 Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleHyperconjugation-controlled molecular conformation weakens lithium-ion solvation and stabilizes lithium metal anodes†
Yuelang
Chen‡
 ab,
Sheng-Lun
Liao‡
ab,
Sheng-Lun
Liao‡
 a,
Huaxin
Gong
a,
Huaxin
Gong
 a,
Zewen
Zhang
a,
Zewen
Zhang
 c,
Zhuojun
Huang
c,
Zhuojun
Huang
 c,
Sang Cheol
Kim
c,
Sang Cheol
Kim
 c,
Elizabeth
Zhang
ac,
Hao
Lyu
c,
Elizabeth
Zhang
ac,
Hao
Lyu
 a,
Weilai
Yu
a,
Weilai
Yu
 a,
Yangju
Lin
a,
Yangju
Lin
 a,
Philaphon
Sayavong
bc,
Yi
Cui
*cde,
Jian
Qin
a,
Philaphon
Sayavong
bc,
Yi
Cui
*cde,
Jian
Qin
 *a and
Zhenan
Bao
*a and
Zhenan
Bao
 *a
*a
aDepartment of Chemical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA. E-mail: jianq@stanford.edu; zbao@stanford.edu
bDepartment of Chemistry, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA
cDepartment of Materials Science and Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA. E-mail: yicui@stanford.edu
dDepartment of Energy Science and Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA
eStanford Institute for Materials and Energy Sciences, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Menlo Park, CA, USA
First published on 14th November 2024
Abstract
Tuning the solvation structure of lithium ions via electrolyte engineering has proven effective for lithium metal (Li) anodes. Further advancement that bypasses the trial-and-error practice relies on the establishment of molecular design principles. Expanding the scope of our previous work on solvent fluorination, we report here an alternative design principle for non-fluorinated solvents, which potentially have reduced cost, environmental impact, and toxicity. By studying non-fluorinated ethers systematically, we found that the short-chain acetals favor the [gauche, gauche] molecular conformation due to hyperconjugation, which leads to weakened monodentate coordination with Li+. The dimethoxymethane electrolyte showed fast activation to >99% coulombic efficiency (CE) and high ionic conductivity of 8.03 mS cm−1. The electrolyte performance was demonstrated in anode-free Cu‖LFP pouch cells at current densities up to 4 mA cm−2 (70 to 100 cycles) and thin-Li‖high-loading-LFP coin cells (200–300 cycles). Overall, we demonstrated and rationalized the improvement in Li metal cyclability by the acetal structure compared to ethylene glycol ethers. We expect further improvement in performance by tuning the acetal structure.
Introduction
The lithium-metal (Li) electrode has attracted enormous research interest.1 However, its high reactivity and large volume change pose significant challenges to battery stability.2,3 Electrolyte design is an effective strategy to overcome the instability.4 In recent years, numerous advanced electrolytes have enabled Li‖Cu half-cell coulombic efficiency (CE) of >99% with the desired chunky Li deposition morphology.5–25 The combination of LiFSI with rationally designed solvent(s) is among the most successful strategies.11,16,26 By controlling the solvation structure of Li+, the FSI−-derived inorganic-rich SEI becomes more dominant,4 which swells less27 and dissolves less28 in the electrolyte and remains mechanically robust and chemically passivating. Following this design, our groups11,17,29 and others20,21,30,31 developed several solvents that enabled quick and effective passivation of the Li electrode, where the initial CE reached >99% within 5 cycles11,17 and stable CE reached 99.9% after 100 cycles in Li‖Cu half cells.11Despite these developments, the understanding of molecular design principles is still limited. Solvent fluorination has been proven effective to tune the Lewis basicity of solvents, and thereby their solvation ability.11,17,32–35 However, fluorinated organic molecules face potential issues with cost, environmental concerns, and toxicity. Therefore, it is of great interest to develop additional molecular design principles. We recently reported steric hindrance as an alternative, effective design strategy.29 However, given the vast tunability of organic molecules, the molecular design space remains largely unexplored.
Herein, we report a new molecular design strategy, where we use solvent molecular conformation to tune the Li+ solvation structure and electrolyte reactivity. Ethylene glycol ethers have a relatively flexible dihedral angle between the two O–CH2 bonds, which enables bidentate chelation with Li+. In contrast, acetals favor a gauche conformation between O–CH3 and O–CH2 bonds due to hyperconjugation, which results in weak monodentate coordination with Li+ (Fig. 1a). Notably, two recent publications37,38 reported the weakly solvating nature of acetal solvents, but they proposed an anti conformation for acetals. Advancing from these previous papers, our work here provides further understanding on (1) the molecular origin of the weakly solvating property of acetals, (2) the cycle stability of acetal electrolytes as determined by ion transport, CE, and interfacial stability, and (3) the Li anode morphology, structure, and SEI properties.
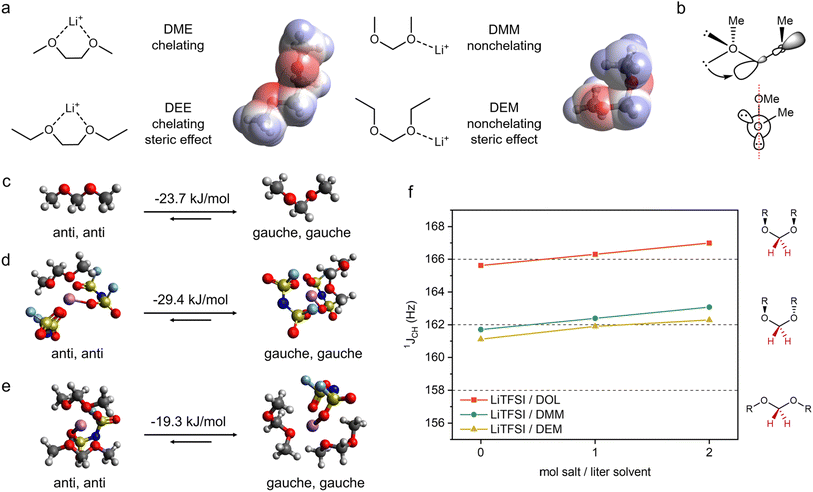 | ||
| Fig. 1 Solvent coordination geometry as a design strategy for LMB electrolytes. (a) The most stable coordination geometries of solvent molecules with Li+. The electrostatic potential surfaces of DME and DMM show different orientations of negative charge density around oxygens. (b) Schematic structure of DMM showing hyperconjugation between the O lone pair electrons and C–O sigma antibonding orbital, of which the orbital alignment is shown in the Newman projection. Note there are two pairs of such interactions per acetal. (c–e) DFT calculated ground state energy difference between structures containing [anti, anti] and [gauche, gauche] conformations of DMM. (c) A single DMM molecule. (d) A solvation structure of 2 FSI− and 1 DMM around Li+. (e) A solvation structure of 1 FSI− and 2 DMM around Li+. (f) 1JCH coupling constants of anomeric –CH2– of DOL, DMM and DEM with various concentrations of LiTFSI. The dashed lines indicate the expected 1JCH for each molecular geometry shown on the right.36 The anomeric position is indicated in red. | ||
The electrochemical performance was evaluated with 0.9 M and 3 M lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (LiFSI), representative of standard and high concentration electrolytes. Both dimethoxymethane (DMM) and diethoxymethane (DEM) as examples of acetals showed faster stabilization of Li CE compared to 3 M LiFSI/DEE.29 Impressively, the DMM electrolytes reached >99% CE within 3 to 5 cycles at 0.5 mA cm−2 and 1 mA h cm−2 in Li‖Cu half cells, which is comparable to that of the best fluorinated ethers.11,17 In addition, the high ionic conductivity and transport number of 3 M LiFSI/DMM enabled low overpotentials of 55 mV at 6 mA cm−2 and 85 mV at 10 mA cm−2 in Li‖Li cells. The overall benefits of fast CE activation, high CE, and good ion transport were seen in thin-Li‖LFP coin cells and anode-free Cu‖LFP pouch cells.
Results and discussion
Molecular structures and design principle
Ethylene glycol ethers, such as 1,2-dimethoxyethane19 (DME) and 1,2-diethoxyethane29 (DEE), are among the most commonly used solvents for Li metal anodes due to their reductive stability. Despite relatively low permittivity,39 these ethers exhibit good Li salt solubility through the chelation effect—the bidentate ligands can form a stable five-membered ring with Li+ (Fig. 1a). However, the strong coordination between the solvent and Li+ results in fewer ion pairs or aggregates and, subsequently, disfavors the formation of an anion-derived SEI.4 Previously, we utilized fluorine substitution11 and steric effects9 to weaken the coordination ability of ethylene glycol ethers. Herein, we report a third molecular design strategy that weakens the Li+-solvent interaction by controlling the conformation of solvent molecules.We demonstrate this strategy by studying the solvation behaviors of dimethoxymethane (DMM) and diethoxymethane (DEM). We hypothesize that acetals are weak monodentate ligands because (1) the stabilization effect from chelation is reduced due to the more strained structure from the shortened distance between two oxygens (Fig. 1a) and (2) the molecular conformation due to hyperconjugation36,40,41 (Fig. 1b, ESI Discussion 1†) leads to the opposite orientations of charge density on each oxygen and significantly reduces chelation with Li+ (Fig. 1a).
Previous work confirmed the [gauche, gauche] conformation of pure DMM and DEM.36,41 However, it is unclear whether Li+ coordination could alter their conformation. Therefore, we used density functional theory (DFT) calculation (ESI Discussion 2†) to determine the optimal solvent conformation within solvation shells (1 Li+, 2 FSI−, 1 DMM and 1 Li+, 1 FSI−, 2 DMM) and outside the solvation shell (Fig. 1c–e). These typical solvation shell compositions were selected based on previous reports on weakly solvating electrolytes,11,17 and they will be confirmed in the later section. Similar to pure DMM, the solvation complexes with [gauche, gauche] DMM are more stable than those with [anti, anti] DMM by 19 to 29 kJ mol−1. The optimized structures show that [anti, anti] DMM is bidentate (i.e. two oxygens per DMM coordinating to one Li+) whereas [gauche, gauche] DMM is monodentate (i.e. one oxygen per DMM coordinating to one Li+). Consistent with our rationales above, the energy gain of chelation is minimal compared to the energy penalty of breaking hyperconjugation in DMM. We expect the same behavior in DEM since the intramolecular steric strain is similar for ethyl and methyl groups in [gauche, gauche] acetals—the nonlinear geometry should be significantly more stable in DEM as well.36
The DFT results above were cross validated by 1D NMR experiments. The carbon–proton one-bond coupling constant at the anomeric position (1JCH) is dependent on conformation.42 Based on a literature report for acetals,361JCH < 158 Hz corresponds to an [anti, anti] conformation, 1JCH ∼162 Hz corresponds to [gauche, gauche] with R groups on the opposite planes, and 1JCH > 166 Hz corresponds to [gauche, gauche] with R groups on the same plane (Fig. 1f). A cyclic acetal, 1,3-dioxolane (DOL), was used as a control since it cannot adopt an [anti, anti] conformation. The 1JCH values of DOL, DMM and DEM were measured with various LiTFSI concentrations. Both pure DMM and DEM have 1JCH close to 162 Hz corresponding to [gauche, gauche], whereas pure DOL shows 1JCH right below 166 Hz due to a puckered conformation as shown in a previous report.43 As LiTFSI concentration increases, the 1JCH values of DMM and DEM are around 162 Hz, corresponding to a [gauche, gauche] conformation. In addition, DMM and DEM follow the same trend as DOL, which further confirms that DMM and DEM do not adopt an [anti, anti] conformation when coordinated with Li+. The same experiment was carried out using LiFSI in DMM and DEM (ESI Fig. S1†), where the same trend was observed.
Based on the DFT calculation and NMR experiment above, we conclude that both DMM and DEM remain in the [gauche, gauche] conformation irrespective of whether they are coordinated with Li+. This molecular conformation prevents DMM and DEM from bidentate chelating with Li+ due to the orientation of negative charge density on each oxygen as well as the distance between two oxygens. Therefore, this suggests that the solvating ability of monodentate DMM and DEM is weaker than that of bidentate DME and DEE.
Solvation structures
To verify our hypothesis above, the solvation structures of LiFSI in various solvents were investigated. For each solvent, 1 and 4 moles of LiFSI per liter of solvent were prepared, corresponding to standard (∼0.9 M) and high (∼3 M) concentration electrolytes, respectively. The molarity and molality for each electrolyte are listed in ESI Table S1.† Notably, these concentrations were not optimized for each electrolyte. They were selected to represent the standard and high concentration electrolytes typically seen in the literature.19,29,44–47 The focus is to uncover the relation between molecular conformation and solvation, which impacts the cycle performance of LMBs.We first quantify the strength of solvation by measuring the difference between the chemical potentials of Li+ in sample electrolytes and a common reference electrolyte, 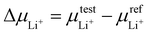 , using the method detailed in our previous work.48 A higher ΔμLi+ correlates to weaker Li+ solvation, and thereby stronger Li+–FSI− interactions.48–50 We found that ΔμLi+ increases in the order of DME < DEE < DMM < DEM, for both 0.9 M and 3 M LiFSI (Fig. 2a), confirming weaker solvation of Li+ by DMM and DEM. Notably, despite being fluorine-free, DMM and DEM electrolytes show similar ΔμLi+ to that of trifluorinated and tetrafluorinated DEE electrolytes at low concentrations,11 which confirms the impact of solvent coordination geometry on solvation ability.
, using the method detailed in our previous work.48 A higher ΔμLi+ correlates to weaker Li+ solvation, and thereby stronger Li+–FSI− interactions.48–50 We found that ΔμLi+ increases in the order of DME < DEE < DMM < DEM, for both 0.9 M and 3 M LiFSI (Fig. 2a), confirming weaker solvation of Li+ by DMM and DEM. Notably, despite being fluorine-free, DMM and DEM electrolytes show similar ΔμLi+ to that of trifluorinated and tetrafluorinated DEE electrolytes at low concentrations,11 which confirms the impact of solvent coordination geometry on solvation ability.
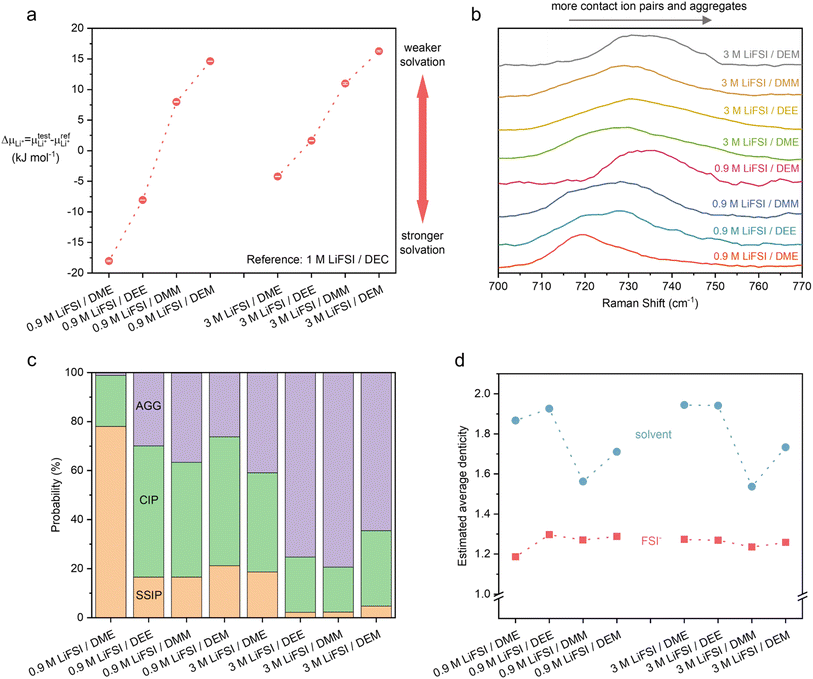 | ||
| Fig. 2 Experimental and computational characterizations of static solvation structures of 0.9 M and 3 M LiFSI in acetals (DMM and DEM) and ethylene glycol ethers (DME and DEE). (a) The difference in Li+ chemical potential in sample electrolytes and reference electrolyte (ΔμLi+).48 A higher ΔμLi+ correlates to weaker Li+ solvation at the same concentration, assuming only small contributions from the difference in activities. Three measurements were averaged for each sample with error bars shown. (b) Raman spectra of the electrolytes. The convoluted peaks between 700 and 760 cm−1 correspond to FSI− in various solvation environments. The increasing wavenumbers roughly correlate to more Li+–FSI− interactions. The data of ethylene glycol ethers were reproduced from ref. 9. (c and d) Solvation structures by MD simulation. (c) Probability of various Li+ solvation environments categorized by solvent-separated ion pairs (SSIP) (0 FSI− around 1 Li+), contact ion pairs (CIP) (1 FSI−), and ion aggregates (AGG) (≥2 FSI−). (d) Estimated average denticity of the coordinating solvent (blue) and FSI− (red) around Li+. | ||
The observation from ΔμLi+ was corroborated by the degree of ion interactions inferred from Raman spectroscopy. The data are shown in Fig. 2b, where the convoluted peaks between 700 and 760 cm−1 correspond to FSI− in various solvation environments. A shift to higher wavenumber indicates a greater proportion of contact ion pairs (CIP) and ion aggregates (AGG), relative to solvent-separated ion pairs (SSIP).51–53 At both 0.9 M and 3 M, the wavenumber increases in the order of DME < DEE ≈ DMM < DEM, which implies the increasing proportion of FSI− in CIP and AGG. The trend is consistent with ΔμLi+, except that the Raman shifts in DEE and DMM electrolytes are comparable. A similar discrepancy has been noted previously,50 which was attributed to the anion–solvent interactions54—ΔμLi+ measurement probes the Li+ solvation environment whereas Raman spectroscopy probes the FSI− solvation environment.
In addition, all-atom molecular dynamics (MD) simulation was carried out to provide a detailed view of the inner solvation shell (ESI Fig. S2†). The Li+ solvation shells are categorized as SSIP, CIP, or AGG when the number of coordinating FSI− is 0, 1, or ≥2 (Fig. 2c).9,11 At the same LiFSI concentration, DEE, DMM, and DEM have more CIP and AGG compared to DME due to their weaker solvation ability. As LiFSI concentration increases, the fraction of CIP and AGG increases, indicating weaker Li+ solvation. Interestingly, at both 0.9 M and 3 M, DEE, DMM, and DEM exhibit similar degrees of CIP and AGG despite their difference in ΔμLi+. This is because in addition to the number of FSI− in the solvation shells, several other factors could impact ΔμLi+: (1) the different enthalpic interactions between Li+ and solvents (ESI Fig. S2c†), (2) the different entropic effects55 due to different solvent permittivity, chelation effects, and configurational freedom in the solvation shells.
From MD results, we further estimated the average denticity of coordinating solvent and FSI− around Li+ (see Method). Denticity is defined as the number of donor groups (e.g. O atoms) per ligand (e.g. DME) that bind to the central metal ion (e.g. Li+). With both 0.9 M and 3 M LiFSI, the average denticity of DME and DEE is higher than that of DMM and DEM (Fig. 2d), which is consistent with our prediction of monodentate DMM and DEM versus bidentate DME and DEE by NMR and DFT (Fig. 1). It is worth noting that MD simulation may have overestimated the average denticity of DMM and DEM (ESI Discussion 3†). Nevertheless, the trend in Fig. 2d clearly shows the diminished chelating ability of DMM and DEM compared to DME and DEE.
Additional insight into solvent coordination geometry is provided by the non-isothermal measurement of electrode potential temperature coefficients (TCs)55 at the same salt concentration. The TC is related to the entropy change (ΔS) of the Li+/Li half-cell reaction and is affected by the solvent coordination geometry and charge screening effect.55 The measured TCs were lower in 3 M LiFSI/DMM (1.34 mV K−1) than 3 M LiFSI/DME (1.69 mV K−1) (ESI Fig. S3†). The larger TC suggests a higher ΔS for the Li+/Li reaction in DME. This can be attributed to the more significant loss in rotational freedom of bidentate-chelated DME, in comparison to the monodentate-coordinated DMM. Since DMM (2.7)56 has a lower dielectric constant than DME (7.3),57 the weaker charge screening effect is expected to lead to a higher TC and ΔS in DMM electrolytes as more solvent molecules are organized or released around Li+ during the half reaction. However, the effect from solvent coordination geometry is strong enough to overcome that of charge screening. Overall, the TC measurement provided additional experimental evidence to support the different coordination geometries proposed for the acetals and ethylene glycol ethers.
Li cycling stability
The benefits of weakly solvating electrolytes have been previously reported, including the preferential anion decomposition and passivation of electrode–electrolyte interfaces from the formation of an inorganic-rich SEI,4 increased Li+/Li equilibrium potential and weakened reduction ability,50 and increased surface energy of deposited Li for a lower surface/volume ratio.49 These reports motivated us to further investigate the electrochemical stability of acetal electrolytes.The Li‖Cu half-cell CE of the acetal electrolytes was benchmarked against the previous state-of-the-art non-fluorinated DEE electrolyte.9 In the initial 20 cycles, 0.9 M and 3 M LiFSI in DMM and DEM significantly outperformed 3 M LiFSI/DEE (Fig. 3a). Remarkably, 0.9 M and 3 M LiFSI in DMM reached >99% CE within 5 and 3 cycles, respectively. This is highly desirable for anode-free LMBs, but it was only previously observed in electrolytes with fluorinated solvents.11,17 In comparison, 3 M LiFSI/DEM and DEE reached >99% CE after 19 and 45 cycles, respectively (Fig. 3a). Their slow activation would lead to quick loss in Li inventory in the initial cycles. The stabilized average CE calculated after the 50th cycle was above 99% for all five electrolytes tested, among which 3 M LiFSI/DMM was the highest at 99.5% (Fig. 3b). The average CE at various stages of Li‖Cu cycling was also calculated (ESI Fig. S4†).
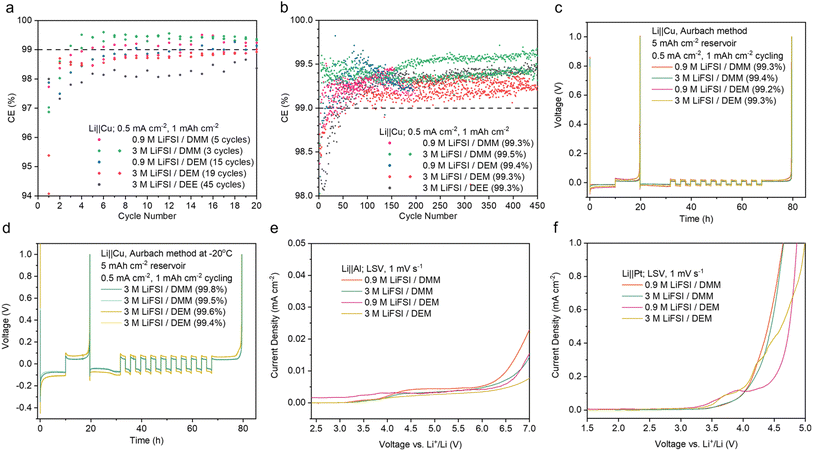 | ||
| Fig. 3 Electrochemical stability of 0.9 M and 3 M LiFSI in DMM and DEM. (a) Initial CE of Li‖Cu cells. The number of cycles to reach 99% is indicated for each electrolyte. (b) Long-term cycling of Li‖Cu cells. The stabilized average CEs were calculated after the 50th cycle. Abnormal cycles due to instrument failure were omitted in the calculation. The best cell was used for calculation when there are replicates. The data of 3 M LiFSI/DEE were taken from ref. 9 The average CEs at various stages of Li‖Cu cycling are shown in ESI Fig. S4.† (c and d) Li‖Cu CE measured by the modified Aurbach method58 at room temperature (c) and −20 °C (d). The data for all attempted cells in (a–d) are shown in ESI Fig. S33–35.† (e and f) Oxidative stability of the electrolytes measured by LSV using Al (e) and Pt (f) as the working electrodes. The Al electrode was used to probe the corrosion or passivation reaction between the Al current collector and the electrolytes, whereas the Pt electrode was used to probe the intrinsic oxidative stability of the electrolytes. | ||
The CE was also measured by the modified Aurbach method58 at room temperature (Fig. 3c). With 0.9 M LiFSI, DMM (99.3%) and DEM (99.2%) both slightly outperformed DEE (99.0%).29 With 3 M LiFSI, DMM (99.4%) and DEM (99.3%) showed similar CEs to that of DEE (99.4%).29 The advantage of acetals compared to DEE was more apparent on bare Cu, whereas cycling on top of excess Li obscured the difference.
Low temperature cycling
Stable cycling (both plating and stripping) of Li at low temperatures is of great interest but rarely demonstrated.21,59–61 We measured the CEs of 3 M LiFSI in DMM, DEM and DEE by the modified Aurbach method at 0 °C. Both acetal electrolytes demonstrated stable CE above 99%, whereas the DEE electrolyte showed significant instability with a large initial overpotential of ∼300 mV and low CE of ∼90% (ESI Fig. S5†). Notably, such instability was not due to bulk ion transport since the ionic conductivities at 0 °C (with Celgard 2325) decreased in the order of DMM > DEE > DEM with 3 M LiFSI (ESI Fig. S6a†). In addition, the CEs were measured at −20 °C. Compared to room temperature (Fig. 3c), the CEs were higher for both acetal electrolytes at −20 °C albeit with slightly larger variations (Fig. 3d). The increase in CE was likely due to kinetically suppressed side reactions at low temperatures. In stark contrast, 3 M LiFSI/DEE failed to achieve stable cycling at −20 °C (ESI Fig. S7†) with a large initial overpotential (ca. −2.3 V) and spiky voltage.The Li deposition morphology on Cu was observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (ESI Fig. S8 and 9†). For the acetal electrolytes, the Li deposition was bulky and uniform at 0 °C and −20 °C. In contrast, the DEE electrolyte showed bulky Li at 0 °C and virtually no deposition at −20 °C. If Li deposition was limited by ion transport due to low ionic conductivity of 3 M LiFSI/DEE at −20 °C (ESI Fig. S6† and notes), we would expect voltage divergence and Li dendrites,62–64 neither of which was observed. Therefore, the poor low-temperature Li cyclability of DEE should be attributed to the slow reaction kinetics as a result of the high energy barrier for Li+ de-solvation due to chelation.21,65
For comparison, the cyclability of 1.2 M LiFSI/F4DEE and F5DEE11 was tested at −20 °C, which showed unstable behavior (ESI Fig. S10†), further indicating the advantage of acetals over ethylene glycol ethers. Furthermore, the low-temperature cyclability was investigated in Li‖Li cells (ESI Fig. S11† and notes), which gave similar observations to those in Li‖Cu cells.
Oxidative stability
A major issue of imide-based salts is their side reaction with an aluminum (Al) cathode current collector at high voltages. Previously, we demonstrated that a weakly solvating electrolyte allowed the buildup of a thick and fluorine-rich passivation layer on Al even when LiFSI was used.9 This was attributed to less dissolution of Al(FSI)x and other reaction products in a weakly solvating electrolyte.66 Therefore, we predicted that the acetal electrolytes should be compatible with the Al current collector. We performed linear scanning voltammetry (LSV) using Li‖Al cells. The acetal electrolytes showed no sharp increase in leakage current below 4.4 V (Fig. 3e), which indicates good stability with the Al current collector. The compatibility of DMM and DEM with Al was similar to that of DEE and significantly better than that of DME with 0.9 M LiFSI (ESI Fig. S12a†). With 3 M LiFSI, all four electrolytes showed similar stability with Al within the practical voltage range (ESI Fig. S12b†).The oxidative stability of the acetal electrolytes was also characterized by Li‖Pt cells. The Pt working electrode is inert and non-reactive. Therefore, electrolyte oxidation can be captured without the passivation effect seen on the Al electrode. The onset of rapid oxidation on Pt was around 4 V (versus Li+/Li) for 0.9 M and 3 M LiFSI in DMM and was slightly lower for DEM electrolytes (Fig. 3f). Significant oxidation occurred at a much lower voltage range on Pt compared to Al, which indicates limited anodic stability of the acetal electrolytes despite good passivation on Al. The acetal electrolytes showed worse anodic stability on Pt compared to DME and DEE electrolytes with both 0.9 M and 3 M LiFSI (ESI Fig. S12c and d†). Therefore, the acetal electrolytes here are not compatible with high-voltage cathodes (such as NMC, ESI Fig. S39† and notes) but rather more suitable with lithium iron phosphate (LFP).
Density, viscosity, and ion transport of HCEs
Considering the overall Li cycling stability and voltage tolerance, 3 M LiFSI/DMM and DEM appeared more suitable than the 0.9 M electrolytes for the stable operation of LMBs. We further evaluated the density and viscosity of 3 M acetal electrolytes as low density and low viscosity are desirable for practical batteries. The density of 3 M acetal is measured to be lower than that of 1–2 M fluorinated ethers (ESI Table S3†), which is beneficial for the gravimetric energy density. The viscosity of 3 M acetals is lower than that of 3 M ethylene glycol ethers and only slightly higher than that of 1–2 M fluorinated ethers (ESI Table S3†), which ensures facile wetting of the cathode and separator.The concentration-dependent ionic conductivity (σ) and molar conductivity (Λ) were measured (ESI Discussion 4 and Fig. S13†). Notably, in both DMM and DEM, 1.7 M and 2.4 M electrolytes have higher Λ than 0.9 M electrolytes, which indicates that ion transport is faster despite higher viscosity in more concentrated solutions. We will further investigate this topic in a separate publication. Overall, the σ of 3 M LiFSI/DMM is similar to that of 3 M LiFSI/DME and DEE, and is higher than that of 1.5 M LiFSI-1.2DME-3TTE and 1.2 M LiFSI/F4DEE and F5DEE (ESI Table S3†). In contrast, 3 M LiFSI/DEM has a low σ, which limits the high-rate capability and stability.
In addition to σ, transport number (t+) is an important property that measures the current fraction under the steady state (anion-blocking condition) relative to the initial state of a Li‖Li cell during chronoamperometry. With both 0.9 M and 3 M LiFSI in the nonfluorinated ethers, t+ increases (DME < DEE < DMM < DEM) as the solvation ability of the solvent decreases (ESI Table S3†), which benefits the fast-charging capability.
The overpotential of Li‖Li cells is a good indicator of ion transport. The cells were cycled at 1 mA cm−2 for 1 mA h cm−2 (Fig. 4a and ESI S14a†). The overpotential in 3 M LiFSI/DMM was significantly lower (∼22 mV after 50 cycles, ∼30 mV after 800 cycles, and ∼34 mV after 1200 cycles) than that of many reported high-CE electrolytes.11,17,67,68 It was also lower than that of 3 M LiFSI/DEE9 despite the sudden increase after 1500 hours. The overpotential in 3 M LiFSI/DEM was the highest among the three, and it increased more quickly. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) indicated the SEI instability contributed to the rapid increase in overpotential in 3 M LiFSI/DEM (ESI Discussion 5, Fig. S15†).
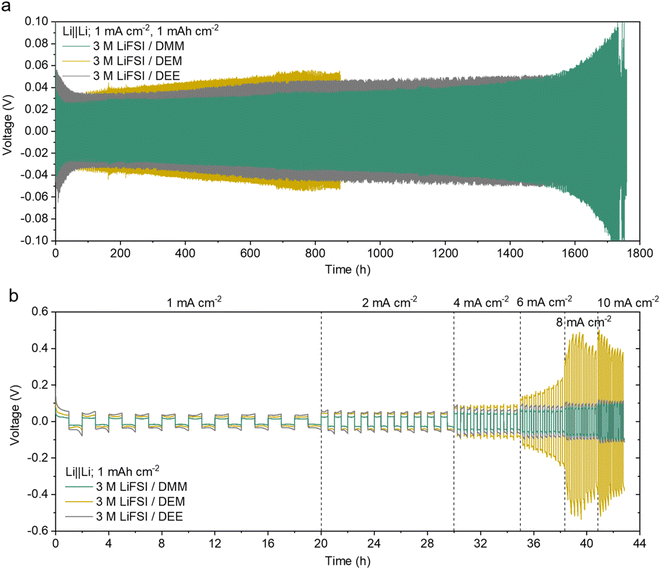 | ||
| Fig. 4 Voltage profiles of Li‖Li cells. (a) Long-term cycling at a low current density. The zoomed-in voltage curves are provided in ESI Fig. S14a.† The data of 3 M LiFSI/DEE were taken from ref. 9. (b) Cycling at 1 to 10 mA cm−2 with 10 cycles at each current density. The zoomed-in voltage curves of the later cycles are provided in ESI Fig. S14b.† The data for all attempted cells are shown in ESI Fig. S36 and 37.† | ||
The rate capability was further tested in Li‖Li cells within a current range of 1 mA cm−2 to 10 mA cm−2 (Fig. 4b and ESI S14b†). Both 3 M LiFSI/DMM and DEE showed a gradual increase in overpotential with current, whereas 3 M LiFSI/DEM showed a sharp increase in overpotential at 6 mA cm−2 due to poor ion transport. Notably, 3 M LiFSI/DMM exhibited overpotentials of around 55 mV at 6 mA cm−2 and 85 mV at 10 mA cm−2, which are among the lowest Li‖Li overpotentials seen in high-CE electrolytes. Overall, 3 M LiFSI/DMM showed great promise for simultaneously achieving high CE and fast Li+ transport.
Full cell performance
The fast activation of CE, high average CE, fast ion transport, and low overpotential make 3 M LiFSI/DMM a promising candidate for anode-free LMBs with high-rate capability. Commercial Cu‖micro-LFP pouch cells (ESI Table S4†) were tested. At C/5, C/2 and 1C charge and 2C discharge, both the DMM and DEM electrolytes achieved around 100 cycles before 80% capacity retention with good reproducibility (Fig. 5a–c). The corresponding CEs were above 99% with small fluctuations (ESI Fig. S16a–c†), indicating good cycling stability. In comparison to 1.2 M LiFSI/F4DEE and F5DEE,11 the DMM and DEM electrolytes achieved similar cycle life with higher capacity utilization at C/5 charge and better cycling stability at C/2 and 1C charge due to faster ion transport (ESI Fig. S17†). At 2C charge, the capacity utilization was significantly higher in 3 M LiFSI/DMM than 3 M LiFSI/DEM (Fig. 5d) due to their difference in ion transport, while CE remained stable in both electrolytes (ESI Fig. S16d†). Notably, F4DEE and F5DEE were selected as the control here because they are among the best-performing LiFSI/single-solvent electrolytes for Cu‖LFP cells,11 whereas DME and DEE were not cycled due to poor performance in the preliminary screening in Li‖Cu cells29 (Fig. 3a). Additional Cu‖micro-LFP pouch cells were cycled at C/2 charge, 2.5C discharge and 1C charge, 1C discharge rates (ESI Fig. S18e, f, S19e and S20†). In all anode-free pouch cells above, cycle life was most likely limited by Li inventory consumption since very little overpotential increase with cycling was observed (ESI Fig. S18 and 19†).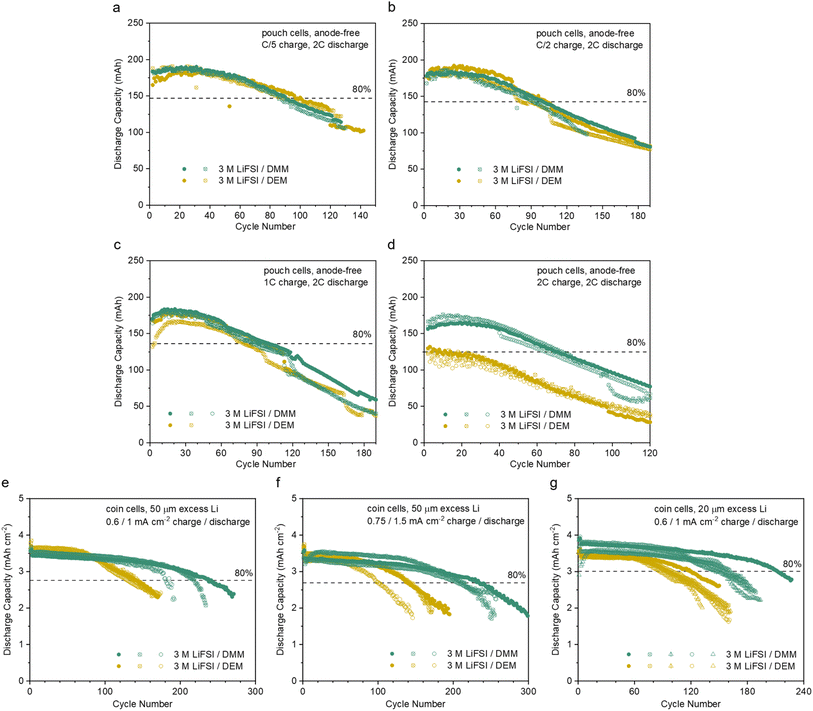 | ||
| Fig. 5 LFP-based full cells cycled with 3 M LiFSI/DMM and 3 M LiFSI/DEM. (a–d) Anode-free Cu‖micro-LFP pouch cells (ca. 210 mA h and 2.1 mA h cm−2 at C/3, 2.5 to 3.65 V, 0.5 mL electrolyte, 1C = 200 mA or 2 mA cm−2). cycled at various charge rates and 2C discharge rate. The first-cycle charge rate was C/10. The 80% capacity retention line is based on the solid trace of 3 M LiFSI/DMM at the 2nd cycle. (e–g) Thin-Li‖micro-LFP coin cells (3.6 to 4 mA h cm−2 at <C/10, 2.5 to 3.65 V, 40 μL electrolyte) with free-standing Li foil of 50 μm (e and f) and 20 μm (g) thickness cycled at various current densities. Two activation cycles were carried out at 0.3 mA cm−2. The 80% capacity retention line is based on the solid trace of 3 M LiFSI/DMM at the 4th cycle. The corresponding CE values are shown in ESI Fig. S16.† The data for every attempted cell are shown in ESI Fig. S38.† | ||
The relatively short cycle life in anode-free cells obscured the difference in long-term stability. Therefore, thin-Li‖micro-LFP coin cells were also tested using a high-loading cathode (nominally 3.6 to 4 mA h cm−2) and limited excess Li (50 or 20 μm thick) cycled at 0.6/1 mA cm−2 or 0.75/1.5 mA cm−2 charge/discharge current densities (Fig. 5e–g and ESI S16e–g†). Under the three testing conditions, 3 M LiFSI/DMM showed significantly longer cycle life than 3 M LiFSI/DEM due to a higher CE and more stable overpotential (ESI Discussion 6†).
Limitations and future improvements
Despite the advantages of fast ion transport and good Li cycling stability of 3 M LiFSI/DMM, the poor oxidation stability, low boiling point, and high salt concentration necessitate further improvement in the solvent design. Compared to ethylene glycol ethers, acetal solvents clearly demonstrate superior stability with the Li electrode. Therefore, by applying the concept of controlling the position and degree of fluorination,11,17 we predict that the resulting fluorinated acetal solvents may simultaneously achieve good stability with a high-voltage cathode and Li anode, high boiling point, reduced flammability, and fast ion transport while maintaining lower salt concentrations.69 A similar concept was recently applied to diluent design.34In addition, given the emphasis on fast charging in the battery industry, the ion transport mechanism in these highly non-ideal electrolytes deserves further investigation.70–72 In this work, we demonstrated that a slight variation in solvent molecular structure could drastically change electrolyte conductivity and transport number, as well as their concentration-dependent trends. It is crucial to uncover the underlying mechanism for these observations in order to address the slow ion transport problem in many advanced electrolytes to date.73
Finally, although we demonstrated the improved Li stability of DMM and DEM electrolytes compared to the DEE electrolyte (Fig. 3a), the detailed mechanisms for such improvement remain unclear (ESI Discussion 7 and related Fig. S23–32†). To improve from the current >99% to the required >99.99% CE for the Li electrode, further investigations are required to identify the origin of small improvement among advanced electrolytes. In particular, factors beyond SEI composition and structure could be important.49,50
Conclusion
We report solvent molecular conformation as an effective design strategy in addition to fluorine substitution11 and steric effects9 to control Li+ solvation. Due to hyperconjugation, DMM and DEM adopt a [gauche, gauche] conformation, which makes them monodentate ligands. This leads to weaker solvation of Li+ in acetals compared to ethylene glycol ethers. Consistent with previous observations in the literature, such weakly solvating electrolytes show improved Li CE. In particular, 0.9 M and 3 M LiFSI/DMM reached >99% CE within 3 to 5 cycles under our standard testing conditions, which is comparable to some of the best fluorinated ethers.11 In addition, 3 M LiFSI/DMM showed low overpotentials of around 55 mV at 6 mA cm−2 and 85 mV at 10 mA cm−2 due to high conductivity and transport number. The fast ion transport and good Li cycling stability of 3 M LiFSI/DMM were demonstrated in anode-free Cu‖LFP pouch cells as well as thin-Li‖LFP coin cells. Various cell conditions and cycling procedures were used to discern the effects of ion transport, CE, and impedance growth on full-cell cycle life. Overall, we demonstrate that acetal structure is a promising alternative to ethylene glycol ether structure for LMBs. Indeed, more recently, a fluorinated acetal was reported to enable high CEs and stable full-cell cycling even under the practical conditions of fast charge and slow discharge.69Despite the improved cycling stability of acetal solvent for Li metal compared to ethylene glycol ether, their poor oxidation stability, low boiling point, and high salt concentration necessitate further improvement in the solvent design.34,69 This work offers a starting point for further design and optimization of molecular analogues. Furthermore, we found the slight variations in solvent molecular structure could drastically change ion transport properties. It is crucial to investigate the ion transport mechanism to overcome the problem of slow ion transport in LMB electrolytes.73 Finally, future work is needed to identify the origin of the small improvement in CE above 99%. Factors beyond the extensively investigated SEI composition and structure could be fructuous.
Methods
Materials
DME (anhydrous, 99.5%, inhibitor-free) and DEM (anhydrous, 99%) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. DEE (99%, ACROS) and DMM (99.5%) were purchased from Fisher Scientific. LiFSI was purchased from Arkema. The Celgard 2325 separator (25 μm thick, polypropylene/polyethylene/polypropylene) was purchased from Celgard. The Cu current collector (25 μm thick) was purchased from Alfa Aesar. Free-standing lithium foil (600, 50 and 20 μm) was purchased from MSE Supplies. 2032-type battery casings, stainless steel spacers, springs and Al-clad coin cell cases were purchased from MTI. Micro-LFP cathode sheets were purchased from Targray. Anode-free Cu‖micro-LFP pouch cells were purchased from Li-Fun Technology.Solvent purification
DEE was purified by vacuum distillation over sodium hydride. DME, DMM and DEM were not distilled. Fresh Li foil was added to the solvents in the glovebox to further remove trace amounts of water.Electrolyte preparation
Electrolytes were prepared by dissolving 1 mmol or 4 mmol of LiFSI per mL of solvent. The accurate molarities were calculated based on densities of the electrolytes, which account for the volume change upon salt dissolution.Electrochemical measurements
2032-type coin cells with a Celgard 2325 separator were used for most electrochemical measurements unless indicated otherwise. Battery fabrication was carried out in an Ar-filled glovebox. Thick Li foil (600 μm, 1 cm2) and 40 μL of electrolyte were used unless otherwise specified. Electrochemical tests were carried out on Land, Arbin and Biologic systems.The oxidation stability of electrolytes was characterized by linear sweep voltammetry on Li‖Al and Li‖Pt cells using Biologic MPG2. The voltage was swept from open-circuit voltage to 7 V vs. Li+/Li at a rate of 1 mV s−1. The leakage current density was calculated based on a working-electrode area of 2.11 cm2.
Coulombic efficiencies were measured by a modified Aurbach method58 on Li‖Cu cells at ambient temperature, 0 °C or −20 °C. The Cu surface was conditioned by plating 5 mA h cm−2 of Li and stripping to 1 V. Then, a Li reservoir of 5 mA h cm−2 was plated onto Cu, followed by 10 cycles of Li plating and stripping at 1 mA h cm−2. Finally, all Li on Cu was stripped to 1 V. The current density was 0.5 mA cm−2 for all steps.
For the long-term cycling of Li‖Cu cells, the Cu surface was conditioned by holding at 10 mV vs. Li+/Li for 5 hours, and then cycling between 0 and 1 V at 0.2 mA cm−2 for 10 cycles. During subsequent cycling, 1 mA h cm−2 of Li was plated onto Cu and was then stripped to 1 V at 0.5 mA cm−2.
Li‖Li symmetric cells were cycled at 1 mA cm−2 for 1 mA h cm−2. In some cells, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy was carried out every 120 cycles to track the evolution of cell impedance. In addition, Li‖Li cells were also cycled for 1 mA h cm−2 with a stepwise increase in current density every 10 cycles from 1 mA cm−2 to 10 mA cm−2. Some Li‖Li cells were also cycled at −20 °C at 0.5 mA cm−2 and 1 mA h cm−2 for 10 cycles.
Li‖LFP coin cells were assembled using 50 or 20 μm free-standing Li and 40 μL of electrolyte. Al-clad cathode cases were used. Al foil was placed inside the cathode cases to avoid defects in the Al cladding. A high-loading micro-LFP cathode was used. The cells were cycled between 2.5 and 3.65 V. Two activation cycles were carried out at 0.3 mA cm−2, which produced second-cycle discharge capacities between 3.6 and 4 mA h cm−2 due to slight variations in the cathode loading. Long-term cycling was carried out at 0.6/1 mA cm−2 or 0.75/1.5 mA cm−2 charge/discharge current densities.
Anode-free Cu‖micro-LFP dry pouch cells were factory manufactured (ca. 210 mA h and 2.1 mA h cm−2 at C/3). The electrolyte (0.5 mL) was injected and the pouch was re-sealed under vacuum. Vises and polycarbonate plates were used to apply ca. 1000 kPa pressure to the pouch cells. The cells were cycled under ambient temperature between 2.5 and 3.65 V at various charge and discharge rates (1C = 200 mA or 2 mA cm−2). The first-cycle charge rate was C/10.
Ionic conductivities were measured by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. A Swagelok-type cell with symmetric stainless-steel electrodes and without separator was used to measure the intrinsic electrolyte conductivity at ambient temperature. 2032-type coin cells with symmetric stainless-steel electrodes and a Celgard 2325 separator were used to measure the temperature-dependent ionic conductivity in the presence of a separator.
Transport number was measured by the Vincent-Bruce method in Li‖Li symmetric cells with a modified procedure.74 The interface was stabilized by 5 cycles at 0.5 mA cm−2 for 1 mA h cm−2. Chronoamperometry (CA) was carried out at 10 mV until a steady-state current was achieved. EIS was carried out before and after the CA step to account for changes in interfacial resistance.
The measurement of 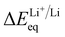 was previously developed by our groups.48 The home-made apparatus consisted of three chambers, each containing a different electrolyte (test, reference or salt-bridge electrolyte), and two porous junctions that separate the three chambers. Four layers of Celgard 2325 separator were used as the porous junction. Two pieces of fresh lithium foil were used as electrodes. The cell voltage was measured using a Biologic VMP3. The voltage was recorded after stabilization, which typically takes up to three minutes.
was previously developed by our groups.48 The home-made apparatus consisted of three chambers, each containing a different electrolyte (test, reference or salt-bridge electrolyte), and two porous junctions that separate the three chambers. Four layers of Celgard 2325 separator were used as the porous junction. Two pieces of fresh lithium foil were used as electrodes. The cell voltage was measured using a Biologic VMP3. The voltage was recorded after stabilization, which typically takes up to three minutes.
The non-isothermal measurement of electrode potential temperature coefficients was previously developed by our groups.55 An H-cell with a porous frit was used. Two pieces of fresh lithium foil were used as electrodes, and the same electrolyte was used on both sides. A thermocouple (Omega, HSTCTT-K-24S-36) was installed in each half cell adjacent to the electrode surface to measure the temperature of the electrolyte/electrode interface using a temperature scanner (Omega, DP1001AM). A Kapton heater was wrapped around one side of the H-cell to provide uniform heating. During the measurement, the heating power was adjusted using a potentiostat (BioLogic VMP3). For each heating power set point, the stabilized temperature and open-circuit voltage were recorded.
Materials characterization
NMR was performed on a Varian 400 MHz spectrometer at 25 °C. The 1JCH coupling constants of the anomeric CH2 group of DMM, DEM, and DOL were extracted from 1D 1H NMR spectra at various LiFSI and LiTFSI concentrations. 7Li pulsed field gradient (PFG) measurements were performed to determine the self-diffusion coefficients of Li+ using a dbppste_cc pulse sequence. The array of gradient strength was set to 2.908 to 12.504 G cm−1 with 12 linear steps. Appropriate diffusion delay (Δ) and gradient pulse duration (δ) were selected to ensure sufficient signal decay. Self-diffusion coefficients were calculated by fitting peak integrals to the Stejskal–Tanner equation.Raman spectra were collected on a Horiba XploRA+ confocal Raman microscope with a 532 nm excitation laser. The electrolytes were sealed under argon in quartz cuvettes.
Viscosity measurements were carried out using an Ares G2 rheometer (TA Instruments) with an advanced Peltier system at 25.0 °C.
Differential scanning calorimetry was carried out on a TA Instruments Q2500. Aluminum hermetic pans were used. The temperature was scanned to 25 °C first, followed by cooling to −75 °C and then heating. The ramp was 10 °C min−1 for all steps.
The physical state of electrolytes was observed after equilibrating for at least 2 hours at 0 °C, −20 °C and −80 °C in a temperature chamber or freezer.
The surface morphology of Li was imaged using an FEI Magellan 400 XHR scanning electron microscope. In Li‖Cu cells, the Cu electrode was pre-conditioned by holding at 0.01 V for 5 hours, and then cycling between 0 and 1 V at 0.2 mA cm−2 for 10 cycles. Li was deposited on Cu at 0.5 mA cm−2 for 0.5 mA h cm−2. After deposition, the cells were disassembled, and the electrodes were rinsed with 80 μL of the corresponding pure solvents. The Li deposition morphology at 0 °C and −20 °C was also imaged after depositing Li at 0.5 mA cm−2 for 5 mA h cm−2 in Li‖Cu cells. In addition, Li electrode morphology in Li‖Li cells cycled at −20 °C was characterized (0.5 mA cm−2 and 1 mA h cm−2 for 10 cycles).
The Li deposition morphology in the presence of an rSEI was imaged using an FEI Magellan 400 XHR scanning electron microscope. The Li‖Cu cells were pre-conditioned at 0.2 mA cm−2 between 0 and 1 V for 10 cycles, followed by 10 cycles at 0.5 mA cm−2 and 1 mA h cm−2 plating and 0.5 mA cm−2 stripping to 1 V to form an rSEI. In the final step, 0.1, 0.5 or 1 mA h cm−2 capacity was plated at 0.5 mA cm−2. The Cu electrodes were rinsed with 80 μL of the corresponding pure solvents before imaging. Alternatively, the 50 μm-Li‖thick-Li cells were pre-cycled at 0.4 mA cm−2 for 2 cycles, followed by 10 cycles at 0.4 or 4 mA cm−2 plating and 4 mA cm−2 stripping, with 4 mA h cm−2 in each step to form an rSEI. In the final step, 0.2, 1 or 4 mA h cm−2 capacity was plated at 0.4 or 4 mA cm−2. The 50 μm-Li electrodes were rinsed with 80 μL of the corresponding pure solvents before imaging.
The cross sections of the rSEI were imaged using an FEI Helios NanoLab 600i DualBeam SEM/FIB. Li‖Cu cells were cycled at 0.5 mA cm−2 for 1 mA h cm−2 for 10 cycles. The active Li was stripped in the final step, leaving the rSEI on the Cu substrate. An air-free transfer vessel was used. Pt was deposited to preserve the top surface of the rSEI. Cross sections were prepared by a Ga+ ion beam.
A ThermoFisher Titan 80–300 environmental transmission electron microscope at an accelerating voltage of 300 kV and a Gatan 626 side-entry holder were used for cryo-TEM and cryo-EDS experiments. Cryo-TEM sample preparations prevent air and moisture exposure and reduce electron beam damage, as described previously.75,76 The TEM is equipped with an aberration corrector in the image-forming lens, which was tuned before imaging. Cryo-TEM images were acquired using a Gatan K3 IS direct-detection camera in the electron-counting mode. Cryo-TEM images were taken with an electron dose rate of around 100 e− Å−2 s−1, and a total of five frames were taken with 0.1 s per frame for each image. The samples were prepared by depositing 0.2 mA h of Li on a bare Cu grid at 1 mA cm−2.
A PHI VersaProbe 3 XPS with a monochromatized Al(Kα) source (1486 eV) and focused ion gun was used to characterize SEI compositions after cycling. An air-tight vessel was used to transfer samples without exposure to air. The samples were sputtered for 1 min to get rid of adventitious carbon. Li‖Cu cells were first pre-conditioned at 0.2 mA cm−2 between 0 and 1 V for 10 cycles, followed by 10 cycles at 0.5 mA cm−2 plating for 1 mA h cm−2 and 0.5 mA cm−2 stripping to 1 V. The fully stripped Cu electrodes were rinsed with 80 μL of the corresponding pure solvents before XPS.
Theoretical calculations
Density functional theory (DFT) with the hybrid exchange–correlation functional B3LYP77 with the Becke–Johnson damping scheme (D3BJ)78,79 was applied for the geometry optimization, and all DFT calculations were performed with the def2-TZVP basis set80 using the ORCA package.81MD simulations were carried out using Gromacs 2021.3 (ref. 82) with the general amber force field (GAFF).83 Topology files were generated using ACPYPE,84 and the atomic partial charges were calculated by the restrained electrostatic potential (RESP) fitting approach in antechamber 22.0,85 where the quantum mechanical molecular electrostatic potential was computed by Gaussian16 at the B3LYP/6-311** level.86 To improve the accuracy of the non-polarizable force field, partial charges for charged ions were scaled by factors ranging from 0.6 to 0.72 to account for electronic screening. The scaling factors were adjusted to match the diffusion coefficients measured by the experiments (ESI Table S2†).
To compute the diffusivity coefficient through the NVT molecular dynamics simulations, molecular dynamics was first equilibrated for 2 ns using the Parrinello-Rahman barostat at a reference pressure of 1 bar. The simulation size box for the following NVT simulations was determined by the average size in the last 1 ns. After that, a 2 ns equilibration step was followed by 80 ns production run with a fixed volume. The Nosé-Hoover thermostat was used throughout with a reference temperature of 300 K. The particle mesh Ewald method was used to calculate electrostatic interactions, with a real space cutoff of 1.0 nm and a Fourier spacing of 0.16 nm. The Verlet cutoff scheme was used to generate pair lists. A cutoff of 1.0 nm was used for non-bonded Lennard-Jones interactions. Periodic boundary conditions were applied in all directions. Bonds with hydrogen atoms were constrained. The trajectories of the production run were used for the analysis.
The visualizations were generated with VMD.87 Solvation shell statistics were calculated using the MDAnalysis Python package88 by histogramming the observed first solvation shells for lithium ions during the production simulation, using a method similar to that in previous work.11,17 The cutoff distance for each species in the first solvation shell was calculated from the first minimum occurring in the RDF (referenced to lithium ions) after the initial peak. The average numbers of coordinating species in the solvation shell of Li+ were calculated by counting (1) solvent molecules and anions and (2) oxygen atoms on solvent molecules and anions. Their ratio was taken as a rough indicator of coordination denticity.
Data availability
Data for this article are available at the Stanford Digital Repository at https://doi.org/10.25740/cr950vj3922.Author contributions
Y. Chen conceived the idea. Y. Chen and S. L. designed the study. Z. B., J. Q., and Y. Cui directed the project. Y. Chen performed electrochemical experiments, cell testing, NMR, SEM, and DSC. S. L. performed MD and DFT calculations. H. G. performed SEM and XPS. Z. Z. performed cryo-EM and EDS. Z. H. performed Raman spectroscopy and viscosity measurements. S. C. K performed Li+ chemical potential and electrode potential temperature coefficient measurements. E. Z. and W. Y. performed XPS. H. L. performed FIB-SEM. Y. L. and P. S. contributed to key discussions. All authors contributed to the analysis, interpretation, and discussion of the data. Y. Chen, S. L., Z. B., J. Q., and Y. Cui wrote and revised the manuscript.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): 1,2-diethoxyethane, dimethoxymethane, and diethoxymethane electrolytes have been filed as International Patent Application No. PCT/US2022/47472; fluorinated diethoxymethane electrolytes have been filed as International Patent Application No. PCT/US2023/021234.Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the Assistant Secretary for Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, Office of Vehicle Technologies of the U.S. Department of Energy under the Battery 500 Consortium program, and Stanford Precourt Institute for Energy under the StorageX Initiative Seed Grants. Y. Cui acknowledges the cryo-EM support from the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Division of Materials Sciences and Engineering (Contract No. DE-AC02-76SF00515). Y. Chen acknowledges the support from the Chevron Fellowship. S. L. acknowledges the support from the LEAP Fellowship. Part of this work was performed at the Stanford Nano Shared Facilities (SNSF), supported by the National Science Foundation under award ECCS-2026822. DFT and MD calculations were performed on the Sherlock cluster. We would like to thank Stanford University and the Stanford Research Computing Center for providing computational resources and support that contributed to these research results.References
- G. M. Hobold, J. Lopez, R. Guo, N. Minafra, A. Banerjee, Y. Shirley Meng, Y. Shao-Horn and B. M. Gallant, Moving beyond 99.9% Coulombic Efficiency for Lithium Anodes in Liquid Electrolytes, Nat. Energy, 2021, 6(10), 951–960, DOI:10.1038/s41560-021-00910-w
.
- S. Kim, G. Park, S. J. Lee, S. Seo, K. Ryu, C. H. Kim and J. W. Choi, Lithium Metal Batteries: From Fundamental Research to Industrialization, Adv. Mater., 2023, 2206625, 1–20, DOI:10.1002/adma.202206625
.
- D. Lin, Y. Liu and Y. Cui, Reviving the Lithium Metal Anode for High-Energy Batteries, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2017, 12(3), 194–206, DOI:10.1038/nnano.2017.16
.
- H. Wang, Z. Yu, X. Kong, S. C. Kim, D. T. Boyle, J. Qin, Z. Bao and Y. Cui, Liquid Electrolyte: The Nexus of Practical Lithium Metal Batteries, Joule, 2022, 6(3), 588–616, DOI:10.1016/j.joule.2021.12.018
.
- C. Niu, D. Liu, J. A. Lochala, C. S. Anderson, X. Cao, M. E. Gross, W. Xu, J. G. Zhang, M. S. Whittingham and J. Xiao,
et al., Balancing Interfacial Reactions to Achieve Long Cycle Life in High-Energy Lithium Metal Batteries, Nat. Energy, 2021, 6(7), 723–732, DOI:10.1038/s41560-021-00852-3
.
- X. Fan, L. Chen, O. Borodin, X. Ji, J. Chen, S. Hou, T. Deng, J. Zheng, C. Yang and S. C. Liou,
et al., Non-Flammable Electrolyte Enables Li-Metal Batteries with Aggressive Cathode Chemistries, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2018, 13(8), 715, DOI:10.1038/s41565-018-0183-2
.
- R. Weber, M. Genovese, A. J. Louli, S. Hames, C. Martin, I. G. Hill and J. R. Dahn, Long Cycle Life and Dendrite-Free Lithium Morphology in Anode-Free Lithium Pouch Cells Enabled by a Dual-Salt Liquid Electrolyte, Nat. Energy, 2019, 4(8), 683–689, DOI:10.1038/s41560-019-0428-9
.
- A. J. Louli, A. Eldesoky, R. Weber, M. Genovese, M. Coon, J. deGooyer, Z. Deng, R. T. White, J. Lee and T. Rodgers,
et al., Diagnosing and Correcting Anode-Free Cell Failure via Electrolyte and Morphological Analysis, Nat. Energy, 2020, 5(9), 693–702, DOI:10.1038/s41560-020-0668-8
.
- Y. Chen, Z. Yu, P. Rudnicki, H. Gong, Z. Huang, S. C. Kim, J.-C. Lai, X. Kong, J. Qin and Y. Cui,
et al., Steric Effect Tuned Ion Solvation Enabling Stable Cycling of High-Voltage Lithium Metal Battery, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143(44), 18703–18713, DOI:10.1021/jacs.1c09006
.
- M. S. Kim, Z. Zhang, P. E. Rudnicki, Z. Yu, J. Wang, H. Wang, S. T. Oyakhire, Y. Chen, S. C. Kim and W. Zhang,
et al., Suspension Electrolyte with Modified Li+ Solvation Environment for Lithium Metal Batteries, Nat. Mater., 2022, 21, 445–454, DOI:10.1038/s41563-021-01172-3
.
- Z. Yu, P. E. Rudnicki, Z. Zhang, Z. Huang, H. Celik, S. T. Oyakhire, Y. Chen, X. Kong, S. C. Kim and X. Xiao,
et al., Rational Solvent Molecule Tuning for High-Performance Lithium Metal Battery Electrolytes, Nat. Energy, 2022, 7(1), 94–106, DOI:10.1038/s41560-021-00962-y
.
- H. Zhang, Z. Zeng, R. He, Y. Wu, W. Hu, S. Lei, M. Liu, S. Cheng and J. Xie, 1,3,5-Trifluorobenzene and Fluorobenzene Co-Assisted Electrolyte with Thermodynamic and Interfacial Stabilities for High-Voltage Lithium Metal Battery, Energy Storage Mater., 2022, 48, 393–402, DOI:10.1016/j.ensm.2022.03.034
.
- D. Yoo, S. Yang, K. J. Kim and J. W. Choi, Fluorinated Aromatic Diluent for High-Performance Lithium Metal Batteries, Angew. Chem., 2020, 132(35), 14979–14986, DOI:10.1002/ange.202003663
.
- A. Eldesoky, A. J. Louli, A. Benson and J. R. Dahn, Cycling Performance of NMC811 Anode-Free Pouch Cells with 65 Different Electrolyte Formulations, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2021, 168(12), 120508, DOI:10.1149/1945-7111/ac39e3
.
- G. Zhang, J. Li, S. S. Chi, J. Wang, Q. Wang, R. Ke, Z. Liu, H. Wang, C. Wang and J. Chang,
et al., Molecular Design of Competitive Solvation Electrolytes for Practical High-Energy and Long-Cycling Lithium-Metal Batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2024, 34(13), 1–11, DOI:10.1002/adfm.202312413
.
- G. Zhang, J. Li, Q. Wang, H. Wang, J. Wang, K. Yu, J. Chang, C. Wang, X. Hong and Q. Ma,
et al., A Nonflammable Electrolyte for High-Voltage Lithium Metal Batteries, ACS Energy Lett., 2023, 8(7), 2868–2877, DOI:10.1021/acsenergylett.3c00706
.
- Z. Yu, H. Wang, X. Kong, W. Huang, Y. Tsao, D. G. Mackanic, K. Wang, X. Wang, W. Huang and S. Choudhury,
et al., Molecular Design for Electrolyte Solvents Enabling Energy-Dense and Long-Cycling Lithium Metal Batteries, Nat. Energy, 2020, 5(7), 526–533, DOI:10.1038/s41560-020-0634-5
.
- Y. Liu, J. Li, X. Deng, S. S. Chi, J. Wang, H. Zeng, Y. Jiang, T. Li, Z. Liu and H. Wang,
et al., Regulating Electrolyte Solvation Structures via Diluent-Solvent Interactions for Safe High-Voltage Lithium Metal Batteries, Small, 2024, 20(31), 1–10, DOI:10.1002/smll.202311812
.
- J. Qian, W. A. Henderson, W. Xu, P. Bhattacharya, M. Engelhard, O. Borodin and J. G. Zhang, High Rate and Stable Cycling of Lithium Metal Anode, Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 6362, DOI:10.1038/ncomms7362
.
- X. Ren, L. Zou, X. Cao, M. H. Engelhard, W. Liu, S. D. Burton, H. Lee, C. Niu, B. E. Matthews and Z. Zhu,
et al., Enabling High-Voltage Lithium-Metal Batteries under Practical Conditions, Joule, 2019, 3(7), 1662–1676, DOI:10.1016/j.joule.2019.05.006
.
- J. Holoubek, H. Liu, Z. Wu, Y. Yin, X. Xing, G. Cai, S. Yu, H. Zhou, T. A. Pascal and Z. Chen,
et al., Tailoring Electrolyte Solvation for Li Metal Batteries Cycled at Ultra-Low Temperature, Nat. Energy, 2021, 6, 303–313, DOI:10.1038/s41560-021-00783-z
.
- H. Liu, J. Holoubek, H. Zhou, A. Chen, N. Chang, Z. Wu, S. Yu, Q. Yan, X. Xing and Y. Li,
et al., Ultrahigh Coulombic Efficiency Electrolyte Enables Li‖SPAN Batteries with Superior Cycling Performance, Mater. Today, 2021, 42, 17–28, DOI:10.1016/j.mattod.2020.09.035
.
- F. Huang, G. Ma, Z. Wen, J. Jin, S. Xu and J. Zhang, Enhancing Metallic Lithium Battery Performance by Tuning the Electrolyte Solution Structure, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6(4), 1612–1620, 10.1039/c7ta08274f
.
- M. S. Lee, V. Roev, C. Jung, J. R. Kim, S. Han, H. R. Kang, D. Im and I. S. Kim, An Aggregate Cluster-Dispersed Electrolyte Guides the Uniform Nucleation and Growth of Lithium at Lithium Metal Anodes, ChemistrySelect, 2018, 3(41), 11527–11534, DOI:10.1002/slct.201800757
.
- W. Xue, M. Huang, Y. Li, Y. G. Zhu, R. Gao, X. Xiao, W. Zhang, S. Li, G. Xu and Y. Yu,
et al., Ultra-High-Voltage Ni-Rich Layered Cathodes in Practical Li Metal Batteries Enabled by a Sulfonamide-Based Electrolyte, Nat. Energy, 2021, 6, 495–505, DOI:10.1038/s41560-021-00792-y
.
- C. Niu, D. Liu, J. A. Lochala, C. S. Anderson, X. Cao, M. E. Gross, W. Xu, J. Zhang, M. S. Whittingham and J. Xiao,
et al., Balancing Interfacial Reactions to Achieve Long Cycle Life in High-Energy Lithium Metal Batteries, Nat. Energy, 2021, 6, 723–732, DOI:10.1038/s41560-021-00852-3
.
- Z. Zhang, Y. Li, R. Xu, W. Zhou, Y. Li, S. T. Oyakhire, Y. Wu, J. Xu, H. Wang and Z. Yu,
et al., Capturing the Swelling of Solid-Electrolyte Interphase in Lithium Metal Batteries, Science, 2022, 375(6576), 66–70, DOI:10.1126/science.abi8703
.
- P. Sayavong, W. Zhang, S. T. Oyakhire, D. T. Boyle, Y. Chen, S. C. Kim, R. A. Vilá, S. E. Holmes, M. S. Kim and S. F. Bent,
et al., Dissolution of the Solid Electrolyte Interphase and Its Effects on Lithium Metal Anode Cyclability, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145(22), 12342–12350, DOI:10.1021/jacs.3c03195
.
- Y. Chen, Z. Yu, P. Rudnicki, H. Gong, Z. Huang, S. C. Kim, J. C. Lai, X. Kong, J. Qin and Y. Cui,
et al., Steric Effect Tuned Ion Solvation Enabling Stable Cycling of High-Voltage Lithium Metal Battery, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143(44), 18703–18713, DOI:10.1021/jacs.1c09006
.
- Z. Li, H. Rao, R. Atwi, B. M. Sivakumar, B. Gwalani, S. Gray, K. S. Han, T. A. Everett, T. A. Ajantiwalay and V. Murugesan,
et al., Non-Polar Ether-Based Electrolyte Solutions for Stable High-Voltage Non-Aqueous Lithium Metal Batteries, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14(1), 868, DOI:10.1038/s41467-023-36647-1
.
- G. X. Li, V. Koverga, A. Nguyen, R. Kou, M. Ncube, H. Jiang, K. Wang, M. Liao, H. Guo and J. Chen,
et al., Enhancing Lithium-Metal Battery Longevity through Minimized Coordinating Diluent, Nat. Energy, 2024, 9, 817–827, DOI:10.1038/s41560-024-01519-5
.
- G. Zhang, J. Chang, L. Wang, J. Li, C. Wang, R. Wang, G. Shi, K. Yu, W. Huang and H. Zheng,
et al., A Monofluoride Ether-Based Electrolyte Solution for Fast-Charging and Low-Temperature Non-Aqueous Lithium Metal Batteries, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14(1), 1–13, DOI:10.1038/s41467-023-36793-6
.
- D. Ruan, L. Tan, S. Chen, J. Fan, Q. Nian, L. Chen, Z. Wang and X. Ren, Solvent versus Anion Chemistry: Unveiling the Structure-Dependent Reactivity in Tailoring Electrochemical Interphases for Lithium-Metal Batteries, JACS Au, 2023, 3(3), 953–963, DOI:10.1021/jacsau.3c00035
.
- Y. Zhao, T. Zhou, P. H. Jeurgens, X. Kong, W. Choi and A. Coskun, Electrolyte Engineering for Highly Inorganic Solid Electrolyte Interphase in High-Performance Lithium Metal Batteries, Chem, 2023, 9, 1–16, DOI:10.1016/j.chempr.2022.12.005
.
- Y. Zhao, T. Zhou, M. Mensi, J. W. Choi and A. Coskun, Electrolyte Engineering via Ether Solvent Fluorination for Developing Stable Non-Aqueous Lithium Metal Batteries, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14, 299, DOI:10.1038/s41467-023-35934-1
.
- J. E. Anderson, K. Heki, M. Hirota and F. S. Jørgensen, Setting the Anomeric Effect against Steric Effects in Simple Acyclic Acetals. Non-Anomeric Non-Classical Conformations. An N.M.R. and Molecular Mechanics Investigation, J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun., 1987,(8), 554–555, 10.1039/C39870000554
.
- T. Ma, Y. Ni, Q. Wang, W. Zhang, S. Jin, S. Zheng, X. Yang, Y. Hou, Z. Tao and J. Chen, Optimize Lithium Deposition at Low Temperature by Weakly Solvating Power Solvent, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2022, 300071, DOI:10.1002/anie.202207927
.
- K. Ding, C. Xu, Z. Peng, X. Long, J. Shi, Z. Li, Y. Zhang, J. Lai, L. Chen and Y. Cai,
et al., Tuning the Solvent Alkyl Chain to Tailor Electrolyte Solvation for Stable Li-Metal Batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14(39), 44470–44478, DOI:10.1021/acsami.2c13517
.
- B. Flamme, G. Rodriguez Garcia, M. Weil, M. Haddad, P. Phansavath, V. Ratovelomanana-Vidal and A. Chagnes, Guidelines to Design Organic Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Batteries: Environmental Impact, Physicochemical and Electrochemical Properties, Green Chem., 2017, 19(8), 1828–1849, 10.1039/c7gc00252a
.
-
F. A. Carey and R. J. Sundberg, Advanced Organic Chemistry, Springer, New York, 5th edn, 2007 Search PubMed
.
- A. Abe, K. Inomata, E. Tanisawa and I. Ando, Conformation and Conformational Energies of Dimethoxymethane and 1,1-Dimethoxyethane, J. Mol. Struct., 1990, 238, 315–323 CrossRef CAS
.
- I. Tvaroska and F. R. Taravel, Carbon-Proton Coupling Constants in the Conformational Analysis of Sugar Molecules, Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem., 1995, 51, 15–61, DOI:10.1016/S0065-2318(08)60191-2
.
- R. U. Lemieux, J. D. Stevens and R. R. Fraser, Observations on the Karplus Curve in Relation To the Conformation of the 1,3-Dioxolane Ring, Can. J. Chem., 1962, 40(10), 1955–1959, DOI:10.1139/v62-300
.
- J. Zhou, Y. Guo, C. Liang, L. Cao, H. Pan, J. Yang and J. Wang, A New Ether-Based Electrolyte for Lithium Sulfur Battery Using S@pPAN Cathode, Chem. Commun., 2018, 54, 5478–5481 RSC
.
- T. T. Beyene, B. A. Jote, Z. T. Wondimkun, B. W. Olbassa, C. J. Huang, B. Thirumalraj, C. H. Wang, W. N. Su, H. Dai and B. J. Hwang, Effects of Concentrated Salt and Resting Protocol on Solid Electrolyte Interface Formation for Improved Cycle Stability of Anode-Free Lithium Metal Batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11(35), 31962–31971, DOI:10.1021/acsami.9b09551
.
- J. Qian, B. D. Adams, J. Zheng, W. Xu, W. A. Henderson, J. Wang, M. E. Bowden, S. Xu, J. Hu and J. G. Zhang, Anode-Free Rechargeable Lithium Metal Batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26(39), 7094–7102, DOI:10.1002/adfm.201602353
.
- R. Younesi and F. Bardé, Electrochemical Performance and Interfacial Properties of Li-Metal in Lithium Bis(Fluorosulfonyl)Imide Based Electrolytes, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7(1), 3–8, DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-16268-7
.
- S. C. Kim, X. Kong, R. A. Vilá, W. Huang, Y. Chen, D. T. Boyle, Z. Yu, H. Wang, Z. Bao and J. Qin,
et al., Potentiometric Measurement to Probe Solvation Energy and Its Correlation to Lithium Battery Cyclability, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143(27), 10301–10308, DOI:10.1021/jacs.1c03868
.
- D. T. Boyle, S. C. Kim, S. T. Oyakhire, R. A. Vila, Z. Huang, P. Sayavong, J. Qin, Z. Bao and Y. Cui, Correlating Kinetics to Cyclability Reveals Thermodynamic Origin of Lithium Anode Morphology in Liquid Electrolytes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144(45), 20717–20725, DOI:10.1021/jacs.2c08182
.
- S. Ko, T. Obukata, T. Shimada, N. Takenaka, M. Nakayama, A. Yamada and Y. Yamada, Electrode Potential Influences the Reversibility of Lithium-Metal Anodes, Nat. Energy, 2022, 7, 1217–1224, DOI:10.1038/s41560-022-01144-0
.
- Y. Yamada, M. Yaegashi, T. Abe and A. Yamada, A Superconcentrated Ether Electrolyte for Fast-Charging Li-Ion Batteries, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 11194–11196, 10.1039/c3cc46665e
.
- X. Cao, L. Zou, B. E. Matthews, L. Zhang, X. He, X. Ren, M. H. Engelhard, S. D. Burton, P. Z. El-Khoury and H. S. Lim,
et al., Optimization of Fluorinated Orthoformate Based Electrolytes for Practical High-Voltage Lithium Metal Batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2021, 34, 76–84, DOI:10.1016/j.ensm.2020.08.035
.
- Z. Jiang, Z. Zeng, X. Liang, L. Yang, W. Hu, C. Zhang, Z. Han, J. Feng and J. Xie, Fluorobenzene, A Low-Density, Economical, and Bifunctional Hydrocarbon Cosolvent for Practical Lithium Metal Batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31, 2005991, DOI:10.1002/adfm.202005991
.
- I. Popov, R. L. Sacci, N. C. Sanders, R. A. Matsumoto, M. W. Thompson, N. C. Osti, T. Kobayashi, M. Tyagi, E. Mamontov and M. Pruski,
et al., Critical Role of Anion-Solvent Interactions for Dynamics of Solvent-in-Salt Solutions, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2020, 124(16), 8457–8466, DOI:10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b10807
.
- H. Wang, S. C. Kim, T. Rojas, Y. Zhu, Y. Li, L. Ma, K. Xu, A. T. Ngo and Y. Cui, Correlating Li-Ion Solvation Structures and Electrode Potential Temperature Coefficients, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143(5), 2264–2271, DOI:10.1021/jacs.0c10587
.
-
A. A. Maryott and E. R. Smith, Table of Dielectric Constants of Pure Liquids, Washington D.C., 1951 Search PubMed
.
- V. Viti and P. Zampetti, Dielectric Properties of 2-Methoxyethanol and 1,2-Dimethoxyethane: Comparison with Ethylene Glycol, Chem. Phys., 1973, 2, 233–238, DOI:10.1016/0301-0104(73)80009-6
.
- B. D. Adams, J. Zheng, X. Ren, W. Xu and J. G. Zhang, Accurate Determination of Coulombic Efficiency for Lithium Metal Anodes and Lithium Metal Batteries, Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(7), 1–11, DOI:10.1002/aenm.201702097
.
- C. S. Rustomji, Y. Yang, T. K. Kim, J. Mac, Y. J. Kim, E. Caldwell, H. Chung and Y. S. Meng, Liquefied Gas Electrolytes for Electrochemical Energy Storage Devices, Science, 2017, 356(6345), eaal4263, DOI:10.1126/science.aal4263
.
- Y. Gao, T. Rojas, K. Wang, S. Liu, D. Wang, T. Chen, H. Wang, A. T. Ngo and D. Wang, Low-Temperature and High-Rate-Charging Lithium Metal Batteries Enabled by an Electrochemically Active Monolayer-Regulated Interface, Nat. Energy, 2020, 5(7), 534–542, DOI:10.1038/s41560-020-0640-7
.
- X. Dong, Y. Lin, P. Li, Y. Ma, J. Huang, D. Bin, Y. Wang, Y. Qi and Y. Xia, High-Energy Rechargeable Metallic Lithium Battery at −70 °C Enabled
by a Cosolvent Electrolyte, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58(17), 5623–5627, DOI:10.1002/anie.201900266
.
- L. Stolz, G. Homann, M. Winter and J. Kasnatscheew, The Sand Equation and Its Enormous Practical Relevance for Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries, Mater. Today, 2021, 44, 9–14, DOI:10.1016/j.mattod.2020.11.025
.
- P. Bai, J. Li, F. R. Brushett and M. Z. Bazant, Transition of Lithium Growth Mechanisms in Liquid Electrolytes, Energy Environ. Sci., 2016, 9(10), 3221–3229, 10.1039/c6ee01674j
.
- C. Brissot, M. Mosso, J.-N. Chazalviel and S. Lascaud, Dendritic Growth Mechanisms in Lithium/Polymer Cells, J. Power Sources, 1999, 81–82, 925–929 CrossRef CAS
.
- G. Cai, J. Holoubek, M. Li, H. Gao, Y. Yin, S. Yu, H. Liu, T. A. Pascal and P. Liu, Solvent Selection Criteria for Temperature-Resilient Lithium – Sulfur Batteries, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2022, 119(28), e2200392119, DOI:10.1073/pnas.2200392119
.
- Y. Yamada, C. H. Chiang, K. Sodeyama, J. Wang, Y. Tateyama and A. Yamada, Corrosion Prevention Mechanism of Aluminum Metal in Superconcentrated Electrolytes, Chemelectrochem, 2015, 2(11), 1687–1694, DOI:10.1002/celc.201500235
.
- X. Cao, X. Ren, L. Zou, M. H. Engelhard, W. Huang, H. Wang, B. E. Matthews, H. Lee, C. Niu and B. W. Arey,
et al., Monolithic Solid–Electrolyte Interphases Formed in Fluorinated Orthoformate-Based Electrolytes Minimize Li Depletion and Pulverization, Nat. Energy, 2019, 4(9), 796–805, DOI:10.1038/s41560-019-0464-5
.
- W. Xue, M. Huang, Y. Li, Y. G. Zhu, R. Gao, X. Xiao, W. Zhang, S. Li, G. Xu and Y. Yu,
et al., Ultra-High-Voltage Ni-Rich Layered Cathodes in Practical Li Metal Batteries Enabled by a Sulfonamide-Based Electrolyte, Nat. Energy, 2021, 6(5), 495–505, DOI:10.1038/s41560-021-00792-y
.
- E. Zhang, Y. Chen, Z. Yu, Y. Cui and Z. Bao, Monofluorinated Ether Electrolyte with Acetal Backbone for High-Performance Lithium Metal Batteries, arXiv, 2023, preprint, arXiv:2305.19580, DOI:10.48550/arXiv.2305.19580.
- G. A. Giffin, The Role of Concentration in Electrolyte Solutions for Non-Aqueous Lithium-Based Batteries, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 5250, DOI:10.1038/s41467-022-32794-z
.
- O. Borodin, J. Self, K. A. Persson, C. Wang and K. Xu, Uncharted Waters: Super-Concentrated Electrolytes, Joule, 2020, 4(1), 69–100, DOI:10.1016/j.joule.2019.12.007
.
- Y. Yamada, J. Wang, S. Ko, E. Watanabe and A. Yamada, Advances and Issues in Developing Salt-Concentrated Battery Electrolytes, Nat. Energy, 2019, 4(4), 269–280, DOI:10.1038/s41560-019-0336-z
.
- Y. Chen, Z. Yu, H. Gong, W. Zhang, P. Rudnicki, Z. Huang, W. Yu, S. C. Kim, D. T. Boyle and P. Sayavong,
et al., Failure Process During Fast Charging of Lithium Metal Batteries with 2 Weakly Solvating Fluoroether Electrolytes, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2024, 128(28), 11487–11497, DOI:10.1021/acs.jpcc.4c01740
.
- Z. J. Hoffman, D. B. Shah and N. P. Balsara, Temperature and Concentration Dependence of the Ionic Transport Properties of Poly (Ethylene Oxide) Electrolytes, Solid State Ionics, 2021, 370, 115751, DOI:10.1016/j.ssi.2021.115751
.
- Y. Li, Y. Li, A. Pei, K. Yan, Y. Sun, C. L. Wu, L. M. Joubert, R. Chin, A. L. Koh and Y. Yu,
et al., Atomic
Structure of Sensitive Battery Materials and Interfaces Revealed by Cryo–Electron Microscopy, Science, 2017, 358(6362), 506–510, DOI:10.1126/science.aam6014
.
- B. S. Interphases, W. Huang, H. Wang, D. T. Boyle, Y. Li and Y. Cui, Resolving Nanoscopic and Mesoscopic Heterogeneity of Fluorinated Species in Battery Solid-Electrolyte Interphases by Cryogenic Electron Microscopy, ACS Energy Lett., 2020, 5, 1128–1135, DOI:10.1021/acsenergylett.0c00194
.
- C. Lee, W. Yang and R. G. Parr, Development of the Colle-Salvetti Correlation-Energy Formula into a Functional of the Electron Density, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 1988, 37, 785–789 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. Grimme, J. Antony, S. Ehrlich and H. Krieg, A Consistent and Accurate Ab Initio Parametrization of Density Functional Dispersion Correction (DFT-D) for the 94 Elements H-Pu, J. Chem. Phys., 2010, 132, 154104, DOI:10.1063/1.3382344
.
- S. Grimme, S. Ehrlich and L. Goerigk, Effect of the Damping Function in Dispersion Corrected Density Functional Theory, J. Comput. Chem., 2011, 32, 1456–1465, DOI:10.1002/jcc
.
- F. Weigend and R. Ahlrichs, Balanced Basis Sets of Split Valence, Triple Zeta Valence and Quadruple Zeta Valence Quality for H to Rn: Design and Assessment of Accuracy, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2005, 7, 3297–3305, 10.1039/b508541a
.
- F. Neese, F. Wennmohs, U. Becker and C. Riplinger, The ORCA Quantum Chemistry Program Package, J. Chem. Phys., 2020, 152, 224108, DOI:10.1063/5.0004608
.
- M. J. Abraham, T. Murtola, R. Schulz, S. Páll, J. C. Smith, B. Hess and E. Lindah, Gromacs: High Performance Molecular Simulations through Multi-Level Parallelism from Laptops to Supercomputers, SoftwareX, 2015, 1–2, 19–25, DOI:10.1016/j.softx.2015.06.001
.
- J. Wang, R. M. Wolf, J. W. Caldwell, P. A. Kollman and D. A. Case, Development and Testing of a General Amber Force Field, J. Comput. Chem., 2004, 25, 1157–1174, DOI:10.1002/jcc.20035
.
- A. W. Sousa Da Silva and W. F. Vranken, ACPYPE - AnteChamber PYthon Parser InterfacE, BMC Res. Notes, 2012, 5, 367, DOI:10.1186/1756-0500-5-367
.
- J. Wang, W. Wang, P. A. Kollman and D. A. Case, Automatic Atom Type and Bond Type Perception in Molecular Mechanical Calculations, J. Mol. Graph. Model., 2006, 25, 247–260, DOI:10.1016/j.jmgm.2005.12.005
.
-
M. J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, G. E. Scuseria, M. A. Robb, J. R. Cheeseman, G. Scalmani, V. Barone, G. A. Petersson, H. Nakatsuji, et al., Gaussian 16, Revision B.01, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2016 Search PubMed
.
- J. Self, K. D. Fong and K. A. Persson, Transport in Superconcentrated LiPF6 and LiBF4/Propylene Carbonate Electrolytes, ACS Energy Lett., 2019, 4(12), 2843–2849, DOI:10.1021/acsenergylett.9b02118
.
- N. Michaud-Agrawal, E. J. Denning, T. B. Woolf and O. Beckstein, Software News and Updates MDAnalysis: A Toolkit for the Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Simulations, J. Comput. Chem., 2011, 32(10), 2319–2327, DOI:10.1002/jcc.21787
.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4sc05319b |
| ‡ Y. Chen and S. L. contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |
