Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleADEL: an automated drop-cast electrode setup for high-throughput screening of battery materials†
Maha
Ismail
 ab,
Maria Angeles
Cabañero
ad,
Joseba
Orive
a,
Lakshmipriya Musuvadhi
Babulal
a,
Javier
Garcia
a,
Maria C.
Morant-Miñana
ab,
Maria Angeles
Cabañero
ad,
Joseba
Orive
a,
Lakshmipriya Musuvadhi
Babulal
a,
Javier
Garcia
a,
Maria C.
Morant-Miñana
 a,
Jean-Luc
Dauvergne
a,
Francisco
Bonilla
a,
Iciar
Monterrubio
a,
Javier
Carrasco
a,
Jean-Luc
Dauvergne
a,
Francisco
Bonilla
a,
Iciar
Monterrubio
a,
Javier
Carrasco
 ac,
Amaia
Saracibar
b and
Marine
Reynaud
ac,
Amaia
Saracibar
b and
Marine
Reynaud
 *a
*a
aCentre for Cooperative Research on Alternative Energies (CIC EnergiGUNE), Basque Research and Technology Alliance (BRTA), Alava Technology Park, Albert Einstein 48, 01510 Vitoria-Gasteiz, Spain. E-mail: mreynaud@cicenergigune.com
bPhysical Chemistry Department, Pharmacy Faculty, Basque Country University (UPV/EHU), 01006 Vitoria-Gasteiz, Álava, Spain
cIKERBASQUE, Basque Foundation for Science, Plaza Euskadi 5, 48009 Bilbao, Spain
dFEV Iberia, Calle Cardenal Gardoqui 1, 48008 Bilbao, Spain
First published on 28th February 2025
Abstract
Screening electrode materials in conventional battery research is time-consuming due to the lengthy and intricate preparation process, where multiple parameters directly influence electrochemical performance. In this work, we present ADEL, an affordable module for the Automated preparation of high-loading Drop-cast ELectrodes, integrated within MAITENA, a Materials Acceleration and Innovation plaTform for ENergy Applications. The process consists of two main steps: (i) the automated preparation of electrode slurries and (ii) the drop-casting of these slurries onto aluminum foils using a pipetting robot, followed by drying under a halogen lamp. ADEL enables the preparation of 48 electrodes per day, allowing for the screening of up to 24 distinct active materials and/or electrode formulations. We demonstrate the method's repeatability using various commercial and lab-synthesized battery materials in different cell configurations, consistently achieving results with less than 3% relative standard deviation. As such, ADEL provides reliable, high-quality datasets for fast screening of battery materials, significantly accelerating research and development efforts.
Introduction
Energy storage needs have dramatically increased driven by the growing demands in transportation and grid-scale applications. Next-generation batteries are expected to provide high energy capabilities, excellent safety measures, extended cycle life, significant sustainability, and cost-effectiveness.1,2 In this context, accelerating research efforts to explore new systems and chemistries is essential to meet the increasing demands and successfully tackle the challenges posed by the global energy transition.3,4The adoption of high-throughput methods, which refer to a workflow of running multiple analogous experiments simultaneously,5 is acknowledged as a crucial step to accelerate the discovery and optimization of new materials. These methods include computational methods,6–9 automated synthesis for combinatorial experimentation,10–15 and advanced characterization,16–18 and have been applied to the development of materials for various energy-related fields such as batteries, electrocatalysis, photocatalysis, photovoltaics, and fuel cells.5,19–22 Moreover, a growing trend toward integrating these approaches with data-driven methods and artificial intelligence aims to elaborate “closed-loop” methodologies – usually implemented in Self-Driving Laboratories (SDLs) or Materials Acceleration Platforms (MAPs) – where feedback from previous trials is used to dynamically adjust and optimize the research process.23–29 Generating extensive and high-quality datasets is of primary importance for developing reliable predictive models, enabling efficient data analysis, and enhancing decision-making processes.30 In this regard, automated setups enhance data reliability by minimizing human error due to manual intervention, ensuring consistency under experimental conditions, and enhancing reproducibility across trials.20
The overall electrochemical performance of batteries depends on the critical properties of their components and their compatibility, which includes electrode active materials, electrolytes, conductive additives, binders, and current collectors.5 Significant work has recently been performed to develop high-throughput testing for liquid electrolytes.30–35 However, screening electrode materials constitutes a greater challenge, as optimizing the electrode manufacturing process involves multiple steps and interdependent variables, resulting in greater complexity and time consumption.36,37 The process requires preparing a well-mixed slurry made of an active material, a binder and a conductive material homogeneously dispersed in a solvent, which is then cast onto a current collector and dried. Each step presents key variables that must be controlled, such as the mixing time and viscosity, conditioned by the solid content, particle size distribution and morphology, as well as the electrode drying protocol. In addition, the electrode formulation and preparation process define the final electrode's porosity and microstructure, which directly impacts the electrochemical performance of the battery in terms of energy density and cyclability.36,38 Therefore, establishing a systematic method for automated lab-scale electrode preparation is essential to facilitate reliable and fast screening of electrode materials within accelerated battery material development workflows.
Various combinatorial and high-throughput methods have been proposed to overcome the time limitation of electrode preparation starting from the early 21st century. Sputtering techniques have been widely used to investigate thin film electrodes using multicell setups.39–45 McCalla et al.44 adopted a multicell setup, developed by Dahn's group41,42 for thin films, to investigate 64 powder cathode materials synthesized through high-throughput coprecipitation employing precise drop-casting of the slurry onto adhered aluminum foil on a printed circuit board. This methodology requires high precision to get good reproducibility and avoid cross-contamination during the assembly of the cell. It led to specific capacities exhibiting a standard deviation of approximately 7.5% across the samples. Another approach involving micro-dispensing and high-speed jetting was investigated for different electrode materials and SiO2-based separators with feature sizes above ca. 0.6–1 mm.46 Although these studies are effective for understanding thin film batteries, they do not necessarily reflect the representative bulk active material behavior in commercial batteries.44,45
While moving beyond thin-film and microscale electrodes appears necessary, studies focusing on testing representative bulk electrode materials remain scarce. Furthermore, they are largely limited to specific multicell designs and have not been extended to common lab-scale cell configurations such as coin cells, Swagelok cells, or tailor-made operando set-ups.15,44,47 Moreover, lab-scale electrodes are typically prepared and tested with low mass loading (ranging from 2 to 4 mg cm−2),48 far from the requirements of commercial batteries, which demand high mass loading to achieve high energy density. Therefore, it is desirable to increase the mass loading of newly tested electrodes to evaluate them under conditions closer to those of actual batteries.48
Here, we present an affordable automated module for high-throughput electrode preparation, named ADEL (Automated Drop-cast Electrodes setup), which is integrated into the self-driving lab MAITENA (Materials Acceleration and Innovation plaTform for ENergy Applications) at CIC EnergiGUNE. This set-up enables the production of reproducible, high-quality electrode mass loadings exceeding those achieved with conventional lab-scale methods. It serves as an alternative to doctor blade casting and punching for electrode testing in various lab cell configurations. The reproducibility and suitability of the method are demonstrated using several state-of-the-art Li-ion cathode materials, and its practical applicability in MAPs is illustrated through a case study screening multiple lithium-rich layered oxides as cathode active materials.
Experimental setup
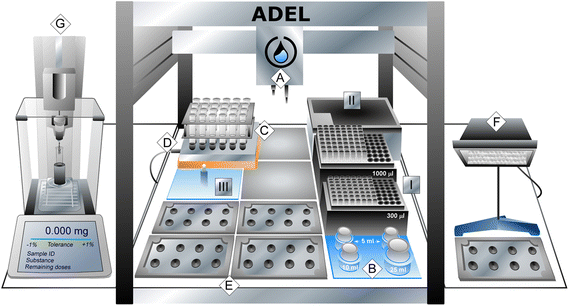
The typical process for electrode preparation consists of casting a slurry of active materials and additives onto a current collector. Automating this procedure can be efficiently achieved through a pipetting workflow executed by liquid-handling robots. The primary challenge in this process lies in managing the pipetting of viscous electrode slurries, which requires thorough optimization to ensure reproducibility. The Ot-2 robot (Opentrons, USA) was chosen as an affordable and efficient solution that is ready to use, easy to operate through protocol designers, and capable of handling high-viscosity liquids.49,50 Considering the limited space available for each deck slot in this compact system, the robot was equipped with a MIXdrive 24 MTP multi-position stirring plate (from MIXdrive 24P), selected as the most suitable option to enable the simultaneous preparation of 24 electrode slurries.Fig. 1 presents a sketch of ADEL, a setup developed to automate the electrode preparation. A photo and a video of the setup are provided in Fig. SI-1(a), Section S1 (ESI).† The module was built around an Ot-2 robot, featuring two pipettes of 300 and 1000 μl ([A] in main elements). This robot was equipped with several 3D-printed custom key components (see Section S2, ESI†), including a multi-vial holder to accommodate the initial binder solutions and solvents [B] (Fig. SI-2†), a holder specifically designed to hold up to 24 test tubes filled with solid powders [C] on top of the multi-position stirring plate [D] (Fig. SI-3†), and up to 6 holders to fix aluminum foils [E] (Fig. SI-4(d)†). A magnet (III in other accessories) was used as a pipette tip to recover the magnetic bars from the tubes when required. In addition, the module includes a halogen lamp [F] to facilitate the drying process, as described later.
The process for preparing electrodes using this setup is described as follows. The initial liquid mixtures [B] are prepared by mixing a defined amount of a binder (e.g. polyvinylidene fluoride, PVDF) and a solvent (e.g. N-methylpyrrolidone, NMP). Weighing the solid powders (active material and carbon source) in the test tubes [C] is carried out separately for each component using an automatic solid dispenser [G] (Mettler Balance XPR106DUHQ, see Fig. SI-1(b) in Section S1, ESI†), placed later in the tube holder of the multi-position stirring plate [D]. The automated electrode preparation process initiates with the pipetting of 500 μl from the mixture [B] onto 100 mg of solid powders within each tube [C]. Following this, two hours of mixing at 900 rpm ensures a well-mixed and homogeneous slurry consistency, ensuring the desired viscosity, which will be discussed later. It is to be noted that the mixing duration may vary depending on the materials' properties (e.g. particle morphology and agglomerates) and, in some cases, may require adjustments based on slurry consistency. However, in this work, the mixing duration was fixed at two hours for all materials studied. The second step involves pipetting 100 μl of the prepared slurry onto the aluminum foils to form each electrode, allowing pipetting 4 electrodes from each tube. The pipetting parameters used for the aspiration/dispensing steps are provided in Table SI-1† and will be described in the pipetting optimization section. The six custom-printed holders [E] enable the preparation of 48 electrodes per run (i.e. at least 2 electrodes from each slurry). The entire process, including automated solid weighting (half an hour), slurry mixing (2 hours), and finally electrode dispensing (half an hour), requires a total of 3 hours per run.
The initial drying of the electrodes is carried out at room temperature for 3 to 4 hours to preserve their shape. Then, they are dried under a halogen lamp [F] for typically 3 hours. Afterward, the electrodes are punched with an automated 12 mm puncher (Nogami) and weighted individually. Finally, the electrodes are dried in a Buchi oven at 120 °C to eliminate any moisture before being transferred to a glove box for cell assembly.
While the drop-casting method is fully automated via the Ot-2 robot, tube transfers from the automated balance to the Ot-2 and Al foil holder transfers to the halogen lamp were done here manually. These brief interventions at the beginning and the end of the process do not require continuous researcher presence, but also serve as key checkpoints for verifying sample quality. Further automation using a robotic arm would be possible given the flexibility of the ADEL setup, but is beyond the scope of this study. Overall, the ADEL setup allows for the screening of up to 24 distinct active materials, with minimal human intervention required for initial and final transfers.
Results and discussion
In order to optimize the automated electrode preparation process, LiNi0.5Mn0.3Co0.2O2 (NMC-532, MTI EQ-Lib-LNCM523) was chosen as a model commercial cathode active material to prepare a series of electrodes using a slurry formulation of 84![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8
8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8 wt% (active material
8 wt% (active material![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) carbon
carbon![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) binder). The optimization of the process includes viscosity evaluation, pipetting and drying optimization steps, as presented in Fig. 2. Given the viscous nature of the slurry, optimizing the aspiration and dispensing protocols was crucial to ensure the reproducibility of the results. This optimization seeks to prevent distorted results caused by potential volume variations of the pipetted liquid, which can arise from bubbles, air gaps, and any residual fluid in the pipette tip during the pipetting process. To this end, two viscous mixtures of glycerin and water, GW75 (75% wt glycerin and 25% wt water) and GW90 (90% wt glycerin and 10% wt water), were first employed to optimize the pipetting parameters and mimic the viscosity of the slurry, with particular emphasis on regulating the flow rate, as depicted in Table SI-1.† Supplementary features of the Ot-2 robot were applied to improve pipetting accuracy, including adjustments of the tip position, timing delays, and utilization of the blowout function (see Table SI-1†). The viscosity values of the NMC slurry as a function of the shear rate fall between the viscosities of the two GW mixtures, as shown in Fig. 2(a) (details of the viscosity test are provided in Section S3, ESI†). In contrast to the Newtonian behavior of the GW mixtures, the viscosity of the NMC slurry decreases with the shear rate, which is indicative of the shear thinning behavior of non-Newtonian slurries. The viscosity values of the NMC slurry are close to 10−2 Pa s across the entire shear rate range and these low values37 can be explained by the low solid content (17 wt%) of the dispersion. This is notably lower than the solid content typically used on the lab scale (25 to 40 wt%) and manufacturing scale (50 to 65 wt%) for slurry preparation.51 This low solid content is required for the drop-casting electrode preparation method employed in this process. To ensure successful pipetting, we adopted the pipetting parameters used for the most viscous sample (GW90) at the pipetting shear rate (1375 s−1), considering the viscosity difference as a safety margin.
binder). The optimization of the process includes viscosity evaluation, pipetting and drying optimization steps, as presented in Fig. 2. Given the viscous nature of the slurry, optimizing the aspiration and dispensing protocols was crucial to ensure the reproducibility of the results. This optimization seeks to prevent distorted results caused by potential volume variations of the pipetted liquid, which can arise from bubbles, air gaps, and any residual fluid in the pipette tip during the pipetting process. To this end, two viscous mixtures of glycerin and water, GW75 (75% wt glycerin and 25% wt water) and GW90 (90% wt glycerin and 10% wt water), were first employed to optimize the pipetting parameters and mimic the viscosity of the slurry, with particular emphasis on regulating the flow rate, as depicted in Table SI-1.† Supplementary features of the Ot-2 robot were applied to improve pipetting accuracy, including adjustments of the tip position, timing delays, and utilization of the blowout function (see Table SI-1†). The viscosity values of the NMC slurry as a function of the shear rate fall between the viscosities of the two GW mixtures, as shown in Fig. 2(a) (details of the viscosity test are provided in Section S3, ESI†). In contrast to the Newtonian behavior of the GW mixtures, the viscosity of the NMC slurry decreases with the shear rate, which is indicative of the shear thinning behavior of non-Newtonian slurries. The viscosity values of the NMC slurry are close to 10−2 Pa s across the entire shear rate range and these low values37 can be explained by the low solid content (17 wt%) of the dispersion. This is notably lower than the solid content typically used on the lab scale (25 to 40 wt%) and manufacturing scale (50 to 65 wt%) for slurry preparation.51 This low solid content is required for the drop-casting electrode preparation method employed in this process. To ensure successful pipetting, we adopted the pipetting parameters used for the most viscous sample (GW90) at the pipetting shear rate (1375 s−1), considering the viscosity difference as a safety margin.
Next, the volume of pipetting was adjusted to ensure the formation of a well-defined 12 mm electrode after drying, as illustrated in Fig. 2(b). To determine the optimal conditions, the dropped volume was varied between 250 and 50 μl. When using volumes higher than 150 μl, the resulting electrodes presented cracks after drying, attributed to the higher concentration of solids in the center of the electrode as the result of the spread of the NMP solvent towards the edges. The best results were eventually obtained using a volume of 100 μl, consistently yielding reproducible 12 mm diameter electrodes free of cracks. Note that, similarly to the doctor blade method, which requires the application of vacuum to maintain the aluminum foil, the shape and quality of electrodes produced in the automated module also depend on the flatness of the Al foils. Therefore, several Al foil tailor-made holder designs were investigated (see Fig. SI-4 in Section S2, ESI†). The final design incorporated neodymium magnets positioned at the corners of the holder, providing optimal fixation of the Al foil. This approach also facilitated the easy handling and removal of the foils after electrode preparation, while reducing both costs and space required for the final setup.
Drying the electrodes right away after pipetting was initially attempted; however, it resulted in crack formation. Therefore, the electrodes were first preconditioned by leaving them at room temperature for 3 to 4 hours to slowly evaporate the solvent. Then, four different drying methods – vacuum oven, heating plate, infrared lamp, and halogen lamp – were evaluated (Fig. 2(c)). The drying process (for the heating plate, infrared lamp, and halogen lamp) was monitored on an hourly basis to assess when it appeared to be relatively completed. Once the electrode was observed to be free of solvent, an additional hour of drying was applied to ensure thorough and complete drying. The standard drying method at 80 °C for 8 hours under vacuum yielded crack-free dried electrodes (Fig. 2(c)). To accelerate the drying step, the use of a heating plate was evaluated, but this resulted in the deformation of the drop shapes (see Fig. 2(c)) and inhomogeneous electrode loading after cutting.
Alternatively, the previously reported use of a round infrared (IR) lamp (PHILIPS PAR38 IR)52 was tested. The homogeneity of this illumination was assessed using an infrared camera to map the apparent temperatures of the whole Al foil surface during the drying process (details of the illumination test are provided in Section S4, ESI†). The recorded data presented in Fig. 3(a) showed that this configuration led to non-uniform heating with variations that could exceed 10 °C across the Al foil. While a rectangular IR lamp should help to mitigate these special variations in illumination, the use of a halogen lamp is a more affordable alternative. Likewise, the temperature gradients provided by the illumination of a halogen lamp (RS PRO Floodlight, 400 W) are presented in Fig. 3(b), showing that the use of this lamp substantially improved the temperature distribution on the electrode area, with a deviation of only 3 °C between the center and the borders. The implementation of this halogen lamp for electrode drying, which to the best of our knowledge has not been reported elsewhere, proved to effectively dry the electrodes within a remarkably short period of 3 hours. This cost-effective and easily accessible solution was subsequently implemented. Regardless of the drying process, the electrochemical performance of all electrodes consistently yields results closely similar to those obtained with the standard lab method (i.e. doctor blade coating) (see Fig. SI-5 in Section S4 and Fig. SI-6 in Section S5, ESI†). Therefore, these results show that using the halogen lamp for drying electrodes offers significant advantages in terms of time savings and affordability, making it an attractive electrode drying option to adopt in any laboratory.
Following the optimization process described above, the electrochemical performance of the NMC-532 electrodes produced by this protocol was first compared to that of electrodes produced using the standard lab-scale doctor blade method, showing very similar results with an average capacity of 168.05 mA h g−1 for the doctor blade method and 169.80 mA h g−1 for the ADEL method (Fig. SI-6 in Sections S5 and S8 for electrochemical testing details, ESI†). To assess the global electrodes' homogeneity, Micro-Computed Tomography (micro-CT) was performed on sections of two of the NMC-532 electrodes, enabling a 3D reconstruction of the electrodes' surface and thickness (see experimental details in ESI, Section S5†). Both reconstructions (shown in Fig. SI-7(a) and (b)†) indicate a consistent thickness across the electrodes, with the ADEL electrode measuring 109.9 ± 9.8 μm and the doctor blade electrode 73.8 ± 5.8 μm. To complement the micro-CT findings and achieve higher resolution, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis was performed on cross-sections of the same samples, prepared using ion milling (IM) techniques (see experimental details in ESI, Section S5†). This approach enabled high-resolution visualization of microstructural features within individual particles, achieving nanometric spatial resolution. By integrating micro-CT for macroscopic thickness measurements with SEM for high-resolution microstructural analysis, a multiscale characterization strategy was established, providing a comprehensive assessment of the electrode's structural integrity and material distribution. As shown in Fig. 4(a) and (b) from the IM cross-section SEM images, a significantly greater thickness – nearly double – was observed for the electrode prepared using the ADEL method, confirming that the drop-cast electrodes exhibited substantially higher mass loading. In addition, both images show a relatively uniform distribution of the active material, conductive additive, and binder across the electrode thickness, regardless of the casting method. In terms of surface homogeneity, some defects were detected on the drop-cast electrode, while the doctor blade electrode appears relatively smooth. However, these defects are minor and within an acceptable range, as supported by the electrochemical results, which will be discussed in detail later. Overall, the comparison of these two methods shows that the automated protocol is faster and more efficient, minimizing material waste by converting the entire slurry into a defined number of drop-cast electrodes that are later assembled in the electrochemical cells. In addition, despite the low solid content of the slurry, the ADEL setup produces high-loading electrodes, closer to actual battery requirements.
 | ||
| Fig. 4 SEM cross-section images of NMC-532 electrodes prepared by (a) the drop-cast ADEL method and (b) the standard lab-scale doctor blade method. | ||
The reproducibility of the slurry preparation was assessed using a series of six NMC-532 drop-cast electrodes from three distinct slurries (i.e. two electrodes per slurry). Fig. 5(a) shows the specific capacity of the cells after cycling at C/20, C/10, C/5, and 1C, respectively (the corresponding data are presented in Table SI-2 and Section S5, ESI†). The six cells exhibit remarkably comparable capacities at each C rate and are in good agreement with the reported data for NMC-532,53 demonstrating the high reproducibility of the prepared slurries.
To go further in the statistical data and calculate the standard deviation of the method, another series of ten drop-cast electrodes of NMC-532 was prepared. They were assembled into coin cells and subjected to the same cycling method as described above. Fig. 5(b) displays the distribution of the specific capacity obtained for each cell at different C-rates, together with their respective relative standard deviation (data presented in Table SI-3, Section S5, ESI†). The average mass loading over 10 electrodes was 12.12 ± 0.72 mg cm−2 (Table SI-3†), which represents a 6% mass variation, indicating a remarkable uniformity of the weight obtained after electrode pipetting. The average capacity obtained at C/20 is 170.4 mA h g−1 with a relative standard deviation of 1.1% between electrodes, while cycling at C/10 and C/5 provides slightly lower average discharge capacities but maintains the relative standard deviation below 1% at both rates. Increasing the C-rate up to 1C leads to an average capacity of 137.6 mA h g−1 with a slightly higher relative standard deviation of 3.5%. Despite this increase, the standard deviation obtained at 1C remains very low, especially considering that the electrodes were not calendared. Generally, numerous factors influence the electrochemical performance of electrode materials beyond electrode preparation,36 including the electrolyte used for the electrode assessment38 as well as cell-to-cell variations due to cell assembly.54 Taking all these parameters into account, the automated protocol presented herein reflects significant reproducibility with a very small standard deviation, and to the best of our knowledge, is not reported elsewhere at these C-rates using other automatization setups.44,55
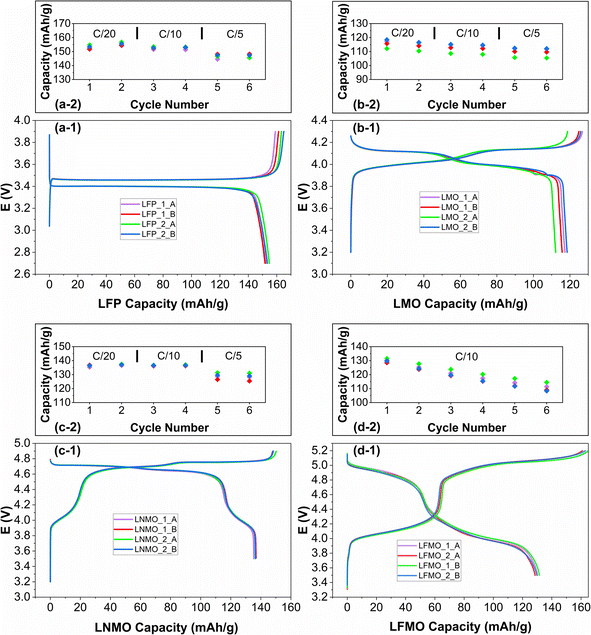
After demonstrating the suitability of ADEL for producing NMC layered oxide electrodes, other state-of-the-art positive electrode materials (i.e. spinel and olivine materials) were tested to validate the versatility of the module toward the main families of Li-ion cathode active materials. In this regard, three commercial electrode materials exhibiting diverse particle size distributions and morphologies were employed: (i) high-voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 (LNMO, TBM-129 from TOPSOE) having spherical particles with an average particle size between 5 and 20 μm, (ii) carbon-coated LiFePO4 (LFP/C, from Advanced Lithium Electrochemistry Co.), consisting of tabular particles with diameters ranging from 50 to 300 nm,56 and (iii) spinel LiMn2O4 presenting nanoparticles with particle sizes below 500 nm (LMO, >99% Sigma-Aldrich). To complete this materials assessment, 5 V spinel LiFe0.5Mn1.5O4 (LFMO) synthesized in our laboratory (see Section S7, ESI†) was also tested to verify that the ADEL automated drop-cast electrode method can be effectively applied to non-optimized materials, which may present larger particle size distribution, non-uniform morphologies, and composition variability. To further validate the reproducibility of the preparation of both the slurries and electrodes, two separate slurries were prepared for each material, and two electrodes were produced from each slurry. The same exact formulation of 84![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8
8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8 wt% (active material
8 wt% (active material![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) carbon
carbon![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) binder) was used for all the selected materials. Fig. 6(a-1)–(d-1) show the charge and discharge curves of the first cycle of the four cells prepared for each material – LFP, LMO, LNMO, and LFMO (electrochemical testing details are provided in Section S8, ESI†). All cycling curves show the characteristic behavior of the tested materials. LFP/C (Fig. 6(a-1)) presents a flat plateau centered at 3.4 V vs. Li+/Li0 with an average capacity of 153.2 ± 1.2 mA h g−1 at C/20.57 The voltage profile and capacity of 115.9 ± 2.4 mA h g−1 obtained for the LMO material (Fig. 6(b-1)) align well with the data reported in the literature.58,59 LNMO (Fig. 6(c-1)) exhibits the characteristic feature of the Mn3+/Mn4+ redox couple around 4.0 V Li+/Li0 in addition to the two high-voltage plateaus associated with Ni2+/Ni3+ and Ni3+/Ni4+ around 4.8 V vs. Li+/Li0, resulting in an average capacity of 136.3 ± 0.5 mA h g−1 upon discharge, consistent with reported cycling data.60 The electrochemical curves of LFMO presented in Fig. 6(d-1) exhibit the typical two high-voltage processes associated with the Mn3+/Mn4+ and Fe3+/Fe4+ redox couples, with an average capacity of 130.0 mA h g−1 ± 1.1 mA h g−1, in line with the best results reported in the literature.61 The low reversibility over the first charge/discharge cycle is not inherent to the electrode preparation but is attributed to electrolyte side reactions at high voltage and to the material itself. It is worth noting that none of the 16 electrodes tested exhibited higher polarization than what is typically observed with conventional electrode preparation. This is particularly relevant for characterizing high-voltage cathode materials such as LNMO or LFMO, which require cycling at voltages up to 5.2 V vs. Li+/Li0. In such cases, any overpotential arising from the electrode preparation can dramatically hinder the material's performance. On the other hand, the evolution of the capacity over the first 6 cycles is also presented for all 16 cells in Fig. 6(a-2)–(d-2), showing high reproducibility with a variation of less than 5 mA h g−1 between the four cells of each material. A higher dispersion of the capacity results is observed at higher C-rates and in the LMO cells, where the nanometric size of the LMO particles may slightly affect the reproducibility of the slurry and electrode drop-casting,62 though it remains within a satisfactory range.
binder) was used for all the selected materials. Fig. 6(a-1)–(d-1) show the charge and discharge curves of the first cycle of the four cells prepared for each material – LFP, LMO, LNMO, and LFMO (electrochemical testing details are provided in Section S8, ESI†). All cycling curves show the characteristic behavior of the tested materials. LFP/C (Fig. 6(a-1)) presents a flat plateau centered at 3.4 V vs. Li+/Li0 with an average capacity of 153.2 ± 1.2 mA h g−1 at C/20.57 The voltage profile and capacity of 115.9 ± 2.4 mA h g−1 obtained for the LMO material (Fig. 6(b-1)) align well with the data reported in the literature.58,59 LNMO (Fig. 6(c-1)) exhibits the characteristic feature of the Mn3+/Mn4+ redox couple around 4.0 V Li+/Li0 in addition to the two high-voltage plateaus associated with Ni2+/Ni3+ and Ni3+/Ni4+ around 4.8 V vs. Li+/Li0, resulting in an average capacity of 136.3 ± 0.5 mA h g−1 upon discharge, consistent with reported cycling data.60 The electrochemical curves of LFMO presented in Fig. 6(d-1) exhibit the typical two high-voltage processes associated with the Mn3+/Mn4+ and Fe3+/Fe4+ redox couples, with an average capacity of 130.0 mA h g−1 ± 1.1 mA h g−1, in line with the best results reported in the literature.61 The low reversibility over the first charge/discharge cycle is not inherent to the electrode preparation but is attributed to electrolyte side reactions at high voltage and to the material itself. It is worth noting that none of the 16 electrodes tested exhibited higher polarization than what is typically observed with conventional electrode preparation. This is particularly relevant for characterizing high-voltage cathode materials such as LNMO or LFMO, which require cycling at voltages up to 5.2 V vs. Li+/Li0. In such cases, any overpotential arising from the electrode preparation can dramatically hinder the material's performance. On the other hand, the evolution of the capacity over the first 6 cycles is also presented for all 16 cells in Fig. 6(a-2)–(d-2), showing high reproducibility with a variation of less than 5 mA h g−1 between the four cells of each material. A higher dispersion of the capacity results is observed at higher C-rates and in the LMO cells, where the nanometric size of the LMO particles may slightly affect the reproducibility of the slurry and electrode drop-casting,62 though it remains within a satisfactory range.
After having validated the automated ADEL method with several state-of-the-art cathode materials, it was employed to screen the electrochemical performance of a series of samples of Li-rich layered oxides. Lithium-rich materials represent a promising and challenging family of high-energy cathode materials, which offer extra capacity by involving anionic redox reactions. Low initial coulombic efficiencies, voltage fading due to structural transformations and limited rate capability in full cells are some of the challenges that can be tackled through the optimization of these materials. In this case study, we investigated the effects of varying Li content and annealing temperature on the coulombic efficiency and discharge capacity of lab-prepared Li1+x(Mn,Ni)O2 (LMR) samples (see Section S7 for material synthesis, and Section S8 for electrochemical testing details in the ESI†). The reproducibility of the slurries and electrodes was firstly assessed considering a specific selected composition, Li1.35(Mn,Ni)O2, by preparing three distinct slurries, with two electrodes per slurry. The discharge capacities of the formation cycles at C/20 and the subsequent two cycles at C/10 for the resulting six LMR electrodes are displayed in Fig. SI-8 (Section S6, ESI†). The obtained discharge capacity values are tabulated in Table SI-4.† Each LMR electrode displayed a similar discharge capacity with an average value of 272.05 mA h g−1 at C/20 and a relative standard deviation of 1.0%. In the second and third cycles at C/10, the electrodes still deliver high discharge capacities around 250 mA h g−1 with a relative standard deviation below 2%. Then, a series of 20 different LMR samples were synthesized at five distinct temperatures with varying lithium content, defined as the lithium to transition metal ratio (Li/TM). Fig. 7 compares the discharge capacity and coulombic efficiency of the formation cycle at C/20 and the second cycle at C/10 obtained from all samples. Discharge capacities for two cells per sample are shown to illustrate the repeatability of the results. As expected, the electrodes exhibited relatively low initial coulombic efficiencies, around 70–80% for the samples with lower lithium contents. Additionally, a declining trend in efficiency was observed for Li/TM ratios above 1.55 (Fig. 7(a)). The coulombic efficiencies were stabilized around 95–98% for the second cycle, but the downward tendency is still evident for the more Li-rich compositions (Fig. 7(b)). Similar behavior was observed for the discharge capacity of the first two cycles (Fig. 7(c) and (d)). All in all, the fast screening of lithium-rich oxides with the ADEL module also enables the identification of candidates with outstanding parameters, such as the specific LMR samples with initial coulombic efficiencies above 90% and discharge capacities greater than 250 mA h g−1 (Fig. 7(a) and (c)).
Conclusion
The automated setup ADEL demonstrates robust capabilities for high-throughput preparation of drop-cast electrodes. It enables the automated preparation of 48 high-loading electrodes in a single batch, allowing for the screening of up to 24 distinct electrode materials per day with minimal human intervention, all within a 10 hour workflow. This includes 3 hours for electrode drop-casting and 7 hours of complete drying. In comparison, it is estimated that the conventional doctor blade casting requires around 1 hour of significant human intervention for each electrode laminate,45 which is followed by 8 hours of drying in a vacuum oven. This results in a total processing time of approximately 32 hours for producing 24 distinct electrodes. While the configuration presented herein allows for a maximum of four electrodes per slurry, it can be easily adapted to scale up the number of drop-cast electrodes per material.In this study, the electrochemical characterization of 72 drop-cast electrodes at varying C-rates in different cell types (coin and Swagelok cells), representing 25 different commercial and lab-synthesized powder cathode active materials, has shown that the ADEL system produces highly reproducible results with a low relative standard deviation below 3% in all cases. While this work focused on cathode active material evaluation, the ADEL methodology can also be applied to screen different anode materials and/or various electrode formulations (e.g., testing different binders or conductive materials and varying their content). In addition, the system is designed to be adaptable and compact, making it suitable for placement inside a glove box.
To the best of our knowledge, the ADEL setup is one of the most affordable and efficient methods for screening the electrochemical performance of over 100 distinct electrode slurries per week. As such, we believe that it constitutes a valuable module for battery-related Materials Accelerated Platforms (MAPs) and Self-Driving Labs (SDLs), which will significantly contribute to the acceleration of battery materials research.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available in the following GitHub repository: https://github.com/Maha24cic/ADEL-CIC. The corresponding DOI is the following: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14905113. This repository includes a video of the module, the 3D-printed component plans permitting to reproductione the setup, and all data associated with this work.Author contributions
Maha Ismail: methodology, investigation, conceptualization, formal analysis, validation, visualization, writing – original draft, and writing – review & editing. Maria Angeles Cabañero: methodology, investigation, conceptualization, validation, and writing – review & editing. Joseba Orive: investigation, formal analysis, visualization, writing – original draft, and writing – review & editing. Lakshmipriya Musuvadhi Babulal: investigation, formal analysis, validation, and writing – original draft. Javier Garcia: software and investigation. Maria C. Morant-Miñana: investigation, formal analysis, and writing – review & editing. Jean-Luc Dauvergne: investigation, formal analysis, and writing – review & editing. Francisco Bonilla: formal analysis and writing – review & editing. Iciar Monterrubio: formal analysis and validation. Javier Carrasco: funding acquisition and writing – review & editing. Amaia Saracibar: supervision, conceptualization, and writing – review & editing. Marine Reynaud: methodology, supervision, conceptualization, funding acquisition, and writing – review & editing.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the ION-SELF project [ref. PID2019-106519RB-I00] and the PhD grant PRE2020-092978, funded by MICIU/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and “ESF Investing in your future” as well as the project SMART [ref. PID2022-140823OB-I00] funded by MICIU/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and ERDF/EU. The authors are grateful to UMICORE for providing the carbonate precursors for LMR materials and to TOPSOE for providing the LNMO materials used for this investigation. The authors acknowledge Ainhoa Bustinza for providing the planes of the 3D designs, Mattia Felice for assisting in the GitHub repository and Luz Granados for performing the micro-CT measurements.References
- S. Duehnen, J. Betz, M. Kolek, R. Schmuch, M. Winter and T. Placke, Toward green battery cells: perspective on materials and technologies, Small Methods, 2020, 4(7), 2000039 CrossRef.
- R. Schmuch, R. Wagner, G. Hörpel, T. Placke and M. Winter, Performance and cost of materials for lithium-based rechargeable automotive batteries, Nat. Energy, 2018, 3(4), 267–278 CrossRef.
- J. Amici, P. Asinari, E. Ayerbe, P. Barboux, P. Bayle-Guillemaud, R. J. Behm, M. Berecibar, E. Berg, A. Bhowmik and S. Bodoardo, A roadmap for transforming research to invent the batteries of the future designed within the european large scale research initiative battery 2030+, Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12(17), 2102785 CrossRef.
- S. Stier, C. Kreisbeck, H. Ihssen, M. Albert Popp, J. Hauch, K. Malek, M. Reynaud, F. Goumans, J. Carlsson, I. Todorov, L. Gold, A. Räder, W. Wenzel, S. T. Bandesha, P. Jacques, F. Garcia-Moreno, O. Arcelus, P. Friederich, S. Clark, M. Maglione, A. Laukkanen, I. E. Castelli, M. Casas Cabanas, J. C. Carrasco, H. S. Stein, T. Vegge, S. Nakamae, M. Fabrizio and M. Kozdras, The Significance of Accelerated Discovery of Advanced Materials to address Societal Challenges, Zenodo, 2023, (1.0.0) Search PubMed.
- A. Benayad, D. Diddens, A. Heuer, A. N. Krishnamoorthy, M. Maiti, F. L. Cras, M. Legallais, F. Rahmanian, Y. Shin and H. Stein, High-throughput experimentation and computational freeway lanes for accelerated battery electrolyte and interface development research, Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12(17), 2102678 CrossRef.
- S. Adams and R. P. Rao, High power lithium ion battery materials by computational design, Phys. Status Solidi A, 2011, 208(8), 1746–1753 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Adams and R. P. Rao, Understanding Ionic Conduction and Energy Storage Materials with Bond-Valence-Based Methods, in Bond Valences, ed. I. D. Brown and K. R. Poeppelmeier, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2014, pp. 129–159 Search PubMed.
- N. A. Katcho, J. Carrete, M. Reynaud, G. Rousse, M. Casas-Cabanas, N. Mingo, J. Rodriguez-Carvajal and J. Carrasco, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2019, 52(1), 148–157 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Jain, S. P. Ong, G. Hautier, W. Chen, W. D. Richards, S. Dacek, S. Cholia, D. Gunter, D. Skinner and G. Ceder, Commentary: The Materials Project: A Materials Genome Approach to Accelerating Materials Innovation, APL Mater., 2013, 1(1), 011002 CrossRef.
- T. Adhikari, A. Hebert, M. Adamic, J. Yao, K. Potts and E. McCalla, Development of high-throughput methods for sodium-ion battery cathodes, ACS Comb. Sci., 2020, 22(6), 311–318 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Liu, B. Guo, T. An, H. Fang, G. Zhu, C. Jiang and X. Jiang, High throughput materials research and development for lithium ion batteries, J. Materiomics, 2017, 3(3), 202–208 CrossRef.
- S. Jia, J. Counsell, M. Adamič, A. Jonderian and E. McCalla, High-throughput design of Na–Fe–Mn–O cathodes for Na-ion batteries, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022, 10(1), 251–265 RSC.
- M. Roberts and J. Owen, High-throughput method to study the effect of precursors and temperature, applied to the synthesis of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 for lithium batteries, ACS Comb. Sci., 2011, 13(2), 126–134 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Yao, Z. Huang, T. Li, H. Wang, Y. Liu, H. S. Stein, Y. Mao, J. Gao, M. Jiao and Q. Dong, High-throughput, combinatorial synthesis of multimetallic nanoclusters, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2020, 117(12), 6316–6322 CrossRef.
- A. Jonderian, S. Jia, G. Yoon, V. T. Cozea, N. Z. Galabi, S. B. Ma and E. McCalla, Accelerated Development of High Voltage Li-Ion Cathodes, Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12(40), 2201704 CrossRef.
- K. Mader, F. Marone, C. Hintermüller, G. Mikuljan, A. Isenegger and M. Stampanoni, High-throughput full-automatic synchrotron-based tomographic microscopy, J. Synchrotron Radiat., 2011, 18(2), 117–124 CrossRef.
- J. Gregoire, D. Van Campen, C. Miller, R. Jones, S. Suram and A. Mehta, High-throughput synchrotron X-ray diffraction for combinatorial phase mapping, J. Synchrotron Radiat., 2014, 21(6), 1262–1268 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Lyu, Y. Liu, T. Cheng and B. Guo, High-throughput characterization methods for lithium batteries, J. Materiomics, 2017, 3(3), 221–229 CrossRef.
- T. Muster, A. Trinchi, T. Markley, D. Lau, P. Martin, A. Bradbury, A. Bendavid and S. Dligatch, A review of high throughput and combinatorial electrochemistry, Electrochim. Acta, 2011, 56(27), 9679–9699 CrossRef.
- G. Tom, S. P. Schmid, S. G. Baird, Y. Cao, K. Darvish, H. Hao, S. Lo, S. Pablo-García, E. M. Rajaonson and M. Skreta, Self-driving laboratories for chemistry and materials science, Chem. Rev., 2024, 124(16), 9633–9732 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. P. Stier, C. Kreisbeck, H. Ihssen, M. A. Popp, J. Hauch, K. Malek, M. Reynaud, T. Goumans, J. Carlsson and I. Todorov, Materials Acceleration Platforms (MAPs) Accelerating Materials Research and Development to Meet Urgent Societal Challenges, Adv. Mater., 2024, 2407791 CrossRef.
- J. Abed, Y. Bai, D. E. Persaud, J. Kim, J. Witt, J. Hattrick-Simpers and E. H. Sargent, AMPERE: automated modular platform for expedited and reproducible electrochemical testing, Digital Discovery, 2024, 3(11), 2265–2274 RSC.
- H. S. Stein and J. M. Gregoire, Progress and prospects for accelerating materials science with automated and autonomous workflows, Chem. Sci., 2019, 10(42), 9640–9649 Search PubMed.
- H. S. Stein, A. Sanin, F. Rahmanian, B. Zhang, M. Vogler, J. K. Flowers, L. Fischer, S. Fuchs, N. Choudhary and L. Schroeder, From materials discovery to system optimization by integrating combinatorial electrochemistry and data science, Curr. Opin. Electrochem., 2022, 35, 101053 CrossRef.
- BIG-MAP project, https://www.big-map.eu/ Search PubMed.
- A. Aspuru-Guzik and K. Persson, Materials Acceleration Platform: Accelerating Advanced Energy Materials Discovery by Integrating High-Throughput Methods and Artificial Intelligence, Mission Innovation: Innovation Challenge 6, 2018, https://nrs.harvard.edu/urn-3:HUL.InstRepos:35164974 Search PubMed.
- M. M. Flores-Leonar, L. M. Mejía-Mendoza, A. Aguilar-Granda, B. Sanchez-Lengeling, H. Tribukait, C. Amador-Bedolla and A. Aspuru-Guzik, Materials acceleration platforms: on the way to autonomous experimentation, Curr. Opin. Green Sustainable Chem., 2020, 25, 100370 CrossRef.
- T. Lombardo, M. Duquesnoy, H. El-Bouysidy, F. Årén, A. Gallo-Bueno, P. B. Jørgensen, A. Bhowmik, A. Demortière, E. Ayerbe and F. Alcaide, Artificial intelligence applied to battery research: hype or reality?, Chem. Rev., 2021, 122(12), 10899–10969 Search PubMed.
- M. Abolhasani and E. Kumacheva, The rise of self-driving labs in chemical and materials sciences, Nat. Synth., 2023, 1–10 Search PubMed.
- S. Matsuda, K. Nishioka and S. Nakanishi, High-throughput combinatorial screening of multi-component electrolyte additives to improve the performance of Li metal secondary batteries, Sci. Rep., 2019, 9(1), 6211 Search PubMed.
- A. Dave, J. Mitchell, S. Burke, H. Lin, J. Whitacre and V. Viswanathan, Autonomous optimization of non-aqueous Li-ion battery electrolytes via robotic experimentation and machine learning coupling, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13(1), 5454 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Cartier, Z. Feng, J. Faulk and D. Scherson, A combinatorial approach toward the discovery of electrolyte formulations for non-aqueous electrochemical energy storage devices, ECS Electrochem. Lett., 2015, 4(9), A110 CrossRef CAS.
- J. T. Yik, L. Zhang, J. Sjölund, X. Hou, P. H. Svensson, K. Edström and E. J. Berg, Automated electrolyte formulation and coin cell assembly for high-throughput lithium-ion battery research, Digital Discovery, 2023, 2(3), 799–808 RSC.
- J. Noh, H. A. Doan, H. Job, L. A. Robertson, L. Zhang, R. S. Assary, K. Mueller, V. Murugesan and Y. Liang, An integrated high-throughput robotic platform and active learning approach for accelerated discovery of optimal electrolyte formulations, Nat. Commun., 2024, 15(1), 2757 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Dave, J. Mitchell, K. Kandasamy, H. Wang, S. Burke, B. Paria, B. Póczos, J. Whitacre and V. Viswanathan, Autonomous discovery of battery electrolytes with robotic experimentation and machine learning, Cell Rep. Phys. Sci., 2020, 1(12), 100264 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Marks, S. Trussler, A. Smith, D. Xiong and J. Dahn, A guide to Li-ion coin-cell electrode making for academic researchers, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2010, 158(1), A51 CrossRef.
- W. B. Hawley and J. Li, Electrode manufacturing for lithium-ion batteries—analysis of current and next generation processing, J. Energy Storage, 2019, 25, 100862 CrossRef.
- F. Dai and M. Cai, Best practices in lithium battery cell preparation and evaluation, Commun. Mater., 2022, 3(1), 64 CrossRef.
- J. Whitacre, W. West and B. Ratnakumar, A Combinatorial Study of LiyMnxNi2−xO4 Cathode Materials Using Microfabricated Solid-State Electrochemical Cells, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2003, 150(12), A1676 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Spong, G. Vitins, S. Guerin, B. Hayden, A. Russell and J. R. Owen, Combinatorial arrays and parallel screening for positive electrode discovery, J. Power Sources, 2003, 119, 778–783 CrossRef.
- M. Fleischauer, T. Hatchard, A. Bonakdarpour and J. R. Dahn, Combinatorial investigations of advanced Li-ion rechargeable battery electrode materials, Meas. Sci. Technol., 2004, 16(1), 212 Search PubMed.
- M. D. Fleischauer, T. D. Hatchard, G. P. Rockwell, J. M. Topple, S. Trussler, S. K. Jericho, M. H. Jericho and J. R. Dahn, Design and testing of a 64-channel combinatorial electrochemical cell, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2003, 150(11), A1465 Search PubMed.
- M. Al-Maghrabi, N. van der Bosch, R. Sanderson, D. Stevens, R. Dunlap and J. Dahn, A new design for a combinatorial electrochemical cell plate and the inherent irreversible capacity of lithiated silicon, Electrochem. Solid-State Lett., 2011, 14(4), A42 CrossRef.
- K. P. Potts, E. Grignon and E. McCalla, Accelerated screening of high-energy lithium-ion battery cathodes, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2019, 2(12), 8388–8393 CrossRef.
- E. McCalla, Semiautomated Experiments to Accelerate the Design of Advanced Battery Materials: Combining Speed, Low Cost, and Adaptability, ACS Eng. Au, 2023, 3(6), 391–402 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Hahn, M. Ferch, K. Tribowski, N. A. Kyeremateng, K. Hoeppner, K. Marquardt, K.-D. Lang and W. Bock, High-throughput battery materials testing based on test cell arrays and dispense/jet printed electrodes, Microsyst. Technol., 2019, 25, 1137–1149 CrossRef.
- K. Takada, K. Fujimoto, T. Sasaki and M. Watanabe, Combinatorial electrode array for high-throughput evaluation of combinatorial library for electrode materials, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2004, 223(1–3), 210–213 CrossRef.
- C. Cao, F. Liang, W. Zhang, H. Liu, H. Liu, H. Zhang, J. Mao, Y. Zhang, Y. Feng, X. Yao, M. Ge and Y. Tang, Commercialization-Driven Electrodes Design for Lithium Batteries: Basic Guidance, Opportunities, and Perspectives, Small, 2021, 17(43), 2102233 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Watson and A. Kanase, Viscous Liquid Handling Automation using Opentrons, OT-2, https://opentrons.com.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Viscous-Liquid-Handling-Automation-using-Opentrons-OT-2.pdf Search PubMed.
- How to handle viscous liquids in Protocol Designer, https://support.opentrons.com/s/article/How-to-handle-viscous-liquids-in-Protocol-Designer Search PubMed.
- L. Ouyang, Z. Wu, J. Wang, X. Qi, Q. Li, J. Wang and S. Lu, The effect of solid content on the rheological properties and microstructures of a Li-ion battery cathode slurry, RSC Adv., 2020, 10(33), 19360–19370 RSC.
- A. Altvater, T. Heckmann, J. C. Eser, S. Spiegel, P. Scharfer and W. Schabel, (Near-) Infrared Drying of Lithium-Ion Battery Electrodes: Influence of Energy Input on Process Speed and Electrode Adhesion, Energy Technol., 2023, 11(5), 2200785 CrossRef.
- S. J. An, J. Li, Z. Du, C. Daniel and D. L. Wood III, Fast formation cycling for lithium ion batteries, J. Power Sources, 2017, 342, 846–852 CrossRef.
- P. Dechent, S. Greenbank, F. Hildenbrand, S. Jbabdi, D. U. Sauer and D. A. Howey, Estimation of Li-Ion Degradation Test Sample Sizes Required to Understand Cell-to-Cell Variability, Batteries Supercaps, 2021, 4(12), 1821–1829 CrossRef.
- B. Zhang, L. Merker, A. Sanin and H. S. Stein, Robotic cell assembly to accelerate battery research, Digital Discovery, 2022, 1(6), 755–762 RSC.
- C. Berlanga, I. a. Monterrubio, M. Armand, T. Rojo, M. Galceran and M. Casas-Cabanas, Engineering, cost-effective synthesis of triphylite-NaFePO4 cathode: a zero-waste process, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2019, 8(2), 725–730 CrossRef.
- H. Zheng, L. Chai, X. Song and V. Battaglia, Electrochemical cycling behavior of LiFePO4 cathode charged with different upper voltage limits, Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 62, 256–262 CrossRef.
- S. Megahed and B. Scrosati, Lithium-ion rechargeable batteries, J. Power Sources, 1994, 51(1–2), 79–104 CrossRef.
- N. S. Choi, Z. Chen, S. A. Freunberger, X. Ji, Y. K. Sun, K. Amine, G. Yushin, L. F. Nazar, J. Cho and P. G. Bruce, Challenges facing lithium batteries and electrical double-layer capacitors, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51(40), 9994–10024 CrossRef.
- M. Fehse, N. Etxebarria, L. Otaegui, M. Cabello, S. Martín-Fuentes, M. A. Cabañero, I. Monterrubio, C. F. Elkjær, O. Fabelo and N. A. Enkubari, Influence of transition-metal order on the reaction mechanism of LNMO cathode spinel: an operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy study, Chem. Mater., 2022, 34(14), 6529–6540 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Eftekhari, Electrochemical performance and cyclability of LiFe0.5Mn1.5O4 as a 5 V cathode material for lithium batteries, J. Power Sources, 2003, 124(1), 182–190 CrossRef.
- K.-S. Chen, R. Xu, N. S. Luu, E. B. Secor, K. Hamamoto, Q. Li, S. Kim, V. K. Sangwan, I. Balla and L. M. Guiney, Comprehensive enhancement of nanostructured lithium-ion battery cathode materials via conformal graphene dispersion, Nano Lett., 2017, 17(4), 2539–2546 CrossRef PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4dd00381k |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |