Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleFacile synthesis of multi-functional elastic polyaniline/polyvinyl alcohol composite gels by a solution assembly method†
Jingjing Wanga,
Hang Chia,
Anan Zhoua,
Renhao Zhenga,
Hua Bai *a and
Tongyi Zhang*b
*a and
Tongyi Zhang*b
aCollege of Materials, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005, P. R. China. E-mail: baihua@xmu.edu.cn
bMaterials Genome Institute, Shanghai University, Shanghai, 200444, P. R. China. E-mail: zhangty@shu.edu.cn
First published on 9th June 2020
Abstract
Polyaniline gels with a three-dimensional network structure are attractive for their broad application prospects in flexible and stretchable electric devices. In this paper, we develop a facile solution assembly method to prepare an elastic polyaniline/poly(vinyl alcohol) composite organogel and a hydrogel. The polyaniline and poly(vinyl alcohol) chains gelate from the homogeneous mixed solution in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone via crystallization of poly(vinyl alcohol), producing a uniform organogel with hydrogen bonds between two polymers, and the organogel can be further converted into a hydrogel by solvent exchange. The composite gels exhibit excellent mechanical properties, which make them one of the best materials for additive manufacture, such as molding and 3D printing. This study develops an efficient method to fabricate polyaniline gels with good processability and multifunctions.
1. Introduction
Polyaniline (PANI) is one of the most attractive conducting polymers owing to its high electrical conductivity, facile synthesis, and abundant electrochemical properties.1–5 PANI gels have attracted considerable attention because the gels' three-dimensional (3D) network structure provides both large specific surface area with rich active sites and interconnected channels for mass diffusion,6,7 thereby having wide applications in many fields, such as energy storage, anti-corrosion, sensors, etc.8–12 However, PANI has poor solubility in most solvents due to its rigid molecular chain and strong interchain interactions. The weak solvation effect makes the PANI gels brittle and limited in flexible and stretchable devices.Hybridization of PANI gels with tough and strong polymers might be an efficient method to improve the mechanical properties of virgin PANI gels. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) possesses excellent mechanical strength and high chemical stability and is commonly used in the preparation of hydrogels.13,14 Researchers have employed PVA as a soft and elastic additive to prepare PANI/PVA composite gels with excellent mechanical strength. For example, a flexible PANI/PVA hydrogel through dynamic boronate bonds between the boric acid-modified PANI and PVA was prepared by in situ polymerization, and it showed a tensile fracture strain of up to 250%.15 A superelastic PANI/PVA composite hydrogel was also fabricated by in situ polymerization of aniline on a PVA hydrogel matrix, which was prepared by the freeze-thawing cycle method.16 Those preparation methods are based on the in situ polymerization, which is the most common strategy to prepare PANI-based materials.17–25 Although in situ polymerization is efficient in depositing PANI on various substrates, it is difficult to control the amount and morphology of PANI precisely. In the 3D porous matrix like a gel, the competition between diffusion and polymerization makes the in situ polymerization even more complicated and leads to uneven distribution of PANI. Also, the in situ polymerization is difficult to scale up. Therefore, it is highly desired to develop a novel approach to prepare PANI-based elastic gels.
In this paper, we developed a new solution assembly method to prepare PANI/PVA composite gel with uniform distribution of PANI and good mechanical properties. In our method, PANI was pre-synthesized and then 3D assembled with PVA chains in N-methyl pyrrolidone (NMP), generating composite organogel. This method avoids aggregation of PANI, controls precisely the gel composition, and is compatible with other processing techniques, including molding and 3D printing. Furthermore, the prepared PANI/PVA gels show excellent tensile and compressive elasticity, and are used to construct flexible energy storage devices and pressure sensors.
2. Experimental
2.1 Materials
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4, 98%), hydrochloric acid (AR), aqueous ammonia (28%), ammonium persulfate (AR), were purchased from XiLong Scientific Co., Ltd. PVA (PVA 124 and 1788) was purchased from Shantou Dahao Fine Chemicals Co., Ltd. Aniline (AR) and NMP (AR) were the products of Aladdin Industry Co., Ltd. All the chemicals were used as received without further purification.2.2 Preparation of PANI powder
PANI was prepared by chemically oxidative polymerization.26 9.313 g aniline was dissolved into 100 mL 1 M HCl under the ice water bath. 28.52 g ammonium persulfate was dissolved in 51.5 mL water and added dropwise to the aniline solution under agitation. After reacting for 3 hours in ice water bath, the product was filtered and washed with deionized water and absolute ethanol until the filtrate was colorless. The obtained filter cake was stirred in 100 mL 20% aqueous ammonia for 24 h, then washed with water and absolute ethanol and finally dried at 60 °C. The Mw of PANI is in the region of 37![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000.26
000.26
2.3 Preparation of PANI pure gel and PANI/PVA composite gels
The dried PANI powder was dissolved in NMP by agitation overnight to form a PANI solution (18.5 mg mL−1). 10 mL of the PANI solution was put into a glass vial and heated at 95 °C, then the PVA 124 powder (555, 740, 925, 1026, or 1110 mg) was added into the PANI solution. After agitation for 5 hours, the PVA was completely dissolved. The gel formed after the solution completely cooled down to room temperature. The mass ratios of PVA to PANI were 3, 4, 5, 5.6 and 6.6 and denoted by PPG3, PPG4, PPG5, PPG5.6, and PPG6.6, respectively. The concentration of PVA in the pure PVA gel is the same as that in PPG5.6. To make the extrusion easier in our 3D printer, the mass ratio of PVA to PANI in the gel for 3D printing was 30, and the PVA used was PVA-1788.2.4 3D printing of PANI/PVA gels
3D printing was conducted on a home-made gel 3D printer with an air pressure driven system. The PANI/PVA gel ink was filled into a 10 mL steel syringe and kept at 70 °C to avoid ink gelation. The gel ink was injected through a nozzle with an inner diameter of 18 G (0.5 mm) and at the pressure levels of 75 psi. The samples were printed at a movement speed of 5 mm s−1 and deposited in the NMP-ethanol coagulation bath (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 in volume).
1 in volume).
2.5 Assembly and test of PANI/PVA gel pressure sensor
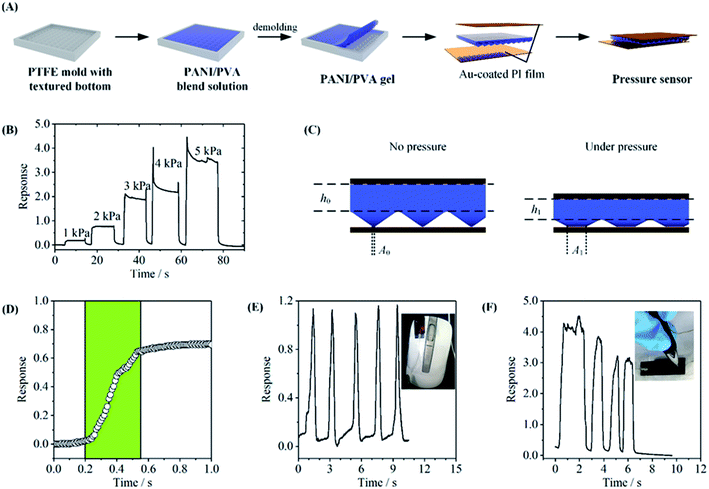
The PANI/PVA blend solution was cast on a polytetrafluoroethylene mold. The prepared gel was then demolded and immersed in 1 M H2SO4 for overnight to protonate PANI. The doped PANI/PVA gel was dialyzed and cut into a rectangle piece of 1 cm × 1.5 cm × 2.22 mm, and was then sandwiched between two pieces of gold-sputtered PI films. The device was encapsulated with 3M tapes.The current of the sensor was measured as the output signal by using an electrochemical workstation. A constant voltage of 1 V was applied onto the sensor, and the current change under different pressure was recorded. The response of the device is defined as ΔI/I0, where ΔI is the current change under pressure, and I0 is the current baseline. The external pressure was applied and measured by using a universal testing machine.
2.6 Assembly and test of all-solid-state PANI/PVA gel electrochemical capacitor
Preparation of PVA/H2SO4 electrolyte:27 6 g of PVA 124 powder and 3.28 mL of H2SO4 were dissolved in 60 mL of water, the mixed solution was stirred at 90 °C until the PVA powder was completely dissolved. The solution can be used after cooling down to room temperature.Assemble of all solid electrochemical capacitors: The PPG5.6 gel was cut into 1 cm × 2.5 cm × 1 mm rectangle pieces, and immersed in a large volume of 1 M H2SO4 for overnight, to replace the NMP by the aqueous electrolyte. The PVA/H2SO4 electrolyte solution was dropped on one side of the gel electrode, and two pieces of such PPG5.6 gel electrode were press together and placed in a fume hood for 12 hours to remove excess water.
The specific capacitance of the device was calculated by GCD tests using the equation:
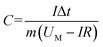 | (1) |
2.7 Characterization
Electrochemical testing was performed by using a CHI 660E electrochemical workstation (Chenhua, China). SEM images were obtained on a SU-70 field emission scanning electron microscope (Hitachi, Japan). The Raman spectra were measured on an XPLORA Raman spectrometer (Hitachi, Japan) using a 532 nm laser. The X-ray diffraction pattern (XRD) was measured on a D8 X-ray diffraction system (Bruker, USA) with a Cu Kα. The conductivity test was conducted on a four-probe analyzer (Guangzhou Four-Probe Electronics, China). The mechanical properties test was carried out on a 5948 universal testing machine (Instron, USA). The tensile test rate was 0.2 mm s−1, and the test sample was 1 cm × 3 cm × 2 mm in size. The compression test rate was 0.2 mm s−1, and the sample was a cylinder with a diameter of 2 cm, and a height of 1.5 cm. The rheological test was performed on an MCR 302 rheometer (Anton Paar, Austria) with a parallel plate rotor (25 mm) and the gap was set to be 1 mm.3. Results and discussion
3.1 Preparation and characterization of PANI/PVA gel
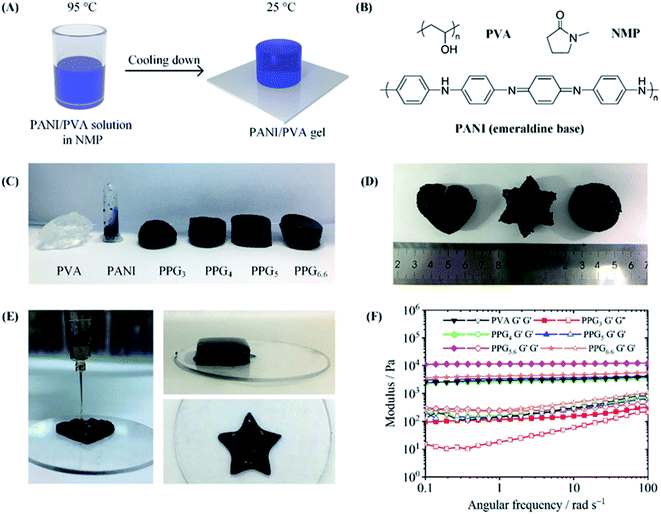
The preparation of PANI/PVA gels is shown in Fig. 1A. A co-solvent of PANI and PVA is the precursor in the solution assembly method. Because of the rigid chain structure and the strong interaction between molecular chains, only the PANI in emeraldine base state has limited solubility in a few polar aprotic solvents, such as NMP and N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF).28,29 On the other hand, NMP is also a good solvent for PVA, because it is a strong hydrogen bond acceptor and displays a strong solvation effect on hydrogen bond donor PVA. Hence, we choose NMP as a co-solvent to dissolve PANI emeraldine base powder and PVA powder. The homogeneous PANI/PVA mixed solution was prepared by dissolving PVA in the PANI solution at 95 °C. After the solution was cooled down to 25 °C, the solvation effect disappeared, resulting in the assembly of PVA molecular chains into a 3D network. Meanwhile, the PANI chains can dynamically adsorb onto the PVA network to generate a composite gel.To investigate the gelation process of the PANI/PVA gels, we prepared a series of gels with different PVA-to-PANI mass ratio. The gel with the mass ratio of 3, 4, 5, 5.6 and 6.6 was denoted as PPG3, PPG4, PPG5, PPG5.6, and PPG6.6. As displayed in Fig. 1C, the solution of PANI in NMP was a fluid, but after PVA was added, the mixture became a free-standing gel as characterized by the tube-inversion method. This phenomenon indicates that PVA increases the viscosity greatly and thus provides the mechanical strength in the PANI/PVA composite gel. The gelation was further investigated by rheological tests. All the PANI/PVA composite gels show strong rheological behavior. In Fig. 1F, the storage moduli (G′) of pure PVA, PPG4, PPG5, PPG5.6, and PPG6.6 gels are almost independent of the angular frequency, which might suggest the gels have stable cross-linked structure.30 The values of G′/G′′ of all PANI/PVA gels are all higher than 5.0 over a broad frequency range. Fig. 1F depicts that G′ grew with the increase of PVA content, and the modulus of the PPG5.6 achieved 105 Pa. However, when the mass ratio of PVA to PANI reached 6.6, the dissolution of PVA became difficult due to the too high viscosity, which resulted in an ununiform structure of PPG6.6, and the reduced modulus. Although the PVA concentrations in PPG5.6 and pure PVA gel are the same, the G′ of PPG5.6 is higher than that of pure PVA gel. This increase in G′ is contributed by the PANI component, revealing that PANI chains assemble into the PVA matrix.
Since the PANI/PVA mixed solution in NMP is flowable when the temperature is higher than 60 °C, it has good processability at that temperature. As displayed in Fig. 1D, PPG5.6 was made to different shapes by mold casting. The solution assembly method also enables us to use 3D printing to process PANI/PVA. The PANI/PVA mixed solution maintained at 70 °C was extruded from a 3D printer into NMP-ethanol coagulation bath (25 °C), in order to accelerate the gelation of the solution. Because ethanol is a poor solvent for both PANI and PVA, the extruded PANI/PVA viscous solution quickly gelatinated when came into contact with the NMP-ethanol bath, and the shape of the printed workpiece was well preserved during 3D printing. Various shapes of PANI/PVA gel constructed by 3D printing were shown in Fig. 1E. 3D printing has irreplaceable advantages in manufacturing unique and complex shapes and the presently synthesized composite gels are good raw materials for 3D printing to manufacture medical products, flexible circuits, sensors, etc.
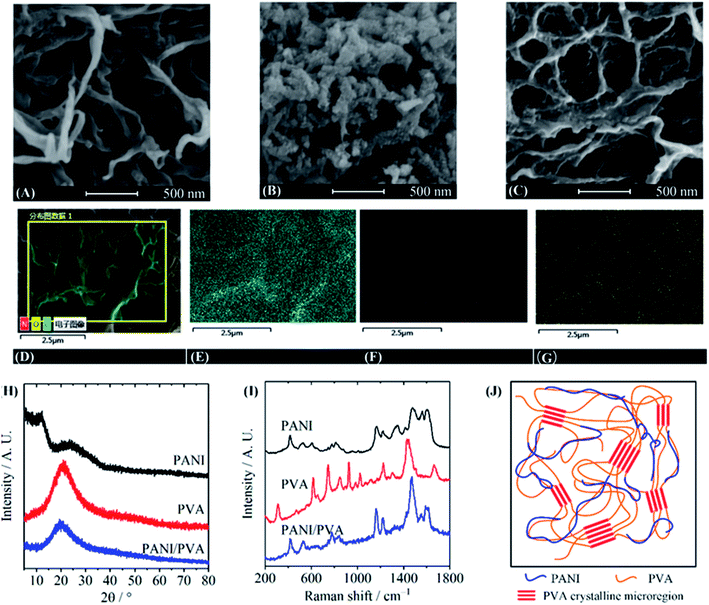
The morphology of PANI/PVA gels was observed by SEM and compared with pure PVA gel and PANI powder. The pure PVA gel exhibited a typical 3D macroporous network structure (Fig. 2A, see Fig. S2(A)–(D)† for energy dispersive spectroscopy, EDS), while the PANI powder is irregular particles (Fig. 2B). PANI/PVA gel shows a similar 3D network as that of the PVA gel, and no large PANI particle was observed (Fig. 2C and S1†). Fig. 2D–G show an SEM image and the corresponding C, N, and O element mappings in a PPG5.6 sample, which are recorded by energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), revealing that PANI is homogeneously distributed in the gel without phase separation. Fig. 2H shows the XRD diffraction patterns, indicating that the pure PVA gel has a broad diffraction peak at 20°, corresponding to (101) diffraction of the PVA crystal.31 It has been well documented that the crystalline microregions serve as the physical crosslinking sites in PVA hydrogels.32 Therefore, the crystalline microregions are also the crosslinking sites in PANI/PVA gels. The broad diffraction peak 24° of PANI film corresponds to the spacing of π–π stacking in the PANI backbone, and the peak at 12° was ascribed to the (011) diffraction peak of PANI. The two peaks prove that PANI powder is in a semi-crystalline state.33 The XRD diffraction peaks of PPG5.6 is identical to that of pure PVA gel, confirming that the composite gel has the same crosslinking site as PVA gel. The absence of peak associated with PANI reveals that there are no crystalline PANI aggregates in the gel because PANI chains are uniformly distributed in the PVA matrix. Fig. 2I shows the Raman spectra of the PVA-NMP gel, PANI/PVA gel, and PANI powder. The characteristic peaks of 1564 cm−1, 1479 cm−1 and 1163 cm−1 of the PANI belong to the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C stretching vibration, C
C stretching vibration, C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N stretching vibration, and C–H in-plane bending of the quinone ring, respectively. The Raman bands at 1225 cm−1 and 1614 cm−1 are attributed to the C–N stretching vibration and C–C stretching vibration of the benzene ring structure.34 The bands of PVA gel at 1670 cm−1 and 1441 cm−1 are assigned to the C–O bending vibration and the CH2 bending vibration of the aliphatic ether, respectively.35 The peaks at 1224 cm−1 are associated with the C–O stretching vibrations of the secondary alcohol. The band of the C–C stretching vibration is at 855 cm−1.18 For PPG5.6, the Raman spectrum is dominated by bands of the PANI, because conducting polymers always have stronger Raman activity. However, the characteristic PANI bands slightly shifted to lower wavenumber by ∼3 cm−1, possibly because of the intermolecular interaction between PANI and PVA chains/NMP molecules, which changes the delocalized distribution of charge in the molecular chain.36 Fourier transform infrared spectra also confirm the interaction between PANI and PVA (Fig. S3†).
N stretching vibration, and C–H in-plane bending of the quinone ring, respectively. The Raman bands at 1225 cm−1 and 1614 cm−1 are attributed to the C–N stretching vibration and C–C stretching vibration of the benzene ring structure.34 The bands of PVA gel at 1670 cm−1 and 1441 cm−1 are assigned to the C–O bending vibration and the CH2 bending vibration of the aliphatic ether, respectively.35 The peaks at 1224 cm−1 are associated with the C–O stretching vibrations of the secondary alcohol. The band of the C–C stretching vibration is at 855 cm−1.18 For PPG5.6, the Raman spectrum is dominated by bands of the PANI, because conducting polymers always have stronger Raman activity. However, the characteristic PANI bands slightly shifted to lower wavenumber by ∼3 cm−1, possibly because of the intermolecular interaction between PANI and PVA chains/NMP molecules, which changes the delocalized distribution of charge in the molecular chain.36 Fourier transform infrared spectra also confirm the interaction between PANI and PVA (Fig. S3†).
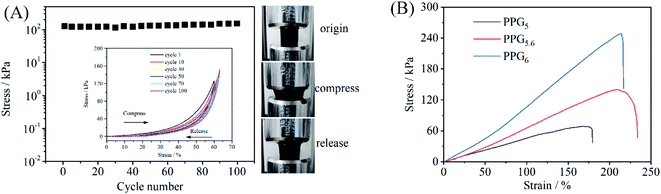
The PVA brings excellent elasticity and mechanical strength to the composite gel. Fig. 3A shows the maximum stresses in the 100 compressive strain cycles with the applied strain range (0, 60%) in the PPG5.6 sample, indicating that the maximum stresses at 60% compressive strain increases slightly from 126 kPa at the first cycle to 152 kPa at the 100th cycle. The inset of Fig. 3A indicates the stress–strain curves, demonstrating that the sizes of hysteresis loops are small and the stresses all return zero as the applied strain is completely released (Fig. 3A and Movie S1†). Fig. 3B shows the stress–strain curves of a PPG5, PPG5.6 and PPG6.6 under tensile test. The Young's modulus, tensile strength, elongation, and toughness of PPG5.6 are 22.7 kPa, 140.1 kPa, 209.0%, and 175.5 kJ m−3 respectively (Table. S1†). With the increase of PVA content, the tensile strength, and Young's modulus of the gels also increase. But PPG6.6 has a smaller elongation, also because of the ununiform structure of PPG6.6 as revealed in the rheological measurement. The tensile and compression stress–strain curves confirm that PPG5.6 is an elastic gel. The good elasticity and anti-fatigue property indicate that the physical crosslinking site of PVA crystalline microregion is mechanically stable. Meanwhile, the other PVA and PANI chains between crystalline microregions are well-solvated and flexible, which can provide large strain without rupture.
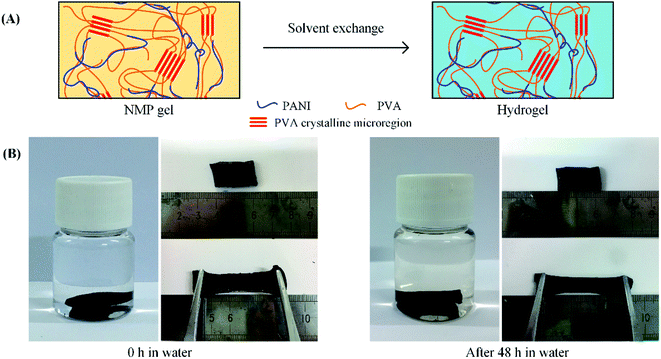
The composite gel can be converted into hydrogels by the simple room-temperature solvent exchange. When PPG5.6 was immersed in water, the NMP in PPG5.6 was quickly replaced by water, due to the strong interaction of NMP with water, and the gel was converted into a hydrogel (PHG5.6). During the solvent exchange, the shape and volume of the gel did not change. The produced PHG5.6 still has good elasticity. As depicted in Fig. 4B, the hydrogel can still be repeatedly stretched to a 100% elongation. These results suggest the cross-linking sites are water-resistant. In fact, both the PVA crystalline microregion and PANI are insoluble in water at 25 °C, and thus the 3D network in the gel can be well preserved in water. Although water is not able to dissolve the crystalline PVA at 25 °C, it is a good solvent of those PVA chains that are already dissolved in NMP. The solvated PVA chains can maintain their flexibility in the water, so the produced hydrogel still has good elasticity. The interaction between PANI and PVA can prevent the aggregation of PANI in the antisolvent water, resulting in a homogeneous hydrogel.
3.2 Resistance pressure sensor
The conductive and elastic gel can be used to fabricate a flexible stress sensor. The structure of the device is shown in Fig. 5A. A PPG5.6 film with a textured surface was prepared by casting on a mold. The film was then de-molded and sandwiched between two flexible Au-coated polyimide (PI) films to give a resistor-type pressure sensor. The response, which is defined as the relative current change (I/I0) of the sensor under the pressure, was measured as a function of the pressure on the device. Fig. 5B describes the response signal of the device under different pressure and Fig. S4† indicates the dynamic response of the pressure sensor with the upper limit of 100 kPa. The current increased with the pressure is attributed to the decrease in both the contact resistance at the gel/electrode interface and the bulk gel resistance, as depicted in Fig. 5C (A1 > A0, h1 < h0).37,38 The pressure sensitivity is defined as the slope of the current response versus pressure, and can be used to evaluate the sensitivity of the device. The fabricated sensor exhibits the sensitivity of 0.8 kPa−1 in the pressure range of 1–5 kPa according to the data shown in Fig. 5B (Fig. S4†) and the response time of 350 ms under 2 kPa pressure (Fig. 5D).To demonstrate the application of the flexible pressure sensor, we use it to monitor the pressure of some daily actions. The sensor was fixed onto the curved button of a mouse, and the actions of clicking mouse were successfully recorded by the current signal, with good repeatability (Fig. 5E). Fig. 5F shows another application, where the pressure during writing the word “OK” was monitored. The signal clearly showed the force difference between strokes. This gel-based pressure sensor may have potential applications in future flexible devices.
3.3 Stretchable electrochemical capacitors
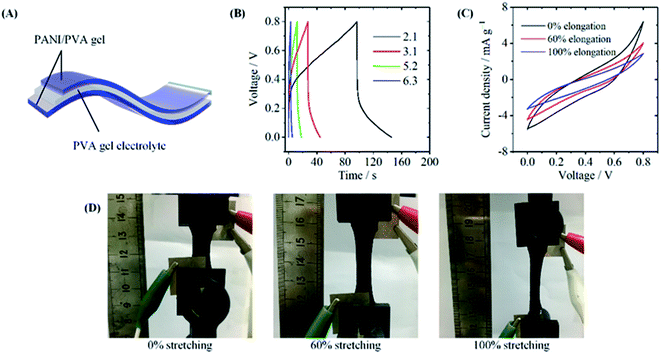
We also used the PANI/PVA hydrogel to fabricate stretchable electrochemical capacitors. Fig. 6A shows the structure of the capacitor, where two PPG5.6 films were used as the electrodes and PVA/H2SO4 as the gel electrolyte. Before assembly of the device, PPG5.6 gel was first immersed in a large volume of 1 mol L−1 H2SO4 aqueous solution to replace NMP by the electrolyte. The cyclic voltammetry (CV) curves (Fig. S5†) and galvanostatic charge/discharge (GCD) curves (Fig. S6†) measured in a three-electrode system show that PPG5.6 gel had characteristic electrochemical properties of PANI.39 Fig. 6B shows the GCD curve of the all-solid-state device, and the specific capacitance of the was calculated 133.3 mF g−1 at 2.1 mA g−1. The low conductivity of the hydrogel (8.0 × 10−5 S cm−1) caused by the non-conductive PVA component is probably the reason for the capacitance. In PANI/PVA gels prepared by the solution assembly method, the PANI chains are uniformly distributed in the PVA matrix, and they are separated by the PVA chains. So their conductivity is relatively low. The good elastic property of the gel makes the electrochemical capacitor flexible. Fig. 6C exhibits the CV curves of the device at the different stretching strains. At the stretching strains of 60%, and 100%, the CV curves became more tilted a compared with the unstretching one. Fig. 6D also shows that no crack was observed when the device was stretched to 100%. The results demonstrate that the device still works when stretched to 100% strain.4. Conclusions
Elastic PANI/PVA gels were prepared by a new solution assembly method. In this method, PVA and PANI were dissolved and blended in 90 °C NMP, and the composite gels formed after the cooling of the solution down to 25 °C. The gels can be easily processed into various shapes by molding and 3D printing. PANI/PVA gels have a uniform 3D network, and the crystalline microregions of the PVA chains might be the physical crosslinking joint sites, while PANI chains were absorbed on the PVA matrix by hydrogen bonds. The composite gels show good elastic property with a tensile elongation of 261%. The gels were used to fabricate pressure sensors and stretchable electrochemical capacitors. The developed solution assembly method may be attractive for the preparation of other conductive polymer-based functional gels.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (21774104, 21975210), Natural Science Foundation of the Fujian Province, China (2018J06015).References
- S. Bhadra, D. Khastgir, N. K. Singha and J. H. Lee, Prog. Polym. Sci., 2009, 34, 783–810 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Eftekhari, L. Li and Y. Yang, J. Power Sources, 2017, 347, 86–107 CrossRef CAS.
- N. A. Kumar, H.-J. Choi, Y. R. Shin, D. W. Chang, L. Dai and J.-B. Baek, ACS Nano, 2012, 6, 1715–1723 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Liu, J. Yan, Z. Guang, Y. Huang, X. Li and W. Huang, J. Power Sources, 2019, 424, 108–130 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Luo, R. Guo, T. Li, F. Li, Z. Liu, M. Zheng, B. Wang, Z. Yang, H. Luo and Y. Wan, ChemSusChem, 2019, 12, 1591–1611 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Tang, J. Lin, J. Wu, C. Zhang and S. Hao, Carbohydr. Polym., 2007, 67, 332–336 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Garai, B. K. Kuila and A. K. Nandi, Macromolecules, 2006, 39, 5410–5418 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Huang, S. Virji, B. H. Weiller and R. B. Kaner, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 314–315 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. R. Small, F. Masdarolomoor and G. G. Wallace, J. Mater. Chem., 2007, 17, 4359–4361 RSC.
- S. Ma, G. Song, N. Feng and P. Zhao, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2012, 125, 1601–1605 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Irimia-Vladu and J. W. Fergus, Synth. Met., 2006, 156, 1401–1407 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Yan, Z. Chen, L. Cai, Z. Chen, J. Fu and Q. Xu, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 356, 39–47 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Weng, Y. Su, D. W. Wang, F. Li, J. Du and H. M. Cheng, Adv. Energy Mater., 2011, 1, 917–922 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Ding, X. Xu, Y. Yue, C. Mei, C. Huang, S. Jiang, Q. Wu and J. Han, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 27987–28002 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Li, F. Gao, X. Wang, N. Zhang and M. Ma, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 9196–9201 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Huang, J. Yao, L. Li, F. Zhu, Z. Liu, X. Zeng, X. Yu and Z. Huang, J. Mater. Sci., 2016, 51, 8728–8736 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Wang, J. Chen, Y. Cong, H. Zhang, T. Xu, L. Nie and J. Fu, Chem. Mater., 2018, 30, 8062–8069 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Wang, X. Zhang, C. Li, X. Sun, Q. Meng, Y. Ma and Z. Wei, Adv. Mater., 2015, 27, 7451–7457 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Pan, G. Yu, D. Zhai, H. R. Lee, W. Zhao, N. Liu, H. Wang, B. C.-K. Tee, Y. Shi and Y. Cui, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2012, 109, 9287–9292 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Guo, W. He, Y. Lu and X. Zhang, Carbon, 2015, 92, 133–141 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Adhikari and P. Banerji, Synth. Met., 2009, 159, 2519–2524 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Stejskal, P. Bober, M. Trchová, A. Kovalcik, J. Hodan, J. Hromádková and J. Prokeš, Macromolecules, 2017, 50, 972–978 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Hu, Y. Zhang, X. Wang, L. Xing, L. Shi and R. Ran, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 44000–44010 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Lai, Z. Fang, L. Cao, W. Li, Z. Lin and P. Zhang, Ionics, 2020, 26, 3015–3025 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Li, Y. Zhang, H. Lu, Y. Wang, J. Xu, J. Zhu, C. Zhang and T. Liu, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 62 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Stejskal, A. Riede, D. Hlavatá, J. Prokeš, M. Helmstedt and P. Holler, Synth. Met., 1998, 96, 55–61 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Meng, C. Liu, L. Chen, C. Hu and S. Fan, Nano Lett., 2010, 10, 4025–4031 CrossRef CAS.
- J.-C. Chiang and A. G. MacDiarmid, Synth. Met., 1986, 13, 193–205 CrossRef CAS.
- H.-K. Lin and S.-A. Chen, Macromolecules, 2000, 33, 8117–8118 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Clark, R. Richardson, S. Ross-Murphy and J. Stubbs, Macromolecules, 1983, 16, 1367–1374 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Ricciardi, F. Auriemma, C. Gaillet, C. De Rosa and F. Lauprêtre, Macromolecules, 2004, 37, 9510–9516 CrossRef CAS.
- P. D. Hong, J. H. Chen and H. L. Wu, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 1998, 69, 2477–2486 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Pouget, M. Jozefowicz, A. Epstein, X. Tang and A. MacDiarmid, Macromolecules, 1991, 24, 779–789 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Baibarac, I. Baltog, C. Godon, S. Lefrant and O. Chauvet, Carbon, 2004, 42, 3143–3152 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Badr, K. Abd El-Kader and R. M. Khafagy, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2004, 92, 1984–1992 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhang, C. Liu and G. Shi, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2005, 96, 732–739 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Lau and W. Tang, J. Appl. Phys., 2009, 105, 124902 CrossRef.
- M. R. Gomez, D. M. French, W. Tang, P. Zhang, Y. Lau and R. Gilgenbach, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2009, 95, 072103 CrossRef.
- Q. Zhang, A. Zhou, J. Wang, J. Wu and H. Bai, Energy Environ. Sci., 2017, 10, 2372–2382 RSC.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/d0ra02238a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |