Molten salt electrolytes with enhanced Li+-transport kinetics for fast-cycling of high-temperature lithium metal batteries†
Shuaishuai
Yan‡
 a,
Nan
Yao‡
a,
Nan
Yao‡
 a,
Hao
Liu
a,
Hao
Liu
 b,
Zheng
Zhang
b,
Zheng
Zhang
 a,
Yang
Lu
a,
Zhi
Liu
a,
Wenhui
Hou
a,
Yang
Lu
a,
Zhi
Liu
a,
Wenhui
Hou
 a,
Pan
Zhou
a,
Hangyu
Zhou
c,
Xiang
Chen
a,
Pan
Zhou
a,
Hangyu
Zhou
c,
Xiang
Chen
 *a,
Kai
Liu
*a,
Kai
Liu
 *a and
Qiang
Zhang
*a and
Qiang
Zhang
 a
a
aState Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China. E-mail: xiangchen@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn; liukai2019@tsinghua.edu.cn
bHefei Institute for Public Safety Research, Tsinghua University, Hefei 230601, Anhui, P. R. China
cNational Academy of Safety Science and Engineering, China Academy of Safety Science and Technology, Beijing 100012, China
First published on 7th January 2025
Abstract
Ideal high-temperature lithium metal battery (LMB) electrolytes should have good thermal stability and compatibility with highly reactive cathodes/anodes. Yet, conventional liquid electrolytes usually show severe degradation and substantial safety risks at high temperatures due to the presence of unstable organic solvents. Herein, we report a solvent-free molten salt electrolyte (SFMSE) composed solely of alkali bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide salts, enabling LMB's high thermal tolerance and fast-cycling ability. In addition to non-volatility and non-flammability, the designed Li–Cs electrolyte shows low activation energy and high Li+ conductivity owing to the strong cation–cation concerted effect, thus exhibiting fast Li+ transport kinetics and excellent electrochemical performance at practical capacities. The electrolyte/electrode interphases derived exclusively from anions are inorganic-rich with great robustness, as evidenced by the high Coulombic efficiency of 98.8% for Li plating/stripping and the stable cycling performance of LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 (NCM811) cells. As a result, the Li–Cs electrolyte achieves a discharge capacity beyond 100 mA h g−1 for NCM811/Li half cells at 10C, and a record capacity retention of 75% for NCM811 (3 mA h cm−2)/Li (40 μm) full cells after 280 cycles at 80 °C. The proposed molten salt electrolyte could inspire further advancements in high-energy-density, high-safety, and high-temperature lithium metal batteries.
Broader contextGiven the growing complexity of application scenarios and the frequent occurrence of extreme high temperatures globally, there is an urgent need for advanced high-temperature electrolytes tailored for lithium metal batteries (LMBs). However, conventional liquid electrolytes usually show severe degradation and substantial safety risks at high temperatures due to the presence of unstable organic solvents. Eliminating the solvent to create a type of solvent-free molten salt electrolyte (SFMSE) seems to be an opportunity for designing high-safety and high-temperature LMBs. However, SFMSEs generally show disadvantages of high eutectic melting points and insufficient Li+ conductivity, resulting in low cycling rates. In this work, we report a SFMSE electrolyte composed solely of alkali bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide salts with enhanced Li+-transport kinetics, which is attributed to the high Li+ content and strong cation–cation concerted effect. The inorganic-rich electrolyte/electrode interphases (both SEI and CEI) solely derived from anions are electrochemically and thermally stable, making the molten salt electrolyte far superior to the routine concentrated ether/ester electrolyte and ionic liquid electrolyte. The as-prepared SFMSE electrolyte enables practical LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 (NCM811)/Li batteries with fast-cycling ability, long-cycling stability and high thermal safety, demonstrating the great potential of molten salt electrolytes for practical high-temperature LMBs. |
Introduction
Lithium (Li) metal rechargeable batteries (LMBs) are considered some of the most promising candidates for energy storage due to the high theoretical specific capacity (3860 mA h g−1) and low redox potential (−3.04 V vs. the standard hydrogen electrode) of the Li metal anode.1–3 However, the application of current LMBs utilizing organic liquid electrolytes is severely hindered by their unsatisfactory cycle life and poor temperature adaptability, especially in high-temperature scenarios (>60 °C), such as in outdoor electronic equipment in summer and desert areas, and downhole operations in the oil and gas industry.4,5 The inferior electrochemical performance of LMBs at elevated temperatures is attributed to several factors. Firstly, due to the high reactivity of Li metal, organic solvents are more prone to decomposition at high temperature, forming a chemically unstable and mechanically fragile solid–electrolyte interphase (SEI).6 The SEI breaks easily during cycling, leading to dendritic deposition, dead Li formation, and irreversible loss of active Li.7,8 Secondly, continuous oxidation parasitic reactions of electrolytes occur in the presence of highly-oxidative delithiated cathodes, causing damage and thickening of the cathode–electrolyte interphase (CEI), especially at high temperature.9 The structural degradation of the cathode material ultimately results in huge capacity loss.10,11 Additionally, the volatility and flammability of organic solvents with low boiling points exacerbate safety risks at high temperature.12–14 Thus, the operating temperature range of LMBs is typically limited to below 60 °C, otherwise the electrolyte, electrolyte/electrode interfacial stability, and battery cycling life will greatly deteriorate.15,16Given the growing complexity of applications and frequent occurrence of extremely high temperatures globally, there is an urgent need for advanced high-temperature electrolytes tailored for LMBs.17–19 Recent works on electrolyte engineering improved high-temperature electrochemical performance through additive optimization,4,20–22 molecular structure modifications of salts/solvents,9,10,23 and employment of ionic liquid electrolytes and high-concentration electrolytes.24–27 Among these approaches, high-concentration electrolytes can significantly reduce the solvent amount in the Li+ solvation sheath, thereby increasing the favorable decomposition of inorganic lithium salts while minimizing the undesired decomposition of organic solvents, which eventually leads to the formation of robust inorganic-rich interphases.28,29 Despite these advances, the current electrolyte design methodology predominantly relies on small organic molecules as medium for dissolving lithium salts to maintain ion conduction, and the dilemma caused by continuous decomposition of organic species remains difficult to eradicate completely. Therefore, removing the solvent from the electrolyte formula seems to be a promising way to address the above issues.
Molten salts, comprising alkali metal cations and fluorinated sulfonimide anions, have garnered increasing attention as potential electrolytes for high-temperature batteries.8,30,31 The molten salt electrolyte does not contain any unstable solvent molecules, showing high intrinsic thermal stability (non-volatility and non-flammability) and electrochemical stability.32–34 While the concept of using molten salts as electrolytes shows promise, there are several limitations and challenges in their current development status: (1) the eutectic melting point is so high that the operating temperature is often above 100 °C, which poses threats to the workability of other cell components.35,36 (2) The insufficient Li+ conductivity and transference number (t+) result in low cycling capacity and rate. The electrochemical performance and fast-cycling ability of full cells with practical high-mass loading cathodes have been rarely investigated.37 (3) The ionic transport mechanisms within molten salt electrolytes are not well understood. Therefore, although many previous works have concentrated on lowering the melting point by adjusting the anion size to weaken the interaction between cations and anions for promoting Li+ movement, the outcome is inferior.38,39 (4) Most of the previous reports on molten salt electrolytes have focused on the cycling of low-voltage cathodes, e.g. LiFePO4, while the compatibility between molten salt electrolytes and high-voltage cathodes, e.g. LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 (NCM811), has been rarely reported.40 Thus, developing a molten salt electrolyte that has fast Li+ transport kinetics and good interfacial stability is still urgently required, especially for the stable cycling of LMBs with high areal capacities (>2 mA h cm−2) at practical charging/discharging rates (i.e. 1C) and high temperatures (>60 °C).
In this study, we report a solvent-free molten salt electrolyte (SFMSE) with fast-cycling ability tailored for high-temperature LMBs. The optimal Li–Cs system (47 mol% LiFSI and 53 mol% CsFSI) shows excellent Li+ transport kinetics, including a low activation energy (0.20 eV), high Li+ conductivity (0.95 mS cm−1 at 80 °C), and high Li+ transference number (0.53). The underlying transport mechanisms were elucidated via molecular dynamics simulations, revealing that the strong cation–cation (Li+–Cs+) concerted effect can promote the Li+ diffusion in the Li–Cs electrolyte, which has been largely ignored in previous studies. Moreover, compared with the state-of-the-art high-temperature electrolytes, e.g. concentrated ether/ester electrolytes and ionic liquid electrolytes, the Li–Cs electrolyte exhibits evident advantages in terms of thermal stability, current collector integrity, and compatibility with both Li metal anodes and nickel-rich layered oxide cathodes (Fig. 1a). The electrolyte/electrode interphases (both SEI and CEI) derived exclusively from bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide anions are inorganic-rich with great electrochemical and thermal stability, making the molten salt electrolyte suitable for high-temperature applications. Therefore, the Li–Cs electrolyte achieved a high Coulombic efficiency (CE) of 98.8% for Li plating/stripping over 500 cycles, and exceptional oxidative stability up to 9 V vs. Li+/Li. The enhanced Li+ transport kinetics allow NCM811/Li half cells to deliver a discharge capacity above 100 mA h g−1 even at a high rate of 10C. Notably, the NCM811/Li full cells comprising a high-loading cathode (3 mA h cm−2) and thin Li foil (40 μm) show a record capacity retention of 75% after 280 cycles at 80 °C, demonstrating the great potential of molten salt electrolytes for practical high-temperature LMBs.
Results
Li+ transport kinetics
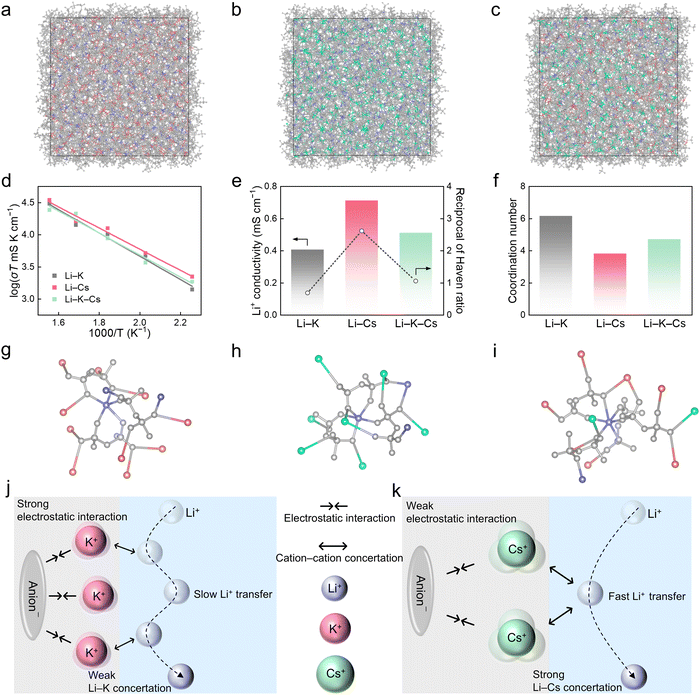
According to the phase diagrams in Fig. S1 (ESI†), three kinds of molten salt electrolytes based on alkali bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide salts with optimal eutectic compositions (41 mol% LiFSI and 59 mol% KFSI, denoted as Li–K; 47 mol% LiFSI and 53 mol% CsFSI, denoted as Li–Cs; 30 mol% LiFSI, 35 mol% KFSI and 35 mol% CsFSI, denoted as Li–K–Cs) were investigated.33,34,41 LiFSI was applied as conducting salts in molten salt electrolytes for lithium-based batteries due to its relatively low melting point (130 °C), good thermal stability and wide electrochemical window. KFSI or CsFSI with different sizes of alkali metal cations and low melting points were usually added to form low eutectic-temperature mixtures in Fig. S2 (ESI†). As for the adoption of the above molten salt electrolytes with specific molar ratios, the deep-eutectic compositions involve several advantages, including the most relaxed Li+ coordination environment and the best rate performance. More systematic explanation for typical Li–Cs electrolyte can be found in Fig. S3 (ESI†). As the differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) curves in Fig. 1b show, the Li–Cs electrolyte exhibits the lowest glass transition temperature (Tg) at −28.8 °C, followed by Li–K–Cs (−24.5 °C) and Li–K (−19.8 °C). A lower Tg means a larger free volume and weaker ion interaction in amorphous/semi-crystalline materials, so, it indicates that the Li–Cs electrolyte has the most relaxed chemical environment among the three. Meanwhile, the trend of melting points (Tm) is different, where the Li–K–Cs electrolyte has the lowest Tm at 45 °C, followed by Li–Cs (63.0 °C) and Li–K (69.7 °C) in Fig. S4 (ESI†). The lower Tm value of the ternary mixture compared to the binary mixture is ascribed to the entropy effect. The temperature-dependent ionic conductivities of three electrolytes were evaluated, as shown in Fig. 1c, Fig. S5 and Table S1 (ESI†). At 80 °C, all three electrolytes have high conductivities >10−3 S cm−1, thus, the subsequent electrochemical tests were conducted at 80 °C unless stated otherwise. It is worth noting that although the Li–Cs electrolyte has the medium total conductivity among the three, it shows the lowest activation energy (Ea) of 0.20 eV for ion transport, followed by Li–K–Cs (0.22 eV) and Li–K (0.27 eV), as shown in Table S2 (ESI†). We can see that the Ea is positively correlated with the Tg rather than Tm, and the Li–Cs electrolyte with a medium total conductivity surprisingly has the lowest Ea. Because only the portion of the current that is carried by Li+ matters in lithium-based batteries, so, we further measured the Li+ transference number by the Bruce–Vincent method in Fig. 1d and Fig. S6 (ESI†).42 The t+ values of three molten salts are 0.45 for Li–K, 0.53 for Li–Cs, and 0.32 for Li–K–Cs. Then, the true Li+ conductivity values are 0.54 mS cm−1 for Li–K, 0.95 mS cm−1 for Li–Cs (the highest one among the three), and 0.75 mS cm−1 for Li–K–Cs. Therefore, the yield obtained by reducing the melting point is less than expected, and the Li+ concentration in the electrolyte and the Tg of the system are also important factors that need to be considered. Overall, among the three molten salts, the Li–Cs electrolyte has the lowest Ea, the highest t+, and the highest Li+ conductivity, which will alleviate the concentration polarization and enhance the fast-cycling ability during battery cycling.The exchange current density (j) extracted from Tafel plots was used to assess the Li+ transport kinetics of three molten salts at the electrode interphases. As shown in Fig. 1e, Li–Cs electrolyte has the highest j value of 1.68 mA cm−2, followed by Li–K–Cs (1.23 mA cm−2) and Li–K (1.15 mA cm−2), which is also supported by the interfacial resistances of Li/Li cells at different temperatures in Fig. S7 and Table S3 (ESI†). The enhanced electrochemical kinetics of Li–Cs electrolyte endows the Li/Li symmetric cells with excellent rate performance (Fig. 1f). As the current density increased from 0.25 to 5.00 mA cm−2, the overpotential of cells using Li–Cs electrolyte is consistently lower than that of Li–K and Li–K–Cs (Fig. S8, ESI†). Besides, the long-term galvanostatic cycling performance of Li/Li cells under 1.00 mA cm−2 and 1 mA h cm−2 was also evaluated in Fig. 1g. No obvious polarization increase was observed within 500 h, and all three electrolytes show good interfacial stability with Li metal. But there are differences in the overpotential. The overpotential of Li–Cs is as low as 24 mV, lower than that of Li–K–Cs (32 mV) and Li–K (43 mV), indicating that the Li–Cs electrolyte has the fastest ion transport properties among the three, both in the bulk electrolyte and at the electrolyte/Li interface.
Ionic transport mechanisms
Molecular dynamics simulations were conducted to probe the underlying mechanisms of the superior Li+ conductivity of the Li–Cs molten salt electrolyte compared with those of the other two systems. Three models corresponding to Li–K, Li–Cs, and Li–K–Cs electrolytes were constructed, each containing a thousand corresponding salt molecules (Fig. 2a–c). The Li+ conductivities of these electrolyte models at high temperatures (443.15, 493.15, 543.15, 593.15, and 643.15 K) were first obtained by maximizing sampling (Fig. 2d), which has been widely demonstrated to afford highly-accurate diffusion properties.43,44 Then, the Li+ conductivities at 80 °C were extrapolated from the high-temperature results and determined to be 0.40, 0.71, and 0.51 mS cm−1 for Li–K, Li–Cs, and Li–K–Cs electrolytes, respectively (Fig. 2e). The theoretical results agree well with experimental values (Fig. 1c), validating the reliability of theoretical simulations. The Haven ratio (H) was further adopted to analyze the diffusion mechanism and its reciprocal (1/H) indicates the degree of multi-ion concerted migration (Fig. 1e).45,46 The 1/H is 0.67, 2.61, and 1.04 in Li–K, Li–Cs, and Li–K–Cs electrolytes, respectively (Table S4, ESI†). The trends of 1/H and Li+ conductivities agree with each other, indicating that a concerted ion transport mechanism dominates in the molten salt electrolytes. In particular, the ion–ion concerted effect is the most significant in the Li–Cs electrolyte (Li–Cs concertation), followed by that in the Li–K–Cs electrolyte (Li–K–Cs concertation), while the Li–K electrolyte has no significant concerted effect (Li–K concertation). The strong ion–ion correlation can promote Li+ diffusion, giving rise to the highest conductivity of the Li–Cs electrolyte. In contrast, the Li–K system lacking such a prominent correlation exhibits the lowest conductivity, with Li–K–Cs falling in between.The solvation structures were further analyzed to reveal the origin of different ion–ion concerted effects in the three molten salt electrolytes (Fig. S9, ESI†). The coordination number distribution of FSI− around Li+ is almost the same within 6 Å across the three systems, indicating very similar Li+–anion interactions and the varied Li+ conductivity should be ascribed to cation–cation interactions. As expected, the coordination number of other cations except for Li+ around FSI− shows a distinct sequence of Li–K (6.16 K+) > Li–K–Cs (4.70 K+ and Cs+) > Li–Cs (3.79 Cs+), which is opposite to the above conductivity trend (Fig. 2f–i and Fig. S10, ESI†). Since the charge distribution of Cs+ is more dispersed than that of K+ due to the larger ionic radius of Cs+, weaker interactions between Cs+ and anions than those between K+ and anions are supposed. Such weak interactions between Cs+ and anions facilitate the strong interactions and the concertation between Cs+ and Li+, ultimately leading to the corresponding high conductivity (Fig. 2j and k).
Fast cycling ability
To evaluate the rate capacity, NCM811/Li half cells using three different molten salt electrolytes were cycled from 0.1C to 10C in the range of 3.0–4.3 V (Fig. 3a). The Li–Cs electrolyte delivers capacities of 196.7, 186.6, 173.4, 163.4, 151.3, and 141.9 mA h g−1 at 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5C, respectively. Even at 10C, a high specific capacity of 101.5 mA h g−1 is still retained. When the rate was set back to 0.5C, the cell can recover to 193.2 mA h g−1 (98.2% retention) and maintain a stable cycling performance in the subsequent cycles. In contrast, the capacities of Li–K and Li–K–Cs electrolytes are much lower than that of Li–Cs at all testing rates, suggesting the Li–Cs electrolyte exhibits enhanced transport kinetics. The impedance tests also indicate that the NCM811/Li cells with the Li–Cs electrolyte have the lowest interfacial resistance at different temperatures in Fig. S11 and Table S5 (ESI†). The long-term cycling performance of three molten salt electrolytes was evaluated in Fig. 3b. Specifically, the NCM811/Li half cells were charged at 1C and discharged at 2C. The initial capacity value of Li–Cs is 190.8 mA h g−1, followed by 159.3 mA h g−1 for Li–K–Cs and 141.8 mA h g−1 for Li–K. During the whole 500 cycles, the discharged capacity of Li–Cs is consistently higher than those of the Li–K and Li–K–Cs electrolytes, indicating that the Li–Cs electrolyte has the best cycling performance among the three. To further verify the fast-cycling ability of the Li–Cs electrolyte, the NCM811/Li half cells were charged at 2C and discharged at 3C in Fig. 3c. A high initial capacity was obtained about 170 mA h g−1, and the final capacity was kept above 103 mA h g−1 after 1000 cycles, showing excellent fast-charging/discharging performance.Moreover, full cells with a high-loading NCM811 cathode and thin Li foil anode (40 μm) were tested to examine the practical applicability of Li–Cs molten salt electrolyte in high-temperature LMBs. In Fig. 3d, the cell with 2 mA h cm−2 areal capacity was charged at 0.93 mA cm−2 and discharged at 1.85 mA cm−2, which is the highest cycling rate among the reported molten salt electrolytes (Fig. 3e and Table S6, ESI†).8,30,37,40 83.3% of its initial capacity is retained after 100 cycles, demonstrating excellent fast-charging/discharging ability. When the cathode capacity was increased to 3 mA h cm−2 (N/P ratio of 2.67), the cell still showed stable discharge capacity and CE over a 300-cycle lifespan, as shown in Fig. 3f. A capacity retention of 75% was observed after 280 cycles. Thanks to the thermal and oxidative stability of the SFMSE, the NCM811/Li cell can even work at 100 °C with good high-temperature tolerance (Fig. S12, ESI†). To the best of our knowledge, the Li–Cs electrolyte shows superior electrochemical performance to those reported advanced electrolytes in terms of cathode loading, cycling lifespan, and operating temperature, as shown in Fig. 3g and Table S7 (ESI†), demonstrating great potential for high-temperature LMBs.4,9,10,20,22,47–49
Thermal stability of molten salt electrolytes
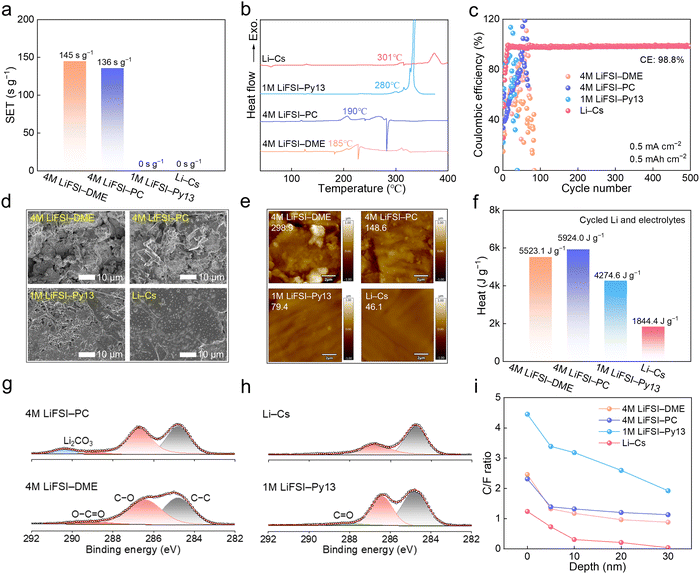
To comprehensively study the superiority of the Li–Cs molten salt as an advanced high-temperature electrolyte, the state-of-the-art high-temperature electrolytes, i.e., concentrated ether electrolyte 4 M LiFSI in 1,2-dimethoxyethane (4 M LiFSI–DME), concentrated ester electrolyte 4 M LiFSI in propylene carbonate (4 M LiFSI–PC), and ionic liquid electrolyte 1 M LiFSI in 1-butyl-3-methylpyrrolidinium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (1 M LiFSI–Py13) were selected for comparison. Firstly, the electrolyte flammability was evaluated using the self-extinguishing time (SET) after ignition. The 4 M LiFSI–DME and 4 M LiFSI–PC exhibit high SET values of 145 s g−1 and 136 s g−1, respectively, suggesting their high flammability (Fig. 4a, Video S1 and S2, ESI†). In contrast, the SETs of the ionic liquid electrolyte and molten salt electrolyte were measured to be 0 s g−1, showing their exceptional non-flammability (Video S3 and S4, ESI†). The thermal stabilities of these electrolytes were further quantitatively measured by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). As shown in Fig. 4b, the onset temperatures for heat release of 4 M LiFSI–DME and 4 M LiFSI–PC are 185 °C and 190 °C, respectively, which are much lower than those of 1 M LiFSI–Py13 electrolyte (280 °C) and Li–Cs electrolyte (301 °C). There is a significant difference in heat released between the latter two electrolytes with −1522 J g−1 for 1 M LiFSI–Py13 and −1069 J g−1 for Li–Cs, which suggests that the Li–Cs SFMSE has the best thermal stability (Fig. S13, ESI†).Interfacial stability of the electrolyte/Li metal anode
The electrochemical and thermal stability of the Li metal anode with the Li–Cs electrolyte was evaluated, and the 4 M LiFSI–DME, 4 M LiFSI–PC, and 1 M LiFSI–Py13 electrolytes were also comparatively studied. The Li plating/stripping reversibility was first explored in asymmetric Li/Cu cells with 0.50 mA cm−2 and 0.5 mA h cm−2 (Fig. 4c). During the long-term test, the cells with Li–Cs electrolyte operated stably over 500 cycles with a stable CE value of 98.8%. In contrast, the CE values of 4 M LiFSI–DME, 4 M LiFSI–PC, and 1 M LiFSI–Py13 experienced severe fluctuation within 50 cycles, implying their poor interfacial stability, which can be attributed to the solvent volatilization at high temperatures for concentrated electrolytes, and poor compatibility with Li metal for the ionic liquid electrolyte. The Li deposition morphology in different electrolytes was investigated using a scanning electron microscope (SEM), as shown in Fig. 4d. Severe pulverization and obvious lithium dendrites were observed in 4 M LiFSI–DME and 4 M LiFSI–PC. Due to the enhanced thermal stability of 1 M LiFSI–Py13, the pulverization has been effectively suppressed, but the dendritic deposition persists. In great contrast, a smooth and compact surface was maintained in the Li–Cs electrolyte, suggesting the stable and homogenous Li+/e− transport across the electrolyte/Li interphase during the repeated plating/stripping. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) tests were conducted to quantify the surface roughness of Li deposition in Fig. 4e. The specific roughness values decrease from 4 M LiFSI–DME (298.9 nm) to 4 M LiFSI–PC (148.6 nm), 1 M LiFSI–Py13 (79.4 nm), and Li–Cs (46.1 nm). Besides, the thickness of Li deposition was also measured to follow the order of 4 M LiFSI–DME (53.6 μm) > 4 M LiFSI–PC (23.8 μm) > 1 M LiFSI–Py13 (15.6 μm) > Li–Cs (9.4 μm) in Fig. S14 (ESI†), which reinforces the conclusion that the Li–Cs electrolyte can guarantee a dense Li deposition upon cycling. The thermal compatibility between the electrolytes and cycled Li metal was further evaluated by DSC in Fig. 4f and Fig. S15 (ESI†). The endothermic peak located at 180 °C is assigned to the melt of Li metal. The total released heat during the heating process upon 400 °C is −5523.1 J g−1 for 4 M LiFSI–DME, −5924.0 J g−1 for 4 M LiFSI–PC, −4274.6 J g−1 for 1 M LiFSI–Py13, and −1844.4 J g−1 for Li–Cs electrolyte, respectively. Compared with concentrated ether/ester and ionic liquid electrolytes, a significant decrease in released heat in Li–Cs electrolyte demonstrates that the reactivity between the molten salt electrolyte and cycled Li metal is effectively suppressed. The improvement not only benefits from the intrinsic thermal stability of Li–Cs SFMSE but also originates from the formation of a stable inorganic-rich SEI layer on Li metal. X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was applied to analyze the chemical composition of the SEI formed in different electrolytes. As the C 1s spectra shown in Fig. 4g and h, the atomic percentage of organic species (such as C–O, C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O, and O–C
O, and O–C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) reaches 13.9% for 4 M LiFSI–DME, 12.6% for 4 M LiFSI–PC, 17.6% for 1 M LiFSI–Py13, and 8.5% for Li–Cs electrolyte, respectively, suggesting that the Li–Cs molten salt electrolyte can significantly reduce the content of organics in the SEI. The continuous decrease of C/F atomic ratio with the sputtering depth indicates an increase of inorganics amount from the surface to the inner layer (Fig. 4i and Fig. S16, ESI†). Overall, the Li–Cs electrolyte has the lowest C/F ratio among the four electrolytes, indicating that the SEI formed in Li–Cs electrolyte is mainly composed of inorganics derived from FSI− anions. This inorganic-rich SEI has great robustness to guarantee a high Li plating/stripping reversibility and interfacial stability at high temperatures.
O) reaches 13.9% for 4 M LiFSI–DME, 12.6% for 4 M LiFSI–PC, 17.6% for 1 M LiFSI–Py13, and 8.5% for Li–Cs electrolyte, respectively, suggesting that the Li–Cs molten salt electrolyte can significantly reduce the content of organics in the SEI. The continuous decrease of C/F atomic ratio with the sputtering depth indicates an increase of inorganics amount from the surface to the inner layer (Fig. 4i and Fig. S16, ESI†). Overall, the Li–Cs electrolyte has the lowest C/F ratio among the four electrolytes, indicating that the SEI formed in Li–Cs electrolyte is mainly composed of inorganics derived from FSI− anions. This inorganic-rich SEI has great robustness to guarantee a high Li plating/stripping reversibility and interfacial stability at high temperatures.
Oxidative stability and Al corrosion behavior
We studied the compatibility of four kinds of electrolytes with high-voltage cathodes. Firstly, the linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) measurements of Al/Li cells were conducted to examine the oxidative stability of 4 M LiFSI–DME, 4 M LiFSI–PC, 1 M LiFSI–Py13, and Li–Cs electrolytes (Fig. S17, ESI†). Compared with concentrated ether/ester electrolytes that undergo severe oxidation before 6 V vs. Li+/Li, the response current of the ionic liquid electrolyte is lower (<100 μA), which is mainly ascribed to the elimination of unstable solvent molecules. The Li–Cs electrolyte shows the greatest resistance to high-voltage oxidation, with a response current consistently below 40 μA throughout the entire testing potential range even up to 9 V vs. Li+/Li. Secondly, the leakage currents of different electrolytes were measured. Al/Li cells were assembled and a polarization voltage of 4.5 V was applied for 10 h. As shown in Fig. 5a, the leakage current of 4 M LiFSI–PC (>100 μA) is much higher than that of 4 M LiFSI–DME (4 μA). For the 1 M LiFSI–Py13 electrolyte, the current value gradually decreases within 1 h and stabilizes at 2 μA for the subsequent time. As for the Li–Cs electrolyte, the current drops dramatically upon applying polarization and eventually stabilizes at an extremely low current (<0.3 μA). Thirdly, the surface morphology of the tested Al current collectors was further observed by SEM, as shown in Fig. S18 (ESI†). Fragments and cracks cover the Al foil surface in 4 M LiFSI–PC, and some pits and holes appear in 4 M LiFSI–DME and 1 M LiFSI–Py13, which means that the Al current collector still has varying degrees of anodic corrosion in highly-concentrated and ionic liquid electrolytes at a high temperature of 80 °C. Remarkably, the Al foil remains intact and shows good stability against corrosion in the Li–Cs molten salt electrolyte. To reveal the underlying mechanisms, Al foils recovered from the chronoamperometry test were characterized by XPS, as shown in in Fig. S19 (ESI†), and the Al dissolution concentration in residual electrolytes was verified using the inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) data from Table S8 (ESI†). The XPS and ICP-OES results jointly confirm that the Li–Cs electrolyte has poor solubility for Alx(FSI)y products, thereby inhibiting further anodic corrosion to Al current collectors. More detailed discussions can be found in the ESI.† Fourthly, NCM811/Li cells were also assembled to evaluate the oxidative stability of these electrolytes in the presence of delithiated NCM811 cathodes with high catalytic activity. The applied voltage starts from 4.3 V and increases at intervals of 0.2 V with each step being held for 3 h (Fig. 5b). The 4 M LiFSI–DME firstly shows a significant leakage current at 4.5 V, followed by 4 M LiFSI–PC at 4.7 V and 1 M LiFSI–Py13 at 4.9 V. As for the Li–Cs electrolyte, the current values are consistently below 50 μA, even at extremely high voltages of 6.1 V. The low leakage current demonstrates that the Li–Cs SFMSE has superb oxidative stability and good compatibility with high-voltage cathodes. Overall, the greatly expanded stability voltage upper limits, the decreased leakage current (both in the Al/Li and NCM811/Li cells), and the intactness of the Al current collector all suggest that (1) the Li–Cs electrolyte is highly resistant to the aggressively oxidative environment on the cathode; (2) the corrosion of the Li–Cs electrolyte to Al current collector has been effectively suppressed.Therefore, NCM811/Li half cells were galvanostatic cycled with a high cut-off voltage of 4.5 V to examine the cycling performance of different electrolytes, as shown in Fig. 5c. A severe overcharging behavior occurred during the first cycle in 4 M LiFSI–DME-based cells, which is attributed to the aggressive decomposition of the DME solvent (Fig. S20, ESI†). Although 4 M LiFSI–PC and 1 M LiFSI–Py13 electrolytes can guarantee cells to cycle at 4.5 V, their capacity degradation is particularly severe. Especially for 1 M LiFSI–Py13, it only maintains a capacity retention of 64% after the first 50 cycles. In comparison, the NCM811/Li cell using Li–Cs electrolyte has a more stable cycling performance with a high capacity retention above 70% after 300 cycles. Even with an increase in cut-off voltage to 4.7 V, the NCM811/Li cells using Li–Cs electrolyte still show good cycling stability, confirming the exceptional oxidative stability of the Li–Cs molten salt (Fig. S21, ESI†). The structural morphology of NCM811 cathodes cycled after 50 cycles were observed by SEM in Fig. S22 (ESI†). In 4 M LiFSI–DME/PC and 1 M LiFSI–Py13 electrolytes, many cracks and severe pulverization occurred on the NCM811 particles. The transition metal ions escaping from the cathode are dissolved into the electrolytes and subsequently deposited on the Li anode, causing a cross-talk effect (Fig. S23, ESI†). But in Li–Cs electrolyte, the structural integrity of NCM811 particles is maintained without micro-cracks generation. As shown in Table S9 (ESI†), the ICP-OES results show the Ni2+ dissolution content in Li–Cs electrolyte (0.38 ppm) is much lower than that in 1 M LiFSI–Py13 (0.64 ppm), 4 M LiFSI–PC (1.88 ppm), and 4 M LiFSI–DME (2.60 ppm), indicating that the transition metal dissolution is effectively suppressed during the periodic delithiation/lithiation at high temperatures.
CEI characterization
The thickness of CEI layers on NCM811 cathodes was determined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), as shown in Fig. 5d. The CEI formed in 4 M LiFSI–DME is as thick as 91 nm, which is caused by the continuous decomposition of DME at high voltages. Thanks to the improved oxidation resistance of the carbonate and ionic liquid, the thickness of CEIs formed in 4 M LiFSI–PC and 1 M LiFSI–Py13 has been reduced to 21 nm and 23 nm, respectively. As for the NCM811 cathode cycled in Li–Cs electrolyte, a thin and uniform CEI layer was constructed with a thickness as low as 7 nm. The absence of organic solvent decomposition, and the dominance of inorganics derived from FSI− anions give rise to this thin and robust CEI. The interfacial stability of the electrolyte/cathode is closely related to the chemical composition of CEI, so, time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (TOF-SIMS) was conducted to elucidate the species composition and spatial distribution of CEI layers formed in different electrolytes. As shown in Fig. 5e and Fig. S24 (ESI†), the 4 M LiFSI–DME shows the highest signal intensity of C2HO− and C2H3O− fragments, which increases constantly with sputtering time. The C2HO− and C2H3O− fragments represent organics, typically produced by the solvent decomposition at the cathode. The result indicates that the CEI formed in this concentrated ether electrolyte is rich in organics and has poor electrochemical stability, which is insufficient to suppress detrimental side reactions. In turn, the C2HO− and C2H3O− fragments are mainly enriched on the surface within the first 20 s sputtering in 4 M LiFSI–PC and 1 M LiFSI–Py13 electrolytes, suggesting that the oxidation of PC and Py13 is limited. As for Li–Cs electrolyte, the intensity of organic fragments remains at a low level throughout the sputtering, indicating that the resultant CEI is poor in organics. Furthermore, an XPS test was also applied to characterize the chemical species of the CEIs formed in different electrolytes. Compared with the cathodes cycled in 4 M LiFSI–DME/PC and 1 M LiFSI–Py13 electrolytes, the one cycled in Li–Cs electrolyte has a much lower proportion of C–O (286.2 eV) and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O (288.9 eV) organics in the C 1s spectra, but a much higher proportion of LiF (684.3 eV) inorganics in the F 1s spectra (Fig. 5f and Fig. S25, ESI†). LiF is one of the desirable CEI components, which has high mechanical strength and thermal/electrochemical stability. Therefore, the CEI derived from Li–Cs electrolyte with a high LiF content can effectively inhibit side reactions and reinforce the structural integrity of NCM811 particles. The detailed atomic percentages of C–O & C
O (288.9 eV) organics in the C 1s spectra, but a much higher proportion of LiF (684.3 eV) inorganics in the F 1s spectra (Fig. 5f and Fig. S25, ESI†). LiF is one of the desirable CEI components, which has high mechanical strength and thermal/electrochemical stability. Therefore, the CEI derived from Li–Cs electrolyte with a high LiF content can effectively inhibit side reactions and reinforce the structural integrity of NCM811 particles. The detailed atomic percentages of C–O & C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O and LiF in the 0 and 10 nm layers are summarized in Fig. 5g and h. From the outer surface to the interior, the CEI formed in Li–Cs electrolyte has the lowest content of organics with 16.01% at 0 nm and 13.41% at 10 nm. While it has the highest content of LiF with 7.76% at 0 nm and 15.1% at 10 nm, which mainly originates from the decomposition of FSI− anions.
O and LiF in the 0 and 10 nm layers are summarized in Fig. 5g and h. From the outer surface to the interior, the CEI formed in Li–Cs electrolyte has the lowest content of organics with 16.01% at 0 nm and 13.41% at 10 nm. While it has the highest content of LiF with 7.76% at 0 nm and 15.1% at 10 nm, which mainly originates from the decomposition of FSI− anions.
Combining the above morphological and chemical analysis, the interfacial structure of Al current collectors and NCM811 cathodes in different electrolytes are schematically illustrated in Fig. 5i and j. In the concentrated electrolyte and ionic liquid electrolyte, the corrosion to an Al current collector cannot be completely inhibited at high temperatures, exposing risks to the loss of electronic contact between an active cathode material and Al current collector. In addition, the ether/ester solvents and heterocyclic pyrrole cations still decompose on the surface of NCM811 particles to produce a thick and organic-rich CEI, which has a poor ability to prevent the occurrence of cracks. In molten salt electrolyte, there is no Al corrosion behavior, and the CEI dominated by the decomposition products of FSI− anions is thin and inorganic-rich, effectively protecting the structural integrity of NCM811 cathodes.
Through the comprehensive comparison of the concentrated electrolytes (4 M LiFSI–DME and 4 M LiFSI–PC), ionic liquid electrolyte (1 M LiFSI–Py13), and molten salt electrolyte (Li–Cs) in this work, their corresponding drawbacks and advantages are clarified in Fig. S26 (ESI†). Eliminating the presence of organic solvents/heterocyclic cations to create a type of molten salt electrolyte can significantly improve the interfacial stability (both SEI and CEI) and electrochemical performance for high-temperature LMBs.
Conclusion
In this study, we report a SFMSE (47 mol% LiFSI and 53 mol% CsFSI) with fast-cycling ability for high-temperature lithium metal batteries. Owing to the high Li+ content and strong cation–cation concerted effect, the Li–Cs electrolyte shows excellent Li+ transport kinetics, including a low activation energy, high Li+ conductivity, and high transference number. The inorganic-rich electrolyte/electrode interphases (both SEI and CEI) solely derived from bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide anions are electrochemically and thermally stable, making the molten salt electrolyte far superior to the routine concentrated ether/ester electrolyte and ionic liquid electrolyte for high-temperature applications. Therefore, the Li–Cs electrolyte promises a high CE of 98.8% for Li plating/stripping over 500 cycles, and extreme high oxidative stability up to 9 V vs. Li+/Li. The fast Li+ transport kinetics and stable interphases enable the NCM811/Li half cells to deliver a discharge capacity above 100 mA h g−1 even at a high rate of 10C, and the NCM811 (3 mA h cm−2)/Li (40 μm) full cells to maintain 75% capacity retention for 280 cycles at 80 °C. This work provides new insights into advanced electrolyte design for next-generation high-temperature batteries.Author contributions
S. Y. conceived the idea and carried out the synthesis and characterization with the guidance of H. L., H. Z., X. C., K. L. and Q. Z., N. Y. and X. C. performed the molecular dynamics simulations. Y. L. and Z. Z. participated in the analysis of experiment results. Z. L., W. H., P. Z., Y. W. and H. Z. provided some helpful scientific discussions and suggestions. S. Y., N. Y., X. C. and K. L. co-wrote the manuscript.Data availability
All data in this study are included in this published article and its ESI.†Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge support from the National Key Research and Development Program (2023YFB2503700, 2023YFC3008804), the National Science Foundation of China (22071133), the Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission (No. Z231100006123003), and the Science Foundation of China Academy of Safety Science and Technology (2023JBKY17).References
- Q.-K. Zhang, X.-Q. Zhang, J. Wan, N. Yao, T.-L. Song, J. Xie, L.-P. Hou, M.-Y. Zhou, X. Chen, B.-Q. Li, R. Wen, H.-J. Peng, Q. Zhang and J.-Q. Huang, Nat. Energy, 2023, 8, 725–735 CrossRef CAS.
- X.-B. Cheng, R. Zhang, C.-Z. Zhao and Q. Zhang, Chem. Rev., 2017, 117, 10403–10473 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Lee, S.-H. Kwon, J. Kim, E. Park, I. Kim, H. C. Ahn, A. Coskun and J. W. Choi, ACS Energy Lett., 2024, 9, 2201–2211 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Zhang, M. Liu, J. Ma, K. Yang, Z. Chen, K. Li, C. Zhang, Y. Wei, M. Zhou, P. Wang, Y. He, W. Lv, Q.-H. Yang, F. Kang and Y.-B. He, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 6966 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Xiao, H. Gao, Y. Chen, T. Teng, X. Yun, D. Lu, G. Zhou, Y. Zhao, B. Li, X. Zhou and C. Zheng, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2024, e202410982 Search PubMed.
- J. Wang, W. Huang, A. Pei, Y. Li, F. Shi, X. Yu and Y. Cui, Nat. Energy, 2019, 4, 664–670 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zheng, M. H. Engelhard, D. Mei, S. Jiao, B. J. Polzin, J.-G. Zhang and W. Xu, Nat. Energy, 2017, 2, 17012 CrossRef CAS.
- A. L. Phan, C. Jayawardana, P. M. L. Le, J. Zhang, B. Nan, W. Zhang, B. L. Lucht, S. Hou and C. Wang, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2023, 33, 2301177 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Piao, X. Wu, H.-R. Ren, G. Lu, R. Gao, G. Zhou and H.-M. Cheng, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145, 24260–24271 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Wang, C. Chen, D. Wang, Y. Zhu and B. Zhang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202303950 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Kim, S. Lee, H. Cho, J. Kim, J. Lee, S. Park, S. H. Joo, S. H. Kim, Y. G. Cho, H. K. Song, S. K. Kwak and J. Cho, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 4705–4712 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Tan, S. Chen, Y. Chen, J. Fan, D. Ruan, Q. Nian, L. Chen, S. Jiao and X. Ren, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2022, 61, e202203693 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Yu, H. Wang, X. Kong, W. Huang, Y. Tsao, D. G. Mackanic, K. Wang, X. Wang, W. Huang, S. Choudhury, Y. Zheng, C. V. Amanchukwu, S. T. Hung, Y. Ma, E. G. Lomeli, J. Qin, Y. Cui and Z. Bao, Nat. Energy, 2020, 5, 526–533 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Amanchukwu, Z. Yu, X. Kong, J. Qin, Y. Cui and Z. Bao, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 7393–7403 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Yan, Y. Lu, F. Liu, Y. Xia, Q. Li and K. Liu, CCS Chem., 2023, 5, 1612–1622 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Nie, W. Luo, Y. Li, C. Yang, H. Pei, R. Guo, W. Wang, F. B. Ajdari and J. Song, Small, 2023, 19, 2302690 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Feng, L. Zhou, H. Ma, Z. Wu, Q. Zhao, H. Li, K. Zhang and J. Chen, Energy Environ. Sci., 2022, 15, 1711–1759 RSC.
- G. Guzmán-González, M. Alvarez-Tirado, J. L. Olmedo-Martínez, M. L. Picchio, N. Casado, M. Forsyth and D. Mecerreyes, Adv. Energy Mater., 2023, 13, 2202974 CrossRef.
- M. Fang, X. Yue, Y. Dong, Y. Chen and Z. Liang, Joule, 2024, 8, 91–103 CrossRef CAS.
- W.-C. Zheng, C.-G. Shi, P. Dai, Z. Huang, J.-X. Lin, H. Chen, M.-L. Sun, C.-H. Shen, C.-X. Luo, Q. Wang, X. Feng, Y.-M. Wei, L. Huang and S.-G. Sun, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022, 10, 21912–21922 RSC.
- Y. Leng, S. Ge, R. S. Longchamps, X.-G. Yang, T. Liu and C.-Y. Wang, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2020, 167, 110544 CrossRef.
- Y. Cao, N. Li, K. Yuan, N. Li, W. Zhang, S. Liang, Z. Hou, D. Lei, T. Jin, J.-G. Wang, K. Xie and C. Shen, Energy Storage Mater., 2023, 60, 102851 CrossRef.
- S. Zhang, F. Sun, X. Du, X. Zhang, L. Huang, J. Ma, S. Dong, A. Hilger, I. Manke, L. Li, B. Xie, J. Li, Z. Hu, A. C. Komarek, H.-J. Lin, C.-Y. Kuo, C.-T. Chen, P. Han, G. Xu, Z. Cui and G. Cui, Energy Environ. Sci., 2023, 16, 2591–2602 RSC.
- F. Wu, S. Fang, M. Kuenzel, A. Mullaliu, J.-K. Kim, X. Gao, T. Diemant, G.-T. Kim and S. Passerini, Joule, 2021, 5, 2177–2194 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Liu, A. Mariani, T. Diemant, M. E. D. Pietro, X. Dong, M. Kuenzel, A. Mele and S. Passerini, Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12, 2200862 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Yamada, J. Wang, S. Ko, E. Watanabe and A. Yamada, Nat. Energy, 2019, 4, 269–280 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Chen, Z. Jin, Y. Liu, X. Zhang, H. Wu, M. Li, W. Feng, Q. Zhang and C. Wang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2022, 61, e202207645 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Qian, W. A. Henderson, W. Xu, P. Bhattacharya, M. Engelhard, O. Borodin and J. G. Zhang, Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 6362 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Fan, L. Chen, X. Ji, T. Deng, S. Hou, J. Chen, J. Zheng, F. Wang, J. Jiang, K. Xu and C. Wang, Chem, 2018, 4, 174–185 CAS.
- M. C. Vu, P. Mirmira, R. J. Gomes, P. Ma, E. S. Doyle, H. S. Srinivasan and C. V. Amanchukwu, Matter, 2023, 6, 4357–4375 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Pang, J. Meng, S. Gupta, X. Hong, C. Y. Kwok, J. Zhao, Y. Jin, L. Xu, O. Karahan, Z. Wang, S. Toll, L. Mai, L. F. Nazar, M. Balasubramanian, B. Narayanan and D. R. Sadoway, Nature, 2022, 608, 704–711 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Kubota, K. Tamaki, T. Nohira, T. Goto and R. Hagiwara, Electrochim. Acta, 2010, 55, 1113–1119 CrossRef CAS.
- T. N. Keigo Kubota and R. Hagiwara, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2010, 55, 3142–3146 CrossRef.
- K. Kubota, T. Nohira and R. Hagiwara, Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 66, 320–324 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Watarai, K. Kubota, M. Yamagata, T. Goto, T. Nohira, R. Hagiwara, K. Ui and N. Kumagai, J. Power Sources, 2008, 183, 724–729 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Wang, J. Yang, P. He and H. Zhou, Energy Environ. Sci., 2021, 14, 4107–4114 RSC.
- K. Kubota and H. Matsumoto, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2014, 161, 902–907 CrossRef.
- K. Kubota and H. Matsumoto, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117, 18829–18836 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Kubota, Z. Siroma, H. Sano, S. Kuwabata and H. Matsumoto, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2018, 122, 4144–4149 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Xu, C. Liu, W. Feng, J. Nie, H. Li, X. Huang and Z. Zhou, Electrochim. Acta, 2014, 135, 217–223 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Yu, W. Zhai, C. Zhang, C. Wu, R. Wei, S. Chen, Y. He, Q. Hu, Y. Yu and W. Liu, ACS Energy Lett., 2023, 8, 1468–1476 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Evans, C. A. Vincent and P. G. Bruce, Polymer, 1987, 28, 2324–2328 CrossRef CAS.
- K. D. Fong, J. Self, K. M. Diederichsen, B. M. Wood, B. D. McCloskey and K. A. Persson, ACS Cent. Sci., 2019, 5, 1250–1260 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. He, Y. Zhu, A. Epstein and Y. Mo, npj Comput. Mater., 2018, 4, 18 CrossRef.
- N. Yao, X. Chen, Z.-H. Fu and Q. Zhang, Chem. Rev., 2022, 122, 10970–11021 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. He, Y. Zhu and Y. Mo, Nat. Commun., 2017, 8, 15893 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhu, S. He, J. Ding, G. Zhao and F. Lian, Nano Res., 2022, 16, 3855–3863 CrossRef.
- P. Xiao, Y. Zhao, Z. Piao, B. Li, G. Zhou and H.-M. Cheng, Energy Environ. Sci., 2022, 15, 2435–2444 RSC.
- D. Feng, S. Chen, R. Wang, T. Chen, S. Gu, J. Su, T. Dong and Y. Liu, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2020, 167, 110544 CrossRef CAS.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Fig. S1–S26, Tables S1–S9 and references. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4ee04657a |
| ‡ These authors contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |