Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleSynthesis and characterization of an electron-deficient conjugated polymer based on pyridine-flanked diketopyrrolopyrrole†
Jialin Yang,
Li Yang ,
Qianqian Chen,
Keke Guo and
Ji-Min Han
,
Qianqian Chen,
Keke Guo and
Ji-Min Han *
*
State Key Laboratory of Explosion Science and Technology, Beijing Institute of Technology, 5 Zhongguancun South Street, Haidian District, Beijing, 100081, China. E-mail: hanjimin@bit.edu.cn; Tel: +86-010-6891-4116
First published on 6th April 2021
Abstract
As classic organic dyes, diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP) derivatives have attracted researchers' attention due to their high charge carrier mobility and good environmental stability. In our study, the pyridine-flanked diketopyrrolopyrrole (PyDPP) with a large conjugated system and 2,2′-bithiazole were used to design and synthesize an all-acceptor (A–A) polymer, poly-(dipyridinyldiketopyrrolopyrrole-bithiazole), named P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz). At the same time, poly-(dipyridinyldiketopyrrolopyrrole-bithiophene), P(PyDPP2OD-2T), was synthesized for comparison and discussion. The A–A polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) synthesized in our research had a highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) energy level of −5.85 eV, and a lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) energy level of −3.65 eV. Its energy band gap was 2.20 eV, which was similar to P(PyDPP2OD-2T). At the same time, measurement of a series of performance characterizations proved that the polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) had good thermal stability. It was judged to be an amorphous polymer with a wide distribution of glassy regions. Based on the above advantages, it is expected to increase the carrier mobility of polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz), and improve its device performance as an n-type organic semiconductor material applied to organic field effect transistors, and find new designs for the development of organic functional materials science ideas.
Introduction
Compared with inorganic materials and small molecule semiconductor materials, conjugated polymers not only have special optical and electrical properties, but also have good mechanical properties and processing properties. In addition, they have low cost, good flexibility, simple device processing technology, abundant raw materials and a designable molecular structure. In recent decades, their various advantages have allowed conjugated polymers to receive extensive attention in scientific research and industrial applications. The conjugated polymer material with a narrow band gap obtained by copolymerization of donor (D) unit and acceptor (A) unit has been reported to have good stability and good field effect performance.1–3 However, this design strategy is limited in the development of n-channel conjugated polymers, because the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) energy of the electron-deficient units is required to be lower than −4 eV for better electron injection and polymer stability. In addition, donor units will reduce the ionization potential and electron affinity, which usually leads to bipolar behavior of OFET devices. That further may lead to unbalanced holes/electrons, resulting in reduced mobility, current leakage and small current on/off ratio (ION/IOFF).4–10According to some reports, the use of all-acceptor (A–A) polymers is a promising way to minimize intramolecular charge transfer and retain low polymer frontier molecular orbitals. The introduction of all-acceptor polymers into conventional transistor devices can produce unipolar n-channel materials.11–17 We can observe that the increased electron affinity promotes electron injection, and the increased ionization potential reduces hole accumulation. However, the synthesis of many receptor units is difficult, which further challenges the research on high-performance A–A polymers.
In order to obtain conjugated polymer semiconductor materials with excellent properties, we consider the following points in the molecular structure design: appropriate molecular energy level, effective π-conjugated system, good solubility and thermal stability, etc. First of all, the stability of the material and the power function of the selected electrode material require that the LUMO energy level of the n-type semiconductor material is preferably below −3 eV and above −4 eV, by introducing a strong electron-deficient group into the main chain of the all-acceptor conjugated polymer. Secondly, the polymers should have a good coplanar backbone structure, which can make them form a tight and orderly stacking method. When the π–π stacking direction between conjugated polymer molecules is aligned parallel to the substrate direction, it is more conducive to carrier transmission. In addition, the type and the density of molecule side chain have a very important impact on the accumulation method of molecules after film formation.1,18,19
The pyridine-flanked diketopyrrolopyrrole (PyDPP) unit has a good coplanar structure and is more electron-deficient than thiophene-flanked diketopyrrolopyrrole. PyDPP uses the pyridine group as the ortho-position of the DPP nucleus, positioning the nitrogen atom with lower steric requirements in the ortho-position of the pyridine. This structure helps to improve the coplanarity of the molecule. Equally importantly, the pyridine group is more electron-deficient than thiophene, furan and benzene rings, which makes PyDPP a stronger electron acceptor. Therefore, PyDPP-based polymers are expected to have a relatively lower LUMO energy level, allowing them to exhibit excellent electron transport characteristics in organic semiconductor material devices. In 2014, Li et al.20 reported the PyDPP molecule for the first time a high-performance bipolar polymer semiconductor material PDBPyBT was synthesized by polymerizing with 2,2′-bithiophene. The polymer exhibits strong self-assembly ability and high crystalline. It also has a π–π stacking distance of only 3.6 nm. The hole mobility and electron mobility reached 2.8 and 6.3 cm2 V−1 s−1 respectively. Experiments have proved that PyDPP is a very promising new type of acceptor unit with efficient electron transport capabilities. Subsequently in 2015, this group reported a new D–A polymer PDBPyTT which showed good bipolar properties. Its hole mobility is 2.65 cm2 V−1 s−1 and electron mobility is 3.36 cm2 V−1 s−1.21 After simple modification of the gate and drain of its OFET, it showed pure N-type material properties and the electron mobility was 2.38 cm2 V−1 s−1. Therefore, this polymer is expected to be a bipolar or n-type semiconductor material for complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) logic circuits. In 2018, Guo Kai et al. synthesized four PyDPP-based “weak donor-strong acceptor” N-type conjugated polymers through direct arylation polycondensation reaction.22 All the four polymers showed lower HOMO and LUMO energy levels. Among them, the devices based on PPyDPP1-4FBT and PPyDPP2-4FBT exhibited typical n-channel transistor behavior, while having high crystallinity and good film morphology. In 2019, Carolyn Buckley et al. designed a semiconducting polymer, PDBPyBTz, using the all-acceptor design strategy and prepared by Stille copolymerization of the electron-deficient 2,2′-bithiazole and bispyridinyl diketopyrrolopyrrole moieties. The BGBC OFET devices fabricated using blade-coated PDBPyBTz active layers demonstrated unipolar n-channel charge transport, with electron mobilities reaching 0.02 cm2 V−1 s−1.23
In this study, we selected 9-(bromomethyl)nonadecane to functionalize the side chain to obtain an electron-deficient conjugated polymer based on PyDPP. The reason why we selected a shorter alkyl chain is because the length of the alkyl chains could significantly influence the performance of the devices. The long alkyl chains can increase the solubility of the polymers, but the molecular packing will be worse due to the alkyl chain disorder. Therefore, on the basis that the material can be processed, we prefer to shorten the alkyl chain as much as possible and improve the material performance. We also used the 2,2′-bithiazole (2Tz) unit to construct the polymer. Compared with dithiophene (2T), the introduction of electronegative nitrogen atoms increases the electron affinity, so that 2Tz is more electron-deficient than 2T. The products are carefully characterized through a series of studies, including theoretical calculations, ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis), electrochemical cyclic voltammetry (CV), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and their thermoelectric properties were preliminary studied. We want to broaden the types of DPP-based conjugated polymers and provide new high-performance, multi-functional conjugated organic semiconductor materials for the development of organic functional materials. At the same time, we synthesized P(PyDPP2OD-2T) for comparison and discussion to explored the effect of introducing electron-deficient groups into the polymer on polymer properties.
Results and discussion
We mainly designed the electron-deficient PyDPP and the relatively weak electron-deficient 2Tz to obtain an A–A polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) via the Stille coupling polymerization reaction successfully. The number average molecular weight (Mn) of P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) measured by GPC was 33.974 kDa, and the polydispersity index (PDI) was 2.58. At the same time, P(PyDPP2OD-2T) was synthesized and discussed to explore the effect of introducing electron-deficient group electrons into the polymer on polymer's performance. The detailed synthetic procedure is provided in the Experimental section below. We have used theoretical calculations, UV-vis, CV, DSC and TGA to preliminarily analyze the thermoelectric properties of monomer and polymers.Computational methodology
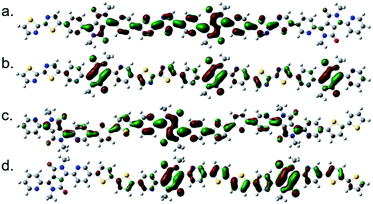
The structure of P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) and P(PyDPP2OD-2T) trimer were optimized by DFT theoretical calculation (B3LYP/6-311+G(d,p)). In order to reduce the amount of calculation, the alkyl side chains of the polymer were replaced by methyl groups. The drawing software was ChewDraw 3D, and the calculation program was Gauss View software and Peking University Supercomputing Center System. Firstly, we calculated the structure optimization calculation for a single repeating unit of the polymer, and used the obtained configuration results to calculate two repeating units. Finally, we repeated the above steps to calculate three repeating units. The calculation results of the obtained trimer are shown in Fig. 1.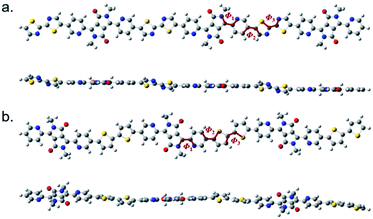 | ||
| Fig. 1 The schematic diagrams of the molecular skeletons of P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) (a) and P(PyDPP2OD-2T) (b) trimers. | ||
In Fig. 1, Φ1 represents the dihedral angle between the DPP core and the pyridine ring, Φ2 represents the dihedral angle between the pyridine ring and the thiazole ring or thiophene ring, and Φ3 represents the dihedral angle between the thiazole ring and the thiazole ring or between the thiophene ring and the thiophene ring. The number of torsion angles is shown in Table 1.
| Polymer | Φ1 | Φ2 | Φ3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) | 0.26° | 22.12° | 0.06° |
| P(PyDPP2OD-2T) | 0.64° | 21.60° | 17.57° |
According to theoretical calculations, in the P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) and P(PyDPP2OD-2T) trimers, the dihedral angle between the DPP core and the pyridine ring is very small, which is 0.26° and 0.64° respectively. The dihedral angles between the pyridine ring and the thiazole rings or thiophene rings are larger, which is 22.12° and 21.60° respectively. However, in the P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) trimer, the dihedral angle between the thiazole ring and the adjacent thiazole ring is only 0.06°. In contrast, the dihedral angle between the thiophene ring and the adjacent thiophene ring in the P(PyDPP2OD-2T) trimer reaches 17.57°. It can also be seen from Fig. 1 that the P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) trimer has a relatively flatter molecular skeleton structure.
It can be seen from Fig. 2 that the electron cloud density of the LUMO level of the P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) trimer is evenly distributed on the DPP core and the bithiophene structure, and the conjugate length is two repeating units. The electron cloud density of the HOMO energy level is mainly distributed on the DPP core structure, and the conjugation length is close to three repeating units. It can be seen from Fig. 2 that the electron cloud density of the LUMO level of the P(PyDPP2OD-2T) trimer is more evenly distributed on the DPP core structure and the bithiophene structure, and the conjugation length is close to three repeating units. The electron cloud density of its HOMO energy level is more evenly distributed on the DPP core and bithiophene structure, and the conjugation length is two repeating units. It can be shown that after the polymerization of small molecule compounds, the conjugation length of the polymer is effectively increased, which is beneficial to the delocalization of π electrons. In addition, the electron cloud density distribution of the LUMO energy level of the two is similar, but the electron cloud density distribution position of the HOMO energy level is quite different. It is speculated that changing one of the donor unit will have a greater impact on the HOMO energy level of the polymer.
Photophysical properties
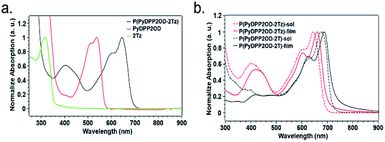
In order to study the optical properties of small molecules and polymers, we used ultraviolet-visible light (UV-vis) absorption spectroscopy for measurement. In our research, the introduction of a long alkyl chain on the N atom of the DPP core greatly improved the solubility of the polymer and made it more soluble in solvents such as chloroform. We tested the absorption spectra of PyDPP2OD and 2Tz in solution and the absorption spectra of P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) and P(PyDPP2OD-2T) in the solution state and the film state respectively.The small molecule and polymers solution sample preparation method was dissolving 2 mg of sample with 1 mL of chloroform, drawing 50 mL solution with a pipette and diluting with 10 mL of chloroform. The concentration of the solution to be tested is 0.01 mg mL−1. After the test, we used Origin software to process the data for graphing and perform normalization processing (Fig. 3).
The maximum absorption peak of 2Tz is at 319 nm, which is the absorption peak produced by the transition of π electrons from the bonding orbital to the antibonding orbital in the molecule. The absorption peak of the charge transfer in the PyDPP2OD appears at 430–570 nm. The maximum absorption peak at 538 nm is 0–0 vibrational absorption, and the shoulder peak at 510 nm is 0–1 vibrational absorption peak. The maximum absorption peak of polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) appears at 645 nm, and the absorption peak generated by the transition of π electrons from the bond orbital to the antibond orbital appears at 350–500 nm.
From the figure, we can see that after the polymerization of two molecules, the absorption peak of polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) at 350–500 nm corresponds to the absorption peak of compound 2Tz at 280–340 nm. And the absorption peak at 500–700 nm corresponds to the absorption peak at 430–570 nm of compound PyDPP2OD. At the same time, the maximum absorption peak of polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) has a red shift of 107 nm relative to that of PyDPP2OD. This is due to the longer π electron delocalization length of polymer relative to small molecules, which is more conducive to the delocalization of π electrons in the molecule, and these results in extremely poor molecular orbital energy, which is a smaller optical band gap, to make it easier to realize charge transfer within the molecule.
Both polymers had absorption peaks in the 350–480 nm and 520–730 nm ranges. The absorption peak at a short wavelength of about 400 nm was caused by the transition from the bonding orbital of the π electron in the molecule to the anti-bonding orbital, and the absorption peak at a long wavelength of 600–700 nm was due to the intramolecular electron transfer. The shoulder peak of polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) at 600 nm corresponded to the 0–1 vibrational absorption of its molecular skeleton. Its maximum absorption peaks in the solution and in the film appeared at 645 nm and 660 nm, respectively. Because of the 0–0 vibration absorption of its molecular skeleton. The shoulder peak of polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2T) at 620 nm corresponded to the 0–1 vibrational absorption of its molecular skeleton. Its maximum absorption peaks in the solution and in the film appeared at 675 nm and 688 nm respectively, corresponding to the 0–0 vibration absorption of its molecular skeleton.
It is obvious from the figure that when bidithiazole in the polymer was replaced by bidithiophene, the 0–0 vibration absorption and 0–1 vibration absorption of the molecular skeleton both had a significant red-shift. In the solution state, the red-shift distance of the lower absorption maximum peak reached 30 nm, and the red-shift distance of the maximum absorption peak in the film state was 28 nm. It was speculated that this was because the thiazole in P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) is more electron-deficient than the thiophene in P(PyDPP2OD-2T), which leads to weaker intermolecular charge transfer to the acceptor. The band gap between HOMO energy level and LUMO energy level increased, so that it had a blue-shifts the relative to polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2T). At the same time, different states of the polymer also affected its absorption. It can be seen from the figure that the absorption peaks of the two polymers in the film state both had a about 15 nm red-shifted from the solution state. This was because the molecules were in the distribution in the solution was more dispersed, and the degree of morphological distortion was greater. In the solid state, the influence of the solvent was eliminated. And the intermolecular arrangement was tightly assembled, and the structure tends to be flat. Therefore, the conjugation length and the absorption strength increased and red-shift occured. We have also considered the fluorescence of polymers, but the experimental results showed that their fluorescence intensities were too low to be distinguished from the background noises. This phenomenon is consistent with the literature, where similar PyDPP polymers' structures were also reported as extremely low fluorescence in both solution and film.
Electrochemical properties
We used cyclic voltammetry (CV) to determine the electrochemical properties of two polymers (Fig. 4). From the electrochemical cyclic volt-ampere characteristic curve, the initial redox potential of each polymer could be obtained by making the intersection of the baseline and the two tangents of the peak positions. The HOMO and LUMO energy levels and band gap were calculated by formula (1)–(3).| HOMO = −[Eox − E (Fc/Fc+) + 4.8] eV | (1) |
| LUMO = −[Ered − E (Fc/Fc+) + 4.8] eV | (2) |
| Eecg = LUMO − HOMO | (3) |
The cyclic voltammetry test used tetrabutylammonium hexafluorophosphate (Bu4NPF6) as the electrolyte and acetonitrile as the solvent to prepare the electrolyte solution with the concentration of 0.1 mol L−1. The methods of preparing polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) and P(PyDPP2OD-2T) are as follows. Firstly, 2 mg of sample was dissolved in 1 mL of chloroform, and the concentration of the resulting solution was 2 mg mL−1. Using a needle to draw 1 mL of the above solution and dropping 1–2 drops on the glassy carbon electrode, it formed a film after the reagent evaporates. The test conditions were room temperature, the oxidation potential was measured in an air atmosphere, the reduction potential was measured in a nitrogen atmosphere, and the solvent was subjected to deoxygenation treatment. In the electrochemical test, the glassy carbon electrode was used as the working electrode, the Ag/AgCl electrode was used as the reference electrode, and the platinum electrode was used as the counter electrode. The scanning speed was 50 mA s−1. In different solvents, the redox potential value of ferrocene relative to the standard hydrogen electrode did not change much, so ferrocene was used for calibration, E (Fc/Fc+) = 0.368 eV.
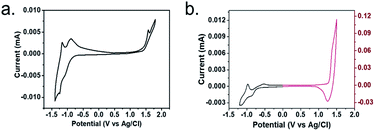 | ||
| Fig. 4 The electrochemical cyclic voltammetry curves of polymers P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) (a) and P(PyDPP2OD-2T) (b). | ||
Table 2 shows the electrochemical data, in which Eoxonset and Eredonset respectively represent the potential value of the starting point of the oxidation and reduction of the polymer, Eecg is the HOMO/LUMO energy band gap, and the unit is eV. Polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) has a potential of 1.42 eV at the oxidation starting point and −0.78 eV at a reduction starting point. The HOMO energy level is −5.85 eV, the LUMO energy level is −3.65 eV, and the optical band gap is 2.20 eV. Polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2T) has a potential of 1.30 eV at the onset of oxidation and −0.75 eV at the onset of reduction. The HOMO energy level is −5.73 eV, the LUMO energy level is −3.68 eV, and the optical band gap is 2.20 eV. The comparison between the two shows that the HOMO energy level of polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) is significantly lower than that of polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2T) about 0.12 eV, which is consistent with the theoretical calculation. The difference between the two LUMO energy levels is only 0.03 eV, the energy level band gap is 0.15 eV higher than that of the polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2T), which is consistent with the conclusion that the optical band gap of the polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) obtained from the ultraviolet-visible spectrum is larger.
| Polymer | Eoxonset (eV) | Eredonset (eV) | HOMO (eV) | LUMO (eV) | Eecg (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) | 1.42 | −0.78 | −5.85 | −3.65 | 2.20 |
| P(PyDPP2OD-2T) | 1.30 | −0.75 | −5.73 | −3.68 | 2.05 |
Thermal properties
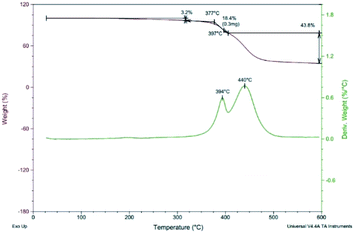
Thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) was used to study the thermal stability of polymers. Fig. 5 shows the TGA curve of polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz). The red curve represents the change curve of sample weight with temperature, and the green curve represents the rate curve of weight decrease with temperature.It can be seen from the curve that under a nitrogen atmosphere, the polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) exhibited good thermal stability. When the temperature rose to 377 °C, there was only about 5.0% weight loss. When the temperature rose from 377 °C to 394 °C, the polymer had a faster weight loss, and when the temperature rose to 440 °C, it completely decomposed. It can be seen that the polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) exhibited good thermal stability and could be used in devices.
Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC) was used to measure the relationship of the power difference and the temperature between the sample and the reference material. The test was carried out in a nitrogen atmosphere, and a 1 mg sample was weighed into a tablet for testing. The reference was an empty aluminum crucible. The setting program was increasing the temperature from 0 °C to 300 °C, then decreasing the temperature from 300 °C to 0 °C, the heating rate is 10 °C min−1, and the nitrogen flow rate is 20 mL min−1.
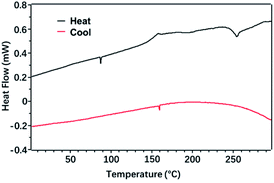
The black curve (-heat) in Fig. 6 represents the heating process, that was the crystal phase of the polymer was destroyed and transformed into an amorphous molten state. The red curve (-cool) represents the cooling process, that was the polymer changed from the amorphous state of the molten state to the crystalline state of the order structure. It can be seen from the figure that during the heating process, when the temperature rose through 153 °C, the baseline of the DSC curve moved toward the endothermic direction. So, 153 °C corresponded to the glass transition temperature (Tg) of the polymer, and the polymer before 153 °C was glass state. The polymer was highly elastic in the range of 150–250 °C. At the same time, the wide distribution of the high elastic temperature range was due to the large molecular weight distribution of the polymer. The exothermic peak at 252 °C corresponded to the phase transition temperature of the polymer, which was presumed to be the crystallization process of the polymer. Polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) did not show obvious endothermic or exothermic peaks during the heating or cooling process, so it was judged to be an amorphous polymer with a wider glassy region distribution, and the PDI measured above was matched.
Experimental
The small molecule compounds were synthesized by reference to previous reports.20,24 The synthesis of the polymer referred to the reaction of other similar polymers for Stille coupling polymerization24 The Stille coupling reaction is a cross-coupling reaction between organotin compounds and halogenated hydrocarbons under the catalysis of palladium complexes. The reaction mechanism is divided into four processes: oxidative addition, metal migration, isomerization, reduction and elimination. This reaction is generally carried out in an anhydrous and oxygen-free inert environment, and the reaction conditions are relatively mild. The catalyst used in this article was tris(dibenzylidneacetone) dipalladium(0).1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectra (NMR) were measured with Bruker ARX-400. All chemical changes are expressed in parts per million (ppm). The chemical shift of 1H NMR was calibrated with TMS (0 ppm), and the chemical shift of 13C NMR was calibrated with CDCl3 (77.0 ppm).
The mass spectrum (MALDI-TOF) was measured by Bruker BIFLEX III mass spectrometer.
Gel permeation chromatography (GPC) was measured with Polymer Laboratories PL-GPC220, the temperature was 150 °C. And 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene (TCB) was used as the eluent.
The absorption spectrum was measured on the PerkinElmer Lambda 750 ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) spectrometer.
The electrochemical voltammetry curve (CV) was measured on the BASI Epsilon workstation. The working electrode is a glassy carbon electrode, the counter electrode is a platinum wire electrode, and the reference electrode is an Ag/AgCl electrode.
A TA Instrument Q600 analyzer was used for thermogravimetric analysis (TGA).
A METTLER TOLEDO Instrument DSC822 calorimeter was used for differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) analysis.
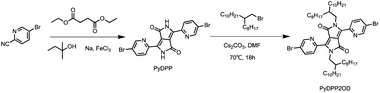
Scheme 1 shows the synthesis route of PyDPP2OD molecule. Firstly, tert-amyl alcohol reacted with sodium metal to form sodium tert-pentoxide which was used to promote the reaction of diethyl succinate and 5-bromo-2-pyridinecarbonitrile. As the base material, the 5-bromo-2-pyridinecarbonitrile reacted to produce PyDPP, in which ferric chloride acted as an electrolyte to accelerate the reaction. The second step was the alkylation reaction. DMF was used as the solvent, and 9-(bromomethyl)nonadecane was substituted with PyDPP to produce PyDPP2OD compound with long alkyl chain. And Cs2CO3 was used as acid binding agent to neutralize the hydrogen ions in reaction. During this reaction, the PyDPP compound produced by the reaction was difficult to dissolve in large polar solvents such as methanol and ethanol and was less soluble in small polar solvents such as petroleum ether. It was also difficult to separate. The solubility of PyDPP2OD with long alkyl chain attached has been greatly improved, but the separation was still difficult.
Synthesis of PyDPP
Under the protection of nitrogen, tert-amyl alcohol (50 mL), FeCl3 (25.00 mg), and metallic sodium (1.05 g, 45.65 mmol) were added sequentially to a 100 mL three-necked round-bottom flask. The temperature was increased to 115 °C slowly. After the metallic sodium disappeared completely, the reflux reaction was continued for 1 h. Then the reaction system was cooled to 60 °C, and the tert-amyl alcohol suspension (10 mL) containing the compound 5-bromo-2-pyridinecarbonitrile (5.00 g, 27.32 mmol) was added to the reaction solution. The color of the reaction system changed to yellow, and finally deepened into a dark brown suspension. Finally, the reaction system was heated to 85 °C, and the compound diethyl succinate (2.30 g, 11.37 mmol) was added dropwise. It could be seen that the color of the reaction system turned black and the reaction was stirred for 4 h. After the reaction, the solution was poured into 150 mL of anhydrous methanol to precipitate a large amount of black red solids. The filtered solids were washed with 200 mL of hot acetone (90 °C) and dried in a Petri dish to obtain black and red solid (4.12 g, crude).Synthesis of PyDPP2OD
Under the protection of nitrogen, PyDPP (1.00 g, 2.23 mmol), 9-(bromomethyl) nonadecane (2.42 g, 6.70 mmol), Cs2CO3 (2.18 g, 6.70 mmol) and DMF (25 mL) were added to a 100 mL double-necked round bottom flask. This reaction system was slowly heated to 70 °C and stiring for 12 h. After the reaction, the solution was diluted with water. The mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate and the organic phases were combined and washed by saturated brine for three times (100 mL × 3). It was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4 and concentrated to obtain crude red solid. The crude product dissolved with 1-4-dioxane (20 mL) and added to a 100 mL eggplant-shaped bottle. After adding concentrated hydrochloric acid (3–4 mL) dropwise, the reaction system was heated to 100 °C reflux, continuing to stir and react for 2 h. Then the deionized water was added to dilute and dichloromethane (DCM) was added to extract for 3 times. The lower organic phase was dried over by anhydrous Na2SO4 and spin-dried in vacuum to obtain red crude product. The residue was purified by column chromatography (petroleum ether/dichloromethane = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) to obtain purple-red solid (1.42 g, total yield 21%), which is the PyDPP2OD. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): δ 8.92 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 8.74 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 2H), 8.01 (dd, J = 2.4, 8.4 Hz, 2H), 4.28 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 4H), 1.50–1.57 (m, 2H), 1.20–1.40 (m, 64H), 0.87 (m, 12H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): δ 162.62, 150.24, 146.19, 139.84, 128.60, 122.72, 111.55, 77.48, 77.16, 76.84, 46.41, 38.34, 32.07, 32.04, 31.56, 31.08, 30.15, 29.82, 29.80, 29.76, 29.70, 29.51, 29.47, 26.50, 22.82, 14.27; MALDI-TOF MS calcd for [M + H]+: 1006.5; found: 1007.5.
1) to obtain purple-red solid (1.42 g, total yield 21%), which is the PyDPP2OD. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): δ 8.92 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 8.74 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 2H), 8.01 (dd, J = 2.4, 8.4 Hz, 2H), 4.28 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 4H), 1.50–1.57 (m, 2H), 1.20–1.40 (m, 64H), 0.87 (m, 12H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): δ 162.62, 150.24, 146.19, 139.84, 128.60, 122.72, 111.55, 77.48, 77.16, 76.84, 46.41, 38.34, 32.07, 32.04, 31.56, 31.08, 30.15, 29.82, 29.80, 29.76, 29.70, 29.51, 29.47, 26.50, 22.82, 14.27; MALDI-TOF MS calcd for [M + H]+: 1006.5; found: 1007.5.
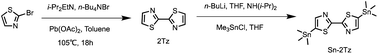
As shown in Scheme 2, the coupling reaction of 2-bromothiazole produced 2,2′-bithiazole (2Tz) molecules which were then substituted with trimethyltin chloride to produce the compound Sn-2Tz, which was the preparation for next step of Stille coupling polymerization reaction. In the first step of the synthesis process, the yield of the product obtained by the first reaction was very low, so we refered to other researches to analyze and change the equivalent of the reactant for many attempts to effectively increase the yield. At the same time, due to the high toxicity of the tin reagent, it was very dangerous. So, it was necessary to operate carefully and promptly handle the experimental tools stained with the tin reagent during the experiment. The compounds 2Tz and Sn-2Tz obtained by the reaction had good solubility and both two are soluble in common solvents such as dichloromethane and ethyl acetate. The detailed synthesis steps are provided in ESI.†
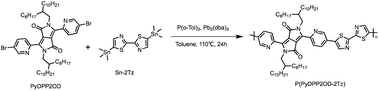
Synthesis of P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz)
The target polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) shown in Scheme 3 is obtained by PyDPP2OD and Sn-2Tz through the palladium-catalyzed Stille coupling reaction. Its solid has good solubility in many organic solvents. The number average molecular weight (Mn) of the polymer measured by GPC was 33.974 kDa, and the PDI was 2.58.PyDPP2OD (100 mg, 0.099 mmol), Sn-2Tz (48.94 mg, 0.099 mmol), P(o-Tol)3 (4.83 mg, 0.016 mmol) and Pb2(dba)3 (3.63 mg, 0.004 mmol) were added to a 25 mL Schlenk bottle with toluene (8 mL) at −78 °C under nitrogen. Then the reaction mixture was returned to room temperature and slowly heated to 110 °C, stirring for 24 h. After 20 min, the reaction solution changed from orange-red to deep red. After 30 min, the reaction solution turned purple-red. After 40 minutes, the reaction solution turned blue-black.
After the reaction, the reaction system was cooled to room temperature, and the palladium removal ligand was added to the reaction solution. Under the protection of nitrogen, the temperature was slowly raised to 80 °C, and the reaction was stirred for 30 min. After the reaction, the reaction solution was poured into 200 mL of anhydrous methanol, and a large amount of blue-black solid was precipitated. After the solid was completely precipitated, the crude blue-black solid was obtained by suction filtration. The crude product is purified by Soxhlet extraction (the solvents are: anhydrous methanol, acetone, n-hexane, tetrahydrofuran, and chloroform). When the solvent is anhydrous methanol, a pale pink solution is obtained; when the solvent is acetone or n-hexane, a pale red solution is obtained; when the solvent is tetrahydrofuran, a dark green solution is obtained; when the solvent is chloroform, a pale green solution is obtained.
The solution under tetrahydrofuran was spin-dried, and the obtained solid was dissolved in chloroform (CF) and dropped into 200 mL of anhydrous methanol. A large amount of dark green solid was precipitated. After suction filtration, a dark green metallic film-like solid was obtained. The target product P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) (112 mg) was obtained by drying in vacuum oven.
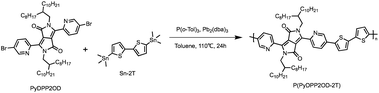
Synthesis of P(PyDPP2OD-2T)
The target polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2T) shown in Scheme 4 is obtained by PyDPP2OD and Sn–2T through the palladium-catalyzed Stille coupling reaction. Its solid solubility was slightly worse than that of P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz), and it was insoluble in tetrahydrofuran solvent. The number average molecular weight (Mn) of the polymer measured by GPC was 40.104 kDa and the PDI was 2.12.PyDPP2OD (50 mg, 0.050 mmol), Sn–2T (24.35 mg, 0.050 mmol), P(o-Tol)3 (2.41 mg, 0.008 mmol) and Pb2(dba)3 (1.81 mg, 0.002 mmol) were added to a 25 mL Schlenk bottle in sequence with toluene (6 mL) at −78 °C.
Then the reaction mixture was returned to room temperature and slowly heated to 110 °C, stirring for 24 h. After 10 min, the reaction solution changed from orange-red to deep red. After 30 min, the reaction solution turned purple-red. After 40 minutes, the reaction solution turned blue-black.
After the reaction, the reaction system was cooled to room temperature, and the palladium removal ligand was added to the reaction solution. Under the protection of nitrogen, the temperature was slowly raised to 80 °C, and the reaction was stirred for 30 min. After the reaction, the reaction solution was poured into 200 mL of anhydrous methanol, and a large amount of blue-black solid was precipitated. After the solid was completely precipitated, the crude blue-black solid was obtained by suction filtration. The crude product is purified by Soxhlet extraction (the solvents are: anhydrous methanol, acetone, n-hexane, tetrahydrofuran, and chloroform). When the solvent is anhydrous methanol, the solution is colorless; When the solvent is acetone, a pale pink solution is obtained; when the solvent is n-hexane and tetrahydrofuran, the solution is transparent; when the solvent is chloroform, an ink blue solution is obtained.
The solution under chloroform was concentrated and the solid obtained was dissolved in chloroform and dropped into 200 mL of anhydrous methanol. A large amount of ink blue solid was precipitated. After filtration, a brown-red metallic luster film-like solid was obtained. The target product P(PyDPP2OD-2T) (40 mg) was obtained by drying in vacuum oven.
Conclusions
In this study, we mainly designed the electron-deficient thiophene-flanked DPP (PyDPP) and the relatively weak electron-deficient 2,2′-bithiazole (2Tz) to obtain an A–A polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) via the Stille coupling polymerization reaction. And we have determined the structure of the molecules by NMR and mass spectrometry. In the course of the experiment, we found that the length of 9-(bromomethyl) nonadecane we selected was appropriate as the side chain. Both intermediates and polymers maintain good solubility, which found a good balance between polymer synthesis and material fabrication. We have used theoretical calculations, UV-vis, CV, DSC and TGA to preliminarily analyze the thermoelectric properties of monomer and polymers. At the same time, P(PyDPP2OD-2T) was synthesized and discussed to explore the effect of introducing electron-deficient group electrons into the polymer on polymer's performance. The results showed that the polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) synthesized in this study had a small twist angle and a relatively flat plane structure. The maximum absorption peak in UV-vis spectrum is at 675 nm. Its HOMO energy level is −5.85 eV and LUMO energy level is −3.65 eV, so that the band gap is 2.200 eV. By comparison, the HOMO energy level of P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) was 0.112 eV lower than −5.73 of P(PyDPP2OD-2T), and its LUMO energy level and band gap were not much different from −3.68 of P(PyDPP2OD-2T). In addition, the thermal properties of the polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) were tested and it was found that its decomposition temperature was 377 °C, which demonstrate a good thermal stability. According to the DSC curve, it was judged to be an amorphous polymer with wide distribution of glassy zone. At the same time, it was found during the experiment that the polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz) also had good solubility and was soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform. Based on the above preliminary research data on the properties of polymer P(PyDPP2OD-2Tz), this polymer exhibited a good planar structure, as well as the optimized optical and thermal properties. Therefore, it may be expected to become a semiconductor material in organic field effect transistors or solar cell devices with good conductivity after doping.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21801016), the State Key Laboratory of Explosion Science and Technology (No. ZDKT19-01), and Beijing Institute of Technology Research Fund Program for Young Scholars. We are very grateful to Professor Pei Jian's research group of Peking University, and especially to Professor Lei Ting and Dr Yan Xinwen for their guidance.Notes and references
- H. N. Tsao, D. M. Cho, I. Park, M. R. Hansen, A. Mavrinskly, D. Y. Yoon, R. Graf, W. Pisula, H. W. Spiess and K. Müllen, Ultrahigh Mobility in Polymer Field-Effect Transistors by Design, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 2605–2612 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Zhang, H. Tsao, W. Pisula, C. Yang, a. Mishra and K. Müllen, Field-Effect Transistors Based on a Benzothiadiazole−Cyclopentadithiophene Copolymer, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 3472–3473 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. N. Tsao, D. Cho, J. W. Andreasen, A. Rouhanipour, D. W. Breiby, W. Pisula and K. Müllen, The Influence of Morphology on High-Performance Polymer Field-Effect Transistors, Adv. Mater., 2009, 21, 209–212 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Cornil, J.-L. Brédas, J. Zaumseil and H. Sirringhaus, Ambipolar Transport in Organic Conjugated Materials, Adv. Mater., 2007, 19, 1791–1799 CrossRef CAS.
- R. P. Ortiz, H. Herrera, C. Seoane, J. L. Segura, A. Facchetti and T. J. Marks, Rational Design of Ambipolar Organic Semiconductors: Is Core Planarity Central to Ambipolarity in Thiophene-Naphthalene Semiconductors?, Chem.–Eur. J., 2012, 18, 532–543 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zaumseil and H. Sirringhaus, Electron and Ambipolar Transport in Organic Field-Effect Transistors, Chem. Rev., 2007, 107, 1296–1323 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. S. Kim, X. Guo, M. D. Watson and S. A. Jenekhe, High-mobility Ambipolar Transistors and High-gain Inverters from a Donor–Acceptor Copolymer Semiconductor, Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 478–482 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. H. Jung, W. Y. Lo, J. Jang, W. Chen, D. Zhao, E. S. Landry, L. Lu, D. V. Talapin and L. Yu, Synthesis and Search for Design Principles of New Electron Accepting Polymers for All-Polymer Solar Cells, Chem. Mater., 2014, 26, 3450–3459 CrossRef CAS.
- M. M. Durban, P. D. Kazarinoff and C. K. Luscombe, Synthesis and Characterization of Thiophene-Containing Naphthalene Diimide n-Type Copolymers for OFET Applications, Macromolecules, 2010, 43, 6348–6352 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Guo, R. P. Ortiz, Y. Zheng, Y. Hu, Y. Y. Noh, K. J. Baeg, A. Facchetti and T. J. Marks, Bithiophene-Imide-Based Polymeric Semiconductors for Field-Effect Transistors: Synthesis, Structure−Property Correlations, Charge Carrier Polarity, and Device Stability, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 1405–1418 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Xiao, A. Onwubiko, W. Yue, H. Sirringhaus, A. Wadsworth, M. Nikolka, D. Baran, H.-Y. Chen, I. McCulloch and A. J. P. White, A Thieno[2,3-b] pyridine-Flanked Diketopyrrolopyrrole Polymer as an n-Type Polymer Semiconductor for All-Polymer Solar Cells and Organic Field-Effect Transistors, Macromolecules, 2018, 51, 71–79 CrossRef.
- G. Kim, A. R. Han, H. R. Lee, J. Lee, J. H. Oh and C. Yang, Acceptor-acceptor Type Isoindigo-Based Copolymers for High Performance n-Channel Field-Effect Transistors, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 2180 RSC.
- J. K. Lee, M. C. Gwinner, R. Berger, C. Newby, R. Zentel, R. H. Friend, H. Sirringhaus and C. K. Ober, High-Performance Electron-Transporting Polymers Derived from a Heteroaryl Bis- (Trifluoroborate), J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 9949–9951 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Stalder, J. Mei, J. Subbiah, C. Grand, L. A. Estrada, F. So and J. R. Reynolds, N-Type Conjugated Polyisoindigos, Macromolecules, 2011, 44, 6303–6310 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Zhao, Y. Wen, L. Ren, L. Ma, Y. Liu and X. Zhan, An Acceptor-Acceptor Conjugated Copolymer Based on Perylene Diimide for High Mobility n-Channel Transistor in Air, J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem., 2012, 50, 4266–4271 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Wang, H. Guo, A. Harbuzaru, M. A. Uddin, I. Arrechea-Marcos, S. Ling, J. Yu, Y. Tang, H. Sun, J. T. López Navarrete, R. P. Ortiz, H. Y. Woo and X. Guo, (Semi)ladder-Type Bithiophene Imide-Based All-Acceptor Semiconductors: Synthesis, Structure–Property Correlations, and Unipolar n-Type Transistor Performance, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 6095–6108 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Yuan, B. Fu, S. Thomas, S. Zhang, G. Deluca, R. Chang, L. Lopez, C. Fares, G. Zhang and J. Bredas, Unipolar Electron Transport Polymers: A Thiazole Based All-Electron Acceptor Approach, Chem. Mater., 2016, 28, 6045–6049 CrossRef CAS.
- R. D. Mccullough, S. Tristram-Nagle, S. P. Williams, R. D. Lowe and M. Jayaraman, Self-orienting Head-to-tail Poly(3-alkylthiophenes): New Insights on Structure-Property Relationships in Conducting Polymers, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1993, 115, 4910–4911 CrossRef CAS.
- B. S. Ong, Y. Wu, P. Liu and S. Gardner, Structurally Ordered Polythiophene Nanoparticles for High-Performance Organic Thin-Film Transistors, Adv. Mater., 2005, 17, 1141–1144 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Sun, W. Hong, Z. Yan, H. Aziz and Y. Li, Record High Electron Mobility of 6.3 cm2V−1s−1 Achieved for Polymer Semiconductors Using a New Building Block, Adv. Mater., 2014, 26, 2636–2642 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Sun, W. Hong, H. Aziz and Y. Li, A Pyridine-Flanked Diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP)-Based Donor–Acceptor Polymer Showing High Mobility in Ambipolar and n-Channel Organic Thin Film Transistors, Polym. Chem., 2015, 6, 938–945 RSC.
- K. Guo, J. Bai, Y. Jiang, Z. Wang, Y. Sui, Y. Deng, Y. Han, H. Tian and Y. Geng, Diketopyrrolopyrrole-Based Conjugated Polymers Synthesized via Direct Arylation Polycondensation for High Mobility Pure n-Channel Organic Field-Effect Transistors, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1801097 CrossRef.
- C. Buckley, S. Thomas, M. Mcbride, Z. Yuan and E. Reichmanis, Synergistic Use of Bithiazole and Pyridinyl Substitution for Effective Electron Transport Polymer Materials, Chem. Mater., 2019, 31, 3957–3966 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Zhang, J. Zhang, W. Zeng, N. Zheng, W. Li, W. Gao, G. Yu and C. Yang, Benzobisthiadiazole-Alt-Bithiazole Copolymers with Deep HOMO Levels for Good-Performance Field-Effect Transistors with Air Stability and a High On/Off Ratio, Polym. Chem., 2016, 7, 2808–2814 RSC.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/d1ra00779c |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2021 |