Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Strain induced reactivity of cyclic iminoboranes: the (2 + 2) cycloaddition of a 1H-1,3,2-diazaborepine with ethene†
Divanshu
Gupta
 ,
Ralf
Einholz
,
Ralf
Einholz
 and
Holger F.
Bettinger
and
Holger F.
Bettinger
 *
*
Institut für Organische Chemie, Universität Tübingen, Auf der Morgenstelle 18, 72076 Tübingen, Germany. E-mail: holger.bettinger@uni-tuebingen.de
First published on 12th December 2023
Abstract
Iminoboranes have gathered immense attention due to their reactivity and potential applications as isoelectronic and isosteric alkynes. While cyclic alkynes are well investigated and useful reagents, cyclic iminoboranes are underexplored and their existence was inferred only via trapping experiments. We report the first direct spectroscopic evidence of a cyclic seven-membered iminoborane, 1-(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)-1H-1,3,2-diazaborepine 2, under cryogenic matrix isolation conditions. The amino-iminoborane 2 was photochemically generated in solid argon at 4 K from 2-azido-1-(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)-1,2-dihydro-1,2-azaborinine (3) and was characterized using FT-IR, UV-vis spectroscopy, and computational chemistry. The characteristic BN stretching vibration (1751 cm−1) is shifted by about 240 cm−1 compared to linear amino-iminoboranes indicating a significant weakening of the bond. The Lewis acidity value determined computationally (LAB = 9.1 ± 2.6) is similar to that of boron trichloride, and twelve orders of magnitude lower than that of 1,2-azaborinine (BN-aryne, LAB = 21.5 ± 2.6), a six-membered cyclic iminoborane. In contrast to the latter, the reduced ring strain of 2 precludes nitrogen fixation, but it unexpectedly allows facile (2 + 2) cycloaddition reaction with C2H4 under matrix isolation conditions at 30 K.
Introduction
Iminoboranes are an important class of BN containing compounds.1–3 The BN/CC isosterism relates iminoboranes and alkynes (Scheme 1a).4 In contrast to the latter, iminoboranes are kinetically unstable towards cyclooligomerization or polymerization and thus special conditions or steric protection are required for their synthesis and isolation.1,2,5–12 The first iminoborane stable at room temperature, F5C6-BN-tBu, was reported by Paetzold et al.,11 and followed by numerous examples.2,9,13–15 Since then, iminoboranes have attracted tremendous attention.16–23 Various iminoboranes have been investigated over the past decades to understand their reactivity24–27 including the formation of BN-doped polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs),28–32 formation of N-heterocyclic carbene coordinated iminoboranes,25,33–36 synthesis of BN containing heterocycles,37–44 (2 + 2) and (2 + 3) cycloaddition reactions with a number of polar double bonds (e.g., RR′C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) and dipolar reagents,45–50 formation of iminoboryl carboranes,19,51 and use of frustrated Lewis pairs to stabilize iminoboranes.19,52–57 A series of ab initio computational studies performed by Gilbert compared iminoboranes and alkynes with respect to the electronic and geometric structure, as well as the reactivity in (2 + 2) and (2 + 4) cycloadditions towards alkenes and alkynes.58–60
O) and dipolar reagents,45–50 formation of iminoboryl carboranes,19,51 and use of frustrated Lewis pairs to stabilize iminoboranes.19,52–57 A series of ab initio computational studies performed by Gilbert compared iminoboranes and alkynes with respect to the electronic and geometric structure, as well as the reactivity in (2 + 2) and (2 + 4) cycloadditions towards alkenes and alkynes.58–60
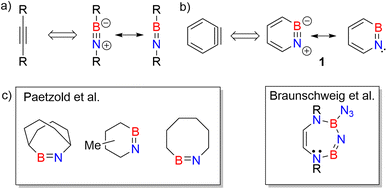 | ||
| Scheme 1 (a) Iminoboranes and their analogy with alkynes. (b) Resonance forms of 1,2-azaborinine (1) and its analogy with ortho-benzyne. (c) Representative examples of cyclic iminoboranes previously inferred as reactive intermediates by Paetzold et al.61 and Braunschweig et al.42 | ||
Studies on cyclic iminoboranes are quite rare.42,61 Due to ring strain, they are more reactive than linear iminoboranes,1 but coordination by N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHC) provides a way of stabilization.36,62,63 A special case of cyclic iminoboranes is the aromatic BN-aryne, 1,2-azaborinine 1, the BN analogue of ortho-benzyne (Scheme 1b).64–66 This was detected by matrix isolation methods by our group and shows remarkably high reactivity towards inert molecules.64–66 The polarity of the strained BN link of 1 results in a bonding situation that differs from that of the strained triple bond in arynes and from that of the BN unit in linear iminoboranes.64,66,67 The dibenzo derivative of 1, dibenzo[c,e][1,2]azaborinine, was inferred as reactive intermediate in solution,68–70 and can even activate the strong Si–F bond for subsequent insertion reaction.70
As iminoborane units in larger than six-membered rings have never been observed directly, but only inferred from trapping experiments (Scheme 1c),42,61 we studied the seven membered 1-(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)-1H-1,3,2-diazaborepine 2 to elucidate the impact of ring size on the reactivity of cyclic iminoboranes. The matrix isolation technique is ideally suited to study such highly reactive intermediates directly, and furthermore probe their reactivity towards interesting compounds. We generated target compound 2 in solid argon by the photolysis of 2-azido-1-(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)-1,2-dihydro-1,2-azaborinine (3) under cryogenic matrix conditions (see Scheme 2). On one hand, ring strain will be reduced in this seven-membered ring iminoborane compared to 1 and this is expected to reduce its reactivity, while on the other hand, the eight π-electron count may induce some degree of antiaromaticity that will potentially destabilize 2. Seven-membered cyclic iminoboranes were never directly observed, but recently inferred as reactive intermediate in the formation of diazadiboretidines by Braunschweig and co-workers.42 We provide here for the first time direct spectroscopic evidence for a cyclic seven-ring iminoborane and reveal its unexpectedly facile (2 + 2) cycloaddition reaction (Scheme 2).
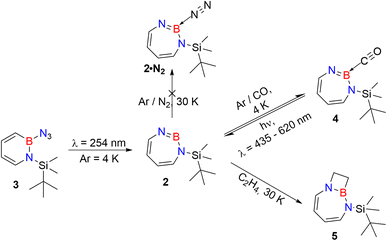 | ||
| Scheme 2 Photogeneration of 1-(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)-1,3,2-diazaborepine 2 under matrix isolation conditions and its reaction with CO and C2H4. | ||
Results and discussion
Generation and characterization of cyclic iminoborane 2
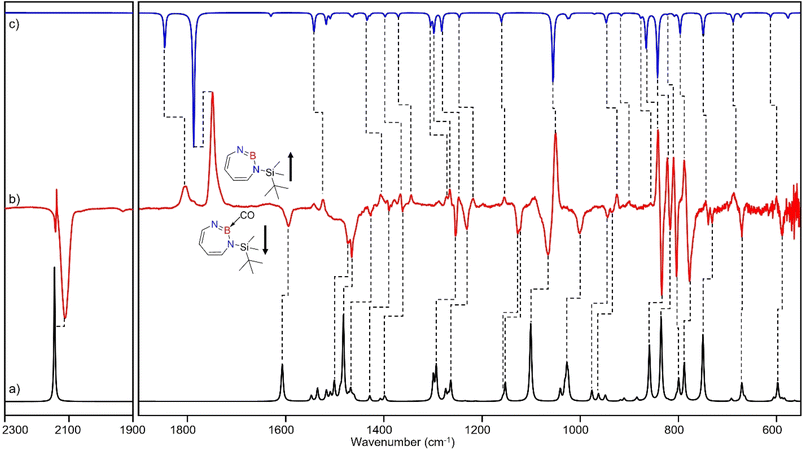
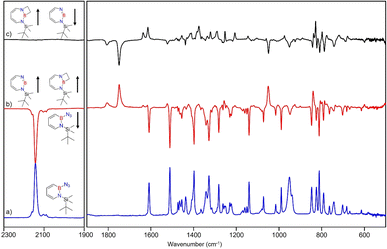
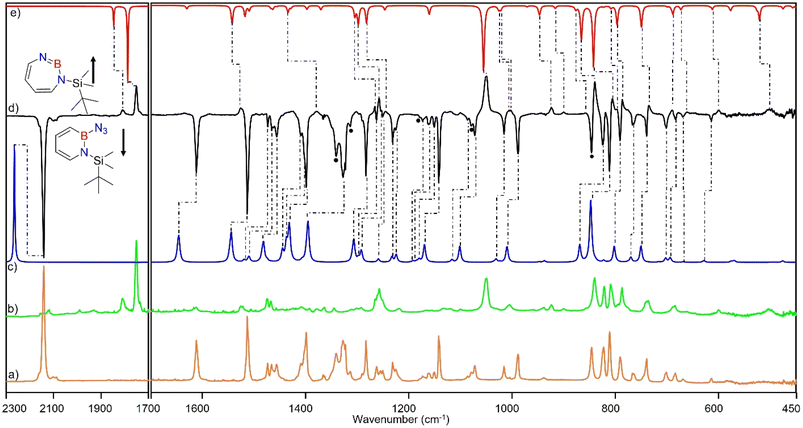
Matrix-isolation infrared spectroscopic studies of 3 were performed in solid Ar at 4 K. The most distinguished peak at 2141 cm−1 corresponds to the azide stretching vibration (Fig. 1, S9, S10 and Table S13 in ESI†). Irradiation of matrix isolated precursor 3 with λ = 254 nm until it was completely bleached, as shown in the difference spectrum (Fig. 1d), resulted in a new set of IR bands. This set is assigned to 2 based on comparison with computational data obtained at the B3LYP-D3(BJ)/6-311+G(d,p) level of theory (Fig. 1e). The formation of the structural isomer 1H-1,2,3-diazaborepine or the triplet boryl nitrene, the expected primary product of N2 extrusion from 3, can be excluded based on the computations (see Fig. S15†). Among the new bands formed during photolysis of 3, the most intense peak, 1751 cm−1 corresponds to the BN stretching vibration of 2 (Table S15†) by comparison with the computations (Fig. 1e). The band at 1809 cm−1 corresponds to the BN stretching vibration of the 10B isotopologue, and the isotopic shift of 58 cm−1 is in good agreement with computations (60 cm−1). The formation of the 1H-1,3,2-diazaborepine isomer is in agreement with the known behavior of azidoboranes: thermolysis or photolysis of diorganyl azidoboranes results in iminoboranes without trappable borylnitrenes,1 while only in the case of donor substitution (X = NR2, OR) the borylnitrenes X2BN could be trapped or directly observed.71–77 The photolysis of azide 3 is thus expected to result in ring enlargement by shift of the carbon rather than the nitrogen center to give the cyclic iminoborane 2.For linear amino-iminoboranes, the BN stretching mode was reported around 1990 cm−1 and 2030 cm−1 for the 11B and 10B isotopologues, respectively.78,79 The large shift of the BN stretching frequency of 2 from linear diorganyl substituted amino-iminoboranes of around 240 cm−1 is due to the cyclic nature of 2 which results in considerable weakening of the BN bond. Note that the BN stretching for 1 at 1637/1634 cm−1 indicates an even weaker BN bond in the six-membered ring.64
UV/vis spectroscopy (Fig. 2) of the azide 3 in Ar at 8 K shows a strong feature around 290 nm with fine structure and maxima at 296 nm, 288 nm, and 244 nm that is typical for 1,2-dihydro-1,2-azaborinines.80,81 Irradiation with λ = 254 nm results in quick decrease of the azide absorption band with an isosbestic point at 313 nm. The photoproduct 2 only has a relatively weaker and broad absorption maximum centered at 305 nm. The measured spectra of 3 and 2 are in good agreement with TD-CAM-B3LYP/6-311+G(d,p) computations (Fig. S8†).
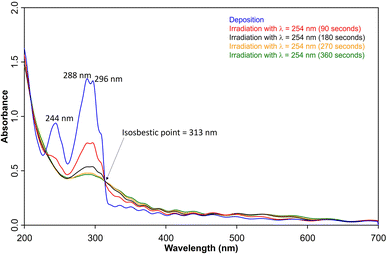 | ||
| Fig. 2 UV-vis spectra of 3 (blue: after deposition at 28 K, λmax = 288 nm) and subsequent formation 2 (λmax = 308 nm) after various irradiation (λ = 254 nm) steps under matrix isolation conditions. | ||
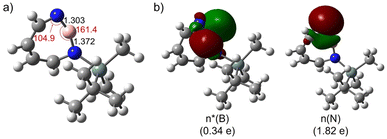
The most remarkable feature of the computed geometry (M06-2X/6-311+G(d,p)) of 2 is the distortion of the heptagon with a small angle of 104.9° at dicoordinated nitrogen and a large angle of 161.4° at boron in the singlet ground state (Fig. 3a). Similarly to the case of 1,2-azaborinine,64 this feature can be rationalized by the difference in electronegativity: the more electronegative N atom prefers to have a σ-type lone pair (HOMO-1), while the more electropositive B atom prefers an empty σ-type orbital (LUMO) which has a strong p character (Fig. 3b). The natural bond orbital (NBO) analysis at the M06-2X/6-311+G(d,p) level of theory arrives at occupancies of 1.82e− and 0.34e− for the lone pair and empty orbitals, respectively. There is a pronounced n(N) → n*(B) interaction [E(2) = 34.5 kcal mol−1] according to the second-order perturbation estimate of the donor–acceptor interaction in the NBO basis that is smaller than that in 1 (39.7 kcal mol−1). The natural charges obtained from the NBO analysis on N and B are large (−0.91 on N and +1.16 on B) while the Wiberg bond index between B and N is only 1.55. Compared to 1,2-azaborinine 1 the Wiberg bond index is larger (1.43 in 1) and the polarity of the BN bond (natural charges in 1: −0.81 on N and +1.00 on B; NBO occupancies of 1.82e− and 0.21e− for the lone pair and empty orbitals) is slightly increased in 2.
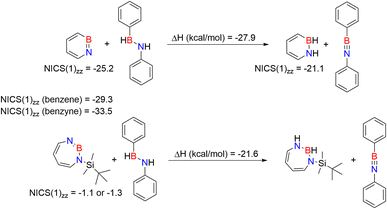
We compared the aromatic character of 2 with that of 1, benzene, and benzyne using nuclear independent chemical shift (NICS) calculations,82–84 placing the dummy atom 1 Å above the center of the ring to get the NICS(1)zz value. 1,2-Azaborinine 1 has a NICS(1)zz value of −25.2 which is lower than that of benzene (−29.3) and benzyne (−33.5), but still suggests aromatic character that is slightly larger than that of 1,2-dihydro-1,2-azaborine (NICS(1)zz = −21.1) (Scheme 3).85 The NICS(1)zz value of −1.1 and −3.1 computed for 2 is significantly lower suggesting that the antiaromaticity expected on the basis of the formal electron count is not relevant (see Fig. S17†). The two slightly differing values for 2 are due to the non-planar ring. The NICS(1)zz value of antiaromatic D2h cyclobutadiene is +10.9 computed at the same level of theory.
We compared the strain of the two cyclic iminoboranes 1 and 2 by considering homodesmotic reactions (Scheme 3). As expected, the strain energy of the seven-membered ring iminoborane 2 is lower than that of 1 by approximately 6.3 kcal mol−1 at the M06-2X/6-311+G(d,p) level of theory. We also computed the Lewis acidities (LAB) of 1 and 2 using the method of Ofial et al. from known Lewis basicities LBB and Lewis acidities LAB, computed equilibrium constants (Scheme 4, 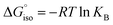 ), and the equation log KB = LAB + LBB.86 Ofial et al.86 obtained the LAB parameters from ΔGiso to give LAB = 8.4 ± 2.0 for BF3, LAB = 9.3 ± 1.8 for BCl3, and LAB = 10.1 ± 1.3 for BBr3. The qualitative ordering obtained by Ofial et al.86 of Lewis acidities LAB with BF3 < BCl3 < BBr3 is in accordance with Lewis acidity rankings based on spectroscopic data.87–89 The individual LAB parameters obtained from ΔGiso for three different reference bases were averaged to give LAB = 21.5 ± 2.6 for 1 and LAB = 9.1 ± 2.6 for 2 (see the ESI† for further details). While the Lewis acidity of 2 is thus similar to that of BCl3, that of 1 is 12 orders of magnitudes larger.
), and the equation log KB = LAB + LBB.86 Ofial et al.86 obtained the LAB parameters from ΔGiso to give LAB = 8.4 ± 2.0 for BF3, LAB = 9.3 ± 1.8 for BCl3, and LAB = 10.1 ± 1.3 for BBr3. The qualitative ordering obtained by Ofial et al.86 of Lewis acidities LAB with BF3 < BCl3 < BBr3 is in accordance with Lewis acidity rankings based on spectroscopic data.87–89 The individual LAB parameters obtained from ΔGiso for three different reference bases were averaged to give LAB = 21.5 ± 2.6 for 1 and LAB = 9.1 ± 2.6 for 2 (see the ESI† for further details). While the Lewis acidity of 2 is thus similar to that of BCl3, that of 1 is 12 orders of magnitudes larger.
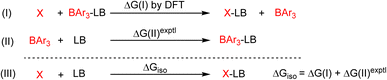 | ||
| Scheme 4 Combining the isodesmic reaction [eqn (I)] with an experimental reference reaction [eqn (II)] allows one to determine the Lewis acidities of X (X= 1 or 2) from ΔGiso [eqn (III)]. The Lewis bases pyridine, acetonitrile, and benzaldehyde and the Lewis acids BAr3 (Ar = C6H5, 4-ClC6H4, 3,4,5-F3C6H2) were chosen as references. The borane Lewis acidity scale is defined so that LAB(triphenylborane) = 0 following Ofial et al.86 | ||
Interaction of 2 with N2
A hallmark of the superelectrophilic 1,2-azaborinine 1 is its ability to bind nitrogen to give adduct 1·N2 under cryogenic conditions.64 In order to study the Lewis acidity of the photogenerated 1H-1,3,2-diazaborepine 2 experimentally, the matrix was annealed up to 35 K. This did not lead to any further spectral changes, indicating that 2 cannot bind the photochemically extruded N2 that is lying in its vicinity. The potential energy paths computed with the B–N2 distance as parameter (B3LYP-D3(BJ)/6-311+G(d,p)) reveal that formation of the dative complex 2·N2 is energetically unfavorable and involves a barrier (Fig. 4a). In contrast, formation of 1·N2 is without barrier and exothermic (Fig. 4b).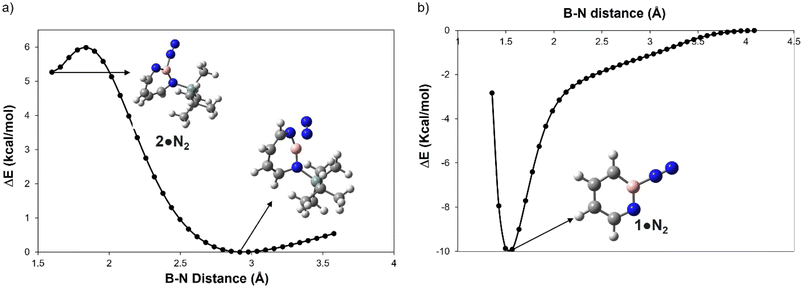 | ||
| Fig. 4 Plot for the relative energy in kcal mol−1 as a function of the boron N2 distance in Å for (a) 2 and (b) 1 computed at B3LYP-D3(BJ)/6-311+G(d,p) level of theory. | ||
Interaction of 2 with CO
The stronger Lewis base CO can undergo formation of adduct 4 as revealed in experiments using mixtures of Ar and CO (1–2% in Ar) (Scheme 2 and Fig. 5). In separate experiments, the isotopologues 13CO and C18O (Fig. S11–S13†) were employed in order to obtain isotopic shifts of vibrational bands for comparison with computations.Irradiation of matrix-isolated precursor 3 with λ = 254 nm forms 2 in the presence of CO. Annealing the matrix to 30 K allows the formation of distinct bands which decrease upon subsequent irradiation with 435 nm > λ > 620 nm, while the bands corresponding to 2 collectively form again (see Fig. 5). We assign the bands formed after annealing of the matrix to 30 K to the Lewis acid–base adduct 4 based on comparison with the vibrational spectrum computed at the B3LYP-D3(BJ)/6-311+G(d,p) level of theory (see Fig. 6). The formation of the (2 + 1) product 4_(2 + 1) can be excluded based on the computations (see Fig. S16†).
The most intense peak at 2112 cm−1 is due to the CO stretching vibration of the Lewis acid–base adduct 4 (Table S16†). It is observable at 2065 cm−1 and 2064 cm−1 for the C18O and 13CO isotopologues, respectively (Tables S17 and S18†). These isotopic shifts of 47 cm−1 (12C18O vs.12C16O) and 48 cm−1 (13C16O vs.12C16O) are in very good agreement with those computed for 4 (47 cm−1 and 50 cm−1, respectively, see Table S19†).
The trapping of 2 with CO demonstrates that Lewis acid–base interaction is significantly preferred over (2 + 1) or (2 + 2) cycloaddition reactions, similar to the reaction of 1,2-azaborinine with CO.66 The formation of 4 has a barrier of 1.3 kcal mol−1 from the complex 4_comp′ at the DLPNO-CCSD(T)/cc-pVTZ//M06-2X/6-311+G(d,p) level of theory (Fig. 7). The formation of the (2 + 1) product 4_(2 + 1) from 4 is energetically uphill and cannot proceed thermally as its barrier of 6.4 kcal mol−1 (Fig. 7) is too high for this reaction to be observable at 30 K under matrix isolation conditions. The formation of the (2 + 2) cycloaddition product via complex 4_comp, the most stable product (−11.2 kcal mol−1 with respect to 2 + CO), is more favourable than 4 or 4_(2+1) by 3.3 kcal mol−1 and 6.8 kcal mol−1, respectively. But as it involves a barrier of 23.1 kcal mol−1 at the DLPNO-CCSD(T)/cc-pVTZ//M06-2X/6-311+G(d,p) level of theory, the reaction to 4_(2+2) cannot proceed under our experimental conditions. The trapping of 2 with CO demonstrates that Lewis acid–base interaction is significantly preferred over (2 + 1) or (2 + 2) cycloaddition reactions.
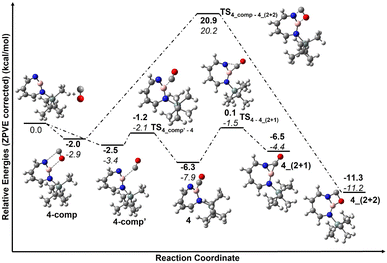 | ||
| Fig. 7 Reaction pathways for the reaction of 2 with CO at (bold: M06-2X/6-311+G(d,p); italics: DLPNO-CCSD(T)/cc-pVTZ//M06-2X/6-311+G(d,p)). Calculated ZPVE corrected energies in kcal mol−1 are shown. | ||
Reaction of 2 with ethene
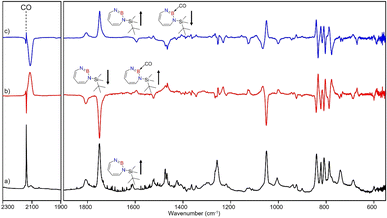
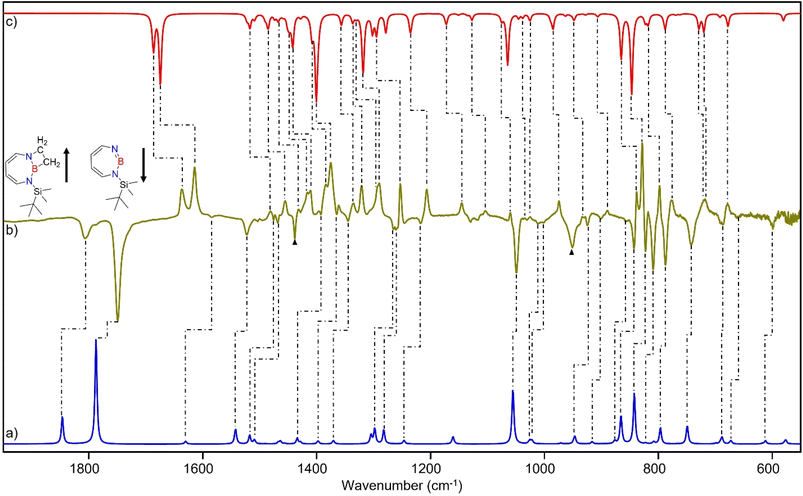
After the successful generation of 2 and its trapping with CO, we used ethene as the simplest olefin for studying of the reactivity of 2 in (2 + 2) cycloaddition reactions. To examine the trapping of 2 with ethene, matrix-isolated precursor 3 was irradiated in the presence of 5% C2H4 in Ar with λ = 254 nm, which again resulted in 1H-1,3,2-diazaborepine 2. But apart from 2, new signals were also observed (Fig. 8) that we assigned with the help of the computed spectrum to 5, the (2 + 2) cycloaddition product between 2 and C2H4 (Scheme 2 and Fig. 9). Subsequently, the matrix was annealed to 30 K and it was observed that the set of signals corresponding to 2 were diminished (Fig. 8c), while the set of signals assigned to 5 increased in intensity (Fig. 8c). This shows that the formation of 5 from 2 and ethene can proceed thermally with a very low activation barrier.The prominent and characteristic signals of 5, 1637 cm−1 and 1615 cm−1, are attributed to the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C stretching vibration of the diazaborepine ring (Tables S20 and S21†). The same C
C stretching vibration of the diazaborepine ring (Tables S20 and S21†). The same C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C stretching vibrations at 1637 cm−1 and 1615 cm−1 were also observed for the C2D4 isotope as the stretching mode does not involve any vibration of the ethene unit (Fig. S14†). The other most intense peaks were observed at 828 cm−1 and 1376 cm−1, which we assigned to a vibration including ring stretching and CH wagging of C2H4 and BN stretching and CH wagging, respectively. In case of C2D4, the most intense peak was observed at 1372 cm−1 attributed to BN stretching and CH wagging while a peak at 813 cm−1 corresponding to CH wagging of C2D4 was not so intense in case of reaction with C2D4. The experimentally observed isotopic shifts are in good agreement with the isotopic shift computed at the B3LYP-D3(BJ)/6-311+G(d,p) level of theory (see Table S22 in ESI†).
C stretching vibrations at 1637 cm−1 and 1615 cm−1 were also observed for the C2D4 isotope as the stretching mode does not involve any vibration of the ethene unit (Fig. S14†). The other most intense peaks were observed at 828 cm−1 and 1376 cm−1, which we assigned to a vibration including ring stretching and CH wagging of C2H4 and BN stretching and CH wagging, respectively. In case of C2D4, the most intense peak was observed at 1372 cm−1 attributed to BN stretching and CH wagging while a peak at 813 cm−1 corresponding to CH wagging of C2D4 was not so intense in case of reaction with C2D4. The experimentally observed isotopic shifts are in good agreement with the isotopic shift computed at the B3LYP-D3(BJ)/6-311+G(d,p) level of theory (see Table S22 in ESI†).
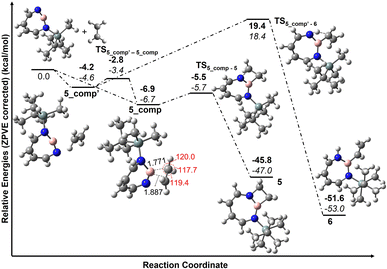
According to computations at the DLPNO-CCSD(T)/cc-pVTZ//M06-2X/6-311+G(d,p) level of theory, 2 can interact with ethene to give two complexes, 5_comp′ and 5_comp, that are lower in energy than the separated reactants by 4.6 and 6.7 kcal mol−1, respectively (see Fig. 10). The interconversion between complexes 5_comp′ and 5_comp is associated with a barrier of 1.2 kcal mol−1. The formation of the (2 + 2) cycloaddition product 5 from complex 5_comp can proceed thermally as its barrier of 1.0 kcal mol−1 (Fig. 10) is small enough for this reaction to be observable at 30 K under matrix isolation conditions. Formation of the C–H insertion product 6via a concerted pathway from complex 5_comp′ involves a barrier of 23.0 kcal mol−1. This is significantly higher than the barrier of (2 + 2) addition product formation (Fig. 10) and explains the preferred formation of 5 in the experiment.
Complex 5_comp has carbon-boron distances (1.771 Å and 1.887 Å) that are shorter than the sum of van-der-Waals radii (3.62 Å) (see Fig. 10) indicative of a Lewis acid–base interaction.90,91 The H–C–H and H–C–C angles have changed so that the sum of bond angles around carbon is 357.1 and 359.6°, showing a slight deviation from planarity around carbon atoms in C2H4. The complex 5_comp is formed due to the interaction between the empty boron orbital with high p-character and the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C π-bond. Further insight into the nature of bonding in 5_comp is provided by natural bond orbital analysis.92–95 The second-order perturbation theory analysis in the NBO basis gives an E(2) value of 314.8 kcal mol−1, implying strong stabilization due to π(C2H4) → n*(B)(empty orbital on boron) delocalization. The corresponding natural localized molecular orbitals (NLMO) have major contributions from the π(C
C π-bond. Further insight into the nature of bonding in 5_comp is provided by natural bond orbital analysis.92–95 The second-order perturbation theory analysis in the NBO basis gives an E(2) value of 314.8 kcal mol−1, implying strong stabilization due to π(C2H4) → n*(B)(empty orbital on boron) delocalization. The corresponding natural localized molecular orbitals (NLMO) have major contributions from the π(C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C) bond orbitals and “delocalization tails” of 20.6% from a slightly hybridized vacant orbital at boron (Tables S11 and S12†).
C) bond orbitals and “delocalization tails” of 20.6% from a slightly hybridized vacant orbital at boron (Tables S11 and S12†).
The comparison of the reaction mechanism for the reaction of ethene with 1,2-azaborinine 1 and 1-(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)-1,3,2-diazaborepine 2 is instructive. The former interacts with ethene to give a Lewis acid–base complex whose formation is thermodynamically highly exothermic (−23.7 kcal mol−1 at CCSD(T)/cc-pVTZ//M06-2X/6-311+G(d,p)).67 This complex is so low in energy that the formation of the (2 + 2) cycloaddition product has a barrier of 14.6 kcal mol−1 at CCSD(T)/cc-pVTZ//M06-2X/6-311+G(d,p).67 This is significantly higher than the barrier for the (2 + 2) cycloaddition product 5 (1.0 kcal mol−1 from 5_comp).67 It is highly interesting and unexpected that the much less Lewis acidic 2 is undergoing unprecedented (2 + 2) cycloaddition with ethene while the highly Lewis acidic 1 is expected to be trapped in the Lewis acid–base complex with ethene as this reaction should not be observable at 30 K under matrix isolation conditions. Preliminary experiments of 1 + C2H4 indicate that thermally initiated (2 + 2) cycloaddition is not occurring under similar matrix isolation conditions.
Conclusions
We here for the first time reveal the generation, spectroscopic detection by matrix isolation, and reactivity studies of a seven-membered cyclic iminoborane of the 1H-1,3,2-diazaborepine type. The precursor 2-azido-1-(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)-1,2-dihydro-1,2-azaborinine (3) undergoes a photoinduced N2 extrusion and rearrangement to the 1-(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)-1H-1,3,2-diazaborepine 2 without detectable intermediates. Detailed combined experimental and computational investigations reveal that 2 shows high reactivity towards carbon monoxide and ethene even at the very low temperature. With CO, 2 reacts to form Lewis acid–base adduct 4 while the alternative (2 + 1) or (2 + 2) cycloaddition reactions were not observed due to high energy barriers. With C2H4, 2 undergoes (2 + 2) cycloaddition reaction to from product 5. The (2 + 2) cycloaddition with ethene discovered here shows that the 2 has the potential to provide novel modes of reactivity for the construction of BN-containing heterocycles.Data availability
The data underlying this study are available in the published article and its ESI.†Author contributions
D. G. investigation and writing of original draft, R. E. investigation and review & editing of the manuscript, H. F. B. conceptualization, supervision, providing resources, acquiring funding, and review & editing of manuscript.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG) through grant BE 3183/6-2 and in part by the Dr K. H. Eberle foundation. The computations were performed on BwForCluster JUSTUS2 cluster. The authors acknowledge support by the state of Baden-Württemberg through bwHPC and the German Research Foundation (DFG) through grant no. INST 40/575-1 FUGG (JUSTUS 2 cluster) for computation facilities.References
- P. Paetzold, in Advances in Inorganic Chemistry, Elsevier, 1987, vol. 31, pp. 123–170 Search PubMed.
- H. Nöth, Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 1988, 27, 1603–1623 CrossRef.
- Y. Fan, J. Cui and L. Kong, Eur. J. Org Chem., 2022, 2022, e202201086 CrossRef.
- Z. Liu and T. B. Marder, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2008, 47, 242–244 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. R. Lory and R. F. Porter, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1973, 95, 1766–1770 CrossRef CAS.
- C. A. Thompson and L. Andrews, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1995, 117, 10125–10126 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Zhang, P. Maksyutenko, R. I. Kaiser, A. M. Mebel, A. Gregušová, S. A. Perera and R. J. Bartlett, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2010, 114, 12148–12154 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. C. Baird and R. K. Datta, Inorg. Chem., 1972, 11, 17–19 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Paetzold, C. V. Plotho, G. Schmid, R. Boese, B. Schrader, D. Bougeard, U. Pfeiffer, R. Gleiter and W. Schüfer, Chem. Ber., 1984, 117, 1089–1102 CrossRef CAS.
- V. M. Rosas-Garcia, J. Theor. Comput. Chem., 2011, 967, 160–164 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Paetzold, A. Richter, T. Thijssen and S. Würtenberg, Chem. Ber., 1979, 112, 3811–3827 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Paetzold and C. von Plotho, Chem. Ber., 1982, 115, 2819–2825 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Paetzold, Pure Appl. Chem., 1991, 63, 345–350 CrossRef CAS.
- E. v. Steuber, G. Elter, M. Noltemeyer, H.-G. Schmidt and A. Meller, Organometallics, 2000, 19, 5083–5091 CrossRef.
- M. Haase and U. Klingebiel, Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 1985, 24, 324 CrossRef.
- R. Guo, T. Li, R. Wei, X. Zhang, Q. Li, L. L. Liu, C.-H. Tung and L. Kong, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143, 13483–13488 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Guo, X. Zhang, T. Li, Q. Li, D. A. Ruiz, L. L. Liu, C.-H. Tung and L. Kong, Chem. Sci., 2022, 13, 2303–2309 RSC.
- D. Schleier, D. Schaffner, M. Gerlach, P. Hemberger and I. Fischer, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022, 24, 20–24 RSC.
- J. Wang, P. Jia, W. Sun, Y. Wei, Z. Lin and Q. Ye, Inorg. Chem., 2022, 61, 8879–8886 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Wrackmeyer, Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem., 2015, 641, 2525–2529 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Bao, Y. Dai, C. Liu and Y. Su, Inorg. Chem., 2022, 61, 11137–11142 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Raiser, H. Schubert, H. F. Bettinger and L. Wesemann, Chem. – Eur. J., 2021, 27, 1981–1983 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Winner, W. C. Ewing, K. Geetharani, T. Dellermann, B. Jouppi, T. Kupfer, M. Schaefer and H. Braunschweig, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 12275–12279 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Braunschweig, A. Damme, J. O. C. Jimenez-Halla, B. Pfaffinger, K. Radacki and J. Wolf, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 10034 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Braunschweig, W. C. Ewing, K. Geetharani and M. Schaefer, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 1662–1665 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Schaefer, N. A. Beattie, K. Geetharani, J. Schaefer, W. C. Ewing, M. Krahfuss, C. Hoerl, R. D. Dewhurst, S. A. Macgregor, C. Lambert and H. Braunschweig, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 8212–8220 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Schaefer, J. Schaefer, R. D. Dewhurst, W. C. Ewing, M. Krahfuss, M. W. Kuntze-Fechner, M. Wehner, C. Lambert and H. Braunschweig, Chem. – Eur. J., 2016, 22, 8603–8609 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Ayhan, T. Eckert, F. A. Plamper and H. Helten, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 13321–13325 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Lorenz, M. Crumbach, T. Eckert, A. Lik and H. Helten, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 2780–2784 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Ayhan, N. A. Riensch, C. Glasmacher and H. Helten, Chem. – Eur. J., 2018, 24, 5883–5894 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Beweries and H. Helten, in Encyclopedia of Inorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry, Wiley Online Library, 2020, pp. 1–25 Search PubMed.
- L. Winner, A. Hermann, G. Belanger-Chabot, O. F. Gonzalez-Belman, J. O. C. Jimenez-Halla, H. Kelch and H. Braunschweig, Chem. Commun., 2018, 54, 8210–8213 RSC.
- D. Franz and S. Inoue, Chem. – Asian J., 2014, 9, 2083–2087 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Braunschweig, R. D. Dewhurst, W. C. Ewing, M. W. Kuntze-Fechner and M. Schaefer, Chem. – Eur. J., 2017, 23, 5953–5956 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Cui, R. Guo, L. Kong and C. Cui, Inorg. Chem., 2020, 59, 5261–5265 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Koner, T. Sergeieva, B. Morgenstern and D. M. Andrada, Inorg. Chem., 2021, 60, 14202–14211 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Prieschl, G. Belanger-Chabot, X. Guo, M. Dietz, M. Mueller, I. Krummenacher, Z. Lin and H. Braunschweig, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 1065–1076 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Noguchi, K. Suzuki, J. Kobayashi, T. Yurino, H. Tsurugi, K. Mashima and M. Yamashita, Organometallics, 2018, 37, 1833–1836 CrossRef CAS.
- M. W. Lui, N. R. Paisley, R. McDonald, M. J. Ferguson and E. Rivard, Chem. – Eur. J., 2016, 22, 2134–2145 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Xie, J. Zhang and C. Cui, Chem. – Eur. J., 2014, 20, 9500–9503 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Xie, J. Zhang, H. Hu and C. Cui, Organometallics, 2013, 32, 6875–6878 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Thiess, G. Belanger-Chabot, F. Fantuzzi, M. Michel, M. Ernst, B. Engels and H. Braunschweig, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 15480–15486 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Matler, M. Arrowsmith, F. Schorr, A. Hermann, A. Hofmann, C. Lenczyk and H. Braunschweig, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2021, 2021, 4619–4631 CrossRef CAS.
- T.-T. Liu, J. Chen, B.-T. Guan, Z. Lin and Z.-J. Shi, Chem. – Eur. J., 2023, 29, e202203676 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Paetzold, C. von Plotho, E. Niecke and R. Rüger, Chem. Ber., 1983, 116, 1678–1681 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Paetzold, K. Delpy, R. P. Hughes and W. A. Herrmann, Chem. Ber., 1985, 118, 1724–1725 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Braunschweig, P. Paetzold and R. Boese, Chem. Ber., 1993, 126, 1571–1577 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Kröckert, K.-H. van Bonn and P. Paetzold, Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem., 2005, 631, 866–868 CrossRef.
- M. Nutz, B. Borthakur, R. D. Dewhurst, A. Deissenberger, T. Dellermann, M. Schaefer, I. Krummenacher, A. K. Phukan and H. Braunschweig, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 7975–7979 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Winner, G. Belanger-Chabot, M. A. Celik, M. Schaefer and H. Braunschweig, Chem. Commun., 2018, 54, 9349–9351 RSC.
- H. Zhang, J. Wang, W. Yang, L. Xiang, W. Sun, W. Ming, Y. Li, Z. Lin and Q. Ye, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 17243–17249 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. L. Frenette, A. A. Omana, M. J. Ferguson, Y. Zhou and E. Rivard, Chem. Commun., 2021, 57, 10895–10898 RSC.
- A. Wong, J. Chu, G. Wu, J. Telser, R. Dobrovetsky and G. Menard, Inorg. Chem., 2020, 59, 10343–10352 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Mehta and J. M. Goicoechea, Chem. Commun., 2019, 55, 6918–6921 RSC.
- A. A. Omana, R. Watt, Y. Zhou, M. J. Ferguson and E. Rivard, Inorg. Chem., 2022, 61, 16430–16440 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. K. Swarnakar, C. Hering-Junghans, K. Nagata, M. J. Ferguson, R. McDonald, N. Tokitoh and E. Rivard, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 10666–10669 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. K. Swarnakar, C. Hering-Junghans, M. J. Ferguson, R. McDonald and E. Rivard, Chem. Sci., 2017, 8, 2337–2343 RSC.
- T. M. Gilbert, Organometallics, 2000, 19, 1160–1165 CrossRef CAS.
- T. M. Gilbert, Organometallics, 2003, 22, 2298–2304 CrossRef CAS.
- T. M. Gilbert, Organometallics, 2005, 24, 6445–6449 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Münster, P. Paetzold, E. Schröder, H. Schwan and T. von Bennigsen-Mackiewicz, Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem., 2004, 630, 2641–2651 CrossRef.
- Z. X. Giustra and S.-Y. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 1184–1194 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. G. Campbell, A. J. V. Marwitz and S.-Y. Liu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 6074–6092 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Edel, S. A. Brough, A. N. Lamm, S.-Y. Liu and H. F. Bettinger, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 7819–7822 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Edel, R. F. Fink and H. F. Bettinger, J. Comput. Chem., 2016, 37, 110–116 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Edel, J. S. A. Ishibashi, S.-Y. Liu and H. F. Bettinger, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 4061–4064 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Gupta and H. F. Bettinger, J. Org. Chem., 2023, 88, 8369–8378 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Müller, C. Maichle-Mössmer and H. F. Bettinger, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 9380–9383 CrossRef.
- H. F. Bettinger and M. Müller, J. Phys. Org. Chem., 2015, 28, 97–103 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Keck, J. Hahn, D. Gupta and H. F. Bettinger, Chem. – Eur. J., 2022, 28, e202103614 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Pieper, D. Schmitz and P. Paetzold, Chem. Ber., 1981, 114, 3801–3812 CrossRef CAS.
- H. F. Bettinger and H. Bornemann, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 11128–11134 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. F. Bettinger, M. Filthaus, H. Bornemann and I. M. Oppel, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2008, 47, 4744–4747 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. F. Bettinger and M. Filthaus, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2010, 8, 5477–5482 RSC.
- M. Filthaus, L. Schwertmann, P. Neuhaus, R. d. W. Seidel, I. M. Oppel and H. F. Bettinger, Organometallics, 2012, 31, 3894–3903 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Müller, C. Maichle-Mössmer and H. F. Bettinger, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 11773–11775 RSC.
- H. F. Bettinger, M. Filthaus and P. Neuhaus, Chem. Commun., 2009, 2186–2188 RSC.
- K.-H. v. Bonn, T. v. Bennigsen-Mackiewicz, J. Kiesgen, C. v. Plotho and P. Paetzold, Z. Naturforsch., B, 1988, 43, 61–68 CrossRef.
- H. Noeth and S. Weber, Z. Naturforsch. B, 1983, 38, 1460–1465 CrossRef.
- A. Chrostowska, S. Xu, A. N. Lamm, A. Mazière, C. D. Weber, A. Dargelos, P. Baylère, A. Graciaa and S.-Y. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 10279–10285 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Edel, X. Yang, J. S. A. Ishibashi, A. N. Lamm, C. Maichle-Mössmer, Z. X. Giustra, S.-Y. Liu and H. F. Bettinger, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 5296–5300 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Chen, C. S. Wannere, C. Corminboeuf, R. Puchta and P. v. R. Schleyer, Chem. Rev., 2005, 105, 3842–3888 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. v. R. Schleyer, C. Maerker, A. Dransfeld, H. Jiao and N. J. R. van Eikema Hommes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1996, 118, 6317–6318 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Gershoni-Poranne and A. Stanger, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 6597–6615 RSC.
- A. G. Papadopoulos, N. D. Charistos, K. Kyriakidou and M. P. Sigalas, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2015, 119, 10091–10100 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. J. Mayer, N. Hampel and A. R. Ofial, Chem. – Eur. J., 2021, 27, 4070–4080 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. B. Sivaev and V. I. Bregadze, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2014, 270–271, 75–88 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Döring, G. Erker, R. Fröhlich, O. Meyer and K. Bergander, Organometallics, 1998, 17, 2183–2187 CrossRef.
- A. Massey and A. Park, J. Organomet. Chem., 1966, 5, 218–225 CrossRef CAS.
- A. v. Bondi, J. Phys. Chem., 1964, 68, 441–451 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Mantina, A. C. Chamberlin, R. Valero, C. J. Cramer and D. G. Truhlar, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2009, 113, 5806–5812 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. E. Reed, L. A. Curtiss and F. Weinhold, Chem. Rev., 1988, 88, 899–926 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Glendening, C. Landis and F. Weinhold, Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: Comput. Mol. Sci., 2012, 2, 1–42 CAS.
- F. Weinhold, J. Comput. Chem., 2012, 33, 2363–2379 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. D. Glendening, C. R. Landis and F. Weinhold, J. Comput. Chem., 2013, 34, 1429–1437 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d3sc04901a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |

![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
: