Themed collection Soft Matter Pioneering Investigators

Designing hydrogel dimensionality to investigate mechanobiology
This review highlights innovative hydrogel platforms—from 2D to 3D, including 2.5D and sandwich systems—that reveal how mechanical cues regulate cell behavior, with translational potential in tissue engineering and disease modeling.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 4551-4572
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM01458H
Experimental models for cohesive granular materials: a review
This review covers experimental approaches to induce controlled adhesive forces between particles and discusses the effects of inter-particle cohesion on granular mechanics across scales, from individual particles to bulk behavior.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 2193-2208
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM01324G
Hacktive matter: data-driven discovery through hackathon-based cross-disciplinary coding
We describe approaches, results and insights from multi-year hackathons to enable their use in soft matter training and innovation.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 5381-5392
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5SM00401B
Transport of partially active polymers in chemical gradients
Connecting active and passive monomers to form partially active polymers can lead to directed transport towards regions of high or low chemical concentration.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 1835-1840
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM01357C
Note on two-point mean square displacement
Two-point mean-square-displacement analysis utilizes trajectories of a pair of probes to quantify their intrinsic mobility and/or motional correlation.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 5871-5882
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5SM00555H
Self-limiting states of polar misfits: frustrated assembly of warped-jigsaw particles
We study the ground state thermodynamics of a model class of geometrically frustrated assemblies, known as warped-jigsaw particles.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 5423-5446
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5SM00136F
Active and passive crosslinking of cytoskeleton scaffolds tune the effects of cell inclusions on composite structure
We demonstrate the ability to engineer composites of microtubules and actin that can entrain bacteria cells while retaining structural integrity.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 4792-4806
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM01527D
Optical, dielectric and electroconvection studies of a five-ring ester-difluoromethoxy linked ferroelectric nematic liquid crystal with a lateral methoxy group
Experimental studies on a five-ring ester-difluoromethoxy linked ferroelectric nematic liquid crystal.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 4455-4466
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5SM00113G
Pattern formation of lipid domains in bilayer membranes
We construct a minimal theoretical model to study pattern formation of lipid domains in bilayer membranes, which is driven by the coupling between the phase separation of lipids and the elastic deformation of the membrane.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 4288-4297
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5SM00276A
Gating and tunable confinement of active colloids within patterned environments
Dielectric pillars induce a frequency-dependent repulsion for metallo-dielectric Janus active particles, changing their effective size in a versatile way to control the spatial distribution of microswimmers.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 3850-3858
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM01512F
Computer vision for high-throughput analysis of pickering emulsions
We demonstrate the circle-Hough transform (CHT) as a highly efficient and general computer vision tool for the quantitative assessment of droplet size from optical microscopy images of Pickering emulsions.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 2339-2348
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM01252F
Lipid bilayer fracture under uniaxial stretch
We show that supported bilayers from ellipsoidal pores that propagate perpendicular to the stretch direction akin the fracturing of soft gels.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 1669-1675
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM01410C
Exploiting photopolymerization to modulate liquid crystalline network actuation
Liquid crystalline networks able to work as photoresponsive actuators were prepared by different photopolymerization approaches. This work shows how the macromolecular structure influences the performances during both thermal and light stimulation.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 1162-1169
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM01360C
The shape of cleaved tethered membranes
Applying longitudinal cuts to the surface of a self-avoiding tethered membrane destabilizes its flat phase and leads to the formation of novel phases fully controlled by the balance between number of cuts and the edge width.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 1134-1140
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM01225A
Taylor's swimming sheet near a soft boundary
We theoretically study Taylor's swimming sheet near a Winkler elastic solid. This minimal approach allows us to explicitly formulate analytically the generic behaviours and mechanisms of microswimming near soft boundaries.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 826-834
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM01153H
Analysis of the internal motions of thermoresponsive polymers and single chain nanoparticles
Proper orthogonal decomposition (POD) and uniform manifold approximation & projection (UMAP) are used to study the relaxation dynamics of thermoresponsive polymers and single-chain nanoparticles with energy-conserving DPD simulations.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 770-780
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM01308E
Nanoparticle adhesion at liquid interfaces
The influence of nanoparticle size, shape and wettability on adhesion at liquid interfaces is explored using a combination of atomic force microscopy and computer simulations.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 585-595
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM01101E
Visualizing fiber end geometry effects on stress distribution in composites using mechanophores
Stress quantification can be observed during single fiber pull-out test in a polymer matrix composite with stress sensing molecules.

Soft Matter, 2025,21, 573-584
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM00967C
Explaining the spread in measurement of PDMS elastic properties: influence of test method and curing protocol
Accuracy in the measurement of mechanical properties is essential for precision engineering and for the interrogation of composition–property relationships.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 9174-9183
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM00573B
A computational method for rapid analysis polymer structure and inverse design strategy (RAPSIDY)
We present our computational framework for the rapid analysis of polymer structure and inverse design strategy (RAPSIDY) that enables inverse design of polymers for desired structures by accelerating multiscale structure stability evaluation.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 8246-8259
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM01037J
Micro-ballistic response of thin film polymer grafted nanoparticle monolayers
μ-Ballistic simulations performed on the PGN thin films reveal a positive influence of cohesive energy density on the performance. PGN with heavier nanoparticles arrest bullets more rapidly, however, lighter particles exhibit a higher 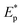 .
.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 7926-7935
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM00718B
Interplay between yielding, ‘recovery’, and strength of yield stress fluids for direct ink writing: new insights from oscillatory rheology
We propose a new framework to characterise yield stress fluids for direct ink writing that enables us to link trends in rheological metrics with printing resolution.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 7429-7447
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM00758A
Lipid membranes supported by polydimethylsiloxane substrates with designed geometry
We present a strategy for obtaining membranes on substrates with tunable geometry and stiffness for biological and material science studies.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 7379-7386
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM00380B
About this collection
Soft Matter is proud to present this Pioneering Investigators collection. This collection highlights the great work being done by mid-career investigators who have firmly established themselves as pioneers of the field of soft matter.