Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleHarnessing exosomes for advanced osteoarthritis therapy
Andrew
Selvadoss
 a,
Helna M.
Baby
b,
Hengli
Zhang
b and
Ambika G.
Bajpayee
a,
Helna M.
Baby
b,
Hengli
Zhang
b and
Ambika G.
Bajpayee
 *ab
*ab
aDepartment of Chemical Engineering, Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115, USA. E-mail: a.bajpayee@northeastern.edu
bDepartment of Bioengineering, Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115, USA
First published on 18th September 2024
Abstract
Exosomes are nanosized, lipid membrane vesicles secreted by cells, facilitating intercellular communication by transferring cargo from parent to recipient cells. This capability enables biological crosstalk across multiple tissues and cells. Extensive research has been conducted on their role in the pathogenesis of degenerative musculoskeletal diseases such as osteoarthritis (OA), a chronic and painful joint disease that particularly affects cartilage. Currently, no effective treatment exists for OA. Given that exosomes naturally modulate synovial joint inflammation and facilitate cartilage matrix synthesis, they are promising candidates as next generation nanocarriers for OA therapy. Recent advancements have focused on engineering exosomes through endogenous and exogenous approaches to enhance their joint retention, cartilage and chondrocyte targeting properties, and therapeutic content enrichment, further increasing their potential for OA drug delivery. Notably, charge-reversed exosomes that utilize electrostatic binding interactions with cartilage anionic aggrecan glycosaminoglycans have demonstrated the ability to penetrate the full thickness of early-stage arthritic cartilage tissue following intra-articular administration, maximizing their therapeutic potential. These exosomes offer a non-viral, naturally derived, cell-free carrier for OA drug and gene delivery applications. Efforts to standardize exosome harvest, engineering, and property characterization methods, along with scaling up production, will facilitate more efficient and rapid clinical translation. This article reviews the current state-of-the-art, explores opportunities for exosomes as OA therapeutics, and identifies potential challenges in their clinical translation.
Introduction
Extracellular vesicles are lipid membrane vesicles released by cells into the extracellular space. They are categorized based on their size, secretion pathway, content, membrane markers, and function. Exosomes represent a specific class of these vesicles, typically ranging from 30–200 nm in diameter, and play diverse roles such as facilitating cell-to-cell communication, immune response, infection, and maintenance of cellular homeostasis.1–4 Due to their natural origin, exosomes exhibit high biocompatibility and low immunogenicity, often possessing intrinsic function reflective of their cell of origin.4,5 As such, recent studies have highlighted exosomes as promising naturally derived nanocarriers for therapeutic delivery and as diagnostic markers.2,6,7Exosome biogenesis
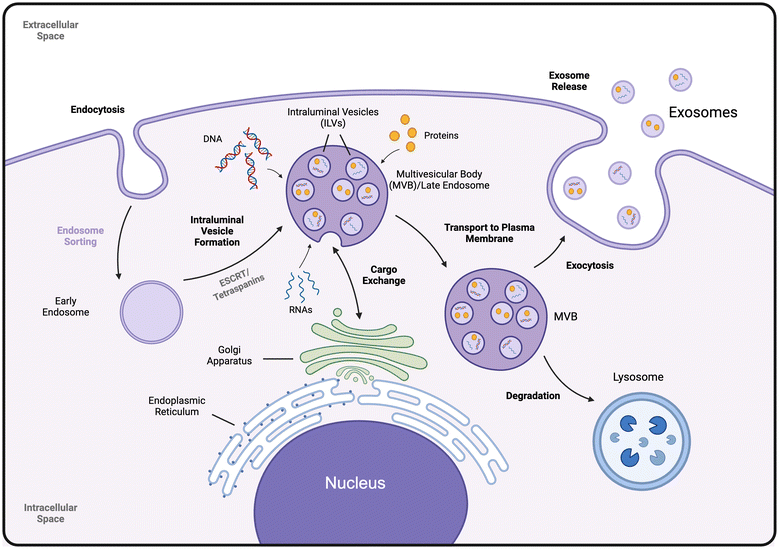
Exosomes originate from endosomal sorting within cells. Endocytosis and inward budding of the cellular membrane create endosomes, which develop into late endosomes that can undergo their own inward budding (Fig. 1). These late endosomes transform into multivesicular bodies (MVBs) containing intraluminal vesicles (ILVs). MVBs play a crucial role in the sorting, cycling, release, and storage of cell contents.2,8 During the formation of ILVs, cargo exchange occurs between the MVB and the cytoplasm, Golgi bodies, and endoplasmic reticulum, allowing the regulation of cellular contents such as proteins and nucleic acids. MVBs have two potential fates: they can either fuse with the plasma cell membrane to release their ILVs as exosomes or be directed to the lysosome for degradation. The exact mechanisms determining which path an MVB will take remain largely unknown, although proteins on the MVB membrane and the content of ILVs have been proposed as influencing factors.9 When fusing with the plasma cell membrane, the ILVs are released into the extracellular space as exosomes (Fig. 1). The formation of MVBs, ILVs, and exosome release is regulated through the endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRT) pathway.1–3,5,10Exosome content
Exosomes derive their content through both the plasma membrane and ILV formation due to their endocytic origin. Because of the ESCRT regulation of MVBs, ILVs and exosomes, ESCRT-associated proteins are ubiquitous in exosomes, regardless of their cell source. These include ESCRT complexes I–III, ALIX, TSG101, HSP70, and HSP90.2–5,8,10 The cell-derived lipid membrane of exosomes also results in the enrichment of plasma membrane proteins in exosomes, including tetraspanins such as CD9, CD63, and CD81, as well as scaffolding proteins and adhesion molecules such as Flotillin-1 and EpCAM.2,5,9,10 Beyond protein content, exosomes have a diverse array of content derived from cargo exchange occurring during ILV formation. They commonly contain functional microRNA (miRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA).11 Other RNA species found in exosomes include mostly non-coding fragments such as pre-miRNA, Y-RNA, circular RNA (circRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and small-interfering RNA (siRNA).2,12,13 Specific RNA enrichment in exosomes is dependent on the cell source.1 Single-stranded DNAs, genomic DNA, and mitochondrial DNA have also been reported in exosomes.12 Additionally, various cytosolic proteins and small molecules such as enzymes, signal transducers, cytokines, amino acids, and metabolites are encapsulated during ILV formation.2,4,5,14 While exosomes have certain ubiquitous content, they exhibit a high heterogeneity based on cell source, harvest method and various other factors.3 More work is needed to standardize the classification and characterization of exosomes.Biological role of exosomes
While exosomes were originally thought to be solely involved in cellular cargo dumping functions, it has been shown that exosome's native functions are more intricate and highly dependent on the cell source. Exosomes are readily internalized by cells either through endocytosis or membrane fusion, facilitating the transfer of contents between cells, which results in exosome-mediated cell-to-cell communication and signaling.1,2 Consequently, the source of exosome and their content define their diverse functions, which include the regulation of immune responses, antigen presentation, programmed cell death, angiogenesis, inflammation, coagulation, morphogen presentation, extracellular matrix regulation, metabolite transfer, and cell homeostasis.2,5,6 In cancer cells, exosomes have been shown to enhance tumor progression and promote tumor cell migration in metastases through the promotion of angiogenesis.15,16 They also play significant roles in the nervous system, such as regulating neurite growth and myelin sheath formation. Exosomes can have immunomodulatory influence, providing both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory effects in various diseases.17,18 For example, mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes have been shown to promote wound-healing and tissue regeneration processes by reducing inflammation through cytokine regulation. These immunomodulatory abilities of exosomes have attracted extensive research on their role in the immunopathogenesis of degenerative musculoskeletal diseases such as osteoarthritis (OA).19–21 This review will discuss the role of exosomes in OA pathogenesis and the various ways they are being engineered as a next generation nanocarrier for OA therapy.Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a debilitating disease that involves the degradation of musculoskeletal joint tissues, particularly cartilage, resulting in decreased mobility and quality of life. Over 500 million people are affected worldwide, with an estimated $80 billion economic burden in the United States alone.22,23 Despite the prevalence of OA, there are no available disease-modifying osteoarthritis drugs (DMOADs). Current treatments focus solely on pain management, providing only short-term relief without altering disease progression, ultimately necessitating surgical intervention.24 The clinical use of DMOADs is limited by a lack of safe and effective drug delivery systems that can specifically target cartilage tissue and deliver sustained doses of DMOADs to chondrocytes residing within the deep cartilage layers.25 While direct administration through intra-articular (IA) injection can increase local drug concentrations, rapid clearance of drugs occurs through the vasculature and lymphatics in the synovial membrane.26 The joint exists in a state of regulated homeostasis that can be disrupted by various risk factors for OA including aging, traumatic joint injury, obesity, and gender.27 Following local damage onset, patients experience cartilage degradation, synovial inflammation, subchondral bone damage, osteophyte formation, ligament degeneration, and angiogenesis.28 This inflammation leads to the production of pro-inflammatory transcription factors and cytokines by both immune cells and chondrocytes in the joint.29 Cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α are produced, resulting in increased joint cellular production of proteases including ADAMTS5, MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-13 that gradually degrade the cartilage extracellular matrix comprising of collagen type II fibers and negatively charged aggrecan glycosaminoglycans (GAGs).26,29,30 Exosomes play a major role in the transport of pro-inflammatory factors between cells, enabling communication between the immune system and various joint tissues and their cells, thereby promoting disease progression. Understanding the native role of exosomes in OA pathogenesis can facilitate their development and use as a novel nanoscale therapeutic platform.Exosomes in the pathogenesis of OA
Exosomes are known to facilitate intercellular communication by transferring their cargo from the parent to recipient cells, thereby playing a role in biological crosstalk across multiple tissues and their cells in both healthy and arthritic joints.19,31,32 A heterogeneous cell population resides in the joint space, including synoviocytes, chondrocytes, macrophages, and fibroblast-like cells in ligaments and tendons (Fig. 2). During the onset of OA, diseased cells begin to produce inflammatory cytokines and the associated non-coding RNAs that are packed within the exosomes originating from these cells.33–37 Exosomes from diseased cells can act as propagators of inflammatory signaling by enabling M1 macrophage polarization, chondrocyte apoptosis, and cartilage ECM catabolism (Fig. 2). Multiple studies have found that in OA patients, macrophage-derived exosomes can induce an inflammatory response in chondrocytes and synoviocytes by overexpressing pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-8 and IL-6, and the resulting ECM degrading enzymes.38,39 Exosome mediated crosstalk promoting inflammation has been observed between numerous other cells and tissues within the joint space including synovial fluid and macrophages, vascular endothelial cells and osteoblasts, and osteoblasts and chondrocytes.40–42 Additionally, exosomes derived from senescent chondrocytes have shown to transfer senescence to non-senescent healthy chondrocytes.43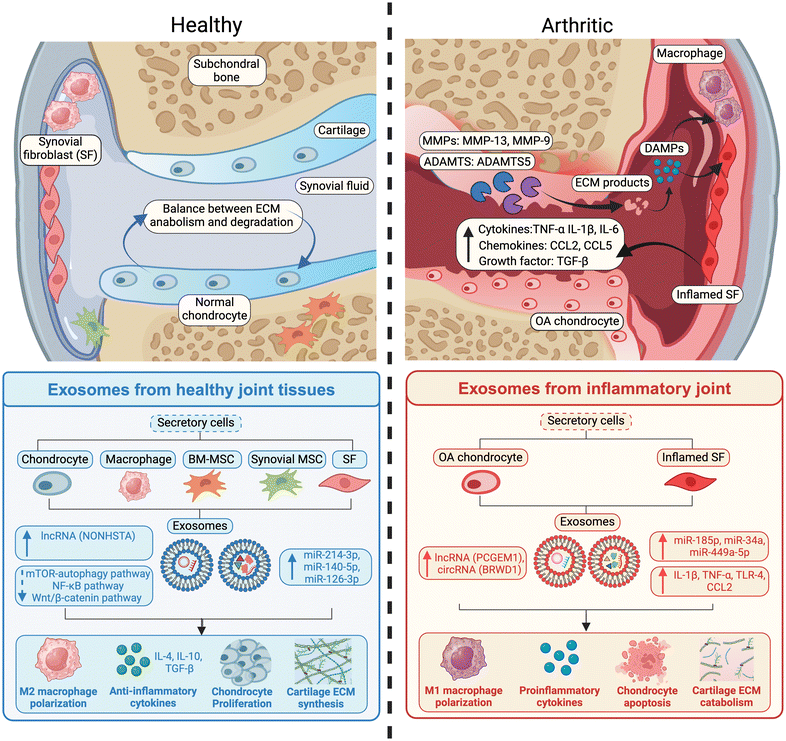 | ||
| Fig. 2 A comparison of the immunomodulatory effects of exosomes derived from various tissues and cells in healthy and osteoarthritic inflamed joint. | ||
Kang and colleagues found that primary chondrocyte derived exosomes had 22 miRNAs upregulated and 29 downregulated in OA patients in comparison to the healthy group.44 A similar observation was found in synovial fluid derived exosomes where miRNA profiling showed that there was a marked difference between OA derived exosomes and normal exosomes.45 Exosomes containing miR-449a-5p from arthritic chondrocytes are known to induce IL-1β production in multiple joint cell types.46 miR-146, miR-26a, miR-34a, and miR-210 have all been shown to be relevant in regulating pro-inflammatory response in the joint through exosomes.43,47 Other non-coding RNAs have also been found to play influential roles in OA pathogenesis through exosomes. For instance, the levels of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) prostate cancer gene expression marker 1 (PCGEM1), which is associated with inhibiting cell apoptosis, were found to increase with OA progression in patients.48 Additionally, circRNA BRWD1, known to promote cell apoptosis, is found at elevated levels in exosomes derived from arthritic chondrocytes, thereby promoting IL-1β production.49 Beyond transcriptomic changes, there are proteomic alterations as well. As an example, exosomes derived from synovial fluid of late-stage OA patients have shown elevated levels of IL-1β, IL-17, IL-10, and IFN-γ.36
Exosomes can also exert beneficial effects in the joint microenvironment. Particularly, macrophages, stem cells, and synovial cells all release exosomes in a healthy environment that facilitate cell proliferation, ECM production, and anti-inflammatory responses. Stem cells contribute positively to the joint by promoting cell proliferation.50–53 Exosomes derived from stem cells contain miR-126 and miR-140, which support tissue regeneration and suppress inflammation in cartilage and chondrocytes.50,51 Similarly, exosomes from synovial fibroblasts exert anti-inflammatory effects through lncRNA NONHSAT, which is involved with cell proliferation, and miR-214, which is involved with cellular apoptosis.54,55 Research has shown that exosomes derived from neutrophils and M2 macrophages can induce tissue regeneration by enhancing the expression of genes like COL2A1 and ACAN, thereby increasing synthesis of type II collagen and GAGs.35,56,57 Given their cellular origin and role in intercellular communication, exosomes play a pivotal role in modulating cell and tissue homeostasis within the joint. They also serve as valuable biomarkers for understanding the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of OA. Understanding the immunomodulatory effects of exosomes presents an opportunity to harness them for therapeutic purposes in OA treatment.
Exosomes as a therapeutic: history and state-of-the-art
Although exosome research and interest have surged in the last two decades, exosomes were first defined in the 1980s (Fig. 3). In 1983, two pivotal studies from the Johnstone and Stahl labs discovered that reticulocytes released endocytosed transferrin receptors via intraluminal vesicles.58,59 These vesicles were named exosomes by Johnstone, Turbide and colleagues in 1987. Between the late 1980s and late 1990s, research elucidated the structure and physical characteristics of exosomes, including their plasma membrane composition, ubiquitous surface proteins, and the lateral diffusion of proteins and lipids on their surfaces.60–62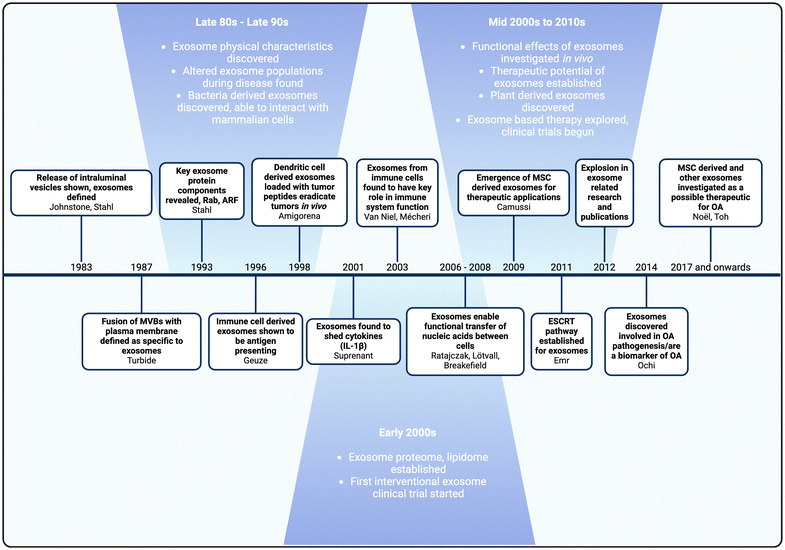 | ||
| Fig. 3 Timeline of exosome research and development. Major milestones in bold, followed by corresponding authors. | ||
Subsequent developments revealed the existence of bacterial-derived exosomes that can interact with mammalian cells, changes in exosome populations during diseased states, and insights into exosome function within the immune system.63–66 Geuze and colleagues discovered that exosomes derived from B lymphocytes contained antigens that elicited antigen-specific responses in T cells.67 This finding inspired Amigorena and colleagues to use dendritic-derived exosomes loaded with tumor peptides to induce an anti-tumoral effect and eradicate tumors in vivo.68 Collectively, these discoveries demonstrated that exosomes could serve as biomarkers of disease, provided significant insights into their native function in immunomodulation, and highlighted their potential as an innovative drug delivery platform.
The role of exosomes in immunomodulation became more evident in the early 2000s, with studies demonstrating that immunoregulatory functions were facilitated through the horizontal transfer of cytokines, proteins and nucleic acids such as mRNAs and non-coding miRNAs.69–73 In addition, the discovery that stem cell derived exosomes exhibited anti-inflammatory effects, promoted cell proliferation, and aided tissue regeneration in vivo promoted the use of exosomes as therapeutics.74 These breakthroughs significantly impacted exosome research, opening new avenues for their application in drug delivery and resulting in an expansion of related studies.
As exosome research grew, so did the understanding of their role and potential in OA. Studies revealed that exosomes facilitate crosstalk between cells and tissues in the joint, establishing them as key mediators in OA pathogenesis.75 The pioneering application of stem cell derived exosomes for OA treatment in in vivo studies marked a significant milestone, leading to various novel applications of exosomes for treatment and drug delivery in OA.76,77 The understanding of exosomes’ native roles in OA and their therapeutic potential has sparked a surge in interest, as evidenced by the increase in published studies from just 16 in 2016 to 162 in 2022.78 This review will examine the potential of exosomes for OA treatment, the current state-of-the-art, and the overall trends in exosome research for OA, both past and future.
Native exosomes for OA treatment
Recent research has shown that native exosomes derived from various cells, such as MSCs, fibroblasts, platelets etc. have the potential to modulate OA through multiple regenerative mechanisms facilitated by their intrinsic genetic material and associated cargos.50,51,79–81 There has been a growing emphasis on using stem cell exosomes for OA treatment due to the tissue-protective and regenerative abilities of stem cells. Stem cell therapy has been studied for regenerative medicine since the 1950s and emerged as a treatment for OA in the 1990s.82,83 The regenerative ability of stem cells is widely attributed to paracrine signaling, with exosomes being key mediators of this process.84 As a result, exosomes have gained attention as a therapeutic option, potentially inducing the same effects as stem cells while avoiding the safety and complexity challenges associated with cell therapy.Numerous studies have examined the effect of intra-articular injection of bone marrow MSC (BMSC) derived exosomes for OA treatment in vivo.77,81,85–90 BMSC-derived exosomes contain a wide array of non-coding nucleic acids such as miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs that can modulate pathways within the joint to induce cell proliferation, inhibition of pro-inflammatory factors and cell apoptosis, and promote ECM synthesis and cartilage regeneration. Cai and colleagues administered BMSC-derived exosomes in a destabilizing medial meniscus (DMM) mouse OA model and found that miR-216a-5p, which modulates the JAK2 cell growth pathway, enabled the exosomes to reduce degeneration and promote cartilage ECM synthesis effectively preventing OA progression.90 Similarly, Xu and colleagues utilized BMSC-derived exosomes in a medial collateral ligament and medial meniscus transection rat OA model and found that the presence of miR-135b regulated cell proliferation and apoptosis to prevent cartilage degradation.91 In addition to BMSC-derived exosomes, studies have also observed similar cell proliferation and tissue regeneration effects from exosomes derived from other stem cells, such as synovial MSCs, amniotic fluid stem cells, adipose tissue derived stem cells, and umbilical cord MSCs.50,92–95 Moreover, emerging evidence suggests that exosomes derived from native joint cells can be analyzed for biomarker differences between OA and healthy conditions to selectively overexpress certain non-coding RNAs for treatment.55 Zhang and colleagues analyzed exosomes from synovial fibroblasts and found miR-214-3p to be under expressed in OA patients. They utilized these exosomes for OA treatment in anterior cruciate ligament transfection and medial meniscectomy mice model, leading to the inhibition of inflammation and cartilage degradation.55
While native exosomes for OA treatment are promising, they have faced numerous challenges in clinical translation. In vivo studies often require high doses to achieve therapeutic efficacy; most studies administer exosomes once a week, and in some cases, even twice a week.88,89,93 This is because exosomes derived from cell sources struggle with low yields during harvest. Additionally, exosomes have low total therapeutic content, and with their relatively larger size and negatively charged lipid bilayer, they suffer from steric and electrostatic hinderances during delivery to cartilage. There have been efforts to increase exosome yield using bioreactors and mechanical stresses, however there is a lack of effective studies analyzing the differences in functionality from these increased yield methods.96 To effectively use exosomes for OA therapy and improve their feasibility as a relevant drug delivery vehicle, methods to engineer exosomes for higher drug loading, increased targeting and retention are needed.
Engineering of exosomes to improve therapeutic potential
Engineering of exosomes falls into two primary approaches, endogenous and exogenous engineering.97–111 Endogenous engineering involves modifying the parent cells from which exosomes are derived. By genetically engineering the parent cells, exosomes produced carry the desired modifications. Examples include overexpressing therapeutic proteins or RNAs in the parent cells, which then become part of the exosomal cargo.97–114 Endogenous engineering is advantageous for scaling up modifications that are difficult to achieve post-isolation. Exogenous engineering involves modifying exosomes directly after they have been isolated from their parent cells.97–114 This approach allows for precise control over the modifications and enables the addition of therapeutic agents that may not be produced endogenously. Techniques for exogenous engineering include surface modification with targeting ligands, loading therapeutic cargo through electroporation, and chemical conjugation.97,104 These methods are versatile and can be applied to pre-isolated exosomes from various sources. Both endogenous and exogenous engineering methods have been applied to OA treatments.31,34,115 A comprehensive understanding of these methods is essential to develop advanced exosomes for future applications in OA and other diseases.Engineered exosomes for OA treatment
Enhancing joint retention
To enhance joint retention for OA therapy, exosomes have been combined with hydrogels and scaffolds. This combination increases the local concentration of exosomes in the joint and prevents clearance through the lymphatic system.116–120 Additionally, embedding exosomes in hydrogels or scaffolds provides benefits such as controlled and sustained release of exosomes, tissue replacement, and lubrication effects. Zhang and colleagues found that MSC-derived exosomes embedded in a hydrogel performed better than exosome treatment alone, due to higher retention and controlled release of exosomes or the encapsulated drug cargo.118 Similarly, it was demonstrated that a 3D printed scaffold, combined with exosomes, accelerated cartilage regeneration in animal studies.120 However, these combination systems are complex to synthesize, and in vivo studies often use cylindrical defect animal models instead of more widely accepted injury-induced OA models, posing translation barriers.Enabling tissue and cell targeting
Another method for engineering exosomes for improved OA therapy involves adding targeting moieties to the exosome surface. Genetic and metabolic engineering of parent cells can produce exosome surface proteins conjugated to targeting moieties.99,105–107,121 Exosomes can be directly modified using click chemistry to conjugate antibodies or aptamers to surface proteins, and by using hydrophobic membrane insertion105–107 and electrostatic interactions,121–125 with the negatively charged lipid bilayer. A combinatorial approach of click chemistry and hydrophobic insertion was used to modify milk derived exosomes with cartilage targeting cationic peptide carriers (Fig. 4b). Exosomes in OA therapy have commonly utilized chondrocyte affinity peptide (CAP) tagging.117,118,126–128 For example, dendritic derived exosomes were modified via genetic transfection of dendritic cells with CAP-lysosome-associated membrane protein-2b (Lamp-2b) to produce CAP-exosomes (Fig. 4c). A similar strategy was employed with subcutaneous fat MSC-derived exosomes.129 Lamp-2b, a common lipid membrane protein, is expressed on both cell and exosome membranes. Exosomes engineered with CAP showed improved delivery of miRNA to chondrocytes compared to native exosomes and exhibited cartilage protection in vivo.126,129Table 1 summarizes recent advances in engineered exosomes for OA therapy, highlighting those that have conducted in vivo.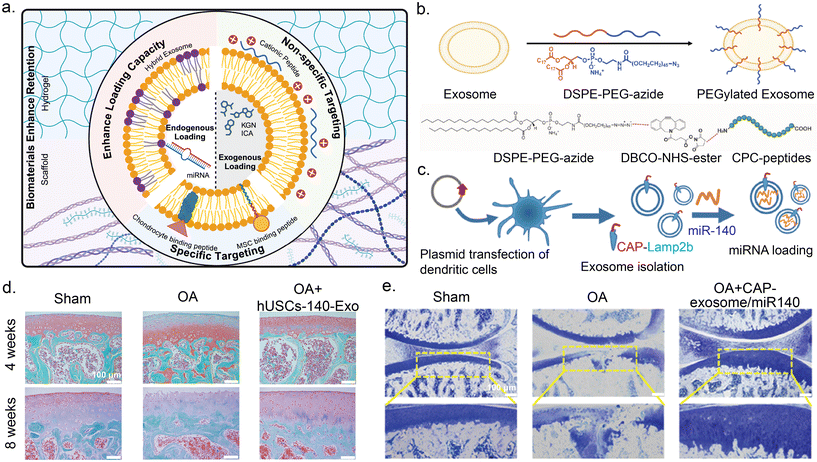 | ||
| Fig. 4 Engineering strategies for exosomes to enhance therapeutic efficacy for OA. (a) Schematic representation of engineering strategies for exosomes, including advanced cargo loading techniques, surface modifications, and integration with biomaterials. (b) Schematic illustration depicting surface modification of exosomes through hydrophobic insertion of DSPE-PEG linker conjugated to cartilage targeting cationic peptide carriers (CPCs) using copper-free click chemistry. (c) Schematic illustration depicting surface modification of exosomes through genetic engineering of dendritic cells with chondrocyte affinity peptide (CAP)-Lamp2b plasmid followed by miR-140 loading by electroporation. (d) Exosomes from human urine-derived stem cells (hUSCs) transfected with miR-140 (hUSC-140-Exos) were IA injected into ACLT and DMM rats. Representative microanatomy images of cartilage tissues in different treatment groups by Safranin-O staining. Scale bar, 100 μm. (e) CAP surface modified and miR-140 loaded exosomes were IA injected in DMM mice. Representative microanatomy images of cartilage tissues in different treatment groups, four weeks after IA injection by Toluidine blue staining. Scale bar, 100 μm. Figure b reproduced from ref. 124 with permission from Wiley, copyright 2024. Figures (c) and (e) are reproduced from ref. 126 with permission from ACS, copyright 2020. Figure (d) is reproduced from ref. 130 with permission from Sage Publishing, copyright 2022. | ||
| Engineering categories | Strategies | Cell source | Exo IA dose | Animal model | Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endogenous loading | Overexpressing miR-126-3p | Synovial fibroblasts (SFCs) | 500 μg mL−1; 20 μg; once per week for 6 weeks | ACLT + MMx rats | Overexpressing miR-126-3p enhances anti-inflammatory signaling to reduce proinflammatory cytokine production | 51 |
| Overexpressing miR-140-5p | Urine derived stem cells (USCs) | 10 particles per mL; 10 particles; once per week for 4 weeks | ACLT + DMM rats | Overexpressing miR-140-5p targets VEGFA, modulating ECM homeostasis and subchondral bone remodeling | 130 | |
| Overexpressing miR-376c-3p | Adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) | 400 μg mL−1; 100 μg; single injection | MIA induced rats | Overexpressing miR-376c-3p represses the WNT-beta-catenin signaling pathway, mitigating chondrocyte degradation and synovial fibrosis | 133 | |
| Overexpressing miR-140-5p | Synovial MSCs | 10 particles per mL; 10 particles; once per week for 4 weeks | MCLT + MMT rats | SMSC exosomes activated YAP to promoted chondrocyte proliferation and migration but inhibit ECM secretion via SOX9. Overexpressing miR-140-5p inhibits RalA to rescue SOX9 | 50 | |
| Overexpressing miR-155-5p | 10 particles per mL; 3 × 10 particles; once per day for 2 weeks | Cold water stimulated mice | Overexpressing miR-155-5p promotes chondrocyte proliferation, migration, and ECM secretion, inhibits apoptosis, and promotes cartilage regeneration | 134 | ||
| TGF-β1 enhanced miR-135b | Bone marrow MSCs | 10 particles per mL;10 particles; single injection | MCLT + MMT rats | TGF-β1 stimulation enhanced miR-135b to regulate cell proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation | 91 | |
| Overexpressing miR-92a-3p | 500 μg mL−1; 7.5 μg; once per week for 3 weeks | Collagenase induced mice | Overexpression of miR-92a-3p targets WNT5a, acting as a Wnt inhibitor | 85 | ||
| Overexpressing MEG-3 | 1000 μg mL−1; 100 μg; once per week for 8 weeks | ACLT + DMM rats | Overexpressing exosomal MEG-3 upregulate MMP-13 and collagen II, downregulate ADAMTS5, and alleviate the senescence and apoptosis induced by IL-1β in chondrocytes | 87 | ||
| Overexpress hsa-circ_0001236 | 500 μg mL−1; 5 μg; once per week for 6 weeks | DMM mice | Overexpressing circRNA_0001236 targets the miR-3677-3p/Sox9 axis to alleviate cartilage degradation | 88 | ||
| Overexpress NEAT1 | 10 μg; twice a week for a month | DMM mice | Exosomal NEAT1 regulated the miR-122-5p/Sesn2/Nrf2 axis | 89 | ||
| Overexpress miR-216a-5p | 1000 μg mL−1; 200 μg; single injection | ACLT + MMT rats | Enrichment of miR-216a-5p promotes chondrocyte proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis to attenuate OA progression | 90 | ||
| Overexpressing lncRNA H19 | Umbilical cord MSCs | 1000 μg mL−1; 200 μg; once per week for 8 weeks | Drill bit cartilage defect rats | Enrichment of lncRNA H19 promotes chondrocyte proliferation, matrix secretion, and inhibition of apoptosis | 135 | |
| Exogenous loading | Chitosan oligosaccharides (COS) conjugate | Adipose mesenchymal stem cells (AMSCs) | 100 μg; once per week for 8 weeks | Cartilage defect rats | COS assist exosome regulating Wnt, PI3K-Akt, AMPK, and MAPK signaling pathways | 136 |
| Surface anchoring cartilage affinity peptide (CAP) and antisense oligonucleotides (ASO)-MMP13 | Expi293F cells | 100 μg; once per week for 4 weeks | ACLT rats | ASO-MMP-13 inhibited the MMP-13 pathway attenuates inflammation, promotes chondrocyte proliferation and collagen synthesis, and reduces apoptosis, thereby restoring joint homeostasis | 128 | |
| Encapsulate icariin and load in CAT-C/DF-PEG hydrogel | Bone marrow MSCs | 150 μL; exo concentration unknown; single injection | Papain OA rats | Enhanced delivery of icariin inhibits MMP-13, NF-κb, Wnt/b-catenin, MAPK. Hydrogel facilitate cell attachment and migration | 116 | |
| Non-specific targeting | ε-Polylysine–polyethylene–distearyl phosphatidylethanolamine (PPD) surface anchoring | Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) derived MSCs | 10 particles per mL; 10 particles; once per 2 weeks for 6 weeks | ACLT mice | PPD reverses the surface charge to enhance the intra-articular bioavailability of exosomes | 137 |
| Cationic peptide carriers (CPCs) surface anchoring | Bovine milk | 2.5 mg mL−1; 25 μg; single injection | DMM mice | Cationic exosomes fully penetrate cartilage, facilitating the efficient delivery of mRNA | 124 | |
| Specific targeting | CAP surface modification and loading of miR-199a-3p | Subcutaneous fat (SC)-derived MSCs | 2 × 10 particles per mL; 10 particles; once per week for 4 weeks | DMM + ACLT mice and rats | Chondrocyte-targeted delivery of miR-199a-3p to mediate the mTOR-autophagy pathway | 129 |
| CAP surface modification and loading of siMMP13 | Expi293F cells | 100 μL; 1000 μg mL−1; once per week for 4 weeks | ACLT rats | Suppressed MMP13 expression, increased COL2A1 expression, and modulated the processes associated with inflammation and proliferation in OA articular cartilage | 132 | |
| CAP surface modification and loading of miR-140 | Dendritic cells | 100 μg; 1000 μg mL−1; once per week for 4 weeks | DMM rats | Chondrocyte-targeted delivery of miR-140 facilitates the inhibition of ADAMTS-5 and MMP-13 | 126 | |
| MSC-binding peptide E7 surface modification, exogenous loading Kartogenin (KGN), and co-delivery with SF-MSCs | 1 mg; 10 mg mL−1; once per week for 4 weeks | DMM rats | Preincubation of KGN-loaded exosomes can promote the chondrogenic differentiation of therapeutic SF-MSCs and simultaneously protect chondrocytes from degeneration | 131 | ||
| Enhance loading capacity | Cas9-sgMMP-13 loaded within hybrid exosome that surface modified with CAP | Dendritic cells | 100 μg, once per week for 4 weeks | DMM rats | Chondrocyte-specific knockdown of MMP-13 with mitigates or prevents cartilage degradation. Hybrid exosomes allow the loading of large molecule Cas9-sgMMP-13 | 127 |
| Cas9-sgFGF18 load within hybrid exosome that surface modified with CAP and encapsulated in methacrylic anhydride-modified hyaluronic (HAMA) hydrogel microspheres | HEK293 cells | 100 μL; exo concentration unknown; once per week for 2 weeks | ACLT rats | Hydrogel microspheres Cas9-sgFGF18 hybrid exosomes enhance chondrocyte proliferation and ECM synthesis and modulate PI3K/AKT signaling, combined with the synergistic effects of FGF18 gene activation and continuous lubrication | 117 | |
| Biomaterials enhance retention | Acellular cartilage extracellular matrix (ACECM) Scaffold implanted | Wharton's jelly MSCs | 25 μg mL−1; 5 μg; once per week for 5 injections | Drill bit cartilage defect rabbit | ACECM scaffolds combined with exosomal miRNAs promote osteochondral regeneration and inhibit inflammation in the joint cavity | 119 |
| 3D printed ECM/gelatin methacrylate (GelMA) scaffold | Bone marrow MSCs | 200 μg mL−1; single inject during surgery | Cartilage defect rabbit | Sustained release of exosomes restores cartilage mitochondrial dysfunction, enhances chondrocyte migration, and polarizes the synovial macrophage response towards an M2 phenotype | 120 | |
| Surface anchoring CAP, and encapsulated HA-SH microgels | Umbilical cord MSCs | 30 μg mL−1, dose unknown; once per 2 weeks for entire 2 injections | ACLT rats | Sustained release of UCMSC-EXOs rejuvenates aging chondrocytes by regulating the p53 pathway | 118 | |
| Overexpressing WNT3a load within collagen type-1 gel | Fibroblast cell (L-cells) | 100 ng ml−1; 1.2 × 10 particles; single injection during surgery | Cylindrical defect mice | Exosomal WNT3a introduced into the avascular cartilage promotes the healing of osteochondral defects | 80 |
Enriching therapeutic cargo
A third engineering focus is increasing endogenous and exogenous drug loading in exosomes for OA treatment. Endogenous loading methods include genetically engineering parent cells to overexpress native or novel therapeutic content.97–114 Shen and colleagues utilized miR-140 loaded exosomes (hUSC-140-Exos), derived through genetic engineering of human urine stem cells to overexpress miR-140, in an anterior cruciate ligament transection (ACLT) and destabilization of medial meniscus (DMM) rats for IA injection.130 hUSC-140-Exos demonstrated improved therapeutic efficacy over native hUSC exosomes as evident through significantly less joint wear evidenced at both 4- and 8-weeks post intervention, highlighting the strong potential of targeting surface modifications (Safranin-o staining, Fig. 4d). Exogenous loading methods involve passive incubation with therapeutics, electrostatic interactions using transfection reagents for nucleic acids, and physical methods like electroporation and sonication to induce transient membrane opening.97–114 For example, CAP-exos loaded with miR-140 utilized in a destabilization of medial meniscus (DMM) mice model led to cartilage morphology almost identical to that of healthy control when analyzed by toluidine blue staining (Fig. 4e). In another example, dendritic-derived exosomes were surface modified through genetic engineering of parent cells with E7, a homing peptide for MSCs, and then using electroporation were loaded with kartogenin, a molecule that differentiates MSCs into chondrocytes.131 These exosomes were proven to show higher chondrogenesis than kartogenin treatment alone. Wang and colleagues utilized Expi293F-derived loaded with MMP13 targeting siRNA through electroporation and surface modified with CAP by hydrophobic insertion, for IA injection in a rat model of anterior cruciate ligament transection induced OA leading to reduced MMP13 levels and increased cartilage collagen and GAG content.132 Another novel approach to improve drug loading in exosomes involves fusing liposomes, synthetic lipid vesicles with high drug loading capacity, with exosomes to create hybrid exosomes.102 These hybrids address the safety concerns of liposomes and overcome the low drug loading issues of exosomes simultaneously. Hybrid exosomes have recently emerged in OA treatment and have been shown to effectively deliver larger therapeutic payloads such as CRISPR/Cas9.117,127 While there exist many different engineering methods for both the therapeutic cargo loading and targeting modification of exosomes they are limited in scale-up due to complexity meaning that such methods have only been employed in vivo and not in a clinical setting.Charge-reversed exosomes for targeted drug delivery to cartilage
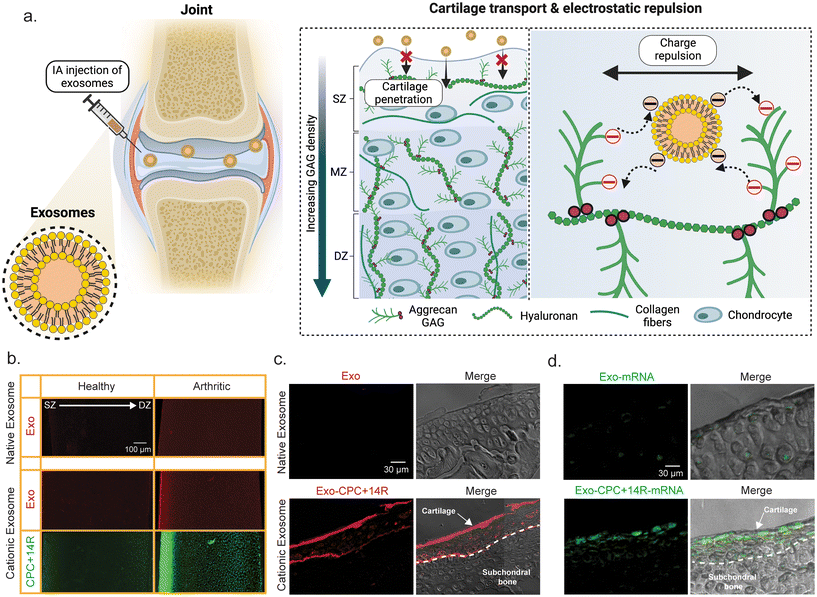
Leveraging electrostatic interactions, the high negative FCD of cartilage offers a unique opportunity to improve cartilage penetration and retention of engineered exosomes by reversing their surface charge to make them positively charged.140,141 Native exosomes cannot penetrate the anionic cartilage matrix because of their negatively charged lipid bilayer (Fig. 5a). When optimally charged cationic drugs are IA injected, their concentration at the synovial fluid-cartilage interface sharply increases due to Donnan partitioning.136,138–143 This results in significantly accelerated transport of positively charged drugs or drug carriers into the cartilage, outpacing clearance from the synovial fluid. By using weak-reversible electrostatic binding interactions, these carriers can transport through the full thickness of cartilage and reach chondrocytes residing in the deep tissue layers. Extensive studies have shown that such optimally charged OA therapeutics can form intra-cartilage drug depots thereby providing sustained therapeutic doses long-term with only a one-time dose.144–155 Early work in reversing the surface charge of exosomes has shown promising results, paving the way for realizing the full potential of exosomes in OA therapy.122–125,137Recent work by Bajpayee and colleagues engineered charge-reversed cationic exosomes for mRNA delivery by anchoring cartilage targeting optimally charged arginine-rich cationic motif (CPC + 14R) into the anionic exosome bilayer by using buffer pH as a charge-reversal switch.124 This led to exosome surface charge reversal from −25.4 ± 1.1 mV to −2.5 ± 1.0 mV.124 Cationic exosomes penetrated through the full-thickness of early-stage arthritic bovine cartilage owing to weak-reversible ionic binding with GAGs (Fig. 5b). When IA injected into destabilized medial meniscus mice knees with early-stage OA, mRNA loaded charge-reversed exosomes overcame joint clearance and rapidly penetrated cartilage, creating an intra-tissue depot and efficiently expressing eGFP; native exosomes remained unsuccessful (Fig. 5c and d). Cationic exosomes thus hold strong translational potential as a platform technology for cartilage-targeted non-viral delivery of any relevant mRNA targets for OA treatment. Considering the FCD differences in other negatively charged tissues, a similar strategy has been used for targeted gene therapy to overcome the intestinal mucus barrier using zwitterionic-modified exosomes122,123 and for targeted gene therapy for delivery to retinal photoreceptors through the topical route.125 Another recent study utilized ε-poly-L-lysine membrane anchored MSC exosomes that exhibited higher penetration and retention in femoral cartilage of ACLT mice compared to native MSC exosomes.137 These exosomes demonstrated alleviation of pathological features of OA including reduced catabolic markers and increased collagen and GAG content in femoral cartilage.
Overall, charge reversal of exosomes presents a non-specific targeting method that can greatly enhance the potential of exosome-based therapies and drug delivery systems for OA. Capitalizing on the unique challenges of cartilage delivery, electrostatic-based delivery has shown early potential to facilitate full-depth penetration of cartilage and long-term retention, paving the way for the translation of exosome-based therapies for OA.
Landscape of clinical trials using exosomes
A comprehensive survey on ClinicalTrials.gov using the index term ‘exosomes’ generated 376 entries for registered trials. Of these, 105 studies are reported to have locations within the United States, and 49 entries were reported for therapeutic interventions. Table 2 summarizes the clinical trials registered in the US, excluding those with unknown status or those that are suspended or terminated. Notably, there has been a surge in clinical trials utilizing exosomes derived from MSCs. Clinical evidence for exosome uses in OA treatment, however, remains limited, with only one reported Phase I trial to date. This study involves the use of human umbilical cord-derived MSC exosomes (ExoOA-1, developed by Cells for Cells (C4C)) administered to moderate OA patients via a single IA injection of 3–5 × 1011 particles per dose (NCT05060107). Data from an earlier case study that involved C4C's MSC exosomes injected into a 56-year-old female patient with knee OA was presented at the International Society for Cellular and Gene Therapies (ISCT) annual summit in San Francisco.156 The patient demonstrated a significant reduction in Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) scores after 6 months of a single IA dose. However, the status of the Phase I trial is unknown. The results from this trial could reveal the clinical potential of MSC exosomes for OA therapy and cartilage repair.| Exosome source | Clinical trial ID | Disease condition, cell type & dose | Phase | Study design | Sponsor, location & status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) | NCT05060107 | Knee OA; umbilical cord; single intra-articular injection of 3–5 × 1011 particles | Phase 1 | An open-label study with 10 participants having moderate knee OA between 30 to 70 years old | University of the Andes, Chile; unknown |
| NCT04798716 | COVID-19; N/A; IV injection every other day for 5 days | Phase 1/phase 2 | A randomized trial with 55 participants, inclusive of all sexes, reported a need for intensive care | AVEM HealthCare Mission Community Hospital, California, USA; not yet recruiting | |
| NCT05387278 | COVID-19; placenta & umbilical cord; IV infusion | Phase 1 | A double-blinded placebo-controlled trial inclusive of all sexes with 20 participants from 18 to 75 years | Vitti Labs, LLC, Missouri, USA; recruiting | |
| NCT04493242 | COVID-19; bone marrow (Exo-Flo); IV infusion of 10 mL Exo-Flo | Phase 2 | A double-blinded, placebo-controlled, multicentered, randomized trial with 102 participants inclusive of all sexes from 18 to 85 years | Direct Biologics LLC, USA; completed | |
| NCT05354141 | COVID-19; bone marrow (Exo-Flo); IV infusion of 15 mL Exo-Flo | Phase 3 | A double-blinded, multicentered, placebo-controlled trial inclusive of all sexes with 970 participants from 18 to 75 years | Direct Biologics LLC, USA; recruiting | |
| NCT04173650 | Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa; N/A; topical application | Phase 1/phase 2 | An open-label, multi-centered study with 10 volunteers from 6 years & older | Aegle Therapeutics, USA; not yet recruiting | |
| NCT06072794 | Premature ovarian insufficiency; placenta; IV injection for 5 days | Phase 1 | An open-label study with 8 female participants between 18 to 43 years | Vitti Labs, LLC, Oklahoma, USA; recruiting | |
| NCT03608631 | Pancreatic cancer; umbilical cord; IV infusion of KrasG12D siRNA loaded exosomes on days 1, 4 & 10, recurring every two weeks for up to 3 courses | Phase 1 | An open-label study with 15 patients that carry KrasG12D mutation inclusive of all sexes from18 years & above | MD Anderson Cancer Center, Texas, USA; active, not recruiting | |
| Plants | NCT01294072 | Colon cancer; grapes; dietary supplement of curcumin-loaded exosomes daily for one week | Phase 1 | A randomized trial with 35 patients inclusive of all genders from 20 years & above | University of Louisville, Kentucky, USA; recruiting |
| NCT01668849 | Oral mucositis; grapes; oral administration daily for 35 days during chemoradiation therapy | Phase 1 | A randomized study with 60 participants inclusive of all sexes between 20 to 85 years | University of Louisville, Kentucky, USA; completed | |
| NCT04879810 | Inflammatory bowel disease; ginger; oral administration of curcumin loaded exosomes daily for 28 days | Pilot study | A randomized trial with 4 participants inclusive of all sexes with ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease of age18 years & above | University of Louisville, Kentucky, USA; completed | |
| Others | NCT04384445 | COVID-19; amniotic fluid (Zofin); IV infusion of 1 mL containing 2–5 × 1011 particles per mL | Phase 1/phase 2 | A double-blinded trial with 20 participants inclusive of all sexes between 18 to 70 years | Zeo ScientifiX Inc, USA; completed |
| NCT05228899 | COVID-19 long haulers; amniotic fluid (Zofin); IV infusion of 1 mL containing 5.24 × 1011 particles per mL | Phase 1/phase 2 | A double-blinded trial with 18 participants inclusive of all sexes between 18 and above | Zeo ScientifiX Inc., USA; completed | |
| NCT06319287 | Diabetic foot ulcers; platelet; topical application of 15 mg mL−1 exosomes in TISSEEL fibrin sealant | Phase 2 | A multi-centered, randomized, placebo-controlled study with 40 participants inclusive of all sexes from 18 years & above | Rion Inc., Professional Education & Research Institute (PERI), Ohio, USA; recruiting | |
| NCT04664738 | Skin graft donor site wound; platelet; topical application of 10 or 20% exosome product | Phase 1 | An open-label, multicentered study with 8 participants inclusive of all sexes from 18 to 75 years that harbors two 2–40 cm split-thickness skin grafts | Rion Inc., International Research Partners in Florida & Mayo Clinic; active, not recruiting |
The use of MSC exosomes has also been prevalent in response to the novel COVID-19 infection, accounting for over 30% of the total interventional studies. Completed trials for COVID-19 infection have involved IV infusion of exosomes harvested from sources such as BM-MSC or amniotic fluid. For example, a non-randomized, open-label study on the safety and efficacy of BM-MSC-derived exosomes (ExoFlo, 15 mL containing 4 × 107 cells per mL) reported downregulation of inflammatory cytokines and restored immunocompetence with no adverse events.157–159 In line with this, the Phase II trial (NCT04493242) using two doses of ExoFlo showed a reduction in mortality associated with COVID-19-related acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) compared to a placebo control.160 Additionally, Zofin, an exosome-based biologic derived from perinatal amniotic fluid has received expanded access for a Phase I trial (NCT04657406) to investigate the safety of IV infusion and its efficacy in mild-to-moderate COVID-19 patients.161,162
The use of exosomes in cancer therapeutics is also increasing, accounting for 20% of exosome based registered trials. Exosomes for cancer treatment are primarily harvested from non-MSC sources such as dendritic cells, macrophages, cargo-engineered autologous tumor cells, or plant sources. The exclusion of MSCs could be due to conflicting results regarding the oncogenic effects of exosomes through their pro-tumorigenic paracrine factors.163,164 Plant-derived exosomes have garnered attention due to their benign attributes and non-immunogenicity compared to mammalian cell-derived exosomes for cancer treatment.165
Conclusion
Exosomes are nanosized, lipid membrane vesicles secreted by cells that play key roles in cell-to-cell communication and in the pathogenesis of OA by mediating inflammatory signaling between tissues and cells. This understanding has paved the way for the application of exosomes as a novel, nanoscale therapeutic for OA. Engineering modifications to enable their joint retention, cell/tissue targeting, and therapeutic content enrichment have significantly increased their potential for OA drug delivery. Notably, charge-reversed exosomes that use electrostatic binding interactions with cartilage anionic GAGs, have demonstrated the ability to penetrate the full thickness of early-stage arthritic cartilage tissue and target chondrocytes. These exosomes offer a non-viral, naturally derived, cell-free carrier for drug and gene delivery applications. Future research in exosome therapy for OA must address two main challenge areas associated with exosome therapy, standardization of harvest and characterization and scale-up of production and engineering. Current exosome characteristics and harvest methods vary greatly based on cell source. Engineering methods for exosomes, while improving their therapeutic efficacy, can be increasingly complex and thus limiting application. Further efforts to standardize and scale-up exosomes will facilitate more efficient and rapid clinical translation for OA therapy.Author contributions
All authors conceptualized, curated data, wrote, reviewed and edited the manuscript before submission.Data availability
No primary research results, software or code have been included and no new data were generated or analyzed as part of this review.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) R01AR075121, National Institute of Biomedical Imagine and Bioengineering (NIBIB) Trailblazer R21EB028385, and National Science Foundation (NSF) CAREER (2141841). Fig. 1, 2, 3, 4a, and 5a created with BioRender.com. Fig. 4b reproduced from ref. 124 with permission from Wiley, copyright 2024. Fig. 4c and e are reproduced from ref. 126 with permission from ACS, copyright 2020. Fig. 4d is reproduced from ref. 130 with permission from Sage Publishing, copyright 2022.References
- E. R. Abels and X. O. Breakefield, Cell. Mol. Neurobiol., 2016, 36, 301–312 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Kalluri and V. S. LeBleu, Science, 2020, 367, eaau6977 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Raposo and W. Stoorvogel, J. Cell Biol., 2013, 200, 373–383 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. M. Doyle and M. Z. Wang, Cells, 2019, 8, 727 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Kalluri, J. Clin. Invest., 2016, 126, 1208–1215 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. M. Patil, S. S. Sawant and N. K. Kunda, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 2020, 154, 259–269 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. J. Bunggulawa, W. Wang, T. Yin, N. Wang, C. Durkan, Y. Wang and G. Wang, J. Nanobiotechnol., 2018, 16, 81 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Gurunathan, M.-H. Kang and J.-H. Kim, Int. J. Nanomed., 2021, 16, 1281–1312 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Ghadami and K. Dellinger, Front. Mol. Biosci., 2023, 10, 1198044 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Gurung, D. Perocheau, L. Touramanidou and J. Baruteau, Cell Commun. Signaling, 2021, 19, 47 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Han, T. W. Jones, S. Dutta, Y. Zhu, X. Wang, S. P. Narayanan, S. C. Fagan and D. Zhang, Processes, 2021, 9, 356 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. G. van den Boorn, J. Daßler, C. Coch, M. Schlee and G. Hartmann, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2013, 65, 331–335 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Li, E. Zeringer, T. Barta, J. Schageman, A. Cheng and A. V. Vlassov, Philos. Trans. R. Soc., B, 2014, 369, 20130502 CrossRef PubMed.
- N. P. Hessvik and A. Llorente, Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 2018, 75, 193–208 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Costa-Silva, N. M. Aiello, A. J. Ocean, S. Singh, H. Zhang, B. K. Thakur, A. Becker, A. Hoshino, M. T. Mark, H. Molina, J. Xiang, T. Zhang, T.-M. Theilen, G. García-Santos, C. Williams, Y. Ararso, Y. Huang, G. Rodrigues, T.-L. Shen, K. J. Labori, I. M. B. Lothe, E. H. Kure, J. Hernandez, A. Doussot, S. H. Ebbesen, P. M. Grandgenett, M. A. Hollingsworth, M. Jain, K. Mallya, S. K. Batra, W. R. Jarnagin, R. E. Schwartz, I. Matei, H. Peinado, B. Z. Stanger, J. Bromberg and D. C. Lyden, Nat. Cell Biol., 2015, 17, 816–826 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. A. Melo, H. Sugimoto, J. T. O'Connell, N. Kato, A. Villanueva, A. Vidal, L. Qiu, E. Vitkin, L. T. Perelman, C. A. Melo, A. Lucci, C. Ivan, G. A. Calin and R. Kalluri, Cancer Cell, 2014, 26, 707–721 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Bakhti, C. Winter and M. Simons, J. Biol. Chem., 2011, 286, 787–796 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Wang, F. Cesca, G. Loers, M. Schweizer, F. Buck, F. Benfenati, M. Schachner and R. Kleene, J. Neurosci., 2011, 31, 7275–7290 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Murphy, J. Withrow, M. Hunter, Y. Liu, Y. L. Tang, S. Fulzele and M. W. Hamrick, Mol. Aspects Med., 2018, 60, 123–128 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. G. Kwon, M. K. Kim, Y. S. Jeon, Y. C. Nam, J. S. Park and D. J. Ryu, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23, 1618 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. J. W. Low, S. A. Sulaiman, N. A. Johdi and N. Abu, Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 2022 DOI:10.3389/fcell.2022.996805.
- H. Long, Q. Liu, H. Yin, K. Wang, N. Diao, Y. Zhang, J. Lin and A. Guo, Arthritis Rheumatol., 2022, 74, 1172–1183 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. D. Steinmetz, G. T. Culbreth, L. M. Haile, Q. Rafferty, J. Lo, K. G. Fukutaki, J. A. Cruz, A. E. Smith, S. E. Vollset, P. M. Brooks, M. Cross, A. D. Woolf, H. Hagins, M. Abbasi-Kangevari, A. Abedi, I. N. Ackerman, H. Amu, B. Antony, J. Arabloo, A. Y. Aravkin, A. M. Argaw, A. A. Artamonov, T. Ashraf, A. Barrow, L. M. Bearne, I. M. Bensenor, A. Y. Berhie, N. Bhardwaj, P. Bhardwaj, V. S. Bhojaraja, A. Bijani, P. S. Briant, A. M. Briggs, N. S. Butt, J. Charan, V. K. Chattu, F. M. Cicuttini, K. Coberly, O. Dadras, X. Dai, L. Dandona, R. Dandona, K. de Luca, E. Denova-Gutiérrez, S. D. Dharmaratne, M. Dhimal, M. Dianatinasab, K. E. Dreinhoefer, M. Elhadi, U. Farooque, H. R. Farpour, I. Filip, F. Fischer, M. Freitas, B. Ganesan, B. N. B. Gemeda, T. Getachew, S.-H. Ghamari, A. Ghashghaee, T. K. Gill, M. Golechha, D. Golinelli, B. Gupta, V. B. Gupta, V. K. Gupta, R. Haddadi, N. Hafezi-Nejad, R. Halwani, S. Hamidi, A. Hanif, N. I. Harlianto, J. M. Haro, J. Hartvigsen, S. I. Hay, J. J. Hebert, G. Heidari, M.-S. Hosseini, M. Hosseinzadeh, A. K. Hsiao, I. M. Ilic, M. D. Ilic, L. Jacob, R. Jayawardena, R. P. Jha, J. B. Jonas, N. Joseph, H. Kandel, I. M. Karaye, M. J. Khan, Y. J. Kim, A.-A. Kolahi, O. Korzh, R. Koteeswaran, V. Krishnamoorthy, G. A. Kumar, N. Kumar, S. Lee, S. S. Lim, S. W. Lobo, G. Lucchetti, M.-R. Malekpour, A. A. Malik, L. G. G. Mandarano-Filho, S. Martini, A.-F. A. Mentis, M. K. Mesregah, T. Mestrovic, E. M. Mirrakhimov, A. Misganaw, R. Mohammadpourhodki, A. H. Mokdad, S. Momtazmanesh, S. D. Morrison, C. J. L. Murray, H. Nassereldine, H. B. Netsere, S. N. Kandel, M. O. Owolabi, S. Panda-Jonas, A. Pandey, S. Pawar, P. Pedersini, J. Pereira, A. Radfar, M.-M. Rashidi, D. L. Rawaf, S. Rawaf, R. Rawassizadeh, S.-M. Rayegani, D. Ribeiro, L. Roever, B. Saddik, A. Sahebkar, S. Salehi, L. S. Riera, F. Sanmarchi, M. M. Santric-Milicevic, S. Shahabi, M. A. Shaikh, E. Shaker, M. Shannawaz, R. Sharma, S. Sharma, J. K. Shetty, R. Shiri, P. Shobeiri, D. A. S. Silva, A. Singh, J. A. Singh, S. Singh, S. T. Skou, H. Slater, M. S. Soltani-Zangbar, A. V. Starodubova, A. Tehrani-Banihashemi, S. V. Tahbaz, P. R. Valdez, B. Vo, L. G. Vu, Y.-P. Wang, S. H. Y. Jabbari, N. Yonemoto, I. Yunusa, L. M. March, K. L. Ong, T. Vos and J. A. Kopec, Lancet Rheumatol., 2023, 5, e508–e522 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Tong, H. Yu, X. Huang, J. Shen, G. Xiao, L. Chen, H. Wang, L. Xing and D. Chen, Bone Res., 2022, 10, 1–17 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. M. Oo, C. Little, V. Duong and D. J. Hunter, Drug Des., Dev. Ther., 2021, 15, 2921–2945 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. H. Evans, V. B. Kraus and L. A. Setton, Nat. Rev. Rheumatol., 2014, 10, 11–22 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. D. Spector and A. J. MacGregor, Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2004, 12, 39–44 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Mobasheri, Curr. Rheumatol. Rep., 2013, 15, 385 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. H. Sohn, J. Sokolove, O. Sharpe, J. C. Erhart, P. E. Chandra, L. J. Lahey, T. M. Lindstrom, I. Hwang, K. A. Boyer, T. P. Andriacchi and W. H. Robinson, Arthritis Res. Ther., 2012, 14, R7 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. G. Bajpayee and A. J. Grodzinsky, Nat. Rev. Rheumatol., 2017, 13, 183–193 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W.-J. Fan, D. Liu, L.-Y. Pan, W.-Y. Wang, Y.-L. Ding, Y.-Y. Zhang, R.-X. Ye, Y. Zhou, S.-B. An and W.-F. Xiao, Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 2022, 10, 949690 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Esa, K. Connolly, R. Williams and C. Archer, Malays. Orthop. J., 2019, 13, 1–7 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Wu, J. Li, Y. Zeng, W. Pu, X. Mu, K. Sun, Y. Peng and B. Shen, Int. J. Oral Sci., 2022, 14, 1–16 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Ni, S. Zhou, S. Li, L. Kuang, H. Chen, X. Luo, J. Ouyang, M. He, X. Du and L. Chen, Bone Res., 2020, 8, 1–18 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Lin, L. Wang, J. Lin and Q. Liu, Molecules, 2021, 26, 4987 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Gao, W. Zhu, H. Li, D. Ma, W. Liu, W. Yu, L. Wang, Y. Cao and Y. Jiang, Mod. Rheumatol., 2020, 30, 758–764 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Yin, M. Li, G. Tian, Y. Ma, C. Ning, Z. Yan, J. Wu, Q. Ge, X. Sui, S. Liu, J. Zheng, W. Guo and Q. Guo, Biomater. Res., 2022, 26, 52 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Peng, Y. Yan, R. Li, H. Dai and J. Xu, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 2021, 1503, 48–59 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. H. W. Distler, A. Jüngel, L. C. Huber, C. A. Seemayer, C. F. Reich, R. E. Gay, B. A. Michel, A. Fontana, S. Gay, D. S. Pisetsky and O. Distler, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2005, 102, 2892–2897 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Domenis, R. Zanutel, F. Caponnetto, B. Toffoletto, A. Cifù, C. Pistis, P. Di Benedetto, A. Causero, M. Pozzi, F. Bassini, M. Fabris, K. R. Niazi, P. Soon-Shiong and F. Curcio, Mediators Inflammation, 2017, 2017, e4814987 Search PubMed.
- R.-Z. Yang, H.-L. Zheng, W.-N. Xu, X.-F. Zheng, B. Li, L.-S. Jiang and S.-D. Jiang, Aging, 2021, 13, 4647–4662 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wu, R. Crawford, Y. Xiao, X. Mao and I. Prasadam, Cells, 2021, 10, 251 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. H. Jeon, D. R. Wilson, C. C. Clement, S. Rathod, C. Cherry, B. Powell, Z. Lee, A. M. Khalil, J. J. Green, J. Campisi, L. Santambrogio, K. W. Witwer and J. H. Elisseeff, JCI Insight, 2019, 4, e125019 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. Mao, S. Hu, Z. Zhang, P. Wu, X. Zhao, R. Lin, W. Liao and Y. Kang, J. Cell. Mol. Med., 2018, 22, 5354–5366 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Withrow, C. Murphy, Y. Liu, M. Hunter, S. Fulzele and M. W. Hamrick, Arthritis Res. Ther., 2016, 18, 286 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Ni, L. Kuang, H. Chen, Y. Xie, B. Zhang, J. Ouyang, J. Wu, S. Zhou, L. Chen, N. Su, Q. Tan, X. Luo, B. Chen, S. Chen, L. Yin, H. Huang, X. Du and L. Chen, Cell Death Dis., 2019, 10, 1–16 Search PubMed.
- R. Kolhe, M. Hunter, S. Liu, R. N. Jadeja, C. Pundkar, A. K. Mondal, B. Mendhe, M. Drewry, M. V. Rojiani, Y. Liu, C. M. Isales, R. E. Guldberg, M. W. Hamrick and S. Fulzele, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7, 2029 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Zhao and J. Xu, Int. Orthop., 2018, 42, 2865–2872 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Guo, H. Wang, F. Zhao, M. Liu, F. Wang, M. Kang, W. He and Z. Lv, Arthritis Res. Ther., 2021, 23, 159 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S.-C. Tao, T. Yuan, Y.-L. Zhang, W.-J. Yin, S.-C. Guo and C.-Q. Zhang, Theranostics, 2017, 7, 180–195 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhou, J. Ming, Y. Li, B. Li, M. Deng, Y. Ma, Z. Chen, Y. Zhang, J. Li and S. Liu, Cell Death Discovery, 2021, 7, 1–15 Search PubMed.
- L. Hu, J. Wang, X. Zhou, Z. Xiong, J. Zhao, R. Yu, F. Huang, H. Zhang and L. Chen, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, 32993 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Dalirfardouei, K. Jamialahmadi, A. H. Jafarian and E. Mahdipour, J. Tissue Eng. Regener. Med., 2019, 13, 555–568 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wu, B. Bian, Z. Lin, C. Wu, Y. Sun, Y. Pan, Y. Dai, T. H. Lui, T. Zhuang and X. Pan, Exp. Cell Res., 2022, 410, 112881 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Lai, B. Liao, S. Peng, P. Fang, N. Bao and L. Zhang, Mol. Cell. Biochem., 2023, 478, 637–649 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. E. Headland, H. R. Jones, L. V. Norling, A. Kim, P. R. Souza, E. Corsiero, C. D. Gil, A. Nerviani, F. Dell'Accio, C. Pitzalis, S. M. Oliani, L. Y. Jan and M. Perretti, Sci. Transl. Med., 2015, 7, 315ra190 Search PubMed.
- J. Bai, Y. Zhang, X. Zheng, M. Huang, W. Cheng, H. Shan, X. Gao, M. Zhang, L. Sheng, J. Dai, Y. Deng, H. Zhang and X. Zhou, Cell Death Dis., 2020, 11, 1–13 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. Harding, J. Heuser and P. Stahl, J. Cell Biol., 1983, 97, 329–339 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B.-T. Pan and R. M. Johnstone, Cell, 1983, 33, 967–978 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Gawrisch, D. Stibenz, A. Möps, K. Arnold, W. Linss and K. J. Halbhuber, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1986, 856, 443–447 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. Vidal and P. D. Stahl, Eur. J. Cell Biol., 1993, 60, 261–267 CAS.
- J. M. Escola, M. J. Kleijmeer, W. Stoorvogel, J. M. Griffith, O. Yoshie and H. J. Geuze, J. Biol. Chem., 1998, 273, 20121–20127 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. M. Kay, A. J. Birss and J. W. Smalley, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 1990, 60, 69–73 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. J. Powell, R. S. Harvey and R. P. Thompson, Gut, 1996, 39, 340–341 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Singh, C. H. Gemmell, P. A. Daly and E. L. Yeo, Can. J. Cardiol., 1995, 11, 1015–1021 CAS.
- Y. J. Lee, W. Jy, L. L. Horstman, J. Janania, Y. Reyes, R. E. Kelley and Y. S. Ahn, Thromb. Res., 1993, 72, 295–304 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Raposo, H. W. Nijman, W. Stoorvogel, R. Liejendekker, C. V. Harding, C. J. Melief and H. J. Geuze, J. Exp. Med., 1996, 183, 1161–1172 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Zitvogel, A. Regnault, A. Lozier, J. Wolfers, C. Flament, D. Tenza, P. Ricciardi-Castagnoli, G. Raposo and S. Amigorena, Nat. Med., 1998, 4, 594–600 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. MacKenzie, H. L. Wilson, E. Kiss-Toth, S. K. Dower, R. A. North and A. Surprenant, Immunity, 2001, 15, 825–835 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Van Niel, J. Mallegol, C. Bevilacqua, C. Candalh, S. Brugière, E. Tomaskovic-Crook, J. K. Heath, N. Cerf-Bensussan and M. Heyman, Gut, 2003, 52, 1690–1697 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Skokos, H. G. Botros, C. Demeure, J. Morin, R. Peronet, G. Birkenmeier, S. Boudaly and S. Mécheri, J. Immunol., 2003, 170, 3037–3045 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Valadi, K. Ekström, A. Bossios, M. Sjöstrand, J. J. Lee and J. O. Lötvall, Nat. Cell Biol., 2007, 9, 654–659 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Ratajczak, K. Miekus, M. Kucia, J. Zhang, R. Reca, P. Dvorak and M. Z. Ratajczak, Leukemia, 2006, 20, 847–856 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Bruno, C. Grange, M. C. Deregibus, R. A. Calogero, S. Saviozzi, F. Collino, L. Morando, A. Busca, M. Falda, B. Bussolati, C. Tetta and G. Camussi, J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 2009, 20, 1053 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Kato, S. Miyaki, H. Ishitobi, Y. Nakamura, T. Nakasa, M. K. Lotz and M. Ochi, Arthritis Res. Ther., 2014, 16, R163 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Zhang, W. C. Chu, R. C. Lai, S. K. Lim, J. H. P. Hui and W. S. Toh, Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2016, 24, 2135–2140 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Cosenza, M. Ruiz, K. Toupet, C. Jorgensen and D. Noël, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7, 16214 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Q. Luo, B. Zhou and H. Xiong, J. Pain Res., 2023, 16, 2171–2188 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. Xu, Z. Mi, Z. Dong, X. Chen, G. Ji, H. Kang, K. Li, B. Zhao and F. Wang, Am. J. Sports Med., 2023, 51, 2975–2985 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. L. Thomas, S. E. Eldridge, B. Nosrati, M. Alvarez, A. Thorup, G. Nalesso, S. Caxaria, A. Barawi, J. G. Nicholson, M. Perretti, C. Gaston-Massuet, C. Pitzalis, A. Maloney, A. Moore, R. Jupp and F. Dell'Accio, J. Extracell. Vesicles, 2021, 10, e12088 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhang, Y. Rong, C. Luo and W. Cui, Aging, 2020, 12, 25138–25152 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Poliwoda, N. Noor, E. Downs, A. Schaaf, A. Cantwell, L. Ganti, A. D. Kaye, L. I. Mosel, C. B. Carroll, O. Viswanath and I. Urits, Orthop. Rev., 2022, 14, 37498 Search PubMed.
- B. Kristjánsson and S. Honsawek, Stem Cells Int., 2014, 2014, e194318 Search PubMed.
- C. Han, X. Sun, L. Liu, H. Jiang, Y. Shen, X. Xu, J. Li, G. Zhang, J. Huang, Z. Lin, N. Xiong and T. Wang, Stem Cells Int., 2016, 2016, 7653489 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. Mao, Z. Zhang, S. Hu, Z. Zhang, Z. Chang, Z. Huang, W. Liao and Y. Kang, Stem Cell Res. Ther., 2018, 9, 247 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Chen, Y. Shi, P. Xue, X. Ma, J. Li and J. Zhang, Arthritis Res. Ther., 2020, 22, 256 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Jin, M. Xu, H. Zhu, C. Dong, J. Ji, Y. Liu, A. Deng and Z. Gu, J. Cell. Mol. Med., 2021, 25, 9281–9294 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Mao, Y. Xu, D. Long, H. Sun, H. Li, R. Xin, Z. Zhang, Z. Li, Z. Yang and Y. Kang, Stem Cell Res. Ther., 2021, 12, 389 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Zhang and Z. Jin, Oxid. Med. Cell. Longevity, 2022, 2022, 5517648 Search PubMed.
- Y. Rong, J. Zhang, D. Jiang, C. Ji, W. Liu, J. Wang, X. Ge, P. Tang, S. Yu, W. Cui and W. Cai, Acta Biomater., 2021, 122, 325–342 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Wang, B. Xu and H. Xu, Cell Cycle, 2018, 17, 2756–2765 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. H. Woo, H. K. Kim, G. Y. Jung, Y. J. Jung, K. S. Lee, Y. E. Yun, J. Han, J. Lee, W. S. Kim, J. S. Choi, S. Yang, J. H. Park, D.-G. Jo and Y. W. Cho, J. Extracell. Vesicles, 2020, 9, 1735249 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Zavatti, F. Beretti, F. Casciaro, E. Bertucci and T. Maraldi, BioFactors, 2020, 46, 106–117 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhou, X. Shen, C. Yan, W. Xiong, Z. Ma, Z. Tan, J. Wang, Y. Li, J. Liu, A. Duan and F. Liu, Stem Cell Res. Ther., 2022, 13, 322 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Hu, L. Dong, Z. Bu, Y. Shen, J. Luo, H. Zhang, S. Zhao, F. Lv and Z. Liu, J. Extracell. Vesicles, 2020, 9, 1778883 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. M. Kronstadt, D. B. Patel, L. J. Born, D. Levy, M. J. Lerman, B. Mahadik, S. T. McLoughlin, A. Fasuyi, L. Fowlkes, L. H. Van Heyningen, A. Aranda, S. N. Abadchi, K.-H. Chang, A. T. W. Hsu, S. Bengali, J. W. Harmon, J. P. Fisher and S. M. Jay, Adv. Healthcare Mater., 2023, 12, 2300584 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. C. de Abreu, C. V. Ramos, C. Becher, M. Lino, C. Jesus, P. A. da Costa Martins, P. A. T. Martins, M. J. Moreno, H. Fernandes and L. Ferreira, J. Extracell. Vesicles, 2021, 10, e12111 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S.-P. Li, Z.-X. Lin, X.-Y. Jiang and X.-Y. Yu, Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 2018, 39, 542–551 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Liang, L. Duan, J. Lu and J. Xia, Theranostics, 2021, 11, 3183–3195 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Lu, Z. Mai, L. Cui and X. Zhao, Stem Cell Res. Ther., 2023, 14, 55 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Luan, K. Sansanaphongpricha, I. Myers, H. Chen, H. Yuan and D. Sun, Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 2017, 38, 754–763 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Mondal, S. Pillarisetti, V. Junnuthula, M. Saha, S. R. Hwang, I.-K. Park and Y.-K. Lee, J. Controlled Release, 2023, 353, 1127–1149 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. N. Moholkar, R. Kandimalla, R. C. Gupta and F. Aqil, Cancer Lett., 2023, 216220 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. N. Kenari, L. Cheng and A. F. Hill, Methods, 2020, 177, 103–113 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Rayamajhi and S. Aryal, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2020, 8, 4552–4569 RSC.
- M. Richter, P. Vader and G. Fuhrmann, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2021, 173, 416–426 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Salunkhe, M. Basak, D. Chitkara and A. Mittal, J. Controlled Release, 2020, 326, 599–614 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Si, S. Kim, E. Zhang, Y. Tang, R. Jaskula-Sztul, J. M. Markert, H. Chen, L. Zhou and X. M. Liu, Biotechnol. J., 2020, 15, 1900163 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Xu, Q. Yang, X. Sun and Y. Wang, Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol., 2020 DOI:10.3389/fbioe.2020.586130.
- Y. Zhang, Q. Liu, X. Zhang, H. Huang, S. Tang, Y. Chai, Z. Xu, M. Li, X. Chen, J. Liu and C. Yang, J. Nanobiotechnol., 2022, 20, 279 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Zhao, J. Huang, Y. Fan, J. Li, T. You, S. He, G. Xiao and D. Chen, Ann. Rheum. Dis., 2019, 78, 676–682 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Hall, S. Prabhakar, L. Balaj, C. P. Lai, R. A. Cerione and X. O. Breakefield, Cell. Mol. Neurobiol., 2016, 36, 417–427 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Liu, G. Yang, Y. Liu and T. Liu, Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol., 2022, 10, 939441 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Mehryab, S. Rabbani, S. Shahhosseini, F. Shekari, Y. Fatahi, H. Baharvand and A. Haeri, Acta Biomater., 2020, 113, 42–62 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Fan, Z. Li and Y. He, Bioengineering, 2022, 9, 99 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zeng, P. Sun, Y. Zhao, X. Fang, Z. Wu and X. Qi, Asian J. Pharm. Sci., 2023, 18, 100799 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Chen, Y. Lu, Y. Liu, Q. Liu, S. Deng, Y. Liu, X. Cui, J. Liang, X. Zhang, Y. Fan and Q. Wang, Adv. Mater., 2024, 36, 2312559 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Cao, M. Chen, X. Cui, Y. Liu, Y. Liu, S. Deng, T. Yuan, Y. Fan, Q. Wang and X. Zhang, ACS Nano, 2023, 17, 13358–13376 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Jiang, G. Tian, Z. Yang, X. Gao, F. Wang, J. Li, Z. Tian, B. Huang, F. Wei, X. Sang, L. Shao, J. Zhou, Z. Wang, S. Liu, X. Sui, Q. Guo, W. Guo and X. Li, Bioact. Mater., 2021, 6, 2711–2728 CAS.
- P. Chen, L. Zheng, Y. Wang, M. Tao, Z. Xie, C. Xia, C. Gu, J. Chen, P. Qiu, S. Mei, L. Ning, Y. Shi, C. Fang, S. Fan and X. Lin, Theranostics, 2019, 9, 2439–2459 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. H. Mohammadi, Z. Ghazvinian, F. Bagheri, M. Harada and K. Baghaei, BioDrugs, 2023, 37, 353–374 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. R. Warren, C. Zhang, A. Vedadghavami, K. Bokvist, P. K. Dhal and A. G. Bajpayee, Biomater. Sci., 2021, 9, 4260–4277 RSC.
- C. Zhang, H. Zhang, H. A. M. Cotto, T. L. Boyer, M. R. Warren, C.-M. Wang, J. Luchan, P. K. Dhal, R. L. Carrier and A. G. Bajpayee, Biomater. Sci., 2024 10.1039/D3BM01089A.
- C. Zhang, T. V. Pathrikar, H. M. Baby, J. Li, H. Zhang, A. Selvadoss, A. Ovchinnikova, A. Ionescu, S. Chubinskaya, R. E. Miller and A. G. Bajpayee, Small Methods, 2024 DOI:10.1002/smtd.202301443.
- H. A. M. Cotto, T. V. Pathrikar, B. Hakim, H. M. Baby, H. Zhang, P. Zhao, R. Ansaripour, R. Amini, R. L. Carrier and A. G. Bajpayee, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2024 10.1039/D4TB00849A.
- Y. Liang, X. Xu, X. Li, J. Xiong, B. Li, L. Duan, D. Wang and J. Xia, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 36938–36947 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Liang, X. Xu, L. Xu, Z. Iqbal, K. Ouyang, H. Zhang, C. Wen, L. Duan and J. Xia, Theranostics, 2022, 12, 4866–4878 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Yan, Y. Li, S. Xie, W. A. Tao, J. Hu, H. Liu, G. Zhang, F. Liu, Y. Nie, X. Chen, X. Zhang, Y. Liu, D. Wei, C. Ma, H. Zhang, H. Xu and S. Wang, Adv. Healthcare Mater., 2024, 2303510 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Zhao, G. Xiu, J. Wang, Y. Wen, J. Lu, B. Wu, G. Wang, D. Yang, B. Ling, D. Du and J. Xu, J. Nanobiotechnol., 2023, 21, 341 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Liu, Y. Zeng, H.-B. Si, L. Tang, H.-Q. Xie and B. Shen, Am. J. Sports Med., 2022, 50, 1088–1105 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Xu, Y. Liang, X. Li, K. Ouyang, M. Wang, T. Cao, W. Li, J. Liu, J. Xiong, B. Li, J. Xia, D. Wang and L. Duan, Biomaterials, 2021, 269, 120539 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhang, W. Yan, J. Wang, S. Xie, W. A. Tao, C.-W. Lee, X. Zhang, G. Zhang, Y. Liu, D. Wei, J. Hu, H. Liu, F. Liu, Y. Nie, X. Chen, H. Xu, J. Xia and S. Wang, J. Controlled Release, 2024, 369, 493–505 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Li, Z. Xu, Z. Xie, X. Sun, C. Li, Y. Chen, J. Xu and G. Pi, Apoptosis, 2023, 28, 362–378 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Wang, K. Yan, G. Ge, D. Zhang, J. Bai, X. Guo, J. Zhou, T. Xu, M. Xu, X. Long, Y. Hao and D. Geng, Cell Biol. Toxicol., 2021, 37, 85–96 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Yan, G. Liu and X. Wu, Clin. Transl. Med., 2021, 11, e255 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Li, J. Liu, S. Liu, W. Jiao and X. Wang, J. Nanobiotechnol., 2021, 19, 343 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Feng, X. Xie, J. Yuan, L. Gong, Z. Zhu, J. Zhang, H. Li, Y. Yang and Y. Wang, J. Extracell. Vesicles, 2021, 10, e12160 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Vedadghavami, C. Zhang and A. G. Bajpayee, Nano Today, 2020, 34, 100898 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Mehta, T. He and A. G. Bajpayee, Curr. Opin. Rheumatol., 2021, 33, 94 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. C. Young, A. Vedadghavami and A. G. Bajpayee, Bioelectricity, 2020, 2, 68–81 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. G. Bajpayee, C. R. Wong, M. G. Bawendi, E. H. Frank and A. J. Grodzinsky, Biomaterials, 2014, 35, 538–549 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. R. Warren and A. G. Bajpayee, Bioelectricity, 2022, 4, 248–258 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. R. Warren, A. Vedadghavami, S. Bhagavatula and A. G. Bajpayee, Biophys. J., 2022, 121, 3542–3561 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Vedadghavami, E. K. Wagner, S. Mehta, T. He, C. Zhang and A. G. Bajpayee, Acta Biomater., 2019, 93, 258–269 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. G. Bajpayee, R. E. De la Vega, M. Scheu, N. H. Varady, I. A. Yannatos, L. A. Brown, Y. Krishnan, T. J. Fitzsimons, P. Bhattacharya, E. H. Frank, A. J. Grodzinsky and R. M. Porter, Eur. Cells Mater., 2017, 34, 341–364 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Mehta, T. L. Boyer, S. Akhtar, T. He, C. Zhang, A. Vedadghavami and A. G. Bajpayee, Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2023, 31, 780–792 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. He, I. Shaw, A. Vedadghavami and A. G. Bajpayee, Cartilage, 2022, 13, 19476035221093072 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. He, C. Zhang, A. Vedadghavami, S. Mehta, H. A. Clark, R. M. Porter and A. G. Bajpayee, J. Controlled Release, 2020, 318, 109–123 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. He, C. Zhang, T. Colombani, S. A. Bencherif, R. M. Porter and A. G. Bajpayee, Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2023, 31, 187–198 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Vedadghavami, T. He, C. Zhang, S. M. Amiji, B. Hakim and A. G. Bajpayee, Acta Biomater., 2022, 151, 278–289 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. G. Bajpayee, M. A. Quadir, P. T. Hammond and A. J. Grodzinsky, Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2016, 24, 71–81 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Vedadghavami, B. Hakim, T. He and A. G. Bajpayee, Arthritis Res. Ther., 2022, 24, 172 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Zhang, A. Vedadghavami, T. He, J. F. Charles and A. G. Bajpayee, ACS Nano, 2023, 17, 6649–6663 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. K. Wagner, A. Vedadghavami, T. D. Jacobsen, S. A. Goel, N. O. Chahine and A. G. Bajpayee, Sci. Rep., 2020, 10, 12017 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. G. Bajpayee, M. Scheu, A. J. Grodzinsky and R. M. Porter, J. Orthop. Res., 2015, 33, 660–667 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. S. Toh, R. Yarani, S. El Andaloussi, B. S. Cho, C. Choi, R. Corteling, A. De Fougerolles, M. Gimona, J. Herz, M. Khoury, P. D. Robbins, D. Williams, D. J. Weiss, E. Rohde, B. Giebel and S. K. Lim, Cytotherapy, 2023, 25, 810–814 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. K. Lim, B. Giebel, D. J. Weiss, K. W. Witwer and E. Rohde, Stem Cells Dev., 2020, 29, 877–878 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. J. Weiss, S. K. Lim, E. Rohde, K. W. Witwer and B. Giebel, Stem Cells Dev., 2020, 29, 1533–1534 CrossRef PubMed.
- V. Sengupta, S. Sengupta, A. Lazo, P. Woods, A. Nolan and N. Bremer, Stem Cells Dev., 2020, 29, 747–754 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. L. Lightner, V. Sengupta, S. Qian, J. T. Ransom, S. Suzuki, D. J. Park, T. I. Melson, B. P. Williams, J. J. Walsh and M. Awili, Chest, 2023, 164, 1444–1453 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. A. Bellio, C. Bennett, A. Arango, A. Khan, X. Xu, C. Barrera, V. Friedewald and M. I. Mitrani, Biomater. Biosyst., 2021, 4, 100031 CAS.
- M. I. Mitrani, M. A. Bellio, A. Sagel, M. Saylor, W. Kapp, K. VanOsdol, G. Haskell, D. Stewart, Z. Abdullah, I. Santos, J. Milberg, A. Arango, A. Mitrani and G. C. Shapiro, Front. Med., 2021, 8, 583842 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Vakhshiteh, F. Atyabi and S. N. Ostad, Int. J. Nanomed., 2019, 14, 2847–2859 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Yassine and N. Alaaeddine, Adv. Biol., 2022, 6, e2101050 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. A. Dad, T.-W. Gu, A.-Q. Zhu, L.-Q. Huang and L.-H. Peng, Mol. Ther., 2021, 29, 13–31 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |