Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Multivalent agents containing 1-substituted 2,3,4-trihydroxyphenyl moieties as novel synthetic polyphenols directed against HIV-1†‡
Aida
Flores
a,
María José
Camarasa
a,
María Jesús
Pérez-Pérez
a,
Ana
San-Félix
a,
Jan
Balzarini
b and
Ernesto
Quesada
*a
aInstituto de Química Médica CSIC, Juan de la Cierva 3, 28006 Madrid, Spain. E-mail: EQ1@iqm.csic.es; Fax: +34 91 564 48 53; Tel: +34 91 258 76 20
bRega Institute for Medical Research, KU Leuven, Minderbroedersstraat 10, B-3000 Leuven, Belgium
First published on 29th April 2014
Abstract
The synthesis and the assessment of the anti-HIV activity of a set of molecules inspired by the multivalent structures of some naturally-occurring polyphenols (tannins) are reported. Different multibranched scaffolds have been derived from pentaerythritol as the central core which distribute spatially synthetic polyphenolic subunits based on 1-substituted 2,3,4-trihydroxyphenyl moieties. A tetrapodal compound (13b) bearing four N-(2,3,4-trihydroxyphenyl)amide groups, exhibits remarkable selective activity against HIV-1 with EC50 values in the micromolar scale, in the same range as those reported for the most representative anti-HIV tannins. Preliminary SAR studies emphasize the importance of the 1-substituted 2,3,4-trihydroxyphenyl moiety, the presence of an amide as the linker and the multivalent architecture of these molecules, since the anti-HIV activity increases with the number of polyphenolic moieties. The data support the interest in synthetic polyphenols and represent a promising starting point for further design and development of selective HIV-1 inhibitors.
Introduction
Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) remains a major global health concern due to its worldwide extension and the high mortality rate still associated with this disease.1 Current antiretroviral therapy against Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), the etiological agent of AIDS, consists of 26 clinically approved drugs,2 which are administrated in combination in the so-called Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART).3 This chemotherapeutic arsenal targets different critical stages of the infectious cycle of the virus and has converted AIDS from a lethal disease into a chronic, controlled condition.4In spite of the positive effects of the HAART multidrug regime, the emergence of resistance to all drugs currently in clinical use as well as the appearance of side effects, particularly after long-term treatment, are major hurdles in the fight against the virus.5,6 Additionally, HAART does not eliminate the persistence of latent long-term reservoirs of HIV.7 As a result, novel strategies and alternative therapeutic agents directed against HIV are still required.8
Polyphenols are a heterogeneous class of naturally-occurring compounds, usually secondary metabolites isolated from higher plants, which have been structurally characterised by the presence of polyhydroxy-aromatic moieties on their molecular frameworks.9 Many polyphenols have been proposed as anti-HIV therapeutics, exerting different modes of action, ranging from virus entry, reverse transcription, integration and virus maturing.10 Some of the most noticeable polyphenols described so far as agents against HIV include catechins,11 theaflavins12 (considered lately as inexpensive and safe microbicide candidates for the prevention of HIV sexual transmission13), or quercetin,14 most of them found in various gallate forms.
Among them, the family of hydrolysable tannins has attracted particularly strong interest due to its remarkable activity against HIV. This heterogeneous group of polyphenols usually comprises a common architecture based on a multibranched molecular core that spatially distributes several galloyl or galloyl-derived subunits, attached to the central scaffold through ester linkages.15 Among these natural products must be noted some structurally simplified polyphenols such as 1,3,4,5-tetragalloylapiitol. This secondary plant metabolite contains an acyclic polyhydroxylated hydrocarbon core (D-apiitol) functionalised with four gallate moieties. This tannin exemplifies how a structurally simple polyol can act as an efficient distributing scaffold for polyphenolic subunits resulting in a molecule endowed with anti-HIV activity.16
The biological activities associated with polyphenols have been mainly attributed to the presence of differently functionalised polyhydroxy-aromatic moieties on their structures. In particular, galloyl subunits are structural motifs widely found in natural polyphenols. The presence of these groups constitutes an essential requisite for any bioactivity in most polyphenolic natural products.17 Very noticeably, flavonols lacking galloyl moieties do not provide effective protection against HIV-1 infection and the number and position of free phenol (–OH) groups determine their biological properties.18
Galloyl residues provide polyphenols with efficient donor and acceptor-functionalities for hydrogen bonding, which give these compounds the potential to bind to proteins and nucleic acids.19,20 Moreover, galloyl-containing polyphenols are notable anti-oxidants. A large body of evidence indicates that the oxidative environment facilitates viral replication21 and that HIV infection is enhanced by free-radical damage.22 In this sense, it has been suggested that gallate groups attenuate AIDS progression due to their anti-oxidant properties23 which weaken the effects of the infection and the ability of the virus to infect new cells.24
As previously mentioned, a remarkable feature of the hydrolysable tannins is their multi-branched structure. Thus, several subunits of the polyhydroxy-aromatic moieties (i.e. gallic acid) are distributed profusely at the periphery of the scaffolds. This architecture provides these compounds with a dense outer array of repeated polyphenolic motifs (multivalency).25 Actually, the multivalent concept of molecular design is currently starting to be successfully employed in anti-HIV drug discovery.26,27 The combined above-mentioned factors (hydrogen bonding ability, anti-oxidative effect and multivalent architecture) allow the biological effect of polyphenols at different levels.
Albeit their intimate mechanisms of action have not been characterized in full detail, polyphenols have been proposed as useful candidates, either alone or in combination with conventional therapeutics, for the treatment and prevention of HIV-1 infection.10a However, naturally-occurring polyphenols are obtained as mixtures of compounds extracted from their natural sources. This is a significant drawback because in many cases antiviral activities are due to complex mixtures of substances (plant extracts) whose composition can only be estimated while further isolation of the active components from the extracts can turn out to be an elusive and difficult task. As a consequence, the development of chemical procedures able to allow access to pure, controlled samples of polyphenols is of great interest. Furthermore, naturally-occurring polyphenols can motivate and inspire researchers to look for novel synthetic compounds based on related architectures and/or new structurally-modified polyphenolic moieties. Surprisingly, and despite this interest, polyphenols have been only rarely explored as inspirational motifs of new anti-HIV agents. Moreover, synthetic polyphenols described to date are analogues in which changes were focused on the nature of the scaffolds that distribute spatially the most ubiquitous polyphenolic moiety, the galloyl residue.28 Thus, the promising antiviral profile of natural polyphenols and the lack of previous work on structurally-modified analogues of these compounds prompted us to initiate a program pursuing the discovery of multivalent compounds containing novel synthetic polyphenolic subunits.
In this sense, we recently described a tripodal receptor containing a triethylbenzene scaffold attached by amide linkers to 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzoyl groups (a galloyl isomer). It was stated that this moiety allowed the formation of an intramolecular hydrogen bond between the bridged-amide function and the ortho-phenolic substituent, thus rigidifying the structures compared to galloyl-containing compounds (3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl isomer). This pre-organisation provided this compound with selective recognition properties for mannose-based polysaccharides, which opened attractive prospects for its potential in anti-infective strategies, including enveloped viruses such as HIV.29
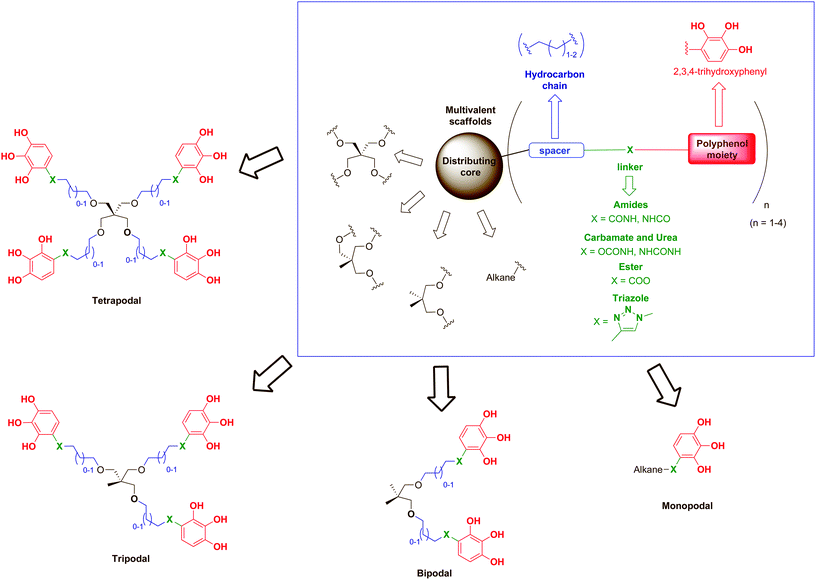
Based on these precedents, we describe herein the synthesis and biological evaluation against HIV of a series of compounds inspired by the architecture of some hydrolysable tannins (such as 1,2,4,5-tetragalloylapiitol) in which the naturally-occurring galloyl group (3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl moiety) has been replaced by a synthetic 2,3,4-trihydroxyphenyl nucleus functionalised at position 1 with different linkers that allow their attachment to suitable scaffolds (Fig. 1).
As scaffolds, a series of simple mono-, bi-, tri- and tetrapodal molecules were used to explore the role of the number of polyphenolic subunits grafted onto a given backbone (multivalency) in the biological activity. Thus, pentaerythritol was proposed as a versatile molecule for construction of the four-branched core.30 The gradual loss of branches of the pentaerythritol core allowed access to tripodal and bipodal scaffolds, while simple linear hydrocarbon chains of different lengths were used for the monopodal molecules. In addition, alkyl chains (2 or 3 methylene groups) have been introduced as spacers to separate the polyphenolic subunits from the central core in order to provide to the scaffolds both flexibility and elongated branches, avoiding steric hindrance. Amide bonds are ubiquitous in nature and chemically stable,31 so they were the first choice for the linking functionalities, but esters, carbamates, ureas or triazoles (all good hydrogen bond donor and acceptor functionalities) were also used in order to evaluate the role of the linker on the biological activity. Thus far, we describe the synthesis and anti-HIV activity of this new family of compounds designed as synthetic polyphenols.
Results and discussion
Synthesis
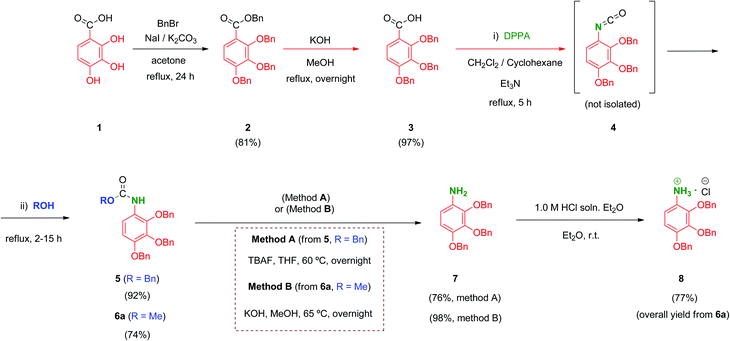
We prepared a first series of compounds in which the selected 2,3,4-trihydroxyphenyl moiety was linked to a polyacid scaffold by amide linkages. With this purpose, 2,3,4-trihydroxy aniline (8) was prepared from the commercially available 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzoic acid (1) according to the pathway depicted in Scheme 1. Perbenzylation of the starting material 1 (acetone, K2CO3, heating),32 followed by saponification of the benzyl ester, gave free acid 333 in high yield. Conversion of the benzoic acid 3 into its aniline analogue 7 was performed following a three-step synthetic sequence. The first transformation involved a Curtius reaction34 using diphenylphosphorylazide (DPPA) as a mild azide-transfer reagent.35 In this reaction, the corresponding acyl-azide derivative of 3 is formed and rearranged in situ to give the intermediate isocyanate 4, which was not isolated from the reaction medium. A subsequent one-pot reaction of 4 with alcohols (BnOH, MeOH) produced the corresponding benzyl (5) and methyl (6a) carbamates respectively in high yield.36 Removal of the Cbz (BnOCO) group in 5 was successfully achieved using an excess of tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF) to afford the free aniline derivative 7 (Scheme 1, method A).37 However, despite the satisfactory overall yield of the conversion, the large excess of TBAF that has to be used to drive the deprotection to completion and the toxicity of this reagent made it difficult to scale up this transformation. Alternatively, the methyl carbamate 6a was efficiently deprotected by alkaline hydrolysis using KOH as reagent giving 7 in 98% yield. This procedure (Scheme 1, method B) performed on 6a proved simpler from a practical point of view, higher yielding overall, easily scalable and inexpensive compared to the TBAF procedure (which is carried out specifically on the CBz-protected aniline 5).Unfortunately, free aniline 7 proved to be unstable and decomposition was observed even when it was stored under controlled conditions (low temperature and inert atmosphere). To solve this limitation, 7 was converted immediately after isolation into its HCl salt 8. Hence, hydrochloride 8 was stable and could be stored at room temperature for months without apparent degradation.
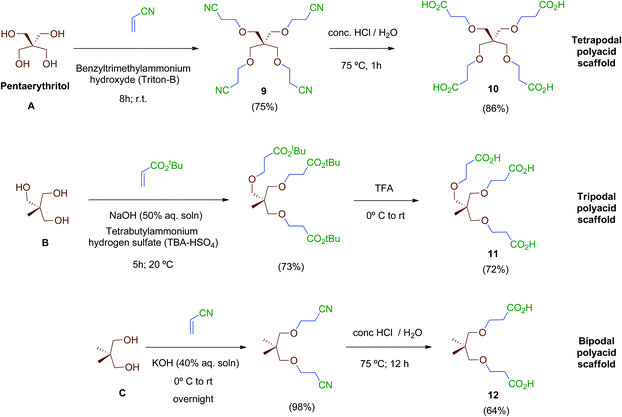
Next, scaffolds 10–12 with 4, 3 and 2 branched carboxylic acids, respectively, were synthesised following a two-step route that involves firstly the conjugate addition of suitable polyols A, B and C to olefins with electron-withdrawing substitutents followed by the conversion of the terminal functionalities (CO2tBu or CN) into the free acids carried out as specifically required (Scheme 2). Thus, tetraacid 10 was synthesised from the inexpensive, commercially available pentaerythritol (A), which reacts readily with acrylonitrile in aqueous media generating tetranitrile intermediate 9 (72% yield), which was finally hydrolysed providing the desired tetraacid 10 in 86% yield.38 Tripodal scaffold 11 was synthesised from the commercially available triol B and tert-butyl acrylate in 73% yield.39tert-Butyl protecting groups were then straightforwardly removed by treatment with TFA, affording triacid 11 in 72% yield.40 Finally, bidentate scaffold 12 was synthesised through a similar two-step sequence involving conjugate addition of commercially available diol C to acrylonitrile in 98% yield41 and subsequent acid hydrolysis of nitrile groups to the corresponding free acids in 64% yield.
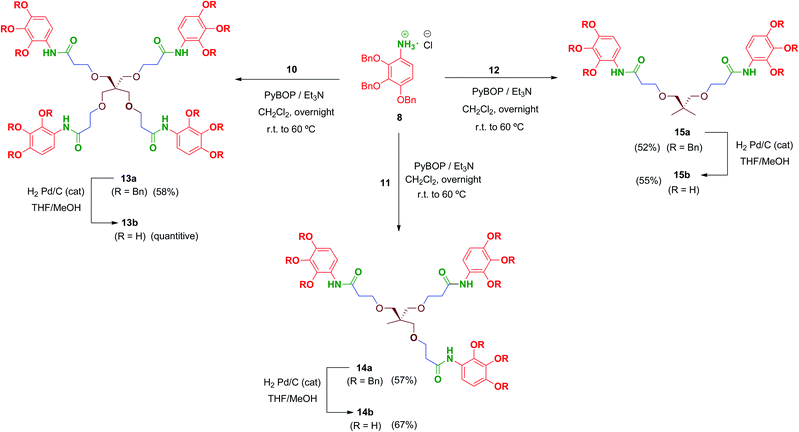
Multivalent benzyl-protected amides 13a–15a were prepared by coupling of 8 and polyacid scaffolds 10–12 mediated by PyBOP/Et3N in dichloromethane as depicted in Scheme 3. Transformations proceeded at room temperature in 48 h, but gentle heating at 60 °C led the reaction to completion in shortened reaction times (overnight) and satisfactory yields.
Hydrogenolysis of all the benzyl-protected compounds 13a–15a (H2, 3.1 bar, 25 °C, catalytic Pd/C) afforded the free-phenols 13b–15b in good yields. The choice of benzyl as protecting group for the phenol functionalities proved successful as easy instrumental procedures and minimal work-up were required to achieve the fully deprotected compounds at high purity (≥95% HPLC).
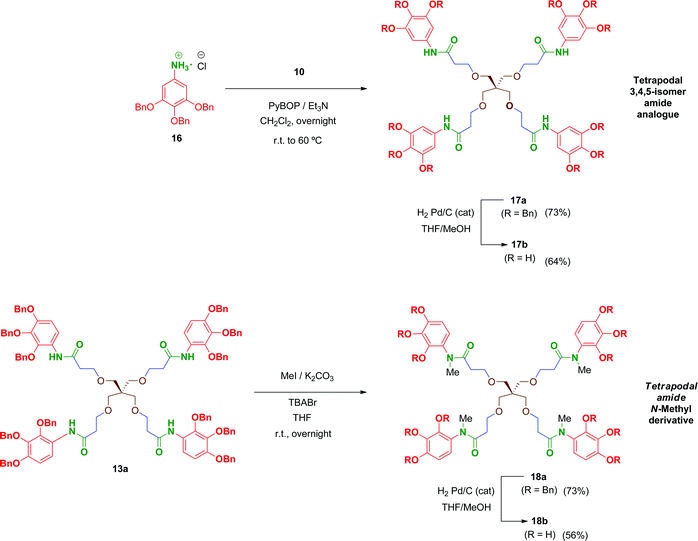
In order to evaluate the influence on the activity of the position of the phenol groups on the aromatic ring, the 3,4,5-isomer derivative of 13b, namely compound 17b, was obtained (Scheme 4). This compound was synthesized similarly to 13b in 47% overall yield after two steps. The first transformation involves a PyBOP-mediated coupling of scaffold 10 and the corresponding 3,4,5-benzyloxy aniline 16 followed by hydrogenolysis of the benzyl groups in 17a to afford 17b. Additionally, with the aim of analysing the role of the free amide proton on the activity, the N-methyl derivative 18b was prepared in 41% overall yield by reaction of 13a with methyl iodide followed by removal of the benzyl groups in 18a by hydrogenation.
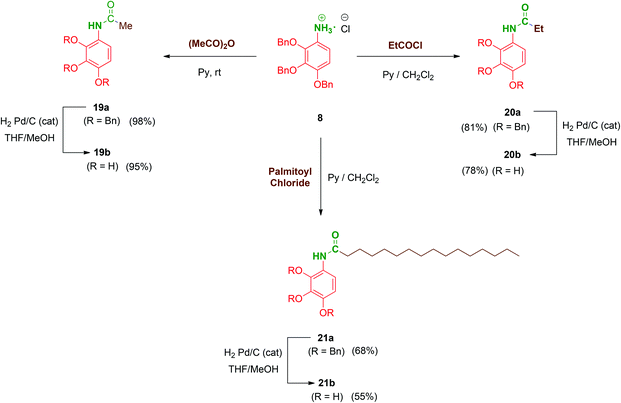
Next, to complete the amide series of compounds with monopodal structures and to properly evaluate the effect of branching on the scaffolds, compounds 19b–21b were prepared. Thus, 8 was straightforwardly functionalised with acetic anhydride in pyridine to afford acetate 19a. Ethyl (20a; short-chained derivative) and palmitoyl (21a; long-chained derivative) monopodal amides were synthesized by reaction of 8 with the corresponding acyl chlorides in order to additionally evaluate the role of the amphiphilic character of these molecules. Finally, hydrogenolysis of the benzyl groups of 19a–21a afforded the monopodal free-phenols 19b–21b in satisfactory yields (Scheme 5).
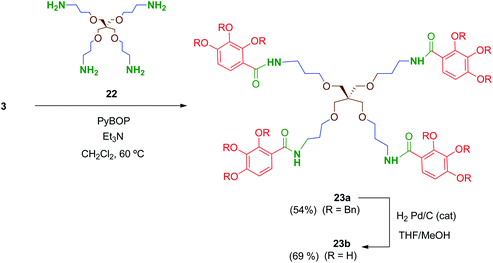
Preliminary biological evaluation of compounds 13b–21b indicated that the tetrapodal compound 13b showed promising anti-HIV-1 activity (see biological evaluation section). We then considered preparing the tetrapodal amide 23b in which the linker is reversed (NHCO instead of CONH), compared to 13b, in order to evaluate the influence of this structural parameter on the activity (Scheme 6). Thus, coupling of the suitable tetraamine 22 (prepared as will be discussed later) with the corresponding acid 3 afforded 23a, whose further deprotection yielded 23b in 69% yield.
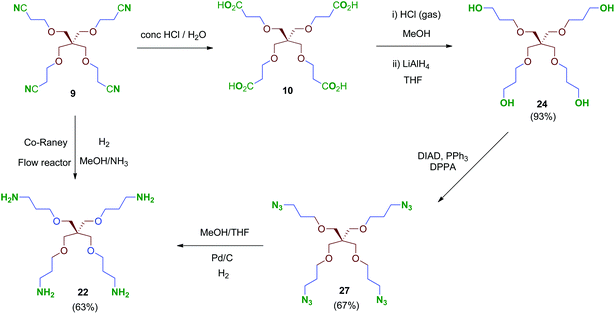
We were encouraged to extend the study to new molecules with modified linkers between the scaffold and the 2,3,4-trihydroxyphenyl moieties. Thus, isocyanate 4 emerged as a key intermediate that allowed its direct conversion into carbamate (OCONH) and urea-linked (NHCONH) derivatives, obtained straightforwardly by reaction of 4 with alcohols and amine-containing cores, respectively (Schemes 9 and 10). For the synthesis of these compounds, scaffolds 22 and 24–26 were prepared as shown in Schemes 7 and 8.
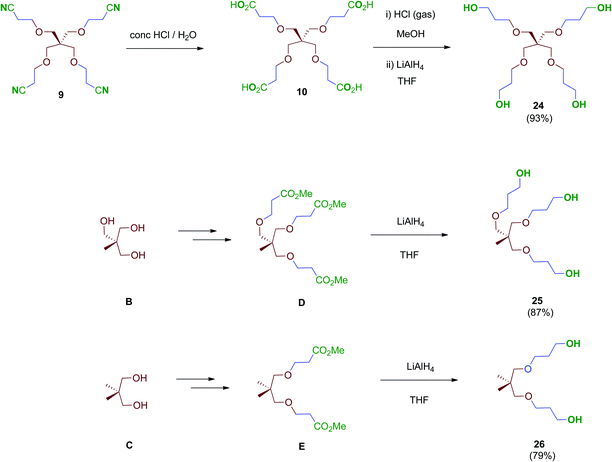
Treatment of tetraacid 10 with HCl gas in methanol42 followed by reduction of the in situ-generated methyl ester intermediate with LiAlH4 afforded tetraol 24. This sequential method proved more reliable than the direct reduction of the tetraacid 10 with borane–THF complex as described.43 Tri- and bipodal alcohols 2544 and 2645 were obtained similarly by reduction of their corresponding methyl ester intermediates D and E (Scheme 7).
Conversion of the polyol 24 into the tetraamine 22 (Scheme 8) was performed firstly via tetraazide intermediate 27, which was obtained by a tandem procedure involving a Mitsunobu activation of the primary alcohols of 24 (DIAD, PPh3) followed by an in situ reaction with diphenylphosphorylazide (DPPA), acting as an azide-transfer reagent. This transformation allows a simple and straightforward synthesis of tetraazide 27 alternatively to the described procedure,46 which involves previous activation of the alcohols as mesylates, isolation and subsequent conversion into their azide derivatives by reaction with sodium azide. Finally, 27 was reduced to the tetraamine 22 in 63% yield by catalytic hydrogenation under standard conditions. Alternatively, compound 22 could be obtained directly from the tetranitrile 9 by hydrogenation at high pressure (70 bar, 70 °C; Scheme 8). This reaction was performed in a continuous-flow reactor using immobilized Co-RANEY® as the catalyst, providing the tetraamine in a single step and quantitative yield. This was finally the method of choice to reach the tetravalent amine-containing scaffold 22.
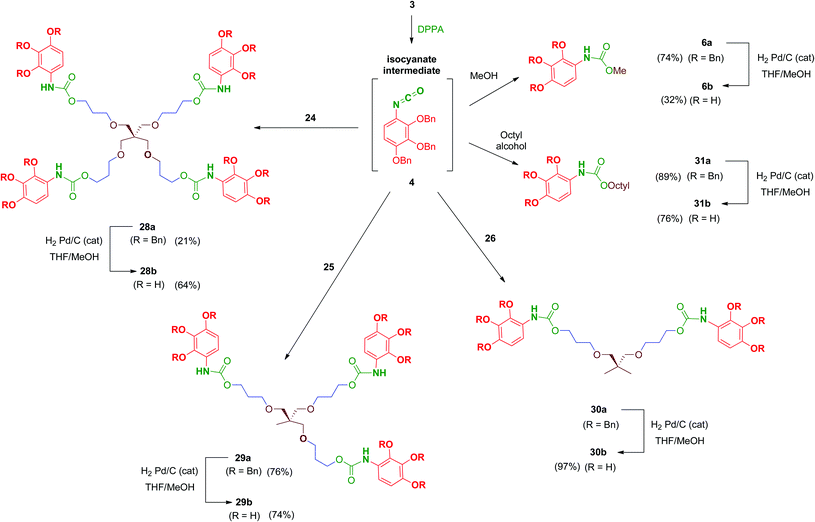
Reaction of polyols 24–26 with 4, generated in situ by the treatment of 3 with DPPA as previously mentioned, afforded carbamates 28a–30a in reasonable yields (Scheme 9). Debenzylation by hydrogenation of 28a–30a proceeded satisfactorily affording free polyphenols 28b–30b. Carbamate-linked compounds were completed with the monodentate methyl derivative 6b (the synthesis of this benzyl-protected derivative was previously described) and the octyl derivative 31b in order to evaluate the effect of the amphiphilic nature of the carbamate.
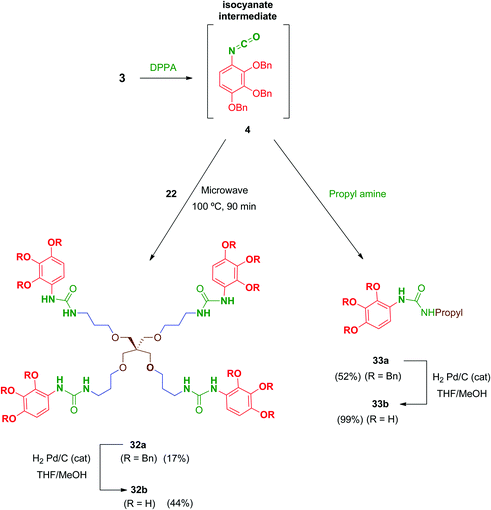
Regarding urea-linked derivatives, tetradentate amine 22 (Scheme 10) reacted very poorly with isocyanate 4. Thus, only by forcing reaction conditions under microwave irradiation (100 °C for 90 min) was it possible to isolate tetrapodal urea 32a, albeit with a poor 17% yield. Additionally, reaction of 4 with propylamine afforded monodentate compound 33a in 52% yield. Monodentate urea 33b containing free phenol groups was successfully isolated in 99% yield after hydrogenation. However, tetradentate urea 32b was not obtained pure after removal of the benzyl protecting groups in 32a. In this case, the material isolated after hydrogenolysis contained several minor by-products. Attempts to purify this crude product (reverse-phase chromatography, recrystallization, exchange resins, etc.) failed to increase purity of this tetradentate urea. Thus, exceptionally, compound 32b was evaluated biologically against HIV with a purity of 82% (as determined by HPLC).
As will be seen in the biological section, the data obtained from the evaluation against HIV of the amide (13b–15b, 17b–21b) and carbamate (6b, 28b–31b) series clearly indicated that the more 2,3,4-trihydroxyphenyl moieties on the periphery of the molecules, the better the anti-HIV activity. Thus, our next series of structural modifications were performed based on these findings and we decided to focus only on the tetrapodal compounds, while the monopodal derivatives were obtained for comparative purposes.
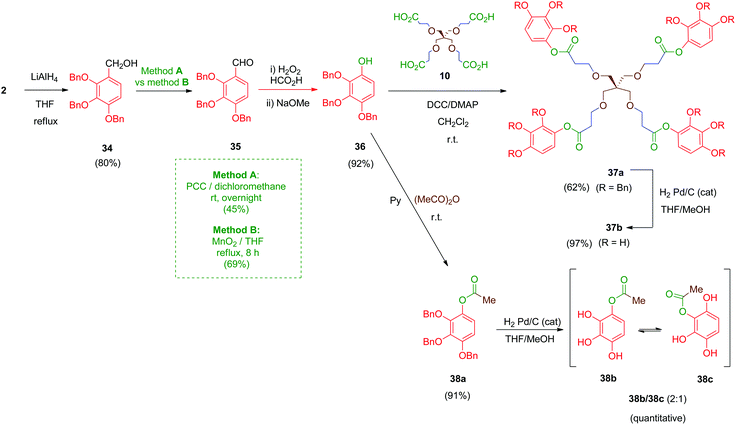
Next, compounds with an ester as the linker were prepared (Scheme 11). In this case, derivative 36 was the key intermediate. This compound was obtained in a three-step sequence by reduction of 2 with lithium aluminium hydride under standard conditions (LiAlH4, THF) to afford benzyl alcohol 34 in 80% yield.47 Subsequent conversion of this alcohol into its aldehyde derivative 35 was initially performed by using pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) as the oxidizing agent (Scheme 11, method A) as described in the literature for the isomeric 3,4,5-trimethoxy analogue of 34.48 However, this transformation afforded, after chromatography, only moderate yields (45%) of the desired aldehyde 35. Alternatively, a MnO2-mediated oxidation (Scheme 11, method B) was assayed giving aldehyde 35 in better yield (69%) and avoiding tedious chromatographic purifications. Finally, a Dakin-type reaction (H2O2–HCO2H) converted the aromatic aldehyde 35 into its phenol derivative 36 as described.49
Coupling of compound 36 with the tetra-acid scaffold 10 was achieved readily by Steglich reaction mediated by DCC and a catalytic amount of DMAP to give tetradentate ester 37a in 62% yield. A simple monodentate ester 38a was also obtained for comparative purposes by treatment of 36 with acetic anhydride in pyridine. Finally, removal of the benzyl ethers in 37a and 38a was carried out by hydrogenolysis using the standard protocol. Deprotected compound 38b undergoes a phenomenon of intramolecular acyl migration between vicinal phenols, producing spontaneously in the hydrogenation medium a (2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) mixture of 1-acetyl/2-acetyl isomers 38b/38c as determined by 1H-NMR. Tetraester 37b did not exhibit this spontaneous trend of transesterification between the phenol groups, although all compounds 37b and 38b/38c proved labile in solution, probably due to partial hydrolysis of the ester moieties.
1) mixture of 1-acetyl/2-acetyl isomers 38b/38c as determined by 1H-NMR. Tetraester 37b did not exhibit this spontaneous trend of transesterification between the phenol groups, although all compounds 37b and 38b/38c proved labile in solution, probably due to partial hydrolysis of the ester moieties.
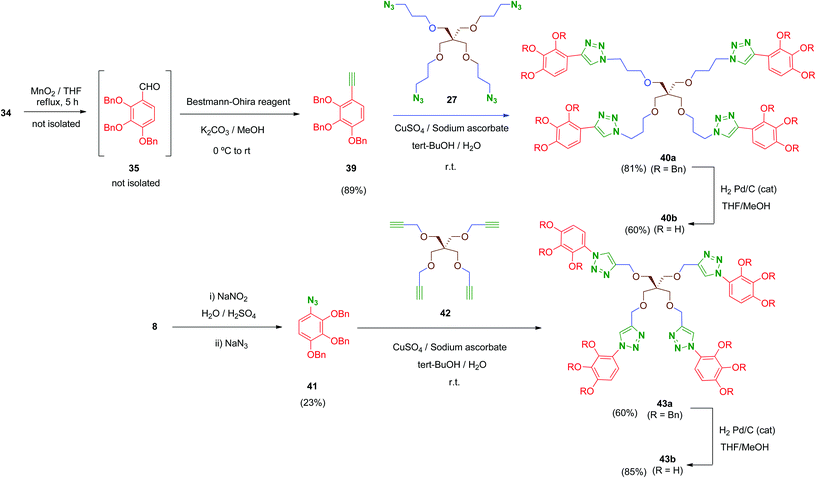
Finally, in order to explore new structural modifications on the linker, we considered it of interest to replace the amide bridge of the most active tetrapodal compound 13b by a non-hydrolysable surrogate. The triazole group has been proposed as a non-classical bioisostere of the amide moiety retaining the main parameters of the original group (electronic properties, lipophilicity, size and geometry) while introducing structural diversity. Additionally, triazole groups have the advantages of a remarkable chemical stability and easy generation (click chemistry).50 Thus, two non-hydrolysable triazole-linked tetrapodal agents 40b and 43b were synthesized as shown in Scheme 12. Two different azide–alkyne pairs were used. For the synthesis of 40b, acetylene 39 was required. Compound 39 was obtained from the benzyl alcohol 34 through a sequential one-pot oxidation–propargylation protocol.51 Thus, 34 was oxidised by activated MnO2 (THF, reflux) with no isolation of intermediate aldehyde 35, which was transformed in situ into the corresponding acetylene 39 by treatment with dimethyl-(1-diazo-2-oxopropyl)phosphonate (Bestmann–Ohira reagent) in the presence of K2CO3 at room temperature.52 Subsequently, Huisgen reaction (Cu(I)-catalysed [1,3]-dipolar cycloaddition)53 between 39 and the previously mentioned tetraazide 27 in the presence of CuSO4 and sodium ascorbate afforded tetra-triazole 40a in good yield (81%).
On the other hand, tetrapodal derivative 43a was obtained by coupling of aryl-azide 41 and its acetylenic pentaerythritol counterpart 42. Compound 41 was obtained from the hydrochloride 8, which was converted into its diazo derivative (not isolated) by treatment with sodium nitrite and subsequently substituted in situ by treatment with sodium azide to afford 41, although in low yield (23%; non-optimised procedure). Huisgen coupling of 41 with 42 (synthesized by O-propargylation of pentaerythritol54) provided 43a in satisfactory yield (60%). Finally, removal of benzyl protecting groups in both 40a and 43a was carried out under standard conditions affording deprotected polyphenols 40b and 43b in 60% and 85% yield, respectively.
Biological assays. Antiviral activity
The new synthetic polyphenols were evaluated for their inhibitory activity against HIV-1(IIIB) and HIV-2 (ROD) in a cell-based assay (CD4+ T-lymphocyte cell culture) where virus infected cells were incubated in the presence of the selected compounds.It must be noted firstly that none of the benzyl-protected polyphenols exhibited activity against HIV at subtoxic concentrations (data not shown), which clearly indicates that free phenol functions are crucial for any antiviral activity in this family of compounds. The results of the biological evaluation of the deprotected compounds against HIV are summarized in Table 1.
| Linker | Multiplicity | Compound | EC50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) a (μM) a (μM) |
CC50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) b (μM) b (μM) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV-1 | HIV-2 | ||||
| a 50% effective concentration or compound concentration required to protect 50% of the cells against the cytopathic effect of the virus. b 50% cytostatic concentration or compound concentration required to inhibit CEM cell proliferation by 50%. All data are mean values (standard deviation for at least three independent experiments). c Compound precipitation was detected at higher concentrations. d Product evaluated with 82% purity. | |||||
| Carbamate | Monopodal | 6b | >10 | >10 | 171 ± 85 |
| Amide | Tetrapodal | 13b | 1.2 ± 0.6 | ≥10 | 25 ± 11 |
| Amide | Tripodal | 14b | 4.2 ± 0.85 | >10 | 24 ± 8.5 |
| Amide | Bipodal | 15b | >10 | >10 | 60 ± 54 |
| Amide (3,4,5-isomer) | Tetrapodal | 17b | 5.6 ± 1.6 | >10 | 21 ± 5.7 |
| Amide (N-Me derivative) | Tetrapodal | 18b | >10 | >10 | 63 ± 37 |
| Amide | Monopodal | 19b | >50 | >50 | 112 ± 0.0 |
| Amide | Monopodal | 20b | >50 | >50 | 108 ± 2.1 |
| Amide | Monopodal | 21b | >2c | >2c | >2c |
| Amide (NHCOAr) | Tetrapodal | 23b | 10 ± 0.0 | >10 | 21 ± 2.8 |
| Carbamate | Tetrapodal | 28b | 8.4 ± 2.3 | >10 | 20 ± 4.2 |
| Carbamate | Tripodal | 29b | >10 | >10 | 24 ± 4.9 |
| Carbamate | Bipodal | 30b | >50 | >50 | 86 ± 17 |
| Carbamate | Monopodal | 31b | >10 | >10 | 124 ± 11 |
| Urea | Tetrapodal | 32b | >10 | >10 | 22 ± 0.0 |
| Urea | Monopodal | 33b | >50 | >50 | >250 |
| Ester | Tetrapodal | 37b | >50 | >50 | 102 ± 21 |
| Ester | Monopodal | 38b/38c | >50 | >50 | >250 |
| Triazole | Tetrapodal | 40b | >10 | >10 | 27 ± 2.8 |
| Triazole | Tetrapodal | 43b | >10 | >10 | 48 ± 30 |
Whereas some of the described compounds inhibited HIV-1 replication in the lower micromolar concentration range, none of these derivatives proved active against HIV-2 at sub-toxic concentrations (Table 1). Therefore, the active compounds should be considered as specific inhibitors of HIV-1 replication in CD4+ T-lymphocyte cells.
With respect to the architecture of the tested compounds, it was shown that the number of polyhydroxyphenyl moieties is important for the activity. Thus, monopodal (6b, 19b–21b, 31b, 33b and 38b,c) and bipodal (15b and 30b) compounds were all inactive against HIV replication at subtoxic concentrations. In the monopodal series of amides (19b–21b) and carbamates (6b and 31b), the length of the hydrocarbon side chain (Me, Et, octyl and palmitoyl) linked to the phenolic moiety did not affect their antiviral behaviour, indicating that the hydrophobic character of the molecule has no significant effect on activity. It should be noted additionally that compound 21b, bearing a long palmitoyl hydrocarbon chain, has a noticeably amphiphilic nature, which precluded its biological testing at a higher concentration of 2 μM due to its limited aqueous solubility.
Among the tripodal derivatives, only compound 14b exhibited a pronounced anti-HIV-1 activity (EC50 = 4.2 μM) although its activity is 5-fold lower than its toxicity threshold (selectivity index ∼6).
Regarding the tetrapodal series, compounds 40b and 43b, with non-hydrolysable triazole linkers, and 37b and 32b, connected to the scaffold with ester and urea linkers respectively, were all inactive. In contrast, the tetrapodal amide-linked derivative 13b was endowed with the highest antiviral activity against HIV-1 (EC50 = 1.2 μM), a concentration markedly below the toxicity threshold, resulting in a selectivity index of ∼20. Very noticeably, reversion in the sequence of the amide linker (NH–CO in 17b instead of CO–NH in 13b) caused a 4- to 5-fold loss of antiviral activity (17b, EC50 = 5.6 μM) keeping similar levels of cytostatic activity (CC50: 21 μM). Also, the tetrapodal derivative 28b attached to the scaffold through a carbamate group (NH–CO–O) was 7-fold less active than 13b (EC50 = 8.4 μM), linked by an amide (NHCO) moiety, but again, kept a similar cytostatic potential as 13b and 17b. Overall, it can be concluded that the best architecture is the tetrapodal configuration and that, despite a common tetrapodal scaffold, the linker group clearly affects the activity.
The amide series (compounds 13b–21b) can help to establish interesting structure–activity relationships. On the one hand, the distribution of the free phenolic OH groups around the aromatic ring is important for the biological activity. Thus, compound 17b, bearing polyphenolic subunits with a galloyl-type distribution (3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl moieties), was 7-fold less active (EC50 = 5.6 μM) than compound 13b, substituted by the 2,3,4-trihydroxyphenyl isomer, showing that this moiety is superior for this series of compounds. Moreover, compound 18b, in which amide NH groups have been eliminated by the introduction of methyl groups, was inactive compared to 13b. This indicates the importance of the free NH groups probably to keep the capacity to form H-bridges with the molecular target. Finally, compared to its less branched tripodal (14b), bipodal (15b) and monopodal (19b–21b) analogs, the antiviral profile of 13b indicates that at least four 2,3,4-trihydroxyphenyl moieties located at the periphery of the molecule are required for antiviral activity. These data support the importance of a multi-branched architecture in the design of these families of compounds. Moreover, it is interesting to notice that the cytostatic activity of the antivirally active test compounds were quite comparable, which opens promising future prospects of further improvement of the selectivity index by optimizing (increasing) the antiviral potency.
Conclusions
Herein we have described the synthesis and anti-HIV properties of a series of synthetic polyphenols containing a central pentaerythritol-based core functionalised with 2,3,4-trihydroxyphenyl subunits. Amide, carbamate, urea, ester and triazole groups have been used as linkers to attach the polyphenolic moieties to the scaffolds. The design of these compounds has been inspired by the multivalent architecture of some representative naturally-occurring tannins. The effect of the number of polyphenolic moieties has been studied by the synthesis of a tetra-, tri- and bipodal series of compounds while monopodal derivatives were obtained for comparative purposes. Multibranched architecture seems to play a crucial role in the design of these compounds, since the increase in the number of peripheral polyphenolic subunits is associated with an increased activity.The tetrapodal amide-linked compound 13b is the most active member of this series, exhibiting low micromolar inhibitory activity against HIV-1, in the same range or even improved compared to those values that have been reported for related naturally-occurring polyphenols.10a The 2,3,4-trihydroxyphenyl moiety present in these compounds proved superior to the naturally-occurring gallate group (3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl moiety). It is noteworthy that any structural changes performed on the linker of the prototype amide-bridged compound 13b led to a decrease in antiviral activity. The specific molecular target of prototype compound 13b as well as its exact mechanism of action are both still under investigation.
Furthermore, it must be noted that naturally-occurring polyphenols are extracts from natural sources whose composition is variable, while the synthesis of the compounds described herein has been carried out through a set of simple and reliable transformations that allowed the isolation of pure, controlled samples of the substances ready for biological evaluation.
For all the above reasons, this contribution can be considered as an encouraging starting point for further development of synthetic polyphenols as selective HIV-1 inhibitors.
Experimental
Chemical synthesis
Mass spectra (low and high-resolution) were registered with a quadrupole mass spectrometer Hewlett-Packard 1100 equipped with an electrospray source (ES) in negative or positive mode of detection. NMR spectra were obtained on Varian INOVA-300, -400, UNITY-500, MERCURY-400 or Bruker AVANCE-300 NMR spectrometers using CDCl3 or methanol-d4 as solvents. 1H and 13C NMR spectra are reported in parts per million (ppm) referred to protonated residual peaks or specific signals due to deuterated solvents as internal references in CDCl3 or CD3OD. The following abbreviations are used to describe peaks: s (singlet), d (doublet), t (triplet), qt (quartet), qn (quintet), m (multiplet) and br (broad).
HPLC analyses were carried out using either a Waters Alliance HPLC/MS system (quoted as HPLC/MS) or on an Agilent 1120 apparatus (quoted as HPLC) eluting with acetonitrile–water. All retention times are quoted in minutes. Elemental analyses were performed with a Carlo Erba CHN-1108 or a Heraeus CHN-O-RAPID microanalyzers. Melting points were measured on a Mettler Toledo model MP70 melting point apparatus and are uncorrected. Lyophilised compounds melt at a wide range of temperatures.
A representative set of compounds are described in this Experimental section. A detailed full description of all the analytical methods, experimental procedures, spectroscopic characterization and selected copies of 1H and 13C-NMR spectra of intermediates and final compounds are provided separately in the ESI‡ available.
Preparation of 2,3,4-tris(benzyloxy)aniline (7) from carbamate precursors
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) v/v as eluent). Free amine 7 was isolated as a waxy solid, converted into a white foam after repeated freeze-drying from CH3CN–H2O (627 mg, 1.5 mmol, 76%). TLC (Rf = 0.32; hexane–EtOAc (3
1) v/v as eluent). Free amine 7 was isolated as a waxy solid, converted into a white foam after repeated freeze-drying from CH3CN–H2O (627 mg, 1.5 mmol, 76%). TLC (Rf = 0.32; hexane–EtOAc (3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2) v/v; CAM); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.45–7.3 (m, 15 H), 6.6 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 6.49 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 5.1 (s, 2H), 5.07 (s, 2H), 5.04 (s, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 145.5, 143.4, 140.8, 137.9, 137.8, 137.7, 135.5, 128.6, 128.5, 128.4, 128.2, 128.0, 127.9, 127.8, 111.7, 110.1, 75.7, 75.2, 72.5; m/z (ESI+) 434 ([M + Na]+, 26%), 412 ([M + H]+, 100%); HPLC/MS: tR = 2.55 min. polar gradient CH3CN–H2O from (70
2) v/v; CAM); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.45–7.3 (m, 15 H), 6.6 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 6.49 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 5.1 (s, 2H), 5.07 (s, 2H), 5.04 (s, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 145.5, 143.4, 140.8, 137.9, 137.8, 137.7, 135.5, 128.6, 128.5, 128.4, 128.2, 128.0, 127.9, 127.8, 111.7, 110.1, 75.7, 75.2, 72.5; m/z (ESI+) 434 ([M + Na]+, 26%), 412 ([M + H]+, 100%); HPLC/MS: tR = 2.55 min. polar gradient CH3CN–H2O from (70![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30) up to (100
30) up to (100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0) in 5 min (98% purity).
0) in 5 min (98% purity).
Preparation of aniline hydrochlorides 8 and 16. General procedure
The free amine was re-dissolved in Et2O and a 1 N solution of HCl in Et2O was added dropwise until an abundant precipitate was formed. The precipitate was filtered off, gently washed with additional amounts of Et2O and then efficiently dried to give a solid that did not need further purification. Hydrochlorides 8 and 16 can be stored without noticeable degradation for months if kept in a cool and dry place.PyBOP-mediated synthesis of multivalent amides 13a–15a and 17a. General procedure
To a suspension of the suitable polyacid (1 mmol) in dry CH2Cl2 (20 mL mmol−1) at 0 °C (ice-bath) was added sequentially PyBOP (1.2 equiv. per acid group) and Et3N (3.75 equiv. per acid group) in a pressure tube. When the acid is solubilized (approx. 5 min), aniline hydrochloride 8 (1.2 equiv. per acid group) was added and the pressure tube sealed. The reaction mixture was warmed to 60 °C and stirred overnight until consumption of the starting material (TLC monitoring). Then, reaction was cooled to room temperature, washed with a 10% citric acid aqueous solution and then with a 10% NaHCO3 aqueous solution, dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under vacuum. The crude product was purified as determined.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3) v/v; CAM); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.80 (br s, 4 H), 7.75 (d, J = 9.3 Hz, 4 H), 7.41–7.27 (m, 60 H), 6.57 (d, J = 9.4 Hz, 4 H), 5.04 (s, 16 H), 5.01 (s, 8 H), 3.44 (t, J = 5.7 Hz, 8 H), 3.18 (s, 8 H), 2.26 (t, J = 5.7 Hz, 8 H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 169.2, 149.2, 142.6, 141.5, 137.4, 137.0, 136.8, 128.7, 128.6, 128.5, 128.3, 128.0, 127.9, 127.5, 126.1, 115.7, 109.4, 76.1, 75.5, 71.2, 69.2, 67.0, 45.0, 37.7; m/z (ESI+) 1000 ([1/2M + 2H]+, 100%); HRMS (ESI+) [M + H]+ C125H121N4O20 requires 1997.8574, found: 1997.8568; Anal. calcd for C125H120N4O20 (1996.3): C, 75.13; H, 6.05; N, 2.80; found: C, 74.93; H, 6.13; N, 2.95%.
3) v/v; CAM); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.80 (br s, 4 H), 7.75 (d, J = 9.3 Hz, 4 H), 7.41–7.27 (m, 60 H), 6.57 (d, J = 9.4 Hz, 4 H), 5.04 (s, 16 H), 5.01 (s, 8 H), 3.44 (t, J = 5.7 Hz, 8 H), 3.18 (s, 8 H), 2.26 (t, J = 5.7 Hz, 8 H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 169.2, 149.2, 142.6, 141.5, 137.4, 137.0, 136.8, 128.7, 128.6, 128.5, 128.3, 128.0, 127.9, 127.5, 126.1, 115.7, 109.4, 76.1, 75.5, 71.2, 69.2, 67.0, 45.0, 37.7; m/z (ESI+) 1000 ([1/2M + 2H]+, 100%); HRMS (ESI+) [M + H]+ C125H121N4O20 requires 1997.8574, found: 1997.8568; Anal. calcd for C125H120N4O20 (1996.3): C, 75.13; H, 6.05; N, 2.80; found: C, 74.93; H, 6.13; N, 2.95%.
The synthesis of compounds 14a–15a and 17a was performed similarly following the general procedure. For full details, see ESI‡ available.
Preparation of carbamates 28a–31a and ureas 32a–33a by Curtius rearrangement. General procedure
To a solution of the appropriate benzoic acid (1 equiv.) in toluene (5 mL mmol−1) under argon was added DPPA (1.1 equiv.) and Et3N (1.1 equiv.) at room temperature. The mixture was heated at 75 °C until complete disappearance of the starting material (as monitored by TLC), yielding the isocyanate intermediate 4 (not isolated). Then, the corresponding alcohols or amines were added (1.2 equiv. per isocyanate group to be functionalised). The reaction was stirred additionally at 75 °C overnight (monitored by TLC), cooled to room temperature and subsequently washed with a 1 N aqueous solution of HCl and then with a saturated aqueous solution of NaHCO3, dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude product was purified as determined.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 95) up to (20
95) up to (20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 80)) and further recrystallized from MeOH to yield 6a (1.22 g, 2.6 mmol, 74%) as a white solid. Mp 89.1–90.7; TLC (Rf = 0.34 hexane–EtOAc (4
80)) and further recrystallized from MeOH to yield 6a (1.22 g, 2.6 mmol, 74%) as a white solid. Mp 89.1–90.7; TLC (Rf = 0.34 hexane–EtOAc (4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) v/v; CAM); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.7 (br d, 1 H), 7.4–7.3 (m, 15 H), 6.89 (br s, 1 H), 6.76 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 1 H), 5.09 (s, 4 H), 5.08 (s, 2 H), 3.71 (s, 3 H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 154.0, 148.4, 141.7, 137.3, 137.0, 136.8, 128.6, 128.5, 128.4, 128.3, 128.1, 127.9, 127.5, 126.2, 113.4, 109.8, 75.8, 75.6, 71.4, 52.2; m/z (ESI+) 492 ([M + Na]+, 59%), 470 ([M + H]+, 100%); Anal. calcd for C29H27NO5 (469.5): C, 74.18; H, 5.80; N, 2.98; found: C, 74.27; H, 6.02; N, 3.20%.
1) v/v; CAM); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.7 (br d, 1 H), 7.4–7.3 (m, 15 H), 6.89 (br s, 1 H), 6.76 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 1 H), 5.09 (s, 4 H), 5.08 (s, 2 H), 3.71 (s, 3 H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 154.0, 148.4, 141.7, 137.3, 137.0, 136.8, 128.6, 128.5, 128.4, 128.3, 128.1, 127.9, 127.5, 126.2, 113.4, 109.8, 75.8, 75.6, 71.4, 52.2; m/z (ESI+) 492 ([M + Na]+, 59%), 470 ([M + H]+, 100%); Anal. calcd for C29H27NO5 (469.5): C, 74.18; H, 5.80; N, 2.98; found: C, 74.27; H, 6.02; N, 3.20%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 90) up to (50
90) up to (50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50)) to afford 28a (100 mg, 0.05 mmol, 21%) as a yellowish oil. TLC (Rf = 0.4 hexane–EtOAc (2
50)) to afford 28a (100 mg, 0.05 mmol, 21%) as a yellowish oil. TLC (Rf = 0.4 hexane–EtOAc (2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3) v/v; CAM); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.66 (br s, 4 H), 7.42–7.29 (m, 60 H), 6.91 (br s, 4 H), 6.71 (d, J = 9.3 Hz, 4 H), 5.06 (s, 8 H), 5.05 (s, 8 H), 5.04 (s, 8 H), 4.16 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 8 H), 3.47 (t, J = 6.3 Hz, 8 H), 3.42 (s, 8 H), 1.87 (qn, J = 6.3 Hz, 8 H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 153.5, 148.3, 141.8, 141.7, 137.4, 137.0, 136.9, 128.6, 128.5, 128.4, 128.3, 128.0, 127.9, 127.5, 126.3, 113.6, 109.8, 75.9, 75.5, 71.4, 69.7, 67.6, 62.4, 45.3, 29.2; HRMS (ESI+) [M + Na]+ C129H128N4O24Na requires 2139.8816, found: 2139.8811.
3) v/v; CAM); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.66 (br s, 4 H), 7.42–7.29 (m, 60 H), 6.91 (br s, 4 H), 6.71 (d, J = 9.3 Hz, 4 H), 5.06 (s, 8 H), 5.05 (s, 8 H), 5.04 (s, 8 H), 4.16 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 8 H), 3.47 (t, J = 6.3 Hz, 8 H), 3.42 (s, 8 H), 1.87 (qn, J = 6.3 Hz, 8 H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 153.5, 148.3, 141.8, 141.7, 137.4, 137.0, 136.9, 128.6, 128.5, 128.4, 128.3, 128.0, 127.9, 127.5, 126.3, 113.6, 109.8, 75.9, 75.5, 71.4, 69.7, 67.6, 62.4, 45.3, 29.2; HRMS (ESI+) [M + Na]+ C129H128N4O24Na requires 2139.8816, found: 2139.8811.
The synthesis of carbamates 29a–31a and ureas 32a–33a was performed similarly following the general procedure. For full experimental details, see ESI‡ available.
Preparation of 1,2,3-triazole-bridged compounds 40a and 43a by copper-catalysed 1,3-dipolar azide–alkyne cycloaddition (Huisgen reaction). General procedure
To a suspension of the corresponding azide (1 equiv. per alkyne) and alkyne (1 equiv. per azide) in tBuOH–H2O (2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) v/v (64 mL mmol−1) at room temperature was added (+)-sodium L-ascorbate (0.4 equiv.) and CuSO4 (0.04 equiv.). The heterogeneous mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight and then treated with H2O. The resulting solid was filtered, washed with H2O and purified as determined.
1) v/v (64 mL mmol−1) at room temperature was added (+)-sodium L-ascorbate (0.4 equiv.) and CuSO4 (0.04 equiv.). The heterogeneous mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight and then treated with H2O. The resulting solid was filtered, washed with H2O and purified as determined.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 60) up to (100
60) up to (100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0) v/v) affording 40a (75 mg, 0.04 mmol, 81%) as a yellowish oil. TLC (Rf = 0.32 hexane–EtOAc (3
0) v/v) affording 40a (75 mg, 0.04 mmol, 81%) as a yellowish oil. TLC (Rf = 0.32 hexane–EtOAc (3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 7) v/v; PMA); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.89 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 4 H), 7.74 (s, 4 H), 7.44–7.28 (m, 60 H), 6.84 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 4 H), 5.10 (s, 8 H), 5.08 (s, 8 H), 5.03 (s, 8 H), 4.31 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 8 H), 3.35 (t, J = 5.7 Hz, 8 H), 3.33 (s, 8 H), 1.97 (qn, J = 6.4 Hz, 8 H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 152.8, 149.9, 143.1, 141.8, 137.5, 137.4, 136.7, 128.6, 128.5, 128.3, 128.1, 128.0, 127.5, 122.5, 122.0, 118.4, 109.9, 75.6, 75.5, 70.9, 69.5, 67.6, 47.2, 45.4, 30.3; HRMS (ESI+) [M + H]+ C133H129N12O16 MH requires 2149.9650, found: 21.9644.
7) v/v; PMA); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.89 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 4 H), 7.74 (s, 4 H), 7.44–7.28 (m, 60 H), 6.84 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 4 H), 5.10 (s, 8 H), 5.08 (s, 8 H), 5.03 (s, 8 H), 4.31 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 8 H), 3.35 (t, J = 5.7 Hz, 8 H), 3.33 (s, 8 H), 1.97 (qn, J = 6.4 Hz, 8 H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 152.8, 149.9, 143.1, 141.8, 137.5, 137.4, 136.7, 128.6, 128.5, 128.3, 128.1, 128.0, 127.5, 122.5, 122.0, 118.4, 109.9, 75.6, 75.5, 70.9, 69.5, 67.6, 47.2, 45.4, 30.3; HRMS (ESI+) [M + H]+ C133H129N12O16 MH requires 2149.9650, found: 21.9644.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 7) v/v; PMA); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.78 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, 4 H), 7.43–7.30 (m, 32 H,) 7.30–7.25 (m, 10 H), 7.21 (dd, J = 9.0, 4.6 Hz, 4 H), 7.18–7.14 (m, 10 H), 7.05–6.98 (m, 8 H), 6.76 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 4 H), 5.08 (s, 8 H), 5.06 (s, 8 H), 4.87 (s, 8 H), 4.54 (s, 8 H), 3.52 (s, 8 H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 153.8, 146.1, 145.0, 142.7, 137.2, 136.4, 136.3, 128.8, 128.7, 128.5, 128.4, 128.3, 127.7, 125.6, 124.8, 120.5, 109.4, 76.4, 75.9, 71.3, 69.5, 65.2, 45.7; HRMS (ESI+) [M + H]+ C125H113N12O16 requires 2037.8398, found: 2037.8392; Anal. calcd for C125H112N12O16 (2038.30): C, 73.66; H, 5.54; N, 8.25; found: C, 73.58; H, 5.51; N, 8.19%.
7) v/v; PMA); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.78 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, 4 H), 7.43–7.30 (m, 32 H,) 7.30–7.25 (m, 10 H), 7.21 (dd, J = 9.0, 4.6 Hz, 4 H), 7.18–7.14 (m, 10 H), 7.05–6.98 (m, 8 H), 6.76 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 4 H), 5.08 (s, 8 H), 5.06 (s, 8 H), 4.87 (s, 8 H), 4.54 (s, 8 H), 3.52 (s, 8 H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 153.8, 146.1, 145.0, 142.7, 137.2, 136.4, 136.3, 128.8, 128.7, 128.5, 128.4, 128.3, 127.7, 125.6, 124.8, 120.5, 109.4, 76.4, 75.9, 71.3, 69.5, 65.2, 45.7; HRMS (ESI+) [M + H]+ C125H113N12O16 requires 2037.8398, found: 2037.8392; Anal. calcd for C125H112N12O16 (2038.30): C, 73.66; H, 5.54; N, 8.25; found: C, 73.58; H, 5.51; N, 8.19%.
Preparation of free polyphenols 6b, 13b–15b, 17b–21b, 23b, 28b–33b, 37–38b/38c, 40b and 43b. Deprotection of benzylated phenols by catalytic hydrogenation. General procedure
A solution of the corresponding benzyl-protected precursors (1 mmol) in a binary mixture of solvents THF–methanol (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) v/v (100 mL) containing catalytic amounts of Pd (on charcoal; 10 wt%) was hydrogenated overnight in a Parr Hydrogenator at 3.1 bar in a thermostated vessel at 25 °C. The Pd catalyst was removed by filtration through a Whatman® filter paper 42 and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure to give the corresponding deprotected free-phenolic derivatives as single products which were treated as specified. All debenzylated compounds should be kept at −20 °C and protected from direct exposure to light.
1) v/v (100 mL) containing catalytic amounts of Pd (on charcoal; 10 wt%) was hydrogenated overnight in a Parr Hydrogenator at 3.1 bar in a thermostated vessel at 25 °C. The Pd catalyst was removed by filtration through a Whatman® filter paper 42 and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure to give the corresponding deprotected free-phenolic derivatives as single products which were treated as specified. All debenzylated compounds should be kept at −20 °C and protected from direct exposure to light.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 90) up to (100
90) up to (100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0) in 5 min (96% purity).
0) in 5 min (96% purity).
The synthesis of compounds 6b, 14b–15b, 17b–21b, 23b, 28b–33b, 37b–38b/38c, 40b and 43b was performed similarly following the general procedure. For full details, see ESI.‡
Antiviral activity
The methodology of the anti-HIV assays was as follows: human CD4+ T-lymphocyte CEM cells (∼3 × 105 cells mL−1) were infected with 100 CCID50 of HIV-1(IIIB) or HIV-2(ROD) mL−1 and seeded in 200 μL wells of a 96-well microtiter plate containing appropriate dilutions of the test compounds. After 4 days of incubation at 37 °C, HIV-induced CEM giant cell formation was examined microscopically. The 50% effective concentration (EC50) was defined as the compound concentration required to inhibit virus-induced cytopathy by 50%. The 50% cytostatic concentration (CC50) was defined as the compound concentration required to inhibit CEM cell proliferation by 50% as counted by a Coulter counter.Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the Spanish MICINN/MINECO (projects SAF2009-13914-C02-01 and SAF2012-39760-C02-01), Comunidad de Madrid (BIPEDD-2 project CM-S2010/BMD-2457) and the KU Leuven (GOA no. 10/014; EF 05/15; PF 10/018). Dr A. Flores acknowledges financial support from a contract JAE-Doc (Programa Junta para la Ampliación de Estudios) co-funded by CSIC and UE (FSE, Fondo Social Europeo). Sonsoles Velázquez is acknowledged for critical reading and valuable comments on this article and Leen Ingels for dedicated technical assistance with the antiviral assays.References
- UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic 2013. Published November 18, 2013. http://www.unaids.org/en/media/unaids/contentassets/documents/epidemiology/2013/gr2013/UNAIDS_Global_Report_2013_en.pdf (accessed February 15th, 2014).
- (a) An up-to-date list of approved drugs against HIV infections is available at http://www.fda.gov (accessed February 15th, 2014); (b) E. De Clercq, Curr. Opin. Pharmacol., 2010, 10, 507 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. T. Butera, in HIV Chemotherapy: A Critical Review, Caister Academic Press, Norwich, 2005 Search PubMed.
- R. J. Pomerantz and D. L. Horn, Nat. Med., 2003, 9, 867 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Menendez-Arias, Antiviral Res., 2013, 98, 93 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Hawkins, Antiviral Res., 2010, 85, 201 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) A. Lefeuillade, Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep., 2012, 9, 121 CrossRef PubMed; (b) T.-W. Chun and A. S. Fauci, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1999, 96, 10958 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) S. G. Deeks, D. Autran, B. Berkhout, M. Benkirane, S. Cairns, N. Chomont, T.-W. Chun, M. Churchill, M. Di Mascio, C. Katlama, A. Lafeuillade, A. Landay, M. Lederman, S. R. Lewin, F. Maldarelli, D. Margolis, M. Markowitz, J. Martinez-Picado, J. I. Mullins, J. Mellors, S. Moreno, U. O'Doherty, S. Palmer, M.-C. Penicaud, M. Peterlin, G. Poli, J. P. Routy, C. Rouzioux, G. Silvestri, M. Stevenson, A. Telenti, C. Van Lint, E. Verdin, A. Woolfrey, J. Zaia and F. Barré-Sinoussi, Nat. Rev. Immunol., 2012, 12, 607 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) S. Broder, Sci. Transl. Med., 2010, 2, 39ps33 Search PubMed.
- V. Lattanzio, P. A. Kroon, S. Quideau and D. Treutter, Plant phenolics: secondary metabolites with diverse functions, in Recent Advances in Polyphenol Research, ed. F. Daayf and V. Lattanzio, Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford, UK, 2008, vol. 1, pp. 1–34 Search PubMed.
- For recent reviews on polyphenols and HIV infection, see: (a) K. Andrae-Marobela, F. W. Ghislain, H. Okatch and R. R. Majinda, Curr. Drug Metab., 2013, 14, 392 CrossRef CAS; (b) S. Yu and G. Zhao, Curr. Med. Chem., 2012, 19, 5536 CrossRef CAS. For a general review on polyphenols, see: (c) S. Quideau, D. Deffieux, C. Douat-Casassus and L. Pouysegu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 586 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhao, F. Jiang, P. Liu, W. Chen and K. Yi, Drug Discovery Today, 2012, 17, 6930 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Yang, L. Li, S. Tan, H. Jin, J. Qiu, Q. Mao, R. Li, C. Xia, Z. H. Jiang, S. Jiang and S. Liu, Fitoterapia, 2012, 83, 348 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Yang, L. Li, H. Jin, S. Tan, J. Qiu, L. Yang, Y. Ding, Z. H. Jiang, S. Jiang and S. Liu, AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses, 2012, 28, 1498 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) Y. B. Yu, H. Miyashiro, N. Nakamura, M. Hattori and J. C. Park, Arch. Pharmacal Res., 2007, 30, 820 CrossRef CAS; (b) M. P. N. Nair, Z. M. Saiyed, N. H. Gandhi and C. N. Ramchand, Am. J. Infect. Dis., 2009, 5, 135 CAS.
- (a) M. Jourdes, L. Pouységu, D. Deffieux, P.-L. Teissedre and S. Quideau, Hydrolysable Tannins: Gallotannins and Ellagitannins, in Natural Products, ed. K. Gopal Ramawat and J.-M. Merillon, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2013, pp. 1975–2010 Search PubMed; (b) P. Buzzini, P. Arapitsas, M. Goretti, E. Branda, B. Turchetti, P. Pinelli, F. Ieri and A. Romani, Mini-Rev. Med. Chem., 2008, 8, 1179 CrossRef CAS; (c) I. Mueller-Harvey, Anim. Feed Sci. Technol., 2001, 91, 3 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Takada, A. Bermingham, B. R. O'Keefe, A. Wamiru, J. A. Beutler, S. F. Le Grice, J. Lloyd, K. R. Gustafson and J. B. McMahon, J. Nat. Prod., 2007, 70, 1647 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) X. Wang, K. S. Song, Q. X. Guo and W. X. Tian, Biochem. Pharmacol., 2003, 66, 2039 CrossRef CAS; (b) C. Braicu, M. R. Ladomery, V. S. Chedea, A. Irimie and I. Berindan-Neagoe, Food Chem., 2013, 141, 3282 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) E. Q. Xia, G. F. Deng, Y. J. Guo and H. B. Li, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2010, 11, 622 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) J. Intra and S. M. Kuo, Chem.-Biol. Interact., 2007, 169, 91 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Takahashi, Y. Kohno and M. Nishio, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 6049 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. S. Yang, X. Wang, G. Lu and S. C. Picinich, Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2009, 9, 429 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) N. Israël and M. A. Gougerot-Pocidalo, Cell Mol. Life Sci., 1997, 53, 864 CrossRef; (b) H. C. Greenspan and O. I. Aruoma, Immunol. Today, 1994, 15, 209 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Coaccioli, G. Crapa, M. Fantera, R. Del Giorno, A. Lavagna, M. L. Standoli, R. Frongillo, R. Biondi and A. Puxeddu, Clin. Ther., 2010, 161, 55 CAS.
- M. A. Edeas and A. Lindenbaum, Bull. l'O.I.V., 2000, 73, 810 CAS.
- F. Nanjo, M. Mori, K. Goto and Y. Hara, Biosci., Biotechnol. Biochem., 1999, 63, 1621 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) L. L. Kiessling, J. E. Gestwicki and L. E. Strong, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2000, 4, 696 CrossRef CAS; (b) C. Fasting, C. A. Schalley, M. Weber, O. Seitz, S. Hecht, B. Koksch, J. Dernedde, C. Graf, E. W. Knapp and R. Haag, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 10472 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Song, P. Zhan, X. Li, D. Rai, E. De Clercq and X. Liu, Curr. Med. Chem., 2013, 20, 815 CAS.
- V. Lozano, L. Aguado, B. Hoorelbeke, M. Renders, M. J. Camarasa, D. Schols, J. Balzarini, A. San-Félix and M. J. Pérez-Pérez, J. Med. Chem., 2011, 54, 5335 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) P. J. King, G. Ma, W. Miao, Q. Jia, B. R. McDougall, M. G. Reinecke, C. Cornell, J. Kuan, T. R. Kim and W. E. Robinson Jr., J. Med. Chem., 1999, 42, 497 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) C. O. R. Junior, S. C. Verde, C. A. M. Rezende, W. Caneschi, M. R. C. Couri, B. R. McDougall, W. E. Robinson Jr. and M. V. de Almeida, Curr. Med. Chem., 2013, 20, 724 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Carrero, A. Ardá, M. Alvarez, E. G. Doyagüez, E. Rivero-Buceta, E. Quesada, A. Prieto, D. Solís, M.-J. Camarasa, M.-J. Peréz-Pérez, J. Jiménez-Barbero and A. San-Félix, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2013, 65–76 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) J. Katajisto, P. Heinonen and H. Loennberg, Curr. Org. Chem., 2004, 8, 977 CrossRef CAS; (b) G. Newkome, J. K. Young, G. R. Baker, R. L. Potter, L. Audoly, D. Cooper and C. D. Weis, Macromolecules, 1993, 26, 2394 CrossRef CAS.
- Hydrolysis in Drug and Prodrug Metabolism: Chemistry, Biochemistry, and Enzymology, ed. B. Testa and J. M. Mayer, Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta, Wiley-VCH, Zurich, 2003, ch. 4, pp. 81–126 Search PubMed.
- F. Belin, P. Barthélémy, K. Ruiz, J. M. Lacombe and B. Pucci, Helv. Chim. Acta, 2003, 86, 247 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) N. Takashi, K. Kumiko, A. Akiko, M. Kenji and T. Koichiro, Jp. PatJP8143525 (A), 1996 Search PubMed; (b) S. Lee, S. Hwang, S. Yu, W. Jang, Y. M. Lee and S. Kim, Arch. Pharm. Res., 2011, 34, 1065 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. A. S. Smith, Org. React., 1946, 3, 337 Search PubMed.
- T. Shioiri, K. Ninomiya and S. Yamada, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1972, 94, 6203 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Maiti, P. V. N. Reddy, M. Sturdy, L. Marler, S. D. Pegan, A. D. Mesecar, J. M. Pezzuto and M. Cushman, J. Med. Chem., 2009, 52, 1873 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- U. Jacquemard, V. Bénéteau, M. Lefoix, S. Routier, J. Y. Mérour and G. Coudert, Tetrahedron, 2004, 60, 10039 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Newkome and C. D. Weis, Org. Prep. Proced. Int., 1996, 28, 242 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) A. Dupraz, P. Guy and C. Dupuy, Tetrahedron Lett., 1996, 37, 1237 CrossRef CAS; (b) tert-Butyl ester intermediate was isolated by high-vacuum distillation (10−2 mbar; b.p. ranging 135–150 °C) in 73% yield.
- S. Aime, C. Cavallotti, G. Cravotto, G. B. Giovenzana and G. Palmisano, Tetrahedron Lett., 2004, 45, 5901 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) M. W. Wilson and J. C. Hodges, Org. Prep. Proced. Int., 1993, 25, 665 CrossRef CAS; (b) Intermediate dinitrile was isolated by high-vacuum distillation (10−2 mbar; bp ranging 120–130 °C) in 98% yield.
- G. R. Newkome and X. Li, Macromolecules, 1991, 24, 1443 CrossRef CAS.
- G. R. Newkome and E. He, J. Mater. Chem., 1997, 7, 1237 RSC.
- Y. Sun and A. E. Martell, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111, 8023 CrossRef CAS.
- S. B. Fredriksen and J. Dale, Acta Chem. Scand., 1992, 46, 574 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. R. Newkome, A. Mishra and C. N. Moorefield, J. Org. Chem., 2002, 67, 3957 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. K. Luscombe, S. Proemmel, W. T. S. Huck, A. B. Holmes and H. Fukushima, J. Org. Chem., 2007, 72, 5505 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. A. Horestein and K. Nakanishi, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111, 6242 CrossRef.
- C. A. Hansen, A. B. Dean, K. M. Draths and J. W. Frost, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1999, 121, 3799 CrossRef CAS.
- H. J. Wadsworth, S. M. Jenkins, B. S. Orlek, F. Cassidy, M. S. G. Clark, F. Brown, G. J. Riley, D. Graves, J. Hawkins and C. B. Naylor, J. Med. Chem., 1992, 35, 1280 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) E. Quesada and R. J. K. Taylor, Tetrahedron Lett., 2005, 46, 6473 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) E. Quesada, S. A. Raw, M. Reid, S. Roman and R. J. K. Taylor, Tetrahedron, 2006, 62, 6673 CrossRef CAS PubMed. For a review on Tandem Oxidation Processes (TOP), see: (c) R. J. K. Taylor, M. Reid, J. Foot and S. A. Raw, Acc. Chem. Res., 2005, 38, 851 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For a review on conversion of carbonyl compounds into alkynes, see: D. Habrant, V. Rauhala and A. M. P. Koskinen, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39, 2007 RSC.
- G. C. Tron, T. Pirali, R. A. Billington, P. L. Canonico, G. Sorba and A. A. Genazzani, Med. Res. Rev., 2008, 28, 278 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) F. G. Calvo-Flores, J. Isac-Garcia, F. Hernández-Mateo, F. Pérez-Balderas, J. A. Calvo-Asín, E. Sánchez-Vaquero and F. Santoyo-González, Org. Lett., 2000, 2, 2499 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) A. Natarajan, W. Du, C. Y. Xiong, G. L. DeNardo, S. J. DeNardo and J. Gervay-Hague, Chem. Commun., 2007, 7, 695 RSC.
- D. D. Perrin, W. L. F. Armarego and D. R. Perrin, in Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 2nd edn, 1980 Search PubMed.
- W. C. Still, M. Kahn and A. Mitra, J. Org. Chem., 1978, 43, 2923 CrossRef CAS.
Footnotes |
| † Paper dedicated to Professor Richard J. K. Taylor on the occasion of his 65th birthday. |
| ‡ Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Detailed experimental procedures for the synthesis of described compounds, as well as characterization data and copies of 1H and 13C NMR spectra of key intermediates and final compounds, are provided. See DOI: 10.1039/c4ob00445k |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 |