Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleSynthesis of oxygen-doped graphitic carbon nitride and its application for the degradation of organic pollutants via dark Fenton-like reactions†
Tian-Jiao Jiang‡
a,
Cai-Wu Luo‡ *abcd,
Chao Xiea,
Yue-Hua Weia and
An Li*e
*abcd,
Chao Xiea,
Yue-Hua Weia and
An Li*e
aSchool of Resource Environmental and Safety Engineering, Cooperative Innovation Center for Nuclear Fuel Cycle Technology and Equipment, University of South China, 421000, China. E-mail: luocaiwu00@126.com; Tel: +86-734-8282345
bResearch Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100085, China
cState Key Laboratory of Safety and Health for Metal Mines, Sinosteel Maanshan General Institute of Mining Research Co., Ltd, 243000, China
dKey Laboratory of Clean Energy Material, LongYan University, 364012, China
eCollege of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, 414000, China. E-mail: anleechn@hotmail.com
First published on 4th September 2020
Abstract
Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) is a promising photocatalyst for environmental protection but its development is greatly limited for its application in dark Fenton-like reactions due to its extremely low specific surface area and lack of suitable active sites. Herein, for the first time, graphitic carbon nitride with large surface area and abundant defect sites was developed by tailoring oxygen via a simple and green method without any templates, namely, the calcination–hydrothermal–calcination successive treatment of melamine. The structure of the catalyst was characterized using several technologies, including XRD, SEM, TEM, N2-physisorption, FT-IR, Raman spectroscopy and XPS. The results revealed that it possessed a large specific surface area (ca. 236 m2 g−1), while changes in its structural properties such as the formation of new defect sites and change in the content of nitrogen atoms were observed. These properties were beneficial for the in situ activation of H2O2 toward reactive oxygen species, as confirmed by the reactive oxygen species capturing experiments. Furthermore, various influencing factors were systemically investigated. The results clearly showed that the oxygen-doped g-C3N4 was light-independent and metal-free Fenton-like catalyst for the enhanced degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater. Compared to the pristine g-C3N4, the oxygen-doped g-C3N4 showed superior performance under various conditions such as broad pH range and excellent stability. Thus, this study provides a novel pathway for the treatment of organic pollutants in water.
1. Introduction
Organic compounds are widely used in many applications of manufactured products, such as plastics, paper, and textiles.1 However, some dye pollutants, such as rhodamine B (RhB) and methylene blue (MB), are not easily degraded in aqueous solution, and thus severely threaten the environment. Therefore, the development of an effective, inexpensive, and benign technology for dealing with these pollutants is an important issue. Several oxidation processes such as Fenton-like reactions have been employed to remove organic compounds from wastewater.2–5 However, there are still many problems, for instance, the abundant Fe- and Cu-based catalysts employed exhibit strong toxicity and limited pH range functionality. Thus, there is a considerable urgency to explore green Fenton-like catalysts with both non-metal participants and strong resistance to a broad range of reaction conditions. Accordingly, g-C3N4 appears to be an ideal candidate material, having many merits, including safety, low cost, and good stability. Currently, this compound exhibits catalytic properties for the degradation of various organic pollutants, which are also strongly dependent on light illumination.1,6 Cui et al.1 first reported a g-C3N4 catalyst activated by H2O2 to degrade RhB in solution under visible light illumination. However, it hardly exhibited any catalytic activity in the dark, which apparently hindered large-scale development in industry. Thus, to solve this problem, much effort has been devoted to achieving excellent performances in the dark for better practical use.7–10 For example, Ge et al.7 prepared a MgO/g-C3N4 catalyst by employing high-temperature calcination. Zhu et al.8 synthesized Cu-g-C3N4 composites via the pyrolysis of [H2mela]2[CuCl5]Cl, and Ding et al.9 developed the g-C3N4-supported iron oxide composite. Their results demonstrated that these catalysts were capable of activating H2O2 to degrade organic compounds in the dark. However, these catalysts still contained metal elements, and their photocatalytic performance and stability need to be improved. Consequently, the development of effective, stable, and non-metal g-C3N4-based catalysts remains pursued with the dark Fenton-like reactions.Oxygen (O)-doped g-C3N4 catalysts have been recognized as promising due to their non-toxicity, abundance, and low cost, and thus have been widely employed in several fields,11–17 including pollutant removal,11 bioimaging probes,13 and singlet O generation.14 However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no report on the application of O-doped g-C3N4 in dark Fenton-like reactions to date. In addition, in the past few years, it has been reported that the synthesis of O-doped g-C3N4 can be carried out in a liquid environment,11–17 mainly including hydrothermal treatment by H2O2,11 HNO3,12 H2SO4/KMnO4,13 and HNO3/H2SO4.14 Clearly, many toxic chemical reactants are required, which can lead to serious environmental pollution. Also, in most cases, the specific surface area of the catalyst is not greater than 100 m2 g−1, and thus not adequate for generating the desired activity. Consequently, the further development of O-doped g-C3N4 is of great interest and necessary. Creating defects in a catalyst is a useful way to regulate its structure and catalytic properties. This can increase the specific surface area of the catalyst via the introduction pore structure and/or altered morphology.18,19 Importantly, it may directly activate oxidants in situ to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are usually observed with metal-based catalysts.20,21 For example, Liu et al.20 demonstrated that the vacancy sites on nickel(II) oxide were crucial for activating peroxydisulfate through a non-radical pathway. Gao et al.21 reported that the O defect sites on Fe2O3/CeO2 could activate H2O2 in situ to produce ˙OH species under an O2 atmosphere. However, the study of non-metal-based catalysts with defect sites in Fenton-like reactions has rarely been reported. As mentioned above, increasing the specific surface area and introducing defects in a catalyst are two effective strategies for strengthening its performance for the degradation of organic pollutants. It will be beneficial for boosting the catalytic performance in dark Fenton-like reactions if the above targets are concurrently achieved in one g-C3N4-based material, and thus organic pollutants can be effectively degraded under light-independent conditions. To date, there are no reports on g-C3N4-based materials with a large specific surface area and many defects to allow dark Fenton-like reactions. Based on the above studies and problems associated with both the synthesis and application of O-doped g-C3N4, it is highly desirable to explore new methods for the synthesis of O-doped g-C3N4 possessing a large surface area and abundant defect sites to meet these requirements. With the aim of introducing O through the hydrothermal treatment of g-C3N4 and defect generation via thermal treatment, this study explores the use of combined hydrothermal and calcination technologies to increase the specific surface area and introduce defect sites in g-C3N4 without the addition of templates. Accordingly, to the best of our knowledge, this practical approach has not been reported to date.
In this study, O-doped g-C3N4 catalysts with high specific surface areas and many defect sites were synthesized in a multistep post-formation treatment for the degradation of organic pollutants in dark Fenton-like reactions. These catalysts showed superior performances under the optimal conditions. In addition, the adsorption and active catalytic sites and ROS were identified and examined based on the degradation efficiencies for organic pollutants in water.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and reagents
All chemical reagents were of analytical grade and used as received without further purification. Deionized water (resistivity 18.2 M) was filtered using a Millipore Milli-Q water purification system.2.2. Preparation of g-C3N4-based catalysts
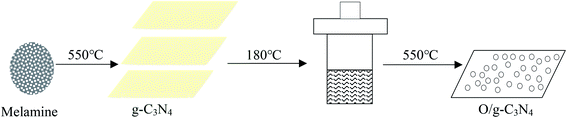
The target catalyst was prepared via a three-step successive treatment from melamine (Scheme 1). Briefly, 10 g of melamine powder was placed in a 50 mL crucible with an aluminum foil cover and then heated to 550 °C for 4 h at a rate of 5 °C min−1 under a static air atmosphere. The obtained yellow sample was denoted as g-C3N4. 0.3 g of the obtained powder was added to 25 mL of deionized water, transferred to a 50 mL Teflon-sealed autoclave, and heated at 180 °C for 4 h. After cooling to room temperature, the sample was washed and dried at 120 °C, which was denoted as g-C3N4(HY), and then the sample was calcined at 550 °C for 4 h at a rate of 5 °C min−1 under a static air atmosphere. The resultant sample was then denoted as g-C3N4(HY-HT). Similarly, g-C3N4 was again calcinated at 550 °C for 4 h at a rate of 5 °C min−1 under a static air atmosphere. The resultant sample was denoted as g-C3N4(HT). 0.3 g of g-C3N4(HT) powder was then hydrothermally treated under the same conditions as that for g-C3N4(HY) and denoted as g-C3N4(HT-HY).2.3. Characterization
X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectroscopy was carried out using a D8-Advance X-ray diffractometer (Bruker Corp., Billerica, MA, USA); N2-physisorption was conducted on an Autosorb-1 instrument (Quantachrome Instruments Corp., Boynton Beach, FL, USA), at liquid-N2 temperature; scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was carried out on a JSM 6700 F instrument (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), operating at an accelerating voltage of 10 kV; transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was conducted on a TALOS F200 X instrument (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA), operating at an accelerating voltage of 200 kV; Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) was recorded on a Varian 3100 spectrometer (Varian, Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA), equipped with a DTGS detector; Raman spectroscopy was recorded on an InviaTM (Renishaw Co., Inc., Gloucestershire, UK), using a 785 nm laser; and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was carried out on a Thermo Fisher Scientific K-Alpha (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.), using an Al-Kα source.2.4. The degradation of organic pollutants in the dark and light illumination
The degradation reaction was conducted in a flask at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. The flask contained a certain amount of catalyst, H2O2 solution (30 wt%), and organic pollutants. The above solution was then stirred rapidly in the dark, with samples taken at fixed time and filtered. The filtrates were collected and measured using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer to quantitate the concentration of residual organic pollutants. Except for LED illumination, the reaction was performed in the dark.3. Results and discussion
3.1. Characterization of the catalysts
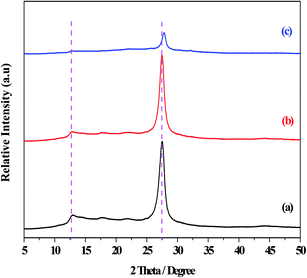
The XRD patterns of the g-C3N4, g-C3N4(HY), and g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalysts showed diffraction peaks at 2θ = 13.0° and 27.5° from g-C3N4, which were assigned to the responses of the repeating tri-s-triazine units in the g-C3N4 unit layer (100) and inter-planar stacking of the unit layers (002), respectively (Fig. 1).1 Besides the characteristic peaks of g-C3N4, both the g-C3N4(HY) and g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalysts exhibited no other diffraction peaks, which indicated that the original structure of g-C3N4 was retained after the treatment. It was also observed that the intensities of the diffraction peaks followed the order of g-C3N4(HY) > g-C3N4 ≫ g-C3N4(HY-HT). On the one hand, these results indicated that the degree of crystallinity of g-C3N4(HY) slightly increased after the hydrothermal treatment, which was consistent with the literature.22 This was most probably due to the flat layered structure being exposed and/or surface impurities being removed from the catalyst surface during the hydrothermal treatment. Wang et al.23 considered repairing the defects of bulk g-C3N4 via the self-assembly of the internal hydrogen bonds of cyano and amino groups. Ming et al.15 considered the formation of contained O in g-C3N4 through hydrolysis and oxidation during hydrothermal processing, and Wang et al.24 suggested that the structure of g-C3N4 nanosheets was rearranged. On the other hand, the structure of g-C3N4(HY-HT) was greatly altered through delamination and depolymerization due to the subsequent calcination. The main reasons for this result are as follows: (i) the contained oxygen groups were generated on the surface and interlayers of the g-C3N4 nanosheets;11 (ii) the accumulated g-C3N4 particles and their intercrystalline structures were seriously destroyed,13 which may have generated a great number of pores or defects; and (iii) the periodic structure of the g-C3N4 nanosheets was reduced.14 The above analysis accounted for the degree of crystallinity of g-C3N4(HY) being relatively higher than that of g-C3N4(HY-HT), which was clearly lower than that of the bulk g-C3N4. In addition, the strongest diffraction peaks from the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst were seen to shift toward higher angles, specifically, 2θ = 27.8°, relative to that of g-C3N4, resulting in a decrease in the interlayer spacing of the layered structure.11 This was mainly attributed to the doping effect of the heteroatoms and distortion of the graphite structure. In the framework of g-C3N4, nitrogen (N) atoms were replaced by O atoms with higher electronegativity during the preparation process, which created stronger interactions between the nanosheets.25 Therefore, the interlayer spacing of the g-C3N4 nanosheets became smaller. Similarly, doping with O atoms disturbed the structure of g-C3N4. The literature demonstrated that amine functional groups were replaced by O atoms.26,27 One electron in an O atom interacted with an adjacent carbon (C) atom to form one C–O group and another electron departed its original location and moved to an in situ conjugate triazine ring structure, leading to an electron-rich state for the targeted product.The SEM micrographs of the g-C3N4, g-C3N4(HY), and g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalysts showed that the g-C3N4 catalyst possessed agglomerated particles consisting of nanosheets with relatively rough surfaces (Fig. 2). However, after hydrothermal treatment, the surfaces became smooth, which may have been due to the partial delamination and depolymerization. Also, a notable change appeared in the morphology of g-C3N4(HY-HT) relative to that of g-C3N4, which may have been because the hydrothermal–calcination treatment led to more delamination and depolymerization, and thus separated more g-C3N4 nanosheets, even forming single g-C3N4 nanosheets. Meanwhile, the evolution of the nanosheets during high temperature calcination generated some cavities due to delamination and depolymerization. This difference was further confirmed by the TEM results (Fig. S1, ESI†). This deduction was further confirmed by examining the main elemental content in g-C3N4 and g-C3N4(HY-HT) via EDS characterization (Table S1, ESI†). The N content was observed to decrease, but the atomic ratio of C and N atoms increased in the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst relative to that of g-C3N4. This indicated that the process of delamination and depolymerization indeed occurred and N atoms were lost, consequently forming some N defect sites. For g-C3N4, the content of O mainly increased, which was derived from physically adsorbed water. The content of O atoms in the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst was about twice that of g-C3N4, which indicated that more O atoms were doped in the framework structure of g-C3N4 during the preparation process. Accordingly, the SEM results offered additional evidence for the delamination and depolymerization of the g-C3N4 nanosheets, as deduced from the XRD characterization.
Interestingly, it appeared that the morphology of the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst was similar to that of graphene, specifically, graphene-like carbon nitride may have been generated. Actually, graphene-like carbon nitride have been reported by researchers in the past few years.19,28 For example, Niu et al.19 reported the thermal oxidation etching of bulk g-C3N4 using dicyandiamide as a precursor. Similarly, Meng et al.28 obtained graphene-like g-C3N4 nanosheets using melamine. In these cases, the specific surface area was generally >100 m2 g−1. In terms of specific surface area, the values obtained in this study are much higher than that in most recent reports (see below).
The N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms for the g-C3N4, g-C3N4(HY), and g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalysts were shown in Fig. S2, ESI,† and the corresponding pore size-distribution profiles using the Barrett–Joyner–Halenda method, were shown in Fig. S3, ESI.† The isotherms for the g-C3N4 and g-C3N4(HY) catalysts were relatively the same over the whole range of relative pressures, which were characteristic of small pore structures. The isotherm for the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst displayed only a low uptake of N2 at p/p0 < 0.1, which was related to limited microporosity, typical of g-C3N4.11–13 This isotherm also contained an H4-type hysteresis loop, which indicated the presence of mesopores with an irregular and slit-like shape in the catalyst.11–13 Mesopores were most probably generated as intercrystal voids through the aggregation of the g-C3N4(HY-HT) nanosheets and/or as intracrystal cavities through the delamination and depolymerization of the bulk g-C3N4 during the subsequent hydrothermal–calcination treatment, but the mesoporous structures were generally limited. The pore sizes for the g-C3N4 and g-C3N4(HY) catalysts were observed to be broadly distributed, covering a range from micropore size up to 10 nm. In contrast, that for the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst was relatively narrow, with its value falling predominantly in the range of 4–7 nm. This result was because the g-C3N4 series catalysts contained nanosheets, and accordingly, the aggregation of the nanosheets in g-C3N4 catalyst was incomplete, thus generating pores with a broad size distribution, compared to the latter. In addition, an appreciably greater amount of pores with sizes <5 nm were observed in the g-C3N4(HY) catalyst compared to that of the bulk g-C3N4, which was most probably due to the generation of additional micropores and mesopores through the delamination and depolymerization after hydrothermal treatment. For the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst, its pore size distribution was broader than that of the g-C3N4 and g-C3N4(HY) catalysts, which was due to the fact that, on the one hand, a proportion of g-C3N4 nanosheets was exposed through the successive hydrothermal–calcination treatment, as evidenced by the SEM and TEM characterizations, and thus the pore size distribution generated via the aggregation of the g-C3N4 nanosheets became broader. On the other hand, additional mesopores may have been generated within the g-C3N4 nanosheets through delamination and depolymerization during hydrothermal–calcination treatment, which also contributed to the broadening of the pore size distribution. Nevertheless, the pore size distribution was not clearly observed in all the catalysts. Generally, a large pore size is favorable for mass transfer in pore channels, and therefore enhances catalytic activity.
The textural properties of the g-C3N4, g-C3N4(HY), and g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalysts were determined via N2 adsorption–desorption experiments (Table 1). The results showed that, from g-C3N4 to g-C3N4(HY) and then g-C3N4(HY-HT), the specific surface area (SBET), first slightly increased and then significantly increased by more than 20-fold. Simultaneously, the total pore volume (Vtotal) first decreased and then remarkably increased by ∼10-fold. In addition, the average pore size (Dp) in all three samples decreased. It is well known that g-C3N4 can be easily obtained from various precursors through high-temperature calcination, but the resulting SBET value is often <10 m2 g−1. This is because the interactions between g-C3N4 layers are very strong, arising from van der Waals forces and/or hydrogen bonds in the material, leading to serious particle aggregation. After hydrothermal treatment, these interactions became weaker due to the attack of water molecules at high temperature and pressure, thus releasing these layers. Subsequently, these exposed nanosheets were further attacked by O in the high-temperature calcination process, and therefore a new morphology appeared, and consequently, the BET greatly increased. Combined with the SEM, TEM, and pore size distribution results, the observed increased BET was concluded to be mainly attributed to the huge morphology changes. Generally, a large SBET is an important factor for strengthening the catalytic performance of materials, which is ascribed to the presence of more exposed adsorption and catalytic active sites.
| Catalyst | Smicro (m2 g−1) | Sext (m2 g−1) | SBET (m2 g−1) | Vmicro (cm3 g−1) | Vmeso (cm3 g−1) | Vtotal (cm3 g−1) | DA (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Smicro, Sext and SBET respectively represented the microporous surface area, external surface area and specific surface area; Vmicro, Vmeso and Vtotal represented the microporous pore volume, mesoporous pore volume and total pore volume, respectively; and DA represented the average pore diameter. | |||||||
| g-C3N4 | 0 | 11.5 | 11.5 | 0.00352 | 0.06565 | 0.06927 | 24.13 |
| g-C3N4(HY) | 0 | 17.02 | 17.02 | 0.00474 | 0.05522 | 0.05996 | 14.09 |
| g-C3N4(HY-HT) | 0 | 236.4 | 236.4 | 0.06221 | 0.57219 | 0.6344 | 10.74 |
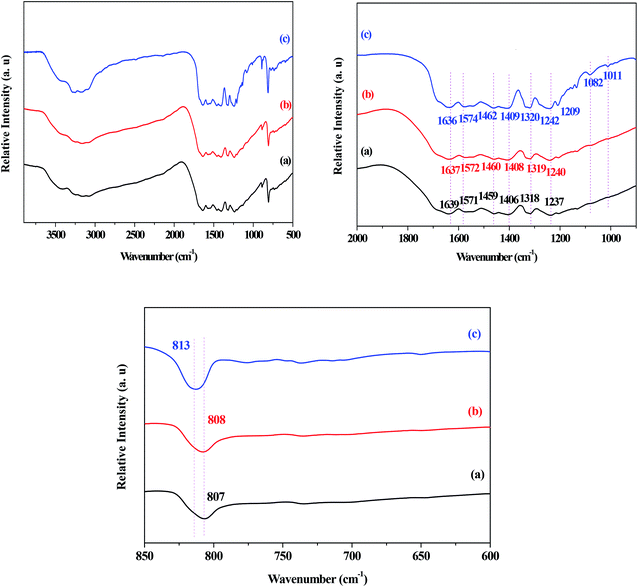
The FT-IR spectra of the g-C3N4, g-C3N4(HY), and g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalysts showed that generally, the absorption bands for g-C3N4 were mainly located in three different regions of 2900–3200 cm−1, 1700–1000 cm−1, and 807 cm−1 (Fig. 3). These bands were assigned to the characteristic peaks of the terminal amino (–NH) and hydroxyl (–OH) groups, typical C–N heterocycles, and tri-s-triazine units, respectively. Similar absorption bands were observed for all the catalysts, indicating that the original graphitic structure was basically maintained after the treatment, which was consistent with the XRD results. Moreover, the absorption bands for g-C3N4(HY-HT) were sharper than that of g-C3N4 and g-C3N4(HY). Combined with the XRD analysis, this further confirmed that tri-s-triazine units with less order in a plane appeared in the g-C3N4(HY-HT) sample. The absorption band at 807 cm−1 for g-C3N4 shifted by 1 and 6 cm−1 toward higher frequencies in g-C3N4(HY) and g-C3N4(HY-HT), respectively. This implied that the interactions between the g-C3N4 nanosheets decreased to some degree, which was due to the partial substitution of N atoms by O atoms. Fang et al.22 suggested that the appearance of this phenomenon could be mainly attributed to an increase in the crystallinity of g-C3N4 and O-doping effects from the hydrothermal treatment. The absorption bands at 3500–2900 cm−1, corresponding to –NH and –OH groups, were almost the same in all three catalysts, which originated from the catalyst and/or physically adsorbed water, respectively. This indicated that –NH groups still existed in the g-C3N4(HY) and g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalysts after the hydrothermal and calcination treatments. In the range of 900–1700 cm−1, the absorption bands for g-C3N4 appeared at 1639, 1571, 1459, 1406, 1318, and 1237 cm−1, which belonged to characteristic peaks of C–N heterocycles, such as C–C and C–N groups. However, due to the near force constant, it was extremely difficult to distinguish the O-containing groups, such as C–O, by FT-IR spectroscopy.25,27 Most of the absorption bands in the g-C3N4(HY) and g-C3N4(HY-HT) samples shifted toward higher wavenumbers compared to that of the g-C3N4 sample. This confirmed that the C–N and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N bonds were enhanced because of the addition of O after the hydrothermal and calcination treatments. For example, the absorption bands at 1406 and 1237 cm−1 for the g-C3N4 sample were assigned to the
N bonds were enhanced because of the addition of O after the hydrothermal and calcination treatments. For example, the absorption bands at 1406 and 1237 cm−1 for the g-C3N4 sample were assigned to the ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C–(sp2) bending and N–sp3 stretching vibrations, respectively.25 After treatment, these peaks shifted by 2–3 and 3–5 cm−1 toward higher wavenumbers, respectively. This was most probably due to the electrophilic effects resulting from the O atoms being located near C–N.27 Also, two new absorption bands appeared at 1082 and 1011 cm−1 for the g-C3N4(HY-HT) sample, which are assigned to the C–O species from the C–O–C and C–OH groups, respectively. Wang et al.24 demonstrated by DFT that the N atoms in two-coordinated positions were preferentially displaced by O atoms due to their remarkably low reaction/formation energy. Accordingly, the present functionalization with different O-containing groups was concluded to have been successfully achieved for the g-C3N4 nanosheets after successive hydrothermal and calcination treatment.
C–(sp2) bending and N–sp3 stretching vibrations, respectively.25 After treatment, these peaks shifted by 2–3 and 3–5 cm−1 toward higher wavenumbers, respectively. This was most probably due to the electrophilic effects resulting from the O atoms being located near C–N.27 Also, two new absorption bands appeared at 1082 and 1011 cm−1 for the g-C3N4(HY-HT) sample, which are assigned to the C–O species from the C–O–C and C–OH groups, respectively. Wang et al.24 demonstrated by DFT that the N atoms in two-coordinated positions were preferentially displaced by O atoms due to their remarkably low reaction/formation energy. Accordingly, the present functionalization with different O-containing groups was concluded to have been successfully achieved for the g-C3N4 nanosheets after successive hydrothermal and calcination treatment.
The Raman spectra for the g-C3N4 and g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalysts showed some characteristic peaks at ∼1613, 1465, 1345, 1308, 1230, 759, 707, 558, and 477 cm−1 for bulk g-C3N4, belonging to the typical characteristic modes of CN heterocycles (Fig. S4†).29 For instance, the peaks at ∼1613 and 1230 cm−1 were assigned to the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N stretching and
N stretching and ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C–(sp2) bending vibrations, respectively. Compared to g-C3N4, g-C3N4(HY-HT) possessed similar characteristic peaks, implying that the successive hydrothermal and calcination treatment for g-C3N4 did not cause any remarkable destruction of the g-C3N4 framework. This was consistent with the XRD and FT-IR analyses. Furthermore, the peaks at 1613, 1345, 1230, 759, and 477 cm−1 slightly shifted toward higher frequencies, and four new peaks appeared at 1567, 1489, 1150, and 1116 cm−1, suggesting that the O-doping effects led to chemical bond changes near the C atoms.
C–(sp2) bending vibrations, respectively. Compared to g-C3N4, g-C3N4(HY-HT) possessed similar characteristic peaks, implying that the successive hydrothermal and calcination treatment for g-C3N4 did not cause any remarkable destruction of the g-C3N4 framework. This was consistent with the XRD and FT-IR analyses. Furthermore, the peaks at 1613, 1345, 1230, 759, and 477 cm−1 slightly shifted toward higher frequencies, and four new peaks appeared at 1567, 1489, 1150, and 1116 cm−1, suggesting that the O-doping effects led to chemical bond changes near the C atoms.
The binding energies of C-1s and N-1s from the XPS characterization of the g-C3N4, g-C3N4(HY), and g-C3N4(HY-HT) samples showed that in the bulk g-C3N4 sample, there were two peaks at 284.9 and 288.4 eV for the C-1s spectra (Fig. 4, Table S2†). These were attributed to the reference C and sp2-hybridized C (N–C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), respectively. Four different peaks at 398.9, 399.8, 401.5, and 404.6 eV appeared in the N-1s spectra, corresponding to the sp2-hybridized N (N–C
N), respectively. Four different peaks at 398.9, 399.8, 401.5, and 404.6 eV appeared in the N-1s spectra, corresponding to the sp2-hybridized N (N–C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N, denoted as sp2(N)), sp3-hybridized N (N–[C]3, denoted as sp3(N)), N–H bonds, and π bands in the localization of heterocycles, respectively (Table S3†).10,11,14–18 In terms of the g-C3N4(HY) and g-C3N4(HY-HT) samples, in their C-1s spectra, besides the two peaks at ∼284.8 and 288.4 eV, a new peak appeared at ∼289 eV, which was attributed to the C–O bonds.10,11,14–18 Notably, the content of C–O species remarkably increased and their binding energy shifted toward lower values in the g-C3N4(HY) sample relative to that of g-C3N4(HY-HT). This indicated that partial oxidation continued to occur after the hydrothermal and high-temperature oxidation calcination. Nevertheless, as observed in the earlier FT-IR analysis, the C–O bonds may have originated from the formation of C–OH and/or C–O–C species. In the N-1s spectra, the g-C3N4(HY) and g-C3N4(HY-HT) samples possessed peaks similar to that of g-C3N4. In addition, the concentration of sp2(N) and ratio of sp2(N) and sp3(N) were observed to first decrease and then increase, whereas the content of the N–H band and sp3(N) initially increased and then decreased for g-C3N4(HY) and g-C3N4(HY-HT) compared to g-C3N4. This accounted for some sp2(N) and sp3(N) atoms being substituted for O atoms during the treatment, specifically, a decrease in sp2(N) atoms meant the formation of C–OH and/or C–O–C by replacing the N atoms in C–NH and C
N, denoted as sp2(N)), sp3-hybridized N (N–[C]3, denoted as sp3(N)), N–H bonds, and π bands in the localization of heterocycles, respectively (Table S3†).10,11,14–18 In terms of the g-C3N4(HY) and g-C3N4(HY-HT) samples, in their C-1s spectra, besides the two peaks at ∼284.8 and 288.4 eV, a new peak appeared at ∼289 eV, which was attributed to the C–O bonds.10,11,14–18 Notably, the content of C–O species remarkably increased and their binding energy shifted toward lower values in the g-C3N4(HY) sample relative to that of g-C3N4(HY-HT). This indicated that partial oxidation continued to occur after the hydrothermal and high-temperature oxidation calcination. Nevertheless, as observed in the earlier FT-IR analysis, the C–O bonds may have originated from the formation of C–OH and/or C–O–C species. In the N-1s spectra, the g-C3N4(HY) and g-C3N4(HY-HT) samples possessed peaks similar to that of g-C3N4. In addition, the concentration of sp2(N) and ratio of sp2(N) and sp3(N) were observed to first decrease and then increase, whereas the content of the N–H band and sp3(N) initially increased and then decreased for g-C3N4(HY) and g-C3N4(HY-HT) compared to g-C3N4. This accounted for some sp2(N) and sp3(N) atoms being substituted for O atoms during the treatment, specifically, a decrease in sp2(N) atoms meant the formation of C–OH and/or C–O–C by replacing the N atoms in C–NH and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N–C. Meanwhile, the decrease in sp3(N) atoms indicates the significant decomposition of the entire g-C3N4 nanosheets. Actually, the mass of g-C3N4(HY-HT) was confirmed to be remarkably reduced relative to that of g-C3N4, which illustrated that N loss preferentially occurred, and thus some N defect sites were formed. In addition, the content of π bands in the heterocycles increased after the treatment, which implied the formation of many more unpaired electrons.
N–C. Meanwhile, the decrease in sp3(N) atoms indicates the significant decomposition of the entire g-C3N4 nanosheets. Actually, the mass of g-C3N4(HY-HT) was confirmed to be remarkably reduced relative to that of g-C3N4, which illustrated that N loss preferentially occurred, and thus some N defect sites were formed. In addition, the content of π bands in the heterocycles increased after the treatment, which implied the formation of many more unpaired electrons.
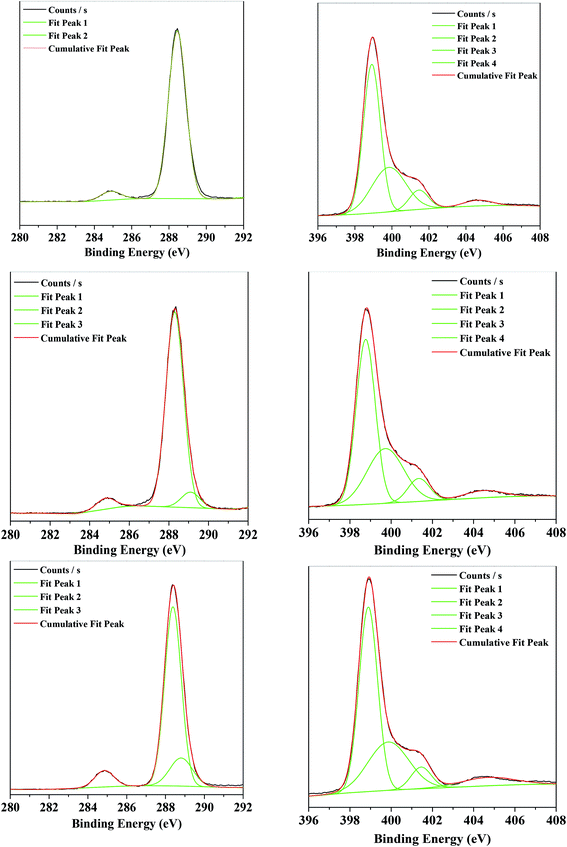 | ||
| Fig. 4 XPS results of C1s (left) and N1s (right) for the various catalysts. (Top) g-C3N4, (middle) g-C3N4(HY), and (Bottom) g-C3N4(HY-HT). | ||
Based on the above characterization results, the mechanism for the preparation of the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst was proposed. Melamine is one of the promising precursors for the synthesis of g-C3N4 and only through high temperature calcination can bulk g-C3N4 be easily generated. Here, once the bulk was generated, a portion of the bulk structure was altered by hydrothermal treatment. During this process, g-C3N4 was induced to generate some new O-containing groups, such as (C3H3N3)3–OH, which were mainly attributed to H2O attack during the delamination and depolymerization.17 With an increase in the hydrothermal time and/or temperature, more (C3H3N3)3–NH2 was transformed into (C3H3N3)3–OH. Also, a weak alkaline solution, arising from NH3, was detected by pH monitoring. Finally, the g-C3N4(HY) catalyst was again treated at high temperature. On the one hand, the g-C3N4(HY) nanosheets were exfoliated at high temperature, and thus fewer layers of nanosheets were obtained. One the other hand, delamination and depolymerization continued to occur through interactions with O2 in the air atmosphere. In this case, the material was vulnerable to decomposition into small molecular gas products, such as CO2, NH3, and NOx. These strong reactions drove these products to cross the layers, specifically, they acted as a gas template. Accordingly, a cotton morphology in the g-C3N4 nanosheets was formed, and concurrently, many defects were generated. For example, some N atoms were preferentially removed from the framework of g-C3N4(HY) under high-temperature calcination, and thus N vacancy defects were formed. Consequently, a higher specific surface area and rich defect population were generated in the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst relative to g-C3N4(HY). Actually, the color of g-C3N4 turned from light yellow to white after calcination, which meant that the degree of oxidation was extremely serious. At a lower calcination temperature was used, the color of the treated catalyst hardly changed from than that of g-C3N4. However, the higher the calcination temperature, the whiter the color of the treated catalyst was obtained. However, it completely disappeared at >600 °C, which was attributed to the structural damage to the catalyst, and therefore, the material was consumed at higher temperature. Notably, the amount of g-C3N4(HY) during calcination was a key factor for the formation of the final products. Under identical conditions, high doses of g-C3N4(HY) barely generated the target products because of insufficient O2 to react with the g-C3N4(HY) nanosheets. In contrast, no product was obtained if the dose of g-C3N4(HY) was too small due to complete oxidation. Accordingly, a suitable dosage of g-C3N4(HY) during the second high temperature treatment was quite important and necessary.
3.2. Catalytic performance for the degradation of RhB under various reaction conditions
| Cu2+ + H2O2 → Cu+ + HOO˙ + OH−, (k = 4.6 × 102 M−1 s−1) | (1) |
| Cu+ + H2O2 → Cu2+ + HO˙ + OH−, (k = 1.0 × 104 M−1 s−1) | (2) |
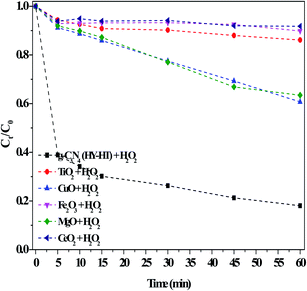
Consequently, with an increase in the reaction time, RhB degradation continued. Similarly, MgO had many alkaline active sites, and therefore was capable of the in situ activation of H2O2 for removing RhB. Wu et al.31 proposed that active O in MgO2 was obtained via the reaction between MgO and H2O2, acting as active sites, and then eliminating MB in solution. Actually, the above results were not ideal because of the limited activating ability of CuO and MgO with H2O2 for producing ROS. In contrast, the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst showed superior activity in this reaction and ∼81% of RhB was decolorized within only 60 min. These results illustrated that, here, the introduction of O in g-C3N4 by post-treatments was beneficial for yielding a high specific surface area, which exposed more active sites. In this case, more ROS were generated from H2O2, thus degrading more RhB in water, and accordingly, remarkably increased the degradation efficiency. Usually, metal ions are extremely difficult to treat in aqueous solution, and thus the use of metal-based catalysts induces secondary pollution. In contrast, here, the catalytic process of g-C3N4(HY-HT) does not release toxic metallic ions since it is a metal-free strategy for the green degradation of organic pollutants.
The catalytic activity of g-C3N4 after the post-treatments for the degradation of RhB in dark Fenton-like reactions was carefully studied (Fig. 6). The degradation efficiency of RhB over g-C3N4(HY) was only ∼14% at 60 min in the presence of H2O2, which was almost the same as that over the bulk g-C3N4. This indicated that this treatment had no effect on the RhB degradation ability, although the former possessed a higher specific surface area than the latter. After the second high-temperature treatment of g-C3N4 (denoted as g-C3N4(HT)), the RhB degradation evidently increased, which showed that catalytic activity was enhanced by the second calcination. However, no useful products were obtained if a third high-temperature calcination was applied. Thus, based on these results for g-C3N4(HT), we speculated about the enhanced catalytic activity observed by introducing hydrothermal treatment (denoted as g-C3N4(HT-HY)). Surprisingly, this resulted in a decrease in the degradation of RhB (ca. 40%) during a 60 min reaction, which indicated that the treatment had a negative impact on RhB degradation after the hydrothermal treatment of the g-C3N4(HT) catalyst. One of the reasons for this may have been that the crystallinity of g-C3N4(HT) increased due to the reduction in defect sites after the hydrothermal treatment, similar to that for the hydrothermal treatment of g-C3N4, which was confirmed by the XRD results. This meant that defects in the catalyst were a necessary factor for enhancing its catalytic activity. Further exploration of how to intensify this effect was underway via sequential hydrothermal and high-temperature treatment for the production of g-C3N4 catalysts. Encouragingly, the degradation of RhB prominently increased in the dark. The synthetic process of g-C3N4(HT) was noted to be similar with that of graphene-like carbon nitride with a high specific area,19 where the latter had not been reported thus far regarding dark Fenton-like reactions. However, these results showed that its catalytic activity was still lower than that of g-C3N4(HY-HT), which illustrated that g-C3N4(HY-HT) possessed a higher degradation efficiency than the current reported non-metal catalysts for the degradation of organic pollutants via dark Fenton-like reactions.
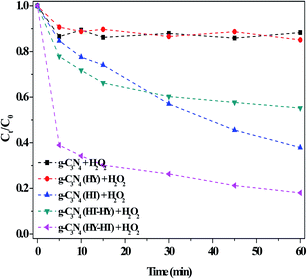 | ||
| Fig. 6 Effect of the preparation method on the degradation of RhB in the dark. Conditions: [RhB]0 = 10 mg L−1, [H2O2] = 36 mM, [Catal.] = 1.0 g L−1, initial pH no adjustment, 25 °C and 60 min. | ||
To gain further insight into this phenomenon, the impact of various catalysts on the degradation of RhB in the dark was systematically studied (Fig. S5†). With an increase in the reaction time, the trend of RhB degradation efficiency initially decreased and then remained unchanged when H2O2 and the g-C3N4-based catalysts were respectively added to the reaction solution. All the degradation efficiencies were no more than 15% at 60 min. With only H2O2, RhB degradation barely occurred due to the limited oxidation. For the g-C3N4-based catalysts, their activity was attributed to adsorption. After the maximum adsorption capacity of catalyst was reached, the degradation process stopped. Also, the degradation significantly increased on the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst relative to g-C3N4 and g-C3N4(HY), which was mainly attributed to its high specific surface area. To alter this situation, a useful strategy was exploited. After the introduction of H2O2 in the solution, a large difference was notably observed, with the highest RhB degradation efficiency over g-C3N4(HY-HT) among them. This was due to the combined action between g-C3N4(HY-HT) and H2O2. As a comparison, the g-C3N4 and g-C3N4(HY) catalysts in the presence of H2O2 exhibited slight degradation in the dark, which was consistent with the literature.1 The principal reason for these results was attributed to the synergistic effect between the increased specific surface area and abundant defects in the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst compared to that of g-C3N4 and g-C3N4(HY). This effect was due to that large surface area of the catalyst, which was beneficial for improving reactant absorption capacity and also offered more catalytic active sites. Meanwhile, the defect sites in the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst activated H2O2 in situ to create more ROS, although its activating ability was not high in this reaction. Actually, RhB was completely degraded after several hours. In summary, the best activity was achieved in the g-C3N4(HY-HT) and H2O2 mixed system. Here, the catalytic activity of g-C3N4(HY-HT) was dramatically strengthened by H2O2 activation without any light irradiation. This is a useful finding regarding Fenton-like reactions since, to the best of our knowledge, there are few reports on the effective degradation of organic pollutants in the dark involving a g-C3N4-based catalyst without any added metal.
Examination of the effects of the dark and LED illumination on the degradation of RhB showed that g-C3N4(HY-HT) with the help of H2O2 exhibited significantly better catalytic activity under light illumination relative to that in the dark (Fig. 7). This was because some new reactions simultaneously occurred based on the dark Fenton-like reactions, and they were further capable of promoting the degradation of RhB, which was a typical photo-Fenton-like reaction process (eqn (3)–(5)).
| Catalyst + hv → h+ + e− | (3) |
| O2 + e− → O2˙− | (4) |
| h+ (or O2˙−) + organics → CO2 + H2O | (5) |
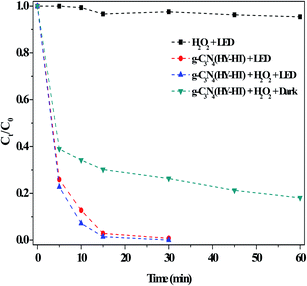 | ||
| Fig. 7 Effect of the dark and light illumination on the degradation of RhB. Conditions: [RhB]0 = 10 mg L−1, [H2O2] = 36 mM, [Catal.] = 1.0 g L−1, initial pH no adjustment, 25 °C and 60 min. | ||
For example, under the light irradiation, a photo-generated hole directly reacted with RhB. In addition, this special electron could have interacted with dissolved oxygen in aqueous solution to form O2˙− species, and thus the degradation of RhB clearly increased. In previous studies,7–9 for metal-g-C3N4-based materials, the degradation of organic pollutants was slightly different in both the dark and under light illumination. This was mainly attributed to be the existence of metal–N bonds. Notably, the present g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst contained abundant defects but still possessed excellent catalytic activity under LED illumination. This result indicated that the defects in the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst played a positive role in the degradation of RhB. In general, these defects can be divided into surface and bulk defects. The former always promotes photocatalytic activity, which is ascribed to its acceleration of the separation of photogenerated charges and role as adsorption sites. The latter inhibits reactions because it becomes the recombination center of photogenerated charges. Therefore, here, g-C3N4(HY-HT) with surface defects exhibited increased photocatalytic activity. The literature11,15 demonstrated that O-containing groups in g-C3N4 remarkably enhanced its photocatalytic activity in many reactions relative to that of the parent catalyst. To examine this hypothesis, g-C3N4 oxidized by H2O2 hydrothermal treatment was employed, which indicated that the degradation efficiency over this catalyst was higher than that of the bulk g-C3N4 (Fig. S6†). Specifically, the defects and O-containing groups in g-C3N4(HY-HT) both played important roles for the degradation of RhB under visible light illumination.
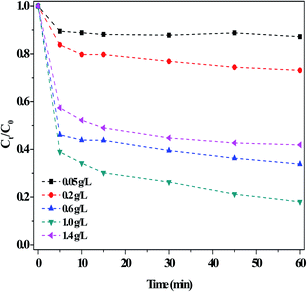 | ||
| Fig. 8 Effect of the dosage of the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst on the degradation of RhB in the dark. Conditions: [RhB]0 = 10 mg L−1, [H2O2] = 36 mM, initial pH no adjustment, 25 °C and 60 min. | ||
The influence of the concentration of H2O2 on the degradation of RhB in the dark was examined, and the degradation efficiency was found to increase with an increase in the H2O2 concentration, reaching a maximum at a C0(H2O2) of 36 mM, and a further increase in the concentration of H2O2 resulted in a decrease in degradation (Fig. S8†). When the H2O2 concentration was low, insufficient ROS were formed. Accordingly, the increase in H2O2 concentration increased RhB degradation. However, too much ROS had some detrimental effects on the degradation of RhB, which was due to reactions by ROS, such as with ˙OH and H2O2. In this case, the possibility of ˙OH species attacking RhB became lower, and therefore the oxidation kinetics were much slower. Cui et al.1 proposed that many side reactions occur, which were derived from the self-effects of radical species.
Examination of the effects of initial pH on the RhB degradation efficiency in the dark Fenton-like reactions showed that the degradation efficiency was ∼81% in 60 min with no adjustment of the solution pH (Fig. 9). After regulating the pH using diluted H2SO4 solution (0.1 M) to strongly acidic (pH = 2), the degradation efficiency remained >40%. This result was satisfactory in principle compared to that of the currently reported results.1,7–9 For instance, Ge et al.7 found that methyl orange degradation over g-C3N4/MgO hardly occurred at pH < 2 and under visible light irradiation. RhB was found here to be more quickly degraded when the initial pH was adjusted to pH 11 using diluted NaOH solution (0.1 M). This result was remarkably better than that under other conditions, where the alkaline conditions reinforced the catalytic activity. However, Ge et al.7 reported that ∼5% of RhB degradation efficiency was lost when the initial pH was increased from 8 to 10. The initial pH had a different influence on the catalyst adsorption capacity (Fig. S9†). It has been reported that the zero potential point (pKa) of g-C3N4 obtained from urea was about 3,22 which meant that the surfaces of g-C3N4-based materials became negatively charged if the pHsolution was above pKa, and similarly, their surface was protonated at pHsolution < pKa. Accordingly, RhB developed a pseudo-positive charge at low pHsolution, thus leading to a surface repulsion effect with the catalyst. Once the pHsolution increased, the effect between catalyst surface and RhB molecule decreased, resulting in an increase in absorption. Clearly, the present catalyst adsorbed less RhB at lower pH, whereas pH had little effect on the degradation of RhB at higher pH. In addition, at pH = 2, H+ covered the catalyst defect sites, and thus generated less ROS in the above dark Fenton-like reactions. Thus, the decrease in RhB degradation at pH = 2 was mainly attributed to the reduced adsorption by catalyst, whereas the increase in degradation at the high pH of 11 was because the electrode potential value of OH−/˙OH decreased with a higher OH− concentration.1 In this case, more ˙OH species were generated, thus resulting the greater degradation of RhB. Specifically, this catalyst, assisted by H2O2, exhibited a good catalytic performance over a broad pH range. Also, the degradation of MB was examined using this catalyst under the above reaction conditions, and the result clearly indicated that MB was effectively removed in a short time (Fig. S10†).
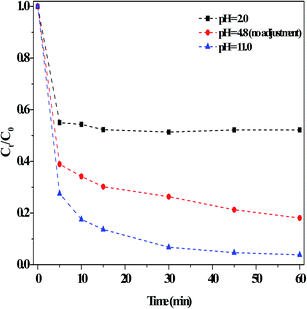 | ||
| Fig. 9 Effect of adjusting the initial pH using H2SO4 or NaOH on the degradation of RhB in the dark. Conditions: [RhB]0 = 10 mg L−1, [Catal.] = 1.0 g L−1, [H2O2] = 36 mM, 25 °C and 60 min. | ||
The stability of g-C3N4(HY-HT) was investigated in cyclic experiments for the degradation of RhB under the same reaction conditions (Fig. S11†). After a reaction period, the catalyst was washed with ultrapure water and ethanol, and then used for the next run. The catalyst activity decreased slightly after five cycles, demonstrating its good stability and reusability (Fig. S11†). This result was further confirmed by XRD and FT-IR characterizations (Fig. S12 and S13,† respectively). According to the results, the structure of the used catalyst was concluded to be fundamentally same as that of the fresh catalyst.
Additionally, the degradation of various organic pollutants in wastewater over the g-C3N4-based catalysts in dark Fenton-like reactions was examined (Table S4†). As is known, g-C3N4 has low photocatalytic activity under visible light illumination,1 and a low RhB degradation efficiency (<10%) is often observed in the dark, even in the presence of H2O2. The main drawbacks associated with this catalyst are its extremely low specific surface area and lack active sites for H2O2. As the substitute for g-C3N4, one current strategy is to use metal-modified g-C3N4. For instance, MgO/g-C3N4,7 Cu/g-C3N4,8,32 and FeOx/g-C3N4 (ref. 33) have been employed to degrade organic pollutants in the dark, but they have many issues, including long reaction time, activity at low pH, high cost, and poor stability. Furthermore, metal ions need to be employed, which easily cause environmental contamination. Thus, these factors constitute the main challenges for their industrial application. To overcome these limitations, an N-g-C3N4 catalyst was employed for the degradation of MB,10 achieving a non-metal-containing catalyst. Nevertheless, the required H2O2 concentration is clearly higher than with metal/g-C3N4 catalysts. In the present study, g-C3N4(HY-HT) was employed as a catalyst for the degradation of organic pollutants in water. Compared to the above catalysts, g-C3N4(HY-HT) is green, non-toxic, and easy to prepare. For this catalyst, a large specific surface area was obtained, and when assisted by H2O2, it exhibited excellent performances over a wide pH range in the dark. More importantly, the activity of this catalyst was further and significantly enhanced under LED illumination. The above merits indicate that the novel method for synthesis of g-C3N4(HY-HT) and its application developed in this study exhibit great potential for commercial application.
(1) Identification of adsorption and catalytic active sites. In advanced oxidation processes, O groups, N species, and defects usually act as catalytic sites for activating oxidation to generate ROS. To confirm the role of O-containing groups in the catalyst, a simulation experiment was conducted, and the g-C3N4 catalyst was hydrothermally treated with H2O2,11 which was one of most common methods for the preparation of O-doped g-C3N4. Many O-containing groups were formed, including –C
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O, –C–O–C–, and –NOx, and the results showed that the degradation of RhB by this catalyst barely increased relative to that by pristine g-C3N4 (Fig. S14†), which indicated that these groups in g-C3N4 were not main active sites in this reaction. In the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst, the O-containing groups were mainly C–O–C and/or C–OH, as confirmed by the FT-IR and XPS results. For example, the C–O–C group was observed in the g-C3N4(HY) catalyst, but catalytic degradation results were almost the same for the g-C3N4 and g-C3N4(HY) catalysts. This indicated that this group was not a catalytically active site. Also, C–OH groups cannot directly activate H2O2. The above results demonstrated that O-containing groups were not responsible for catalyzing H2O2 to generate ROS for the degradation of organic pollutants in solution. As previously mentioned, g-C3N4(HY-HT) possessed abundant defects, and its enhanced RhB degradation confirmed this. It has been reported that defects not only increased reactant adsorption, but also prolonged the bond length of H2O2 and reduced the reaction free energy.34 To further confirm these deductions, an experiment was performed in which g-C3N4(HY-HT) was first treated with NaF to exchange its –OH groups.11 The results indicated that the removal of RhB was not obvious, which implied that defect sites, besides the –OH groups, were the main adsorption sites in this reaction (Fig. S15†). Specifically, defects served as both adsorption and catalytic active sites in this reaction, with these defects dynamically filled with reactants and/or products during reactions. Accordingly, this process resulted in a reduction of the defect site concentration, and therefore decreased the generation of ROS. With an increase in the reaction time, the RhB degradation rate became much slower. As proof of this effect, RhB decolorization in aqueous solution required several hours (Fig. S16†). After washing, the catalyst was easily regenerated, and its initial catalytic activity was recovered.
O, –C–O–C–, and –NOx, and the results showed that the degradation of RhB by this catalyst barely increased relative to that by pristine g-C3N4 (Fig. S14†), which indicated that these groups in g-C3N4 were not main active sites in this reaction. In the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst, the O-containing groups were mainly C–O–C and/or C–OH, as confirmed by the FT-IR and XPS results. For example, the C–O–C group was observed in the g-C3N4(HY) catalyst, but catalytic degradation results were almost the same for the g-C3N4 and g-C3N4(HY) catalysts. This indicated that this group was not a catalytically active site. Also, C–OH groups cannot directly activate H2O2. The above results demonstrated that O-containing groups were not responsible for catalyzing H2O2 to generate ROS for the degradation of organic pollutants in solution. As previously mentioned, g-C3N4(HY-HT) possessed abundant defects, and its enhanced RhB degradation confirmed this. It has been reported that defects not only increased reactant adsorption, but also prolonged the bond length of H2O2 and reduced the reaction free energy.34 To further confirm these deductions, an experiment was performed in which g-C3N4(HY-HT) was first treated with NaF to exchange its –OH groups.11 The results indicated that the removal of RhB was not obvious, which implied that defect sites, besides the –OH groups, were the main adsorption sites in this reaction (Fig. S15†). Specifically, defects served as both adsorption and catalytic active sites in this reaction, with these defects dynamically filled with reactants and/or products during reactions. Accordingly, this process resulted in a reduction of the defect site concentration, and therefore decreased the generation of ROS. With an increase in the reaction time, the RhB degradation rate became much slower. As proof of this effect, RhB decolorization in aqueous solution required several hours (Fig. S16†). After washing, the catalyst was easily regenerated, and its initial catalytic activity was recovered.
(2) Identification of ROS. It is well known that ROS generation in H2O2-based Fenton-like reactions generally involve ˙OH, O2˙−, and 1O2. Thus, to reveal the activation mechanism, a series of quenching experiments were conducted to identify the dominant ROS in the “g-C3N4(HY-HT) + H2O2” system. Different scavengers, including isopropanol (2-PrOH), potassium iodide (KI), 1,4-benzoquinone (BQ), and furfuryl alcohol (FFA), were added separately to this reaction system (Fig. S17†). The RhB degradation efficiency was observed to decrease by up to 65% after 60 min with 30 mM 2-PrOH compared to the control experiments, which showed that the surface-bound ˙OH radicals were an important active species here (Fig. S17a†). Meanwhile, the addition of KI appeared to have little effect on the degradation, which indicated that the ˙OH in the aqueous solution did not play a role in the catalytic reaction because of its extremely short lifetime. With the addition of BQ, the RhB degradation efficiency reached >80% after 60 min of reaction, which indicated that O2˙− radicals were also not the active species here (Fig. S17b†). In addition, the addition of FFA, as a capture agent, hardly had any influence on the RhB degradation efficiency (Fig. S17c†), which indicated that singlet oxygen (1O2) was also not an active ROS here. The above results clearly showed that the ˙OH radicals were the main ROS in this reaction. Thus, it was concluded that the degradation pathway in this reaction was a simultaneous adsorption and surface-reaction process. Specifically, adsorption through a non-radical pathway occurred, while the surface-reaction step involved the typical radical route. The good adsorption observed mainly originated from the large catalyst surface area, while the defect sites were main contributor for activating H2O2 for subsequent damage to the molecular structure of organic pollutants, as evidenced by the UV-Vis results (Fig. S18†) and also the reaction pathway shown in Fig. S19.†
4. Conclusions
In this work, a novel O/g-C3N4 catalyst possessing a large surface area and defect sites for the efficient degradation of organic pollutants was successfully developed through a three-step post-treatment method. The g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst possessed the highest specific surface area and more defects relative to that of the g-C3N4 and g-C3N4(HY) catalysts, which was used for treating organic pollutants via H2O2 activation. The g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst exhibited the best catalytic performance among various catalysts. Furthermore, the influencing factors were optimized, e.g., catalyst dosage, concentration of H2O2 and initial pH. Besides, this catalyst retained good stability after use in five cycles. The huge surface area and defects in the g-C3N4(HY-HT) catalyst played a key role in the degradation of organic pollutants in the dark Fenton-like reaction system. The degradation pathway was dominated by the synergistic effect between adsorption and chemical oxidation. This work offers a new catalyst with the ability to in situ activate H2O2 for the degradation of organic pollutants via dark Fenton-like reactions.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51978648), Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 2018JJ3427), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2019M660824), Open Project of Cooperative Innovation Center for Nuclear Fuel Cycle Technology and Equipment (No. 2019KFY02), Hunan Environmental Protection Scientific Research (No. Hunan Finance and construction (2019)0011), Open Project Program of Provincial Key Laboratory of Clean Energy Material, LongYan University (No. QJNY-201802), and Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Safety and Health for Metal Mines (No. 2019-JSKSSYS-04).References
- Y. Cui, Z. Ding, P. Liu, M. Antonietti, X. Fu and X. Wang, Metal-free activation of H2O2 by g-C3N4 under visible light irradiation for the degradation of organic pollutants, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14, 1455–1462 RSC.
- N. Liu, W. Huang, X. Zhang, L. Tang, L. Wang, Y. Wang and M. Wu, Ultrathin graphene oxide encapsulated in uniform MIL-88A(Fe) for enhanced visible light-driven photodegradation of RhB, Appl. Catal., B, 2018, 221, 119–128 CrossRef.
- W. Iqbal, B. Yang, X. Zhao, M. Rauf, M. Waqas, Y. Gong, J. Zhang and Y. Mao, Controllable synthesis of graphitic carbon nitride nanomaterials for solar energy conversion and environmental remediation: the road travelled and the way forward, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2018, 8, 4576–4599 RSC.
- S. An, G. Zhang, T. Wang, W. Zhang, K. Li, C. Song, J. T. Miller, S. Miao, J. Wang and X. Guo, High-density ultra-small clusters and single-atom Fe sites embedded in graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) for highly efficient catalytic advanced oxidation processes, ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 9441–9450 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Li, A. N. Pham, R. Dai, Z. Wang and T. D. Waite, Recent advances in Cu-Fenton systems for the treatment of industrial wastewaters: Role of Cu complexes and Cu composites, J. Hazard. Mater., 2020, 392, 122261 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Gan, C. Huang, Y. Shen, Q. Zhou, D. Han, M. Jin, S. Liu and Y. Zhang, Preparation of carbon nitride nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation method with high yield and enhanced photocatalytic activity, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2020, 31, 513–516 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Ge, Z. Peng, W. Wang, F. Tan, X. Wang, B. Su, X. Qiao and P. K. Wong, g-C3N4/MgO nanosheets: light-independent, metal-poisoning-free catalysts for the activation of hydrogen peroxide to degrade organics, J. Mater. Chem. A., 2018, 6, 16421–16429 RSC.
- J.-N. Zhu, X.-Q. Zhu, F.-F. Cheng, Li Peng, F. Wang, Y.-W. Xiao and W.-W. Xiong, Preparing copper doped carbon nitride from melamine templated crystalline copper chloride for Fenton-like catalysis, Appl. Catal., B, 2019, 256, 117830 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Ding, L. Frank, Y. Lam and X. Hu, Complete degradation of ciprofloxacin over g-C3N4-iron oxide composite via heterogeneous dark Fenton reaction, J. Environ. Manage., 2019, 244, 23–32 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wang, D. Li and Z. Nan, Effect of N content in g-C3N4 as metal-free catalyst on H2O2 decomposition for MB degradation, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2019, 224, 152–162 CrossRef.
- G. Dong, Z. Ai and L. Zhang, Efficient anoxic pollutant removal with oxygen functionalized graphitic carbon nitride under visible light, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 5553–5560 RSC.
- H. Wei, Q. Zhang, Y. Zhang, Z. Yang, A. Zhu and D. D. Dionysiou, Enhancement of the Cr(VI) adsorption and photocatalytic reduction activity of g-C3N4 by hydrothermal treatment in HNO3 aqueous solution, Appl. Catal., A, 2016, 521, 9–18 CrossRef.
- J. Oh, R. J. Yoo, S. Y. Kim, Y. J. Lee, D. W. Kim and S. Park, Oxidized carbon nitrides: water-dispersible, atomically thin carbon nitride-based nanodots and their performances as bioimaging probes, Chem.–Eur. J., 2015, 21, 6241–6246 CrossRef.
- H. Wang, S. Jiang, S. Chen, D. Li, X. Zhang, W. Shao, X. Sun, J. Xie, Z. Zhao, Q. Zhang, Y. Tian and Y. Xie, Enhanced singlet oxygen generation in oxidized graphitic carbon nitride for organic synthesis, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 6940–6945 CrossRef.
- L. Ming, H. Yue, L. Xu and F. Chen, Hydrothermal synthesis of oxidized g-C3N4 and its regulation of photocatalytic activity, J. Mater. Chem. A., 2014, 2, 19145–19149 RSC.
- X. Hao, X. Ji and Q. Zhang, Effective improvement of the photocatalytic efficiency of g-C3N4 by a green hydrothermal treatment method, Mater. Lett., 2016, 185, 29–31 CrossRef.
- X. Wu, F. Chen, X. Wang and H. Yu, In situ one-step hydrothermal synthesis of oxygen-containing groups-modified g-C3N4 for the improved photocatalytic H2-evolution performance, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2016, 427, 645–653 CrossRef.
- M. Wu, Y. Gong, T. Nie, J. Zhang, R. Wang, H. Wang and B. He, Template-free synthesis of nanocage-like g-C3N4 with high surface area and nitrogen defects for enhanced photocatalytic H2 activity, J. Mater. Chem. A., 2019, 7, 5324–5332 RSC.
- P. Niu, L. Zhang, G. Liu and H.-M. Cheng, Graphene-like carbon nitride nanosheets for improved photocatalytic activities, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2012, 22, 4763–4770 CrossRef.
- L. Liu, Q. Liu, Y. Wang, J. Huang, W. Wang, L. Duan, X. Yang, X. Yu, X. Han and N. Liu, Nonradical activation of peroxydisulfate promoted by oxygen vacancy-laden NiO for catalytic phenol oxidative polymerization, Appl. Catal., B, 2019, 254, 166–173 CrossRef.
- P. Gao, X. Chen, H. Mengjie, F. Xiao and S. Yang, Oxygen vacancy enhancing the Fe2O3-CeO2 catalysts in Fenton-like reaction for the sulfamerazine degradation under O2 atmosphere, Chemosphere, 2019, 228, 521–527 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Fang, J. Liu, Y. Lei, Z. Jiang and W. Shangguan, Novel (Na, O) co-doped g-C3N4 with simultaneously enhanced absorption and narrowed bandgap for highly efficient hydrogen evolution, Appl. Catal., B, 2017, 209, 631–636 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Wang, Z. Yang, W. Yao, X. Gao and D. Tao, Defects modified in the exfoliation for g-C3N4 nanosheets via a self-assembly process for improved hydrogen evolution performance, Appl. Catal., B, 2018, 238, 629–637 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Wang, H. Fan, X. Ren, J. Ma, J. Fang and W. Wang, Hydrothermally induced oxygen doping of graphitic carbon nitride with a highly ordered architecture and enhanced photocatalytic activity, ChemSusChem, 2018, 11, 700–708 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Li, B. Shen, Z. Hong, B. Lin, B. Gao and Y. Chen, A facile approach to synthesize novel oxygen-doped g-C3N4 with superior visible-light photoreactivity, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 12017–12019 RSC.
- S. N. Guo, Y. Zhu, Y. Y. Yan, Y. L. Min, J. C. Fan and Q. J. Xu, Holey structured graphitic carbon nitride thin sheets with edge oxygen doping via photo-Fenton reaction with enhanced photocatalytic activity, Appl. Catal., B, 2016, 185, 315–321 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Yang, J. Huang, L. Shi, L. Cao, Q. Yu, Y. Jie, J. Fei, H. Ouyang and J. Ye, A surface modification resultant thermally oxidized porous g-C3N4 with enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production, Appl. Catal., B, 2017, 204, 335–345 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Meng, Y. Xie, T. Cai, Z. Sun, K. Jiang and W.-Q. Han, Graphene-like g-C3N4 nanosheets/sulfur as cathode for lithium-sulfur battery, Electrochim. Acta, 2016, 210, 829–836 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Jiang, L. Ou-yang, L. Zhu, A. Zheng, J. Zou, X. Yi and H. Tang, Dependence of electronic structure of g-C3N4 on the layer number of its nanosheets: A study by Raman spectroscopy coupled with first-principles calculations, Carbon, 2014, 80, 213–221 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Qin, Y. Liu, X. Li, T. Sun and Y. Xu, Enhanced heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation of methylene blue by reduced CuFe2O4, RSC Adv., 2018, 8, 1071–1077 RSC.
- D. Wu, Y. Bai, W. Wang, H. Xia, F. Tan, S. Zhang, B. Su, X. Wang, X. Qiao and P. K. Wong, Highly pure MgO2 nanoparticles as robust solid oxidant for enhanced Fenton-like degradation of organic contaminants, J. Hazard. Mater., 2019, 374, 319–328 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Xu, H. Zhu, W. Cao, Z. Wen, J. Wang, C. P. François-Xavier and T. Wintgens, Cu-Al2O3-g-C3N4 and Cu-Al2O3-C-dots with dual-reaction centres for simultaneous enhancement of Fenton-like catalytic activity and selective H2O2 conversion to hydroxyl radicals, Appl. Catal., B, 2018, 234, 223–233 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Ma, Q. Yang, Y. Wen and W. Liu, Fe-g-C3N4/graphitized mesoporous carbon composite as an effective Fenton-like catalyst in a wide pH range, Appl. Catal., B, 2017, 201, 232–240 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Zhang, Y. Liu, P. Gu, R. Ma, T. Wen, G. Zhao, L. Li, Y. Aia, C. Hu and X. Wang, Enhanced photodegradation of toxic organic pollutants using dual-oxygen doped porous g-C3N4: Mechanism exploration from both experimental and DFT studies, Appl. Catal., B, 2019, 248, 1–10 CrossRef CAS.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/d0ra05202g |
| ‡ T. -J. Jiang and C.-W. Luo contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |