 2019, 25, 6980–6987 CrossRef CAS.
- The catalytic competency of the Pd3 cluster has been validated in Suzuki–Miyaura cross-couplings, see: F. Fu, J. Xiang, H. Cheng, L. Cheng, H. Chong, S. Wang, P. Li, S. Wei, M. Zhu and Y. Li, ACS Catal., 2017, 7, 1860–1867 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) D. P. Hruszkewycz, J. Wu, N. Hazari and C. D. Incarvito, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 3280–3283 CrossRef CAS; (b) P. Leoni, E. Vichi, S. Lencioni, M. Pasquali, E. Chiarentin and A. Albinati, Organometallics, 2000, 19, 3062–3068 CrossRef CAS.
- The reaction of Pd(OAc)2/2PPh3 in MeOH gives complex VIII in 41% yield, see. M. B. Hursthouse, O. D. Sloan, P. Thornton and N. P. C. Walker, Polyhedron, 1986, 5, 1475–1478 CrossRef CAS.
- In [Pd3(Cl)(PPh2)2(PPh3)3]OAc we specify the non-coordinating anion as acetate, which serves to balance the full chemical reaction equation. As the reaction is run with an excess of CH2Cl2, exchange of acetate for chloride could occur under the reaction conditions used.
- A. S. Berenblyum, A. P. Aseeva, L. I. Lakhman and I. I. Moiseev, J. Organomet. Chem., 1982, 234, 219–235 CrossRef CAS.
- K. R. Dixon and A. D. Rattray, Inorg. Chem., 1978, 17, 1099–1103 CrossRef CAS.
- C. J. Diehl, T. Scattolin, U. Englert and F. Schoenebeck, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 211–215 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) K. Matos and J. A. Soderquist, J. Org. Chem., 1998, 63, 461–470 CrossRef CAS; (b) A. F. Schmidt, A. A. Kurokhtina and E. V. Larina, Russ. J. Gen. Chem., 2011, 81, 1573–1574 CrossRef CAS; (c) B. P. Carrow and J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 2116–2119 CrossRef CAS; (d) C. Amatore, A. Jutand and G. Le Duc, Chem.–Eur. J., 2011, 17, 2492–2503 CrossRef CAS; (e) C. Amatore, A. Jutand and G. Le Duc, Chem.–Eur. J., 2012, 18, 6616–6625 CrossRef CAS; (f) A. J. J. Lennox and G. C. Lloyd-Jones, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 7362–7370 CrossRef CAS; (g) A. A. Thomas, H. Wang, A. F. Zahrt and S. E. Denmark, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 3805–3821 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Pd3Br·Br was selected for control experiments as we hypothesized that excess bromide would be generated the SMCC reaction, i.e. bromide would be liberated during each catalyst turnover.
- A catalyst loading approximation (1.5 mol% of II) was made for comparison of catalytic activity for the in situ generation of Pd3Br·OAc and 4a, which takes into consideration that degradation of II is expected under the real working reaction conditions.
- (a) S. Blanchard, L. Fensterbank, G. Gontard, E. Lacte, G. Maestri and M. Malacria, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 1987–1991 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) A. Monfredini, V. Santacroce, P.-A. Deyris, R. Maggi, F. Bigi, G. Maestri and M. Malacria, Dalton Trans., 2016, 45, 15786–15790 RSC; (c) A. Monfredini, V. Santacroce, L. Marchio, R. Maggi, F. Bigi, G. Maestri and M. Malacria, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2017, 5, 8205–8212 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Full experimental details and characterization data for all compounds is provided, including NMR spectra, X-ray diffraction data and computational data (as a PDF file). CCDC 1894927–1894931 and 1901195. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c9sc01847f |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 |