Langevin dynamics simulations for the critical adsorption of end-grafted active polymers†
Abstract
The critical adsorption of end-grafted active polymer chains on an attractive surface is studied using Langevin dynamics simulations. The active polymers are composed of an active Langevin particle located at the head and a sequential passive chain. Results show that the active force exerted by the active head pulls the active polymer away from the surface. Consequently, the adsorption of the active polymer is hindered, and the critical surface attraction strength, 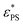 , increases proportionally to the square of the active force, Fa2. The increase in
, increases proportionally to the square of the active force, Fa2. The increase in 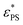 depends on the rotation behavior of the active head. Specifically, for the restricted rotating active polymer (RRAP) chain with a longer rotational persistence time as the rotation of the active head is restricted,
depends on the rotation behavior of the active head. Specifically, for the restricted rotating active polymer (RRAP) chain with a longer rotational persistence time as the rotation of the active head is restricted, 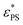 increases significantly with Fa. On the other hand, for the freely rotating active polymer (FRAP) chain with a shorter rotational persistence time as the rotation of the active head is free,
increases significantly with Fa. On the other hand, for the freely rotating active polymer (FRAP) chain with a shorter rotational persistence time as the rotation of the active head is free, 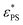 shows a weak dependence on Fa. The results show that the active force has a significantly stronger pulling effect on the RRAP chain than on the FRAP chain. Furthermore, knotted conformations are observed for the adsorbed RRAP chain at large Fa. These knots reduce the adsorption of monomers near the grafted end. In contrast, no knotted conformations are observed for the FRAP chains due to the comparatively weaker pulling effect of the active force.
shows a weak dependence on Fa. The results show that the active force has a significantly stronger pulling effect on the RRAP chain than on the FRAP chain. Furthermore, knotted conformations are observed for the adsorbed RRAP chain at large Fa. These knots reduce the adsorption of monomers near the grafted end. In contrast, no knotted conformations are observed for the FRAP chains due to the comparatively weaker pulling effect of the active force.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...