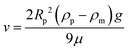Effective modulus of particle-packing containing hard and soft particles†
Om Prakash
Bamboriya
and
Mahesh S.
Tirumkudulu
 *
*
Department of Chemical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Powai, Maharashtra 400076, India. E-mail: mahesh@che.iitb.ac.in
First published on 4th February 2025
Abstract
Drying films of colloidal dispersion containing hard particles crack while fast drying drops of similar dispersion buckle, both caused by the capillary pressure exerted by the liquid menisci between particles. For drying films on substrates, there exists a maximum crack-free thickness while for fast drying drops, there is a maximum buckle-free shell size, with both quantities depending on particle size, elastic modulus of the particles and nature of particle packing. Here, we measure the critical cracking thickness for a drying colloidal film made of a mixture of hard and soft elastic particles to extract the effective modulus of the film for various ratios of hard and soft particles. Scanning electron images of the cross section of the film reveal the spatial distribution of the hard and soft particles. The measured effective modulus exhibits a trend that is identical to that obtained using the nanoindentation technique indicating that measurement of the critical cracking thickness gives a quantitative measure of the effective modulus of the packing. The values of effective modulus from the two techniques fall between the two limits obtained from the simple rule of mixtures for composite materials. The deviation from either limit is attributed to particle segregation caused by sedimentation of the heavier particles.
1 Introduction
When a thin, liquid film containing colloidal particles is dried, the particle distribution is determined by the Peclet number that measures the competition between the particle diffusion timescale and the convection timescale, the latter induced by drying, Pe = Ėh/D.1–5 Here, h is the film thickness, Ė is the evaporation rate, and D is the diffusion coefficient. As the film thickness reduces, the particles close to the interface diffuse away from the concentrated region into the bulk of the film. At high Peclet numbers, the particles accumulate at the surface resulting in the formation of a particle-packed layer (or skin). In the lateral direction, the edges of the film are the first to reach the particle-packed concentration due to both the higher evaporation rate at the edge and the lower thickness.6,7 The curvature of the menisci at the top layer of the particle-packed edge reduces the liquid pressure inside the saturated packing, causing the liquid to be convected from the central regions of the film to the edges of the film.8,9 Alternatively, the pinned contact lines at the edge would also convect the liquid to the edges so as to satisfy the contact line boundary condition resulting in the well-known “coffee-ring” effect.10–13The presence of liquid menisci formed between the particles induces negative pressure (relative to atmospheric pressure) in the liquid phase. The strong bonding between the film and the substrate resists deformation in the transverse direction leading to transverse tensile stress generation. If the stored elastic energy exceeds the surface energy required for the nucleation of a crack, a flaw may nucleate into a crack.14,15 Thus, understanding the critical condition for cracking is important for engineering the desired mechanical properties of colloidal films.4,16–18 The mechanical properties are set by the nature of particle packing and the properties of the particles. The packing of particles in the film in turn depends on the inter-particle interactions, evaporation rate of the solvent, particle sedimentation, and particle diffusion. If the particles are soft with low glass transition temperature, the particle deformation may lead to coalescence resulting in a continuous phase such as those observed for architectural coatings.1,4,19,20 In the case of hard particles, the solvent may evaporate leaving behind a porous packing of undeformed particles.
While the aforementioned studies have investigated dispersions of monodisperse particles of identical mechanical properties, few have investigated mixtures of particles of varying moduli or sizes.17,21–24 Such mixtures are important industrially since they enhance the film formation capabilities of particles without sacrificing film's mechanical properties in the dried state.25 In mixed colloidal films, the mechanical properties are set by the inter-particle contact forces and the nature of particle-packing.22 Such systems find applications in waterborne paints where stable synthetic latex is used primarily as a binder while the hard pigments give strength to the film.19,21,26
Martinez and Lewis23 investigated the stress profile in binary mixtures and found that the hard phase was responsible for the initial stress rise, whereas the latex phase played a significant role in setting the residual stress of a mixed film. A higher fraction of hard latex in the blend increases the stiffness of the films.21,27,28 In a related study, Singh et al.17 experimented with a binary suspension and determined the maximum crack-free thickness of the film. They observed that the crack-free thickness increased with increasing fraction of hard particles. The effective modulus of the film was determined from the theoretical expression relating the critical cracking thickness (CCT) to the modulus of the film.16,18 Separately, a theory proposed to account for the varying deformation of hard and soft particles predicted an effective modulus of the particle packing that deviated from measurements. The difference was attributed to the large scale, viscous (permanent) deformation of the soft particles since the glass transition temperature of the particles was less than the ambient value. The latter contradicted the assumption of the theory, which requires purely elastic deformation of both hard and soft particles.
An alternative and direct method for measuring the mechanical properties of thin films that is often used for metals, alloys, films, and coatings, is the nanoindentation technique.29–32 Here, an indenter deforms the film while the deformation versus force data is captured by a computer. Since the displacements are measured in the sub-micron range, it allows the measurement of the deformation of films in the elastic limit. Specifically, the method involves a cycle of loading and unloading, and the modulus is determined by fitting models to the initial part of the loading or unloading curve.22,33
The nanoindenter technique has been used by Yin et al.33 to measure the mechanical properties of a monolayer film of hollow silica particles having a diameter ranging from 200 nm to 600 nm. The load-depth data was fit to the Hertzian contact model for the loading part of the cycle. The same group34 extended the study to a packing of hollow colloidal particles and found that the effective modulus of the packing reduced as the thickness was increased from a monolayer to a trilayer of ∼500-nm-diameter hollow silica particles. The behavior is explained by modelling the packing as connected springs where the effective modulus is that of springs connected in series. Roth et al.22 investigated dense amorphous aggregates of monodisperse poly-methyl methacrylate (PMMA) particles of diameter 1.6 μm via nanoindentation in combination with confocal microscopy. They show that when the applied force is low, the particle deformation is largely elastic but for large forces, particles slide past each other and the process is irreversible. They used the unloading curve of the cycle to extract the modulus of the packing.
In this study, we determine the effective elastic modulus of a packing of hard and soft colloidal particles of equal size. We employ two different techniques for the measurement. First, we measure the critical cracking thickness of films as a function of the relative fraction of hard and soft particles. Scanning electron images of the cross section of films were used to determine the distribution of hard and soft particles in the film. The theoretical expression derived by Singh and Tirumkudulu,16 and corrected for the Hertzian deformation of particle contacts,18 is used to extract the effective modulus. Next, we measure the effective modulus using the nanoindentation technique by following the experimental procedure of Yin et al.34 The effective modulus for the particle blend is determined from the loading part of the cycle. We show that the effective moduli obtained from the two methodologies are in good agreement.
The measurements are compared with the theoretical prediction obtained from the simple rule of mixtures, which shows that the measurements lie between the lower and the upper bound of the predictions.34,35 Here, the lower bound modulus refers to the modulus obtained by assuming the “spring-in-series” model while the upper bound is the “spring-in-parallel” model. Finally, we comment on the recent study on the buckling of fast drying drops of particle mixtures,36 wherein a shell forms at the drop surface and buckles due to the compressive stresses generated by liquid menisci. Here, the effective elastic modulus was obtained from the expression for the critical shell size below which the drop does not buckle. The observed trend is in reasonable agreement with the lower bound modulus obtained from the simple rule of mixtures, thereby suggesting that the latter is a power tool to characterise the effective modulus of packings with hard and soft particles and thereby tailor the mechanical properties of mixed particle films.
2 Materials and methods
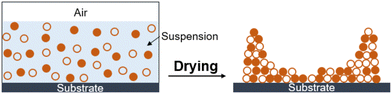
Experiments were performed with 0.5 μm size hard (silica) and soft (polystyrene, PS) particle suspensions, both purchased from Sigma Aldrich. The initial volume fraction of particles was varied from 0.02 to 0.08, which allowed control of the film thickness and to measure the critical thickness for cracking of the film. The dispersion was subjected to ultrasonication (Branson, 5510) to ensure a uniform particle distribution. The suspension was concentrated using a centrifuge (Rotina 35R, 6000 rpm for 20 minutes), followed by homogenization using ultrasonication. The particle composition of the mixture is represented by α, which is the volume fraction of hard particles in the total particle mixture and ranges from 0 (pure PS) to 1 (pure silica).A 5 μL droplet of mixed particle suspension was deposited by a micropipette on a clean glass substrate and left to dry in a vacuum oven chamber at 25 °C and 500 mmHg vacuum. The dried film had a high thickness at the edges relative to the centre region due to the “coffee-ring” effect (Fig. 1).4,10,12,13,37 The resulting dried film had multiple cracks at the edges because of the high thickness. Cracks in the dried film were observed under an inverted optical microscope (Olympus, IX71). The film thickness was determined using a surface profilometer (Dektak-150), which allowed the determination of the maximum crack-free thickness. Each experiment was repeated 3 to 4 times, and we considered the lowest value as the critical cracking thickness of the film.
The spatial distribution of the hard and soft particles across the thickness was determined by placing the dried film at 200 °C for 60 minutes in an oven. This caused the PS particles to deform as their glass transition temperature is around 100 °C. The silica particles, on the other hand, retain their spherical shape – the melting temperature of silica is around 1700 °C. We captured scanning electron images (SEM, Jeol 7600F) of the cross-section and the top surface of the film both before and after the heat treatment.
The high temperature melted the PS particles while the silica particles were unaffected. The cross section of the film was viewed using a scanning electron microscope, which allowed us to determine qualitatively the spatial distribution of the hard and soft particles.
The effective shear modulus of the mixed particle film was extracted from the expression for the critical cracking thickness (hmax, CCT),16,18
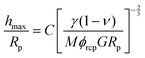 | (1) |
The above expression may be obtained using simple scaling analysis following a similar analysis presented previously.16 The constitutive relation for the saturated packing is obtained as, σ ∼ MϕrcpG/(1 − ν)ε3/2, where σ and ε are the stress and strain of the film, respectively. When a thin colloidal film is under tensile stress, the cracking of the film is governed by the Griffith's criteria,38 namely, the stored elastic energy is expended in creating the new crack surface. For a film of thickness of h, the elastic energy for a unit advance of the crack is given by, h2σε. This energy is converted into surface energy, γh, where γ is the interfacial tension between liquid and air since the packing is assumed to be saturated with liquid and the crack surface coated with a thin liquid film. Equating the two, gives the critical stress for cracking, σc ∼ (γ/h)3/5(MϕrcpG/(1 − ν))2/5. If the maximum critical stress for cracking is greater than the maximum possible stress, which is set by the curvature of the menisci (∼1/Rp), the critical film thickness for cracking is given by, hmax/Rp ∼ (γ(1 − ν)/GMϕrcpRp)−2/3.
As part of the study, we also measured the effective modulus of the mixed-particle films using the nanoindentation technique. The measurements were made on a nanoindenter (Hysitron Ti Premier Nanoindenter, Bruker Corporation, USA) with a spherical conical indenter made of diamond (Part number Ti-0227). The nominal and true radius of curvature of the tip were 10 μm and 8.15 μm, respectively. Thus the indenter size is approximately 40 times larger than the particle size, so that the indenter is in contact with many particles during the deformation of the packing.
The effective modulus of the different fractions of hard and soft particle films is calculated based on the load–penetration curve. The load is increased slowly over 20 s from 0 to 100 μN, held at the maximum value for 20 s followed by the unloading process over the same time (20 s). For each film, measurements were made at 12 different locations, each separated by at least 100 μm. The loading curve was fit to the Hertzian contact model to determine the modulus of the film,34,37,39 where the indentation force, f, is related to the penetration depth, s,
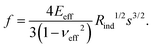 | (2) |
As in the case of (1), the above expression (2) may also be derived from a simple scaling analysis. Following Hertzian contact mechanics, consider the contact between an elastic half-space and a rigid spherical indenter of radius Rind. The penetration depth, s, for small deformations, can be related to the radius of the indenter, Rind, and the contact radius (r) of the indenter with the elastic half-space via simple geometry, r ∼ (sRind)1/2. The contact radius depends on the applied load, indenter radius, and elastic properties of the materials. The total force exerted by the indenter is given by, f ∼ P0r2, where the scaling for the maximum pressure is, P0 ∼ E*(s/Rind)1/2 and that for Young's modulus is, E* = E/(1 − ν2). Substituting P0 and r values in the total force expression gives the required scaling.37,39,40
3 Results and discussion
3.1. Particle distribution in the dried film
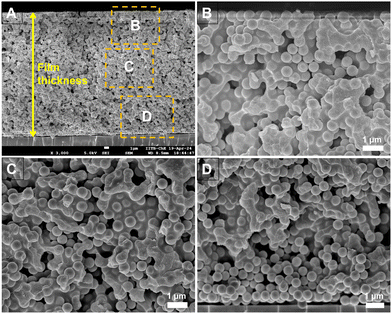
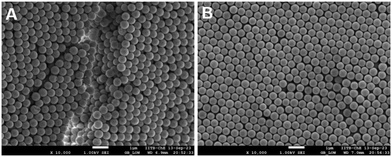
In our experiments, we used different fractions of silica and PS particles to form dried films. In order to determine the spatial distribution of hard and soft particles across the thickness, we image the cross-section of the film using a scanning electron microscope. Fig. 2(A) presents the image of the cross-section of the film for α = 0.5. The regions marked with boxes are magnified in images (B), (C) and (D) that correspond to the top, center, and bottom parts of the cross-section. Clearly, the PS particles have completely deformed and they encapsulate the silica particles at many locations. The distribution of the soft particles appears to be nearly the same for sections B and C. In the bottom section of the film (D), the bottom few layers appear to be devoid of soft particles but the rest of the layers are comparable to B and C. This suggests that there is some segregation at the bottom of the packing with more silica particles compared to PS particles. The SEM of the top layer of the film, imaged from the top, is presented in Fig. S1 (ESI†) and it confirms the uniform distribution of soft particles across the top surface.We investigated if the difference in the surface charge of the soft and hard particles was responsible for the depletion of the soft particles from the bottom layer. The zeta potentials of the silica and PS particles (under dilution) were found to be −44.2 mV and −49.7 mV, respectively, which are not significantly different to influence the particle distribution. On the other hand, the density of silica particles is 2.65 g cm−3 compared to 1.05 g cm−3 for the PS particles. Consequently, the higher settling rate of silica particles may be responsible for their higher concentration at the bottom of the packing. The Stoke's settling velocity in a dilute suspension is given by,
For water as the suspending liquid (ρm = 1.0 g cm−3), the terminal velocity of a 500 nm diameter silica particle is 0.2 μm s−1. Note that the calculation applies for initial times when the particle volume fraction is low. The settling rate is expected to reduce as the concentration builds up. Irrespective of this fact, it is instructive to determine the settling distance for the dilute case. Since a typical film dries over 5 minutes, the silica particles are expected to settle over 60 μm during this time. The settling speed for PS particles, on the other hand, is two orders of magnitude lower since their density is close to water. These differences in the settling speed are significant to explain the difference in the relative number density of silica and PS particles at the bottom of the film.
3.2. Effective modulus from critical cracking thickness
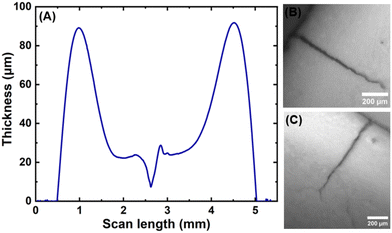
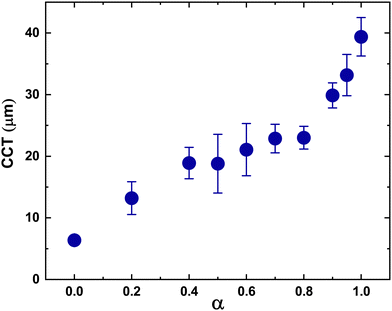
Films containing particle mixtures were dried and the same were inspected for cracks under a microscope, while the thickness profile was obtained using a profilometer. Fig. 3(A) shows the thickness profile of the film. At the edges, the film is thick, around 90 μm, while the thickness reduces towards the center, reaching a value of about 10 μm. The stress generated in regions of higher thickness causes the film to crack, as shown in Fig. 3(B) and (C). The crack propagates from the thick region at the edge towards the thinner region in the interior and stops where the critical thickness is reached. Measuring the thickness at the location of the crack-tip allows the determination of critical cracking thickness.As expected from (1), the critical crack-free thickness decreased with increasing fraction of soft particles in suspension. The CCT decreases rapidly for α values from 1.0 to 0.8, after which the decrease is somewhat slower, see Fig. 4. Fig. 5 presents the variation of the effective shear modulus (Geff), obtained from (1), as a function of α. There is a steep decrease in the effective modulus even when a small fraction of the soft particles is added to the hard particle film. We compare the extracted value of effective shear modulus with the lower-bound obtained from the rule of mixtures, which assumes the “springs-in-series” configuration,
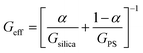 | (3) |
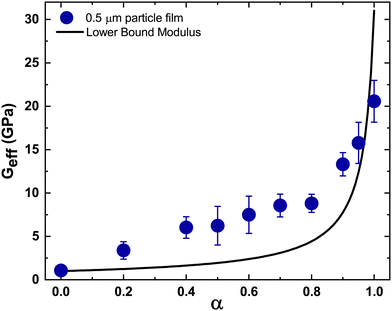 | ||
| Fig. 5 Experimental results from CCT measurements compared with model predictions. The symbols represent the effective shear modulus obtained from eqn (1) by substituting the measured CCT for varying fractions of silica particles. The solid black line represents the lower bound shear modulus obtained from the simple rule of mixtures, eqn (3). For all cases, ϕrcp = 0.64, N = 6,41 and γ = 0.072 N m−1. Furthermore, ν = 0.34 and G = 1.0 GPa for the PS particles,42 whereas for silica,43 those values are 0.17 and 31 GPa. The effective Poisson's ratio was assumed to vary linearly between the Poisson ratio values of PS and silica. | ||
There is a steep variation in the effective modulus for α = 0.8–1.0, which is closer to the trend exhibited by the lower bound modulus. For lower values of α, the measurements deviate from the model predictions (Fig. 5). Overall, these results suggest that the soft particles dominate the response except when their fraction is very small.
We also captured SEM images of dried films of particle packing before the heat treatment. Fig. 6 shows that both PS and silica particles are spherical suggesting that the deformation during the drying process is purely elastic. This supports the assumption of purely elastic deformation in deriving the model eqn (1). Furthermore, the silica and the PS particles cannot be distinguished necessitating the heat treatment for distinguishing the two particles.
3.3. Effective modulus from the nanoindentation technique
Next, we determined the effective modulus of packing via the nanoindentation technique. Following the previously established protocols for colloidal packings31,34 and packing of emulsion droplets,44 only the initial portion of the loading curve of the force-penetration data was fit to the Hertzian model to extract the effective modulus of the film.31,34 Specifically, the loading data was fitted to the Belehradek expression, f = a(s − b)c, using a least square method, where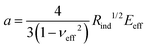 , s is the penetration depth, b is a fitting parameter that is indicative of zero-force location, νeff is the effective Poisson ratio of the packing and c is fixed at 3/2.
, s is the penetration depth, b is a fitting parameter that is indicative of zero-force location, νeff is the effective Poisson ratio of the packing and c is fixed at 3/2.
Initially, we applied a small pre-load force of 2 μN to compact any loose particles and to ensure that the particles under the tip are all in contact with each other. Next, the force was increased at a slow rate up to a maximum load of 100 μN and the displacement was recorded. The penetration at the maximum load depends on the effective modulus of the packing. For films with a high fraction of hard particles, the penetration depth is less than 100 nm for the applied load of 100 μN, while for the film containing a large fraction of soft particles, the penetration depth is much larger. To ensure uniformity in measurement across the packings, we consider the profile up to a fixed depth of 100 nm.
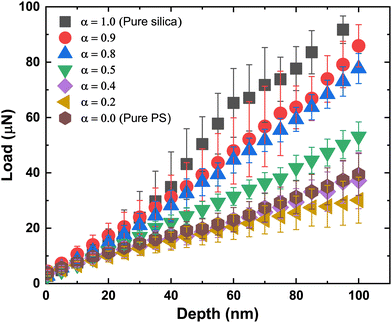
The nanoindentation tests were performed at various locations across the film, including the edge and centre of each film, and an averaged force versus penetration depth curve was obtained. Fig. 7 shows the averaged data for different α along with error bars. When the fraction of PS particles is high (small α), the penetration force is below 40 μN at a penetration depth of 100 nm. The load profile rises with increasing α reaching a force of about 95 μN at 100 nm depth for the pure silica particles (α = 1.0), see also Fig. S2 in the ESI† for the full loading and unloading curve.
The indentation modulus of the film was extracted from the load–penetration curve – the values obtained from the fits for different values of α are presented in Fig. 8. The mean effective modulus is obtained by averaging the effective modulus obtained from curve fits for the loading curve at different locations of the film for a fixed value of α – these fits are shown in Fig. S3–S11 in the ESI.† The trend follows that obtained from the CCT data in that the effective modulus changes slowly with increasing α until about 0.8, after which the modulus increases steeply. However, we found that the modulus at α = 0.2 was slightly lower than that obtained for the two neighboring values of α = 0 and 0.4. This is also seen in the loading curve, where the curve for α = 0.2 is below the two neighboring curves (Fig. 7). The experiments were repeated multiple times with measurements taken at different regions of the film, but the discrepancy remained. We have included two different points, each at 0 and 0.2, obtained from separate sets of experiments to confirm the reproducibility of our measurements (Fig. 8). At present, the reasons for the small discrepancy are unclear.
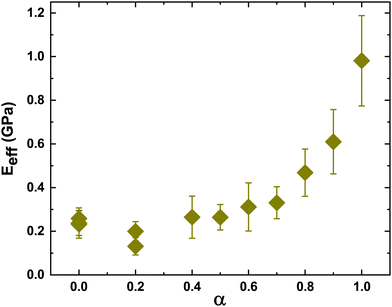 | ||
| Fig. 8 Effective Young's modulus extracted from load versus penetration depth data by fitting the Hertzian contact model, eqn (2). Mechanical stiffness decreases with increased fraction of soft particles. | ||
3.4. Comparison of effective modulus
We have used two different methods to obtain the effective modulus of the particle packed films. The two data sets, normalized with the value obtained for pure silica film, along with the prediction obtained from the simple mixture theory for lower-bound modulus are plotted in Fig. 9. We also plot the upper bound modulus obtained by assuming the “springs-in-parallel” configuration,| Geff = αGsilica + (1 − α)GPS. | (4) |
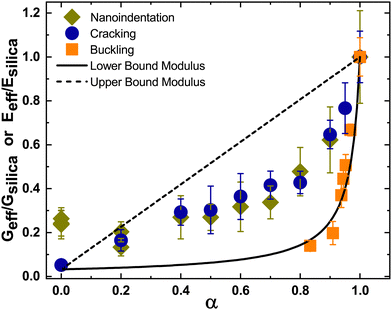 | ||
| Fig. 9 The normalized effective modulus obtained from the indentation test (Eeff/Esilica), cracking (Geff/Gsilica) and buckling (Geff/Gsilica) phenomenon is compared with both the lower and upper bound of the packing modulus obtained from the simple mixture theory. The lower and upper bound modulus are also normalized (Geff/Gsilica). The effective shear modulus obtained from buckling experiments was taken from Bamboriya and Tirumkudulu.36 | ||
We also include data reported recently36 for the buckling of spherical shells made of a binary mixture of hard and soft particles. Here, drops of water containing a mixture of silica and PS particles, both of 5 μm diameter, were placed on a super-hydrophobic surface and dried at a fast rate in a heated, vacuum oven. The experiments mimicked the conditions of fast drying experienced by droplets in a spray drier. The rapidly retracting interface separating the liquid–gas phase traps the particles forming a particle-packed shell at the interface. As the liquid continues to evaporate, the capillary menisci at the top layer of the shell exert compressive stress on the packing. If the stress exceeds a critical value, the shell buckles. The buckling phenomenon is analogous to that for cracking except that the latter is caused by tensile stress while the former is induced by compressive stress. Increasing the particle size or decreasing the shell radius reduced the tendency for buckling.
Bamboriya and Tirumkudulu36 compared the critical conditions for buckling of a shell obtained from a theory proposed by Tirumkudulu45 with that obtained from experiments and showed excellent agreement for experiments performed with homogenous particles, all of the same size. The theoretical expression was next used to extract the effective modulus by measuring the critical shell radius for buckling of a shell made of a binary mixture of hard and soft particles of the same size (5 μm each). The same data is also included in Fig. 9. Note that the buckling data could be extracted only for values of α lying between 0.8 and 1.0 since the transition from buckling to non-buckling shells at lower values of α required very small sized shells (or drop sizes), which could not be achieved using a sessile drop experiment.
Overall, the effective modulus from the buckling experiments matches more closely with the lower bound theory compared to that obtained from either nanoindentation or cracking experiments. We attribute the deviation to the sedimentation of silica particles in the drying films where the drying time is about 5 minutes, resulting in Peclet numbers of the order of 102. On the other hand, the buckling drops were dried at an extremely fast rate in a heated, vacuum oven resulting in Peclet numbers (ĖR/D) of the order of 104, where R is the radius of the drop. It is possible that the high drying rates and rapid formation of particle-packed shell eliminates sedimentation leading to a more homogenous packing. More work is needed to investigate these differences.
4 Conclusions
This study presents measurement of the effective modulus of particle packing containing particles of the same size but two different moduli. The modulus was determined in two different ways. First, the measured values of critical cracking thickness for dried films of particle mixtures were fit to an established theory to extract the effective modulus of the particle packing. Next, the same quantity was obtained via the nanoindentation technique, where the loading curve was fit to the Hertzian contact model. There is remarkable agreement between the values obtained via the two measurement techniques suggesting that the measurement of CCT gives a reliable measure of the effective mechanical properties of the particle packing. This is one of the most important outcomes of the study. The measurements were also compared to previously obtained data for buckling of drying shells of particle packings. The effective modulus obtained from cracking/nanoindentation lies between the upper and lower bounds of the simple mixture theory, while those obtained from the buckling experiments are closer to the lower bound. These differences are attributed to particle segregation caused by the sedimentation of silica particles in drying films. Overall, the study opens up avenues for further investigations of mixtures containing particles of different sizes and mechanical properties and thereby tailoring the mechanical properties of particulate films.Author contributions
MST and OPB designed the study. OPB performed all the experiments and related calculations. OPB and MST wrote the manuscript.Data availability
The data supporting this article have been included as part of the ESI.†Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.Acknowledgements
The authors thank Prof. Prita Pant for insightful discussions. The authors would like to express their appreciation for the support from Nanoindentation at the Metallurgical Engineering and Materials Science (ME&MS) facility of IIT Bombay and the Cryo-Field Emission Gun – Scanning Electron Microscope Facility (FIST) at Chemical Engineering, IIT Bombay. OPB thanks IIT Bombay for financial support. The project was funded in part by the Department of Science and Technology, India under grant #CRG/2022/004288 and Department of Biotechnology, India under grant #BT/PR48280/MED/32/829/2023.Notes and references
- A. F. Routh and W. B. Russel, Langmuir, 1999, 15, 7762–7773 CrossRef CAS
.
- T. Narita, P. Hebraud and F. Lequeux, Eur. Phys. J. E: Soft Matter Biol. Phys., 2005, 17, 69–76 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
-
J. Keddie and A. F. Routh, Fundamentals of Latex Film Formation: Processes and Properties, Springer Science & Business Media, 2010 Search PubMed
.
- A. F. Routh, Rep. Prog. Phys., 2013, 76, 046603 CrossRef PubMed
.
- J. Zhou, Y. Jiang and M. Doi, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2017, 118, 108002 CrossRef PubMed
.
- A. G. Marin, H. Gelderblom, D. Lohse and J. H. Snoeijer, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2011, 107, 085502 CrossRef PubMed
.
- P. Lilin, M. Ibrahim and I. Bischofberger, Sci. Adv., 2024, 10, eadp3746 CrossRef PubMed
.
- L. Schmitt, T. Forsans and F. Santarelli, Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr., 1994, 411–427 CrossRef
.
- M. S. Tirumkudulu and W. B. Russel, Langmuir, 2004, 20, 2947–2961 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- R. D. Deegan, O. Bakajin, T. F. Dupont, G. Huber, S. R. Nagel and T. A. Witten, Nature, 1997, 389, 827–829 CrossRef CAS
.
- P. Ball, Nature, 1997, 389, 788 CrossRef CAS
.
- R. D. Deegan, Phys. Rev. E: Stat. Phys., Plasmas, Fluids, Relat. Interdiscip. Top., 2000, 61, 475–485 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- R. G. Larson, Nature, 2017, 550, 466–467 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. S. Tirumkudulu and W. B. Russel, Langmuir, 2005, 21, 4938–4948 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- I. Cantat, Phys. Fluids, 2013, 25, 031303 CrossRef
.
- K. B. Singh and M. S. Tirumkudulu, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2007, 98, 218302 CrossRef PubMed
.
- K. B. Singh, G. Deoghare and M. S. Tirumkudulu, Langmuir, 2009, 25, 751–760 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- W. B. Russel, N. Wu and W. Man, Langmuir, 2008, 24, 1721–1730 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. Schulz and J. Keddie, Soft Matter, 2018, 14, 6181–6197 RSC
.
- A. F. Routh and W. B. Russel, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2001, 40, 4302–4308 CrossRef CAS
.
- J. Feng, M. A. Winnik, R. R. Shivers and B. Clubb, Macromolecules, 1995, 28, 7671–7682 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Roth, C. Schilde, P. Lellig, A. Kwade and G. K. Auernhammer, Eur. Phys. J. E: Soft Matter Biol. Phys., 2012, 35, 1–12 CrossRef PubMed
.
- C. J. Martinez and J. A. Lewis, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2002, 85, 2409–2416 CrossRef CAS
.
- H. Abdeldaim, B. Reck, K. J. Roschmann and J. M. Asua, Macromolecules, 2023, 56, 3304–3315 CrossRef CAS
.
- N. Jiménez, N. Ballard and J. M. Asua, Macromol. Mater. Eng., 2024, 309, 2400026 CrossRef
.
- L. Pauchard, Phys. Fluids, 2023, 35, 067107 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. A. Winnik and J. Feng, J. Coat. Technol., 1996, 68, 39–50 CAS
.
- S. Lepizzera, C. Lhommeau, G. Dilger, T. Pith and M. Lambla, J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polym. Phys., 1997, 35, 2093–2101 CrossRef CAS
.
- W. C. Oliver and G. M. Pharr, J. Mater. Res., 1992, 7, 1564–1583 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. R. VanLandingham, J. S. Villarrubia, W. F. Guthrie and G. F. Meyers, Macromol. Symp., 2001, 15–44 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Wang, K. M. Liechti, J. M. White and R. M. Winter, J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 2004, 52, 2329–2354 CrossRef CAS
.
- J. Hay, Exp. Tech., 2009, 33, 66–72 CrossRef
.
- J. Yin, M. Retsch, J.-H. Lee, E. L. Thomas and M. C. Boyce, Langmuir, 2011, 27, 10492–10500 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. Yin, M. Retsch, E. L. Thomas and M. C. Boyce, Langmuir, 2012, 28, 5580–5588 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. Vella, A. Mann, H. Kung, C. Chien, T. Weihs and R. Cammarata, J. Mater. Res., 2004, 19, 1840–1848 CrossRef CAS
.
- O. P. Bamboriya and M. S. Tirumkudulu, Soft Matter, 2023, 19, 2605–2611 RSC
.
- L. Pauchard, F. Parisse and C. Allain, Phys. Rev. E: Stat. Phys., Plasmas, Fluids, Relat. Interdiscip. Top., 1999, 59, 3737 CrossRef CAS
.
- A. A. Griffith, Philos. Collect. R. Soc. London, 1921, 221, 163–198 Search PubMed
.
-
L. D. Landau and E. M. Lifshitz, Theory of Elasticity, Elsevier, Oxford, UK, 1986 Search PubMed
.
-
V. L. Popov, Contact Mechanics and Friction, Springer, 2010 Search PubMed
.
- L. Uri, T. Walmann, L. Alberts, D. K. Dysthe and J. Feder, Phys. Rev. E: Stat., Nonlinear, Soft Matter Phys., 2006, 73, 051301 CrossRef PubMed
.
- P. H. Mott, J. R. Dorgan and C. Roland, J. Sound Vib., 2008, 312, 572–575 CrossRef
.
- Silica – Silicon Dioxide (SiO2), https://www.azom.com/properties.aspx?ArticleID=1114, Accessed: 2024-09-06.
- D. Filip, V. Uricanu, M. H. Duits, D. Van den Ende, J. Mellema, W. Agterof and F. Mugele, Langmuir, 2006, 22, 560–574 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. S. Tirumkudulu, Soft Matter, 2018, 14, 7455–7461 RSC
.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4sm01366b |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |