Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleApplication of the aza-Wittig reaction for the synthesis of carboranyl Schiff bases, benzothiazoles and benzoselenazolines†
Pablo
Crujeiras
,
Irene
Vázquez-Carballo
and
Antonio
Sousa-Pedrares
 *
*
Departamento de Química Inorgánica, Universidade de Santiago de Compostela, 15782 Santiago de Compostela, Spain. E-mail: antonio.sousa.pedrares@usc.es
First published on 9th January 2025
Abstract
The aza-Wittig reaction was successfully applied to the synthesis of carboranyl-imines, which are difficult to obtain by classical methods. A variety of functionalized carboranyl Schiff bases was obtained proving the great scope of the methodology. All compounds were fully characterized, including the solid-state structures of six of them. The aza-Wittig reaction was modified to permit the synthesis in one step of carboranyl-benzothiazole and carboranyl-benzoselenazoline derivatives. The stability studies show that the carboranyl-imines and benzothiazole promote deboronation to the nido-derivatives, which is achieved by simple reaction with methanol or protic solvents. The structures of the nido-derivatives were also studied by X-ray diffraction. In contrast, the saturated derivatives, amine and benzoselenazoline, do not promote deboronation and are stable in protic solvents.
Introduction
Icosahedral ortho-closo-dodecaborane C2B10H12 is the type of heteroborane cluster that has been most extensively studied due to its special electronic and chemical properties. Their functionalized derivatives have found several applications, mainly in the fields of material science,1 catalysis2 and medicine.3 However, this uniqueness can affect the synthesis of different derivatives and impede progress in the study of some well-established functionalities. An example that stands out is the case of imine derivatives.Imines, azomethines or Schiff bases, are compounds that have an imino group, R1HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N–R2, i.e. a carbon-nitrogen double bond with the nitrogen atom attached to an alkyl or aryl group (not hydrogen).4 Due to the presence of a donor nitrogen atom, Schiff bases can be used as ligands for the preparation of coordination compounds. In fact, Schiff base ligands are one of the most studied and used types of ligands, due to their ease of preparation and extensive coordination chemistry.4 Schiff base ligands form metal complexes with virtually all metal ions. These compounds have many interesting applications, especially in biology and catalysis.5 Thus, compounds derived from Schiff bases have been found with antibacterial, antifungal, anticancer, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial and antiviral activity.5,6 In addition, many complexes with Schiff bases have high catalytic activity, for example in processes of olefin polymerization, hydrocarbon oxidation, alkene epoxidation, ketone reduction, and Heck reaction, among others.5,7 The most common synthesis of Schiff bases is very simple and involves the condensation reaction between an aldehyde (or ketone) and a primary amine.
N–R2, i.e. a carbon-nitrogen double bond with the nitrogen atom attached to an alkyl or aryl group (not hydrogen).4 Due to the presence of a donor nitrogen atom, Schiff bases can be used as ligands for the preparation of coordination compounds. In fact, Schiff base ligands are one of the most studied and used types of ligands, due to their ease of preparation and extensive coordination chemistry.4 Schiff base ligands form metal complexes with virtually all metal ions. These compounds have many interesting applications, especially in biology and catalysis.5 Thus, compounds derived from Schiff bases have been found with antibacterial, antifungal, anticancer, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial and antiviral activity.5,6 In addition, many complexes with Schiff bases have high catalytic activity, for example in processes of olefin polymerization, hydrocarbon oxidation, alkene epoxidation, ketone reduction, and Heck reaction, among others.5,7 The most common synthesis of Schiff bases is very simple and involves the condensation reaction between an aldehyde (or ketone) and a primary amine.
In the specific case of carboranes, we have to distinguish two types of derivatives: those in which the imino group is connected to the cluster through the nitrogen atom, carborane–N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C–R, and those in which it is connected through the carbon atom, carborane–C
C–R, and those in which it is connected through the carbon atom, carborane–C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N–R. In the case of derivatives of the first type, carborane–N
N–R. In the case of derivatives of the first type, carborane–N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C–R, the usual synthesis method gives good results, and the small number of examples is due to the difficulty in obtaining the 1-amino-carborane precursors,8 or 1,2-diamino-carborane,9 whose syntheses have been perfected recently. In the case of derivatives of the second type, carborane–C
C–R, the usual synthesis method gives good results, and the small number of examples is due to the difficulty in obtaining the 1-amino-carborane precursors,8 or 1,2-diamino-carborane,9 whose syntheses have been perfected recently. In the case of derivatives of the second type, carborane–C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N–R, which are more relevant to this work, although the precursor aldehyde C-formyl-carborane can be easily obtained,10 the low number of described examples is surprising. This is undoubtedly due to the difficulty in carrying out their synthesis, because the classical method of synthesis can give bad results. This usual method has been described for the synthesis of a few carboranyl-imines, although under inert gas conditions.10–14 However, in the case of other derivatives the method needs especial conditions, such as the use of silica-alumina catalyst support grade 135,15 which the authors consider crucial, stating that “other reaction conditions proceeded with very poor yields”. It seems that the success in the synthesis by the classical method depends greatly on the desired final product. An alternative method has also been described for the synthesis of one imine-carborane, by reaction between carboranyl-lithium and imidoyl chloride,16 but this is far from being a general method of synthesis for this type of compounds.
N–R, which are more relevant to this work, although the precursor aldehyde C-formyl-carborane can be easily obtained,10 the low number of described examples is surprising. This is undoubtedly due to the difficulty in carrying out their synthesis, because the classical method of synthesis can give bad results. This usual method has been described for the synthesis of a few carboranyl-imines, although under inert gas conditions.10–14 However, in the case of other derivatives the method needs especial conditions, such as the use of silica-alumina catalyst support grade 135,15 which the authors consider crucial, stating that “other reaction conditions proceeded with very poor yields”. It seems that the success in the synthesis by the classical method depends greatly on the desired final product. An alternative method has also been described for the synthesis of one imine-carborane, by reaction between carboranyl-lithium and imidoyl chloride,16 but this is far from being a general method of synthesis for this type of compounds.
The lack of examples of carboranyl-imines should not be mistaken for a lack of potential applications of these compounds. They have been used as precursors of functionalized porphyrins with potential use in cancer therapies as boron neutron-capture therapy (BNCT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT).11,17 The imine group has been used as a directing group for the B-functionalization of carboranes,12–14 which coupled with the removable nature of the imine moiety can lead to the synthesis of carborane analogs of known drugs, which in some cases produces an improvement of their activity.13 Besides, the few reported metal complexes with the nido form of these imine ligands were also active catalysts for the polymerization of ethylene.15
The aza-Wittig method is an alternative method for the synthesis of Schiff bases that, despite being well known,18 has never been applied to the field of carboranes. This method involves the direct reaction between an aldehyde (or ketone) and an iminophosphorane, leading to imino bond formation under mild conditions. This process requires the preparation of the iminophosphorane precursors in a first step. These compounds, with the general formula R3P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NR′, have a P
NR′, have a P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N double bond and can be easily obtained using the Staudinger reaction19 or the Kirsanov reaction.20 The aza-Wittig reaction is the nitrogen equivalent of the Wittig reaction, which has already been successfully tested for the production of alkenyl carboranes.21 The aza-Wittig reaction proceeds through a tandem [2 + 2] cycloaddition-cycloreversion mechanism. The formation of C
N double bond and can be easily obtained using the Staudinger reaction19 or the Kirsanov reaction.20 The aza-Wittig reaction is the nitrogen equivalent of the Wittig reaction, which has already been successfully tested for the production of alkenyl carboranes.21 The aza-Wittig reaction proceeds through a tandem [2 + 2] cycloaddition-cycloreversion mechanism. The formation of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N and O
N and O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) P bonds occurs at the same time as the breaking of N
P bonds occurs at the same time as the breaking of N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) P and C
P and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bonds, producing the target imine and phosphine oxide as a by-product.18 The nucleophilicity of the iminophosphorane and the electrophilicity of the aldehyde promote the aza-Wittig reaction. Considering the great electron-withdrawing character of the C-carboranyl group, the starting material C-formyl-carborane seems especially prone to this reaction. In the present work, the aza-Wittig method will be used to obtain carboranyl-imine compounds.
O bonds, producing the target imine and phosphine oxide as a by-product.18 The nucleophilicity of the iminophosphorane and the electrophilicity of the aldehyde promote the aza-Wittig reaction. Considering the great electron-withdrawing character of the C-carboranyl group, the starting material C-formyl-carborane seems especially prone to this reaction. In the present work, the aza-Wittig method will be used to obtain carboranyl-imine compounds.
The aza-Wittig method can also be modified to access other types of important carboranyl derivatives as benzothiazole an benzoselenazoline (vide infra). Benzothiazoles are a very important class of compounds, due to their biological and pharmacological properties.22 However, in the field of carboranes there are not many known examples of their derivatives. Literature examples of ortho-carboranyl-benzothiazoles include the direct connection of a C-ortho-carboranyl group to 2-benzothiazole,23 the connection through a phenyl24,25 or a sulfide spacer,26 a B3-derivative27 and the direct connection of a boron atom of a o-nido-carborane moiety to the nitrogen atom of the heterocycle.28 Examples of meta-carborane derivatives include compounds with the connection of the benzothiazole carbon atom to a carbon of the cluster29 and to the B9 position of the cluster.30 In the case of carboranyl-benzoselenazolines (and benzoselenazoles) there are no reported examples of such compounds.
Results and discussion
Synthesis
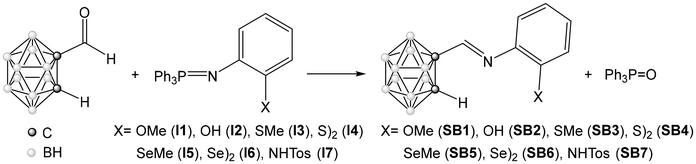
A variety of functionalized carboranyl Schiff Bases was obtained following the aza-Wittig methodology, i.e. by simply refluxing C-formyl-carborane10 with the appropriate iminophosphorane precursor in commercial chloroform, as shown in Schemes 1 and 2.The functionalized iminophosphorane precursors are non-commercial compounds that have to be previously obtained. Compounds I1–4 and I8 have been described in the literature31–35 and the rest of them can be easily prepared using the Kirsanov method,20 by direct reaction of commercial dibromotriphenylphosphine with the corresponding amine in the presence of dry triethylamine, in dry toluene at reflux (see Experimental section). The characterization of the compounds confirmed the formation of the expected iminophosphoranes. In particular, the IR spectra show a very intense band between 1346 and 1328 cm−1, due to the stretching vibration of the P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N bond, and the 31P{1H} NMR spectra show a single signal between 6.9 and −0.3 ppm due to the presence of the iminophosphorane group in the compounds.
N bond, and the 31P{1H} NMR spectra show a single signal between 6.9 and −0.3 ppm due to the presence of the iminophosphorane group in the compounds.
The aza-Wittig method used to produce the functionalized carboranyl Schiff bases SB1–7 (Scheme 1) is experimentally very simple and requires the use of few precautions. It was very efficient in all cases, producing the desired products in very good yields (75–99%). The production of the bis-imine SB8 was also possible (Scheme 2), although less efficiently (35%). The success in the synthesis of the bis(carboranyl-imine) derivative SB8 also proves that this method can be used for the synthesis of compounds containing several imine-carborane groups. The only limitation is the fact that this reaction cannot be controlled by stoichiometry. Thus, when bis(iminophosphorane) I8 is treated with one equivalent of C-formyl-carborane under the described conditions, only the bis(imine-carborane) SB8 is obtained.
All compounds SB1–8 were characterized by IR spectroscopy, 1H, 13C and 11B NMR spectroscopy, mass spectrometry and elemental analysis. The IR spectra of these compounds show the B–H stretching between 2635 and 2565 cm−1, which is compatible with the presence of a closo-carborane cluster, and a band associated with the imine bond, ν(C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), between 1639 and 1634 cm−1, due to the formation of the Schiff bases. The imine carbon also appears in the 13C{1H} NMR spectra, between 154.3 and 149.5 ppm. The 1H NMR spectra show the resonance of the iminic proton between 8.01 and 7.65 ppm, which also confirms the success of the method. The Ccluster–H signal, between 4.56 and 4.29 ppm, indicates the formation of mono-substituted ortho-carboranyl derivatives. The range of the signals obtained in 11B{1H} NMR, between −1.8 and −14.8 ppm, also confirms the presence of the closo-carborane cluster in the final products.
N), between 1639 and 1634 cm−1, due to the formation of the Schiff bases. The imine carbon also appears in the 13C{1H} NMR spectra, between 154.3 and 149.5 ppm. The 1H NMR spectra show the resonance of the iminic proton between 8.01 and 7.65 ppm, which also confirms the success of the method. The Ccluster–H signal, between 4.56 and 4.29 ppm, indicates the formation of mono-substituted ortho-carboranyl derivatives. The range of the signals obtained in 11B{1H} NMR, between −1.8 and −14.8 ppm, also confirms the presence of the closo-carborane cluster in the final products.
Single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained for all the Schiff bases, except for the diselenide derivative SB6 and for the bis-imine derivative SB8. All crystals were obtained from solutions in a mixture of dichloromethane and hexane. The solid-state studies confirmed the expected molecular structures for all Schiff bases, shown in Fig. 1. The crystallographic data can be found in Table S1 (ESI†). Selected bond lengths and angles for these compounds are collected in Tables S2 and S3 (ESI†).
 | ||
| Fig. 1 Molecular structure of carboranyl Schiff bases SB1–SB5 and SB7. Thermal ellipsoids are shown at the 40% probability level. | ||
In all cases, the carborane substituents are distorted icosahedra with the expected order of bond lengths: C–C < C–B < B–B. The C–C distances of the clusters are all very similar, in the range 1.622(3)–1.637(2) Å, and very similar to the mean value of 1.631 Å found for the only 12 structures of carboranyl Schiff bases reported in the literature.12–15 Likewise, the imine bond distances, in the range 1.248(5)–1.272(5) Å, are similar to the mean value of 1.253 Å found for the literature examples, and typical of a C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N double bond.
N double bond.
The synthesized imine-carboranes SB1–7 present different potentially donating functional groups on the ortho position of the phenyl ring attached to the iminic nitrogen atom. The success of their synthesis shows the great scope of the aza-Wittig method and its compatibility with other functional groups. It is interesting to remember that the literature examples only present non-functionalized aromatic groups attached to the imine nitrogen atom, apart from two examples with an ortho-phenol group,12,14 like the new compound SB2. In contrast, the synthesized compounds SB1–7 have been designed to be potential bidentate chelating ligands (N, X) X = O, S, Se, N, capable of forming five-membered chelate rings by complexation with metal atoms. These ligands are also potential hemilabile ligands that could be exploited for homogeneous catalysis, a category with not many examples in carborane chemistry.36
We also checked the scope of the reaction by using carboranyl iminophosphoranes, due to the experience of the research group with these compounds.34,37,38 Kennedy had already described the Cc-methyl and Cc-phenyl substituted C-triphenyliminophosphorane-carboranes as “unreactive substrates for the aza-Wittig reaction”,39 but we wanted to try the reaction with the activated C-formyl-iminophosphorane. Unfortunately, under our described conditions the unsubstituted 1-triphenyliminophosphorane-carborane34 did not react with the carboranyl-aldehyde, and the reactants were recovered unchanged. We also checked if this unreactivity was due to the low basicity of the iminophosphorane caused by the electron-withdrawing character of the C-carboranyl group. Thus, we prepared and characterized the previously not reported B3-triphenyliminophosphorane-carborane (IB3), as the B3-carboranyl group is less electron-withdrawing than the C-carboranyl one.38 This compound is easily obtained from 3-amino-carborane (see Experimental section), and shows the typical features of the other iminophosphoranes, i.e. a strong band at 1432 cm−1 in the IR spectrum due to the ν(P–N) stretching and a signal at 8.8 ppm in the 31P{1H} NMR spectrum. It also presents the signals associated with an ortho-carborane derivative, as the strong ν(B–H) band at 2578 cm−1 in the IR spectrum and the signal at 3.39 ppm in 1H NMR due to the two equivalent CH protons of the cluster. The 11B{1H} NMR spectrum is the typical one associated with closo-B3-derivatives,38 with signals in the range (2.6)–(−22.1) ppm, with the signal for the B3 substituted atom at low field, 2.6 ppm. It was also possible to study its solid-state structure using X-ray crystallography (see ESI, Fig. S1†). Unfortunately, the more donor character of this iminophosphorane did not result in improved reactivity and, under the described conditions, it did not produce any amount of the expected carboranyl imine.
Stability and reactivity
All the closo-carboranyl Schiff bases SB1–8 can also be used as precursors of other carboranyl derivatives, as the nido analogs or the corresponding closo-carboranyl amines (Scheme 3).nido-Carboranes are usually obtained by treatment of the closo derivatives with a strong base or a nucleophile.40 However, it has been shown that some substituents on carbon atoms strongly influence the tendency of carborane to undergo deboronation. Thus, electron-withdrawing substituents increase the electrophilicity of borons adjacent to carbons, which increases their reactivity. For example, ester, aldehyde, sulfoxide and electron-withdrawing aromatic rings are known to favor the evolution to the nido form in neutral media.41 Xie and co-workers showed that the imine group is another one of these groups and that Schiff base derivatives of carborane evolve to nido derivatives simply by reaction with methanol, without the need for additional nucleophiles.15 We have also observed this tendency with the functionalized Schiff bases SB1–8. Thus, during the recrystallization of the Schiff bases in air, it was observed that solutions of these compounds in alcohols and water-miscible solvents evolved over time, becoming darker. Analysis of these solutions by 11B{1H} NMR and IR spectroscopy revealed degradation to the nido derivatives. The solvents tested were methanol, ethanol, acetone, acetonitrile and THF. However, solutions of these compounds in water-immiscible solvents did not evolve over time in air. In this case, the solvents tested were ethyl ether, ethyl acetate, hexane, toluene, dichloromethane and chloroform. This means that special care must be taken in the choice of solvents when using these compounds.
As an example, Schiff base SB3 was refluxed in dry methanol, which produced its total conversion to the nido analog, nido-SB3 (Scheme 3). IR spectroscopy, as well as 1H and 11B{1H} NMR spectroscopy, are techniques that clearly show the formation of the nido derivative. The shift to a lower wave number of about 50 cm−1 of the ν(B–H) band in the spectrum of the nido compound (2545 cm−1) with respect to the closo compound (multiple band between 2635 and 2565 cm−1) confirms the degradation. On the other hand, the 1H NMR spectrum shows a broad signal at −2.27 ppm due to the hydrogen bridge in the open C2B3 face. The 11B{1H} NMR spectrum shows a greater number of signals with respect to the closo compound in a wider range (−5.2 to −31.3 ppm). The formation of nido-SB3 was also confirmed by its crystal structure (see Fig. 2). The X-ray diffraction studies show that the compound presents a zwitterionic structure, with the imino group protonated and the negative charge located on the open C2B3 face.
The carboranyl Schiff bases SB1–8 can also be transformed to the corresponding amines by reduction.10,11 As an example, Schiff base SB3 was treated with cyanoborohydride, affording the saturated amine-SB3 (Scheme 3). The reduction of the imino group to the amino group is easily observed using techniques such as IR and NMR spectroscopy. Thus, the IR spectrum shows the disappearance of the imino group band, ν(C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), and the appearance of the ν(N–H) band at 3366 cm−1, due to the new amino group formed. The 1H NMR spectrum shows the disappearance of the iminic proton and the appearance the new CH2 and NH groups, at 3.97 and 4.80 ppm, respectively. In addition, the crystal structure of amine-SB3 could be studied by single-crystal X-ray diffraction (Fig. 3). These studies confirmed that the compound obtained was the expected amine.
N), and the appearance of the ν(N–H) band at 3366 cm−1, due to the new amino group formed. The 1H NMR spectrum shows the disappearance of the iminic proton and the appearance the new CH2 and NH groups, at 3.97 and 4.80 ppm, respectively. In addition, the crystal structure of amine-SB3 could be studied by single-crystal X-ray diffraction (Fig. 3). These studies confirmed that the compound obtained was the expected amine.
In contrast to the parent imine, amine-SB3 is stable to the treatment in methanol and its closo cluster remains unaffected after 12 hours of reflux in dry methanol.
Apart from these two general transformations that can be performed with all carboranyl Shiff bases, the disulfide SB4 and the diselenide SB6 permit more specific reactions.
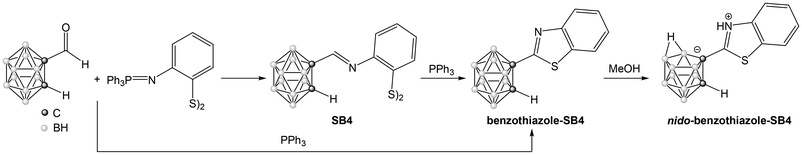
Treatment of the disulfide Schiff Base SB4 with triphenylphosphine (Scheme 4) produces its transformation to the cyclic benzothiazole (benzothiazole-SB4), as described in the literature for organic analogues.42 This reaction proceeds through the initial formation of the thiolate, intramolecular attack to the imine bond to form the benzothiazoline and subsequent aerial oxidation to the benzothiazole derivative. The general aza-Wittig protocol can be modified to include triphenylphosphine in the initial reaction mixture, as shown in Scheme 4, producing the benzothiazole in one step with good yield (73%). The 1H NMR spectrum of benzothiazole-SB4 shows the disappearance of the signal corresponding to the iminic proton of the parent Schiff base and the IR spectrum shows the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N stretching vibration band shifted from 1639 cm−1 to 1504 cm−1. These features indicate the formation of the cyclic benzothiazole. The range of signals found in 11B{1H} NMR spectrum indicates that the closo form of the cluster is retained after the reaction.
N stretching vibration band shifted from 1639 cm−1 to 1504 cm−1. These features indicate the formation of the cyclic benzothiazole. The range of signals found in 11B{1H} NMR spectrum indicates that the closo form of the cluster is retained after the reaction.
The benzothiazole-SB4 with a C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N bond adjacent to the cluster carbon atom is also sensitive to the reaction with methanol, affording the nido derivative, as described before for the carboranyl Schiff bases. Thus, recrystallization from methanol produced the formation of nido-(benzothiazole-SB4). This compound shows the typical features of a nido derivative, with a wider range of signals in 11B{1H} NMR (from −5.1 to −32.9 ppm) and a shift of the ν(B–H) band in the IR spectrum to lower wavenumbers (from 2575 cm−1 to 2527 cm−1). The structure of this nido derivative was also confirmed by X-ray crystallography (Fig. 4). The compound exhibits a zwitterionic structure, with the nitrogen of the benzothiazole group protonated and the negative charge on the open face of the cluster, as discussed before for nido-SB3.
N bond adjacent to the cluster carbon atom is also sensitive to the reaction with methanol, affording the nido derivative, as described before for the carboranyl Schiff bases. Thus, recrystallization from methanol produced the formation of nido-(benzothiazole-SB4). This compound shows the typical features of a nido derivative, with a wider range of signals in 11B{1H} NMR (from −5.1 to −32.9 ppm) and a shift of the ν(B–H) band in the IR spectrum to lower wavenumbers (from 2575 cm−1 to 2527 cm−1). The structure of this nido derivative was also confirmed by X-ray crystallography (Fig. 4). The compound exhibits a zwitterionic structure, with the nitrogen of the benzothiazole group protonated and the negative charge on the open face of the cluster, as discussed before for nido-SB3.
 | ||
| Fig. 4 Molecular structure of nido-(benzothiazole-SB4). Thermal ellipsoids are shown at the 40% probability level. | ||
The synthesis of the same compound, benzothiazole-SB4, has been reported in the literature by condensation of o-carboryne and benzothiazole, although in smaller scale and yield.23 The new aza-Wittig protocol can provide easy access to multigram quantities of this compound. It can also provide access to substituted carboranyl-2-benzothialzoles, starting from substituted amine-disulfides.
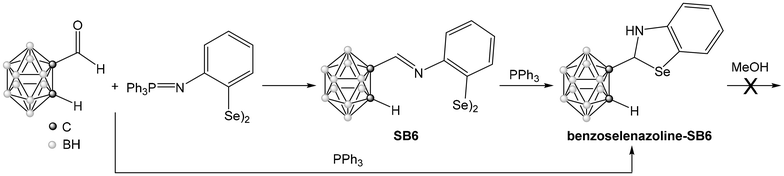
In contrast to the disulfide Schiff Base SB4, the reaction of the diselenide Schiff Base SB6 with triphenylphosphine leads to the formation of the benzoselenazoline (Scheme 5). The same product (benzoselenazoline-SB6) can also be obtained in one step using the aza-Wittig reaction, including triphenylphosphine in the reaction mixture with the iminophosphorane diselenide I6 and C-formyl-carborane (Scheme 5). The 1H NMR spectrum of the final product shows the disappearance of the signal corresponding to the iminic proton of the Schiff base SB6, and the appearance of the signals of the CH group (5.89 ppm) and the NH group (4.74 ppm) formed after cyclization. The IR spectrum does not show an imine band, but a new band at 3370 cm−1 due to the NH group. These results indicate that the benzoselenazoline cycle has been formed. The range of signals found in 11B{1H} NMR indicates that the closo form of the cluster is retained after the reaction. The formation of this compound is due to the intramolecular attack on the imine bond by the selenolate formed in situ. However, in this case the cycle is not oxidized to the benzoselenazole, as found for the sulfur analog previously discussed. Although the result was unexpected, the difference in reactivity could be an effect of the different nature of the chalcogen, as the disulfide could aid in the second oxidation step. This is in line with recent literature, that indicates that the starting disulfide can photosensitize molecular oxygen and facilitate the dehydrogenation step that completes the formation of the benzothiazole.43
Following our stability studies benzoselenazoline-SB6 was refluxed with methanol. This compound was stable to this treatment, as observed for the amine-SB3, and the starting material was recovered after the reaction. Thus, only the derivatives with a –C(H)![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N– bond attached to the carbon atom of the ortho-carborane cluster (Schiff base, benzothiazole) promote the conversion to the nido derivative, while the derivatives with reduced version –C(H)2–NH– (amine, benzoselenazoline) are more stable towards this conversion.
N– bond attached to the carbon atom of the ortho-carborane cluster (Schiff base, benzothiazole) promote the conversion to the nido derivative, while the derivatives with reduced version –C(H)2–NH– (amine, benzoselenazoline) are more stable towards this conversion.
Conclusions
The aza-Wittig reaction was successfully used to synthesize carborane Schiff bases, by reaction of C-formyl-carborane and an aryl iminophosphorane. The method is experimentally very simple and very efficient, permitting the obtention of the otherwise difficult to obtain carboranyl-imines in multigram quantities. The method tolerates the presence of different functional groups, as shown by the preparation of a variety of compounds. All compounds were fully characterized including the solid-state.The closo-carboranyl Schiff bases have been shown to promote the evolution to the nido derivatives. They can also be used as precursors of the corresponding closo-carboranyl-amines, more resistant to deboronation. Thus, the aza-Wittig methodology could provide BNCT researchers with a method to connect carborane clusters to carrier molecules through imine or amine groups, with a different tendency to evolve to their nido form or to retain their closo structure, respectively.
The aza-Wittig methodology has also been modified to generate in one step carboranyl-benzothiazole and carboranyl-benzoselenazoline, starting with the iminophosphorane disulfide or diselenide, respectively. Incidentally, this method has provided the first route to the previously unknown benzoselenazoline derivative. These compounds show a similar stability of the carborane cluster as the imine and amine derivatives, i.e., a tendency to evolve to the nido derivative for the carboranyl-benzothiazole and a resistance to deboronation for the carboranyl-selenazolidine.
Experimental section
General
All manipulations of water-sensitive compounds were carried out under an atmosphere of dry argon using standard Schlenk techniques. Toluene and triethylamine were distilled from calcium hydride prior to use. Acetonitrile was distilled from P4O10 prior to use. THF was distilled from sodium benzophenone prior to use. Methanol was dried by reaction with magnesium powder and distilled prior to use. The iminophosphoranes I1,31I2,32I3,33I4,34I8,35 and the starting materials 2-(methylseleno)-aniline,44 2-aminophenyl diselenide,45N-tosyl-1,2-diaminobencene,46 3-amino-carborane,47 and C-formyl-carborane,10 are non-commercial products that were prepared using literature procedures. All further reagents were purchased from commercial sources and used as such without further purification.Analytical methods
Elemental analyses were performed with a Thermo Finnigan Flash 1112 microanalyzer. IR spectra were recorded as KBr mulls with a Bruker IFS 66 V spectrophotometer. Mass spectra were determined using a Micromass Autospec instrument (positive electronic impact), except for compound IB3 which was determined using a Bruker Microtof instrument in the ESI+ mode. NMR spectra were recorded on a Varian Inova 500 (1H 500 MHz; 13C 126 MHz; 11B 160 MHz, 31P 202 MHz), Varian Inova 400 (1H 400 MHz; 31P 162 MHz); Varian Mercury 300 (1H 300 MHz; 31P 121 MHz) and Bruker DPX 250 (1H 250 MHz). All NMR spectra were recorded in CDCl3 solutions at 25 °C. Chemical shift values for 1H and 13C NMR were referenced to SiMe4 (TMS), those for 31P were referenced to 85% H3PO4 and those for 11B NMR spectra were referenced to external BF3·OEt2. Chemical shifts are reported in units of parts per million downfield from the reference, and all coupling constants are reported in Hertz.Synthesis of iminophosphoranes I5–7
The iminophosphorane precursors not described in the literature were obtained following the Kirsanov reaction, using the same general procedure:A 250 mL two-neck round-bottom flask is charged with commercial dibromotriphenylphosphine and placed under an inert argon atmosphere. A condenser equipped with a gas inlet is attached to the flask and the solid is suspended in 120 mL of dry toluene. The corresponding amine and dry triethylamine are added to the suspension. The reaction mixture is refluxed overnight (14 hours). Once reflux is complete the reaction mixture is allowed to cool and the salt formed (triethylammonium bromide, Et3NHBr) is separated by filtration. The filtrate is concentrated to dryness using a rotary evaporator. The solid obtained is purified by recrystallization. The solid is isolated by filtration, washed with diethyl ether and dried under vacuum.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). Brown solid, 4.51 g (77%).
1). Brown solid, 4.51 g (77%).
1
H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 7.84 (m, 6H, o-PPh3), 7.52 (m, 3H, p-PPh3), 7.45 (m, 6H, m-PPh3), 7.09 (dd, 1H), 6.72 (m, 2H), 6.38 (m, 1H), 2.24 (s, 3H, SeCH3, 77Se satellites, 2JSe–H = 12 Hz). 31P{1H} NMR (202 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −0.3. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 1568m, 1482m, 1463vs, 1433s, 1328vs ν(P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 1286m, 1107s, 1066m, 1032m, 1016s, 741m, 715s, 690s, 588m, 528vs, 505m. MS (EI, m/z): 447.0 (94%) [M]+, 431.9 (14%) [M − Me]+, 366.0 (93%) [M − SeMe]+, 261.8 (91%) [PPh3]+, 182.8 (100%) [PPh2 − H]+. EA (%): C 67.9, H 5.0, N 3.2. Calculated for C25H22NPSe: C 67.3, H 5.0, N 3.1.
N), 1286m, 1107s, 1066m, 1032m, 1016s, 741m, 715s, 690s, 588m, 528vs, 505m. MS (EI, m/z): 447.0 (94%) [M]+, 431.9 (14%) [M − Me]+, 366.0 (93%) [M − SeMe]+, 261.8 (91%) [PPh3]+, 182.8 (100%) [PPh2 − H]+. EA (%): C 67.9, H 5.0, N 3.2. Calculated for C25H22NPSe: C 67.3, H 5.0, N 3.1.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). Light brown solid, 2.82 g (45%).
1). Light brown solid, 2.82 g (45%).
1
H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 7.87 (m, 12H, o-PPh3), 7.50 (m, 20H: 18H m,p-PPh3 + 2H), 6.76 (m, 2H), 6.57 (m, 2H), 6.37 (m, 2H). 31P{1H} NMR (202 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 0.7. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 1569w, 1460s, 1434m, 1340m ν(P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 1107m, 1056w, 1015m, 745m, 717m, 694m, 526m. MS (EI, m/z): 860.5 (33%) [M − H]+, 431.7 (72%) [M1/2]+, 349.8 (72%) [M1/2 − Se]+, 273.8 (66%) [M1/2 − Se − Ph]+, 182.8 (100%) [PPh2 − H]+. EA (%): C 65.7, H 4.6, N 3.2. Calculated for C48H38N2P2Se2: C 66.8, H 4.4, N 3.2.
N), 1107m, 1056w, 1015m, 745m, 717m, 694m, 526m. MS (EI, m/z): 860.5 (33%) [M − H]+, 431.7 (72%) [M1/2]+, 349.8 (72%) [M1/2 − Se]+, 273.8 (66%) [M1/2 − Se − Ph]+, 182.8 (100%) [PPh2 − H]+. EA (%): C 65.7, H 4.6, N 3.2. Calculated for C48H38N2P2Se2: C 66.8, H 4.4, N 3.2.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). Brown solid, 4.59 g (58%).
1). Brown solid, 4.59 g (58%).
1
H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 7.58 (m, 19H: 15H o,p,m-PPh3 + 4H SO2PhMe), 7.00 (m, 2H), 6.58 (m, 2H), 6.21 (d, 1H, NH), 2.27 (s, 3H, CH3). 31P{1H} NMR (121 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 6.9. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3182w, 3059w, 1593m, 1483vs, 1437s, 1400m, 1346vs ν(SO2)a + ν(P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 1167vs ν(SO2)s, 1115s, 1047m, 1020m, 914w, 814w, 743s, 721s, 694s, 559s, 542s, 527s. MS (EI, m/z): 522.0 (13%) [M]+, 367.2 (100%) [M − SO2PhMe]+, 277.2 (26%) [Ph3P = NH]+, 262.1 (8%) [PPh3]+, 182.9 (44%) [PPh2 − H]+. EA (%): C 70.2, H 5.3, N 5.2, S 5.9. Calculated for C31H27N2O2PS: C 71.2, H 5.2, N 5.4, S 6.1.
N), 1167vs ν(SO2)s, 1115s, 1047m, 1020m, 914w, 814w, 743s, 721s, 694s, 559s, 542s, 527s. MS (EI, m/z): 522.0 (13%) [M]+, 367.2 (100%) [M − SO2PhMe]+, 277.2 (26%) [Ph3P = NH]+, 262.1 (8%) [PPh3]+, 182.9 (44%) [PPh2 − H]+. EA (%): C 70.2, H 5.3, N 5.2, S 5.9. Calculated for C31H27N2O2PS: C 71.2, H 5.2, N 5.4, S 6.1.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 97) as eluent. White solid, 1.11 g (84%).
97) as eluent. White solid, 1.11 g (84%).
1 H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): δ 7.70 (dd, 3JP–H, H–H = 12.6, 7.2 Hz, 6H, o-PPh3), 7.54 (d, 3JH–H = 5.6 Hz, 3H, p-PPh3), 7.47 (td, 3JH–H = 7.6, 5.0 Hz, 6H, m-PPh3), 3.39 (s, 2H, Ccage–H), 2.77–1.08 (m, 9H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 131.2 (d, 2JCP = 10.4 Hz, o-PPh3), 130.8 (s, p-PPh3), 130.77 (s, 1JCP = 18.2 Hz, P–C), 127.5 (d, 3JCP = 12.3 Hz, m-PPh3), 56.2 (s, CcageH). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 2.6, −6.3, −12.4, −14.1, −15.1, −15.9, −22.1. 31P{1H} NMR (162 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 8.8. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3062m ν(C–H), 2578vs ν(B–H), 1432vs ν(P–N), 1110s, 719vs, 696vs, 528vs. LR-ESI-MS (m/z): 420.30 [M + H]+. EA (%): C 57.4, H 6.4, N 3.3. Calculated for C20H26B10NP: C 57.3, H 6.2, N 3.3.
Synthesis of schiff bases SB1–8
The Schiff Bases were obtained following the Aza-Wittig reaction, using the same general procedure:A 100 mL one-neck round-bottom flask is charged with C-formyl-carborane and the corresponding iminophosphorane precursor. The solids are dissolved in 50 mL of commercial chloroform and the solution is heated at reflux for 16 hours. Once reflux is complete, the solution is concentrated to dryness using a rotary evaporator. The crude product is purified by column chromatography.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4). Pale yellow solid, 0.75 g (94%).
4). Pale yellow solid, 0.75 g (94%).
1
H RMN (500 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 8.00 (s, 1H, HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 7.23 (m, 1H), 6.94 (m, 3H), 4.51 (s, 1H, CcageH), 3.84 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.00–1.50 (bm, 10H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 153.7 (HC
N), 7.23 (m, 1H), 6.94 (m, 3H), 4.51 (s, 1H, CcageH), 3.84 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.00–1.50 (bm, 10H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 153.7 (HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 151.9 (C), 136.6 (C), 128.5 (CH), 123.1 (CH), 121.0 (CH), 111.9 (CH), 73.1 (Ccage–[HC
N), 151.9 (C), 136.6 (C), 128.5 (CH), 123.1 (CH), 121.0 (CH), 111.9 (CH), 73.1 (Ccage–[HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N]), 56.2 (CcageH), 55.8 (OCH3). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −2.1, −3.3, −9.0, −10.8, −12.8. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3071 m ν(Ccage–H), 2595vs ν(B–H), 1634m ν(C
N]), 56.2 (CcageH), 55.8 (OCH3). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −2.1, −3.3, −9.0, −10.8, −12.8. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3071 m ν(Ccage–H), 2595vs ν(B–H), 1634m ν(C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 1589m, 1495s, 1468m, 1254s, 1117m, 1026m, 750s. MS (EI, m/z): 277.2 (57%) [M]+, 262.1 (6%) [M − Me]+, 246.1 (6%) [M − OMe]+, 134.0 (100%) [M − C2B10H11]+. EA (%): C 43.0, H 7.0, N 4.9. Calculated for C10H19B10NO: C 43.3, H 6.9, N 5.0.
N), 1589m, 1495s, 1468m, 1254s, 1117m, 1026m, 750s. MS (EI, m/z): 277.2 (57%) [M]+, 262.1 (6%) [M − Me]+, 246.1 (6%) [M − OMe]+, 134.0 (100%) [M − C2B10H11]+. EA (%): C 43.0, H 7.0, N 4.9. Calculated for C10H19B10NO: C 43.3, H 6.9, N 5.0.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4). Pale yellow solid, 1.14 g (99%).
4). Pale yellow solid, 1.14 g (99%).
1
H RMN (500 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 8.01 (s, 1H, HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 7.26 (t, 1H), 7.12 (d, 1H), 7.00 (d, 1H), 6.89 (t, 1H), 6.50 (s, 1H, OH, exchanges with D2O), 4.29 (s, 1H, CcageH), 3.00–1.50 (bm, 10H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 152.2 (C), 149.5 (HC
N), 7.26 (t, 1H), 7.12 (d, 1H), 7.00 (d, 1H), 6.89 (t, 1H), 6.50 (s, 1H, OH, exchanges with D2O), 4.29 (s, 1H, CcageH), 3.00–1.50 (bm, 10H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 152.2 (C), 149.5 (HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 131.7 (C), 131.4 (CH), 120.5 (CH), 116.5 (CH), 116.2 (CH), 72.6 (Ccage–[HC
N), 131.7 (C), 131.4 (CH), 120.5 (CH), 116.5 (CH), 116.2 (CH), 72.6 (Ccage–[HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N]), 56.7 (CcageH). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −2.8, −3.9, −9.8, −12.1, −13.6. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3470m ν(O–H), 3057w ν(Ccage–H), 2590vs ν(B–H), 1634m ν(C
N]), 56.7 (CcageH). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −2.8, −3.9, −9.8, −12.1, −13.6. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3470m ν(O–H), 3057w ν(Ccage–H), 2590vs ν(B–H), 1634m ν(C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 1589m, 1487s, 1357m, 1215s, 1018m, 748m. MS (EI, m/z): 263.2 (56%) [M]+, 121.1 (100%) [M − C2B10H11]+. EA (%): C 41.1, H 6.7, N 5.2. Calculated for C9H17B10NO: C 41.0, H 6.5, N 5.3.
N), 1589m, 1487s, 1357m, 1215s, 1018m, 748m. MS (EI, m/z): 263.2 (56%) [M]+, 121.1 (100%) [M − C2B10H11]+. EA (%): C 41.1, H 6.7, N 5.2. Calculated for C9H17B10NO: C 41.0, H 6.5, N 5.3.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 9). Yellow solid, 0.94 g (99%).
9). Yellow solid, 0.94 g (99%).
1
H RMN (500 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 7.78 (s, 1H, HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 7.29 (m, 1H), 7.21 (dd, 1H), 7.15 (m, 1H), 6.85 (dd, 1H), 4.56 (s, 1H, CcageH), 2.46 (s, 3H, SCH3), 3.20–1.60 (bm, 10H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 152.3 (HC
N), 7.29 (m, 1H), 7.21 (dd, 1H), 7.15 (m, 1H), 6.85 (dd, 1H), 4.56 (s, 1H, CcageH), 2.46 (s, 3H, SCH3), 3.20–1.60 (bm, 10H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 152.3 (HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 144.7 (C), 134.6 (C), 128.3 (CH), 125.1 (CH), 124.7 (CH), 117.2 (CH), 72.6 (Ccage–[HC
N), 144.7 (C), 134.6 (C), 128.3 (CH), 125.1 (CH), 124.7 (CH), 117.2 (CH), 72.6 (Ccage–[HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N]), 56.6 (CcageH), 14.5 (SCH3). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −3.1, −4.2, −10.0, −11.8, −13.9. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3067m ν(Ccage–H), 2635s, 2589vs, 2565vs ν(B–H), 1634m ν(C
N]), 56.6 (CcageH), 14.5 (SCH3). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −3.1, −4.2, −10.0, −11.8, −13.9. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3067m ν(Ccage–H), 2635s, 2589vs, 2565vs ν(B–H), 1634m ν(C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 1468m, 1438m, 1124m, 1070m, 1016m, 750m, 725m. MS (EI, m/z): 293.0 (34%) [M]+, 149.9 (100%) [M − C2B10H11]+. EA (%): C 40.9, H 6.8, N 4.4, S 10.5. Calculated for C10H19B10NS: C 40.9, H 6.5, N 4.8, S 10.9.
N), 1468m, 1438m, 1124m, 1070m, 1016m, 750m, 725m. MS (EI, m/z): 293.0 (34%) [M]+, 149.9 (100%) [M − C2B10H11]+. EA (%): C 40.9, H 6.8, N 4.4, S 10.5. Calculated for C10H19B10NS: C 40.9, H 6.5, N 4.8, S 10.9.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4). Yellow solid, 0.72 g (89%).
4). Yellow solid, 0.72 g (89%).
1
H RMN (500 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 7.83 (s, 2H, HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 7.56 (m, 2H), 7.23 (m, 4H), 6.92 (m, 2H), 4.51 (s, 2H, CcageH), 3.20–1.30 (bm, 20H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 152.9 (2 HC
N), 7.56 (m, 2H), 7.23 (m, 4H), 6.92 (m, 2H), 4.51 (s, 2H, CcageH), 3.20–1.30 (bm, 20H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 152.9 (2 HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 145.2 (2 C), 132.1 (2 C), 128.8 (2 CH), 127.7 (2 CH), 127.0 (2 CH), 117.4 (2 CH), 72.5 (2 Ccage–[HC
N), 145.2 (2 C), 132.1 (2 C), 128.8 (2 CH), 127.7 (2 CH), 127.0 (2 CH), 117.4 (2 CH), 72.5 (2 Ccage–[HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N]), 56.5 (2 CcageH). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −2.7, −3.9, −9.9, −11.7, −13.8. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3062m ν(Ccage–H), 2592vs ν(B–H), 1639m ν(C
N]), 56.5 (2 CcageH). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −2.7, −3.9, −9.9, −11.7, −13.8. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3062m ν(Ccage–H), 2592vs ν(B–H), 1639m ν(C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 1576m, 1462m, 1340w, 1197w, 1160m, 1126m, 1036m, 756m, 724m. MS (EI, m/z): 557.5 (2%) [M]+, 278.1 (100%) [M1/2]+, 136.0 (97%) [M1/2 − C2B10H11]+. EA (%): C 39.1, H 5.8, N 5.1, S 11.7. Calculated for C18H32B20N2S2: C 38.8, H 5.8, N 5.0, S 11.5.
N), 1576m, 1462m, 1340w, 1197w, 1160m, 1126m, 1036m, 756m, 724m. MS (EI, m/z): 557.5 (2%) [M]+, 278.1 (100%) [M1/2]+, 136.0 (97%) [M1/2 − C2B10H11]+. EA (%): C 39.1, H 5.8, N 5.1, S 11.7. Calculated for C18H32B20N2S2: C 38.8, H 5.8, N 5.0, S 11.5.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4). Yellow solid, 0.98 g (99%).
4). Yellow solid, 0.98 g (99%).
1
H RMN (500 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 7.76 (s, 1H, HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 7.27 (m, 2H), 7.17 (m, 1H), 6.84 (dd, 1H), 4.52 (s, 1H, CcageH), 2.28 (s, 3H, SeCH3), 3.20–1.60 (bm, 20H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 152.1 (HC
N), 7.27 (m, 2H), 7.17 (m, 1H), 6.84 (dd, 1H), 4.52 (s, 1H, CcageH), 2.28 (s, 3H, SeCH3), 3.20–1.60 (bm, 20H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 152.1 (HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 145.8 (C), 130.4 (C), 128.6 (CH), 127.6 (CH), 126.1 (CH), 117.1 (CH), 72.6 (Ccage–[HC
N), 145.8 (C), 130.4 (C), 128.6 (CH), 127.6 (CH), 126.1 (CH), 117.1 (CH), 72.6 (Ccage–[HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N]), 56.6 (CcageH), 5.2 (SeCH3). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −1.9, −3.0, −8.9, −10.7, −12.8. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3068m ν(Ccage–H), 2622s, 2587vs, 2566vs ν(B–H), 1634m ν(C
N]), 56.6 (CcageH), 5.2 (SeCH3). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −1.9, −3.0, −8.9, −10.7, −12.8. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3068m ν(Ccage–H), 2622s, 2587vs, 2566vs ν(B–H), 1634m ν(C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 1574w, 1466m, 1427m, 1263m, 1123m, 1067m, 1035m, 1026m, 803m, 752m, 722m. MS (EI, m/z): 341.2 (43%) [M]+, 325.2 (7%) [M − Me]+, 246.2 (64%) [M − SeMe]+, 198.0 (100%) [M − C2B10H11]+. EA (%): C 36.0, H 5.8, N 4.1. Calculated for C10H19B10NSe: C 35.3, H 5.6, N 4.1.
N), 1574w, 1466m, 1427m, 1263m, 1123m, 1067m, 1035m, 1026m, 803m, 752m, 722m. MS (EI, m/z): 341.2 (43%) [M]+, 325.2 (7%) [M − Me]+, 246.2 (64%) [M − SeMe]+, 198.0 (100%) [M − C2B10H11]+. EA (%): C 36.0, H 5.8, N 4.1. Calculated for C10H19B10NSe: C 35.3, H 5.6, N 4.1.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4). Pale yellow solid, 0.71 g (75%).
4). Pale yellow solid, 0.71 g (75%).
1
H RMN (250 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 7.88 (s, 2H, HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 7.61 (d, 2H), 7.25 (m, 4H), 6.97 (d, 2H), 4.52 (s, 2H, CcageH), 3.20–1.60 (bm, 20H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 152.4 (2 HC
N), 7.61 (d, 2H), 7.25 (m, 4H), 6.97 (d, 2H), 4.52 (s, 2H, CcageH), 3.20–1.60 (bm, 20H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 152.4 (2 HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 145.6 (2 C), 130.2 (2 CH), 129.4 (2 CH), 128.1 (2 CH), 127.8 (2 C), 117.0 (2 CH), 72.5 (2 Ccage–[HC
N), 145.6 (2 C), 130.2 (2 CH), 129.4 (2 CH), 128.1 (2 CH), 127.8 (2 C), 117.0 (2 CH), 72.5 (2 Ccage–[HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N]), 56.6 (2 CcageH). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −1.8, −2.6, −8.8, −10.7, −12.7. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3061m ν(Ccage–H), 2589vs ν(B–H), 1638m ν(C
N]), 56.6 (2 CcageH). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −1.8, −2.6, −8.8, −10.7, −12.7. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3061m ν(Ccage–H), 2589vs ν(B–H), 1638m ν(C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 1459m, 1262m, 1093m, 1065m, 1044m, 1028m, 1015m, 803m, 755m, 722m. MS (EI, m/z): 324.8 (13%) [M1/2]+, 184.4 (100%) [M1/2 − C2B10H11]+. EA (%): C 33.4, H 4.8, N 4.1. Calculated for C18H32B20N2Se2: C 33.2, H 5.0, N 4.3.
N), 1459m, 1262m, 1093m, 1065m, 1044m, 1028m, 1015m, 803m, 755m, 722m. MS (EI, m/z): 324.8 (13%) [M1/2]+, 184.4 (100%) [M1/2 − C2B10H11]+. EA (%): C 33.4, H 4.8, N 4.1. Calculated for C18H32B20N2Se2: C 33.2, H 5.0, N 4.3.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8.5). Yellow solid, 1.19 g (75%).
8.5). Yellow solid, 1.19 g (75%).
1
H RMN (500 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 7.70 (s, 1H, HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 7.66 (dd, 1H), 7.57 (d, 2H), 7.36 (s, 1H, NH), 7.31 (m, 1H), 7.19 (d, 2H), 7.10 (m, 1H), 6.91 (dd, 1H), 4.22 (s, 1H, CcageH), 2.38 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.20–1.60 (bm, 10H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 152.2 (HC
N), 7.66 (dd, 1H), 7.57 (d, 2H), 7.36 (s, 1H, NH), 7.31 (m, 1H), 7.19 (d, 2H), 7.10 (m, 1H), 6.91 (dd, 1H), 4.22 (s, 1H, CcageH), 2.38 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.20–1.60 (bm, 10H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 152.2 (HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 144.2 (C), 137.0 (C), 136.2 (C), 132.6 (C), 130.0 (CH), 129.7 (2 CH), 126.9 (2 CH), 125.6 (CH), 122.5 (CH), 117.2 (CH), 72.2 (Ccage–[HC
N), 144.2 (C), 137.0 (C), 136.2 (C), 132.6 (C), 130.0 (CH), 129.7 (2 CH), 126.9 (2 CH), 125.6 (CH), 122.5 (CH), 117.2 (CH), 72.2 (Ccage–[HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N]), 56.7 (CcageH), 21.5 (CH3). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −1.8, −8.8, −11.2, −12.7, −13.7. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3281m ν(N–H), 3072m ν(Ccage–H), 2590vs ν(B–H), 1634w ν(C
N]), 56.7 (CcageH), 21.5 (CH3). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −1.8, −8.8, −11.2, −12.7, −13.7. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3281m ν(N–H), 3072m ν(Ccage–H), 2590vs ν(B–H), 1634w ν(C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 1491m, 1393m, 1342m ν(SO2)a, 1325m, 1261m, 1169vs ν(SO2)s, 1094s, 1018m, 914w, 812s, 758m, 721m, 683m, 573m, 538m. MS (EI, m/z): 415.8 (1%) [M]+, 262.1 (100%) [M − SO2PhMe]+, 154.8 (17%) [SO2PhMe]+. EA (%): C 45.6, H 5.9, N 6.4, S 7.2. Calculated for C16H24B10N2O2S: C 46.1, H 5.8, N 6.7, S 7.7.
N), 1491m, 1393m, 1342m ν(SO2)a, 1325m, 1261m, 1169vs ν(SO2)s, 1094s, 1018m, 914w, 812s, 758m, 721m, 683m, 573m, 538m. MS (EI, m/z): 415.8 (1%) [M]+, 262.1 (100%) [M − SO2PhMe]+, 154.8 (17%) [SO2PhMe]+. EA (%): C 45.6, H 5.9, N 6.4, S 7.2. Calculated for C16H24B10N2O2S: C 46.1, H 5.8, N 6.7, S 7.7.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 7). Pale yellow solid, 0.30 g (35%).
7). Pale yellow solid, 0.30 g (35%).
1
H RMN (300 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 7.65 (s, 2H, HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 7.28 (d, 2H, o-PPh3), 6.98 (t, 2H, m-PPh3), 4.41 (s, 2H, Ccage–H), 2.85–1.60 (bm, 10H, B–H).13C RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 154.3 (HC
N), 7.28 (d, 2H, o-PPh3), 6.98 (t, 2H, m-PPh3), 4.41 (s, 2H, Ccage–H), 2.85–1.60 (bm, 10H, B–H).13C RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 154.3 (HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 140.8 (C), 128.5 (CH), 120.7 (CH), 72.1 (Ccage–[HC
N), 140.8 (C), 128.5 (CH), 120.7 (CH), 72.1 (Ccage–[HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N]), 56.9 (Ccage–H). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −1.8, −2.8, −8.8, −10.9, −12.7, −13.6, −14.8. IR (IR-ATR, v/cm−1): 3074m, 2604s, 2577s v(B–H), 1656m, 1634w v(C
N]), 56.9 (Ccage–H). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −1.8, −2.8, −8.8, −10.9, −12.7, −13.6, −14.8. IR (IR-ATR, v/cm−1): 3074m, 2604s, 2577s v(B–H), 1656m, 1634w v(C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 1478w, 1340w, 1262w, 1198w, 1128m, 1109m, 1065w, 1039w, 1016m, 800w, 759m, 722m, 704w, 695w. MS (EI, m/z): 273.5 (100%) [M − (carboranil)]+, 416.7 (7.4%) [M]+. EA (%): C 34.1, H 6.5, N 6.4. Calculated for C12H28B20N2: C 34.6, H 6.7, N 6.7.
N), 1478w, 1340w, 1262w, 1198w, 1128m, 1109m, 1065w, 1039w, 1016m, 800w, 759m, 722m, 704w, 695w. MS (EI, m/z): 273.5 (100%) [M − (carboranil)]+, 416.7 (7.4%) [M]+. EA (%): C 34.1, H 6.5, N 6.4. Calculated for C12H28B20N2: C 34.6, H 6.7, N 6.7.
1
H RMN (500 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 10.70 (bs, 1H, NH), 8.40 (d, 1H, HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N, 3JH–H = 16 Hz), 7.65 (m, 1H), 7.48 (m, 2H), 7.35 (m, 1H), 2.52 (s, 3H, SCH3), 2.42 (s, 1H, CcageH), −2.27 (bs, 1H, BHB). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −5.2, −5.7, −11.3, −12.7, −17.8, −24.0, −29.1, −31.3. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3423w, 3197w ν(N–H), 2927w ν(Ccage–H), 2545vs ν(B–H), 1637s ν(C
N, 3JH–H = 16 Hz), 7.65 (m, 1H), 7.48 (m, 2H), 7.35 (m, 1H), 2.52 (s, 3H, SCH3), 2.42 (s, 1H, CcageH), −2.27 (bs, 1H, BHB). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −5.2, −5.7, −11.3, −12.7, −17.8, −24.0, −29.1, −31.3. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3423w, 3197w ν(N–H), 2927w ν(Ccage–H), 2545vs ν(B–H), 1637s ν(C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 1585m, 1475w, 1452w, 1435w, 1396w, 1385w, 1359w, 1322w, 1291m, 1211w, 1166m, 1064w, 1007m, 975w, 959w, 757m ν(C–S). MS (EI, m/z): 283.2 (32%) [M]+, 267.1 (21%) [M − Me]+, 139.0 (100%) [1-NH2 − 2-SMe − Ph]+, 124.0 (96%) [1-NH2 − 2-S − Ph]+. EA (%): C 42.1, H 7.3, N 4.7, S 10.7. Calculated for C10H20B9NS: C 42.3, H 7.1, N 4.9, S 11.3.
N), 1585m, 1475w, 1452w, 1435w, 1396w, 1385w, 1359w, 1322w, 1291m, 1211w, 1166m, 1064w, 1007m, 975w, 959w, 757m ν(C–S). MS (EI, m/z): 283.2 (32%) [M]+, 267.1 (21%) [M − Me]+, 139.0 (100%) [1-NH2 − 2-SMe − Ph]+, 124.0 (96%) [1-NH2 − 2-S − Ph]+. EA (%): C 42.1, H 7.3, N 4.7, S 10.7. Calculated for C10H20B9NS: C 42.3, H 7.1, N 4.9, S 11.3.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). The solution is cooled with an ice/water bath (0 °C) and sodium cyanoborohydride (NaBH3CN) (0.76 g, 12.10 mmol) is added in small portions, observing a loss of color from yellow to colorless. The cooling bath is removed and the reaction is stirred at room temperature overnight (16 h). The THF is removed in a rotary evaporator and the acetic acid is neutralized with a saturated solution of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3). The crude product is dissolved in 50 mL of dichloromethane and washed with water (2 × 30 mL). The organic phase is dried with anhydrous Na2SO4, and concentrated in a rotary evaporator. The residue obtained is purified by column chromatography using a mixture of ethyl acetate and hexane (2
1). The solution is cooled with an ice/water bath (0 °C) and sodium cyanoborohydride (NaBH3CN) (0.76 g, 12.10 mmol) is added in small portions, observing a loss of color from yellow to colorless. The cooling bath is removed and the reaction is stirred at room temperature overnight (16 h). The THF is removed in a rotary evaporator and the acetic acid is neutralized with a saturated solution of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3). The crude product is dissolved in 50 mL of dichloromethane and washed with water (2 × 30 mL). The organic phase is dried with anhydrous Na2SO4, and concentrated in a rotary evaporator. The residue obtained is purified by column chromatography using a mixture of ethyl acetate and hexane (2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8), yielding a colorless oil that solidifies overnight in the refrigerator (1.08 g, 100%).
8), yielding a colorless oil that solidifies overnight in the refrigerator (1.08 g, 100%).
1 H RMN (500 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 7.43 (dd, 1H), 7.21 (m, 1H), 6.79 (m, 1H), 6.65 (dd, 1H), 4.80 (bs, 1H, NH), 3.97 (s, 2H, CH2), 3.77 (s, 1H, CcageH), 2.34 (s, 3H, SCH3), 3.10–1.50 (bm, 10H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 145.8 (C), 134.6 (CH), 129.6 (CH), 121.0 (C), 119.4 (CH), 110.0(CH), 75.4 (Ccage–C), 58.4 (CcageH), 49.3 (CH2), 18.6 (SCH3). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −3.2, −6.1, −10.2, −12.6, −14.1. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3366m ν(N–H), 3067w ν(Ccage–H), 2923w, 2585vs ν(B–H), 1587s, 1504vs, 1454m, 1361w, 1322m, 1284m, 1266m, 1165m, 1112m, 1042m, 1018m, 750s, 725m. MS (EI, m/z): 295.1 (100%) [M]+, 280.0 (10%) [M − Me]+, 247.0 (22%) [M − SMe]+, 151.8 (93%) [M − (1,2-C2B10H11)]+, 135.7 (62%) [M − (1,2-C2B10H11) − Me]+. EA (%): C 39.3, H 7.1, N 4.5, S 9.7. Calculated for C10H21B10NS: C 40.6, H 7.2, N 4.7, S 10.8.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4). Pale brown solid, 1.10 g (73%).
4). Pale brown solid, 1.10 g (73%).
1
H RMN (500 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 7.97 (m, 1H), 7.85 (m, 1H), 7.53 (m, 1H), 7.46 (m, 1H), 4.75 (s, 1H, CcageH), 3.20–1.70 (bm, 10H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 161.1 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 151.7 (C), 135.9 (C), 127.1 (CH), 126.6 (CH), 123.7 (CH), 121.6 (CH), 70.8 (Ccage–C), 59.2 (CcageH). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −2.5, −3.2, −8.4, −10.4, −11.0, −12.8. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3071s ν(Ccage–H), 2594vs, 2575vs ν(B–H), 1504w ν(C
N), 151.7 (C), 135.9 (C), 127.1 (CH), 126.6 (CH), 123.7 (CH), 121.6 (CH), 70.8 (Ccage–C), 59.2 (CcageH). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −2.5, −3.2, −8.4, −10.4, −11.0, −12.8. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3071s ν(Ccage–H), 2594vs, 2575vs ν(B–H), 1504w ν(C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N)thiazole, 1458m, 1433m, 1261m, 1153m, 1067m, 1016m, 804m, 754s, 725s. MS (EI, m/z): 277.2 (100%) [M]+, 135.9 (91%) [M − (1,2-C2B10H11)]+, 124.0 (74%) [C6H6NS]+. EA (%): C 38.8, H 5.4, N 4.9, S 10.5. Calculated for C9H15B10NS: C 39.0, H 5.5, N 5.1, S 11.6.
N)thiazole, 1458m, 1433m, 1261m, 1153m, 1067m, 1016m, 804m, 754s, 725s. MS (EI, m/z): 277.2 (100%) [M]+, 135.9 (91%) [M − (1,2-C2B10H11)]+, 124.0 (74%) [C6H6NS]+. EA (%): C 38.8, H 5.4, N 4.9, S 10.5. Calculated for C9H15B10NS: C 39.0, H 5.5, N 5.1, S 11.6.
Recrystallization of a sample of benzothiazole-SB4 in methanol produced the formation of single crystals of nido-(benzothiazole-SB4).
11 B{ 1 H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −5.1, −7.7, −11.0, −15.3, −17.3, −21.9, −30.5, −32.9. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3538m ν(N–H), 2527vs ν(B–H), 1606w, 1584w, 1541m, 1443m, 1288w, 1252w, 1208w, 1159w, 1072w, 1004m, 761m.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4). Orange solid, 0.60 g (70%).
4). Orange solid, 0.60 g (70%).
1 H RMN (500 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 7.12 (dd, 1H), 7.06 (m, 1H), 6.82 (m, 1H), 6.70 (dd, 1H), 5.89 (d, 1H, HC–NH, 3JH–H = 4 Hz), 4.74 (bd, 1H, NH), 4.27 (s, 1H, CcageH), 3.20–1.00 (bm, 10H, BH). 13C{1H} RMN (126 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 145.8 (C), 127.1 (CH), 124.8 (CH), 121.7 (CH), 119.5 (C), 111.0 (CH), 81.6 (Ccage–C), 62.7 (HC–NH), 61.9 (CcageH). 11B{1H} RMN (160 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): −3.0, −4.5, −8.2, −9.0, −10.3, −12.7, −13.7. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 3370m ν(N–H), 3067w ν(Ccage–H), 2572vs ν(B–H), 1579w, 1513w, 1469m, 1436w, 1411w, 1330w, 1293w, 1260m, 1187w, 1087m, 1040w, 1017m, 924w, 747m, 719m, 692w, 560w. MS (EI, m/z): 326.0 (8%) [M − H]+, 183.9 (100%) [M − (1,2-C2B10H11)]+. EA (%): C 33.3, H 5.4, N 4.1. Calculated for C9H17B10NSe: C 33.1, H 5.3, N 4.3.
Author contributions
P. C.: experimental work; I. V.-C.: experimental work and manuscript preparation; A. S.-P. research conception, research supervision, single crystal X-ray analysis and manuscript preparation.Data availability
The data supporting this article have been included as part of the ESI.†Crystallographic data for compounds SB1–SB5, SB7, nido-SB3, amine-SB3, nido-benzothiazole-SB4 and IB3 have been deposited at the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre under CCDC 2393159–2393168.†
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the following FEDER co-funded grants: Consellería de Cultura, Educación e Ordenación Universitaria, Xunta de Galicia GRC GI-1584 (ED431C 2023/02), and Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Project PID2021-127531NB-I00 (AEI/10.13039/501100011033/FEDER/UE). I. V.-C. thanks the “Programa de axudas á etapa predoutoral”, ED481A/IN606A, Xunta de Galicia.References
- (a) X. Zhang, L. M. Rendina and M. Müllner, Carborane-Containing Polymers: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications, ACS Polym. Au, 2024, 4, 7–33, DOI:10.1021/acspolymersau.3c00030; (b) Y. Meng, X. Lin, J. Huang and L. Zhang, Recent Advances in Carborane-Based Crystalline Porous Materials, Molecules, 2024, 29, 3916–3933, DOI:10.3390/molecules29163916; (c) W. Guo, Z. Yang, L. Shu, H. Cai and Z. Wei, The First Discovery of Spherical Carborane Molecular Ferroelectric Crystals, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2024, 63, e202407934, DOI:10.1002/anie.202407934; (d) Z. Li, R. Núñez, M. E. Light, E. Ruiz, F. Teixidor, C. Viñas, D. Ruiz-Molina, C. Roscini and J. Giner Planas, Water-Stable Carborane-Based Eu3+/Tb3+ Metal-Organic Frameworks for Tunable Time-Dependent Emission Color and Their Application in Anticounterfeiting Bar-Coding, Chem. Mater., 2022, 34, 4795–4808, DOI:10.1021/acs.chemmater.2c00323; (e) L. Gan, A. Chidambaram, P. G. Fonquernie, M. E. Light, D. Choquesillo-Lazarte, H. Huang, E. Solano, J. Fraile, C. Viñas, F. Teixidor, J. A. R. Navarro, K. C. Stylianou and J. G. Planas, A Highly Water-Stable meta-Carborane-Based Copper Metal-Organic Framework for Efficient High-Temperature Butanol Separation, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 8299–8311, DOI:10.1021/jacs.0c01008; (f) A. Saha, E. Oleshkevich, C. Viñas and F. Teixidor, Biomimetic Inspired Core-Canopy Quantum Dots: Ions Trapped in Voids Induce Kinetic Fluorescence Switching, Adv. Mater., 2017, 1704238–1704245, DOI:10.1002/adma.201704238; (g) R. Núñez, I. Romero, F. Teixidor and C. Viñas, Icosahedral boron clusters: a perfect tool for the enhancement of polymer features, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45, 5147–5173, 10.1039/c6cs00159a; (h) A. M. Cioran, A. D. Musteti, F. Teixidor, Z. Krpetic, I. A. Prior, Q. He, C. J. Kiely, M. Brust and C. Viñas, Mercaptocarborane-Capped Gold Nanoparticles: Electron Pools and Ion Traps with Switchable Hydrophilicity, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 212–221, DOI:10.1021/ja203367h; (i) A. Vöge and D. Gabel, Boron Derivatives for Application in Nonlinear Optics, in Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, ed. N. S. Hosmane, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, ch. 13, pp. 295–318 Search PubMed; (j) P. Kaszynski, closo-Boranes as Structural Elements for Liquid Crystals, in Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, ed. N. S. Hosmane, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, ch. 14, pp. 319–354 Search PubMed; (k) P. A. Jelliss, Photoluminescence from Boron-Based Polyhedral Clusters, in Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, ed. N. S. Hosmane, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, ch. 15, pp. 355–382 Search PubMed; (l) B. Grüner, J. Rais, P. Selucký and M. LucanIkova, Recent Progress in Extraction Agents Based on Cobalt Bis(Dicarbollides) for Partitioning of Radionuclides from High-Level Nuclear Waste, in Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, ed. N. S. Hosmane, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, ch. 19, pp. 463–490 Search PubMed; (m) C. Viñas, R. Nunez and F. Teixidor, Large Molecules Containing Icosahedral Boron Clusters Designed for Potential Applications, in Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, ed. N. S. Hosmane, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, ch. 27, pp. 701–740 Search PubMed; (n) B. P. Dash, R. Satapathy, J. A. Maguire and N. S. Hosmane, Carborane Clusters Versatile Synthetic Building Blocks for Dendritic, Nanostructured, and Polymeric Materials, in Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, ed. N. S. Hosmane, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, ch. 26, pp. 675–699 Search PubMed; (o) A. Vöge and D. Gabel, Boron in Weakly Coordinating Anions and Ionic Liquids, in Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, ed. N. S. Hosmane, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, ch. 29, pp. 807–825 Search PubMed.
- (a) F. Teixidor, C. Viñas, J. Giner Planas, I. Romero and R. Núñez, Advances in the catalytic and photocatalytic behavior of carborane derived metal complexes, Advances in Catalysis, 2022, 71, 1–45. DOI:10.1016/bs.acat.2022.04.001; (b) R. N. Grimes, Carboranes in Catalysis, in Carboranes, Academic Press, London, UK, 3rd edn, 2016, pp. 929–944. DOI:10.1016/B978-0-12-801894-1.00015-9; (c) H. Shen and Z. Xie, Constrained-Geometry Titanacarborane Monoamides From Synthesis and Reactivity to Catalytic Applications, in Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, ed. N. S. Hosmane, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, ch. 21, pp. 517–528 Search PubMed; (d) S. Bauer and E. Hey-Hawkins, Phosphorus-Substituted Carboranes in Catalysis, in Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, ed. N. S. Hosmane, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, ch. 22, pp. 529–577 Search PubMed.
- (a) R. J. Grams, W. L. Santos, I. R. Scorei, A. Abad-García, C. A. Rosenblum, A. Bita, H. Cerecetto, C. Viñas and M. A. Soriano-Ursua, The Rise of Boron-Containing Compounds: Advancements in Synthesis, Medicinal Chemistry, and Emerging Pharmacology, Chem. Rev., 2024, 124, 2441–2511, DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00663; (b) Z. J. Lesnikowski, New Opportunities in Boron Chemistry for Medical Applications, in Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, ed. N. S. Hosmane, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, ch. 1, pp. 3–20 Search PubMed; (c) S. Stadlbauer and E. Hey-Hawkins, Bioconjugates of Carbaboranyl Phosphonates, in Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, ed. N. S. Hosmane, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, ch. 2, pp. 21–40 Search PubMed; (d) P. Rezacova, P. Cigler, P. Matejicek, M. Lepšik, J. Pokorná, B. Grüner and J. Konvalinka, Medicinal Application of Carboranes: Inhibition of HIV Protease, in Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, ed. N. S. Hosmane, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, ch. 3, pp. 41–72 Search PubMed; (e) H. K. Agarwal, S. Hasabelnaby, R. Tiwari and W. Tjarks, oron Cluster (Radio) Halogenation in Biomedical Research, in Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, ed. N. S. Hosmane, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, ch. 6, pp. 107–144 Search PubMed; (f) Z. Yinghuai, J. A. Maguire and N. S. Hosmane, Recent Developments in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy Driven by Nanotechnology, in Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, ed. N. S. Hosmane, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, ch. 7, pp. 147–163 Search PubMed; (g) H. Nakamura, Liposomal Boron Delivery System for Neutron Capture Therapy of Cancer, in Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, ed. N. S. Hosmane, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, ch. 8, pp. 165–179 Search PubMed; (h) V. I. Bregadze and I. B. Sivaev, Polyhedral Boron Compounds for BNCT, in Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, ed. N. S. Hosmane, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, ch. 9, pp. 181–207 Search PubMed; (i) M. Sibrian-Vazquez and M. G. H. Vicente, Boron Tumor Delivery for BNCT Recent Developments and Perspectives, in Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, ed. N. S. Hosmane, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, ch. 10, pp. 209–241 Search PubMed; (j) J. F. Valliant, K. J. Guenther, A. S. King, P. Morel, P. Schaffer, O. O. Sogbein and K. A. Stephenson, The medicinal chemistry of carboranes, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2002, 232, 173–230, DOI:10.1016/S0010-8545(02)00087-5.
- B. Sreenivasulu, Schiff Base and Reduced Schiff Base Ligands, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, Chichester, 2012 Search PubMed.
- A. M. Abu-Dief and I. M. A. Mohamed, A review on versatile applications of transition metal complexes incorporating Schiff bases, Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci., 2015, 4, 119–133, DOI:10.1016/j.bjbas.2015.05.004.
- L. K. A. Karem, F. Y. Waddai and N. H. Karam, Schiff base complexes of some drug substances (Review), J. Pharm. Sci. Res., 2018, 10, 1912–1917 Search PubMed.
- K. C. Gupta and A. K. Sutar, Catalytic activities of Schiff base transition metal complexes, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2008, 252, 1420–1450, DOI:10.1016/j.ccr.2007.09.005.
- (a) Y. Nie, Y.-F. Wang, J.-L. Miao, Y.-X. Li and Z.-W. Zhang, Synthesis and characterization of carboranyl Schiff base compounds from 1-amino-o-carborane, J. Organomet. Chem., 2015, 798, 182–188, DOI:10.1016/j.jorganchem.2015.05.046; (b) Y. Nie, H. Zhang, J. Miao, X. Zhao, Y. Li and G. Sun, Synthesis, aggregation-induced emission and mechanochromism of a new carborane-tetraphenylethylene hybrid, J. Organomet. Chem., 2018, 865, 200–205, DOI:10.1016/j.jorganchem.2018.03.034.
- (a) J. Li, R. Pang, Z. Li, G. Lai, X.-Q. Xiao and T. Müller, Exceptionally Long C−C Single Bonds in Diamino-o-carborane as Induced by Negative Hyperconjugation, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 1397–1401, DOI:10.1002/anie.201812555; (b) R. Pang, J. Li, Z. Cui, C. Zheng, Z. Li, W. Chen, F. Qi, L. Su and X.-Q. Xiao, Synthesis, structure and DFT calculations of 1,2-N-substituted o-carboranes, Dalton Trans., 2019, 48, 7242–7248, 10.1039/C8DT04877K.
- P. Dozzo, R. A. Kasar and S. B. Kahl, Simple, High-Yield Methods for the Synthesis of Aldehydes Directly from o-, m-, and p-Carborane and Their Further Conversions, Inorg. Chem., 2005, 44, 8053–8057, DOI:10.1021/ic0506660.
- R. Luguya, L. Jaquinod, F. R. Fronczek, M. G. H. Vicente and K. M. Smith, Synthesis and reactions of meso-(p-nitrophenyl)porphyrins, Tetrahedron, 2004, 60, 2757–2763, DOI:10.1016/j.tet.2004.01.080.
- X. Zhang, H. Zheng, J. Li, F. Xu, J. Zhao and H. Yan, Selective Catalytic B-H Arylation of o-Carboranyl Aldehydes by a Transient Directing Strategy, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 14511–14517, DOI:10.1021/jacs.7b07160.
- C.-X. Li, Q. Ning, W. Zhao, H.-J. Cao, Y.-P. Wang, H. Yan, C.-S. Lu and Y. Liang, Rh-Catalyzed Decarbonylative Cross-Coupling between o-Carboranes and Twisted Amides: A Regioselective, Additive-Free, and Concise Late-Stage Carboranylation, Chem. – Eur. J., 2021, 27, 2699–2706, DOI:10.1002/chem.202003634.
- H.-J. Cao, M. Chen, F. Sun, Y. Zhao, C. Lu, X. Zhang, Z. Shi and H. Yan, Variable Metal Chelation Modes and Activation Sequence in Pd-Catalyzed B-H Poly-arylation of Carboranes, ACS Catal., 2021, 11, 14047–14057, DOI:10.1021/acscatal.1c04473.
- M. Gao, Y. Tang, M. Xie, C. Qian and Z. Xie, Synthesis, Structure, and Olefin Polymerization Behavior of Constrained-Geometry Group 4 Metallacarboranes Incorporating Imido-Dicarbollyl Ligands, Organometallics, 2006, 25, 2578–2584, DOI:10.1021/om060125y.
- (a) H. Wang, J. Zhang, Z. Lin and Z. Xie, The synthesis and structure of a carbene-stabilized iminocarboranyl-boron(I) compound, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 16817–16820, 10.1039/C5CC06818E; (b) T. L. Chan and Z. Xie, The synthesis, structure and reactivity of an imine-stabilized carboranylphosphorus(I) compound, Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 7280–7283, 10.1039/C6CC03368G; (c) H. Wang and Z. Xie, Synthesis, Structure, and Reactivity of Carboranyl-Supported Germylenes: Approaching Germanones, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2017, 38–39, 4430–4435, DOI:10.1002/ejic.201700496.
- M. W. Renner, M. Miura, M. W. Easson and M. G. H. Vicente, Recent Progress in the Syntheses and Biological Evaluation of Boronated Porphyrins for Boron Neutron-Capture Therapy, Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem., 2006, 6, 145–157, DOI:10.2174/187152006776119135.
- F. Palacios, C. Alonso, D. Aparicio, G. Rubiales and J. M. de los Santos, The aza-Wittig reaction: an efficient tool for the construction of carbon-nitrogen double bonds, Tetrahedron, 2007, 63, 523–575, DOI:10.1016/j.tet.2006.09.048.
- H. Staudinger and J. Meyer, Über neue organische Phosphorverbindungen III. Phosphinmethylenderivate und Phosphinimine, Helv. Chim. Acta, 1919, 2, 635–646, DOI:10.1002/hlca.19190020164.
- A. V. Kirsanov, Chemistry of amides of sulphuric acid, Isv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser, Khim., 1950, 45, 426–437 ( Chem. Abstr. , 1951 , 45 , 1053 ) Search PubMed.
- A. Sousa-Pedrares, C. Viñas and F. Teixidor, Using the Wittig reaction to produce alkenylcarbaboranes, Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 2998–3000, 10.1039/B921122E.
- (a) N. D. Badgujar, M. D. Dsouza, G. R. Nagargoje, P. D. Kadam, K. I. Momin, A. S. Bondge, S. P. Panchgalle and V. S. More, Recent Advances in Medicinal Chemistry with Benzothiazole-Based Compounds: An In-Depth Review, J. Chem. Rev., 2024, 6, 202–236, DOI:10.48309/jcr.2024.436111.1290; (b) S. Agarwal, D. Gandhi and P. Kalal, Benzothiazole: A Versatile and Multitargeted Pharmacophore in the Field of Medicinal, Chem. Lett. Org. Chem., 2017, 14, 729–742, DOI:10.2174/1570178614666170707160654; (c) R. S. Keri, M. R. Patil, S. A. Patil and S. Budagumpi, A Comprehensive Review in Current Developments of Benzothiazole-Based Molecules in Medicinal Chemistry, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2015, 89, 207–251, DOI:10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.10.059; (d) A. Rouf and C. Tanyeli, Bioactive thiazole and benzothiazole derivatives, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2015, 97, 911–927, DOI:10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.10.058; (e) Y. I. Asiri, A. Alsayari, A. B. Muhsinah, Y. N. Mabkhot and M. Z. Hassan, Benzothiazoles as potential antiviral agents, J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 2020, 1459–1480, DOI:10.1111/jphp.13331.
- D. Zhao, J. Zhang and Z. Xie, Dearomative [2 + 2] Cycloaddition and Formal C-H Insertion Reaction of o–Carboryne with Indoles: Synthesis of Carborane-Functionalized Heterocycles, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 9423–9428, DOI:10.1021/jacs.5b05426.
- K. Liu, G. Wang, N. Ding, J. Zhang, J. Kong, T. Liu and Y. Fang, High-Performance Trichloroacetic Acid Sensor Based on the Intramolecular Hydrogen Bond Formation and Disruption of a Specially Designed Fluorescent o-Carborane Derivative in the Film State, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 19342–19350, DOI:10.1021/acsami.1c03331.
- Z.-J. Yao, Y.-X. Jin, W. Deng and Z.-J. Liu, Synthesis and Optoelectronic Properties of Cationic Iridium(III) Complexes with o–Carborane-Based 2–Phenyl Benzothiazole Ligands, Inorg. Chem., 2021, 60, 2756–2763, DOI:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c03625.
- O. Crespo, M. C. Gimeno and A. Laguna, Synthesis of some new mono- and di-substituted o-carborane derivatives with thiolate and carbamate moieties: crystal structure of 1-(SNC5H4)-1,2-C2B10H11, Polyhedron, 1999, 18, 1279–1283, DOI:10.1016/S0277-5387(98)00430-6.
- D. Zhao and Z. Xie, Visible-Light-Promoted Photocatalytic B-C Coupling via a Boron-Centered Carboranyl Radical: Facile Synthesis of B(3)-Arylated o-Carboranes, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 3166–3170, DOI:10.1002/anie.201511251.
- Z. Yang, W. Zhao, W. Liu, X. Wei, M. Chen, X. Zhang, X. Zhang, Y. Liang, C. Lu and H. Yan, Metal-Free Oxidative B-N Coupling of nido-Carborane with N-Heterocycles, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 11886–11892, DOI:10.1002/anie.201904940.
- K. B. Gona, J. L. V. N. P. Thota, Z. Baz, V. Gómez-Vallejo and J. Llop, Synthesis and 11C-Radiolabelling of 2-Carboranyl Benzothiazoles, Molecules, 2015, 20, 7495–7508, DOI:10.3390/molecules20057495.
- H. A. Mills, J. L. Martin, A. L. Rheingold and A. M. Spokoyny, Oxidative Generation of Boron-Centered Radicals in Carboranes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 4586–4591, DOI:10.1021/jacs.0c00300.
- L. Monnereau, D. Sémeril and D. Matt, Calixarene-derived mono-iminophosphoranes: highly efficient ligands for palladium- and nickel-catalysed cross-coupling, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2013, 355, 1351–1360, DOI:10.1002/adsc.201300091.
- A. Fernández-Figueiras, F. Lucio-Martínez, P. Munín-Cruz, P. Polo-Ces, F. Reigosa, H. Adams, M. T. Pereira and J. M. Vila, Palladium iminophosphorane complexes: the precursors to the missing link in triphenylphosphine chalcogenide metallacycles, Dalton Trans., 2018, 47, 15801–15807, 10.1039/C8DT03062F.
- (a) M. Takahashi and M. Ohba, Synthesis of 2-substituted 1,3-benzothiazoles by aza-Wittig reaction of 2-methylthio-N-triphenylphosphoranylideneaniline with acid chlorides, Heterocycles, 1995, 41, 455–460, DOI:10.3987/COM-94-6949; (b) S. Ramírez-Rave, F. Estudiante-Negrete, R. A. Toscano, S. Hernández-Ortega, D. Morales-Morales and J.-M. Grévy, Synthesis and characterization of new Pd(II) non-symmetrical Pincer complexes derived from thioether functionalized iminophosphoranes. Evaluation of their catalytic activity in the Suzuki–Miyaura couplings, J. Organomet. Chem., 2014, 749, 287–295, DOI:10.1016/j.jorganchem.2013.09.038.
- P. Crujeiras, J. L. Rodríguez-Rey and A. Sousa-Pedrares, Deactivation of the coordinating ability of the iminophosphorane group by the effect of ortho-carborane, Dalton Trans., 2017, 46, 2572–2593, 10.1039/C6DT04592H.
- H. G. Alt, K. J. Schneider and E. Funk, Catalytic Dimerization of Propene with Diiminophosphorane Nickel(II) Complexes in the Presence of Phosphine Additives, Jordan J. Chem., 2008, 3, 367–379 CAS.
- P. Coburger, G. Kahraman, A. Straubea and E. Hey-Hawkins, Rhodium(I) complexes with carborane-substituted P,N ligands: investigations of electronic structure and dynamic behaviour, Dalton Trans., 2019, 48, 9625–9630, 10.1039/C9DT00628A.
- P. Crujeiras, J. L. Rodríguez-Rey and A. Sousa-Pedrares, Coordinating Ability of the Iminophosphorane Group in ortho-Carborane Derivatives, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2017, 4653–4667, DOI:10.1002/ejic.201700487.
- J. L. Rodríguez-Rey, D. Esteban-Gómez, C. Platas-Iglesias and A. Sousa-Pedrares, Electronic versus steric control in palladium complexes of carboranyl phosphineiminophosphorane ligands, Dalton Trans., 2019, 48, 486–503, 10.1039/C8DT04006K.
- R. D. Kennedy, Stabilization of acyclic phosphazides using the ortho-closo-dicarbadodecaboranyl residue, Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 4782–4784, 10.1039/C0CC00426J.
- For example; (a) R. A. Wiesboeck and M. F. Hawthorne, Dicarbaundecaborane(13) and Derivatives, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1964, 86, 1642–1643, DOI:10.1021/ja01062a042; (b) M. A. Fox, W. R. Gill, P. L. Herbertson, J. A. H. MacBride, K. Wade and H. M. Colquhoun, Deboronation of C-substituted ortho- and meta-closo-carboranes using “wet” fluoride ion solutions, Polyhedron, 1996, 15, 565–571, DOI:10.1016/0277-5387(95)00297-6; (c) J. Yoo, J. W. Hwang and Y. Do, Facile and Mild Deboronation of o-Carboranes Using Cesium Fluoride, Inorg. Chem., 2001, 40, 568–570, DOI:10.1021/ic000768k; (d) B. Wrackmeyer, E. V. Klimkina, W. Milius, T. Bauer and R. Kempe, Synthesis and Reactivity of 4,5-[1,2-Dicarba-closo-dodecaborano(12)]-1,3-diselenacyclopentane: Opening of the Icosahedron to Give a Zwitterionic Intermediate and Conversion into 7,8-Dicarba-nido-undecaborate(1−), Chem. Eur. J., 2011, 17, 3238–3251, DOI:10.1002/chem.201002277.
- C. L. Powell, M. Schulze, S. J. Black, A. S. Thompson and M. D. Threadgill, Closo → nido cage degradation of 1-(substituted-phenyl)-1,2-dicarbadodecaborane(12)s in wet DMSO under neutral conditions, Tetrahedron Lett., 2007, 48, 1251–1254, DOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2006.12.034 and references therein.
- S. Aiello, G. Wells, E. L. Stone, H. Kadri, R. Bazzi, D. R. Bell, M. F. G. Stevens, C. S. Matthews, T. D. Bradshaw and A. D. Westwell, Synthesis and Biological Properties of Benzothiazole, Benzoxazole, and Chromen-4-one Analogues of the Potent Antitumor Agent 2-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-5-fluorobenzothiazole (PMX 610, NSC 721648) (1), J. Med. Chem., 2008, 51, 5135–5139, DOI:10.1021/jm800418z.
- H. S. Hwang, S. Lee, S. S. Han, Y. K. Moon, Y. You and E. J. Cho, Benzothiazole Synthesis: Mechanistic Investigation of an In Situ-Generated Photosensitizing Disulfide, J. Org. Chem., 2020, 85, 11835–11843, DOI:10.1021/acs.joc.0c01598.
- H. Wójtowicz, M. Chojnacka, J. Mlochowski, J. Palus, L. Syper, D. Hudecova, M. Uher, E. Piasecki and M. Rybka, Functionalized alkyl and aryl diselenides as antimicrobial and antiviral agents: synthesis and properties, Il Farmaco, 2003, 58, 1235–1242, DOI:10.1016/j.farmac.2003.08.003.
- M. Mbuyi, M. Evers, G. Tihange, A. Luxen and L. Christiaens, The 1,3-benzotellurazole: A new heterocyclic system, Tetrahedron Lett., 1983, 24, 5873–5876, DOI:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)94224-2.
- E. Labisbal, L. Rodriguez, A. Vizoso, M. Alonso, J. Romero, J. A. García-Vázquez, A. Sousa-Pedrares and A. Sousa, Electrochemical Synthesis and Characterization of Tin(IV) Complexes of Dianionic Terdentate Schiff Base Ligands, Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem., 2005, 631, 2107–2114, DOI:10.1002/zaac.200570025.
- L. I. Zakharkin, V. N. Kalinin and V. V. Gedymin, Synthesis and some reactions of 3-amino-o-carboranes, J. Organomet. Chem., 1969, 16, 371–379, DOI:10.1016/S0022-328X(00)89762-4.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Crystallographic details and selected bonds and angles for all crystal structures. Molecular structure of compound IB3. NMR spectra for all compounds. CCDC 2393159–2393168. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4dt03378g |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |