Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Correction: Malachite green: a long-buried water-soluble AIEgen with near-infrared fluorescence for living cell nucleus staining
Yuan
Luo†
a,
Lihua
Zhou†
b,
Lili
Du†
c,
Yangzi
Xie
a,
Xiang-Yang
Lou
d,
Lintao
Cai
a,
Ben Zhong
Tang
e,
Ping
Gong
*a and
Pengfei
Zhang
*a
aGuangdong Key Laboratory of Nanomedicine, CAS-HK Joint Lab of Biomaterials, CAS Key Laboratory of Biomedical Imaging Science and System, Shenzhen Engineering Laboratory of Nanomedicine and Nanoformulations, CAS Key Lab for Health Informatics, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen 518055, P. R. China. E-mail: ping.gong@siat.ac.cn; pf.zhang@siat.ac.cn
bSchool of Applied Biology, Shenzhen Institute of Technology, No. 1 Jiangjunmao, Shenzhen, P. R. China
cSchool of Life Sciences, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, 212013, P. R. China
dGTS-UAB Research Group, Department of Chemistry, Facultat de Ciències, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, 08193 Bellaterra, Spain
eSchool of Science and Engineering, Shenzhen Institute of Aggregate Science and Technology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen (CUHK-Shenzhen), Guangdong 518172, China
First published on 10th October 2024
Abstract
Correction for ‘Malachite green: a long-buried water-soluble AIEgen with near-infrared fluorescence for living cell nucleus staining’ by Yuan Luo et al., Chem. Commun., 2024, 60, 1452–1455, https://doi.org/10.1039/D3CC05535C.
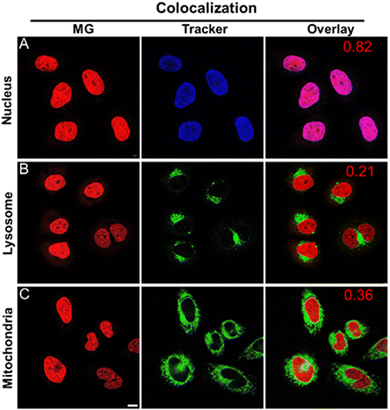
The authors regret that Fig. 3 was incorrect in the original article. The MG images in row A (nucleus) and row C (mitochondria) in this figure were swapped in error. The correct Fig. 3 is as shown below. This does not affect the conclusions of the article.
The Royal Society of Chemistry apologises for these errors and any consequent inconvenience to authors and readers.
Footnote |
| † These authors contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |