Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Correlations between experiments and simulations for formic acid oxidation†
Alexander
Bagger‡
 *a,
Kim D.
Jensen‡
*a,
Kim D.
Jensen‡
 a,
Maryam
Rashedi
a,
Maryam
Rashedi
 ab,
Rui
Luo
ab,
Rui
Luo
 ac,
Jia
Du
ac,
Jia
Du
 d,
Damin
Zhang
d,
Damin
Zhang
 d,
Inês J.
Pereira
d,
Inês J.
Pereira
 a,
María
Escudero-Escribano
a,
María
Escudero-Escribano
 aef,
Matthias
Arenz
aef,
Matthias
Arenz
 ad and
Jan
Rossmeisl
ad and
Jan
Rossmeisl
 a
a
aUniversity of Copenhagen, Department of Chemistry, Universitetsparken 5, 2100 Kbh-Ø, Denmark. E-mail: alexander@chem.ku.dk
bCollege of Science, University of Tehran, Enghelab Square, Tehran, Iran
cSchool of Environmental and Biological Engineering, Nanjing University of Science & Technology, Nanjing 210094, China
dUniversity of Bern, Department of Chemistry, Biochemistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences, CH-3012 Bern, Switzerland
eCatalan Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (ICN2), CSIC, Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology, UAB Campus, 08193 Bellaterra, Barcelona, Spain
fICREA, Pg. Lluís Companys 23, 08010 Barcelona, Spain
First published on 26th October 2022
Abstract
Electrocatalytic conversion of formic acid oxidation to CO2 and the related CO2 reduction to formic acid represent a potential closed carbon-loop based on renewable energy. However, formic acid fuel cells are inhibited by the formation of site-blocking species during the formic acid oxidation reaction. Recent studies have elucidated how the binding of carbon and hydrogen on catalyst surfaces promote CO2 reduction towards CO and formic acid. This has also given fundamental insights into the reverse reaction, i.e. the oxidation of formic acid. In this work, simulations on multiple materials have been combined with formic acid oxidation experiments on electrocatalysts to shed light on the reaction and the accompanying catalytic limitations. We correlate data on different catalysts to show that (i) formate, which is the proposed formic acid oxidation intermediate, has similar binding energetics on Pt, Pd and Ag, while Ag does not work as a catalyst, and (ii) *H adsorbed on the surface results in *CO formation and poisoning through a chemical disproportionation step. Using these results, the fundamental limitations can be revealed and progress our understanding of the mechanism of the formic acid oxidation reaction.
Introduction
Tremendous efforts are currently going into out-phasing fossil fuels in favor of sustainable fuels.1 This is motivated by our need to close the carbon cycle2 and pave the way for new fuel production routes.3 Electrocatalytic technologies can in the future possibly allow direct electrification of chemical and fuel production. Examples include reduction of CO2 towards CO, HCOOH, C2H4, C2H5OH and H2O towards H2.1 Efficient fuel consumption through fuel cells (FCs) also holds great potential.4 Liquid fuels such as formic acid and methanol have attracted a lot of attention due to their viable energy density per mass- and volume, attractive handling/storage properties and potential uses in other non-fuel applications, e.g. as high value chemical building blocks for industry.3Some liquid fuels, such as methanol, are notoriously limited in the oxidation toward CO2 since the process goes through a CO intermediate.5 CO oxidation then becomes the limiting factor determining the performance of direct methanol FCs (DMFCs). Formic acid as liquid fuel behaves differently; it has a CO2-like structure with two hydrogens attached. This molecular structure predicates that the oxidation process only requires the removal of two hydrogen atoms. Consequently, formic acid oxidation should ideally circumvent the problem of CO-poisoning.
To gauge formic acid's efficiency as a fuel we compare the single round trip efficiency of relevant closed-loop chemical compounds, i.e. hydrogen, formic acid, methanol and lithium batteries as seen in Table 1. Here we observe that the Li-battery storing and release of energy exhibits the highest efficiency followed by hydrogen. However, both Li-batteries and H2 suffer from low energy density. Storing energy as methanol and formic acid is very similar in terms of the cost in electrolyzer energy. The major difference between formic acid and methanol arises when using the chemical in a fuel cell, where methanol is limited by CO oxidation.6
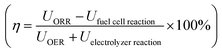 calculated using the difference in energy potentials. Common for hydrogen, formic acid, and methanol we use UOER = 1.6 VRHE and UORR = 0.8 VRHE
calculated using the difference in energy potentials. Common for hydrogen, formic acid, and methanol we use UOER = 1.6 VRHE and UORR = 0.8 VRHE
| Energy stored (electrolyzer) | Energy released (fuel cell) | Round trip efficiency, η | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a Here only the cost of syngas production is considered, not the full formation of methanol. b Typical charge/discharge efficiency. | |||
| Hydrogen | U HER = −0.1 VRHE | U HOR = 0.1 VRHE | ≈41% |
| Formic acid | U CO2→HCOOH = −0.8 VRHE | U FAOR = 0.2 VRHE | ≈25% |
| Methanola | U CO2→CO+H2 = −0.6 VRHE | U CO→CO2 = 0.65 VRHE | ≈7% |
| Li-batteryb | ≈90% | ||
Depending on the UFAOR, direct formic acid fuel cells (DFAFCs) can be considered an attractive alternative to methanol fuel cells. Methanol provides 6 protons per reacted molecule and formic acid only two and therefore methanol has a ∼3 times higher volumetric energy density. However, the potential of a formic acid fuel cell is high; even a few hundred millivolts reduction in overpotential can allow formic acid to output more energy than methanol per molecule.
Key to understanding the limitation of formic acid oxidation is the direct link to the reverse electrochemical reaction, i.e. the CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR).7,8 CO2RR to formic acid and the formic acid oxidation reaction (FAOR) can be written in the form:
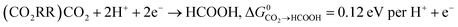 | (1) |
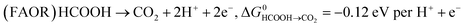 | (2) |
CO2RR selectivity is highly dependent on the catalyst material used and the crystal orientation.9–12 Hori et al. showed that hydrogen is produced on Pt, Ru, Fe and Ni, carbon monoxide is produced on Au, Ag, Zn, Ga and Pd (with limited amounts of H2), and finally, formic acid is produced on Pb, In, Hg, Sn, Cd and Tl with almost 100% faradaic efficiency.11 Importantly, hydrocarbons are uniquely produced on Cu.11 Using simulations, we were able to classify the CO2RR product distributions towards hydrogen, hydrocarbons, CO and formic acid due to the catalyst's affinity towards adsorbed *H and *CO.10 Interestingly, we noted that the CO2RR appears selective towards formic acid when weakening *H binding (i.e. when there is no *H on the catalyst surface). Moreover, from this study10 we noted that the *OOCH vs. the *COOH intermediate cannot be used to distinguish the CO or formic acid product formation. Where previous works used *OOCH as a descriptor for formic acid oxidation and *COOH as a descriptor for CO production, and even recent discussion for CO2 reduction highlights the possible formic acid formation through *COOH.13 These findings and discussion are readily usable when considering the reverse reaction FAOR, which involves similar reaction intermediates to CO2RR and vice versa.
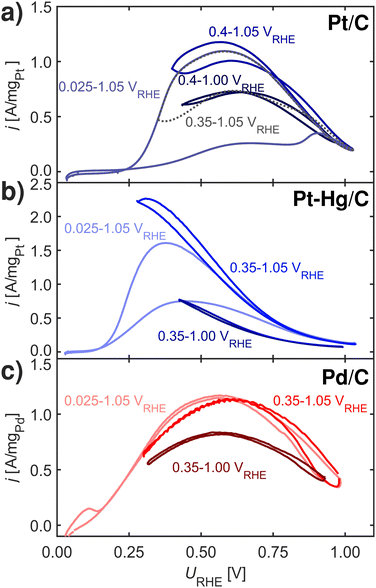
FAOR exhibits the highest intrinsic activity on Pt and Pd.14–19 However, the reaction is affected by high overpotential and formation of various poisoning and site-blocking intermediates.20 The following observations are reported in the literature, as also shown in ESI Fig. S1:† (i) FAOR onsets at low potentials does not necessarily correspond to high FAOR currents. (ii) Hysteresis between anodic and cathodic scans is a common occurrence, showing a higher current in cathodic scans in than anodic ones, which shows that the reaction rate depends on the prehistory. Typically, this “memory effect” is related to unwanted reactions which form species that block the surface, i.e. poisoning species. (iii) Pt(111) is more active than Pd(100) in the low overpotential region; however, interestingly, this relationship shifts at higher potentials. (iv) As an observation it is known that there is a difference for Pt and Pd with respect to the CO poisoning during FAOR.8 The ideal FAOR catalyst on the other hand should show reversible cyclic voltammetry (CV), high activity, low onset potential and stable currents, as illustrated in Fig. S2.†
To understand the mechanism of this important reaction numerous attempts have been made to map possible FAOR pathways,20–24 which we illustrate by the literature study overview in Fig. 1. A dual-pathway mechanism for formic acid oxidation is established by the community:25,26 The direct pathways, which leads to the desired final product of CO2 through the formate adsorption,27 and another path where adsorbed CO, the poisoning species, is formed. The CO formation can be thought of as being formed through a so-called chemical disproponation reaction, where an activated formic acid intermediate reacts with a hydrogen to form water and CO (e.g. *COOH + *H → *CO + H2O). However, the nature of the reactive intermediate in the direct pathway is still under strong debate and it is not given that it is the most stable intermediate (e.g., formate) should also be the reaction intermediate. The community has focused on elucidating the reaction mechanism and attempted to circumvent poisoning issues: through pathway engineering,21,22 changing electrolyte composition,23 or inclusion of sites with the ability to remove poisoning or site-blocking species.24,28–30 CO-poisoning from partial HCOOH oxidation is often considered the principal culprit28 and various works suggest CO formation can be avoided utilizing a single/dual-site catalyst.31–34 However, catalysts such as Au–Pt,21 Pt–Hg/C35 and Pd–Hg/C36 exhibit limited catalytic improvement over their pure metal counterparts, for some overviews see Fig. S4 in ESI.† In this work, we will take a new view on all possible pathways for working catalysts. We carry out electrochemical characterization on Pd/C and Pt/C catalyst as well as Pt–Hg/C,35 Pd–Hg/C36 and Pt–Bi/C,37 following the protocols reported in the literature for the preparations of these catalysts. Furthermore, we try to validate the possible reaction path for not/low performing catalysts (e.g., Ag) for formic acid oxidation.
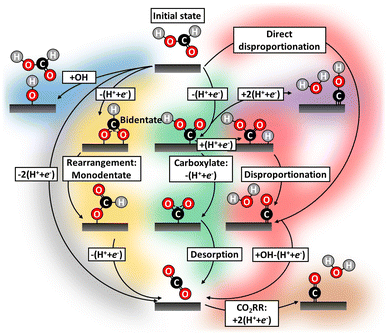 | ||
| Fig. 1 Literature study highlighting all the conceived FAOR reaction pathways during potential cycling.38 Historically, FAOR has been split into the direct (gray)39,40 and indirect (green and yellow)16,39,41,42 pathways. Further, partial FAOR and catalyst oxidation forming unwarranted surface blocking have been suggested, e.g. COxHy species (purple),20,25,43 CO (red)44 and hydroxide/oxides (blue).38 Even CO2RR induced CO formation by applying too cathodic potential (brown)40 have been suggested. Recently, formate (yellow)28,39,45,46 in various arrangements has gained attention as potential catalyst site-blocking agents. | ||
In this work, we address the following fundamental questions in FAOR:
(i) Is the FAOR activity correlated with the *COOH or the *OOCH intermediate?
(ii) How is CO formed during the FAOR?
To probe the scientific questions, we use a combination of experimental tools based on cyclic voltammetry (CV) and chronoamperometric (CA) and for simulations we use density functional theory (DFT) calculations on the binding of carboxyl, *COOH, formate bidentate, *OOCH, and hydrogen, *H.
Results and discussion
Fig. 2 summarizes experimental electrochemical data of Pt/C, Pd/C, Pt–Hg/C, Pd–Hg/C and Pt–Bi/C. Here we investigate only known and active FAOR catalyst, and both extended surfaces as Pt/C and Pd/C, but also single site catalyst Pt–Hg/C and Pd–Hg/C and the noteworthy very active Pt–Bi/C system. These investigated catalysts are synthesized from the same starting materials, i.e. premade Pd or Pt catalyst which we then modified by (electro)deposition of Hg or Bi at room temperature. Consequently, it is reasonable to expect that no significant impact of the catalysts' surface area arises due to the modification, allowing for catalyst comparison. However, verifying this expectation using standard electrochemical surface area (ECSA) evaluation (e.g. utilizing *CO-stripping or hydrogen under potential deposited, H-UPD, charges) is not possible as these species do not adsorb specifically on Hg and Bi modified catalysts.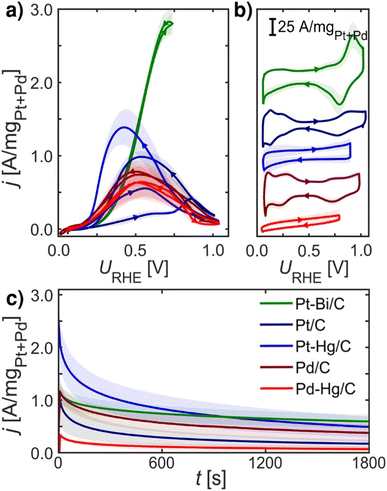 | ||
| Fig. 2 Electrochemical data recorded at room temperature of equal loading nanoparticle catalysts: Pt/C (navy blue), Pd/C (crimson), Pt–Hg/C (blue), Pd–Hg/C (red) and Pt–Bi/C (green) systems on glassy carbon in Ar-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 with 0.1 M HCOOH at 1600 rpm, unless otherwise stated. (a) FAOR CVs at 10 mV s−1. (b) Base CVs in Ar-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 at 400 rpm and 50 mV s−1. (c) CA at 0.55 VRHE for 30 min. All measurements were repeated at least three times (shade represents standard deviation), IR-compensated and post-corrected, for experimental details see ESI and Fig. S5–S8.† Note, Pt–Bi/C was unstable at higher potentials (see ESI†) hence a reduced potential range was utilized. | ||
Fig. 2a shows the formic acid oxidation CV during rotation and 10 mV s−1 scan-rate on the five catalysts. Fig. 2b depicts the base CVs exhibiting suppressed hydrogen underpotential deposition (HUPD) on the Pt–Bi/C, Pt–Hg/C and Pd–Hg/C compared to the Pd/C and Pt/C counterparts. Fig. 2c displays the formic acid oxidation CA at 0.55 VRHE for 30 min, illustrating the loss in activity at this potential due to the formation of poisoning or blocking species. For Pt/C and Pt–Hg/C, an apparent hysteresis is seen in the oxidation between the forward and backward scans of Fig. 2a indicating an irreversible change in the catalyst going to low potentials. Interestingly, taking a combined view on Fig. 2a and c shows that forming single-sites of Pt through Hg alloying35,36 tend to improve the FAOR onset. In contrast, Pd-based catalysts generally do not exhibit any hysteresis. The Pt–Bi/C system exhibit the highest FAOR current with least hysteresis, but also with the highest overpotential. Additional relevant electrochemical studies can be found in the ESI,† represented through Fig. S10–S13.† To explain these observations in Fig. 2 we turned to DFT.
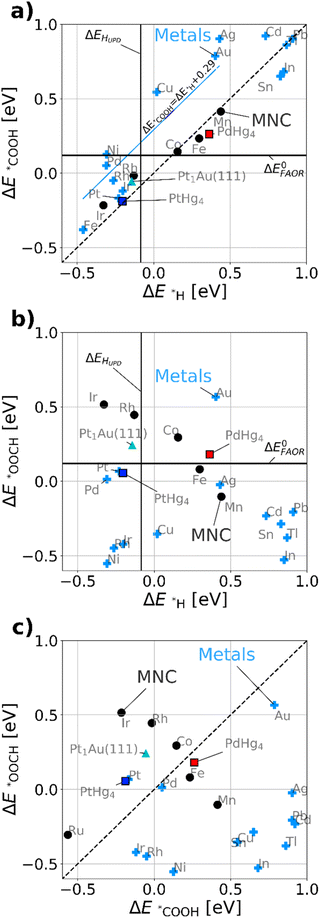
Fig. 3a maps out the DFT calculated *COOH vs. *H binding energies of the most relevant model metal (111) facets and single-site catalysts, such as MNCs, PtHg4,35 PdHg4 (ref. 36) and single Pt atoms in Au, Pt1Au(111)21 (for computational details see ESI†). Via simulations we study both metals and the single-site-catalysts as they both have a linear scaling: ΔE*COOH = ΔE*H + b. However, b is about 0.29 eV as previously47 observed for metals and 0.0 eV for single-site catalysts, respectively. This allows for a fundamental destabilization of *H vs. *COOH at the single-site catalyst motifs as compared to metals, which is beneficial for improved FAOR by limiting the disproportionation reaction. Besides the scaling, a vertical- and a horizontal line indicating HUPD (ΔEHUPD = 0 for 1/2H2 ↔ *H) and formic acid's thermodynamic equilibrium potential have been included in Fig. 3a and b. Here its assumed that ΔE0FAOR ≈ ΔG0FAOR, as thermodynamic corrections and water stabilization are expected to cancel out for the intermediates. The challenge to understand the implications of Fig. 3a is that one needs to compare *H as a reduction from H2O and *COOH as oxidation from HCOOH. This means that *H stabilizes with negative potential, while *COOH stabilizes with positive potential during FAOR. Essentially, from Fig. 3a it can be inferred that materials to the left of approximately ΔEHUPD are limited by disproportionation at low potentials. While materials to the right are limited by weak binding *COOH. Most importantly, the fundamental scaling between *COOH and *H matter as adsorption of *H on the surface leads to the possibility of disproportionation towards CO. In conclusion, the single-atom catalyst scaling crosses the FAOR thermodynamic potential at values significantly above ΔEHUPD, which suggests that single-atom catalyst may work for FAOR near the FAOR equilibrium potential without carrying out the disproportionation reaction.
Fig. 3b displays the DFT calculated binding energies of *OOCH vs. *H. Conversely to Fig. 3a, there is no apparent scaling between formate bidentate and adsorbed hydrogen. However the oxygen bond for *OOCH scales with *OH and (bi)-carbonate (HCO3/CO3), which have surface binding through oxygen. Carbonate species could be formed over time due to the equilibrium with CO2 and hence poisoning the surface, revealing a decaying activity as observed in Fig. 2c for all working FAOR catalysts. Investigating *OOCH as a function of *H is important as *OOCH has been suggested as an important reaction intermediate. Fig. 3b shows that the binding energy of the *OOCH intermediate on Ag is slightly too strong, but very close to the thermodynamic potential and similar to Pt and Pd. Essentially, if *OOCH was the important reaction intermediate for FAOR, then Ag should be working as FAOR catalyst at very low potential, and furthermore Ag does not suffer from disproportionation (as Ag *H binding far exceeds ΔEHUPD). However, Ag is experimentally shown to be inert for the FAOR. The role of formate in the reaction is clearly a puzzle. For FAOR surface-enhanced IR absorption on Pt has experimentally confirmed formate on the surface27 above 0.7 VRHE and further for CO2RR in situ surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy on Ag has experimentally confirmed formate on the surface.48 As Pt converts formic acid to CO2 and Ag converts CO2 to CO, there seems no relation between the experimental observation of formate on the surface as reaction intermediate. We note that *OOCH scales with *OH, the *OOCH binding can be considered a probe of the oxidation affinity of the catalyst, i.e. having a strong *OOCH binding results in a lower oxidation potential.
Fig. 3c shows the *OOCH vs. *COOH binding for the catalyst, with a dashed line indicating the affinity towards carbon or oxygen. Depending on the catalyst we can see whether formate bidentate or carboxyl is favored. The working catalyst is Pt, which is well above the diagonal and Pd which is at the diagonal, while poorly working FAOR catalysts e.g. Ir49 or Au50 are slightly below the diagonal. Catalysts having stronger *OOCH binding vs. *COOH (below the diagonal), are basically oxidized before they can carry out FAOR.
The type of analysis illustrated in Fig. 3 is a powerful tool able to identify which catalyst suffers from disproportionation, poisoning or oxidation. By virtue of the *COOH vs. *H scaling-relations,10 it gives fundamental insights into why literature historically has shown no significant FAOR activity at the thermodynamic potential for a metal catalysts. Implicitly Fig. 3a shows disproportionation occurring at low potential arising from the HUPD and the consequent creation of *CO poisoning species. The creation of *CO leads to hysteresis between the anodic and cathodic sweeps in FAOR CVs. From this insight, one would expect that disproportionation is mitigated in the CVs by simply staying above HUPD potentials.
Fig. 4 shows FAOR CVs of Pt/C, Pt–Hg/C and Pd/C cycled with varying potential limits. The potential ranges from 0.00–1.05 VRHE reveals that Pt/C and Pt–Hg/C are poisoned in anodic sweeps. While, changing to potentials, ranging from 0.40–1.05 VRHE for the Pt/C and 0.35–1.05 VRHE for the Pt–Hg/C, significantly increases the anodic activity. Hence, this allows us to indicate that HUPD mediated disproportionation account for poisoning through CO on Pt catalysts. For Pd/C in Fig. 5c, decreasing the lower potential limit has no influence on the almost non-existing FAOR hysteresis. In this context, it is important to note that Pd is well-known to form Pd-hydride phases51 below 0.2 VRHE, which then competes with *H adsorbed, i.e. at potentials relevant for both FAOR and CO2RR. In relation to CO2RR, we also note that Pd-hydride, leads to a high faradaic efficiency towards formate,52 whereas at higher overpotentials CO and H2 will dominate.11
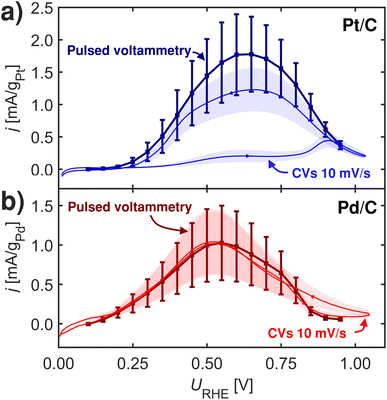 | ||
| Fig. 5 2 s pulsed voltammetry and CVs at 10 mV s−1 at room-temperature at 1600 rpm in Ar-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 with 0.1 M HCOOH. (a) Pt/C. (b) Pd/C. Measurements repeated three times. | ||
Concerning Fig. 4, one could erroneously assume that lowering the upper potential limit would not affect the CVs, while staying above the CO oxidation potential. This is however not the case, cycling 50 times from 0.35–1.00 VRHE reveals some form of deactivation of both Pt/C, Pt–Hg/C and Pd/C. We do not know what the origin of this deactivation is. Various studies reported in the literature suggests different reasons including deactivation to irreversible metal oxidation53,54 due to insufficient surface reduction or accumulation of either *OOCH,55 *COH,38 *OCOH56 or *CO species. Interesting is that in situ Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) work57,58 has shown that Pt, contrary to Pd, continuously form CO above HUPD potential during FAOR.
Finding that *H limits FAOR activity at low potential via disproportionation, allows one to hypothesize about the Pt–Bi and Pt–Hg systems, which perform better than Pt on two different perspectives. Pt–Bi shows no hysteresis and is active at higher overpotential as compared to Pt. The absence of a hysteresis in the CV indicates that Pt–Bi somehow circumvent the disproportionation reaction, potentially by blocking the surface for *H at low potential as onset for Pt–Bi is higher than on Pt. Pt–Hg on the other hand is more active in the negative sweep, particular at lower potential, but does show clear hysteresis. Further we hypothesize that the Pt single-sites in Pt–Hg destabilizes *H shifting the onset to lower potentials and increasing the activity at low potential, simply due to a limited disproportionation reaction.
To gauge how the FAOR is affected in the potentials regions above HUPD we conducted pulsed voltammetry inspired by Clavilier et al.59 In this type of pulsed voltammetry experiments, each potential investigated is separated by a surface re-initialization (at 1.05 VRHE) cleaning the surface for all poisons through surface oxidation. The impact from dissolution at this oxidizing potential should be minimal.60,61
Fig. 5 shows pulsed voltammograms and corresponding CVs for Pt/C and Pd/C samples. Interestingly Pt/C becomes more active when pulsing, which is in contrast to Pd/C that does not show any changes from the pulsing. This experiment challenges *OOCH species as site-blocking species. Since Pd has stronger relative *OOCH to *COOH binding than Pt, and it should hence be on Pd where activity was affected by blocking of *OOCH species. One view for this observation could be given in the recent work by Koper and coworkers,8 who noted that formate adsorption is important for formic acid oxidation, not as an active intermediate, but more as a self-protector against CO poisoning.
Beyond Pd and Pt catalyst, in Fig. 6, we tested Cu, Ni and Ag wires as FAOR catalyst. The experiments revealed that Ni indeed seems very active to oxidize either HCOOH or Ni. However, going to potentials above 0.2 VRHE tended to bring out a yellowish tinge in the electrolyte, and by looking into Ni's Pourbaix diagrams62 it appears to readily dissolve as Ni2+ at 0.15 VRHE at pH 1, consequently making it a poor FAOR catalyst (unless there is some very narrow window that Ni is stable enough to oxidize HCOOH without dissolving). Similarly, Cu shows no FAOR activity only the well-known Cu oxidation current at potentials larger than 0.2 VRHE is observable. Ag is perhaps active towards FAOR but again this occur close to Ag dissolution potentials suggesting it to be a rather poor FAOR catalyst.
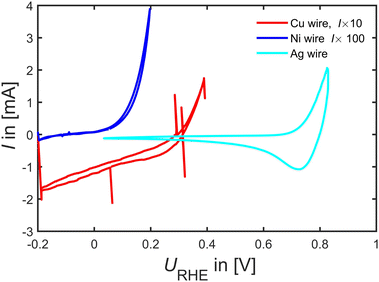 | ||
| Fig. 6 FAOR data on a Cu, Ni and Ag wire at 50 mV s−1 at room-temperature Ar-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 with 0.1 M HCOOH taken at 50 mV s−1. | ||
Most interesting when combining the observation of similar intermediate binding energetics in Fig. 3, we identified that Ag has similar binding energetics of formate as Pd and Pt, whereas Cu and Ni do not follow the energetic of Pd and Pt. Hence Cu and Ni can be used as test catalysts far from known working catalysts. However, as tested here in Fig. 6 there appears no significant FAOR on Ag, Cu and Ni.
Conclusion
In conclusion we have correlated the FAOR activity with simulated DFT binding energies of *COOH, *OOCH and *H across multiple metal catalysts. We have observed that for an ideal catalyst, the FAOR equilibrium potential should be above its corresponding HUPD potential in order to avoid the disproportionation. We found that *COOH and *H binding scale on both metal and single-site catalysts. This creates the fundamental limiting potential due to HUPD mediated disproportionation on the surface. The carbon–hydrogen scaling is indeed a fundamental limitation, analog to the *OH and *OOH scaling for oxygen evolution and reduction. Experimentally, we show that a good performing FAOR catalyst should have the attributes of: (i) an onset close to the fundamental derived onset, (ii) no hysteresis between anodic- and cathodic CV scans and (iii) high and stable FAOR CA currents above the derived onsets fundamental limits. Interestingly, this works concludes on the direct relation between FAOR and CO2RR; *H in combination with *COOH forming CO in both FAOR and CO2RR.Abbreviations
| CA | Chronoamperometry |
| CV | Cyclic voltammogram/voltammetry |
| CO2RR | CO2 reduction reaction |
| DFAFC | Direct formic acid fuel cell |
| DMFC | Direct methanol fuel cell |
| DFT | Density functional theory |
| fcc | Face centered cubic |
| FAOR | Formic acid oxidation reaction |
| FC | Fuel cell |
| HER | Hydrogen evolution reaction |
| HUPD | Hydrogen underpotential deposition |
| MNC | Metal–nitrogen–carbon |
| OER | Oxygen evolution reaction |
| ORR | Oxygen reduction reaction |
| RHE | Reversible hydrogen electrode |
| ESI | Electronic supporting information |
Data availability
Data is available here: https://nano.ku.dk/english/research/theoretical-electrocatalysis/katladb/formic_acid_oxidation_reaction/.Author contributions
The manuscript was written through the contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Center for High Entropy Alloy Catalysis (CHEAC) funded by the Danish National Research Foundation (DNRF 149) and the Villum Foundation through the Villum Center for the Science of Sustainable Fuels and Chemicals (#9455) for funding this work. M. E.-E. and K. D. J. would like to thank the Independent Research Fund Denmark for the award of a DFF-Research Project 1 grant (9041-00224B). M. E.-E. acknowledges the Villum Foundation for financial support through a Villum Young Investigator Grant (project number: 19142). J. D. D. Z. would like to thank the funding from the China Scholarship Council (CSC). A. B would like to thank the Carlsberg foundation (CF21-0144).References
- Z. W. Seh, J. Kibsgaard, C. F. Dickens, I. Chorkendorff, J. K. Nørskov and T. F. Jaramillo, Combining Theory and Experiment in Electrocatalysis: Insights into Materials Design, Science, 2017, 355(6321), eaad4998, DOI:10.1126/science.aad4998.
- S. C. Peter, Reduction of CO2 to Chemicals and Fuels: A Solution to Global Warming and Energy Crisis, ACS Energy Lett., 2018, 3(7), 1557–1561, DOI:10.1021/acsenergylett.8b00878.
- S. Cherevko, A. R. Zeradjanin, A. A. Topalov, N. Kulyk, I. Katsounaros and K. J. J. Mayrhofer, Dissolution of Noble Metals during Oxygen Evolution in Acidic Media, ChemCatChem, 2014, 6(8), 2219–2223, DOI:10.1002/cctc.201402194.
- B. C. Ong, S. K. Kamarudin and S. Basri, Direct Liquid Fuel Cells: A Review, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(15), 10142–10157, DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.01.117.
- T. Yajima, H. Uchida and M. Watanabe, In-Situ ATR-FTIR Spectroscopic Study of Electro-Oxidation of Methanol and Adsorbed CO at Pt-Ru Alloy, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108(8), 2654–2659, DOI:10.1021/jp037215q.
- D. S. Mekazni, R. M. Arán-Ais, A. Ferre-Vilaplana and E. Herrero, Why Methanol Electro-Oxidation on Platinum in Water Takes Place Only in the Presence of Adsorbed OH, ACS Catal., 2022, 1965–1970, DOI:10.1021/acscatal.1c05122.
- S. Nitopi, E. Bertheussen, S. B. Scott, X. Liu, A. K. Engstfeld, S. Horch, B. Seger, I. E. L. Stephens, K. Chan, C. Hahn, J. K. Nørskov, T. F. Jaramillo and I. Chorkendorff, Progress and Perspectives of Electrochemical CO2 Reduction on Copper in Aqueous Electrolyte, Chem. Rev., 2019, 119(12), 7610–7672, DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00705.
- X. Chen, L. P. Granda-Marulanda, I. T. McCrum and M. T. M. Koper, How Palladium Inhibits CO Poisoning during Electrocatalytic Formic Acid Oxidation and Carbon Dioxide Reduction, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13(1), 1–11, DOI:10.1038/s41467-021-27793-5.
- Y. Hori, I. Takahashi, O. Koga and N. Hoshi, Selective Formation of C2 Compounds from Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 at a Series of Copper Single Crystal Electrodes, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2002, 106(1), 15–17, DOI:10.1021/jp013478d.
- A. Bagger, W. Ju, A. S. Varela, P. Strasser and J. Rossmeisl, Electrochemical CO2 Reduction: Classifying Cu Facets, ACS Catal., 2019, 9(9), 7894–7899, DOI:10.1021/acscatal.9b01899.
- Y. Hori, H. Wakebe, T. Tsukamoto and O. Koga, Electrocatalytic Process of CO Selectivity in Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 at Metal Electrodes in Aqueous Media, Electrochim. Acta, 1994, 39(11–12), 1833–1839, DOI:10.1016/0013-4686(94)85172-7.
- P. Sebastián-Pascual, S. Mezzavilla, I. E. L. Stephens and M. Escudero-Escribano, Structure-Sensitivity and Electrolyte Effects in CO2 Electroreduction: From Model Studies to Applications, ChemCatChem, 2019, 11(16), 3626–3645, DOI:10.1002/cctc.201900552.
- T. Zheng, C. Liu, C. Guo, M. Zhang, X. Li, Q. Jiang, W. Xue, H. Li, A. Li, C.-W. Pao, J. Xiao, C. Xia and J. Zeng, Copper-Catalysed Exclusive CO2 to Pure Formic Acid Conversion via Single-Atom Alloying, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2021, 16(12), 1386–1393, DOI:10.1038/s41565-021-00974-5.
- M. Baldauf and D. M. Kolb, Formic Acid Oxidation on Ultrathin Pd Films on Au(Hkl) and Pt(Hkl) Electrodes, J. Phys. Chem., 1996, 100(27), 11375–11381, DOI:10.1021/jp952859m.
- L. A. Kibler, A. M. El-Aziz, R. Hoyer and D. M. Kolb, Tuning Reaction Rates by Lateral Strain in a Palladium Monolayer, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2005, 44(14), 2080–2084, DOI:10.1002/anie.200462127.
- A. Ferre-Vilaplana, J. V. Perales-Rondón, C. Buso-Rogero, J. M. Feliu and E. Herrero, Formic Acid Oxidation on Platinum Electrodes: A Detailed Mechanism Supported by Experiments and Calculations on Well-Defined Surfaces, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(41), 21773–21784, 10.1039/c7ta07116g.
- T. Shen, S. Chen, R. Zeng, M. Gong, T. Zhao, Y. Lu, X. Liu, D. Xiao, Y. Yang, J. Hu, D. Wang, H. L. Xin and H. D. Abrunã, Tailoring the Antipoisoning Performance of Pd for Formic Acid Electrooxidation via an Ordered PdBi Intermetallic, ACS Catal., 2020, 10(17), 9977–9985, DOI:10.1021/acscatal.0c01537.
- R. Rizo and B. Roldan Cuenya, Shape-Controlled Nanoparticles as Anodic Catalysts in Low-Temperature Fuel Cells, ACS Energy Lett., 2019, 4(6), 1484–1495, DOI:10.1021/acsenergylett.9b00565.
- E. Plaza-Mayoral, I. J. Pereira, K. Nicole Dalby, K. D. Jensen, I. Chorkendorff, H. Falsig, P. Sebastián-Pascual and M. Escudero-Escribano, Pd–Au Nanostructured Electrocatalysts with Tunable Compositions for Formic Acid Oxidation, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2022, 5(9), 10632–10644, DOI:10.1021/acsaem.2c01361.
- A. Capon and R. Parsons, The Oxidation of Formic Acid at Noble Metal Electrodes Part 4. Platinum + Palladium Alloys, J. Electroanal. Chem., 1975, 65(1), 285–305, DOI:10.1016/0368-1874(75)85124-0.
- P. N. Duchesne, Z. Y. Li, C. P. Deming, V. Fung, X. Zhao, J. Yuan, T. Regier, A. Aldalbahi, Z. Almarhoon, S. Chen, D. Jiang, N. Zheng and P. Zhang, Golden Single-Atomic-Site Platinum Electrocatalysts, Nat. Mater., 2018, 17(11), 1033–1039, DOI:10.1038/s41563-018-0167-5.
- J. M. Feliu and E. Herrero, Formic Acid Oxidation, Handb. Fuel Cells, 2010 DOI:10.1002/9780470974001.f206048.
- J. Joo, T. Uchida, A. Cuesta, M. T. M. M. Koper and M. Osawa, Importance of Acid-Base Equilibrium in Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Formic Acid on Platinum, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(27), 9991–9994, DOI:10.1021/ja403578s.
- N. M. Marković, H. A. Gasteiger, P. N. Ross, X. Jiang, I. Villegas and M. J. Weaver, Electro-Oxidation Mechanisms of Methanol and Formic Acid on Pt-Ru Alloy Surfaces, Electrochim. Acta, 1995, 40(1), 91–98, DOI:10.1016/0013-4686(94)00241-R.
- A. Capon and R. Parsons, The Oxidation of Formic Acid at Noble Metal Electrodes Part III. Intermediates and Mechanism on Platinum Electrodes, J. Electroanal. Chem., 1973, 45(2), 205–231, DOI:10.1016/S0022-0728(73)80158-5.
- A. Betts, V. Briega-Martos, A. Cuesta and E. Herrero, Adsorbed Formate Is the Last Common Intermediate in the Dual-Path Mechanism of the Electrooxidation of Formic Acid, ACS Catal., 2020, 10(15), 8120–8130, DOI:10.1021/acscatal.0c00791.
- A. Miki, S. Ye and M. Osawa, Surface-Enhanced IR Absorption on Platinum Nanoparticles: An Application to Real-Time Monitoring of Electrocatalytic Reactions, Chem. Commun., 2002, 2(14), 1500–1501, 10.1039/b203392e.
- A. Ferre-Vilaplana, J. V. Perales-Rondón, J. M. Feliu and E. Herrero, Understanding the Effect of the Adatoms in the Formic Acid Oxidation Mechanism on Pt(111) Electrodes, ACS Catal., 2015, 5(2), 645–654, DOI:10.1021/cs501729j.
- J. V. Perales-Rondón, A. Ferre-Vilaplana, J. M. Feliu and E. Herrero, Oxidation Mechanism of Formic Acid on the Bismuth Adatom-Modified Pt(111) Surface, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(38), 13110–13113, DOI:10.1021/ja505943h.
- N. M. Marković and P. N. Ross Jr, Surface Science Studies of Model Fuel Cell Electrocatalysts, Surf. Sci. Rep., 2002, 45(4), 117–229, DOI:10.1016/S0167-5729(01)00022-X.
- Á. Cuesta, M. Escudero-Escribano, B. Lanova and H. Baltruschat, Cyclic Voltammetry, FTIRS, and DEMS Study of the Electrooxidation of Carbon Monoxide, Formic Acid, and Methanol on Cyanide-Modified Pt(111) Electrodes, Langmuir, 2009, 25(11), 6500–6507, DOI:10.1021/la8041154.
- K. Jiang, H. X. Zhang, S. Zou and W. B. Cai, Electrocatalysis of Formic Acid on Palladium and Platinum Surfaces: From Fundamental Mechanisms to Fuel Cell Applications, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014, 16(38), 20360–20376, 10.1039/c4cp03151b.
- A. Cuesta, At Least Three Contiguous Atoms Are Necessary for CO Formation during Methanol Electrooxidation on Platinum, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128(41), 13332–13333, DOI:10.1021/ja0644172.
- W. Zhong, Y. Qi and M. Deng, The Ensemble Effect of Formic Acid Oxidation on Platinum-Gold Electrode Studied by First-Principles Calculations, J. Power Sources, 2015, 278, 203–212, DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.12.071.
- S. Siahrostami, A. Verdaguer-Casadevall, M. Karamad, D. Deiana, P. Malacrida, B. Wickman, M. Escudero-Escribano, E. Paoli, R. Frydendal, T. W. Hansen, I. Chorkendorff, I. E. L. Stephens and J. Rossmeisl, Enabling Direct H2O2 Production through Rational Electrocatalyst Design, Nat. Mater., 2013, 12(12), 1137–1143, DOI:10.1038/nmat3795.
- A. Verdaguer-Casadevall, D. Deiana, M. Karamad, S. Siahrostami, P. Malacrida, T. W. Hansen, J. Rossmeisl, I. Chorkendorff and I. E. L. Stephens, Trends in the Electrochemical Synthesis of H2O2: Enhancing Activity and Selectivity by Electrocatalytic Site Engineering, Nano Lett., 2014, 14(3), 1603–1608, DOI:10.1021/nl500037x.
- A. Sáez, E. Expósito, J. Solla-Gullón, V. Montiel and A. Aldaz, Bismuth-Modified Carbon Supported Pt Nanoparticles as Electrocatalysts for Direct Formic Acid Fuel Cells, Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 63, 105–111, DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2011.12.076.
- S. G. Sun, J. Clavilier and A. Bewick, The Mechanism of Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Formic Acid on Pt (100) and Pt (111) in Sulphuric Acid Solution: An Emirs Study, J. Electroanal. Chem., 1988, 240(1–2), 147–159, DOI:10.1016/0022-0728(88)80319-X.
- W. Gao, J. A. Keith, J. Anton and T. Jacob, Theoretical Elucidation of the Competitive Electro-Oxidation Mechanisms of Formic Acid on Pt(111), J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(51), 18377–18385, DOI:10.1021/ja1083317.
- C. Rice, S. Ha, R. I. Masel and A. Wieckowski, Catalysts for Direct Formic Acid Fuel Cells, J. Power Sources, 2003, 115(2), 229–235, DOI:10.1016/S0378-7753(03)00026-0.
- N. V. Rees and R. G. Compton, Sustainable Energy: A Review of Formic Acid Electrochemical Fuel Cells, J. Solid State Electrochem., 2011, 15(10), 2095–2100, DOI:10.1007/s10008-011-1398-4.
- M. Neurock, M. Janik and A. Wieckowski, A First Principles Comparison of the Mechanism and Site Requirements for the Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Methanol and Formic Acid over Pt, Faraday Discuss., 2009, 140, 363–378, 10.1039/b804591g.
- X. H. Xia and T. Iwasita, Influence of Underpotential Deposited Lead upon the Oxidation of HCOOH in HClO4 at Platinum Electrodes, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1993, 140(9), 2559–2565, DOI:10.1149/1.2220862.
- A. Tripković, K. Popović and R. Adžić, Structural Effects in Electrocatalysis: Oxidation of Formic Acid on Single Crystal Platinum Electrodes and Evidence for Oscillatory Behaviour, J. Chim. Phys., 1991, 88, 1635–1647, DOI:10.1051/jcp/1991881635.
- J. Joo, T. Uchida, A. Cuesta, M. T. M. Koper and M. Osawa, The Effect of PH on the Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Formic Acid/Formate on Platinum: A Mechanistic Study by Surface-Enhanced Infrared Spectroscopy Coupled with Cyclic Voltammetry, Electrochim. Acta, 2014, 129, 127–136, DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2014.02.040.
- M. R. Gennero de Chialvo, G. C. Luque and A. C. Chialvo, Formic Acid Electrooxidation on Platinum, Resolution of the Kinetic Mechanism in Steady State and Evaluation of the Kinetic Constants, ChemistrySelect, 2018, 3(34), 9768–9772, DOI:10.1002/slct.201801725.
- A. Bagger, W. Ju, A. S. Varela, P. Strasser and J. Rossmeisl, Single Site Porphyrin-like Structures Advantages over Metals for Selective Electrochemical CO2 Reduction, Catal. Today, 2017, 288, 74–78, DOI:10.1016/j.cattod.2017.02.028.
- D. Bohra, I. Ledezma-Yanez, G. Li, W. de Jong, E. A. Pidko and W. A. Smith, Lateral Adsorbate Interactions Inhibit HCOO − While Promoting CO Selectivity for CO2 Electrocatalysis on Silver, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58(5), 1345–1349, DOI:10.1002/anie.201811667.
- R. Gómez and M. J. Weaver, Electrochemical Infrared Studies of Monocrystalline Iridium Surfaces. 3. Adsorbed Nitric Oxide and Carbon Monoxide as Probes of Ir(100) Interfacial Structure, J. Phys. Chem. B, 1998, 102(19), 3754–3764, DOI:10.1021/jp980098s.
- A. Cuesta, G. Cabello, F. W. Hartl, M. Escudero-Escribano, C. Vaz-Domínguez, L. A. Kibler, M. Osawa and C. Gutiérrez, Electrooxidation of Formic Acid on Gold: An ATR-SEIRAS Study of the Role of Adsorbed Formate, Catal. Today, 2013, 202(1), 79–86, DOI:10.1016/j.cattod.2012.04.022.
- A. Rose, S. Maniguet, R. J. Mathew, C. Slater, J. Yao and A. E. Russell, Hydride Phase Formation in Carbon Supported Palladium Nanoparticle Electrodes Investigated Using in Situ EXAFS and XRD, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2003, 5(15), 3220–3225, 10.1039/b302956e.
- D. Gao, H. Zhou, F. Cai, D. Wang, Y. Hu, B. Jiang, W. B. Cai, X. Chen, R. Si, F. Yang, S. Miao, J. Wang, G. Wang and X. Bao, Switchable CO2 Electroreduction via Engineering Active Phases of Pd Nanoparticles, Nano Res., 2017, 10(6), 2181–2191, DOI:10.1007/s12274-017-1514-6.
- J. M. Tura, P. Regull, L. Victori and M. D. de Castellar, XPS and IR (ATR) Analysis of Pd Oxide Films Obtained by Electrochemical Methods, Surf. Interface Anal., 1988, 11(8), 447–449, DOI:10.1002/sia.740110807.
- V. A. Saveleva, V. Papaefthimiou, M. K. Daletou, W. H. Doh, C. Ulhaq-Bouillet, M. Diebold, S. Zafeiratos and E. R. Savinova, Operando Near Ambient Pressure XPS (NAP-XPS) Study of the Pt Electrochemical Oxidation in H2O and H2O/O2 Ambients, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016, 120(29), 15930–15940, DOI:10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b12410.
- E. Herrero and J. M. Feliu, Understanding Formic Acid Oxidation Mechanism on Platinum Single Crystal Electrodes, Curr. Opin. Electrochem., 2018, 9, 145–150, DOI:10.1016/j.coelec.2018.03.010.
- T. Al Najjar, N. Ahmed and E. N. El Sawy, Mechanistic Effects of Blending Formic Acid with Ethanol on Pd Activity towards Formic Acid Oxidation in Acidic Media, RSC Adv., 2021, 11(37), 22842–22848, 10.1039/d1ra01209f.
- H. Miyake, T. Okada, G. Samjeské and M. Osawa, Formic Acid Electrooxidation on Pd in Acidic Solutions Studied by Surface-Enhanced Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2008, 10(25), 3662, 10.1039/b805955a.
- G. Samjeské and M. Osawa, Current Oscillations during Formic Acid Oxidation on a Pt Electrode: Insight into the Mechanism by Time-Resolved IR Spectroscopy, Angew. Chem., 2005, 117(35), 5840–5844, DOI:10.1002/ange.200501009.
- J. Clavilier, Pulsed Linear Sweep Voltammetry with Pulses of Constant Level in a Potential Scale, a Polarization Demanding Condition in the Study of Platinum Single Crystal Electrodes, J. Electroanal. Chem., 1987, 236(1–2), 87–94, DOI:10.1016/0022-0728(87)88020-8.
- E. Pizzutilo, S. Geiger, S. J. Freakley, A. Mingers, S. Cherevko, G. J. Hutchings and K. J. J. Mayrhofer, Palladium Electrodissolution from Model Surfaces and Nanoparticles, Electrochim. Acta, 2017, 229, 467–477, DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2017.01.127.
- S. Cherevko, N. Kulyk and K. J. J. Mayrhofer, Durability of Platinum-Based Fuel Cell Electrocatalysts: Dissolution of Bulk and Nanoscale Platinum, Nano Energy, 2016, 29, 275–298, DOI:10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.03.005.
- A. Jain, S. P. Ong, G. Hautier, W. Chen, W. D. Richards, S. Dacek, S. Cholia, D. Gunter, D. Skinner, G. Ceder and K. A. Persson, Commentary: The Materials Project: A Materials Genome Approach to Accelerating Materials Innovation, APL Mater., 2013, 1(1), 011002, DOI:10.1063/1.4812323.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Relevant aspects of the computational model and methods and the experimental methodology are included herein. (PDF). Additionally, atomicstructures and analysis scripts are available on the webpage: https://chem.ku.dk/research_sections/nanochem/theoretical-electrocatalysis/. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d2sc05160e |
| ‡ These authors contributed equally. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2022 |